B1.1-Carbohydrates-and-Lipids
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Macromolecules
Large biological molecules made from many smaller units (e.g., carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids).
Monomers
Small molecules that can join together to form polymers.
Polymers
Large molecules made by linking many monomers together.
Covalent Bonds
Strong chemical bonds formed when atoms share electrons; hold biological molecules together.
Organic Compound
A carbon-containing compound (excluding CO₂ and carbonates) found in living organisms.
Inorganic Compound
Compounds of non-biological origin, such as water or mineral salts.
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; used for energy, storage, and structure (e.g., sugars, starch, cellulose).
Monosaccharide
A single sugar molecule that cannot be hydrolysed further (e.g., glucose, fructose).
Disaccharide
A sugar made of two monosaccharides joined by a condensation reaction (e.g., sucrose).
Polysaccharide
Large carbohydrates formed from many monosaccharides joined together (e.g., starch, glycogen, cellulose).
Pentose Sugars
Monosaccharides with 5 carbon atoms (e.g., ribose).
Hexose Sugars
Monosaccharides with 6 carbon atoms (e.g., glucose).
Glycosidic Bond
The covalent bond that joins monosaccharides together in carbohydrates.
Starch
A plant storage polysaccharide made of amylose and amylopectin.
Amylose
A polysaccharide of α-glucose with 1–4 glycosidic bonds; forms long, unbranched chains.
Amylopectin
A highly branched polysaccharide of α-glucose; allows rapid glucose release in plants.
Glycogen
A highly branched polysaccharide used as an energy store in animals (liver and muscles).
Cellulose
A structural polysaccharide made of β-glucose; forms plant cell walls.
Cellulose Microfibrils
Bundles of cellulose molecules that provide high tensile strength to plant cell walls.
Storage Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates used to store energy (e.g., starch in plants, glycogen in animals).
Structural Polysaccharide
A carbohydrate used for support and structure (e.g., cellulose, chitin).
Condensation Reaction
A reaction that joins two molecules together using a covalent bond and releases water.
Hydrolysis Reaction
A reaction that breaks a bond using water, splitting polymers into monomers.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrate chains attached; involved in cell recognition and signaling.
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates covalently bonded to lipids; important in cell membranes and recognition.
Antigens
Molecules (often glycoproteins) that trigger an immune response.
Lipids
A group of organic molecules including fats, oils, waxes, and steroids; insoluble in water.
Triglyceride
A lipid made of one glycerol molecule bonded to three fatty acids.
Fatty Acids
Long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group; building blocks of lipids.
Fats
Triglycerides that are solid at room temperature (usually saturated).
Oils
Triglycerides that are liquid at room temperature (usually unsaturated).
Saturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids with no double bonds; carbon atoms are fully bonded to hydrogen.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids containing one or more double bonds.
Monounsaturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids with one double bond.
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids with two or more double bonds.
Cis
Configuration where hydrogen atoms are on the same side of a double bond, causing a bend.
Trans
Configuration where hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides of a double bond; straight chain.
Steroids
Lipids with four fused carbon rings (e.g., cholesterol, hormones).
Sterols
A subgroup of steroids, including cholesterol and plant sterols.
Cholesterol
A sterol found in animal cell membranes; precursor to steroid hormones and vitamin D.
Isomer
Molecules with the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements.
Polypeptides
Polymers of amino acids (proteins).
Nucleic Acids
Macromolecules (DNA and RNA) that store genetic information.
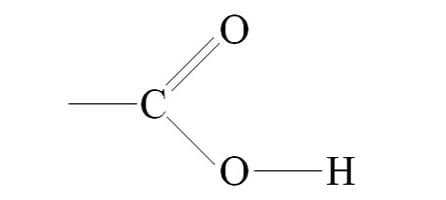
carboxyl group
a carbon atom double-bonded to one oxygen (carbonyl) and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (–OH)