Leisure Sport and Tourism:t2 national scale
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
hotspot
an area of intense leisure activities that attract above average number of visitors due to accessible primary and secondary resources
factors determining where a hotspot is
climate: eg.If the area is too cold, then it could serve as a skiing hotspot ( such as in the Alps).
culture: Mecca is a hotspot for Islamic pilgrims who visit the Holy Site as a form of religious worship.
Natural Landscape: If it is low-lying, it would be adequate for football, rugby, golf etc. If it is mountainous and cold, it would be adequate for skiing or an attractive area for biodiversity
sporting events: eg. london 2012 olympics attracted 31 mill international tourists
rural hotspot example
machu picchu: ancient inca city built in 15th centuaryc
considered site of spiritual significance+ ashlar architecture
panaramic views of surrounding valley+ majestic mountain peaks
7 wonder of the world
1.5 mill visitors annually, capped at 4500 a day
urban hotspot example
venice: island city developed on deposits of alluvial salt, cannals running through v picturesque. 277 cannals
movies filmed here eg. james bond filmed here, landmakrs eg. bridge of sighs
studies show city is subsiding 1-2mm annually, ‘sinking city’ people feel as need to rush to see it.
3 mill annual visitors
define the sphere of influence of a sporting event
area from which the sporting event draws its competitors and supporters. determined by range and threshold
range:maximum distance that people are prepared to travel to attend a sporting event or visit a tourist facility.
threshold: minimum number of people required or needed for a sporting activity or tourist facility to be operational.
high order sporting facilities
high spehere of influence, usually located in urban areas as require large thershold population
olympics, tour de france
low order sporting facilities
fewer people are prepared to travel long distances or pay more to enjoy the service. They may include local parks, gyms, restaurants and cinemas etc.
usually located in both rural+ urban areas
leisure hierarchy
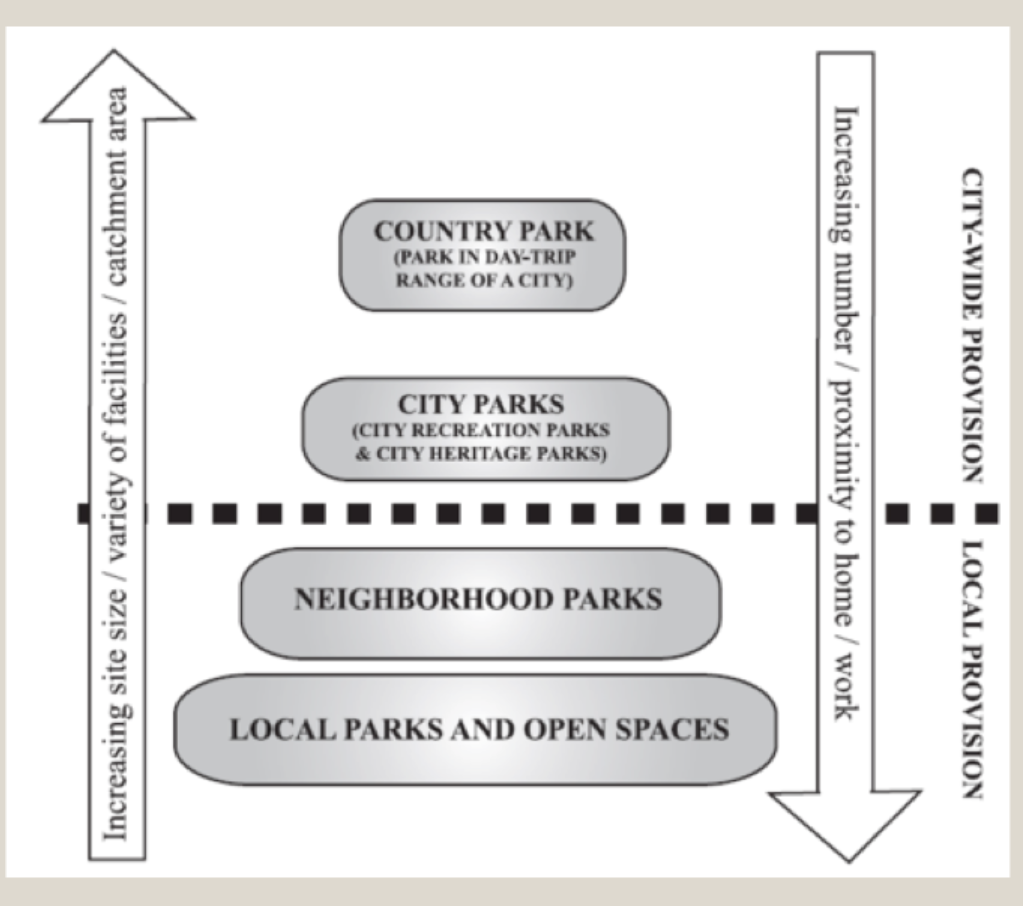
Factors influencing the sphere influence of different kinds of sporting and touristic facilities (4)
affluence: higher incomers can afford to patronise sporting events through stadium attendance, television views, souvenirs etc. And are more likely to support through these means.
popularitty: Well-known sports have a higher sphere of influence than sports that are not well-known.
marketing in new areas: eg.football teams play games in countries eg. china+ usa increasing theyre supporer base+ people who buy merch ect
if the clubs play or compete at international levels, their sphere of influence increases
Intra-urban leisure hierarchy
urban areas, high land values mean often leisure facilities that have large spectator base but occupy a limited space eg. museum, cinema, sports stadium
facilities that require large space/land would be located far from the city centre, close to the suburbs or urban-rural fringe e.g country park, specialist sports fields
case study for Factors affecting the geography of a national sports league
the premier leauge
how does the premier leauge work
hierarchy based on performance
- point system, 3 points = win, 1 point= draw, 0= loss . In the 2017/2018 premier league, Manchester City was at the top.
The top four teams get the opportunity of playing in the Champions League
bottom two are relegated to Championship
what affects the location of teams
teams are usually named after settlements they are based in eg. manchester city is based in manchester. however where there is a dense population eg. london teams are named after suburbs eg. chelsea, arsenal ect.
Clubs are usually located in places where fans have a reasonable level of income to be able to buy the tickets to support the clubs
high pop density: patronize the club to enable them to get revenue and run the club
The topography or landscape will determine the location of certain sports or teams. For example, beach soccer can only be played in coastal areas
premier leauge team locations
7/20 based in london
liverpool, manchester+ birmingham both have 2 teams also
high level of infrastructure here
requires a largely youthful and working population so nearer big cities
teams at the top of the premier leauge hierarchy comp to the bottom
located in majour urban areas, higher sphere of influence incl. international supporters
lower teams, many people in their habitual areas likely to support teams that are higher in the hierarchy.
factors affecting distribution of supporters
The town’s population is expected to be the main support base of the club.
globalisation however has increased the sphere of influence beyond the towns and cities they are located in. For instance, Chelsea has supporters in , South Africa, China and Nigeria.
it has also allowed the purchasing of players beyond home location eg.Fosu Mensah, a Ghanaian footballer who plays for Manchester United who has drawn supporters from Ghana.(most freq. searched team in ghana)
how does media affect the sphere of influence of a sport
television money generates high levels of income for top-level professionals
makes a sport more appealing to sponsors elucidating this.
makes people more aware/ want to see or join
reaches a larger audiance
factors affecting the sphere of influence of a club
Media
Sponsorships and advertisements
The country of origin of the players
Globalization
The level of success of the club.
festival in rural location case study
glastonbury
about glastonbury
culture tourism, temporary site of leisure
began in 1970,
accomidates up to 250,000 people on 800 acres of land
factors affecting the location of glastonbury
Located in a rural area a large space (about 800 acres) is required. flat relief here
There is little disruption to the population of fewer than 10,000 people. (extends southernly from town of pilton to cockmill wood)
One limitation is the lack of proximity to a major access route. encourages to use there transport
Congestion on narrow rural routes is a problem during the festival weekend.
economic benefits of glastonbury
Provides employment to the rural population. (100 people)
Each visitor spends about £293. This money makes substantial contributions to charities such as Water Aid and Oxfam
also supports local projects such as the rebuilding of piltons playing fields pavillion
renevue of 82 mill
economic costs of glastonbury
it costs over 750,000 to clear up after the festival(however revenue far outweights cost)
performers cost atleast 2 mill
(many stakeholders involved)
social benefits and costs of glastonbury(2 each)
:)In 2015, a blood donation exercise was held leading to an increase in blood stocks in the area.
:)Glastonbury benefits from a wider sphere of influence of tourists. In 2007 over 700 journalists reported on the festival.
:(Dealing with huge numbers of tourists, drug and substance abuse.
:(88 crimes were reported to the police in 2017
environmental costs of glastonbury
Noise pollution: many performances continue late into the night disturbing local residents.
Air pollution: Carbon dioxide emissions rise as car transports are still popular because of convenience.
Provision of resources: High energy consumption as over 120 generators are used. Food and water (1 mill gallons) also need to be supplied.
Large amounts of waste are generated because of the large crowd. Costs £780,000 to clean up
environmental benefits of glastonbury
Since 2000, Glastonbury Festival has planted over 10,000 native trees and hedge plants to support and enhance the local environment.
encouraging people to travel by public transport