UWCSEA - IB Biology 2025 - Topic B1.1 Carbohydrates and Lipids SL and HL
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
B1.1.1—What element is all life based on? Why is this?
Carbon;
due to it forming 4 bonds;
allowing it to form up to four single bonds;
or a combination of single and double bonds;
allows molecules with branched or unbranched chains;
and single or multiple rings;
B1.1.2 What are monomers? What are polymers?
Monomers are single units; e.g. monosaccharides or amino acids;
Polymers are long chains of repeating units; e.g. polysaccharides like starch;
B1.1.2—How are macromolecules formed in living things from individual units?
Monomers combine through condensation reactions;
forming polymers;
with the removal of water;
this happens with the formation of polysaccharides, polypeptides and polynucleotides;
What is the diagram of a condensation reaction and hydrolysis reaction?
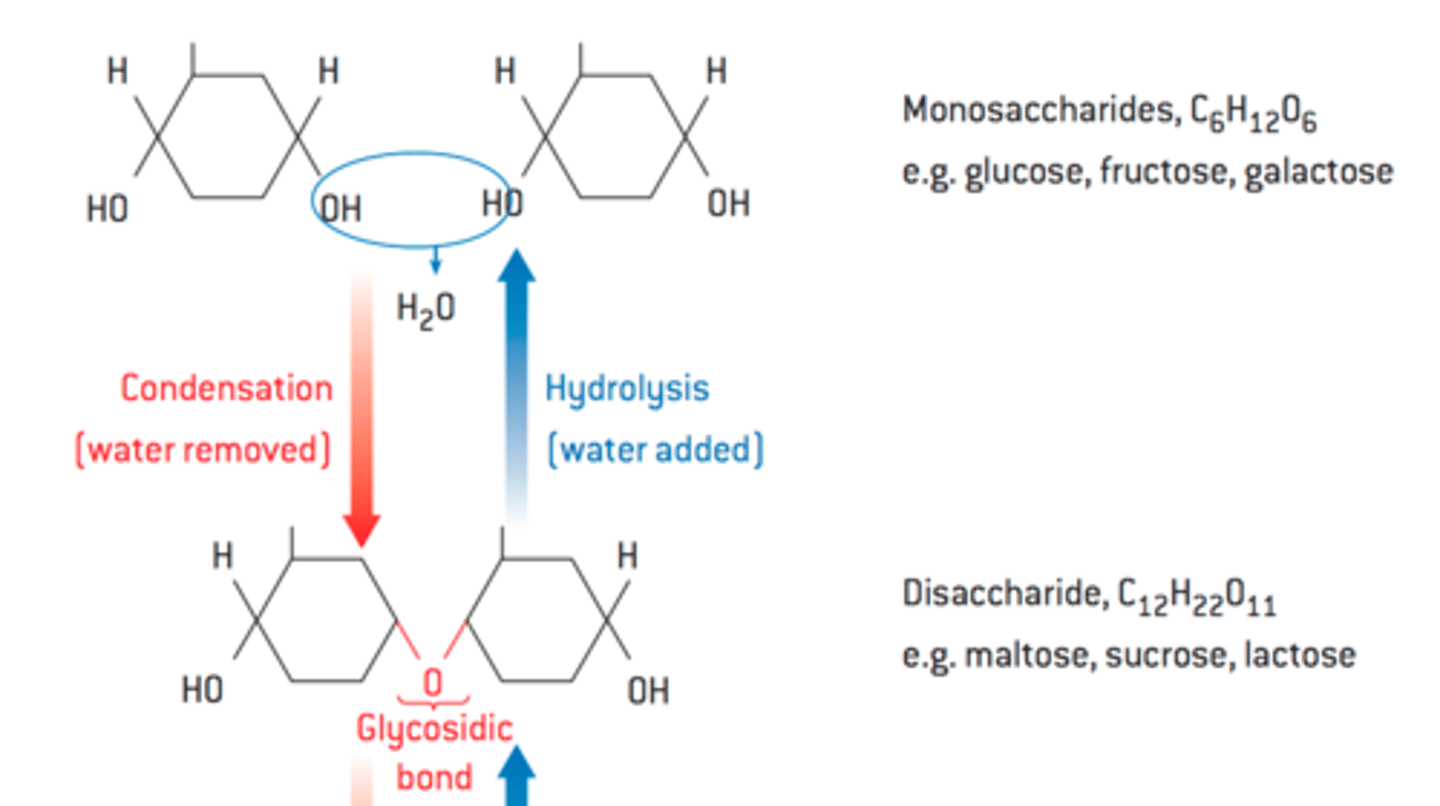
B1.1.3—How are polymers broken down into smaller units?
Through digestion;
by enzymes; in a hydrolysis reaction;
where water is added; giving H and OH groups;
breaking the existing bonds and forming monomers;
B1.1.4—What are monosaccharides? What are the form and functions of monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are single sugars; e.g glucose and fructose;
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides linked together; e.g. lactose and sucrose;
Polysaccharides consist of many monosaccharides linked together; e.g. starch and glycogen;
Form - can form 5 carbon rings, pentose sugars, like deoxyribose;
can form 6 carbon rings, hexose sugars, like glucose;
Function - Glucose
Glucose is very soluble so can be dissolved in water e.g. in blood, and transported;
it is chemically stable and can be stored as a polysaccharide as starch or glycogen, so it does not effect osmosis;
it has a high energy yield when broken down to release energy in respiration;
B1.1.5 How is the polysaccharide starch (and/or glycogen) used by living things? What is its structure?
Starch is a polysaccharide used by plant cells to store glucose (energy); Glycogen in animals;
made from alpha glucose linked together at the first carbon of branched and coiled during polymerisation;
causing it to be a compact store of energy;
which is insoluble, due to its large size;
it is easy to add alpha glucose by condensation to store;
or break off alpha glucose to mobilise energy stores;
B1.1.6 How is cellulose used in plants? What is its structure and function?
cellulose is a polysaccharide made by linking beta glucose together from carbon 1-4;
causing a straight chain;
glucose in bundles and cross-linked with hydrogen bonds;
leads to high tensile strength for cell walls;
to prevent bursting of cells;
B1.1.7— What are glycoproteins? How are glycoproteins used in cell-cell recognition?
Glycoproteins are proteins with short chains of sugars at the end; e.g. a polysaccharide end;
they are used to help recognise cells;
as receptors;
they stick out of cells; e.g. ABO antigens which are blood glycoproteins;
they allow for cells to recognise self or non-self cells;
B1.1.8 What are lipids? What are their properties?
Lipids are substances in living organisms that dissolve in non-polar solvent;
not soluble (only sparingly) in aqueous solvents;
lipids include fats, oils, waxes and steroids;
they are hydrophobic;
B1.1.9—What are triglycerides? How are they formed?
Through condensation of 3 fatty acids and glycerol;
removing 3 water molecules;
forming an ester bond;
between the COOH group of the fatty acid and the OH group of the glycerol;
glycerol can also link to two fatty acid molecules and one phosphate group.
What is the diagram for triglyceride formation?
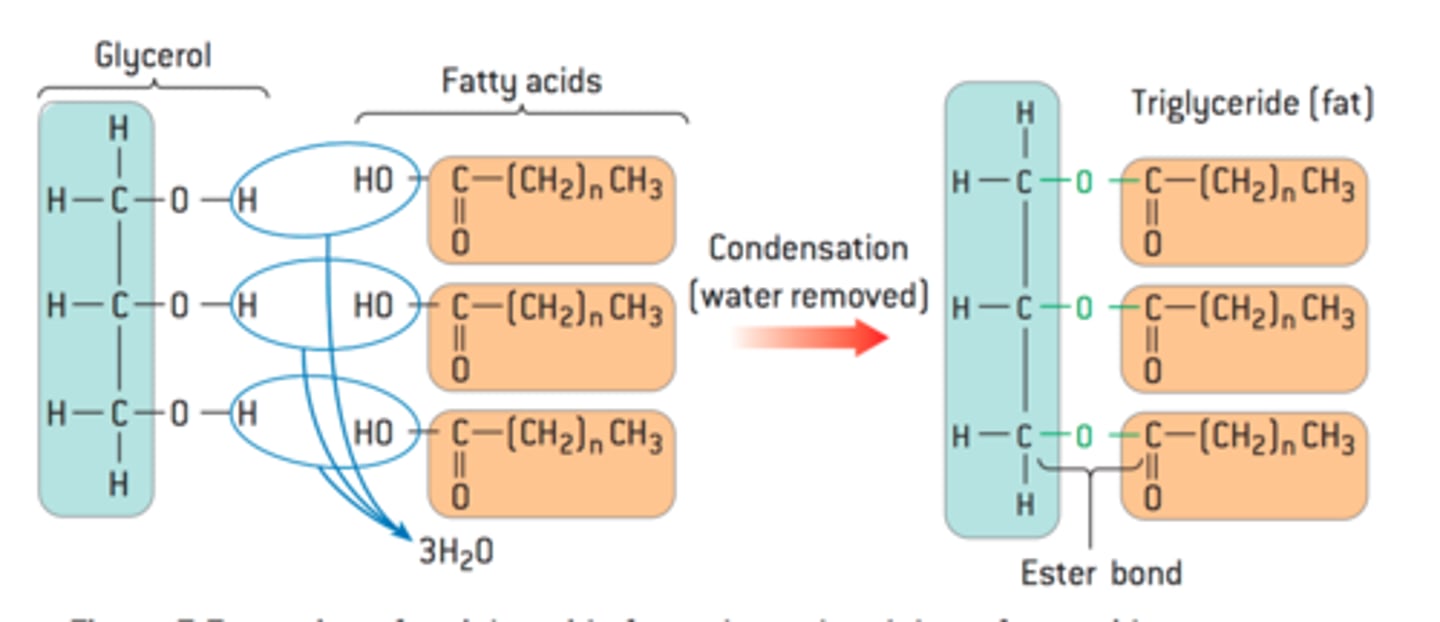
B1.1.10—What is the difference between saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids? What are these used for in plants and animals?
Saturated fats; have only single bonds between carbons and no double bonds;
monounsaturated have one double bond;
polyunsaturated have 2 or more double bonds;
double bonds lower melting point;
polyunsaturated fats are oils at rooms temp;
fatty acids are used as storage of energy in plants; and insulation and storage in endotherms (animals that maintain body temp;
B1.1.11 How are the properties of triglycerides useful in long-term storage and insulation?
Triglycerides contain a lot of energy per gram;
are also good insulators;
makes them useful as long-term energy stores and also as thermal insulators;
for organisms such as seals; which need to maintain body temp in cold conditions;
B1.1.12 What are phospholipids? How are lipid bilayers (in cell membranes) the consequence of the properties of phospholipids?
phospholipids are part lipid and part phosphate;
the lipid region is hydrophobic and the phosphate group is hydrophilic;
this means they are amphipathic as they have both polar and non-polar properties;
they arrange in a bilayer forming the cell membranes of living things;
B1.1.13—What molecules can pass directly through the phospholipid bilayer?
non-polar substances;
as the cell membrane is largely non-polar;
oestradiol and testosterone are non-polar, steroid hormones and can pass directly through the membrane;
steroids have a ring shape;