Biology EOY
1/546
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
547 Terms
Unicellular
single cell
multicellular
many cells
cell
functional unit of life in which chemical reactions that maintain life takes place within
What is a eukaryote and what cells are they?
true nucleus
plants, animals
has true nucleus containing genetic material [DNA] enclosed within the nuclear envelope
What is a prokaryote and what cells are they?
before the nucleus
bacteria, archaea
lacks true nucleus → genetic material lies freely in cytoplasm
Size comparisons

Three major structural features that make up the protoplasm of a cell
cell surface membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
Protoplasm
cell living matter
What’s inside the cytoplasm of a cell
cytosol
organelles
cytoskeleton
cytosol
fluid component, aqueous solution of essential ions [soluble organic compounds like sugar and amino acids; soluble proteins like enzymes]
cytoskeleton
network of fine strands of globular proteins, support cell and maintain overall shape
ultrastructure
structure of cells
organelles
compartments in cytoplasm, might have membrane, has its own function, specific chemical reactions within each
which organelles are double membrane?
nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast = double membrane
ribosomes have _____ membrane
no membrane
Which organelles are single membrane
lysosomes, vacuole = single membrane
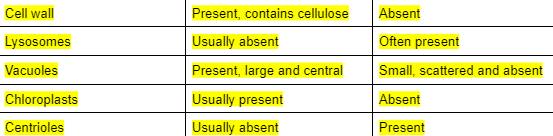
Similarities of plant cell and animal cell (4)
Cell surface membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm with ER, GA, mitochondria, ribosomes
Chromosomes composed of linear DNA wound around proteins
Differences between plant cell and animal cell (5)
cell wall, lysosome, vacuole, chloroplast, centriole
Nucleus structure
Spherical or ovoid
Double-membrane known as nuclear envelope
> outer – continuous with ER
> inner – in contact with nucleus contentsnuclear envelope has pores → nuclear pores
contains nearly all cell’s DNA (organised into chromosomes)
one or more nucleolus within nucleoplasm
nucleus functions (4)
controlling cellular activities
regulate protein + enzyme synthesis
nuclear division (basis of cell replication)
nucleolus — synthesis and partial assembly of ribosomes
what does the nucleolus do
synthesis and partial assembly of ribosomes
nuclear division
basis of cell replication
cell surface membrane structure
phospholipid bilayer
hydrophobic tails on interior
hydrophilic heads on exterior
What is a phospholipid made up of?
Phospholipid is made up of
> glycerol molecule attached to a phosphate group and 2 fatty acid chains
Additional components in cell surface membrane
cholesterol
glycoproteins
glycolipids
transport proteins
cell surface membrane function
partially permeable membrane which acts as a barrier between cytoplasm and environment
prevents most water-soluble substances from entering/leaving
ribosome structure
no membranes
2 subunits – large subunit and small subunit
Where can ribosomes be found in a eukaryotic cell?
Found attached to the rER
Found as free ribosomes in cytosol
what are ribosomes made up of?
Made up of protein and ribonucleic acid (ribosomal RNA)
ribosome function
protein synthesis
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) structure
Where does ER originate from and consist of?
Originates from outer membrane of nuclear envelope
Consists of a network of membranous tubes/sacs called cisternae
Rough ER (rER)
Smooth ER (sER)
Cisternae
a network of membranous tubes/sacs in ER
a stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs in GA
Difference between rough ER structure and smooth ER structure
rER has ribosomes present while sER lacks ribosomes.
sER are more tubular.
rER function
protein synthesis
sER function
lipid synthesis
What does the golgi apparatus consist of? Tell me about its structure.
Consists of a stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae
Continually being formed at cisface by vesicle fusion from ER
Continually budded off at trans face where vesicles are pinched off
GA function
Chemically modifies, sorts and transports molecules
Lysosome formation
Mitochondria structure/shape
Rod-shaped or cylindrical-shaped organelle
Double membrane separated by intermembrane space
> outer membrane - smooth, continuous boundary
> inner membrane - extensively folded to form cristae which project into the interior (matrix)The matrix contain hereditary materials [circular DNA, RNA] and ribosomes
What is the double membrane in a mitochondria separated by?
intermembrane space
Compare the inner and outer membrane of a mitochondria.
outer membrane - smooth, continuous boundary
inner membrane - extensively folded to form cristae which project into the interior (matrix)
What does the matrix of a mitochondria contain?
hereditary materials (circular DNA, RNA)
ribosomes
mitochondria function
cellular respiration → to release energy
Lysosome structure
small, spherical vesicles
Lysosomes are formed by _____
Golgi Apparatus
GA apparatus forms ____
lysosomes
Lysosomes are ____ in plants
larger
Lysosomes contain __________________________
hydrolytic digestive enzymes
Lysosome function
Digestion of materials taken in by cells (during endocytosis and exocytosis)
Autophagy
Autolysis
Autophagy
digestion of worn-out/improperly functioning organelles
Autolysis
self digestion of a cell by release of lysosome contents within cell
Differences of vacuoles in animal cells and plant cells
In an animal cell → small, less permanent and are called vesicles
In a plant → large, central, permanent and surrounded by a membrane (tonoplast) which contains cell sap
vacuole structure
Fluid-filled structures bound by single membrane
Vacuole functions
Water entry
Cell expansion during cell growth
Contains pigments [anthocyanins]
Hydrolytic enzymes make vacuoles act as lysosome
Stores waste products
Stores food
Vacuoles contain _____ called ________
pigments called anthocyanins
What makes vacuoles act like lysosomes?
hydrolytic digestive enzymes
centriole structure
Cylindrical (tube-like) structure
What are centrioles composed of?
microtubules
What does 1 centriole consist of?
1 centriole consists of 9 microtubule triplets arranged as a cylinder
How many centrioles make up a centrosome?
2 centrioles = 1 centrosome
How can centrioles be found?
Found in pairs in cytoplasm, outside nucleus but close to it
Found as single structures at the base of cilia and flagella
centriole function
Produce spindle fibres which attach to chromosomes and separates them during cell division
Formation of cilia and flagella
Chloroplast structure
Large
Double membrane — outer, inner
Compare the outer and inner membrane of chloroplasts
outer — smooth, continuous
inner — give rise to lamellae or thylakoids which extends through interior
What is in the interior of a chloroplast?
Interior is a gel-like matrix called stroma
stroma
gel-like matrix in interior of chloroplast
what happens in stroma/chloroplast interior?
In stroma, thylakoids are stacked into grana, which are joined together by intergranal lamellae
What does chloroplast contain?
Contains chlorophyll which make chloroplasts appear green
chloroplast function
photosynthesis
cell wall structure of plant cells
Surrounds plant cells, external to cell surface membrane
Made of cellulose
Strong yet permeable materials
Allowing free passage of substances in and out of cell
cell wall function
Mechanical support
Protective layer
What are the two methods of protein synthesis?
Proteins secreted out of the cell (extracellular) → Protein secretory pathway
Proteins needed within the cell → Synthesised by free ribosomes
Protein secretory pathway (8)
Ribosome bound to rER synthesise the polypeptide chain into the rER
Protein becomes enclosed in an ER/transport vesicle
ER vesicle containing the protein bud off from the ER
The vesicle travels and fuses with the cis-face of the GA
The GA chemically modifies, sorts and transports the proteins
The proteins move through the GA by Golgi vesicles budding off from one cisterna and fusing with another
The secretory vesicle containing the protein buds off from the trans-face of the GA, travels and fuses with the cell surface membrane
The protein is released out of the cell
Which elements does carbohydrate contain?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Cx(H2O)y
Three different forms of carbohydrates
monosaccharide
disaccharide
polyscaccharide
Hexose sugars
Glucose, fructose, galactose
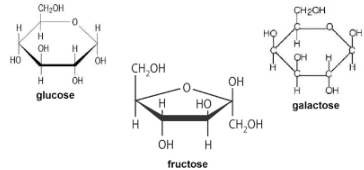
monosaccharide definition
Carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed to simpler carbohydrates
(CH2O)n
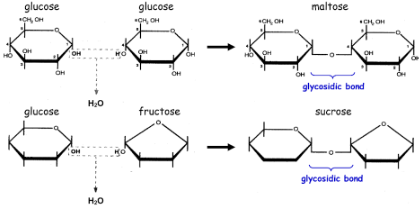
Disaccharide definition
How are disaccharides formed?
Formed by a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides, one molecule of water is removed from the pair of monosaccharides
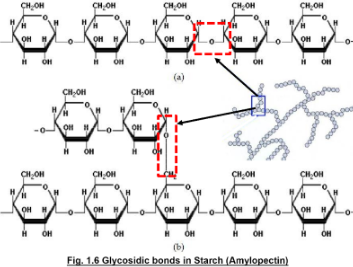
Glycosidic bond
bond formed between 2 monosaccharides
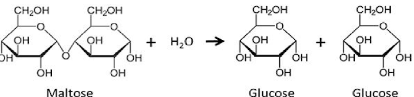
Glucose + Glucose
Maltose
Disaccharide examples
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Glucose + Galactose
Lactose
Glucose + Fructose
Sucrose
Polysaccharide definition
Polymers of monosaccharides
Examples of polysaccharides
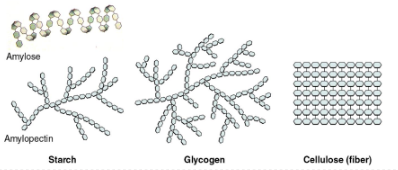
starch
glycogen
cellulose
What is starch used for?
storage in plants
What is glycogen used for?
storage in humans
What is cellulose used for?
structural in plants
Starch is a polymer of _____
glucose
Starch’s structure
Amylose and Amylopectin
Amylose structure
> straight chain structure with a helical structure for more compact structure
> several thousand glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds
Amylopectin structure
> compact
> highly branched structure
> glucose units within and between branches are held together by glycosidic bonds
> has two times glucose units than amylose
Functions of carbohydrates (5)
source of energy
sucrose → good transport sugar in phloem of plants
polysaccharides like starch, glycogen → good storage molecules
cellulose → good structural polysaccharides
monosaccharides → synthesise nucleic acids (deoxyribose, ribose), disaccharides, polysaccharides
Why is sucrose a good transport sugar in plant phloem?
very soluble → can be moved in high concentrations
chemically unreactive
Why are some polysaccharides like starch and glycogen, good storage molecules?
large
insoluble
indiffusible through partially permeable membrane
compact shapes → allow more carbohydrates to be stored
easily hydrolysed into monosaccharides
Why is cellulose a good structural polysaccharide in plants?
Found in all cell walls → good cell wall material
Good tensile strength
Permeable to water and solutes
deoxyribose
constituent of DNA
ribose
constituent of RNA
Which carbohydrates are reducing sugars?
Monosaccharides, Lactose, Maltose
How does Benedict’s test work?
Benedict’s test – sugars can reduce copper from valency 2 to 1
Alkaline copper (II) sulphate (CuSO4) → reduced to → insoluble copper (I) oxide (Cu2O) [a brick red precipitate]
Cu2+ (blue solution) + e- → Cu+ (brick-red precipitate)
Reducing Sugar Procedure (4)
To 2 cm3 of the sample, add an equal volume of Benedict’s solution
Mix well
Place the test tube in boiling water bath for 2 minutes
Observe colour changes