GI E1- Esophageal disorders
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Retrosternal burning sensation is known as ______
heartburn / pyrosis
Difficulty swallowing is known as _____
dysphagia
A sharp, substernal pain with swallowing that reflects erosive or infectious esophagitis is known as _____
odynophagia
The persistent, non painful sensation of a lump in the throat caused by the cricopharyngeal muscle becoming too tight is known as _____
globus pharyngeus / hystericus
What muscle acts as a sphincter to prevent reflux after swallowing and is responsible for globus pharyngeus?
cricopharyngeal muscle
What test allows direct visualization and biopsy and is the study of choice for persistent heartburn, odynophagia, & abnormalities noted on barium studies?
upper endoscopy / EGD
What test differentiates between mechanical and motility disorders, evaluates strictures, and is NOT used to diagnose GERD?
barium esophagography (BA swallow, UGI series)
What test is catheter based or wireless systems and is used to correlate acid reflux to a patients symptoms?
Esophageal pH recording
Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring, typically wireless capsule, is used for ____
pre-operative evaluation
what is the gold standard for assessing motility disorders?
esophageal manometry (high resolution esophageal pressure topography)
What is the cardinal symptom of GERD?
heartburn sensation that may originate in the epigastrium and radiate upward into chest
What foods exacerbate GERD sx?
chocolate, onions, peppermint, coffee/caffeine, high fat foods, spicy foods
Which kind of hiatal hernia is usually asymptomatic, can cause heartburn, and is caused by weakened muscle tissue surrounding the hiatus?
sliding
What kind of hiatal hernia is uncommon, includes peritoneal layer that forms true hernia sac, and requires surgery only when reflux sx fail to resolve or emergent conditions?
paraesophageal
What clinical findings are associated with GERD?
heartburn that occurs 30-60 min after meals and is immediately relieved w/ antacids for ~2 hours
How is GERD dx?
clinical- H&P, studies not necessary and rx can be started empirically
What can be a co-factor of asthma, chronic cough, laryngitis, or CP causing atypical symptoms & requiring further cardio/pulm evaluation?
GERD
What pH would gastric fluid cause esophagitis and strictures?
< 4.0
Barium radiographs, manometry, and screening for H. pylori are ______ for GERD
NOT recommended
What is the first non pharmacological recommended treatment for GERD?
lifestyle modifications: wt loss, avoid lying down 2-3 hrs after meals, avoid meals 2-3 hrs before HS, elevated head of bed 6”, diet, d/c alcohol & stoking
What is the pharmacological treatment for GERD?
tx empirically: PPIs (most effective, 1st line), H2RAs (w/o erosive dz)
refer if unresponsive or alarm sx
What medication?
onset of action: 30 min - 2.5 hr
duration: 4-10 hrs
MOA: inhibit histamine at H2 receptors of gastric parietal cells to reduce gastric acid secretion
ex: ranitidine, cimetidine, famotidine, nizatidine
H2RAs
What medication?
onset of action: w/in 30 min
duration: 12-24 hrs, can last 3-5 days
MOA: activated in parietal cell and irreversibly bind to H+/K+ATPase pump, inactivating it & stopping HCl secretion
first line tx for- mod-severe GERD, erosive esophagitis, NSAID ulcers, H. pylori ulcers
ex: omeprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole, dexlansoprazole
PPIs
How are PPIs administered?
QD before the first meal of the day- must be taken 30-60 min before meals
What are adverse reactions of PPIs?
inc risk of PNA, MI, CV mortality, C diff, bone fractures, hypomag, hypocal, low B12 and iron
*can be used w/ clopidogrel to prevent risk of CV events
What condition consists of squamous epithelium at the distal esophagus and is replaced by metaplastic columnar epithelium, increasing the risk of progression to adenocarcinoma?
Barrett’s esophagus
What are the only agents that heal ulcers and erosions?
PPIs
How is Barrett’s Esophagus diagnosed and treated?
EGD & long term PPI
What is the management for Barrett’s with NO dysplasia?
EGD q 3-5 years
What is the management for Barrett’s with low grade dysplasia?
surveillance vs eradication
What is the management for Barrett’s with high grade dysplasia?
esophagectomy, laser ablation, photodynamic tx
What condition is a reflux induced ulceration that causes fibrous tissue production and collagen deposition in the esophagus, leading to the gradual development of solid food dysphagia?
stricture
How are strictures diagnosed and treated?
EGD (r/o malignancy), dilation (fixed size dilators or balloons), & long term PPIs
What are possible complications of GERD?
Barrett’s Esophagus and Strictures
What is the treatment for severe GERD?
surgery: Nissen Fundoplication or Belsey Mark IV Fundoplication
What pathogens cause infectious esophagitis?
Candida albicans (uncontrolled DM, immunosuppression, systemic corticosteroids)
HSV
CMV (AIDS, solid organ transplants)
What condition?
mainly in mmunocompromised patients
sx: odynophagia and dysphagia
Candida tx: fluconazole, itraconazole, or ampthotericin B
HSV tx: acyclovir, famciclovir, valacyclovir, or EGD w/ bx if no response
CMV tx: gangciclovir
infectious esophagitis
What condition?
chronic, inflammatory, immune mediated
UGI sx assoc w/ dense eosinophilic infiltration of squamous esophageal epithelium or deeper tissue
allergic inflammation & remodeling → assoc w/ food & environmental ags
MC in young adult males w/ hx atopic conditions
common finding → multiple concentric rings
dx: endoscopy w/ bx
eosinophilic / allergic esophagitis
What are symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis?
adults → dysphagia & food impaction (MC), heartburn, CP, abd pain, V, can be assoc w/ narrow esophagus and strictures
children → GERD & reflux sx, N, V
What is the long term treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis?
elemental & elimination diets, aerosolized/oral/topical corticosteroids, PPIs, esophageal dilation PRN, refer allergy testing
What pills can cause erosions & esophagitis?
NSAIDs, KCl, bisphosphonates, doxy
How can pill induced esophagitis be prevented?
swallow meds w/ water
remain upright for 30 min post taking meds
dont prescribe offending meds if esophageal dysmotility or strictures
consider routes other than PO
Which occurs higher in the esophagus-
reflux esophagitis or pill-induced esophagitis?
pill-induced esophagitis
What condition?
accidental or intentional (suicidal)
sx: severe burning, CP, gagging, dysphagia, drooling, wheezing/stridor
mgmt: airway (laryngoscopy), imaging, EGD, esophagectomy, psych referral
NO NG tube or oral antidotes
Caustic esophageal injury
What condition is a muscle tear at the GE junction (non penetrating) that involves underlying venous/arterial plexus and is usually caused by prolonged vomiting/retching?
Mallory-Weiss Tear
What are symptoms of Mallory Weiss Tears?
hematemesis, hx of vomiting & retching, alcoholism is predisposing factor
what is the treatment for mallory Weiss tear?
most heal uneventfully w/in 24-48 hrs; IV fluids, endoscopic hemostatic therapy (epi injection, cautery, mechanical compression)
A full thickness (transmural) tear in the esophagus that usually occurs with overindulgence _____
Boerhaave syndrome / effort rupture
what condition?
MC in males age 50-70
forceful vomiting from overindulgence → transmural tear in esophagus, usually left posterior distal rupture
chemical then infectious mediastinitis
Hammans sign → crunchy raspy sounds heard over precordium due to pneumomediastinum
severe CP, sepsis, shock, pyopneumothorax
rx: fluids, abx, surgical consult
boerhaave’s syndrome
How is Boerhaave syndrome diagnosed?
CXR: mediastinal air, L pleural effusion, pneumothorax, widened mediastinum
UGI series w/ gastrografin (diatrizoic acid) - water soluble
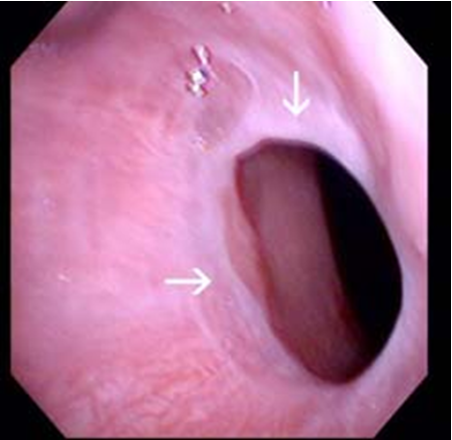
what condition?
thin fibrous protrusion of squamous epithelium in upper esophagus
can be asx or cause dysphagia +/- IDA
uncommon; increased in women
dx: EGD, BA xray studies
rx: endoscopy, esophageal dilation
esophageal webs
what condition is associated with the following?
Plummer vinson syndrome - in middle aged women w/ IDA, increased incidence SCC
bullous diseases → pemphigus, pemphigoid
GVHD
celiac dz
Esophageal Webs
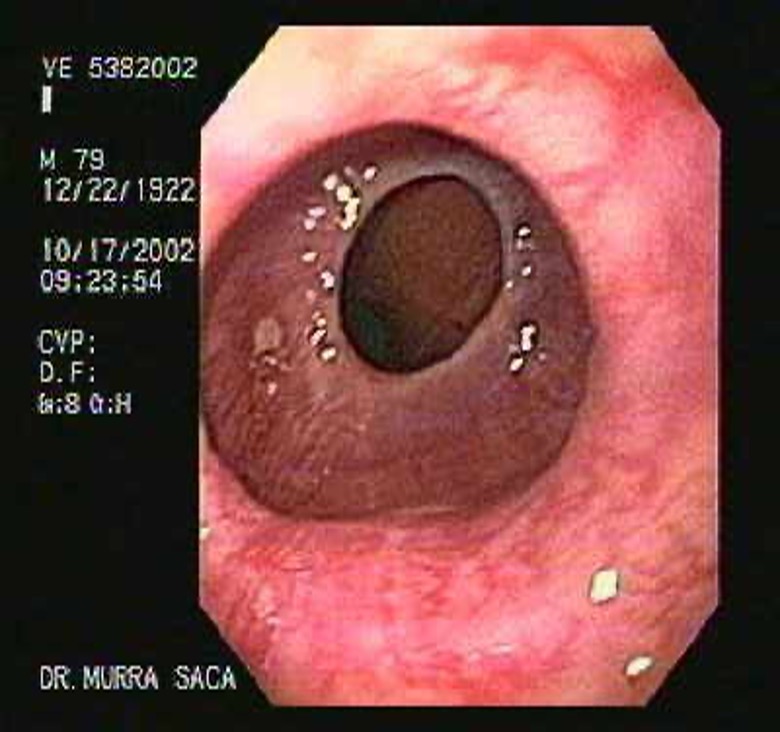
What condition?
thin, weblike constriction at/near border of LES (distal esophagus)
common cause of intermittent solid food dysphagia
worse with eating quickly and inadequate mastication
reflux sx (chronic GERD may play role)
dx: BA esophagram
rx: esophageal dilation
esophageal / schatski’s rings
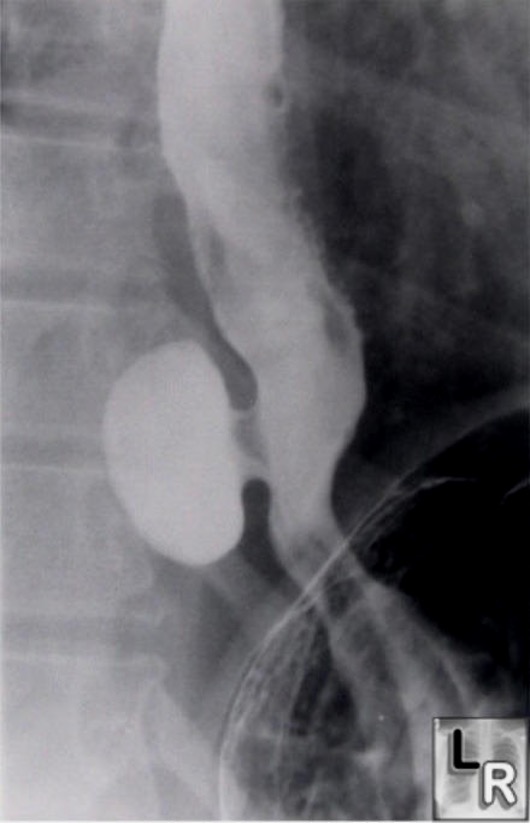
Out pouchings in the mid or distal esophageal wall secondary to motility disorders or strictures are known as ______
diverticula
what is the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal diverticula?
dx- barium swallow, endoscopy to r/o other, manometry;
often asx so no treatment

What condition?
pharyngeal mucosa protrusion at posterior hypopharyngeal wall
appears as natural zone of weakness (Killian’s triangle)
sx: regurgitation of saliva/food consumed several days prior, dysphagia w/ enlargement, severe halitosis, choking, gurgling, neck protrusion
dx: BA esophagram
tx: surgery is symptomatic
zenker’s diverticulum
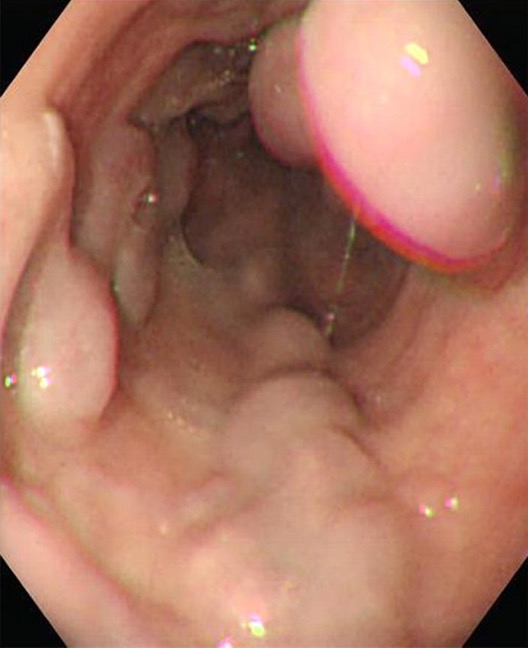
What are enlarged venous collateral channels that dilate as a result of portal HTN, and has highest mortality/morbidity of any UGI bleed?
esophageal varices
The following is the pathogenesis of what condition?
inc portal pressure → collateral venous pathways dilate in attempt to transport blood from splanchnic bed surrounding cirrhotic liver to the heart
this venous network is below mucosa at prox stomach & esophagus
inc portal pressure → massive rupture
exsanguination occurs 10-15% of time even in hospital setting
Esophageal Varices
What are possible etiologies of esophageal varices?
alcoholism, viral hepatitis, chronic schistosomiasis (particularly in developing tropical countries)
What are sx of esophageal varices?
acute GI bleed (hypovolemia) → hematemesis, melena, hematochezia
what is the treatment for esophageal varices?
spontaneous resolution in 50% (1/2 of these rebleed in 6-8 wks)
fluid resuscitation; FFP/plts
emergent endo (2-12 hrs) → banding, sclerotherapy
IV Octreotide (somatostatin analog), vasopressin, NTG
Vit K (abnormal PT)
chronic BP mgmt: nonselective BB (propranolol, nadolol), long acting nitrates (isosorbide mononitrate)
what invasive treatment options are used for esophageal varices when other methods are unsuccessful?
portal decompressive procedures: TIPS (pts waiting liver transplant), portosystemic shunt surgery
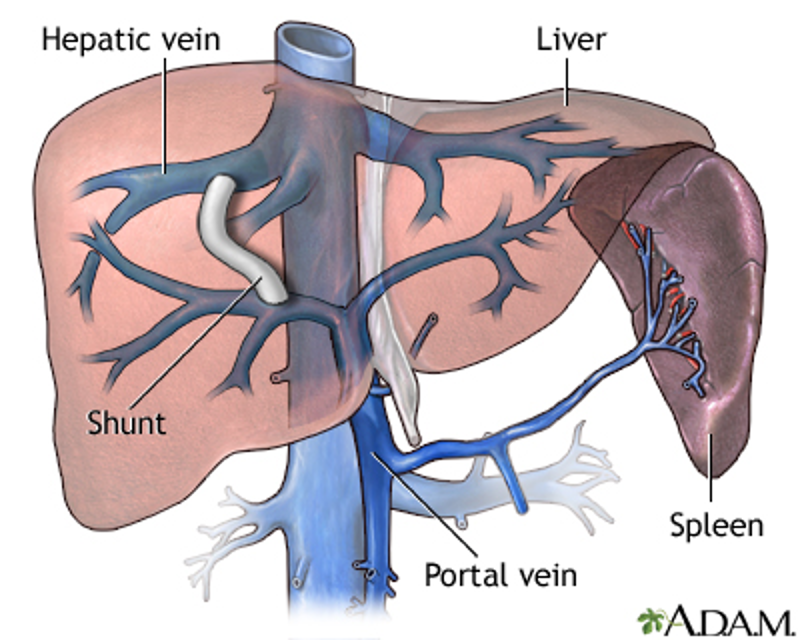
what can be done to prevent rebreeding of esophageal varices?
band litigation +/- BBs and nitrates, TIPS reserved for recurrent bleeds (comps- encephalopathy & CHF), liver transplant
Who is at highest risk for esophageal cancer?
men, age 50-70
Which of the two histological types of esophageal cancer is the most common form- squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma?
adenocarcinoma
Esophageal adenocarcinoma is more common in ______ ; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is more common in ______
white males ; african americans
What are symptoms of esophageal cancer?
progressive solid food dysphagia
odynophagia
anorexia / wt loss
hoarseness / voice changes
anemia
signs of metastatic dz → supraclavicular or cervical LAD, hepatomegaly
What is the workup for esophageal cancer?
BA esophagram, upper endo w/ bx, CXR, stage TNM
Most esophageal cancers arise in the ______ of the esophagus
middle third
What are risk factors for esophageal cancer?
tobacco, alcohol, chronic GERD, Barrett’s esophagus
what are the treatment options for esophageal cancer?
most too advanced for surgery; palliative care - RT, chemo, dilation & ablation, photodynamic therapy, prostheses/stents
The most important predictor of survival of esophageal cancer is if ____
spread to lymph node
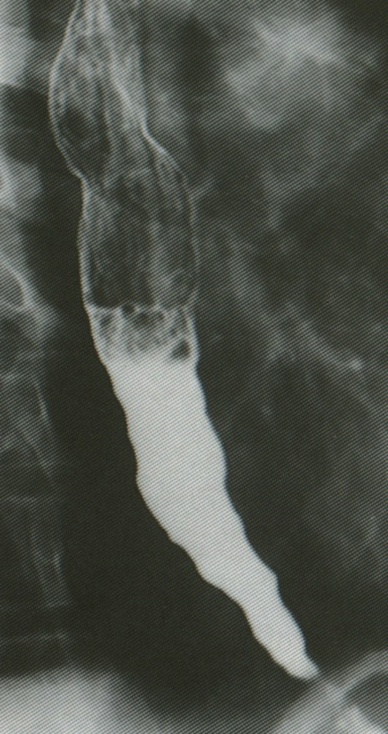
what condition?
aperistalsis in distal 2/3 of esophagus → failure/incomplete relaxation of LES
progressive loss of inhibitory neurons in esophagus; primary dz → degeneration of Auerbach’s plexus
unknown eti
achalasia
Primary or secondary achalasia?
results from defect in inhibitory vagal innervation
smooth muscle function is affected
primary
Primary or secondary achalasia?
due to cancer, lymphoma, chagas dz (trympanosomiasis)
secondary
How should a patient positive for Barett’s with NO dysplasia be managed?
EGD q 3-5 yrs
What condition?
progressive solid food dysphagia, possible liquid dysphagia
sx due to stasis of food & esophageal dilation → cough, heartburn, wt loss, aspiration
pts attempt to enhance esophageal emptying by lifting neck, throwing shoulders back, valsalva maneuvers
Achalasia
How is achalasia diagnosed?
BA esophogram → “birds beak tapering” of esophagus; dilation (late finding)
endoscopy to r/o neoplasm
confirm w/ manometry
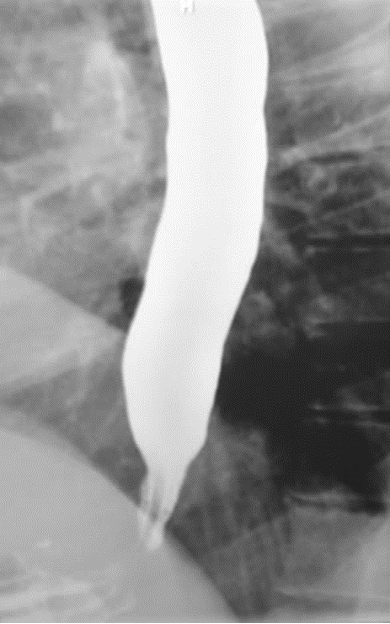
what are treatment options for achalasia?
Pneumatic dilation of LES
Surgery (better for relieving dysphagia): PEOM, Heller w/ partial nissen
Rx (failed other tx): CCBs (nifedipine), botulinum toxin injection into LES (older, debilitated pts)
What condition?
hypertensive peristalsis
esophageal contractions are coordinated but amplitude excessive
CP > dysphagia
nutcracker esophagus
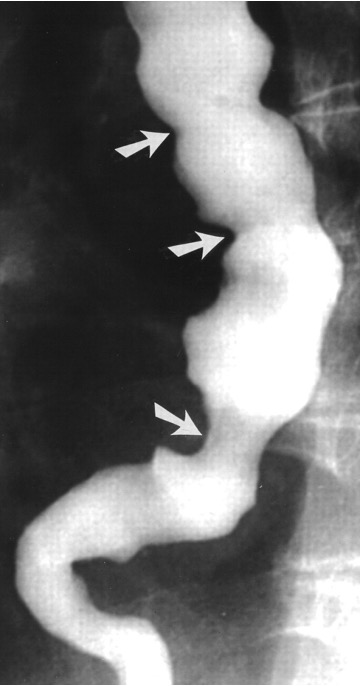
What condition?
simultaneous uncoordinated, non propulsive contractions of segments of esophagus
prevents normal movement of food bolus
seen in 5% patients w/ unexplained CP
unknown cause
corkscrew appearance
excellent prognosis
diffuse esophageal spasm
what are symptoms of diffuse esophageal spasm?
severe retrosternal CP min-hrs, intermittent dysphagia
sx worse by - hot/cold food, rapid eating, large meals, carbonated drinks, stress/emotion
How are diffuse esophageal spasm diagnosed?
BA esophageal → corkscrew appearance of esophagus
esophageal manometry
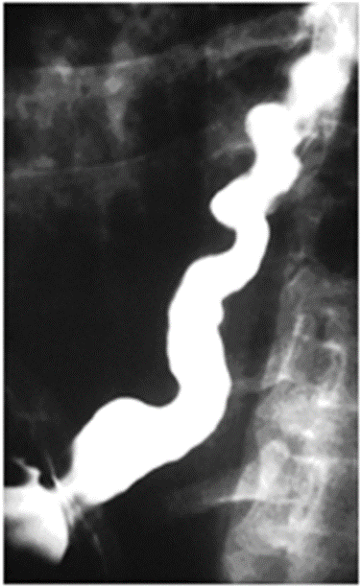
What condition is often confused with angina pectoris due to CP relieve w/ NTG?
Diffuse Esophageal Spasm
What is the treatment for diffuse esophageal spasms?
first → acid suppression w/ PPIs
spasm relief: sublingual NTG & CCBs (can inc GERD sx)
alter esophageal perception: antidepressants (trazodone, nortriptyline)
botox into LES & distal esophagus
surgery if refractory