Bioethics Final Exam
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What are deontological ethics?
"Rule following" or "duty" based ethics, rules of reason tell us what to do.
What does Deontological ethics emphasize?
Law & rational conformity to moral law.
What can reason be the basis of?
A true, universal moral law that everyone has a duty to follow?
Who is the person relating to deontological ethics?
Immanuel Kant
What is Deontological ethics a product of?
The Enlightenment.
What is a good will?
Does not act out of self-benefit but out of respect for moral law, what is good/right
Is unconditionally good, doing good for no other sake other than it is good or right to do.
What does duty include?
A good will.
What is a duty?
Doing good is within our control & can be what we freely choose to do. We can freely "will" to do good because our reason instructs us that we must.
Where does moral law come from?
Does not come from Church or State, but comes from within our own rational human nature.
What is our common rational nature?
The basis of our duty is to consult reason in making moral decisions.
What does it mean to be an equally "rational moral chooser"
To have "equal moral ground" through reason.
What can we do because we are free, reasoning beings?
1. Freely & rationally decide for ourselves
2. Arrive to the same rational conclusions
What is Heteronomy?
When one's decisions suffer coercion or restraint.
What is Autonomy?
When one freely decides for oneself.
What is a maxim?
A rule that one personally follows.
What is a universal law?
A rule that everyone should follow.
How do we know we are doing good, according to Kant?
Ask if our maxims could be able to become "universal laws" that everyone else could follow all of the time.
Main idea: Can you "universalize" your "maxim"?
What is an imperative?
A command.
What is a hypothetical imperative?
Tells us what to do based on the end results. If X then Y, X justifies Y because of the end result.
What is a hypothetical statement?
Conditional, "If" this .... "then" that.
Goodness depends on consequences.
What is a categorical imperative?
Tells us what to do regardless of circumstance or situation. "Never do X" or "Always do Y".
Do personal circumstances, viewpoints, and emotions subtract the "wrongness" of an immoral, evil action?
No.
What does the categorical imperative do?
Unconditionally forbids certain actions & unconditionally approves of others.
What is an example of a categorical imperative?
Never lie, always tell the truth.
Who created the three versions of the categorical imperative?
Kant.
How many versions of the categorical imperative did Kant formulate?
Three.
What is the first version of the categorical imperative that Kant formulated?
"Act only according to that maxim whereby you can, @ the same time, will that it should become a universal law?"
What is the second version of the categorical imperative that Kant formulated?
"Act in such a way that you treat humanity, whether in your own person or in the person of any other, always at the same time as an end & never merely as a means to an end."
What is the third version of the categorical imperative that Kant formulated?
"Every rational being must act as if s/he were through his/her maxim always a legislating member in the universal kingdom of ends."
What is a Kingdom of Ends?
An ideal version of a world where all moral choosers always act as if they are part of a larger "moral democracy".
What is everyone treated like in a Kingdom of Ends?
With dignity, value, & respect that they deserve as fellow rational moral choosers.
What makes sure everyone is treated equally in a Kingdom of Ends?
The categorical imperative.
What did Utilitarianism begin as?
An 18th & 19th century social & legal theory to improve society.
What can Utilitarianism also be known as, and why?
Consequentialism, because it uses consequence-based thinking.
What is the Principle of Utility?
The Greatest good for the greatest # of people.
Which does the Principle of Utility use?
Hypothetical Imperative.
1 multiple choice option
What does Utilitarianism want as an end result?
"Good", thus it has no value.
What is instrumental value?
Having value as a way to produce results.
What is intrinsic value?
Having value in and of itself.
What are the 3 principle candidates for "good"?
1. Good is pleasure
2. Good is happiness
3. Good is ideals
What is the meaning of "Good is pleasure"?
Physical pleasures / satisfaction of body the body.
Who is the person associated w/ "Good is pleasure"?
Jeremy Bentham.
1 multiple choice option
What is the meaning of "Good is happiness"?
Intellectual pleasures & fulfillment of the mind / achieving goals.
Who is the person associated w/ "Good is happiness"?
John Stuart Mill.
1 multiple choice option
What is the meaning of "Good is ideals"?
Refined states of consciousness such as art, love, and beauty.
Who is the person associated w/ "Good is Ideals"?
G.E. Moore.
1 multiple choice option
What is Hedonism?
What feels good is good. Measured goodness in terms of pleasure/pain.
What is pleasure?
The enjoyable feeling we experience when a state of deprivation is replaced by fulfillment.
What are the steps in Hedonistic Calculus?
1. Intensity
2. Duration
3. Certainty / Uncertainty
4. Propinquity
5. Fecundity
6. Purity
What is the meaning of Intensity in Hedonistic Calculus?
How strong?
What is the meaning of Duration in Hedonistic Calculus?
How long?
What is the meaning of Certainty/Uncertainty in Hedonistic Calculus?
How likely?
What is the meaning of Propinquity in Hedonistic Calculus?
How remote in time?
What is the meaning of Fecundity in Hedonistic Calculus?
Will it recur?
What is the meaning of Purity in Hedonistic Calculus?
How free from pain?
What did John Stuart Mill believe?
Happiness, not "mere" pleasure, should be the standard of utility.
What did John Stuart Mill choose when it came to pleasure?
Quality of pleasure over simple quantity of pleasure.
What was John Stuart Mill concerned with?
Intellectual fulfillment: Flourishing & growth of the individual as a whole person.
What is Act-Utilitarianism?
Rightness of action depends solely on the overall good or well-being produced by individual actions.
What is Rule-Utilitarianism?
Right actions are those that conform to a rule that, if followed consistently, would create the most balance of good or well-being over suffering.
What were Mills criticisms of Bentham?
- Came to be known as "the pigs' philosophy"
- Seems to ignore higher values that are not mere bodily pleasures
- Doesn't account for pleasures of intellectual beings
What were Benthams criticisms of Mill?
- Intellectual pleasures or fulfillment is more difficult to measure
- Can lead to living only a life of mind (to neglect of body)
- What makes you happy & makes me happy may be different. How to judge competing conceptions of happiness
1 multiple choice option
What did Act Utilitarians think?
We should perform the action that will create the greatest net utility.
In an act-utilitarian view, when should the principle of utility be applied?
A case-by-case basis.
What type of action yields the most utility?
The right action in a particular situation, rather than other available actions.
What is an example of performing an action resulting in the greatest net utility?
A doctor chooses the treatment w/ the fewest side effects as this will likely provide a better outcome for that patient.
What do rule-utilitarians think?
A specific action is morally justified if it conforms to a justified moral rule.
When is a moral rule justified?
If its inclusion into our moral code would create more utility than other possible rules (or no rule @ all).
What do rule-utilitarians apply the utilitarian principle to?
Directly to the evaluation of rules and then evaluate whether those rules will produce the most utility in a larger context.
What did G.E. Moore believe in?
Striving to maximize ideal values: knowledge, art, beauty, freedom, love, and justice.
How can you resolve J.S. Mill's problem of how to choose between competing conceptions of intellectual fulfillment/happiness?
Appealing to common ideals.
What did G.E. Moore say?
The world will certainly be a better place with more knowledge, art, beauty, love, freedom, and justice.
What was the criticism relating to G.E. Moore?
Moore is even more intellectualized than Mill. What if people refuse these ideals or decide it doesn't make them happy?
What is the greek form of virtue?
Arete.
Meaning: Excellence, obtained through practice.
What are the two parts of the Golden Mean?
Virtue & Vice
What is the golden mean?
Finding the mean between extremes and virtue.
Who is associated with the Golden Mean?
Aristotle.
What is phronesis?
Practical experience.
Golden mean
Middle: Virtue
Left side: Vice / Defect
Right side: Vice / Excess
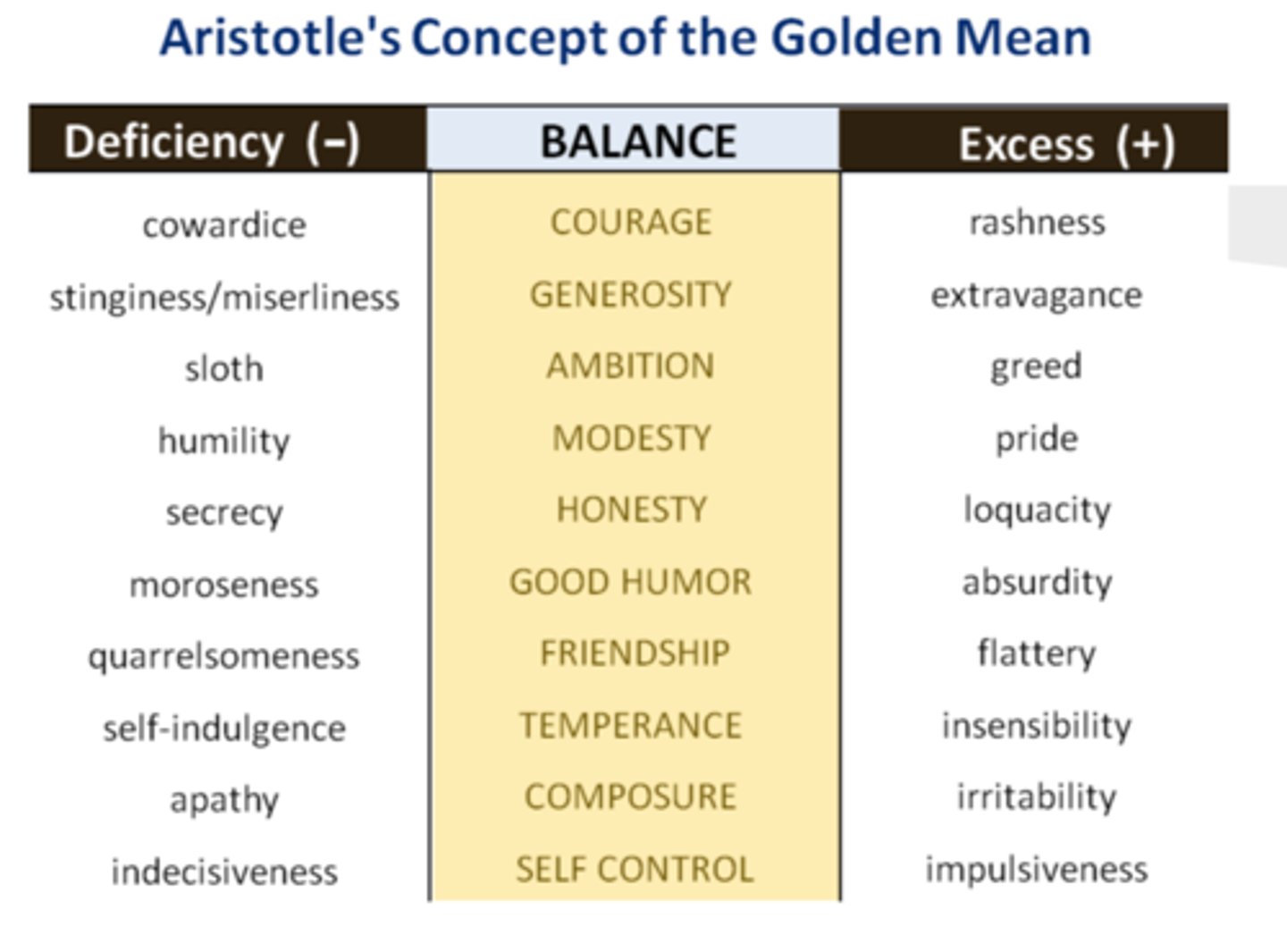
What is an example of golden mean?
Defect Vice: Cowardice
Virtue: Courage
Excess Vice: Brazen / Reckless
3 multiple choice options
What does care equal?
Human Welfare.
Second essay question:
Kant.
3 versions of the categorical imperative.
First essay question:
Aristotle.
The Golden Mean.