Waves
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
1
New cards
Energy
the ability to do work
2
New cards
heat
energy that is transferred from one body to another as a result of a temperature difference
3
New cards
convection
heat transfer by the flow of matter
4
New cards
conduction
heat transfer by direct contact
5
New cards
radiation
heat transfer by em waves
6
New cards
conductor
a substance that allows electricity to flow
7
New cards
insulator
a substance that does not readily allow the the flow of electricity or heat
8
New cards
wavelength
the distance in which the waves shape repeats
9
New cards
frequency
the amount of vibrations per second
10
New cards
amplitude
the maximum displacement from its equilibrium
11
New cards
speed
the distance the wave travels in a given amount of time
12
New cards
hertz
the unit for frequency
13
New cards
velocity
the speed of a wave in a given direction
14
New cards
medium
the substance that transfers the energy or light
15
New cards
features of a transverse wave
1. wavelength
2. trough
3. amplitude
4. crest
2. trough
3. amplitude
4. crest
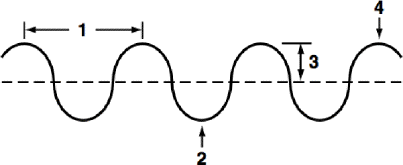
16
New cards
features of a longitudinal wave
a. compression
b. rarefaction
c. wavelength
b. rarefaction
c. wavelength
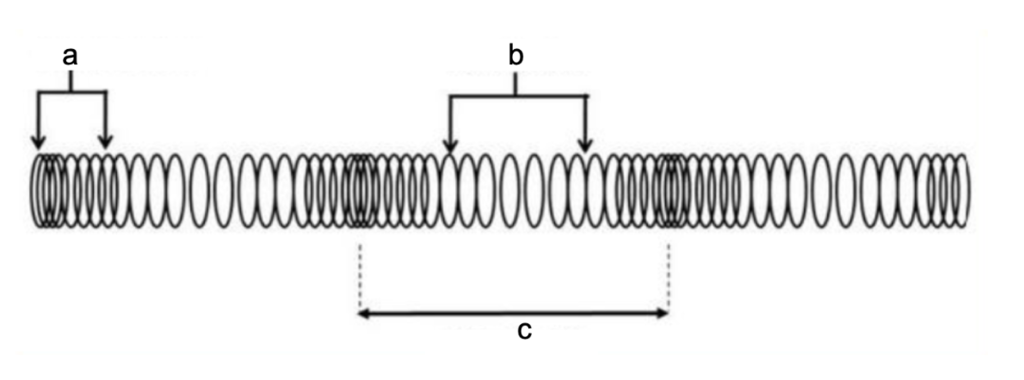
17
New cards
what type of waves are sound waves
sound waves are longitudinal waves
18
New cards
how do sound waves transfer energy
energy is transferred through the vibration of air particles of a solid through which the sound travels
19
New cards
what is the EM spectrum
the EM spectrum is the range of all EM radiation frequencies. it consists of radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, UV, x-rays, and gamma rays.
20
New cards
wave equation
v/f lambda
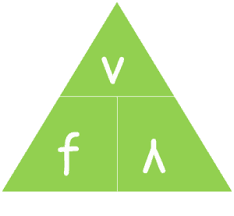
21
New cards
what is ionising radiation
ionising radiation is radiation with atoms that have enough energy to ionise other atoms by removing electrons from them.
22
New cards
how does radiation on the EM spectrum differ in terms of wavelength and frequency
radio waves have the lowest frequency, lowest energy and largest wavelength and gamma rays have the highest frequency, highest energy and smallest wavelength.
23
New cards
1 use of radiowaves
used to broadcast radio and television
24
New cards
1 use of microwaves
used in microwaves to heat up food
25
New cards
1 use of infrared
thermal imagery
26
New cards
1 use of visible light
allows things to be seen
27
New cards
1 use of UV
is used in the medical industry for a variety of purposes such as creating fluorescent lighting effects
28
New cards
1 use of x-rays
used to view inside of bodies and objects
29
New cards
1 use of gamma rays
used to kill cancer cells in medicine
30
New cards
reflection
light bouncing off a medium without absorbing it.
31
New cards
refraction
the bending of light from one medium to another. refraction is caused by different optical densities, the change in direction is caused by a change in speed.
32
New cards
absorption
a process in which light is absorbed and converted into energy
33
New cards
use of reflection
mirror
34
New cards
use of refraction
magnifying glass
35
New cards
focal length
distance from focal point to the centre of the lens
36
New cards
law of reflection
on reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray
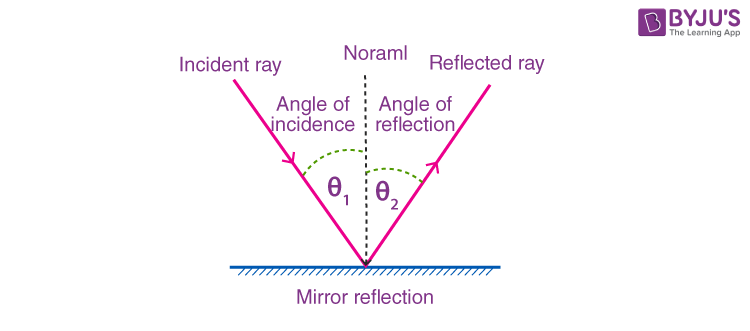
37
New cards
multicellular
consisting of many cells
38
New cards
unicellular
having or consisting of a single cell
39
New cards
role of digestive system + 4 components
The role of the digestive system is to transport, digest and absorb food, extracting nutrients used for energy, growth and cell repair. Organs:
Stomach
Mouth
Liver
Small and Large intestines
Stomach
Mouth
Liver
Small and Large intestines
40
New cards
role of circulatory system + 4 components
The role of the Circulatory system is to transport and deliver oxygen and nutrients to the cells and remove waste products such as carbon dioxide.. Organs:
Heart
Veins
Arteries
Capillaries
Heart
Veins
Arteries
Capillaries
41
New cards
role of respiratory system + 4 components
The role of the respiratory system is to aid the body in breathing. The respiratory tract conveys air from the mouth and nose to the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the alveoli and the capillaries. Organs:
Lungs
Alveoli
Trachea
Diaphragm
Lungs
Alveoli
Trachea
Diaphragm
42
New cards
role of excretory system + 4 components
The role of the urinary/excretory system is to maintain the volume and composition of bodily fluids and ridding the body of waste products. Organs:
Urethra
Ureter
Kidneys
Bladder
Urethra
Ureter
Kidneys
Bladder
43
New cards
stimuli
anything that can trigger a reaction
44
New cards
central nervous system
the portion of the vertebrate nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord
45
New cards
peripheral nervous system
the section of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord
46
New cards
neurotransmitter
a neurochemical that transmits nerve impulses across a synapse
47
New cards
synapse
the junction between two neurons or between a neuron and a muscle
48
New cards
brain
an organ that coordinates the function of the nervous system
49
New cards
spinal cord
a major part of the central nervous system which conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain
50
New cards
gland
any of the various organs that secrete particular chemical substances for use in the body
51
New cards
hormones
a regulatory substance produced in an organism to influence mood or action
52
New cards
somatic nervous system
A component of the peripheral system that connects the nervous system to the muscles to control voluntary movement and reflex arcs
53
New cards
autonomic nervous system
a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates physiological processes such as heart rate, blood pressure and respiration.
54
New cards
nerve
any bundle of nerve fibres running to various organs and tissues of the body that carry electrical impulses between the body and the brain
55
New cards
sensory neuron
are cells that are activated by sensory input from the environment. They transmit sensory impulses to the brain.
56
New cards
motor neuron
Motor neurons transmit impulses from the spinal cord to the muscles and skeletal system, hence controls movement
57
New cards
receptor
Receptors detect environmental change and in response stimulate electrical impulses.
58
New cards
effector
An effector converts impulses sent from the nervous system into an action
59
New cards
role of the soma
A soma contains genetic information and maintains the neuron structure
60
New cards
role of the dendrite
Dendrites receive synaptic inputs from axons, they process these signals and transfer the information to the soma
61
New cards
role of the axon
Axons transport electrical impulses away from the cell body to be received by other neurons
62
New cards
reflex reaction
an involuntary and sudden response to stimuli
63
New cards
reflex arc
the nerve pathway involved in a reflex reaction
64
New cards
reflex pathway
1. receptor senses a stimulus
2. sensory neuron transmits signal up the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system
3. central nervous system decodes the signal and sends it back to the motor neurons and then the brain
4. motor neurons send directions beck to the site of the stimulus
5. effector cells respond by contracting or secreting
2. sensory neuron transmits signal up the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system
3. central nervous system decodes the signal and sends it back to the motor neurons and then the brain
4. motor neurons send directions beck to the site of the stimulus
5. effector cells respond by contracting or secreting
65
New cards
endocrine system
the system of glands that produce endocrine secretions that help to control bodily metabolic activity
66
New cards
describe the adrenal gland, the hormones it produces and its effect
produces adrenaline. Adrenaline triggers the fight, flight or freeze response by increasing bp and heart rate by redirecting blood toward major muscle groups providing muscles with the requirements to either fight, flight or freeze
67
New cards
describe the thyroid, the hormones it produces and its effect
produces thyroxine. increase metabolic rate, regulates bone growth and increases the body's sensitivity to catecholamines
68
New cards
describe the thymus, the hormones it produces and its effect
produces thymosin. stimulates T-cell production. it ensures the cells are mature so that they can perform their duties within the immune system.
69
New cards
homeostasis
the body's ability to maintain a stable state
70
New cards
function of testicle
produce sperm and testosterone
71
New cards
function of scrotum
holds and protects testicles. holds them outside body to keep them cool
72
New cards
function of epididymis
carries and stores sperm to mature it after it leaves the testes
73
New cards
function of sperm duct (vas deferens)
moves sperm away from its storage place to the outside body.
74
New cards
function of prostate
produces prostatic fluid. contributes additional fluid to ejaculate
75
New cards
function of seminal vesicle
produces a sugar rich fluid that provides sperm with energy and helps with the sperms ability to move
76
New cards
function of penis
Used for sexual intercourse and acts as a conduit for urine to leave the body
77
New cards
function of urethra
Carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In males it also serves as a mode of expelling semen (ejaculation) when orgasming
78
New cards
function of ovaries
produce/store eggs for fertilisation and produce the hormones oestrogen and progesterone
79
New cards
function of fallopian tubes
serves as a pathway for the ova to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tubes.
80
New cards
function of uterus
implantation of the fertilised egg occurs. It is the location of the baby development before birth
81
New cards
function of vagina
where the penis is inserted during sexual intercourse. The baby exits the females body through the vagina and is the route through which menstrual blood is expelled
82
New cards
function of cervix
allows the passage of sperm through the production of mucus to facilitate sperm entry
83
New cards
summarised journey of sperm to ova (8 steps)
1. sperm cells released into female reproductive system
2. once through the cervix cells swim through uterus to fallopian tubes following signals (chemotaxis) emitted by the cumulus cells of the egg
3. on the way sperm cells undergo physical and biochemical changes
4. sperm cells meet the barrier of cumulus cells, to pass through the zona pellucida the cells undergo a crosome reaction that releases an enzyme that allows for entry
5. tail detaches
6. other cells cannot enter (becomes impermeable)
7.fertilisation occurs forming a zygote
8. zygote moves back to uterus and implants itself in the inner wall.
2. once through the cervix cells swim through uterus to fallopian tubes following signals (chemotaxis) emitted by the cumulus cells of the egg
3. on the way sperm cells undergo physical and biochemical changes
4. sperm cells meet the barrier of cumulus cells, to pass through the zona pellucida the cells undergo a crosome reaction that releases an enzyme that allows for entry
5. tail detaches
6. other cells cannot enter (becomes impermeable)
7.fertilisation occurs forming a zygote
8. zygote moves back to uterus and implants itself in the inner wall.
84
New cards
disease
an impairment of health or a condition of abnormal functioning
85
New cards
non-infectious disease
illnesses not caused by pathogens and therefore cannot be spread from one person to another
86
New cards
immunity
the ability for an organism to resist a certain infection or toxin
87
New cards
pathogen
any disease-producing agent
88
New cards
health
a healthy state of wellbeing free from disease
89
New cards
infectious disease
illnesses caused by the spread of microorganisms or prions to other humans, animals or the environment.
90
New cards
vaccination
the injection of a small weakened version of a disease into the body in order to develop the antibodies needed to fight the real virus.
91
New cards
infectious disease examples + the pathogen that causes them (4)
bacteria - tuberculosis
virus - covid
fungi - ring worm
protozoans - malaria
virus - covid
fungi - ring worm
protozoans - malaria
92
New cards
non infectious disease factors + examples (5)
environmental - skin cancer (excessive exposure to UV radiation in sunlight)
metabolic - diabetes (destruction of insulin producing beta cells in the pancreas)
inherited - cystic fibrosis (defective gene)
mental - schizophrenia (affects a persons ability to think, feel, and behave clearly)
nutritional - vitamin C deficiency (lack of vitamin c in ones diet)
metabolic - diabetes (destruction of insulin producing beta cells in the pancreas)
inherited - cystic fibrosis (defective gene)
mental - schizophrenia (affects a persons ability to think, feel, and behave clearly)
nutritional - vitamin C deficiency (lack of vitamin c in ones diet)
93
New cards
Innate Immune system - 1st line of defence
role is to prevent pathogens from entering the body. Physical barriers: skin, cilia, urine. Chemical barriers: stomach acid. both: tears, saliva, mucus
94
New cards
Innate Immune system - 2nd line of defence
a general response to infection. consists of fever (an increase in body temp to slow or kill pathogens), phagocytes (a type of white blood cell that 'swallows' pathogens to destroy them) and inflammation (painful redness or swelling around the site of infection)
95
New cards
Adaptive Immune system - 3rd line of defence
role is to identify and destroy specific pathogens as well as build a long lasting immunity against the pathogen in case of reinfection.
96
New cards
how does vaccination prevent illness
97
New cards
role of radiation in medical technology
98
New cards
biosphere
regions of the earths surface and atmosphere occupied by living organisms
99
New cards
atmosphere
The envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet
100
New cards
geosphere/lithosphere
the rocks and minerals of the earth, contains the crust and upper mantle