Biology 30 - Assessment #3
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
transitional endoplasmic reticulum
where proteins are butted off in vesicles
Where are proteins matured?
golgi apparatus
_____ makes membranes more rigid
cholestero
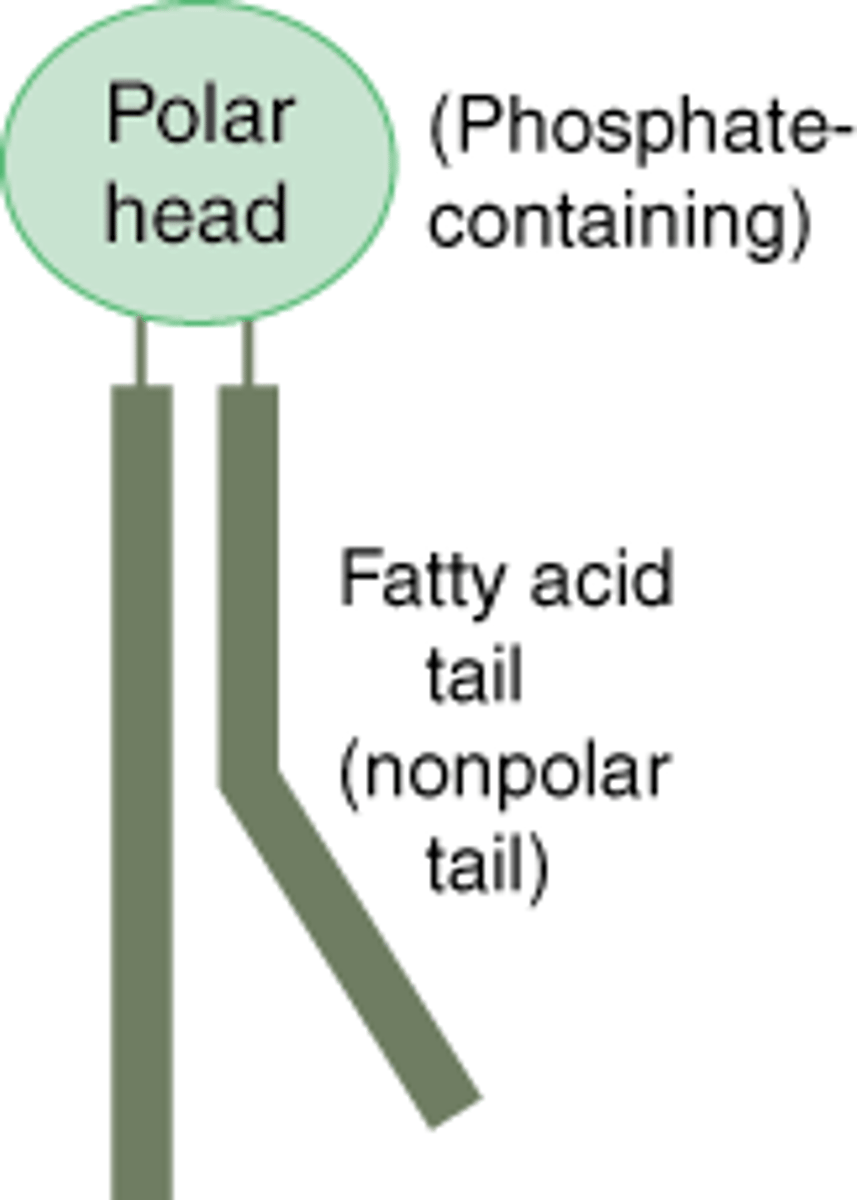
What parts of a phospholipid are hydrophobic and hydrophilic?
The phosphate heads are hydrophilic and the fatty tails are hydrophobic
Why does oil and water separate?
Oil is no polar and water is polar, so they push against each other.
dipole-dipole
Like dissolves like
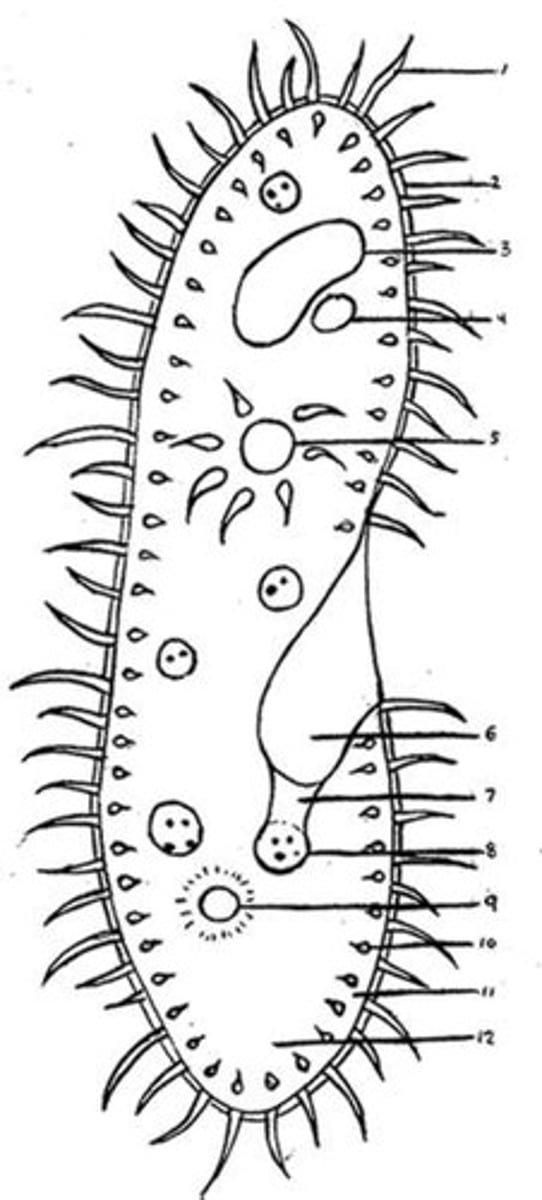
cilia
Slender protuberances that project from much larger cells
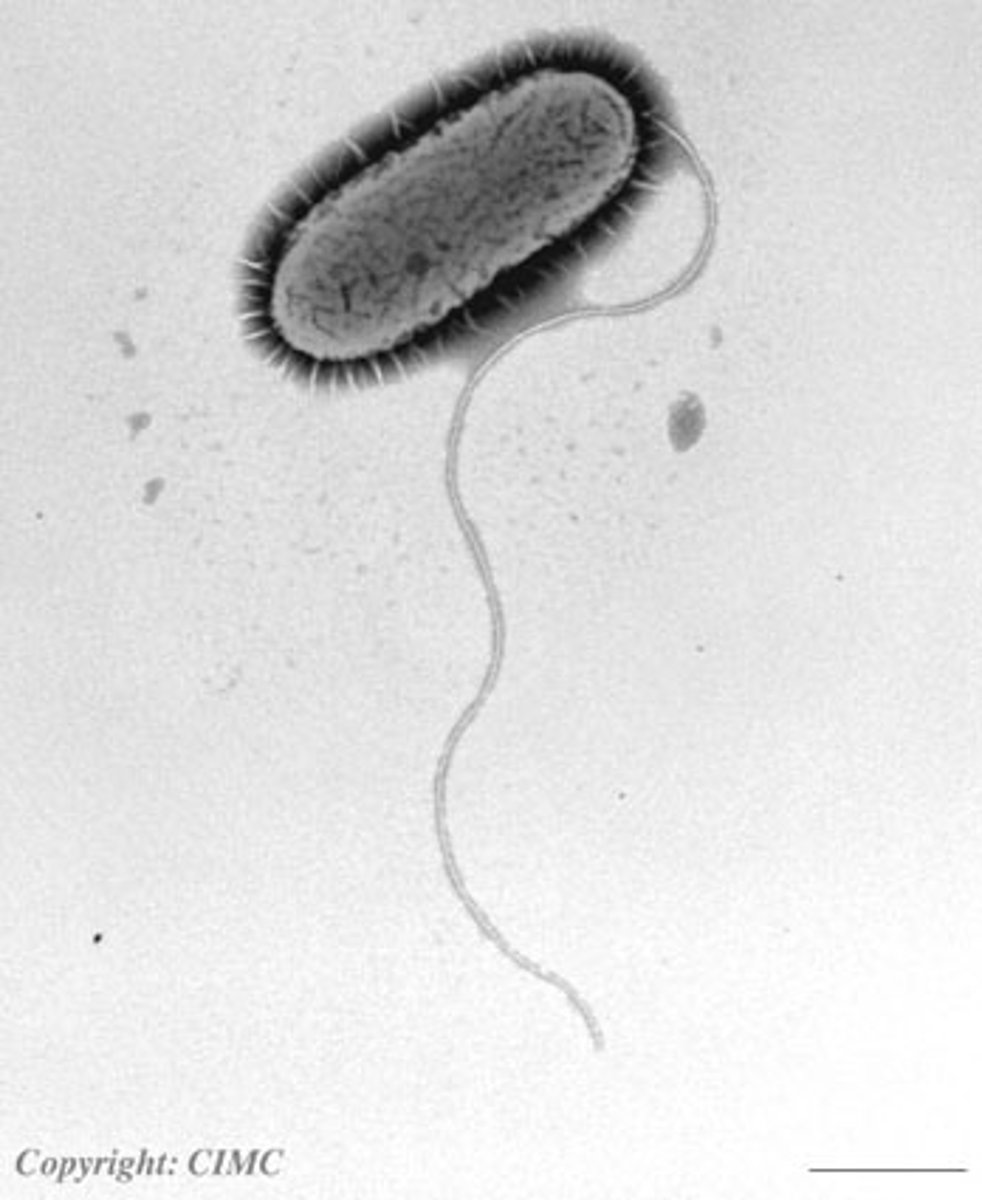
flagella
lash-like appendage that protrudes from cell body
Amphipathic
Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts (e.g. soap)
What are three types of lipids?
phospholipid, triglyceride, steroid
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fats
Saturated fats can stack and have single bonds between all carbon pairs. Unsaturated fats have kinds or bends in their structure from double bonds between one or more pairs of carbon atoms.
What kind of fatty acids do heat loving organisms have?
They have saturated fats to keep their membranes more solid/keep from dissolving at higher temps
What kind of fatty acids do cold loving organisms have?
They have unsaturated fatty acids to keep their membranes fluid at lower temps
The cytoskeleton is composed of what type of biomolecules(s)?
Mainly proteins
What's the purpose of actin/microfilaments?
They serve as a track for myosin, muscle contraction, cytokinesis after mitosis, highways for cargo transport, assemble and disassemble quickly.
What role do intermediate fibers play in the cytoskeleton?
They are playing a mainly structural role for cells and organelles (e.g. keratin)
what role do microtubules play in the cytoskeleton?
They provide a track for kinesin and dyne in motor proteins; play a structural role and help cells resist compression
What gives bacteria their shape?
cytoskeletal proteins
If you want to maximize surface area to volume, which type of lipids should you use?
cholesterol-rich lipid mix
Where are lysosomes found?
only in animal cells
What can't pass through the cellular membrane easily?
Polar/hydrophilic substances
where do you expect to find receptors for lipid soluable signaling molecules?
Cytoplasmic receptors
Where is the receptor for a water-soluable hormone?
in the plasma membrane
where is the receptor for a lipid-soluable hormone?
in the nucleus or cytoplasm
What is signal transduction?
the transmission of molecular signals from a cell's exterior to its interior
what is the sympathetic nervous system?
"Fight or flight" where heart rate increases and digestive process slows down as blood goes to important organs.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
"rest and digest", where heart rate is slow and healthy, body is relaxed.
Is epinephrine hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic
Where do you expect the receptor for epinephrine to be located?
The cell membrane
Where is epinephrine produced?
the adrenal glands
Process of Signal Transduction
1. Signal molecule binds to receptor and receptor changes shape
2. Alpha subunit dissociates & travels to hit intramembrane amplifier enzyme (GDP replaces DTP)
3. cAMP activates protein kinase A
4. kinases causes phosphorylation
Antagonist
repressor, prevents ligand from binding
Agonist
Same as ligand response but synthetic
G-Protein
Composed of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. Carry signal transduction from the receptor to the cytoplasm
During Fight or flight what do you want to do?
a) Release free glucose from stored glycogen
b) Stop making more glycogen
c) Store more glucose as glycogen
d) A & B only
D) A & B only
How many transmembrane a helices does epinephrine receptor have?
7
How is epinephrine's interaction with its receptor?
Epinephrine will eventually diffuse away from its receptor
Blocking epinephrine signaling means...?
Less glucose release
cAMP is produced from ______
ATP
Stress response
stress/fear -> epinephrine -> receptor -> G-protein -> adenylyl cyclase -> cAMP (many)
What does phosphorylation do to an enzyme?
Phosphorylation always changes the target enzyme's structure and therefore its function
If you added a toxin that prevented cAMP from changing into AMP, what effect on blood glucose release would you expect?
Glucose levels would increase (continued to be released into the bloodstream for longer)
Telomeres
protective endcaps of DNA that promote DNA stability and integrity
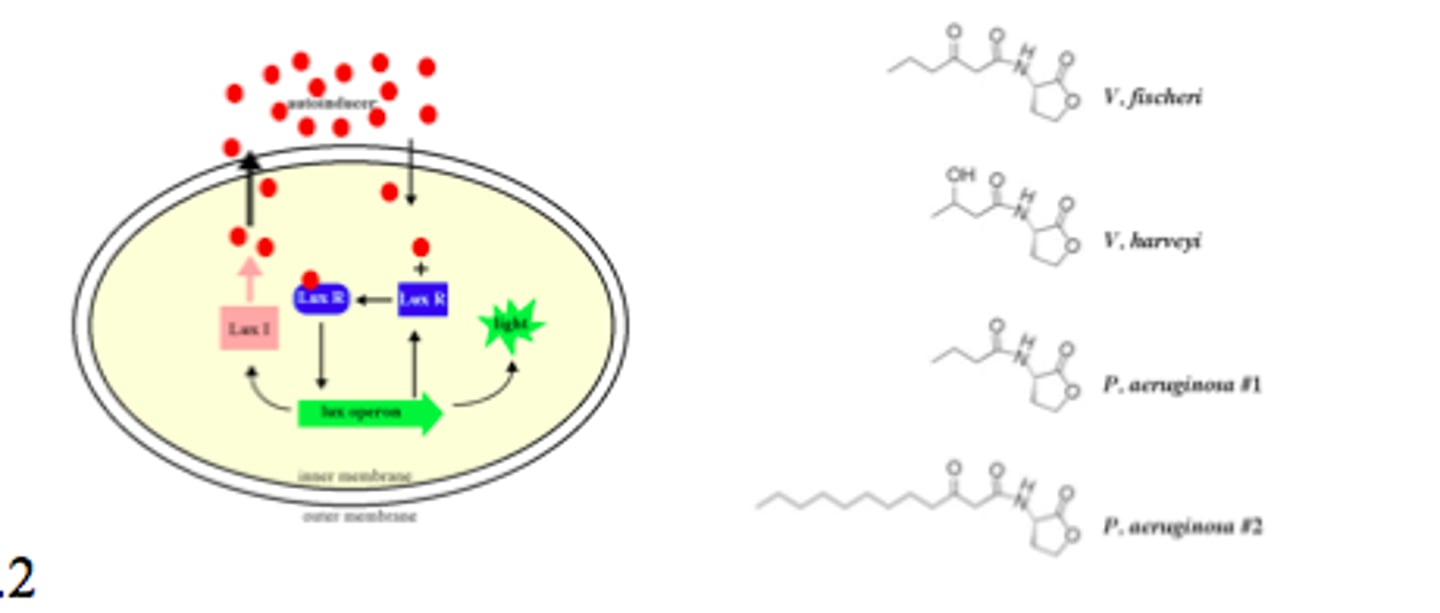
LuxR + autoinducer
transcription factor that induces luciferase production
When would you have the most autoinducer available in the extracellular fluid?
When there are a lot of bacteria around
quorum sensing
The ability of bacteria to sense the presence of other bacteria via secreted chemical signals.
Autoinducers Common Structure
Biofilms
a thin film of mucus created by and containing a colony of bacteria and other microorganisms
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Gram negative disease causing bacterium that has very low susceptibility to antibiotics
If you block LuxI, how will this treat bacterial infection?
It will prevent the production of virulence factors
passive transport
open tunnel that anything can pass through without need for energy
Diffusion concentration levels
High concentration means more molecules in the same volume clumped together. Low concentration spreads them around until they're evenly diffused.
transmission depends on movement of _____
ions
Na+/K+ ATPase
3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in (grows less positive when pump is active)
Which ion controls when the pump is phosphorylation in Na+/K+ pump regulation?
Na+
2nd Law of Thermodynamics (Entropy)
an isolated system that is not in equilibrium will tend to increase over time
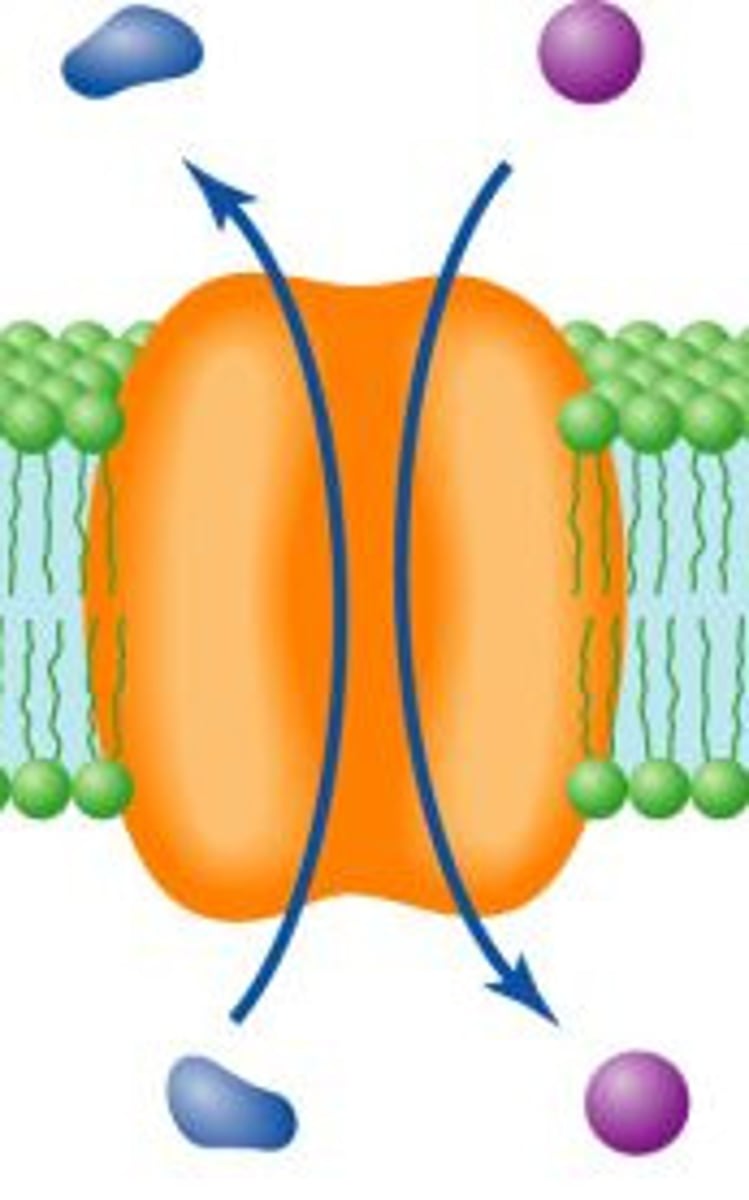
Antiport
two substances move in opposite directions
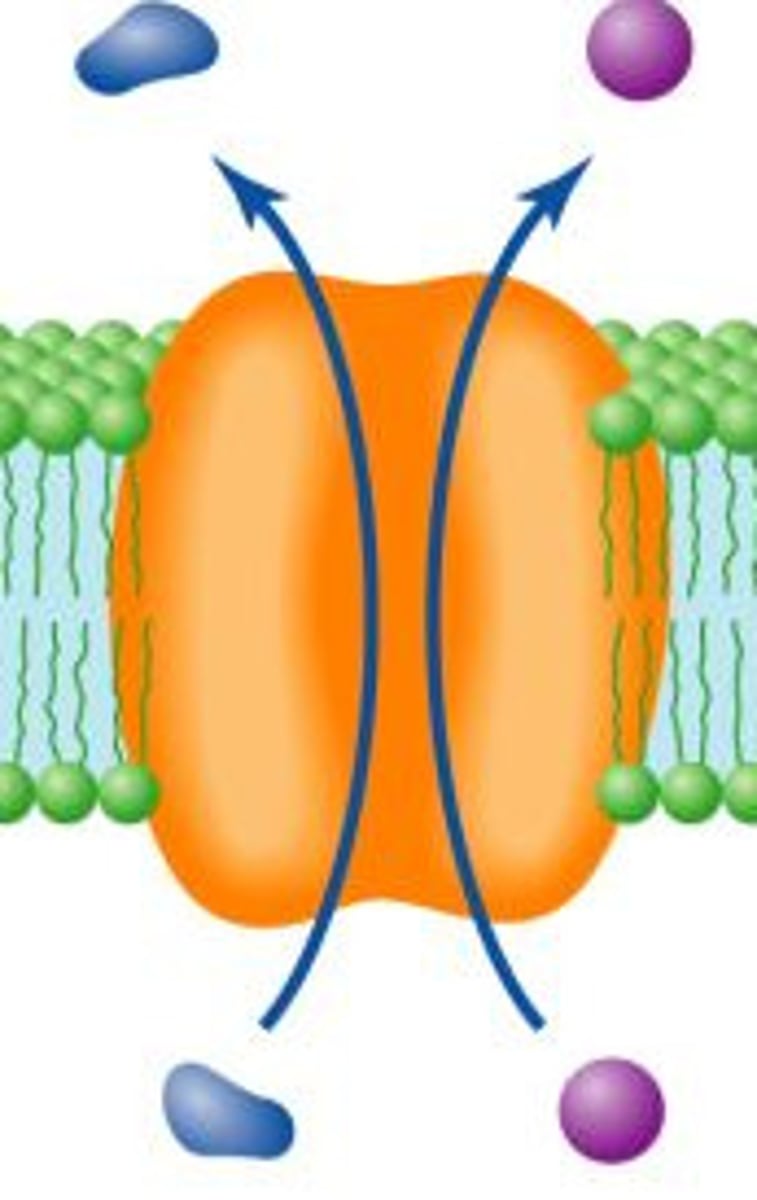
Symport
two molecules travel in the same direction
What mV is resting membrane potential at?
-70 mV
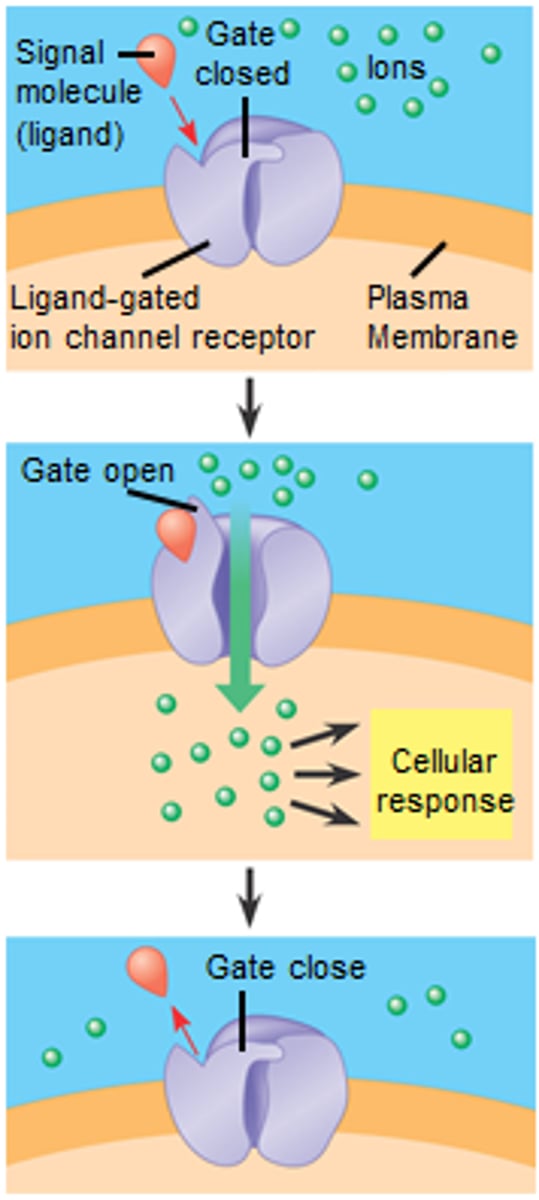
Ligand-gated channel
the binding of a specific substance (ligand) to channel leads to transition in the protein causing it to open or close (neurotransmitters act at ligand gated channels at post-synaptic membrane). Starts the process
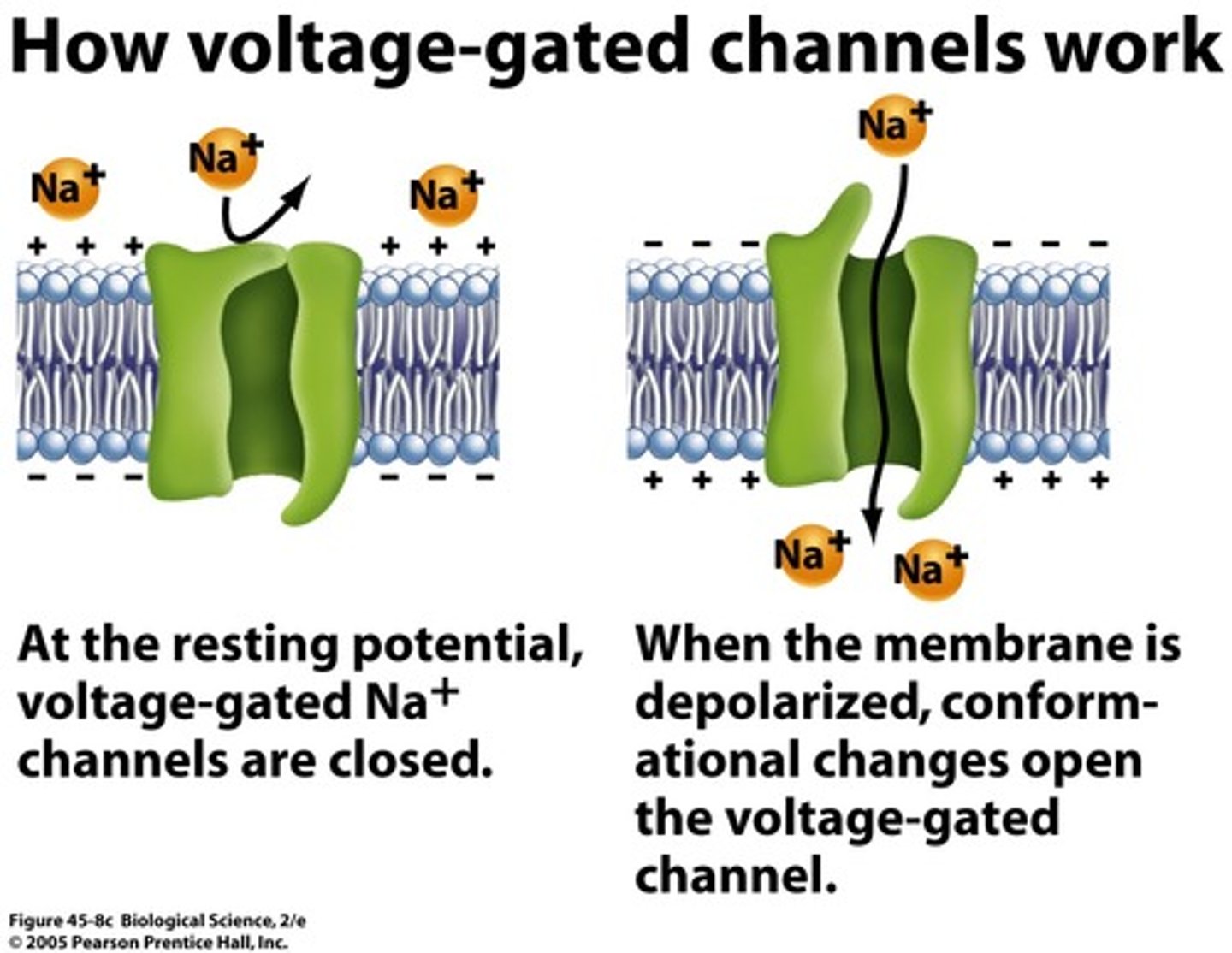
Voltage gated channel
the gate senses voltage change and opens
Mechanically gated channel
the gate senses pressure and open (can sense muscle stretching)
Dr. Francisco Bezanilla
discovered ball and chain mechanism with voltage gated channels
Action Potential
the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
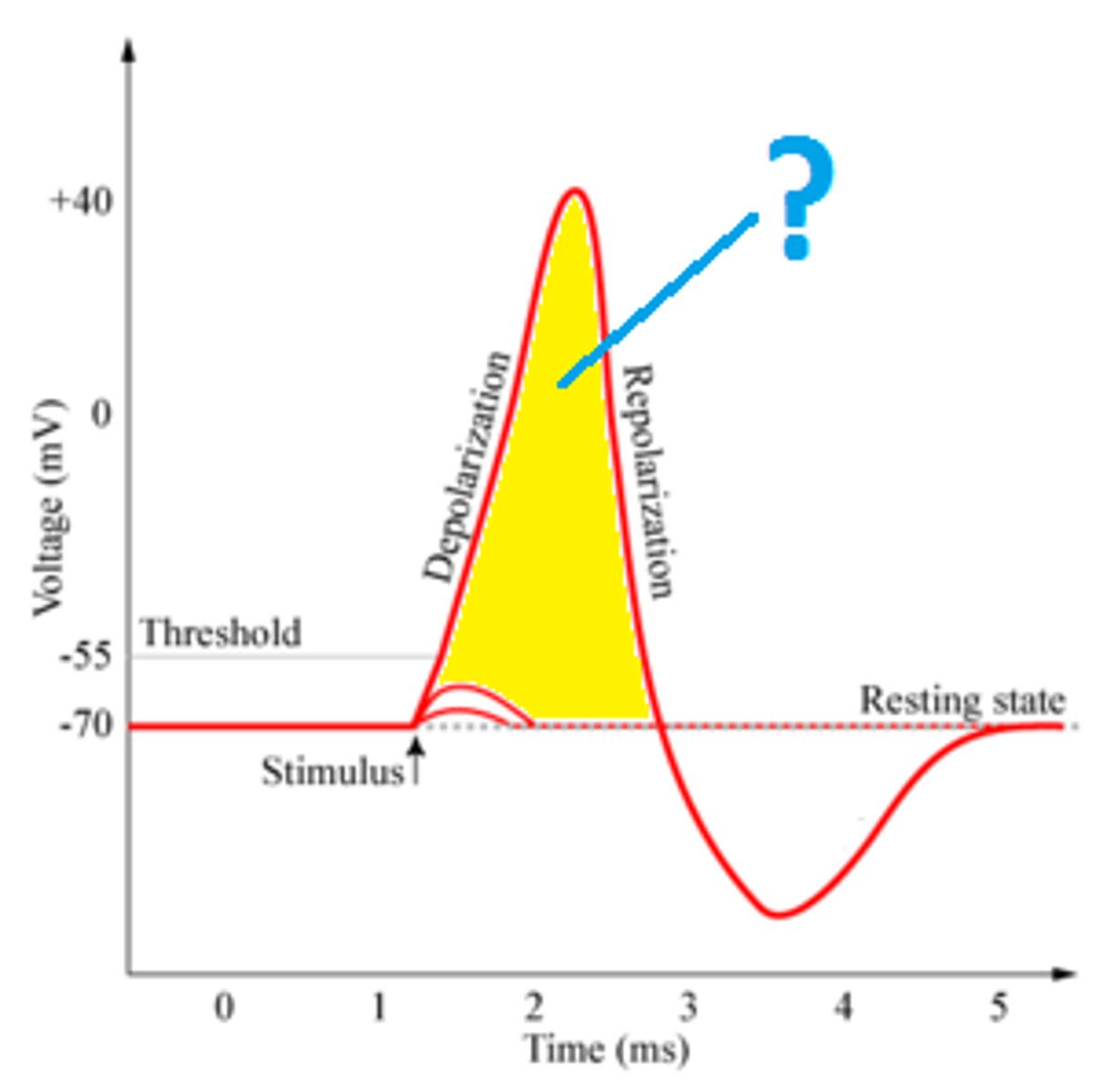
If you opened Na+ Channels, where would Na+ move?
Into the cell
The Na+K+ ATPase relies on which mechanism to work?
covalent modifications of the pump (phosphorylation)
Luigi Galvani
discovered that muscles of dead frogs' legs twitched when struck with an electric spark
Signal propagation
once depolarization occurs, the signal is propagated down the length of the axon (like a wave)
Why can action potentials go backwards?
Action potentials can't go backwards because ion signal goes inactive after passing on the information
Proprioception
the sense of body position in space
What is the purpose of mouth, tongue, and salivary glands?
Mechanical and chemical digestion through chewing and adding enzymes (lingual lipase and amylase) to make bolus
Why is the stomach acidic?
To denature proteins, keep stomach at the optimal pH for protease pepsin, and to kill any micro-organisms to prevent infection
Why is pepsinogen inactive (pepsin = active)?
Only to have protease activity in the stomach and to minimize destruction of your own cellular proteins
What is the layer closest to the lumen (the cavity) of the stomach?
The mucosa
What parietal cells produce?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Is stomach acid produced all the time?
No, only when there is food in the stomach
When should stomach acid be produced?
When the stomach is stretched
Acetylcholine
activates parietal cells directly and indirectly to produce HCl
Histamine
Stimulates parietal cells to produce HCl
Gastrin
activates parietal cells directly to produce HCl
Which of the following will decrease stomach acid production?
Histamine antagonist
If the parietal cells produce secretes HCl into the stomach lumen, what should happen to parietal cells directly intracellular pH?
The pH increases
How do you protect stomach lining from being eaten up by acid?
Excretion of basic bicarbonate (HCO3-) into mucus layer
How long does it take for the digestive process?
30-40 hours
Peristalsis
series of defined muscular contractions triggered from the nerves in the esophagus
What are the different sections of the small intestine?
duodenum, Jejunum,
and ileum
How much food can the human stomach store?
Up to 4 liters of food
Chief cells
secrete pepsinogen
Mucus cells
release mucin to coat stomach so HCl or pepsin don't degrade the stomach
William Prout
discovered stomachs secrete HCl
What is a major contribution to a rise in intracellular pH?
The Na+/H+ exchange
Who studied the SGLT1 transmembrane protein?
Pia Röder
What is the function of the SGLT1 transmembrane protein?
It is responsible for transporting glucose into epithelial cells.
Can glucose exit epithelial cells after entering through SGLT1?
No, glucose can enter but can't get out.
What role does GLUT2 -/- play in glucose transport?
GLUT2 -/- transports glucose into villi to be picked up by blood capillaries.
What is more difficult to digest: plants or meats?
plants (think of triceratops eating rocks to digest better)
Why do we need invertase?
To cleave sucrose into glucose and frutose
enteroendocrine cells
Can release hormones that can adjust activity in the stomach
When H leaves, the intracellular pH ____
increases
When Na enters, the intracellular pH ____
decreases