trig terms identities etc
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Trigonometry - means triangle measure
The relationships between sides and angles of triangles - in particular right triangles. We study triangle and circles. We study oscillatory behavior in a graph.
Circle
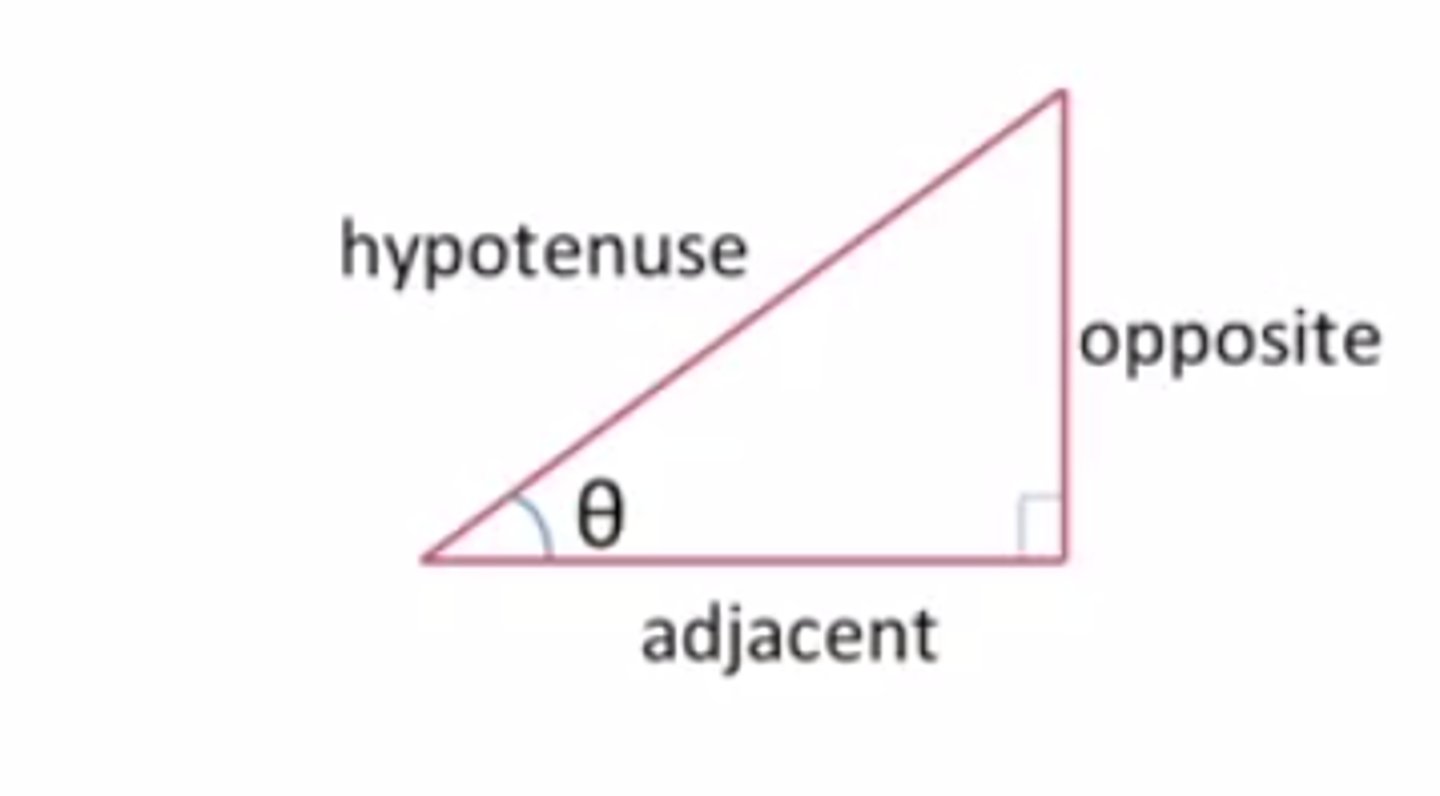
Names of a triangle
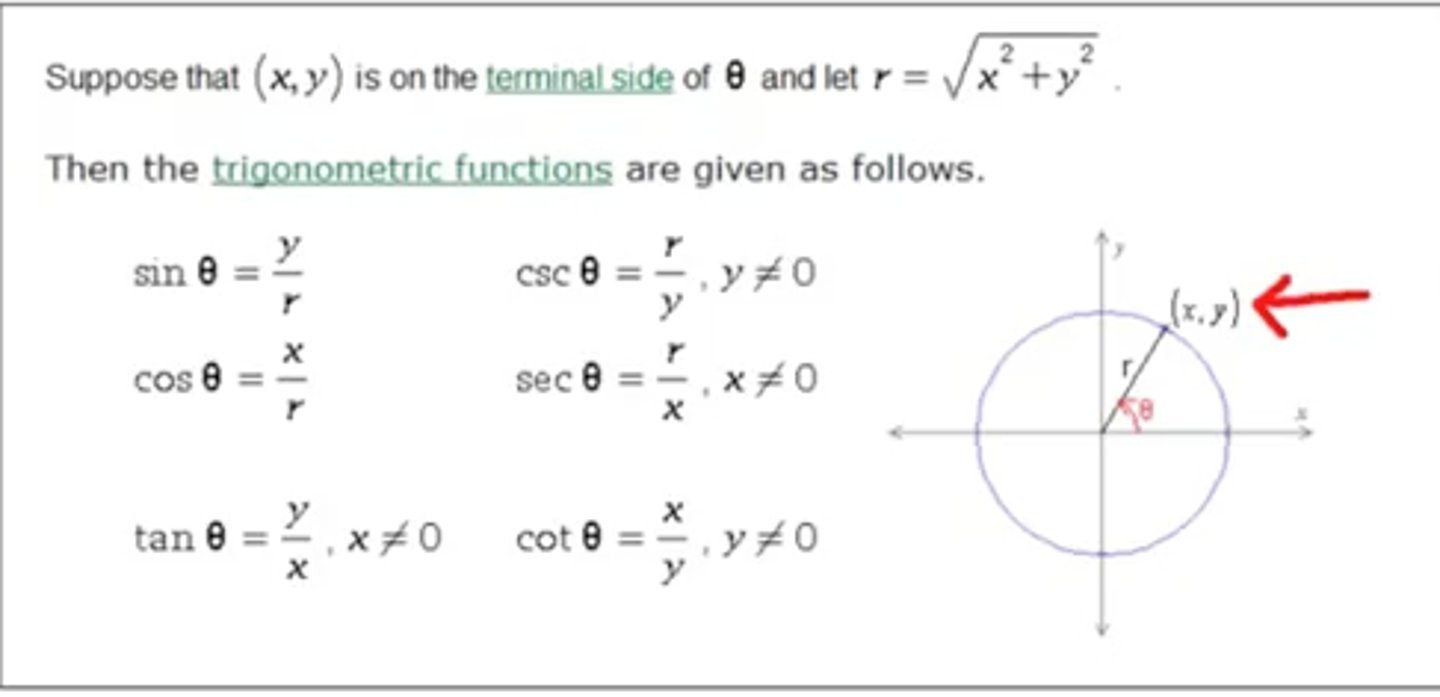
Trigonometric Functions
SOH CAH TOA (sine is opposite over hypotenuse, etc.)

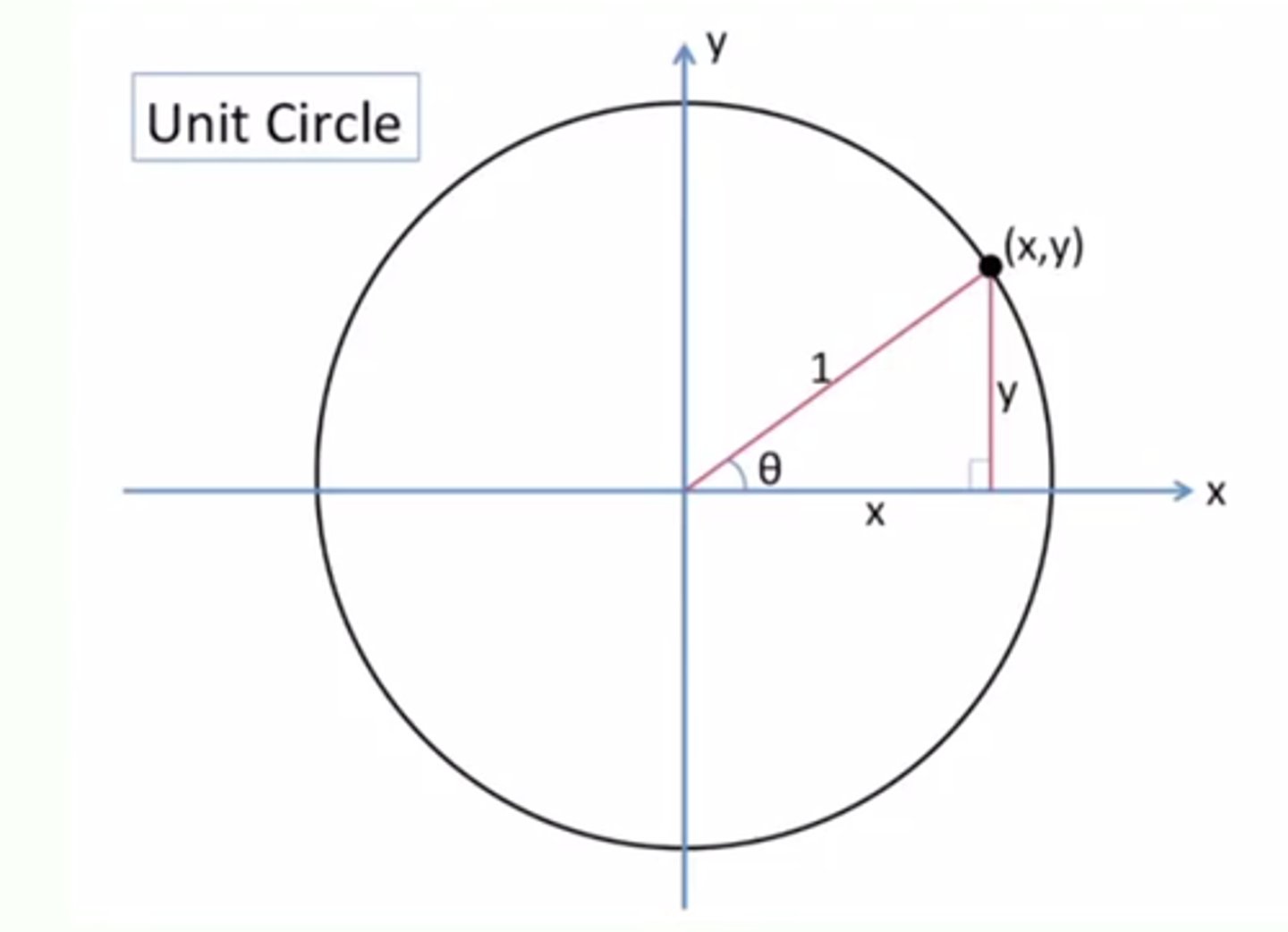
Unit Circle
A special circle with the radius of 1. These are the ones where the (x,y) coordinates along the circle are easy to fine.
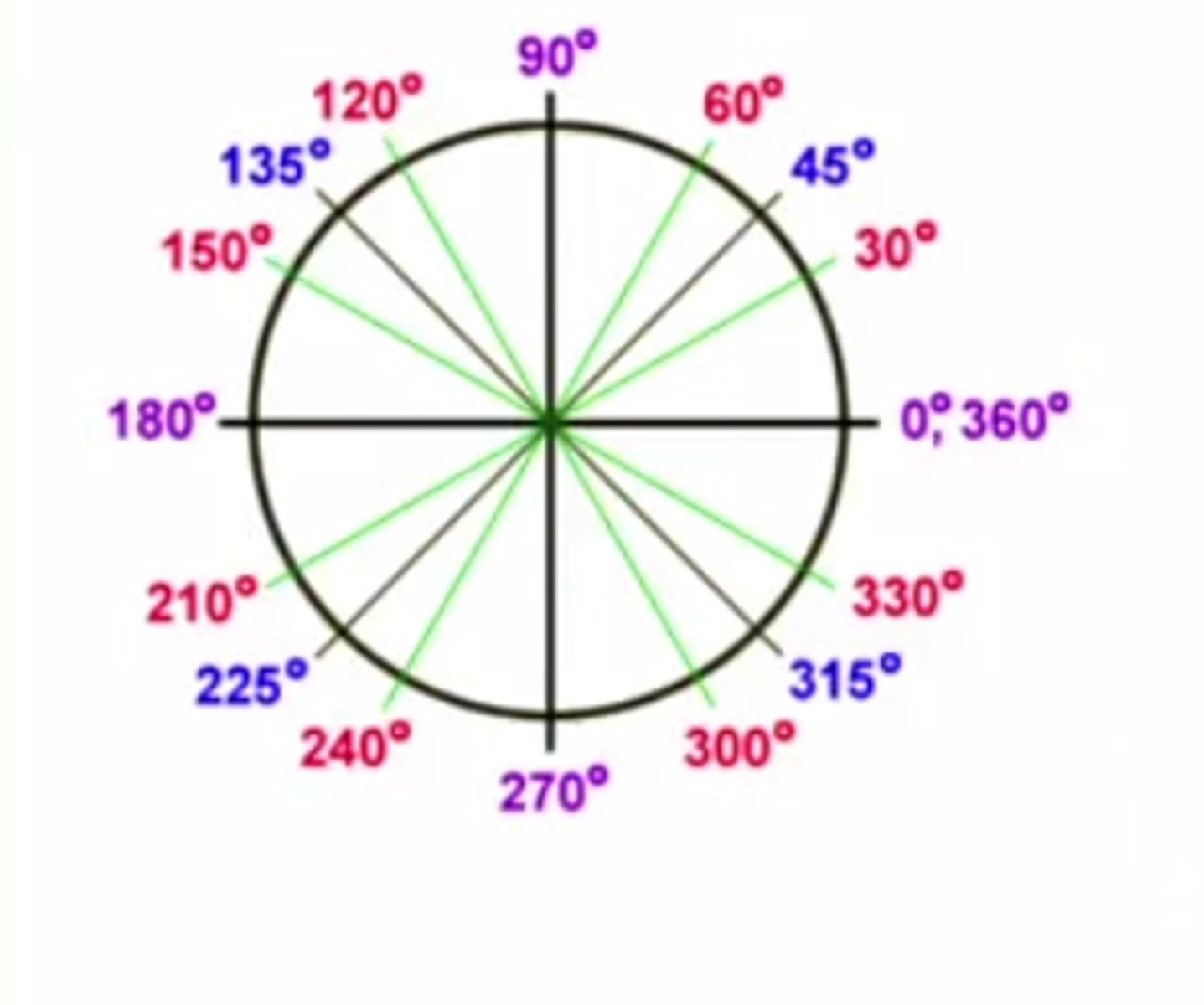
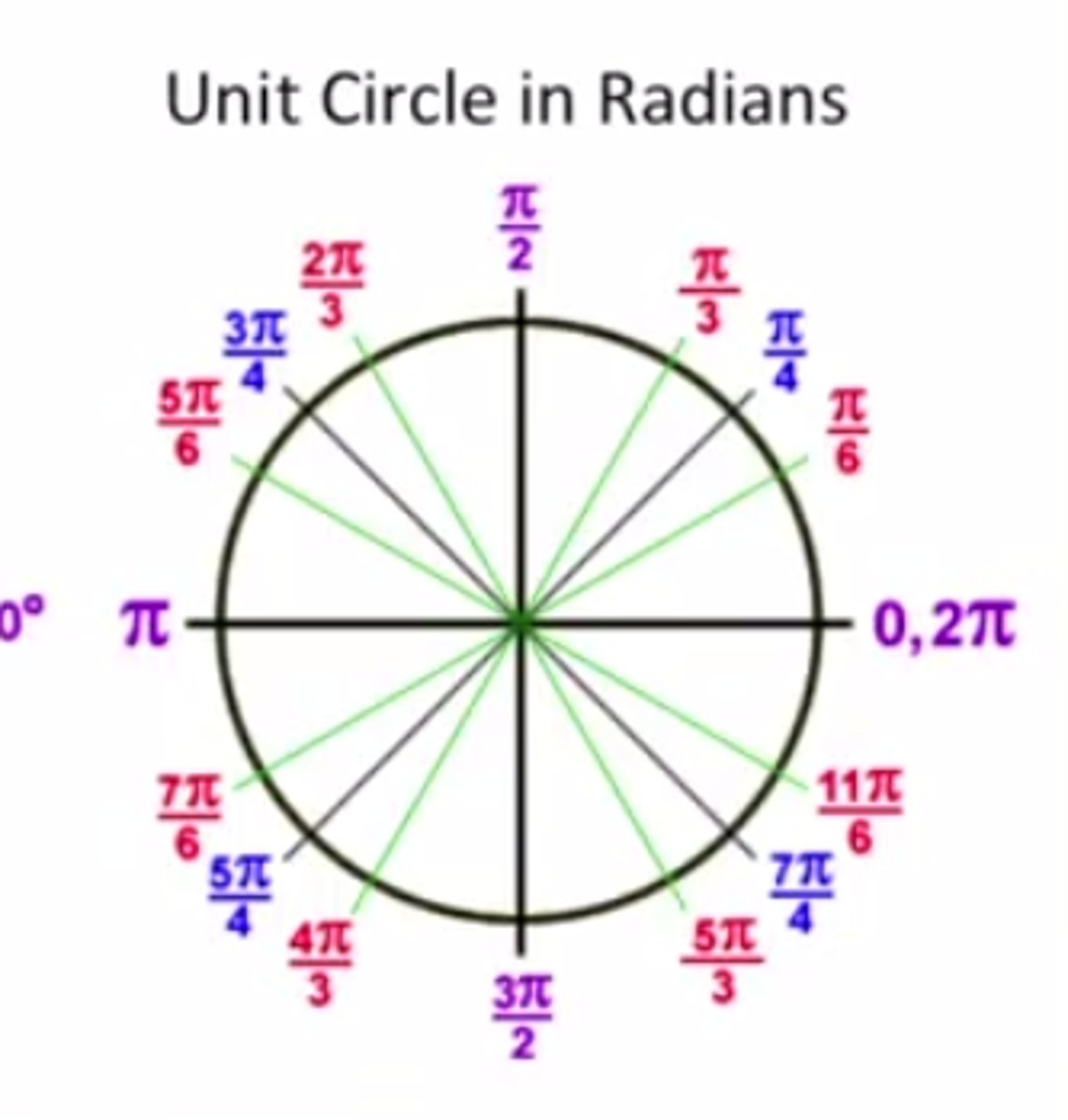
Degrees and Radians
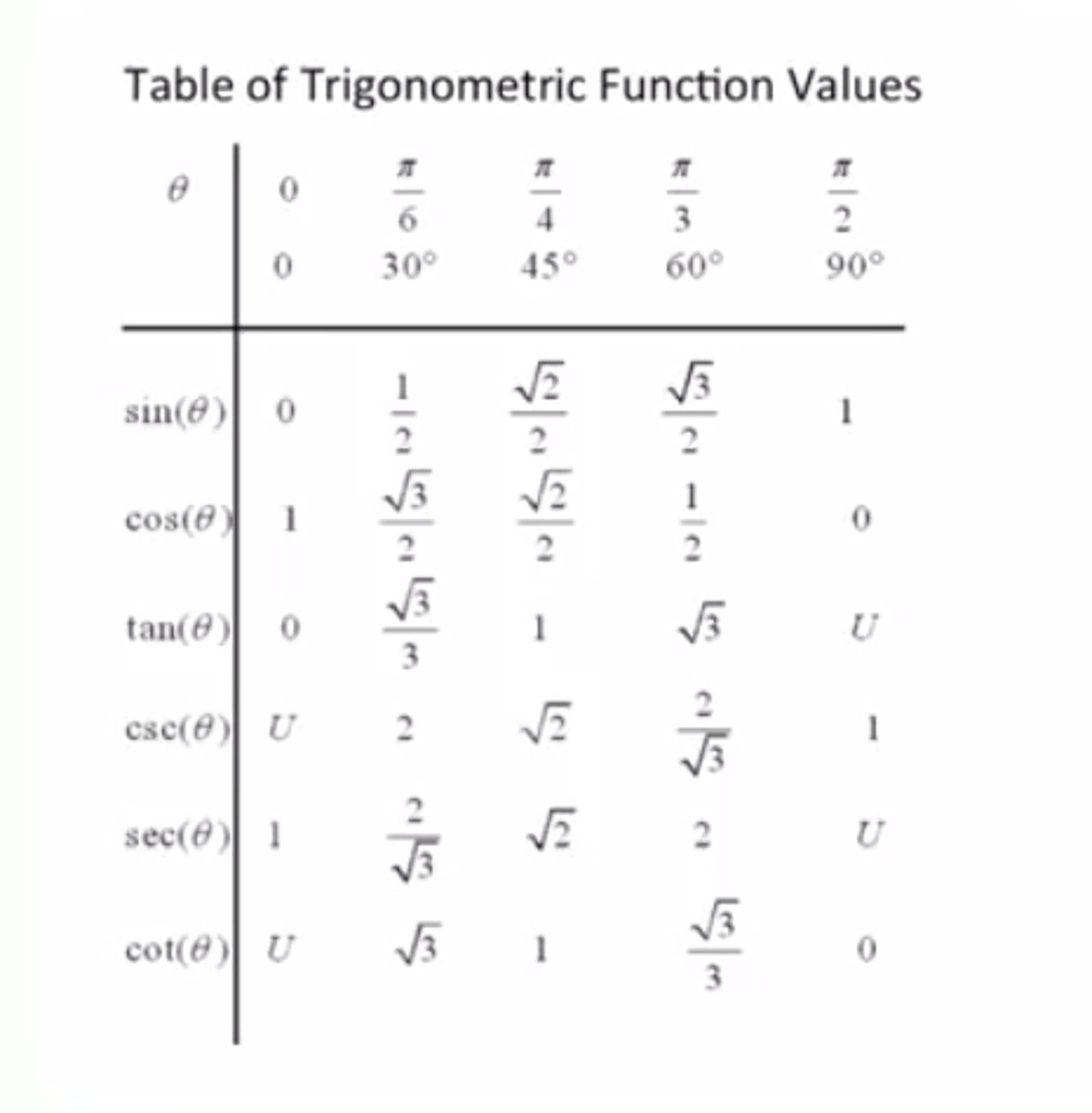
Memorize this table to master trig values
Inverse Trig Functions
Cosecant, secant, cotangent

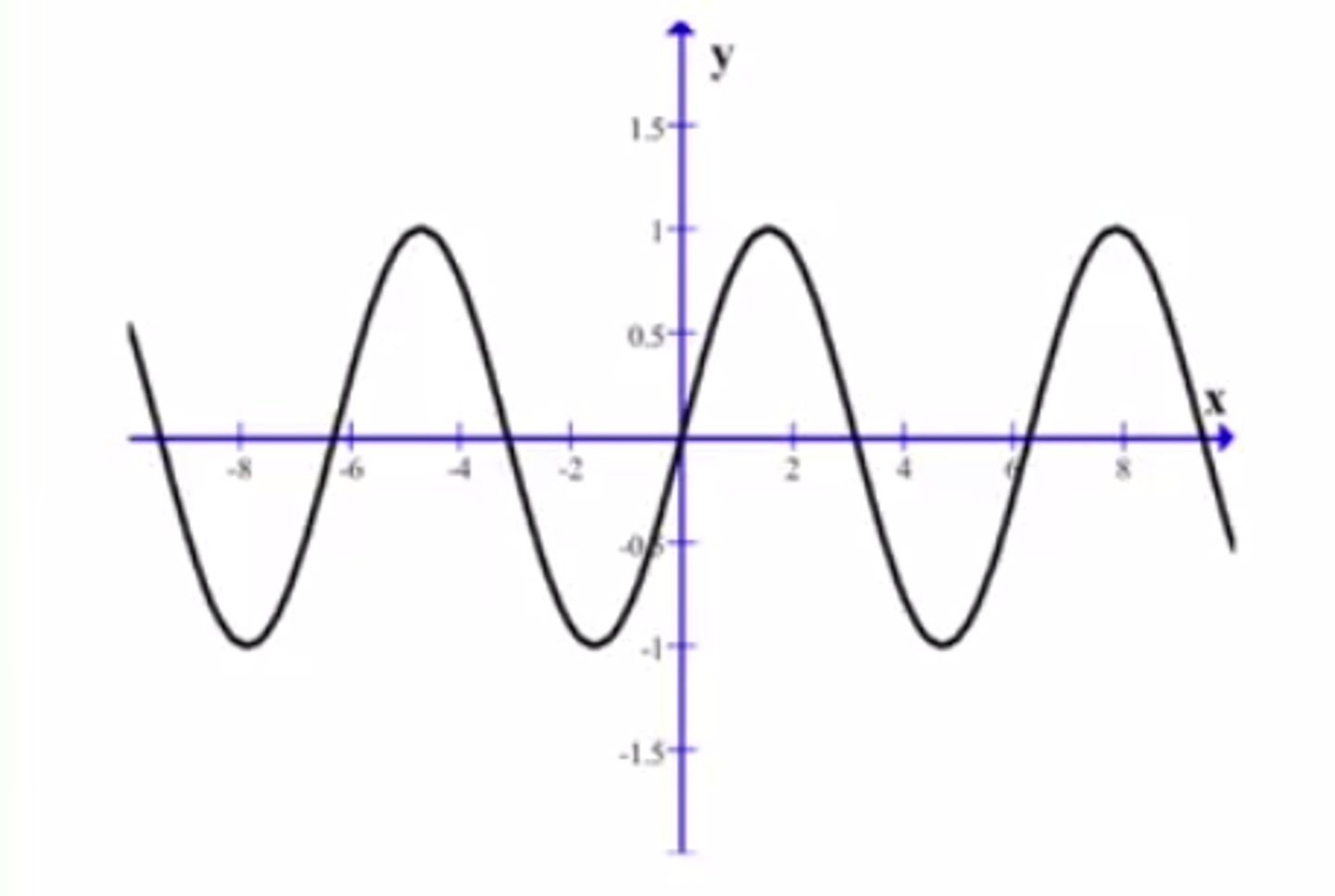
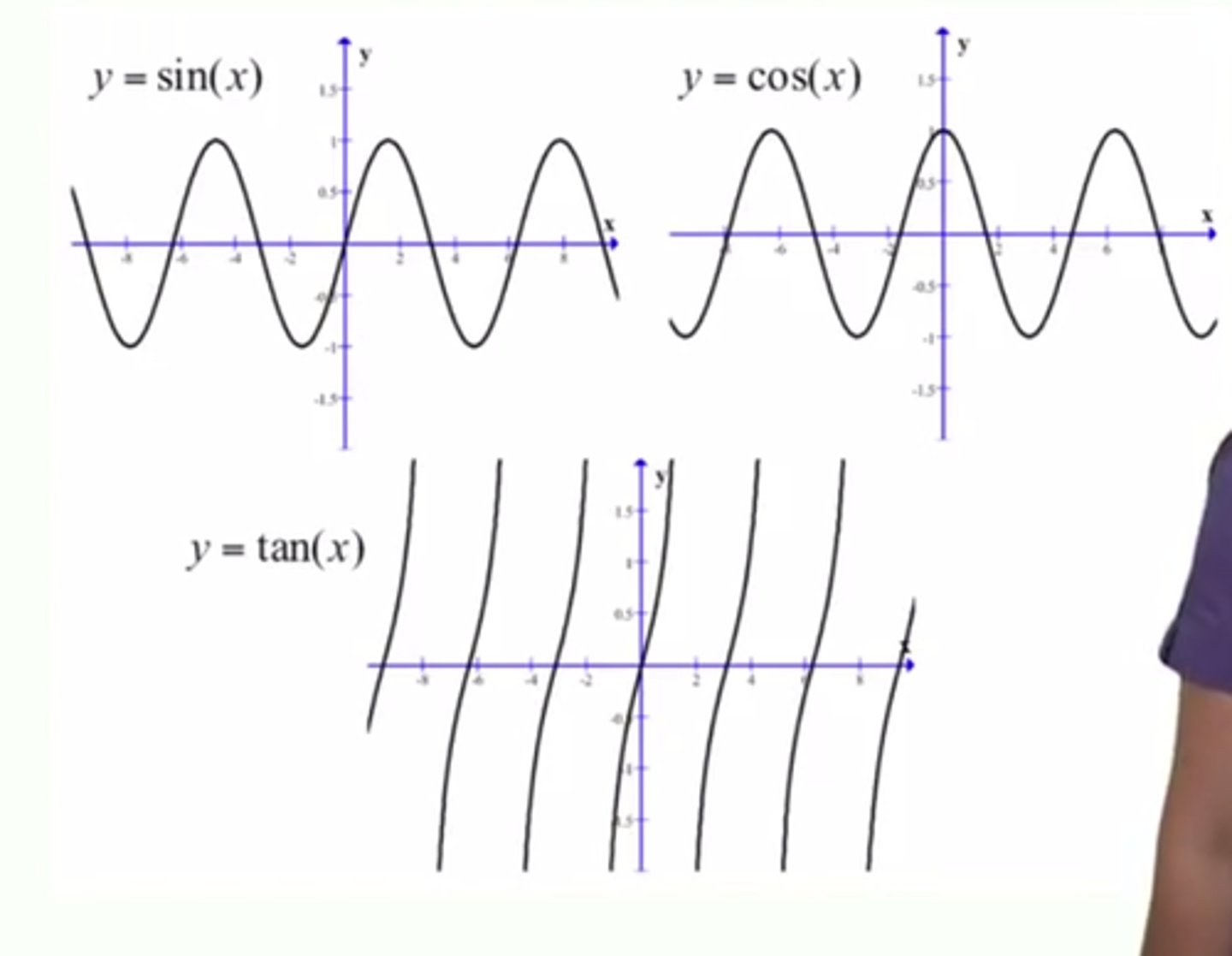
Graphs of Trig Functions
Each function has a characteristic period - the amount of time until it repeats again.
Trig Identity:
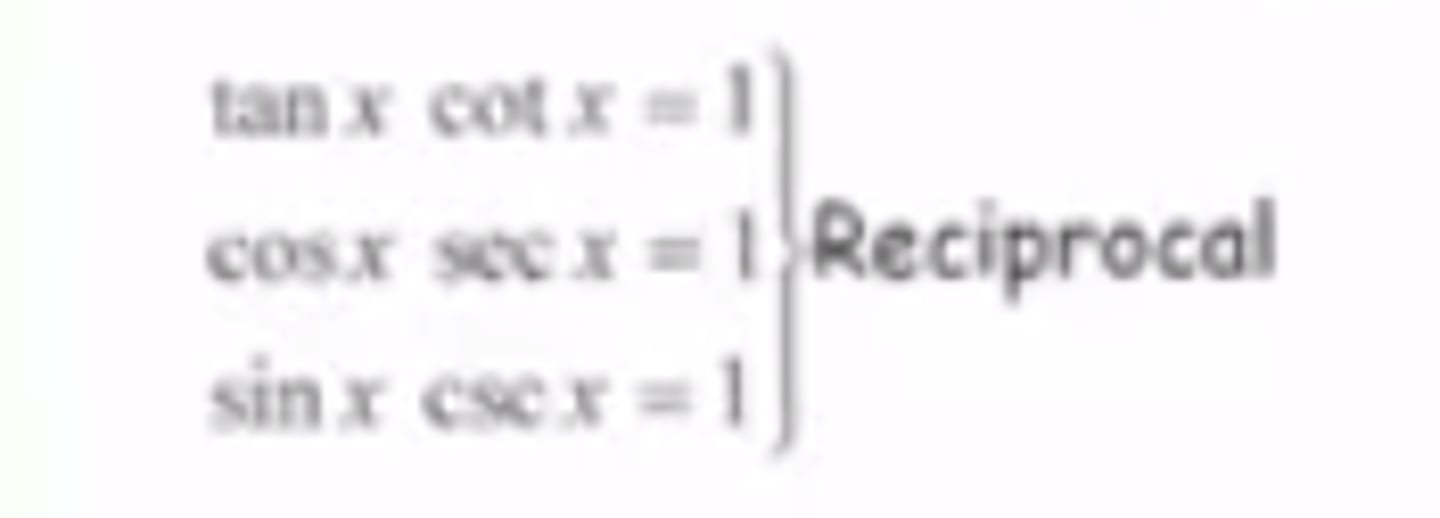
Pythagorean Theroem
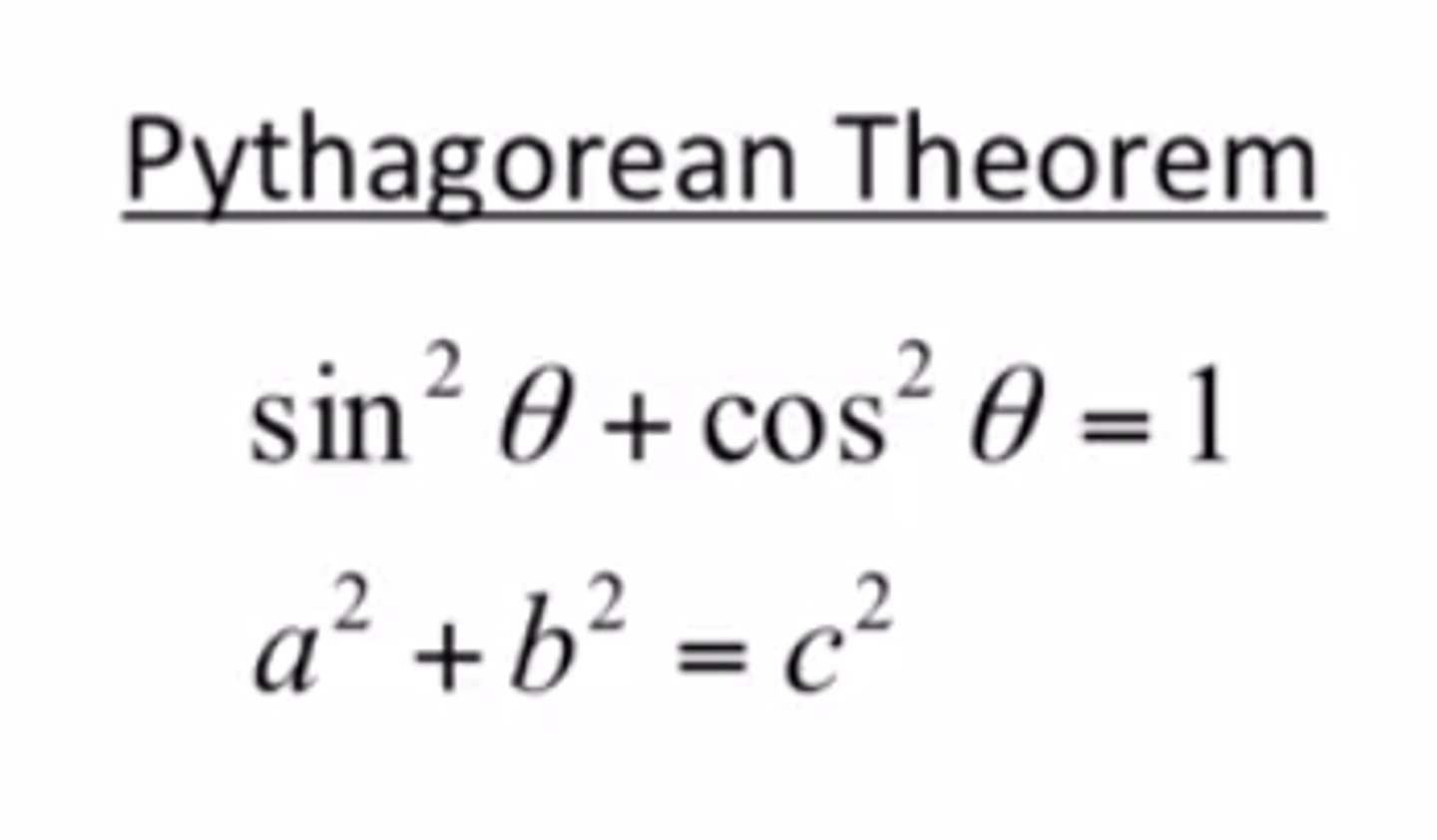
Trig Identity:
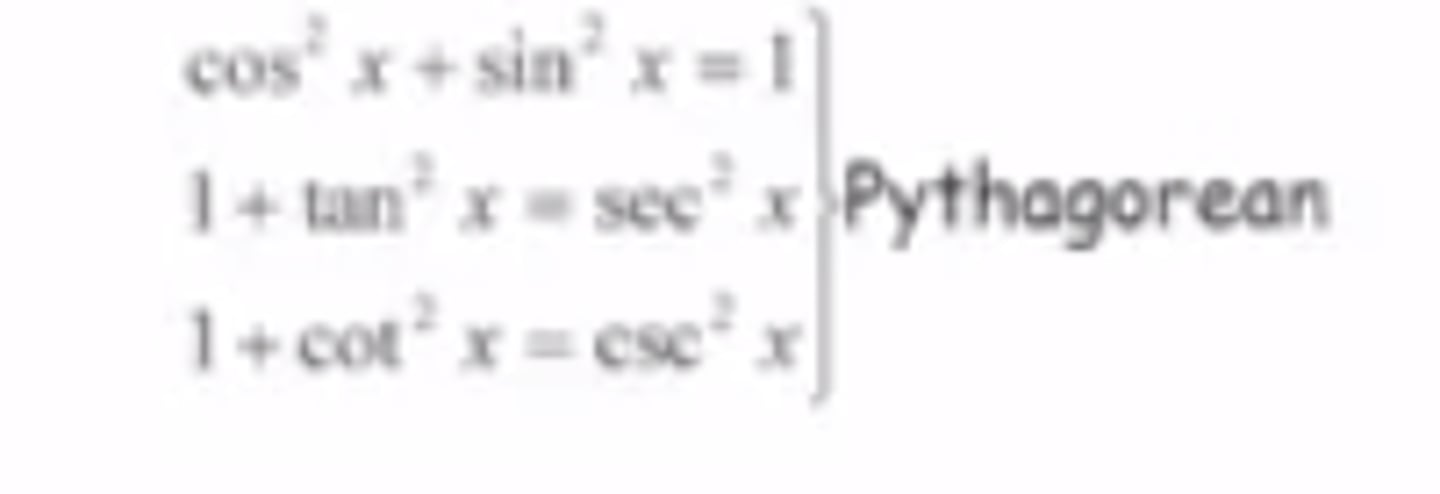
Trig Identity:
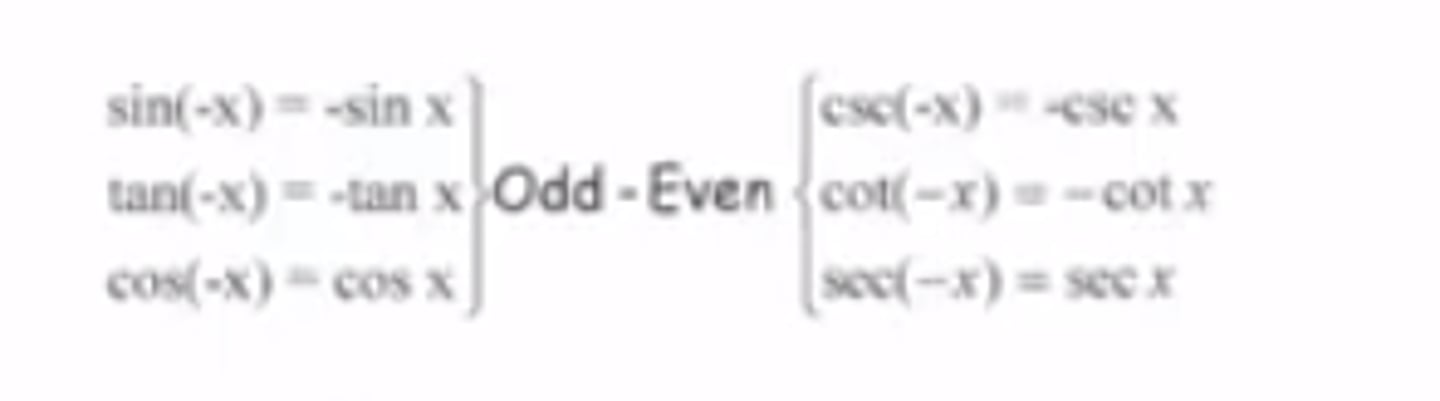
Trig Identity:
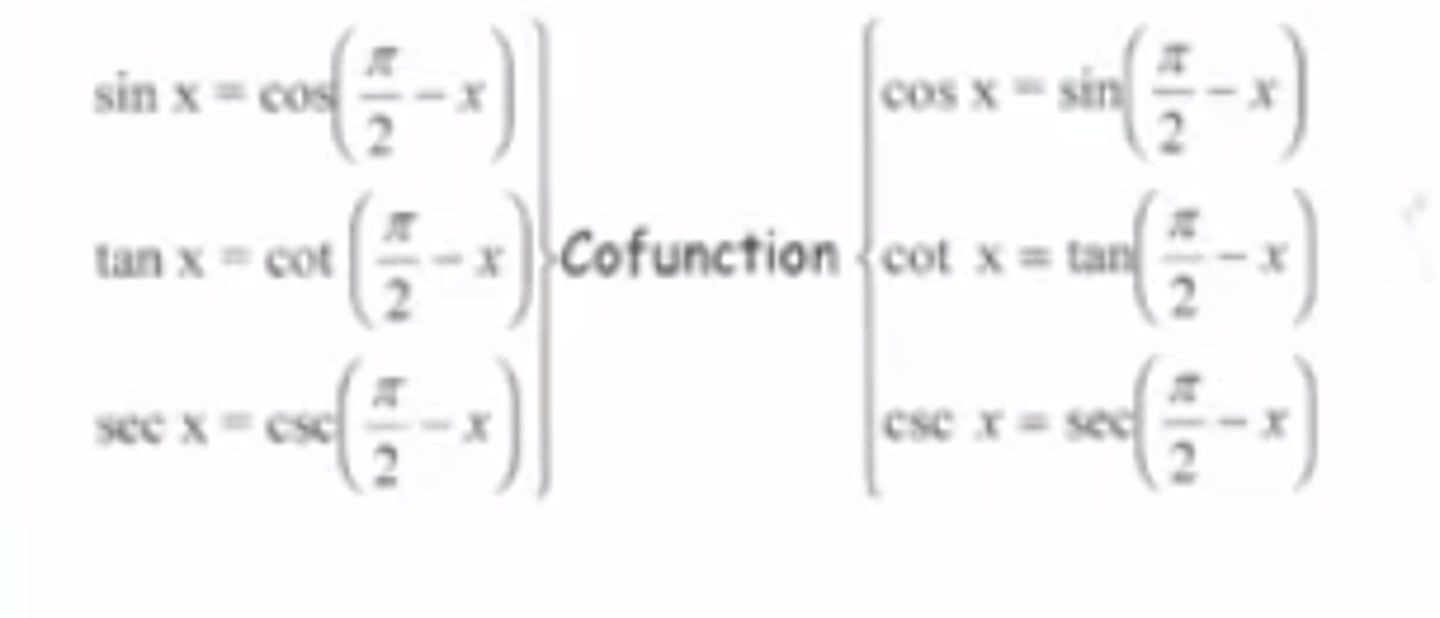
Trig Identity:
...
Trig Identity:
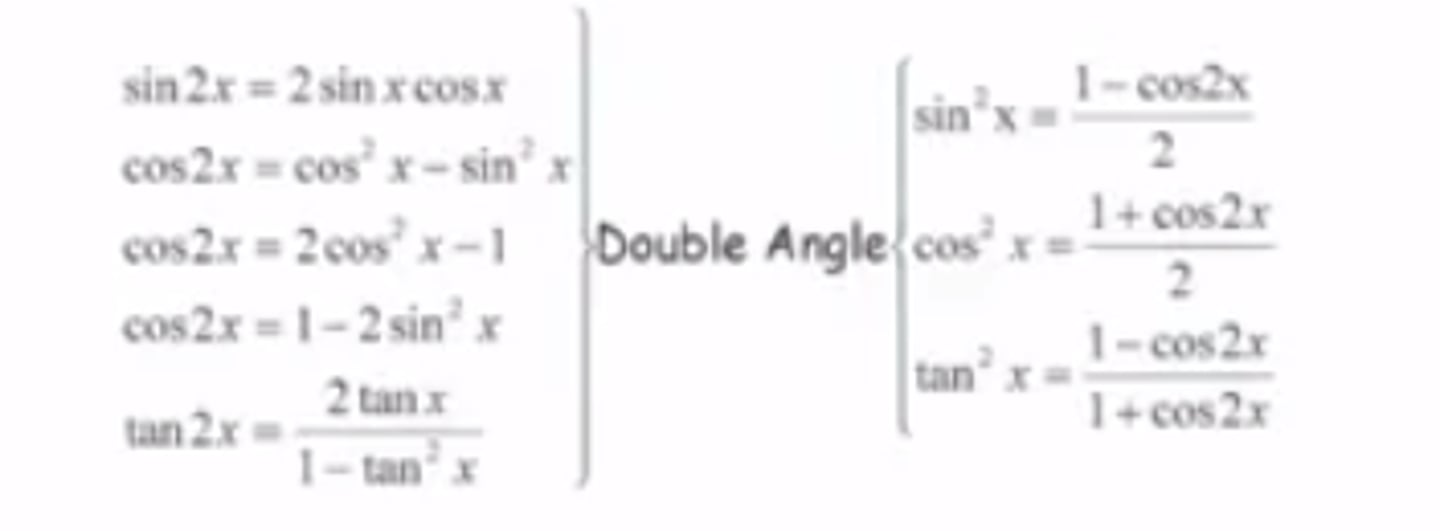
Trig Identity:

Trig Identity:
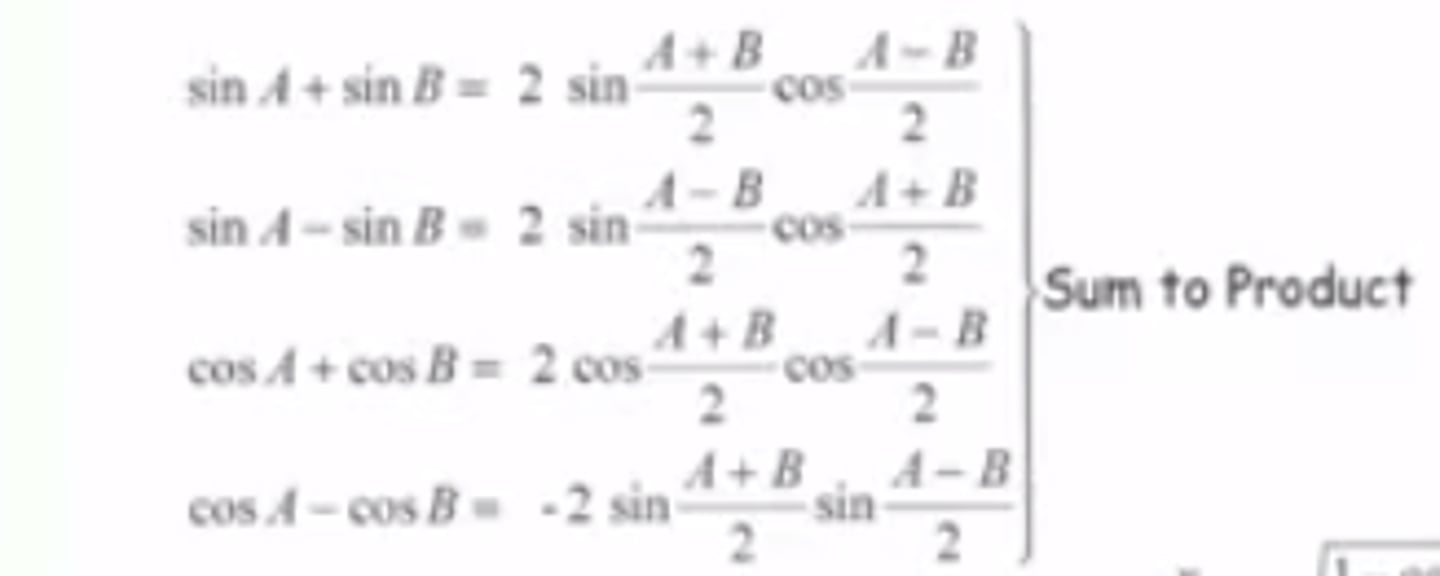
Trig Identity:
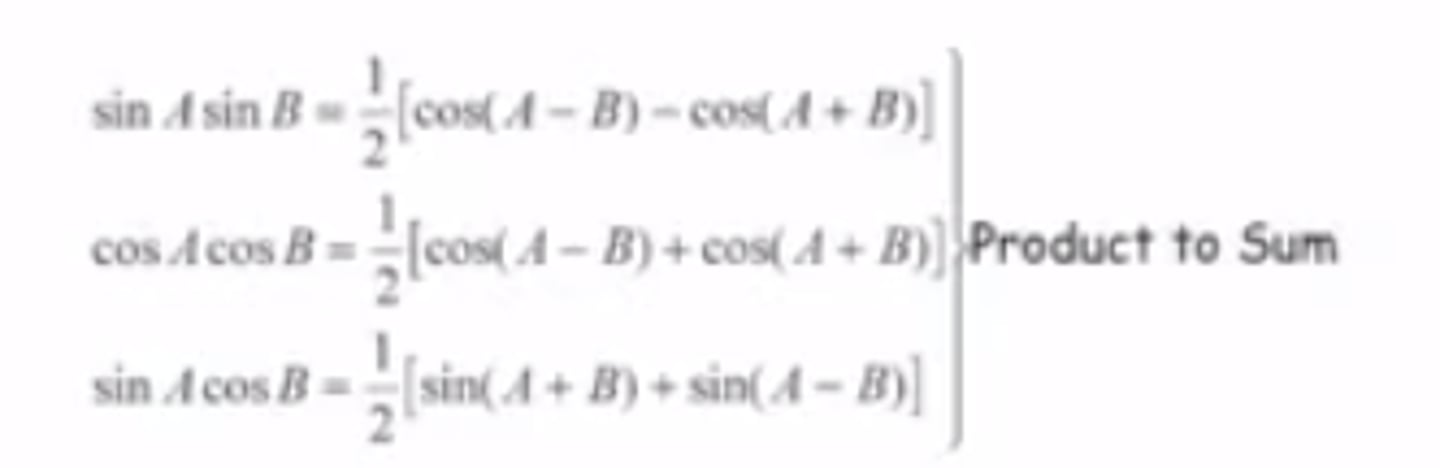
Trig Identity:
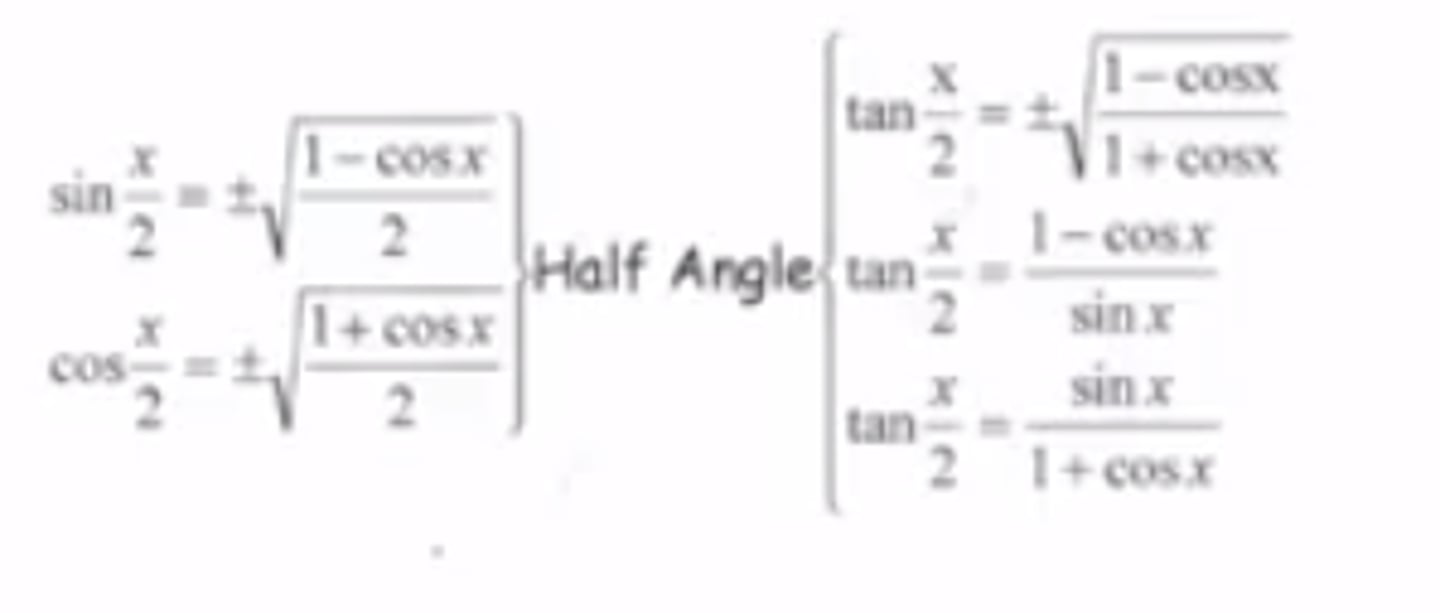
Trig Identity:
...
Why do we use trig?
Anything that uses a triangle or a wave
Astronomy - where will the heavenly body be?
Geometry
Optics
Architecture
Seasonal Phenomena (weather)
Signal Processing
Converting between Degrees-minutes-seconds and degrees
1 degree = 60 minutes
1 minute = 60 seconds
1 minute = 1/60 degrees
1 second = 1/3600 degrees

Degrees and Radians
The radian measurement is the measure of the arc of the circumference covered by the angle

One rotation around the unit circle
Measures 2 pi radians because the radius is 1 so the circumference is 2 pi r
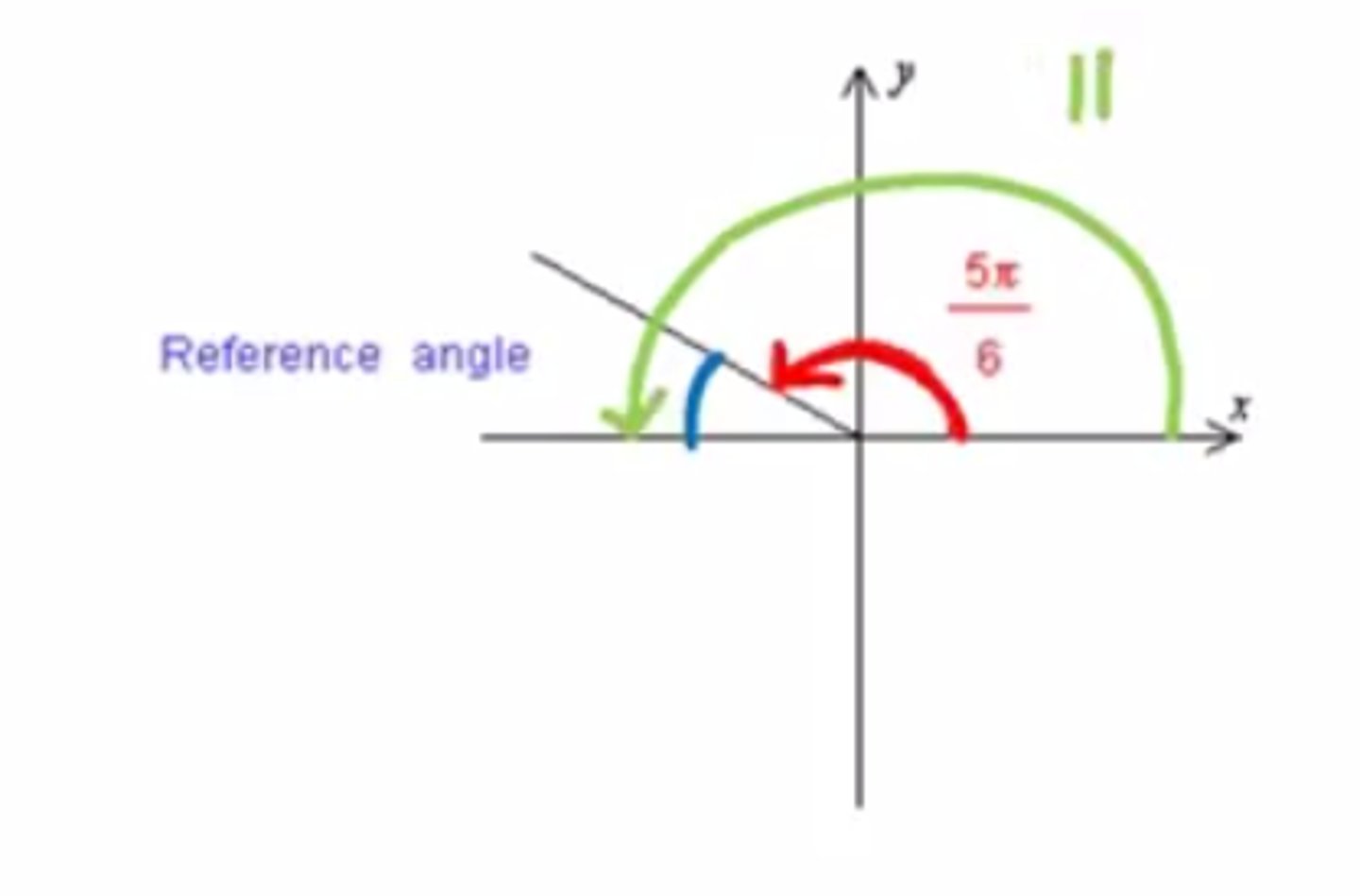
Reference Angle
The acute positive angle formed by the terminal side of theta and the x axis.
Coterminal Angles
They must share the same initial and terminal sides. Be really careful if they are asking you for a positive angle or a negative angle.
Looking at trig ratios when you have the coordinates on a unit circle.

Trigonometric Values of Special Angles (sin)
The sin of an angle is equal to the y coordinate of the point of intersection of the terminal side of the angle intersects the unit circle
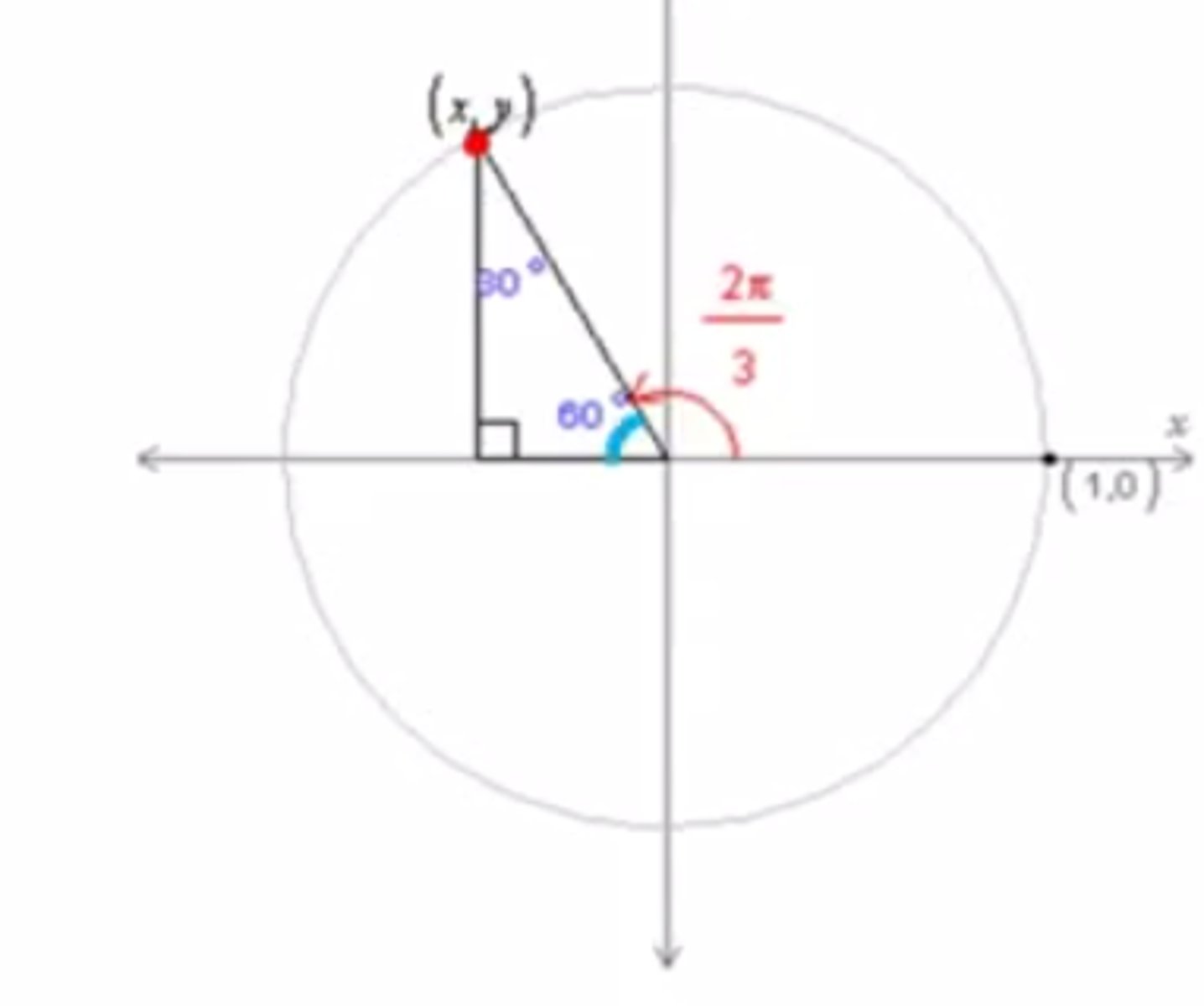
30,60,90 triangle
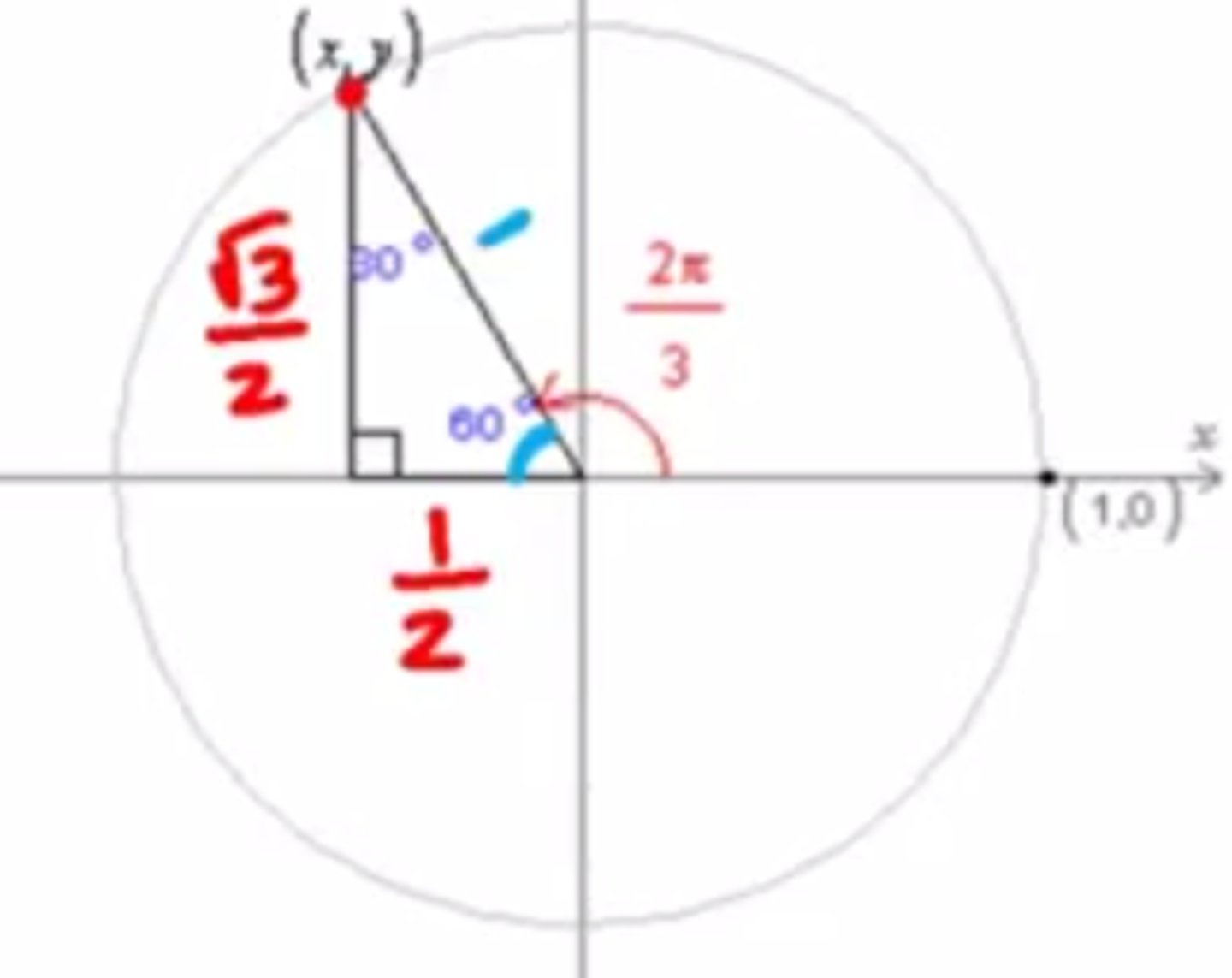
Trigonometric Values of Special Angles (cos)
The cos of an angle is the x coordinate of the point of intersection of the point of intersection of the terminal side of the angle and the unit circle
45,45,90 triangle
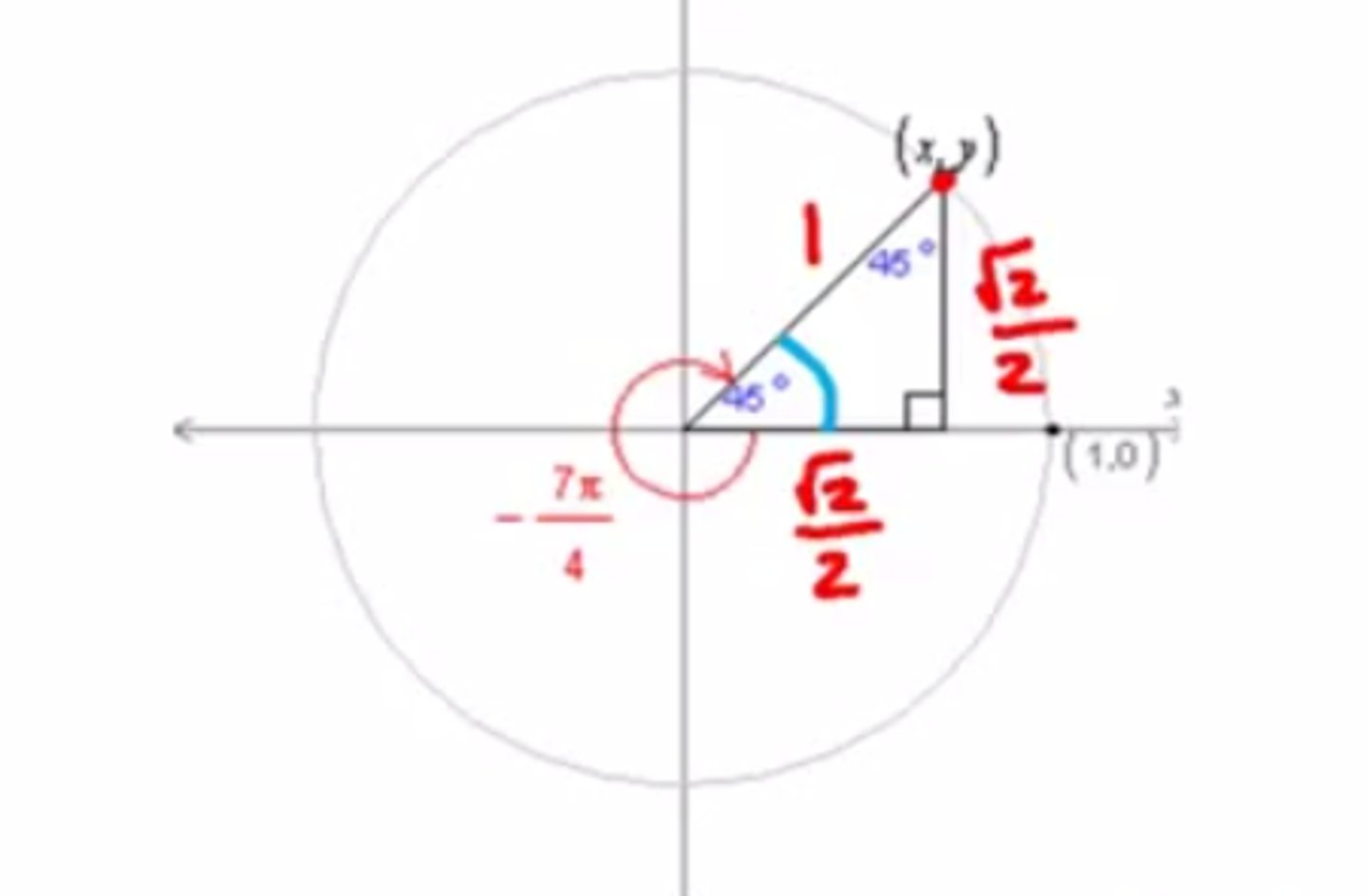
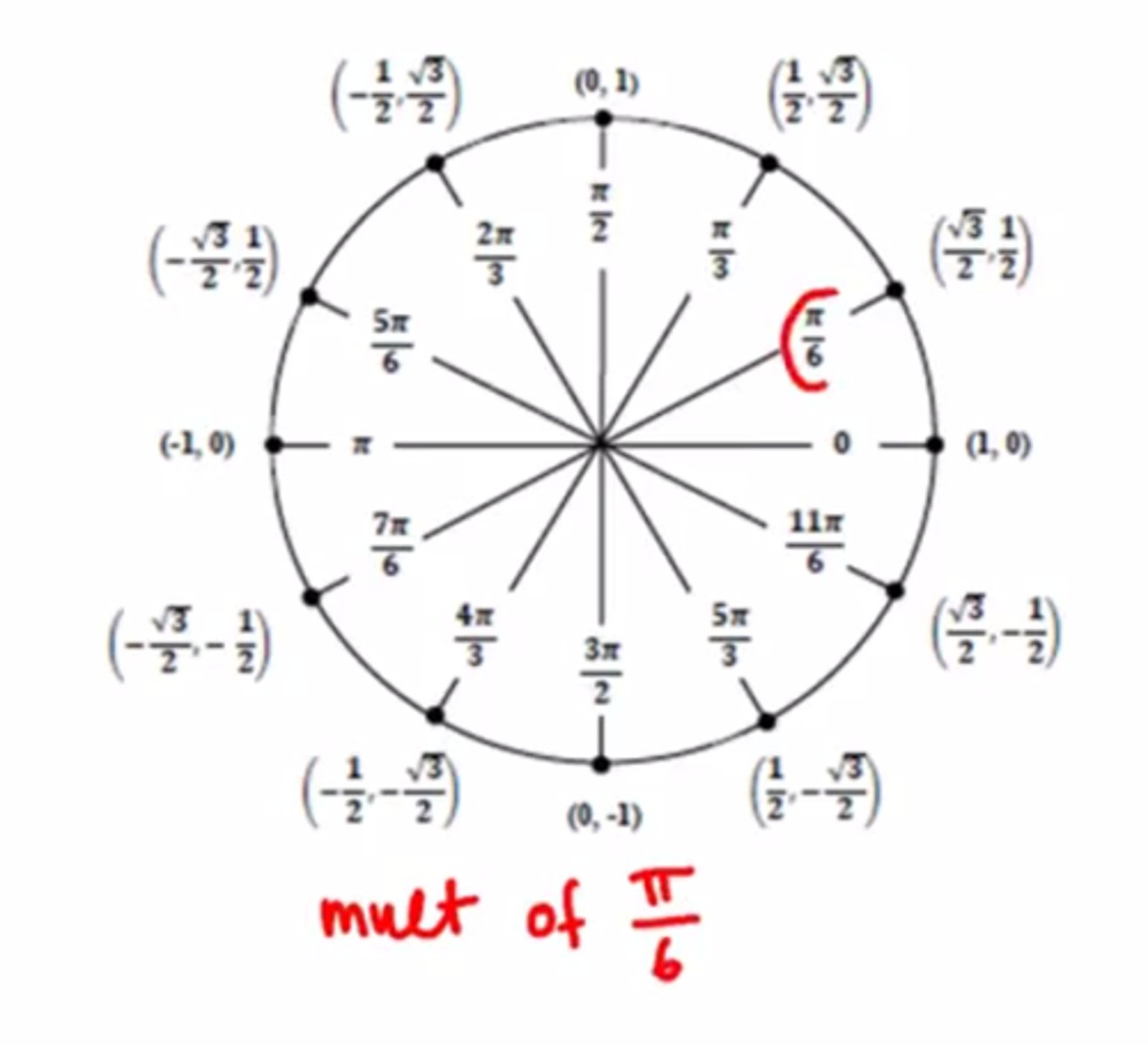
Multiples of pi/6
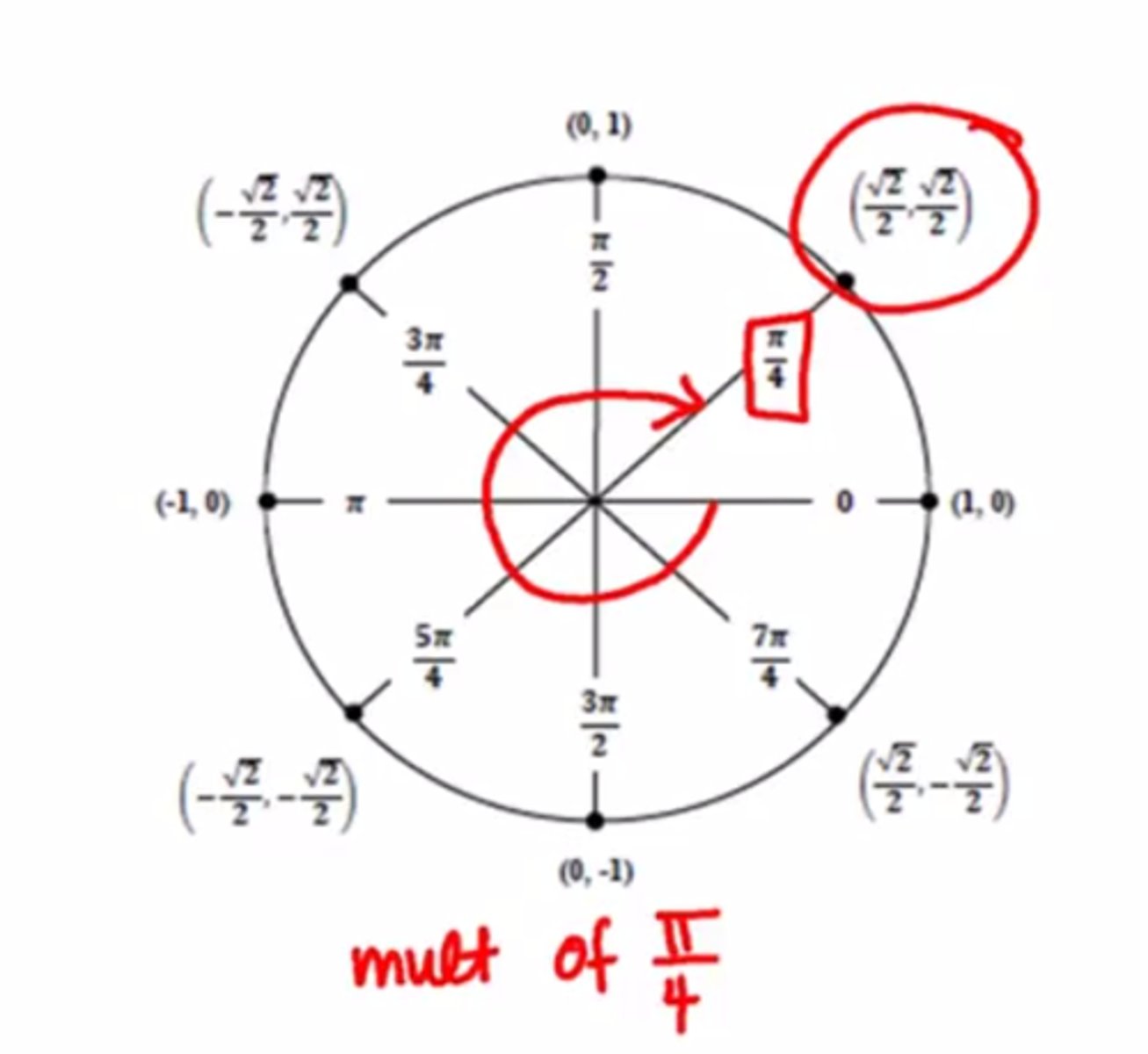
Multiples of pi/4
Common Trigonometric Ratios
3,4,5
What do you do if you have a point that does not lie on the unit circle? Using the "r" value - the missing hypotenuse or radius of the non-unit circle.