Chemistry - Unit 2 (Read Description)
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Atoms
building blocks of matter
subatomic particles
Protons (+1), electrons (-1), neutrons
Proton
+1 charge, large, found in nucleus
Neutron
No/neutral charge, large, found in nucleus
Electron
-1 charge, very small, found outside of nucleus in electron cloud/orbital
Nucleus
holds protons and neutrons
elements
composed of many atoms of the same kind
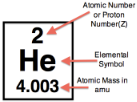
Atomic Number
Indicates the number of protons in an atom, which is what defines the element of the atom. The periodic table is arranged in order of increasing the number of protons.

Atomic Mass
Average mass of all of the isotopes of an element. Measured in amu (always remember your units!)
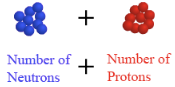
Mass number
the # of protons + # of neutrons which is the atomic mass rounded to a whole number. (changes if # of neutrons changes)
Ions
An atom of molecule with a charge either positive or negative. When the number of protons does NOT equal the number of electrons
Cation
A positively charged atom (less electrons than protons)
Anion
A negatively charged atom (more electrons than protons)
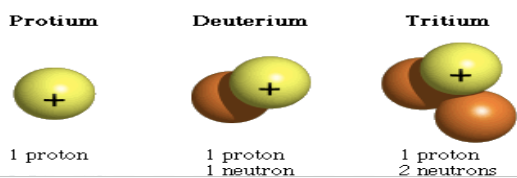
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (This changes the mass number. Same element, but may have different properties)
The Periodic Table
a chart that organizes elements according to their atomic number and their chemical and physical properties
Groups
a column on the periodic table (there are 18 on the periodic table)
Period
a row on the periodic table (there are 7 on the periodic table)
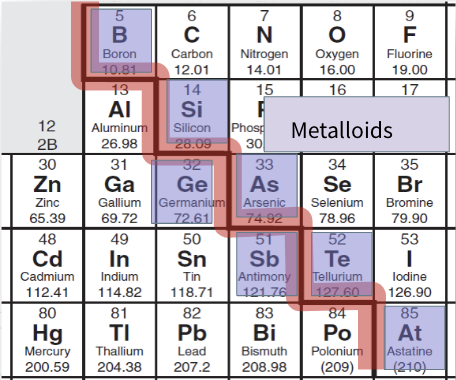
Metalloids
All are solids at room temp and in between a metal and non-metals. Found directly to either side of the staircase.
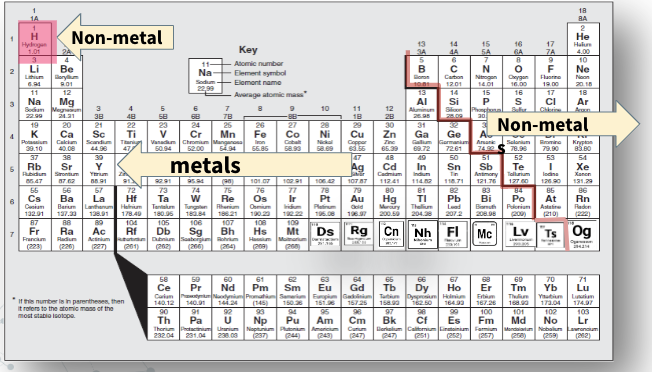
metals
solid at room temperature except for mercury, which is a liquid
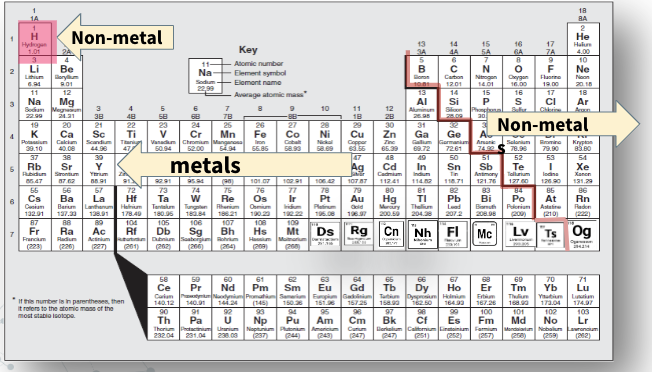
Non-metals
Most are gases at room temp, except for bromine which is a liquid, and 5 are solids (carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, iodine)
Chemical Families
a group (column) that contains elements with similar properties because each group has the same number of valence electrons
Transition metals
MOST are hard, strong, and lustrous with high melting points & conduct heat/electricity
Halogens
very reactive nonmetals, combined in nature with other elements
Noble gases
non-reactive gases
Lanthanides: Elements 57-71
Shiny, silvery, soft metals (rare earth metals)
Actinides: Elements 89-103
radioactive metals (many are extremely toxic)
molecule
formed when two or more atoms are joined together chemically (ex: O2, H20)
compound
formed when two atoms of two or more different elements join together chemically (ex: H20, C6H12O6 )
Chemical bond
The force of attraction that holds two or more atoms together (due to the attraction between the positive nucleus & negative electrons)
Valence Electrons
the electrons in the outer shell/orbital that bond with other atoms and have the highest energy
Octet Rule
Atoms try to get 8 valence electrons so they can become stable by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons
Core electrons
under the valence electrons; they are closer to the nucleus
inert
does not react with other atoms
Ionic Bonds
result of the attraction between ions when a metal gives their valence electrons to non-metal (intramolecular)
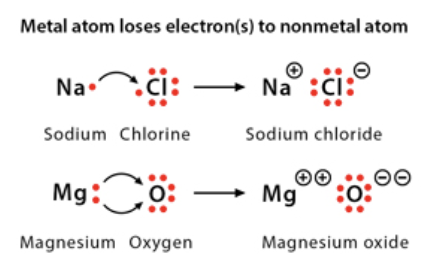
Covalent Bonds
when an atom shares one or more pairs of electrons with another atom & forms a bond and is common between two nonmetals (weaker and most common chemical bond in living organisms) (intramolecular)
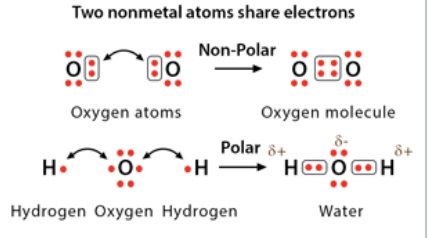
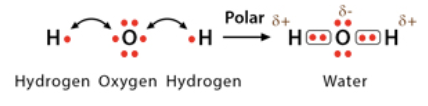
Polar covalent bond
electrons are unequally shared between two atoms which causes one atom to be slightly negative, and one to be slightly positive
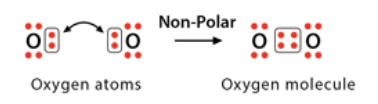
Nonpolar covalent bonds
electrons are equally shared between two atoms so the atoms remain neutral in charge
Electronegativity
the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself
hydrogen bonds
An Intermolecular force and these bonds are weak compared to covalent & ionic bonds (It bonds water molecules together)
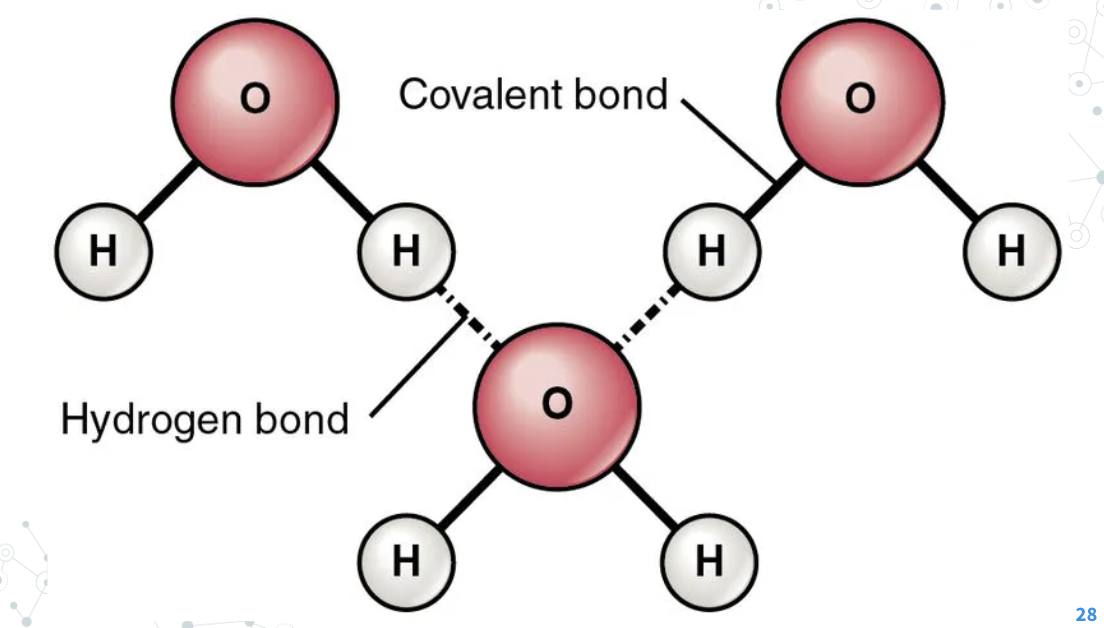
Intermolecular force
bonds between molecules
intramolecular force
forces between atoms
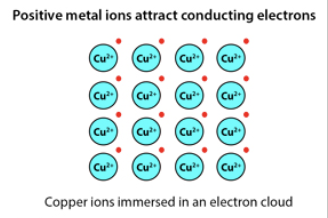
Metallic bonds
A force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance (Metal + Metal) and are solids made up of tightly packed atoms as a result, valence electrons move freely from one atom to another and they share an electron cloud (intramolecular)