Muscle Physiology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Tendon
Cordlike CT. Connects muscles to bone
Aponeurosis
Thin, Flat sheet of CT, Connects muscles to bone
Deep Fascia
Separates different muscles while
binding them together
Superficial Fascia
Areolar and adipose tissue, Separates muscles from skin.
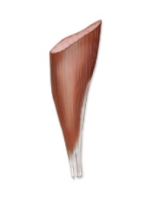
Unipenate Muscle
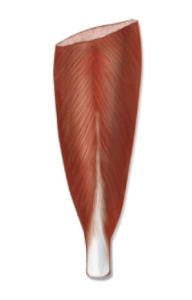
Bipenate Muscle
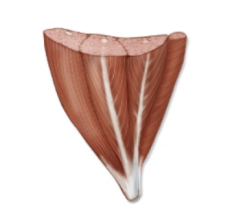
Multipenate : branched tendon
Agonist
Prime mover muscle, Creates main movement
Antagonist
Opposes / Brings skeleton back to its original shape after movement from agonist
Synergist
a muscle that helps an agonist perform its movement. helps stabilize the skeleton.
The origin is the _____ point of attachment
fixed
The insertion is the _____ point of attachment
moving
During Myoblasts, muscle cells fuse to become
long muscle fibers
Some myoblasts become _________ , which support and repair muscle fibers
satelite cells
myoblasts
muscle making cells
Each muscle cell is a singular cell with ______
multiple nuclei
The entire muscle is wrapped in a layer of dense CT ______
epimysium
fascicles are surrounded by
perimysium
the ____ surrounds and reinforces every muscle fiber
endomysium
muscle fibers are also called
muscle cells
sarcomere
the contracting unit of the muscle
Sarcoplasm
the ‘cytoplasm’ (fluid) of the sarcomere. contains organelles and myofibrils
Myofibrils
‘thick’ and ‘thin’ filaments
Sarcolema
the membrane of a muscle cell
invaginations in the sarcolema create ____
T-Tubules
Transverse Tubules (T-Tubules)
Run perpendicular to the myofibrils in a muscle cell. Runs deep and helps transmit electrical signals that move muscles using ion gated channels.
Actin
“thin filaments” have active sites where myosin bind onto
Myosin
“thick filaments” have heads that bind to active sites on actin
Z line
Where a sarcomere ends, and where a new one begins.
Thin filaments attach onto ______
Z-lines
Thick filaments attach onto ___
M-lines
M-line
the center attachment point for myosin in a muscle. anchors myosin and keeps the structural integrity of a muscle as it contracts.
Muscle fibers have abundant _____ for the large amount of energy they need to work
mitochondria
Myoglobin
a protein in the muscle cell that stores and transports oxygen (saves oxygen for aerobic atp production)
Lots of myoglobin in an animals meat can give it a _______ color
dark red
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Surrounds each myofibril. When a nerve impulse travels down the T-Tubules is triggered to release calcium into the sarcoplasm resulting in contraction
Terminal Cisternae
Sacs of SR found next to the T-tubules that serve as calcium reservoirs.
Calcium Pumps
Uses Active Transport (Transport against the gradient) using ATP to move calcium from the sarcoplasm back into the SR when the muscle is relaxed.
Calcium Channels
Voltage sensitive channels that respond to electrical signals from the T-Tubules. When they open calcium floods into the sarcoplasm. results in a contraction
G-Actin
individual actin proteins.
F-Actin
Formed when G-Actin strands come together. Like beads on a string. Made of 2 thin strands intertwined.
Tropomyosin
Protein that blocks receptor heads on the actin when the muscle is relaxed
Troponin
Protein bound to tropomyosin. When calcium binds to it, causes tropomyosin to move off of the active sites, so myosin heads can attach and cause contraction.
A band
The whole length of the thick filament.
H zone
the part of the thick filament with no thin filaments that overlap. shortens with muscle contraction
I band
thin filaments and Titin (elastic filament that anchors thin filaments). shortens with muscle contraction
during contraction myosin pulls on actin, creating an
overlap of the filaments, resulting in contraction.
Synapse
where a motor neuron meets a muscle cell
Synaptic cleft
the gap between the neuron and the muscle. where neurotransmitters travel
The motor neuron of a muscle is usually found at its __
center / mid region
Synaptic Knob / Vesicles
Filled with ACh, calcium pumps, and channels in the membrane
When an AP (action potential) travels down a motor neuron ___
Ion channels on the neuron open, letting calcium in.
When calcium enters the neuron ___
Synaptic vesicles fuse with the synaptic membrane and releases ACh into the synaptic cleft (exocytosis)
When the ACh releases down the synaptic cleft ____
Binds to ACh receptors on ion gated channels on the muscle cell
When the ion gated channels on the muscle cell open
Sodium travels into the muscle fiber, and potassium exits the muscle fiber. The membrane becomes less negative
Acetylcholineesterase
breaks down ACh after neurotransmission ceases.
End plate potential (EPP)
Occurs when enough sodium has traveled into the muscle fiber and changes the charge of the motor end plate to be less negative
When the EPP has reached its threshold ____
an action potential is triggered down the sarcolemma, t-tubules and the SR
When an AP is triggered down the sarcolema ___
It travels down the T-tubules which open its calcium channels that flood into the muscle fiber, causing the filaments to slide past each other and contract.
Calcium binds to ______ which makes tropomyosin move out of the way so that the myosin heads can attach onto the actin
troponin
When ATP is on a myosin head ___
it hydrolyzes, and becomes ADP and inorganic phosphate
When ADP and Phosphate are on the Myosin head ___
It can bind to an actin receptor, creating a cross bridge.
The Powerstroke occurs when ____
The ATP and P from the myosin head release, and the head pulls to shorten the sarcomere (pulls actin inward)
The myosin detaches from the actin active site when ____ attaches to the myosin head
ATP. Head recocks and process can continue again. Tropomyosin also recovers the actin active site.
When muscle contraction stops, calcium is brought back into the SR using ____
active transport