IB Business Management HL UNIT 4 | Quizlet
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Market Orientation
A firm that is market oriented will look to the market to see what consumers need and want.
Product Orientated Firms
A firm that is product oriented will look at what they can make instead of making products that they can sell.
What is marketing?
To identifying the needs and wants of customers.
Anticipate and predict what customers want in the future.
Considering the price, product, place and promotion
Earning a profit
Advantages and disadvantages of market oriented
firms
ADV
Greater flexibility
Able to respond quickly to the changes in the market because of its use of market information
Lower risk
Firms can be confident their products will sell as they are tailored to meet the needs and wants of consumers.
DISADV
Market research is needed
This is to find out what consumers want. This can be very expensive.
No guarantee this approach will work
This is due to the dynamic nature of the external environment.
Advantages and disadvantages of product oriented
firms
ADV
Quality can be assured
More control over operations
DISADV
Needs of the market are generally ignored
High risk strategy with high failure rate
High research and development costs
Market share
Market share refers to an organization's share of the total value of sales within a specific industry.
CALCULATION
Market share = ( firm sales revenue / industry sales revenue ) x 100
The importance of market share
Firms with high market share benefit from their status, price setting abilities and are less threatened by competition.
Market growth
Market growth refers to the rate at which the size of a market is increasing
CALCULATION
Market growth rate = (( current market size - original market size ) / original market size ) x 100
Market leadership
Market leadership refers to the position of the business having the largest market share in a given market.
Benefits of being a market leader
Premium pricing
Economies of scale
Longer product life cycles
Favorable distribution terms
Greater publicity and brand exposure
Easier to attract and recruit highly qualified employees
Extrapolation
Identifies the trend by using past data extending this trend to predict future sales.
Time series analysis
A forecasting method that uses historical sales data to discover patterns in the firm's sales over time and generally involves seasonal, random, and cyclical variations from economic booms and slumps.
Cost-plus (markup) pricing
adding a percentage markup to the cost of the product
Selling price = Cost + profit margin
Penetration pricing
Setting a low initial price on a new product to appeal immediately to the mass market
Loss leader
An item priced at or below cost to draw customers into a store.
Predatory pricing
The practice of charging a very low price for a product with the intent of driving competitors out of business or out of a market
Premium pricing
Pricing the highest-quality or most versatile products higher than other models in the product line
Dynamic pricing
The practice of changing prices for products and services in real time in response to supply and demand conditions
Competitive pricing
Occurs when producers sell products at lower prices to lure customers away from rival producers, while still making a profit
Contribution pricing
A method of pricing where the price charged is based on the variable costs of production.
All direct costs + all allocation of indirect costs = selling price
Price elasticity of demand (PED)
Measures the degree of responsiveness of demand for a product due to a change in the price of a product.
Price elastic (experience a large change in demand when there is a small change in price)
Price inelastic (experience a small change in demand when there is a change in price)
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
Publicity
This is the process of promoting a business and its products by getting media coverage without directly paying for it.
Celebrities are often given free products from businesses in the hope they will be photographed using them publicly.
Public relations (PR)
This refers to marketing activities aimed at establishing and protecting the desired image of an organization.
The goal of PR is to get the media to report events in a positive way from the point of view of the business.
Examples of PR events:
Product launch parties
Press conferences
Radio, podcasts and interviews on news and talk shows
Book signings
Making prominent donations
Methods of promotion
Above the line ATL)
This is any form of paid-for promotional method through independent mass media sources.
Below the line (BTL)
This is the use of non-mass media promotional activities, allowing the business to have direct control.
on
Through the line (TTL)
This is the use of strategies that involve both ATL and BTL methods in an integrated marketing approach
Importance of branding
Branding can bring many advantages to a business which include:
Acting as a legal instrument
Risk reduction
Image enhancement
Earning higher revenues
Premium price setting ability
Recognition and loyalty
Distribution benefits
Brand value
This refers to the premium that customers are willing to pay for a brand name over and above the value of the product itself.
The benefits of having a strong brand value include:
Higher market share
Higher barriers to entry
Premium prices
Brand loyalty
This occurs when customers buy the same brand time and time again. They are devoted to the brand since they have a preference over other brand names.
The opposite is brand switching where customers turn to alternative brands.
Brand awareness
This measures the extent to which potential customers, or the public, recognises a particular brand.
Brand awareness can benefit the business by bringing:
Higher sales revenues
Competitive advantages
Repeat purchases
Brand development
This refers to the marketing process of improving and enlarging the brand name.
Successful brand development helps to extend the product's life cycle.
Some brands are so famous they are often mistaken for the name of the product itself.
Market research
The process of systematically gathering data from consumers, which can be used to influence business decisions
Marketing
The aim of marketing is to help identify, anticipate and satisfy consumer needs and wants profitab
Niche markets
Niche marketing occurs when businesses identify and satisfy the demands of a small group of consumers within the wider market
Mass markets
In mass markets, products are aimed at broad market segments.
Prduction usually happens on a small scale
Mass marketing occurs when businesses selltheir products to most of the available market
Production usually happens on a large scale
Oligopolies
a state of limited competition, in which a market is shared by a small number of producers or sellers.
Low market concentration
A low market concentration is where market share is spread across marketleaders and smaller competitors
These markets tend to be more competitive
High market concentration
A high market concentration is where market leaders have a very high combined market share
These markets are not very competitive
Market leadership advantages
Brand Recognition
Economies of Scale
Innovation and Resources
Distribution channels
Competitive advantage
Attractive to highly-qualified job applicants
But they often face significant pressure
Market planning
Marketing planning is the process of formulating marketing strategies and tactics that will help a business achieve its marketing objectives
Three tools of marketing planning include
Market segmentation
Market mapping
Market positioning
Marketing Objectives (SMART)
These are specific SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound) goals and include
Increasing market share
Maximising sales revenue in a particular region or for a certain product
Achieving distribution targets
Improving brand awareness
Marketing Resources
Planning which resources are required and where they will come from
This may include finance, staff time and expertise, as well as the capital expenditure require achieve the marketing objectives
Marketing Research
Marketing research identifies the factors expected to impact upon the marketing plan, such as...
Market size and growth
Market segments
Competitor positioning
Customert astes, preferences and views
The nature of distribution channels
The marketing mix
The marketing mix
This involves planning the medium- and short-term marketing activities the business intends to undertake and who is responsible for them, including...
Pricing strategies and tactics
Promotional activity
Distribution and logistical plans
Product specifications, features and packaging
Physical evidence such as branding
How people and process are developed to support delivery ofthe rest of the marketing mix
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is the process in which a single market is divided into sub markets or 'segments'
Each segment represents a slightly different set of consumer characteristics
Firms often segment their markets according to factors such as social status, geographical location, religion, gender, or lifestyle
A target market is one or more market segments at which a product or service is primarily aimed
Unique Selling Point (USP)
A unique selling point(USP) is a distinguishing factor or characteristic of a product, service or brand that sets it apart from its competitors
The USP helps a business to differentiate itself and give customers a reason to choose
Developing a brand identity
Achieving a competitive advantage over rivals
Effective communication with customers
The attraction and retention of customers
Achieving power over pricing
Encouraging innovation and adaption
Methods of differentiation
Marketing and branding, packaging, functions and features, customisation, customer service.
Secondary market research
Secondary market research is when a company uses existing information from other sources, like reports, articles, or surveys, to learn about its market and customers.
Government statistics, organisational bodies, and the internet.
Primary market research
Primary research is research you conduct yourself (or hire someone to do for you.)
Surveys, interviews, observations, and ethnographic research.
Extension Strategies
Extension strategies referto the techniques used by businesses to extend the life of a product
beyond its natural life cycle
These strategies are designed to boost sales and maintain profitability for a product that has reach
the decline stage of its life cycle
There are two types of extension strategies:
Product-related extension strategies
Promotion-related extension strategies
Product-related extension strategies
These extension strategies involve changing or modifying the product to make it more appealing to customers and extend its life cycle and can be achieved in one of three ways:
Product improvements with upgraded features and improvements to the previous model
Line extensions e.g. Coca-Cola introduced Diet Coke and Coke Zero as line extensions of its original Coca-Cola
Repositioning e.g. when IBM's personal computer division started losing market share to other brands, it repositioned its products as high-end business machines and focused on the enterprise market
Promotion-related extension strategies
These extension strategies involve changing the promotional aspects to extend a product's life cycle and could include one or more of the following changes:
Changes to advertising
Price promotions e.g. Cyber Monday occur on the first Monday after Thanksgiving in the USA or discount prices
Sales promotions e.g. many coffee shops offer a loyalty program where customers can have a free drink for every six drinks consumed
SWOT analysis
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats a framework used to evaluate a company's competitive position and to develop strategic planning.
STEEPLE analysis
An analytical framework used to examine the opportunities and threats of the external environment
(social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical environments) on business activity.
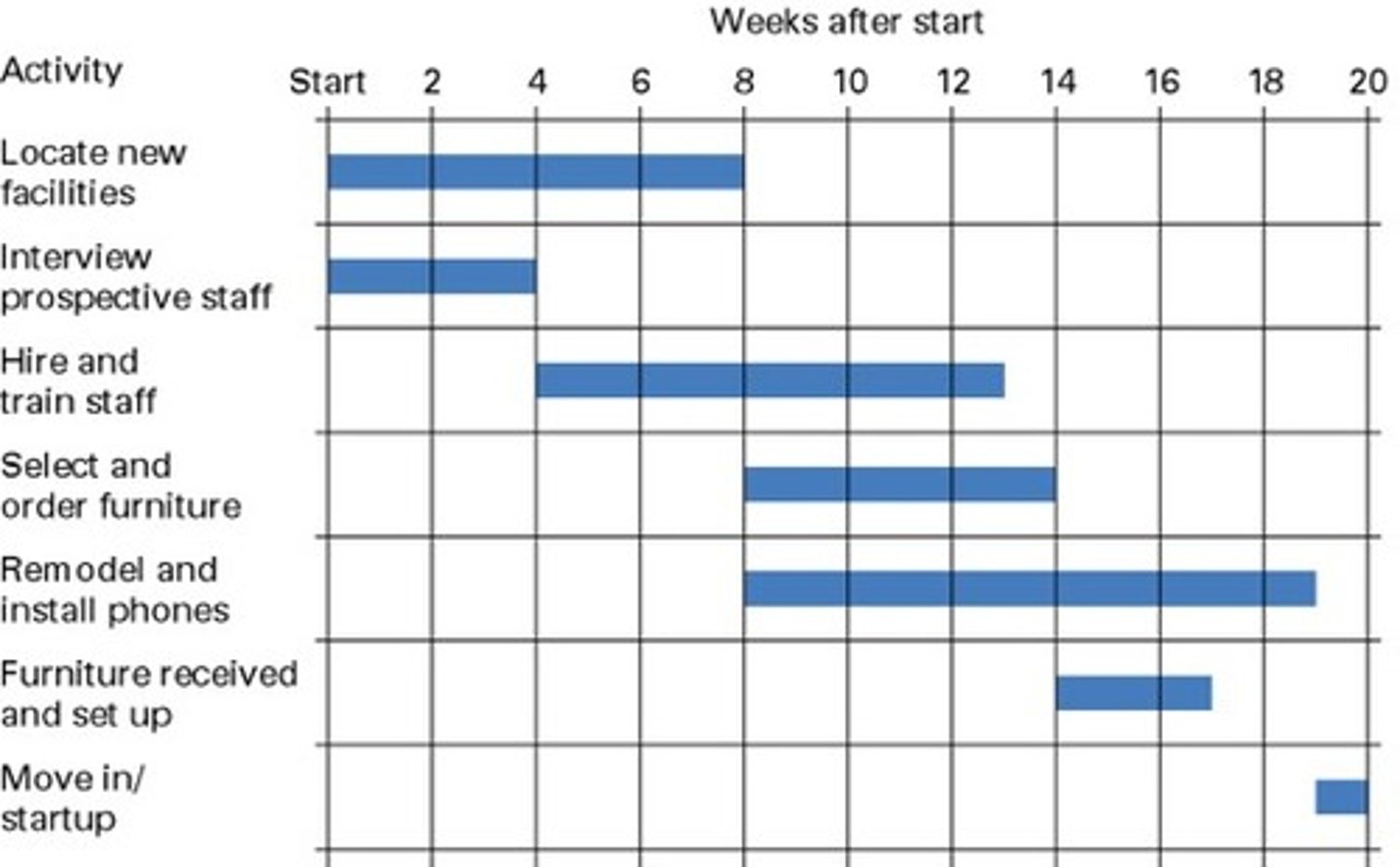
GANTT Chart
A time and activity bar chart that is used for planning, managing, and controlling major programs that have a distinct beginning and end.
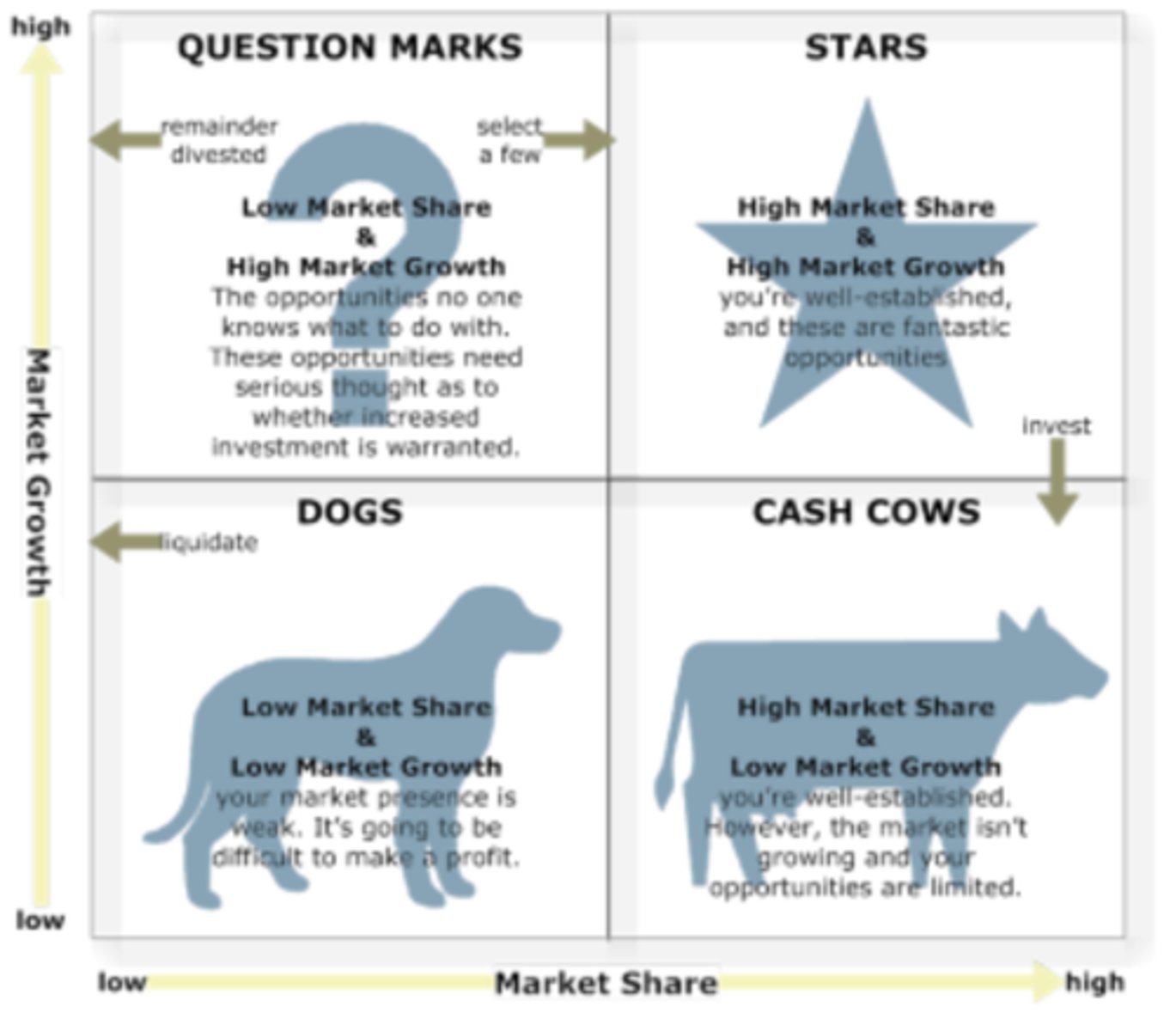
The Boston Matrix
The Boston Matrix describes the impact of market share and market growth on businesses by using four categories: dogs, cash cows, question marks (or problem children) and stars.
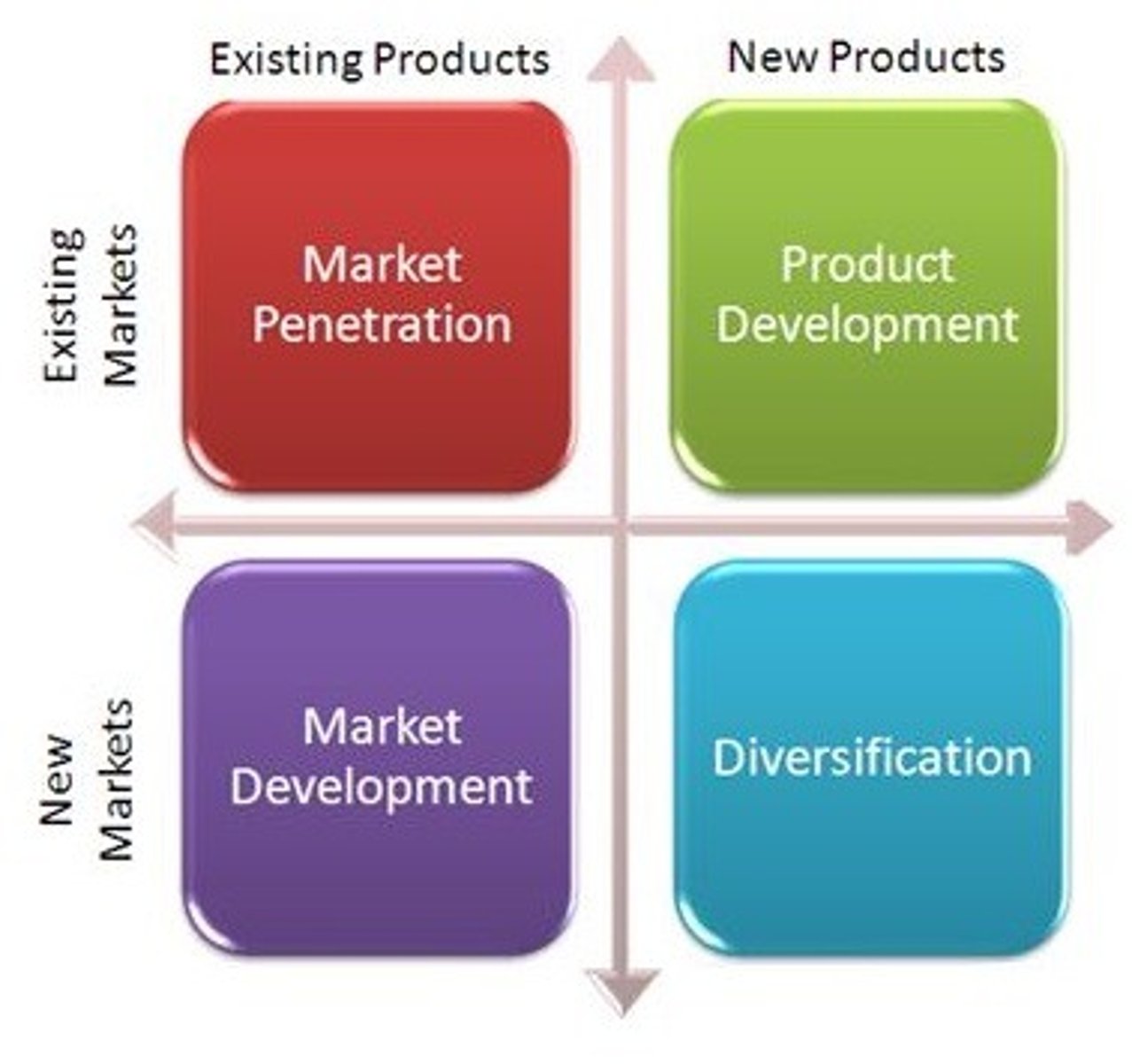
ANSOFF Matrix
An analytical tool to devise various product and market growth strategies, depending on whether businesses want to market new or existing products in either new or existing markets.