Ch 102 final
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
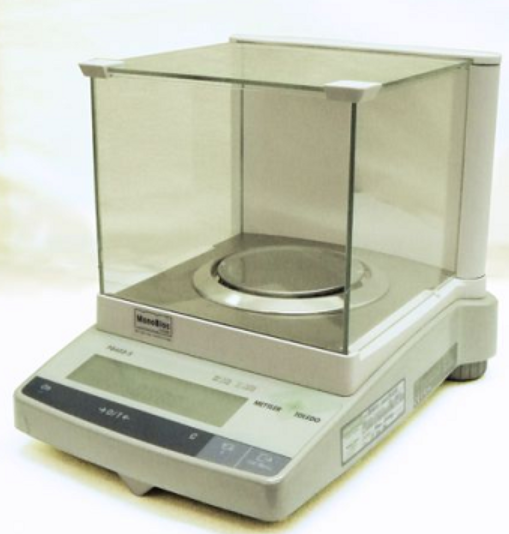

Analytical balance
Used for very accurate, quantitative measurements of mass to the nearest 0.001 g. (Some read to 0.0001 g.) These are delicate instruments, subject to errors caused by vibration and drafts. These problems can be minimized with care and a certain amount of common sense
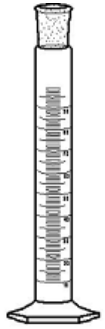
Graduated cylinder
Used to measure and dispense known volumes of liquids. They are manufactured to contain the measured volume with an error of 0.5 to 1%. For 100 mL, this would be an error of 0.5 to 1.0 mL. Measurements made with these can be reported to three significant figures
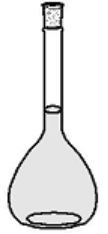
Volumetric flasks
Available in sizes ranging from 1 mL to 2 L, is designed to contain a specific volume of liquid, usually to a tolerance of a few hundredths of a milliliter, about 0.1% of the capacity. It has a calibration line engraved on the narrow part of its neck. It is filled with liquid so the bottom of the meniscus is on this engraved line. The calibration line is specific to a given type; a set of them is built to contain the same volume and will have lines at different positions.

Buret
A long, narrow tube with a stopcock at its base. It is used for accurately dispensing variable volumes of liquids or solutions. It is graduated in 0.1 mL increments, with the 0.00 mL mark at the top and the 50.00 mL mark near the bottom. Notice that the marks do not go all the way to the stopcock. Therefore it actually will hold more than 50.00 mL of solution. Those with liquid capacities of 25.00 mL and 10.00 mL are also available

Pipets
Designed to deliver a known volume of a liquid. Their volumes range from less than 1 mL to about 100 mL. There are several types, which vary in accuracy and in the type of task for which they are optimum

Bunsen burner
One of the primary means of heating in the laboratory. It is designed so that gas and airflow can be regulated separately and manually. Gas is delivered from the lab bench gas valve to the base via a rubber tube. Gas flow is regulated with the small knob at the base of the burner and rotating the sleeve at the base of the burner to open or close air inlet holes regulates airflow

Centrifuge
High-speed rotation will be used to rapidly settle precipitates in solution. When loading test tubes into the it, two tubes of approximately equal volume must be placed opposite each other to balance the rotor. If other groups are not ready to go in, you can simply put deionized water into an extra test tube for balance. Note the letter or number near the position of your tube(s) so you can identify it (them) when the process is complete. Never put stoppers or other items in this with your tubes. Only test tubes are allowed in it