ENT Week 1 - Introduction/Basics/Otitis Externa
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
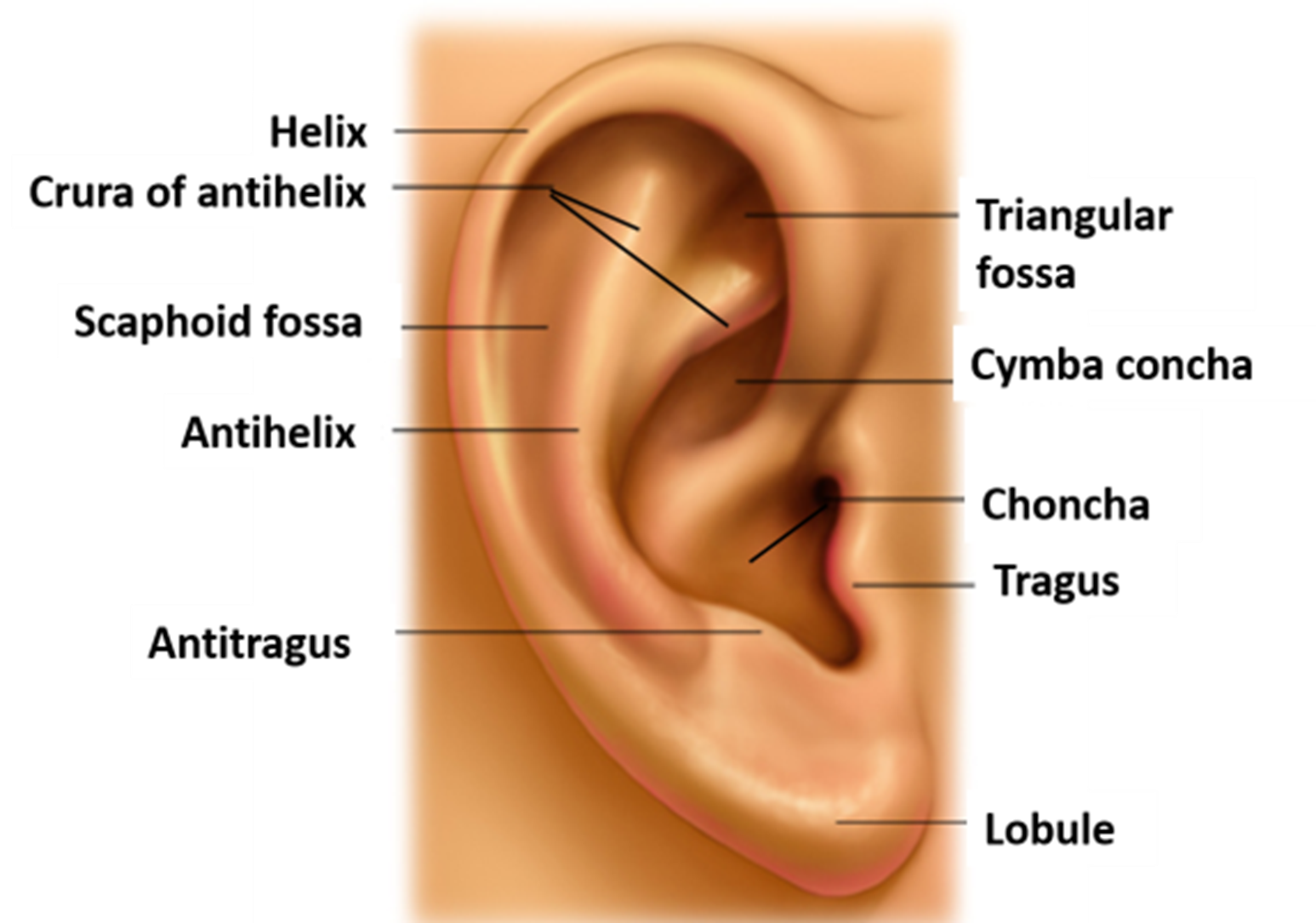
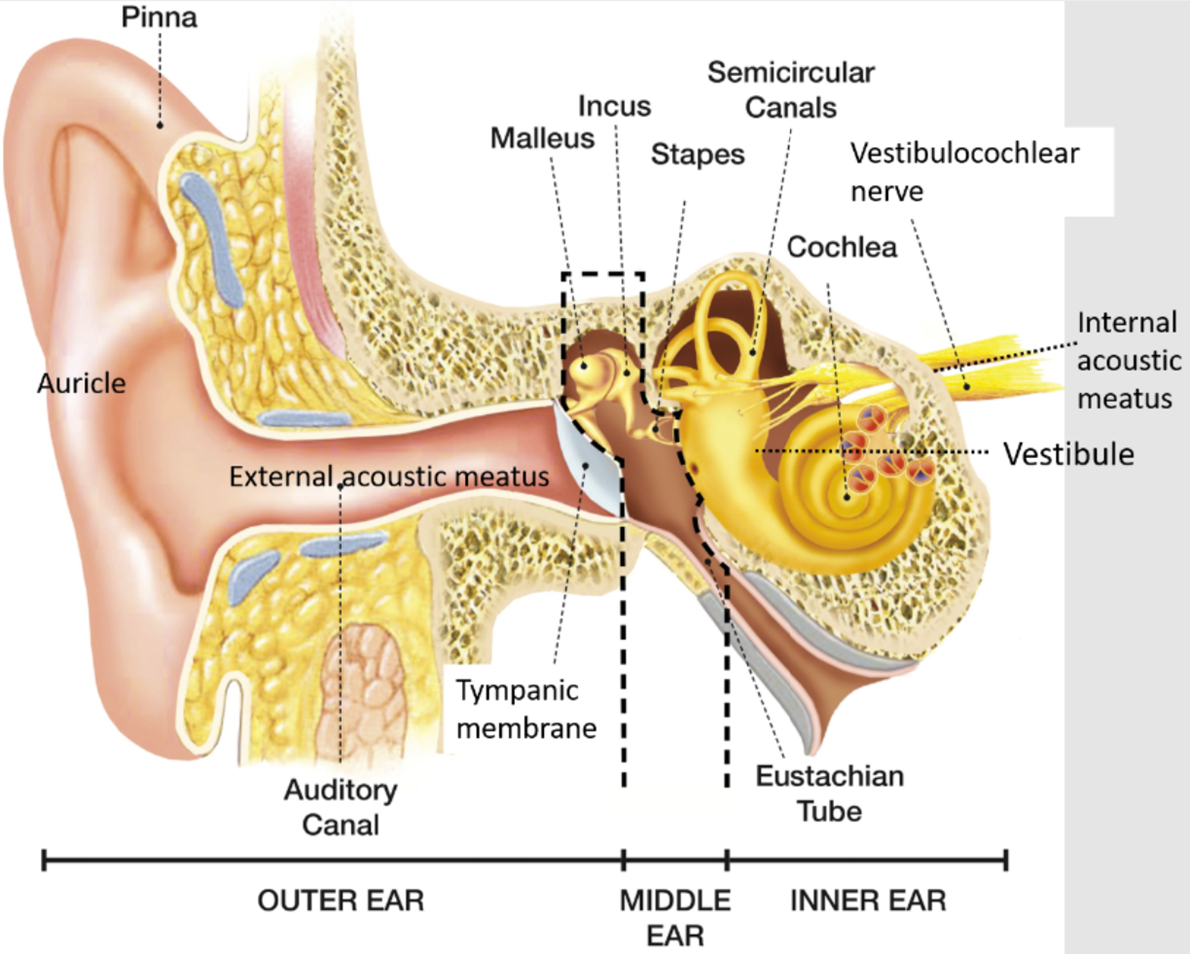
Anatomy of the outer ear (picture)
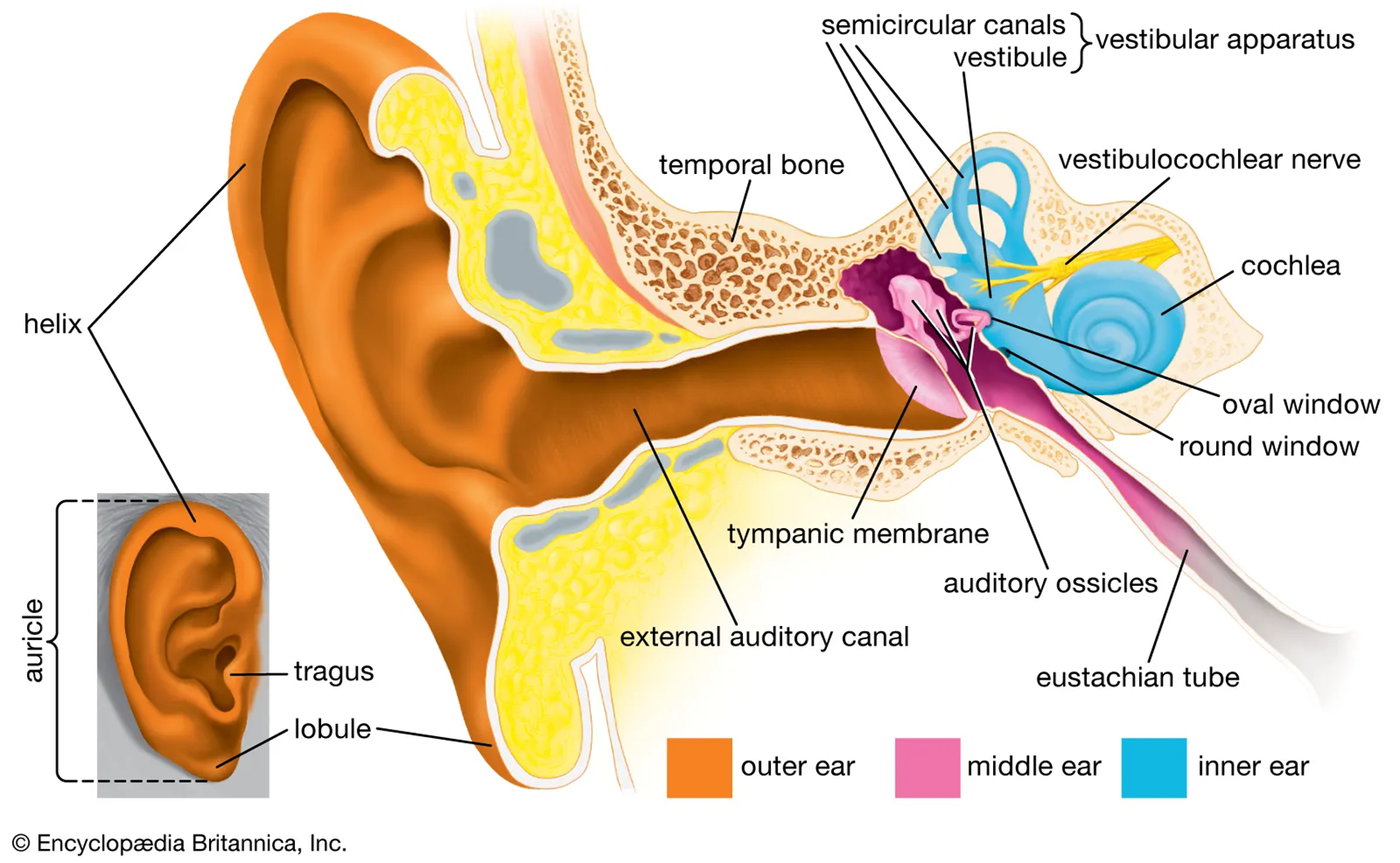
Anatomy of the middle/inner ear (picture)
Cochlea
Fluid-filled structure within the inner ear that contains hair cells that convert sound waves into electrical impulses that are carried along the auditory nerve to the brain.
Vestibular Apparatus
vestibule + semicircular canals
important in maintaining the sense of equilibrium
detects movement and the position of the head
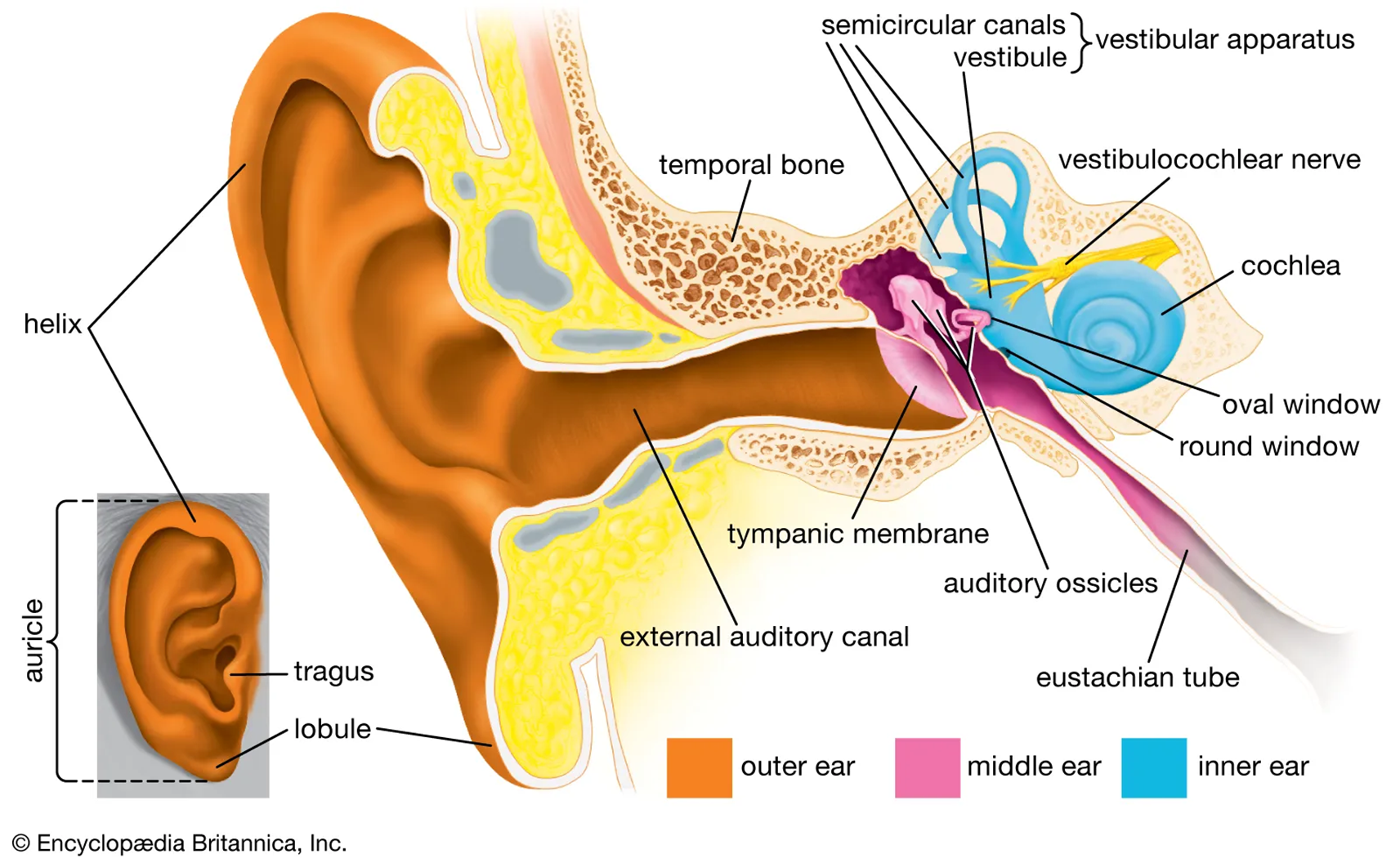
Middle ear ossicular chain
malleus —> incus —> stapes —> oval window displacement —> pressure wave in the fluid within the inner ear
Three regions of the ear overview
External ear
Auricle and external acoustic meatus
Middle ear
Tympanic cavity (with middle ear bones)
Epitympanic recess
Eustachian tube*
Inner ear
vestibulocochlear organs
innervation by vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
Germ layer
One of the primary layers of cells formed during embryonic development
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesenchyme
Inner ear embryology
return
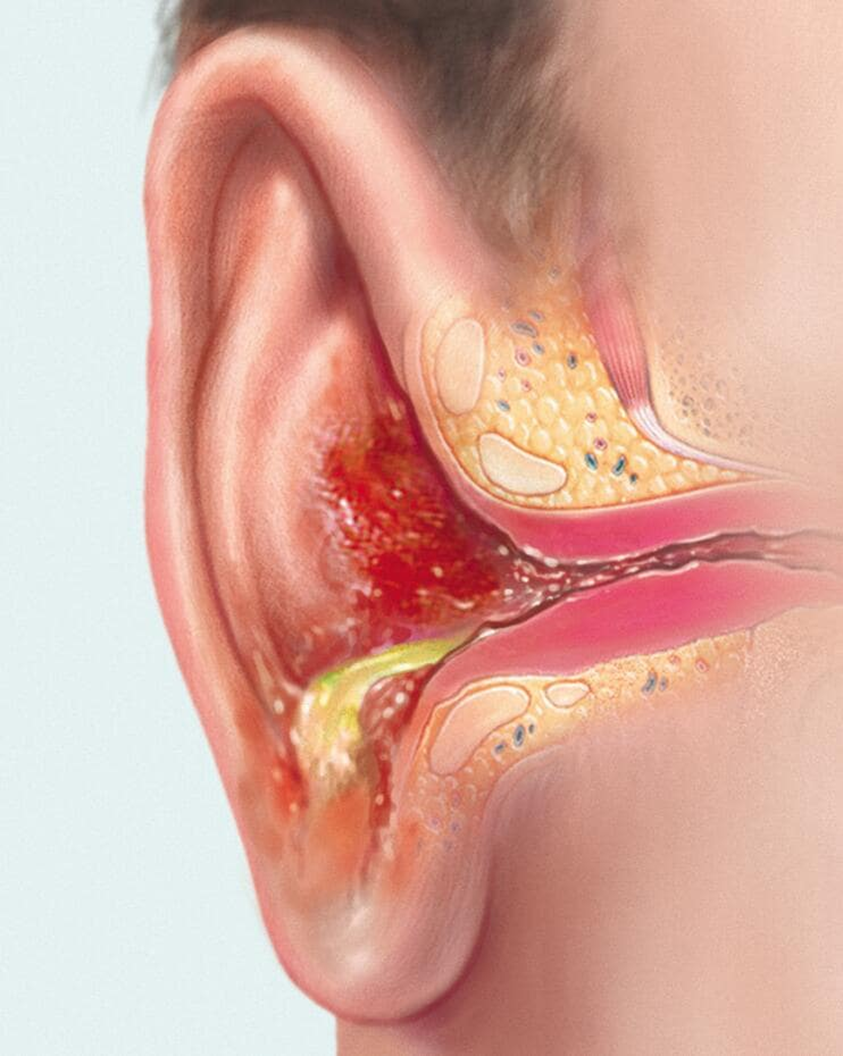
Uncomplicated Otitis Externa (UOE)
Inflammation of the outer ear / external auditory canal caused by bacteria or fungus. Also known as “swimmer’s ear.”
Symptoms include ear canal swelling, ear pain with tragus palpation or pulling on the ear superiorly / inferiorly, itching (more common with fungal etiology), otorrhea
Acute Bacterial Otitis Externa is the most common OE seen by PCPs
vinegar can prevent
Pathogens causing UOE
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38%)
Staph species (9%)
Fungus infrequently, although infections are more common after bacterial treatment
Greatest risk factors for otitis externa
Water in the ear canal, and trauma
Treatment of UOE
Aural toilet*** — irrigation to remove any wax, purulent material, dead skin
drying the canal after irrigation is beneficial
mainstay of treatment for both bacterial and fungal presentations
Initiate treatment with topical therapy (antibiotic route)
Ciprodex (4 drops BID x 7 days)
Floxin (5 drops BID x 7 days)
Cortisporin Otic (4 drops QID x 7 days)
Sulfonamides do not treat Pseudomonas**
(Fungal route)
Clotrimazole or miconazole swabs / powder
Malignant Otitis Media - Key Facts
Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Often seen in those immunocompromised (90% diabetics; includes cancer, HIV, etc.)
Progressive condition = fatigue, nausea, changes in vision and mental status may occur. Ear pain and discharge unresponsive to normal interventions = warning sign
Can progress to skull base osteomyelitis
Malignant Otitis Externa - Imaging
begin with CT of temporal bone
MRI for dura to assess nerve involvement
Malignant Otitis Externa - Treatment and Outcomes
4-6 weeks of IV fluoroquinolones
MRI with contrast to evaluate progress
Cure rate is greater than 80%