Mosby's RT ARRT Board Review: QA & Equipment
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
Superficial therapy aka Crookes tubes range?
50 to 100 kV.
The treatment distance is 15 to 20 cm source to skin distance (SSD).
Who developed medium energy tubes and what are they also known as?
Medium energy tubes were developed by William Coolidge and are also known as 'hot cathode' tubes.
They operate in the range of 100 to 200 kV with a treatment distance of 50 cm SSD.
What is required for superficial and orthovoltage machines?
They require an x-ray tube and a mobile collimator system, along with filters like aluminum, tin, or copper to harden the beam.
What was the treatment distance and range for supervoltage units aka cascading tubes?
The treatment distance was 80 to 100 cm SSD.
Range 500 kV or more
What are megavoltage units and when did they emerge in the United States?
Megavoltage units (1 MV and greater), including the cobalt machine and linear accelerator, emerged in the 1940s.
Who invented the linear accelerator and when was it first used medically?
William Hansen invented the linear accelerator, with the first medical use occurring in 1954.
What historical significance does radium have in cancer treatment?
Radium was used to treat deep tumors and was discovered in 1898 by Marie and Pierre Curie.
What innovation did L.G. Grummet, MD, introduce in 1949?
He designed a container for the use of cobalt-60 as a substitute for radium.
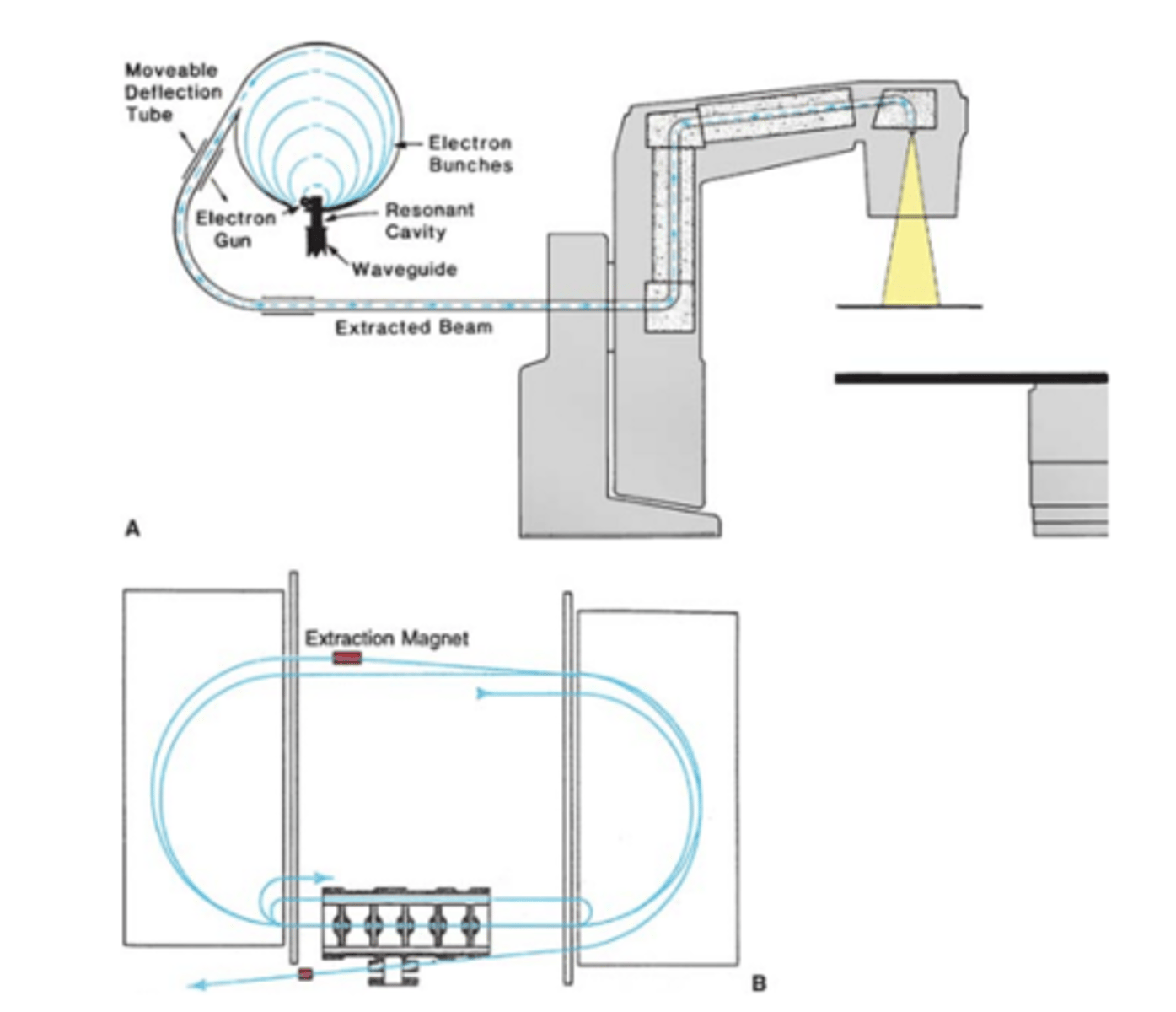
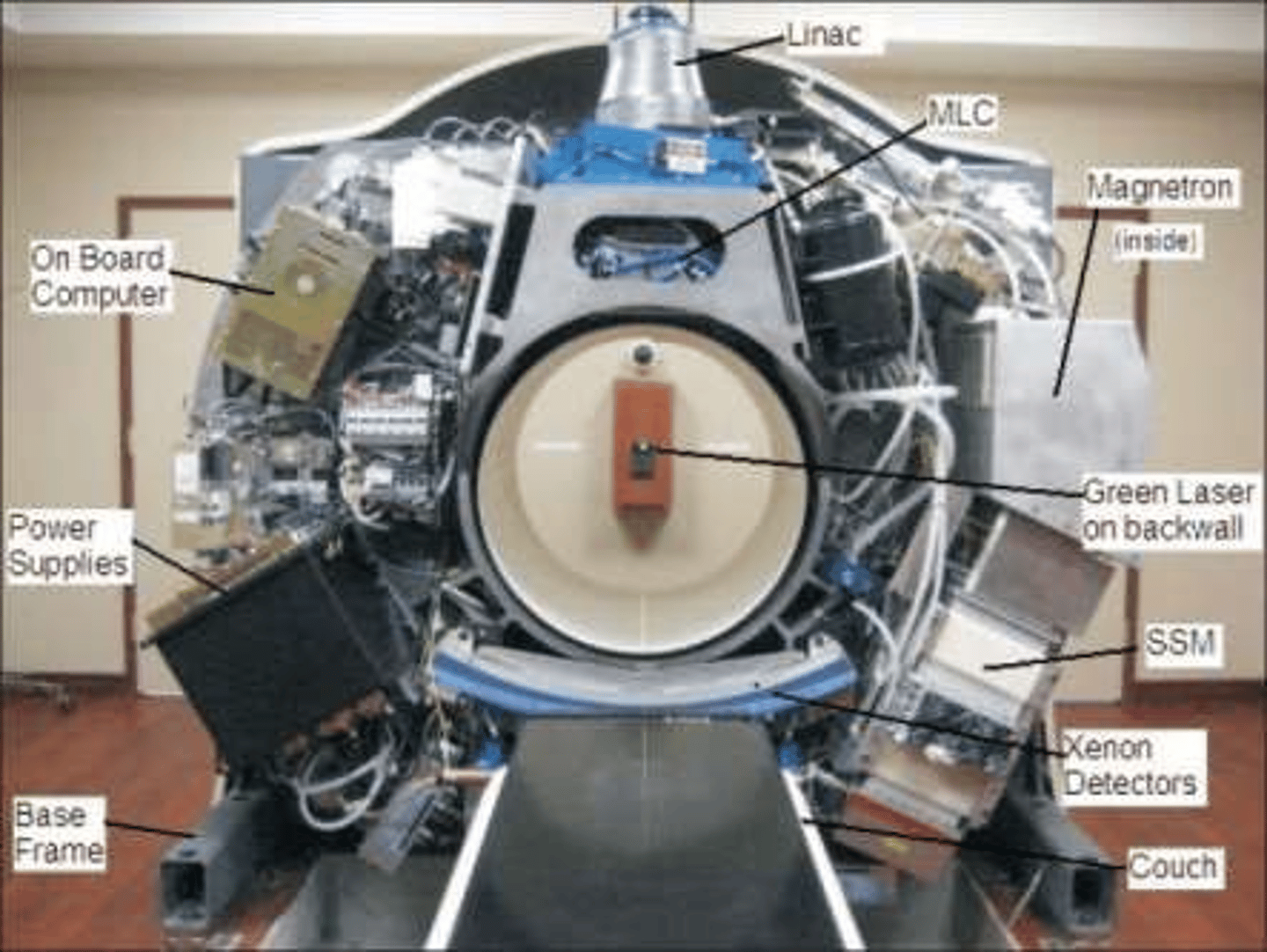
The typical accelerator consists of five main components:
drive stand, gantry, patient support assembly (PSA), electronic cabinet, and console.
What is the purpose of the drive stand?
The drive stand contains the apparatus that drives the accelerator.
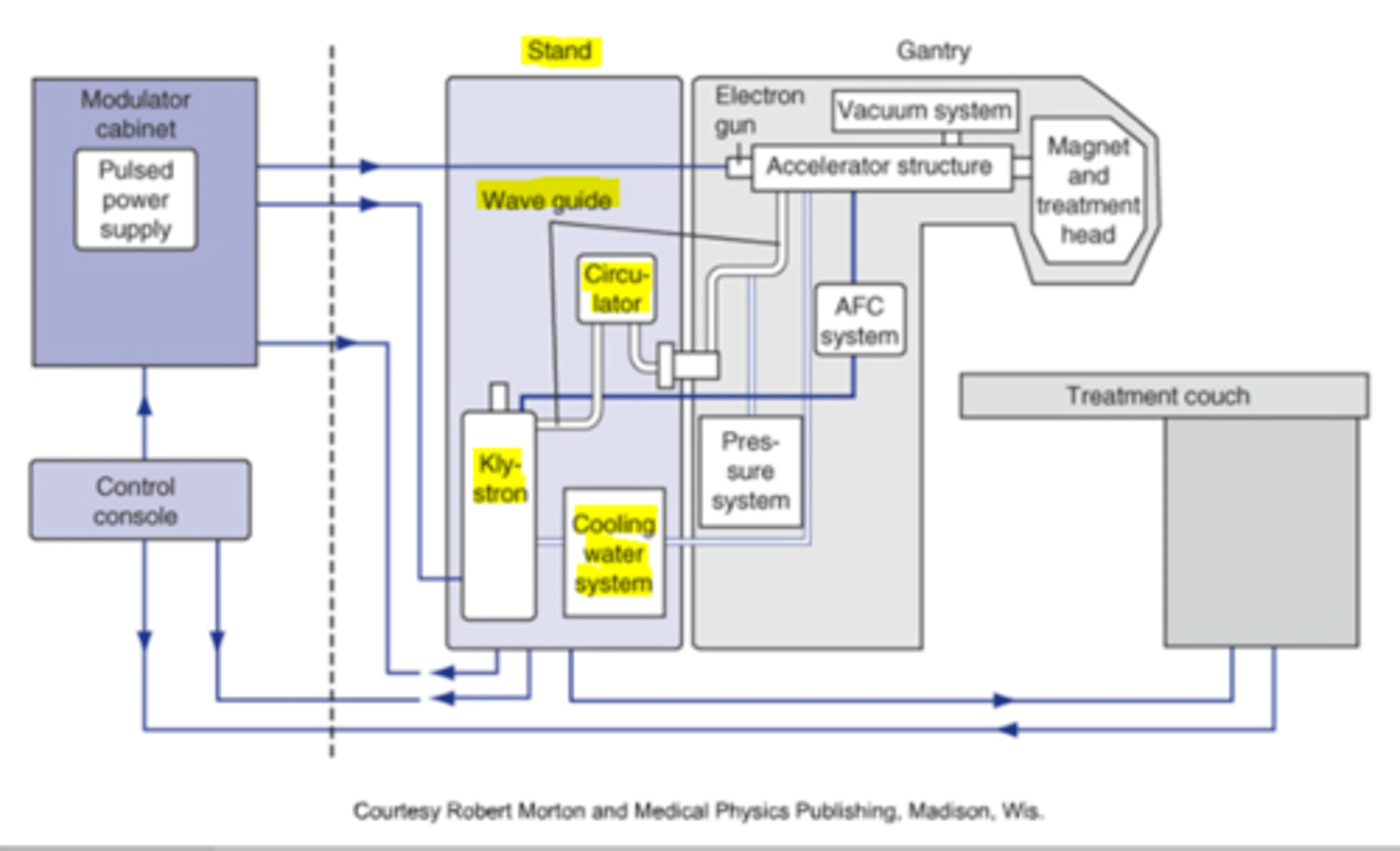
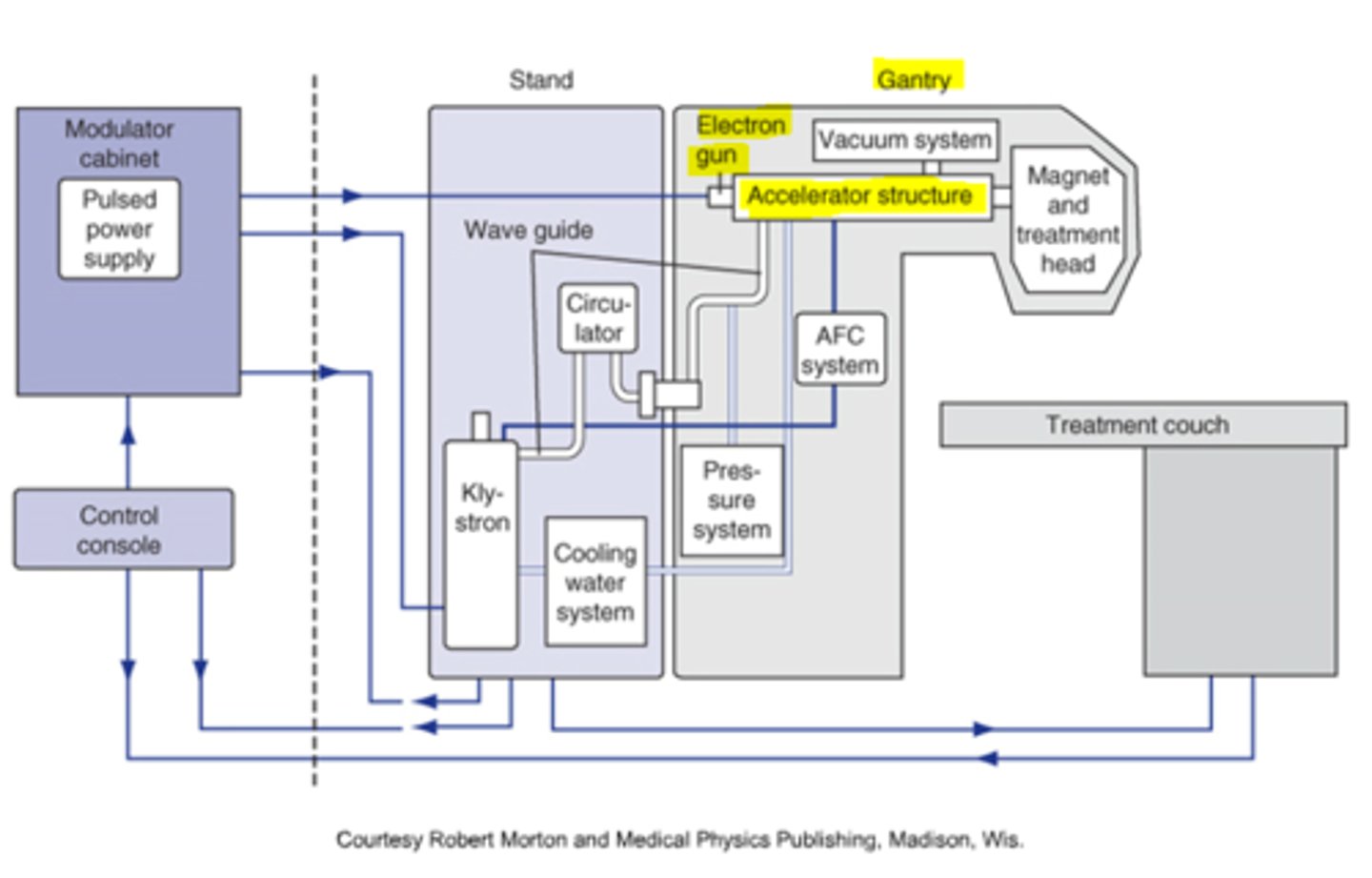
What is the primary function of the gantry?
The gantry is responsible for directing the beam out toward the patient.
What are the major components of the gantry?
The major components are the waveguides, electron gun, accelerator structure, and collimator head.
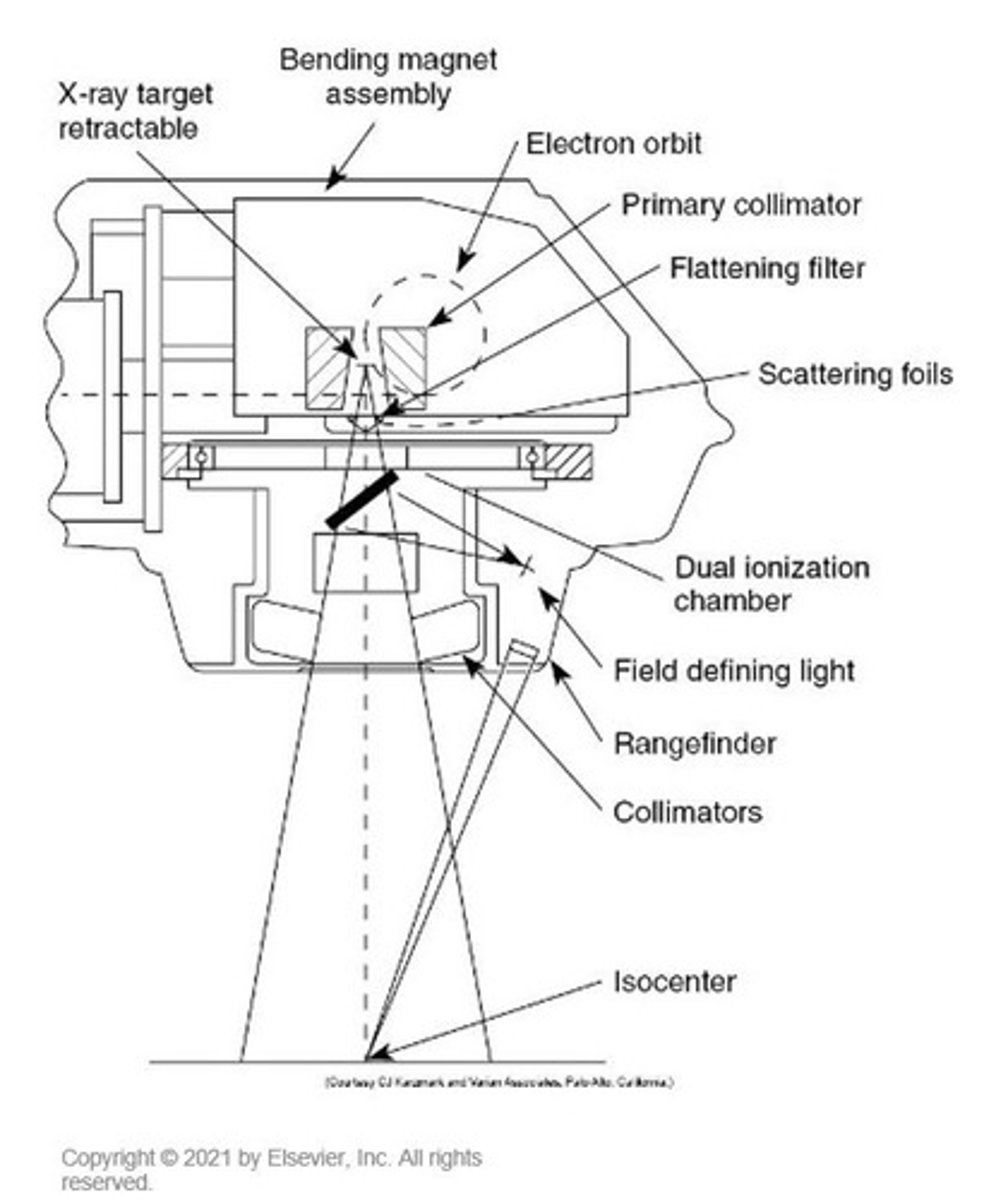
What intricate parts are contained in the treatment gantry head?
The treatment gantry head contains the bending magnet, target, primary collimators, monitor ion chamber, mirror and bulb assembly, secondary collimators, scattering foils, and flattening filter.
How do electrons gain energy in the electron gun?
They start from rest and gain energy through intense acceleration by microwaves.
What is the relationship between final electron energy and waveguide length?
The final electron energy is directly proportional to the length of the waveguide.
What technology allows for a shorter accelerating tube in clinical linear accelerators?
Standing wave accelerator guide. (coolidge cascading theory)
What occurs when two electromagnetic waves are present at the same place in the standing wave guide?
Their energy potential increases across the tube.
What provides the microwave power necessary in the waveguide?
A magnetron or klystron.
What is the primary use of a magnetron?
It is usually used in low energy linacs to generate high frequency microwave power.
What is the function of a klystron?
It generates high frequency microwaves and amplifies them, required for higher energy units.
Why do high energy machines need to be positioned horizontally?
They have long accelerator tubes.
What is the purpose of the bending magnet in high energy machines?
To direct the horizontal stream of electrons down and out toward the target and collimator opening.
two types of bending magnets
90 & 270 (minimizes spatial divergence of the bem
Raw electron beam is :
pencil beam, 2 mm diameter, high intensity in the center
Scattering foil
- Primary - spreads out electrons
- Secondary - flattens electron beam
- Lead
The electron field size is typically defined by attachable cones; cones help control:
the free scattering of electrons in the air.
What is the purpose of the flattening filter in photon therapy?
To evenly distribute the energy of the photon beam.
What materials are commonly used to make flattening filters?
Lead, tungsten, uranium, steel, aluminum, or a combination of heavy metals.
What is the function of a primary collimator in a radiation beam?
The primary collimator collimates the exiting beam.
What is the purpose of monitoring ion chambers?
Monitoring ion chambers keep track of dose rate and field symmetry.
What happens to the beam after it passes through the ion chamber?
The beam is further collimated by a mobile pair of collimators and/or multileaf collimators.
What is the typical size limitation of the collimator area opening?
The collimator area opening is typically limited to 40 cm x 40 cm.
What is the field size setting in radiation therapy?
The field size setting is the actual measured field size at the isocenter of the linac.
What is the purpose of the patient support assembly (PSA) in radiation therapy?
The PSA holds the patient and allows for horizontal, vertical, lateral movement, and rotation around the isocenter.
Where can the electronic cabinet be found?
Within the treatment vault or positioned outside on an opposing wall.
What systems does the electronic cabinet house?
The auxiliary and primary power distribution systems. Cooling system, circuit breakers.
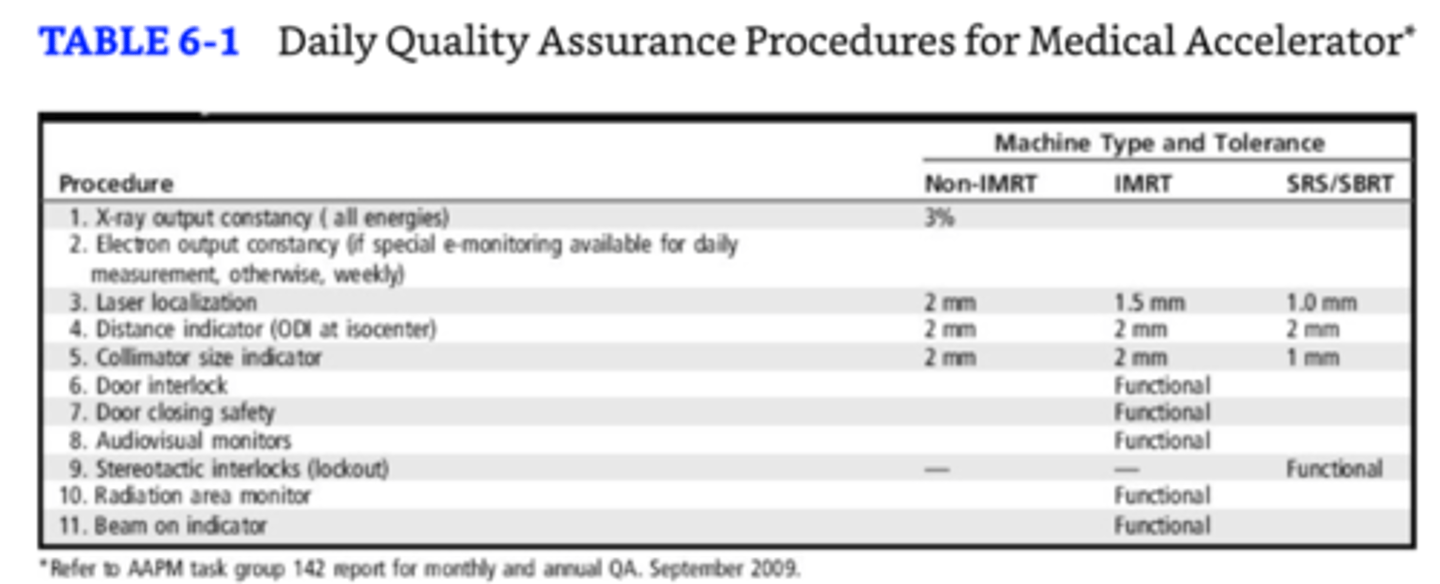
What is the priority for quality assurance procedures related to treatment delivery and safety?
They should be verified daily. Others should be monthly or yearly during equipment overhaul.
Daily QA
How is Cobalt-60 produced?
Cobalt-60 is produced in a nuclear reactor by bombarding stable cobalt with neutrons.
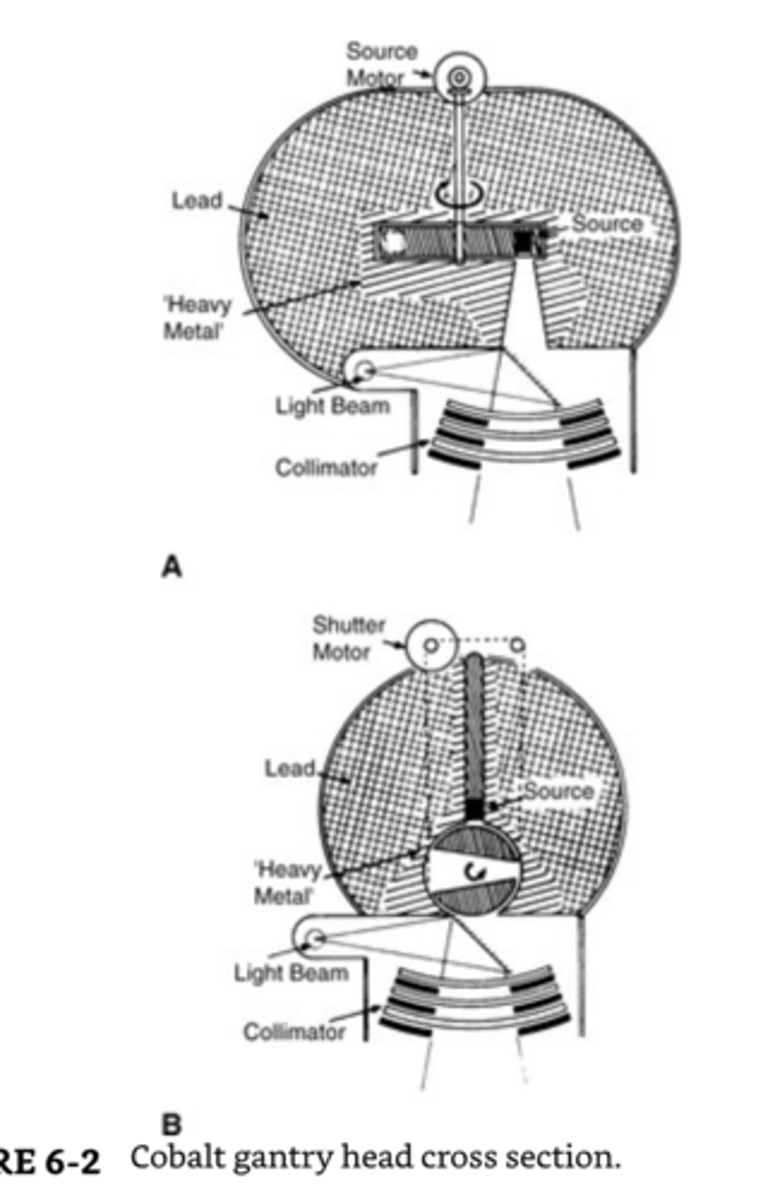
What particles are emitted when Cobalt-60 decays?
Beta particles and two gamma photons are emitted.
What are the energies of the gamma photons emitted by Cobalt-60?
The energies are 1.17 MV and 1.33 MV.
What is the average energy of the gamma photons emitted by Cobalt-60?
The average energy is 1.25 MV.
What is the decay correction rate for Cobalt-60 output?
The decay correction rate is about 1.09% per month.
What is the maximum allowed transmission percentage of the protective housing for Cobalt 60?
The housing should only allow 0.1% transmission.
What should be added to calculated treatment times for Cobalt 60?
Timer error should be added to account for source traveling time on the drawer or wheel mechanism.
Penumbra Formula
S = source size
D = depth SSD = source to skin distance
SDD = source to diaphragm distance (collimator)
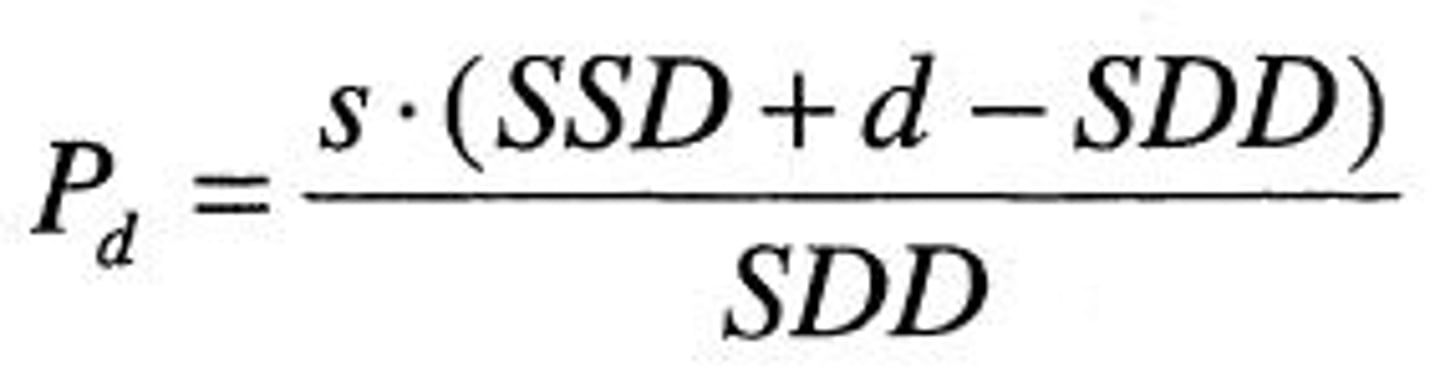
Cobalt is affected by _____________.
penumbra
(Trimmer bars aka tertiary collimators help to reduce penumbra)
For Cobalt-60 linacs, Beam indicators such as light field, collimators, and crosshairs should be verified:
monthly
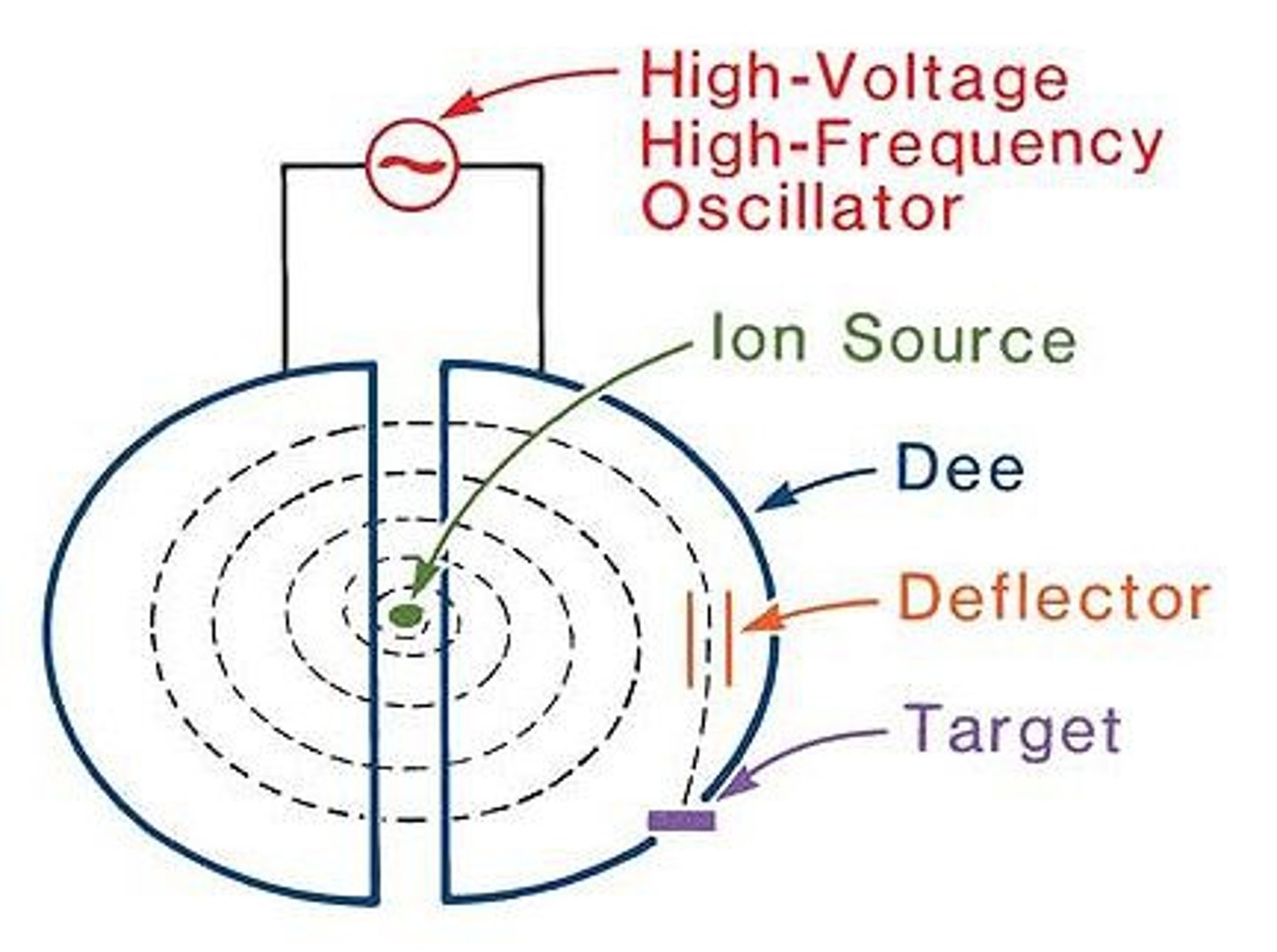
.Cyclotron
Used in nuclear power plants to produce radioisotopes. Flourine-18 used in PET imaging
Produces deuteron, neutron, and proton beams.
Particles are accelerated in a spiral pathway inside two evacuated D-shaped cavities, called dees by a uniform magnetic field. The dees have a small space between them and have opposite polarity.
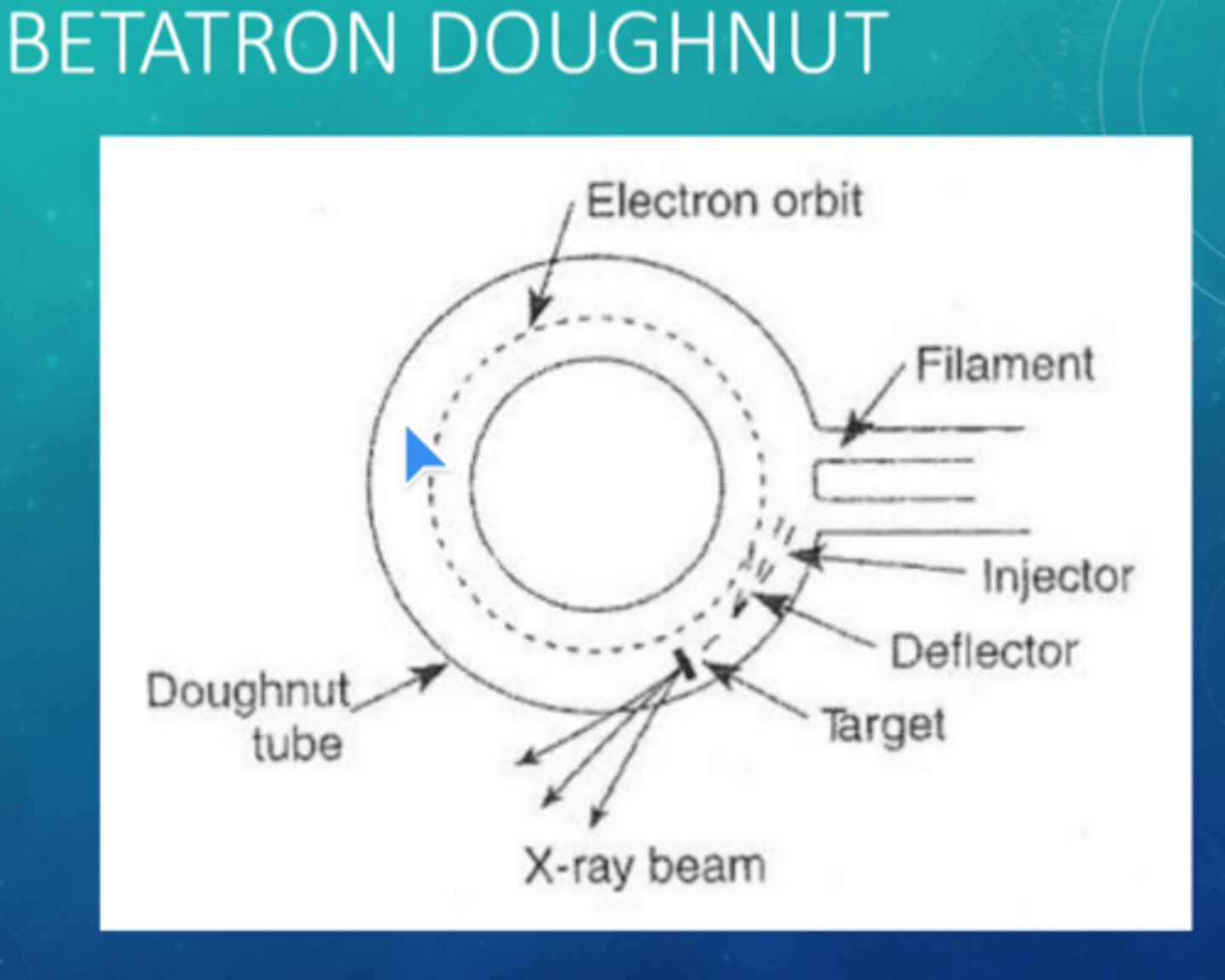
The betatron
accelerates electrons and consists of a magnet fed by an alternating current of high frequency waves.
microtron
Electron accelerator combining linear and cyclotron principles.
What is the design and energy of the tomotherapy machine?
The tomotherapy machine has a ring gantry design similar to a CT scanner.
6Mv.
What is the collimator called in tomotherapy?
The binary multileaf collimator, used for beam shaping and intensity modulation.
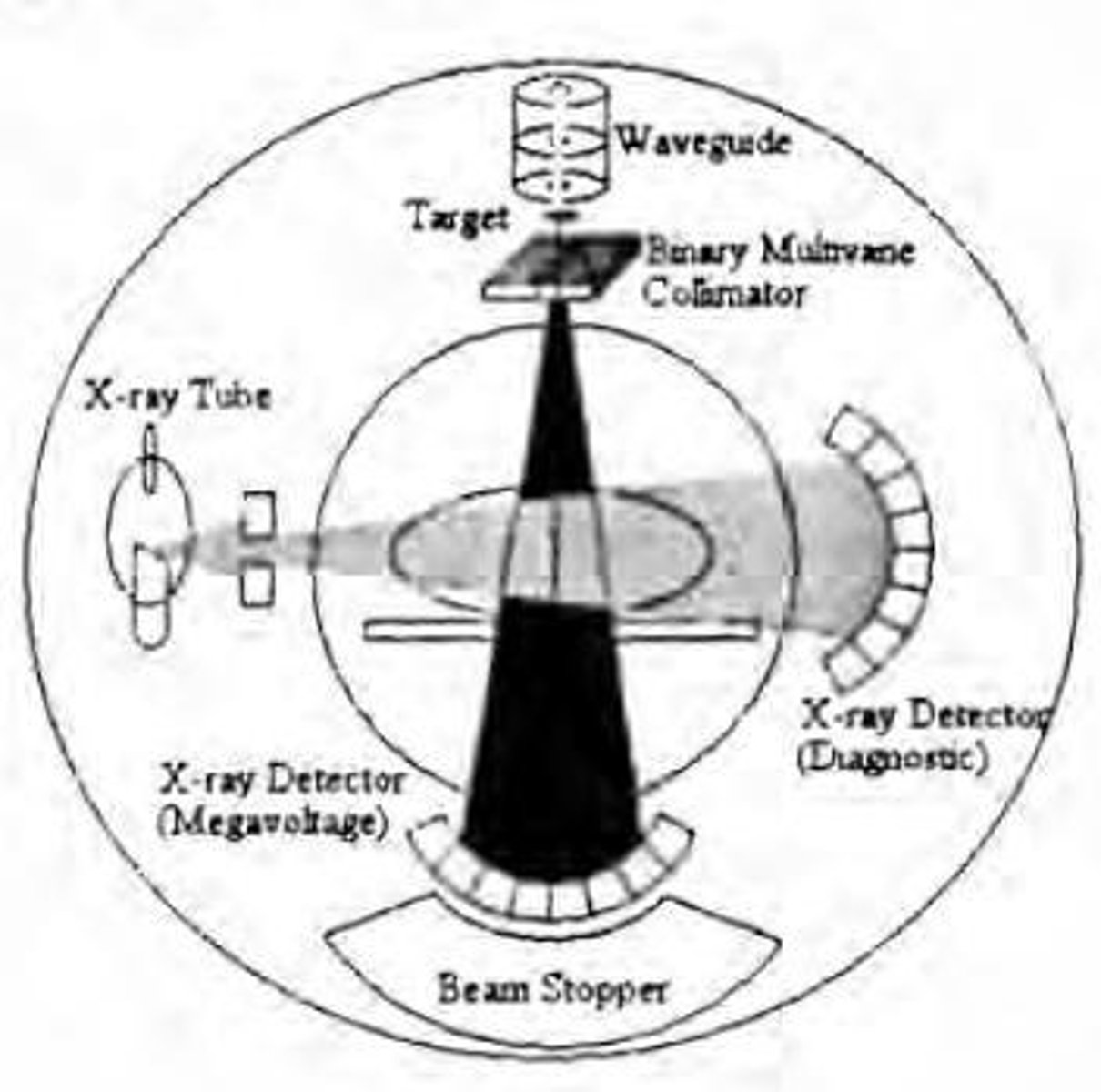
How does the tomotherapy machine deliver radiation therapy?
It delivers helical fan-beam intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) from all angles around the patient.
What is the width of the fan beam in tomotherapy?
The width of the fan beam is 40 cm.
What is the maximum length the moving couch can accommodate in tomotherapy?
The maximum length the moving couch can accommodate is 160 cm.
How does tomotherapy improve dose delivery compared to traditional IMRT?
Tomotherapy allows for more conformal delivery to small target volumes by delivering modulated dose 360 degrees around the patient.
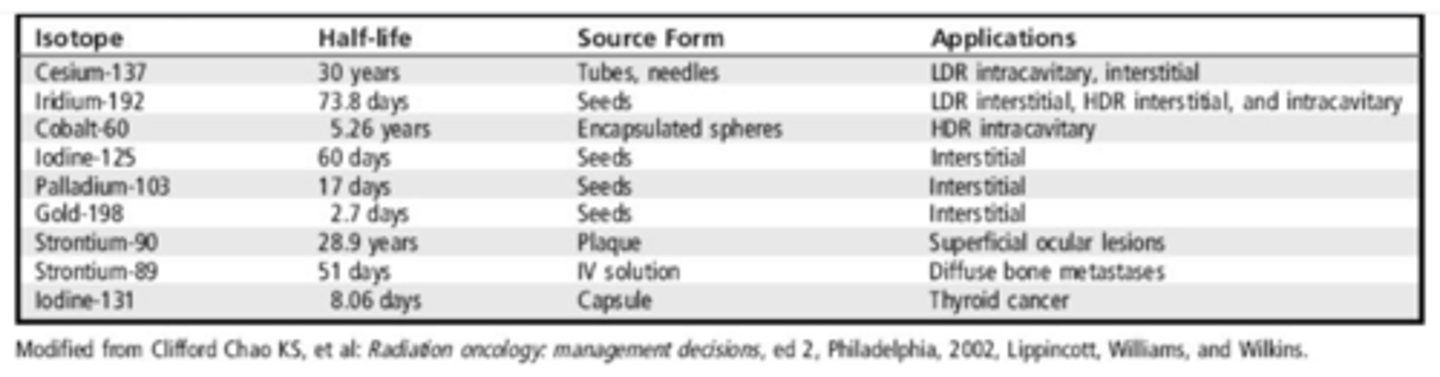
What types of radioactive sources are used in brachytherapy?
Radioactive sources used in brachytherapy are available as sealed or unsealed.
What forms can sealed radioactive sources take in brachytherapy?
Sealed sources come in pellets, seeds, capsules, needles, buttons, or metal rods.
How can pellets be contained in brachytherapy?
Pellets can be contained in small catheters with spacer material.
How are unsealed radioactive sources used in brachytherapy?
Unsealed sources can be suspended in liquid for injection or ingestion.
What are plaques in the context of brachytherapy?
Radioactive isotopes may be electronically infused into dense materials known as plaques for surface applications.
What is required for traditional manual loading of sources in brachytherapy?
Traditional manual loading of sources requires the use of special applicators/holders.
What are some examples of special applicators used in brachytherapy?
Examples include tandem, ovoids, trocars, and in-dwelling catheters.
Today, there are remote, afterloading applicators, such as:
accelerated breast irradiation devices (MammoSite, and electronic HDR units)
Commonly used radioisotopes
How should brachytherapy sources be inspected?
Sources themselves should be inspected for physical integrity by visual inspection, leak testing, and activity measurement.
Physical integrity should be checked before each use.
Source strength or activity should be checked upon receipt and then verified at an agreed-upon interval depending on the half-life;
Activity should be checked against the stated manufacturer's value.
When radioactive sources are used, dose rates are critical for reference at any point in time. Dose rates of radioactive isotopes are given by the use of _______________.
radiation detectors
What must source strength calibrations be traceable to?
A national standards laboratory.
How can source uniformity and symmetry be checked?
Using radiographic procedures.
How often must all sources in inventory be wipe tested for leakage radiation?
Semiannually at a minimum.
When should wipe testing be performed for sources with long half-lives?
Upon receipt and then at 6-month intervals.
How can afterloading devices be checked?
Using radiographic imaging for source position.
What should remote afterloaders be checked for?
Functional performance and source activity.
When must radiation surveys be performed after implantation?
Immediately in and around the patient's room.
What is the maximum allowable radiation level in adjoining rooms if the patient remains in the hospital?
Lower than 0.2 mSv per hour.
What is the maximum allowable radiation level at 1 meter for patients with permanent implants being released?
Less than 0.5 mSv/hour.
What should be documented in the quality assurance program for brachytherapy?
Written prescription, date, identification of the patient, treatment area, related calculations, and any deviations from standard practices or complications.
What is one objective of the quality assurance program in brachytherapy?
Appropriate documentation of treatment details.
Conventional simulators
Diagnostic-range x-ray tubes mounted in a rotational gantry that mimic the commonly used linear accelerator
2D
What device converts exiting photon energy to visible light in conventional simulators?
An image intensifier, positioned opposite of the tube.
Differnce between CT simulators & Conventional Simulator
Conventional simulators use fluoroscopy and plain X-ray films to create 2D images for treatment planning, while...
CT simulators utilize Computed Tomography to generate 3D images of the patient's anatomy. This allows for more precise tumor targeting and avoidance of critical structures in CT simulation.
Daily QA Conventional Simulator
Lasers: 2mm
ODI: 2mm
Daily QA for CT Simulators
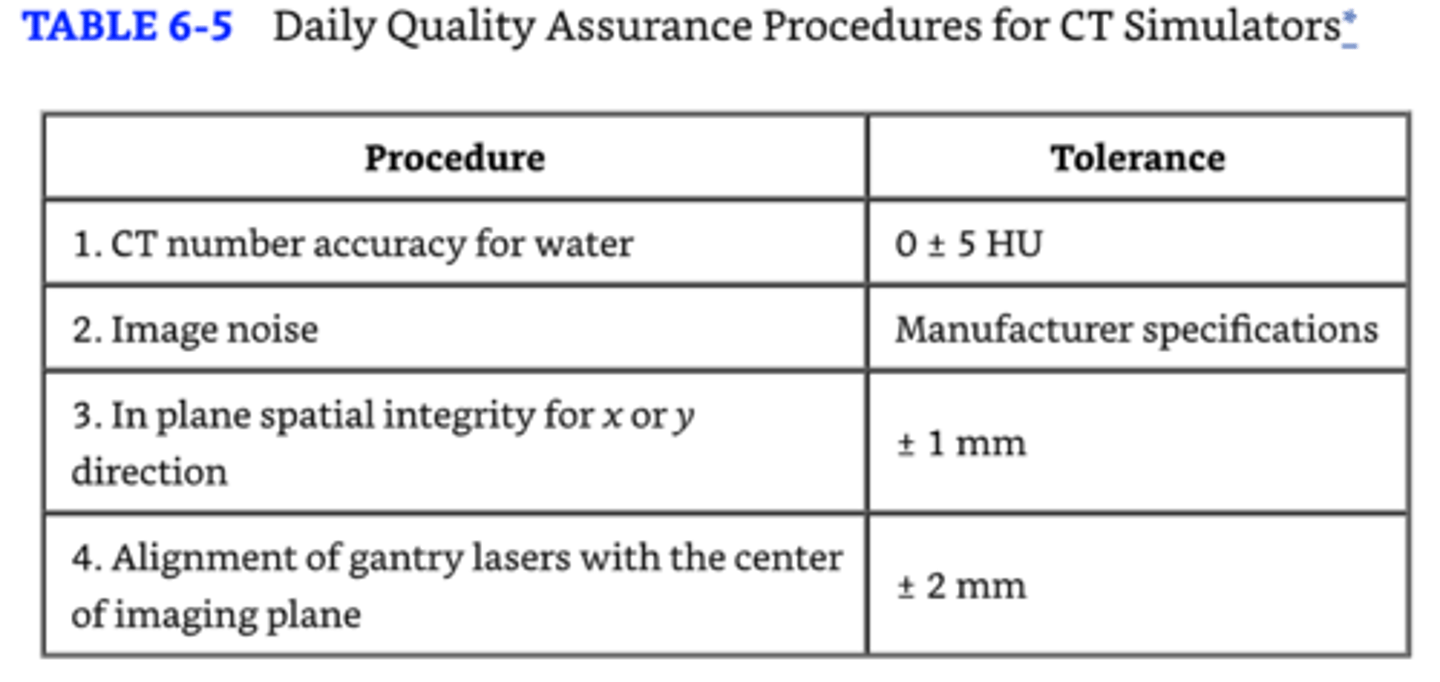
CBCT
- 3D, cone shaped
- KV (retractable arm at 90 degrees) or MV
- back projection algorithm reconstructs the images
Onboard Imaging Systems, aka EPID (Field Verification)
CBCT
Kv X-ray tube
Fluoroscopic Portal imaging processor
IGRT
Ultrasound BAT
Brain Lab
Respiratory gating
What are the main components of a portal imaging device?
A simple image detection unit, digital image processor, and color monitor.
Where are the detection unit and image processor mounted in an OBI device?
To the linac gantry.
What is the purpose of the digital image processor in a portal imaging device?
To substitute poor contrast MV images with high x-ray energy digital fluoroscopy images.
How quickly can an image be produced using the OBI device?
In 1 second.
What is the maximum exposure required for image production in the OBI device?
Three monitor units or less.
How is the portal image formed on the fluoroscopic screen transferred to the camera?
Via a high reflectance mirror positioned at 45 degrees under the fluoroscopic screen.
How often should the detector in an OBI device be calibrated?
Monthly or whenever it may have been bumped or moved.
What is the primary application of BAT ultrasound unit-B-mode acquisition and targeting in medical imaging?
IGRT: Localization of the prostate gland
What system is similar to BAT and what does it use?
The BrainLab system uses a reflective marker array attached to an ultrasound probe
IONIZATION CHAMBER DETECTOR (OBI/EPID)
-Grid of electrodes 90 degrees apart on each plate
-Two metal plates spaced about 1 mm apart, with the space filled with isobutene -.
-. Voltage is applied between electrodes and ionization at the intersection is measured
-. 2D image converted into a gray scale image
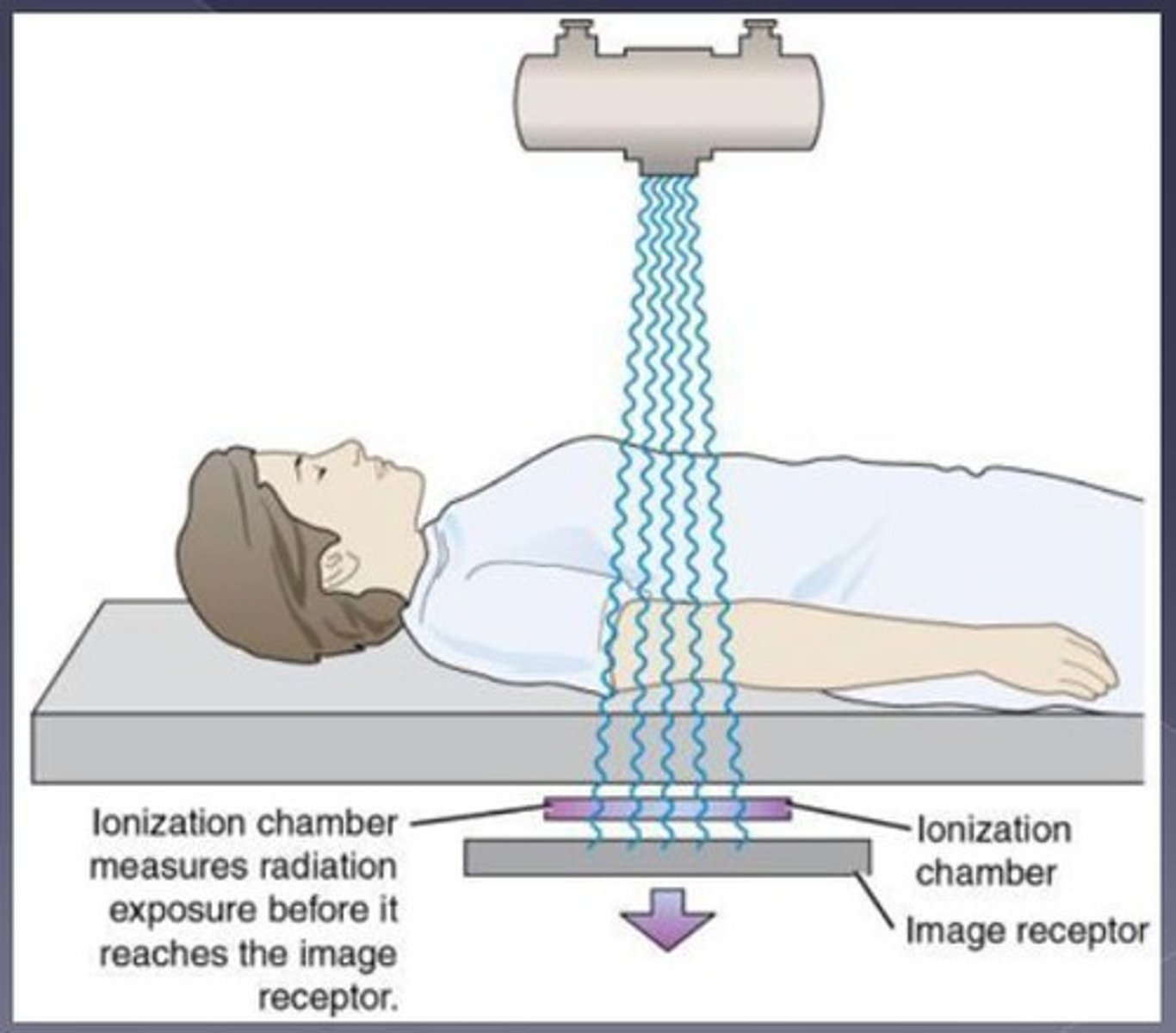
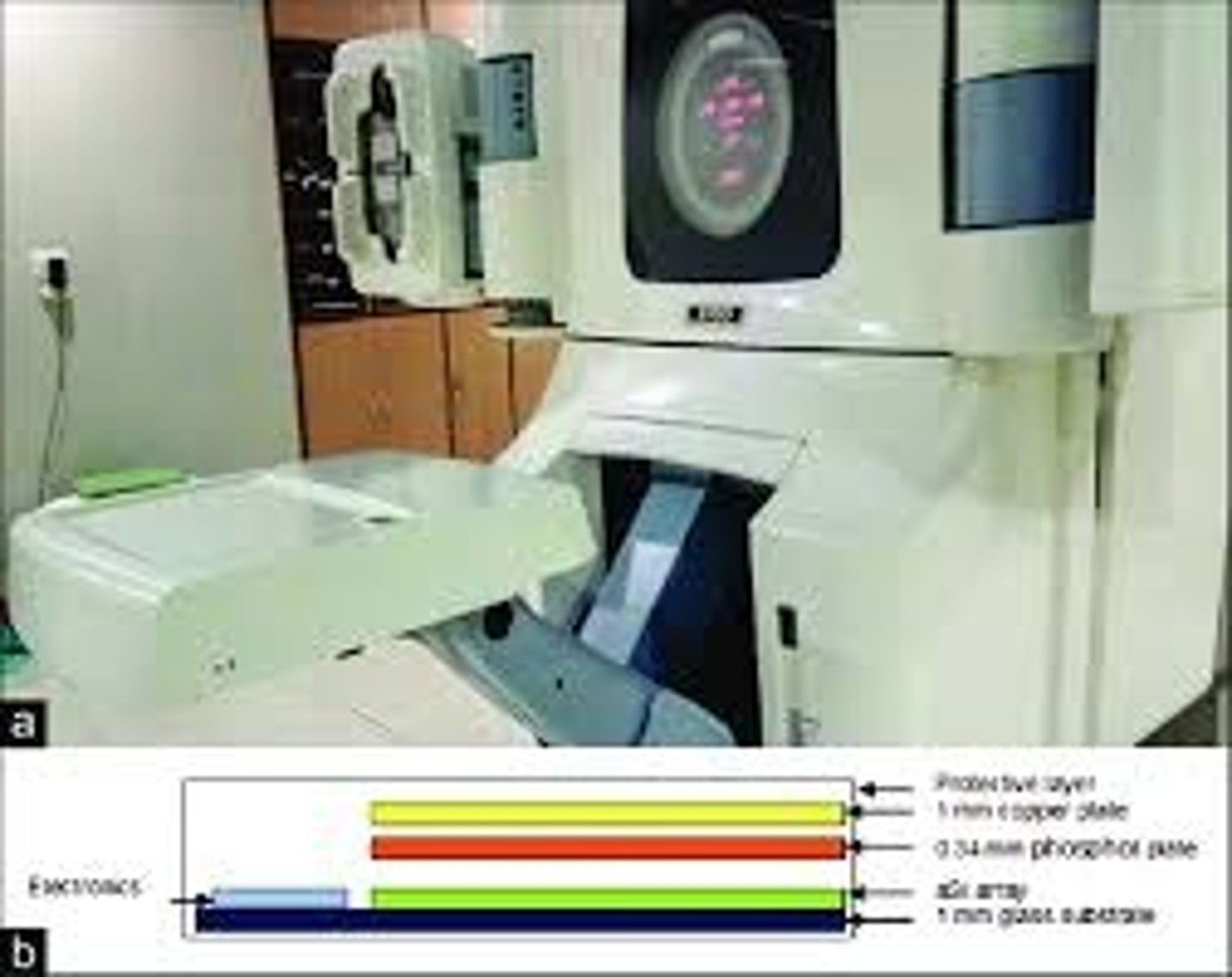
Amorphous silicon flat panel detector (EPID/OBI)
-. Solid state array or amorpnous silicone photodiodes and field effect transistors
-. Metal plate fluorescent screen combination
-. Light photons produce electron hole pairs in the photodiodes; quantity is proportional to intensity, allowing an image to be produced
Systems such as the Theraview system send what weekly message ?
indicating that the fluoroscopic screen needs to be exposed so that adjustments may be made to the detector.
What distinguishes SRT/SRS from other radiation therapies?
The use of circular beams, arc angles, and often multiple isocenters through multiple planes to achieve high dose concentration.
What is the difference between SRS and SRT in terms of treatment fractions?
SRS is performed in a single fraction, while SRT is performed in multiple fractions.