Cellular Reproduction chapter 8
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts from the lecture on Cellular Reproduction, encompassing processes of cell division, checkpoints in the cell cycle, and the implications of cancer.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
doesn’t require sperm or eggs.
Chromosomes
Copying of DNA
DNA is packaged into chromosomes
Humans have 46
Mitosis
The process of nuclear division that results in two identical daughter nuclei, part of the M phase of the cell cycle.
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm following mitosis, resulting in two separate daughter cells.
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome, joined together at the centromere, created during DNA replication.
The basics of cellular reproduction
Multicellular organisms
we grow to replace worn-out/ damaged tissue
Chromatin
Thin thread appearance
Chromosome Compaction
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
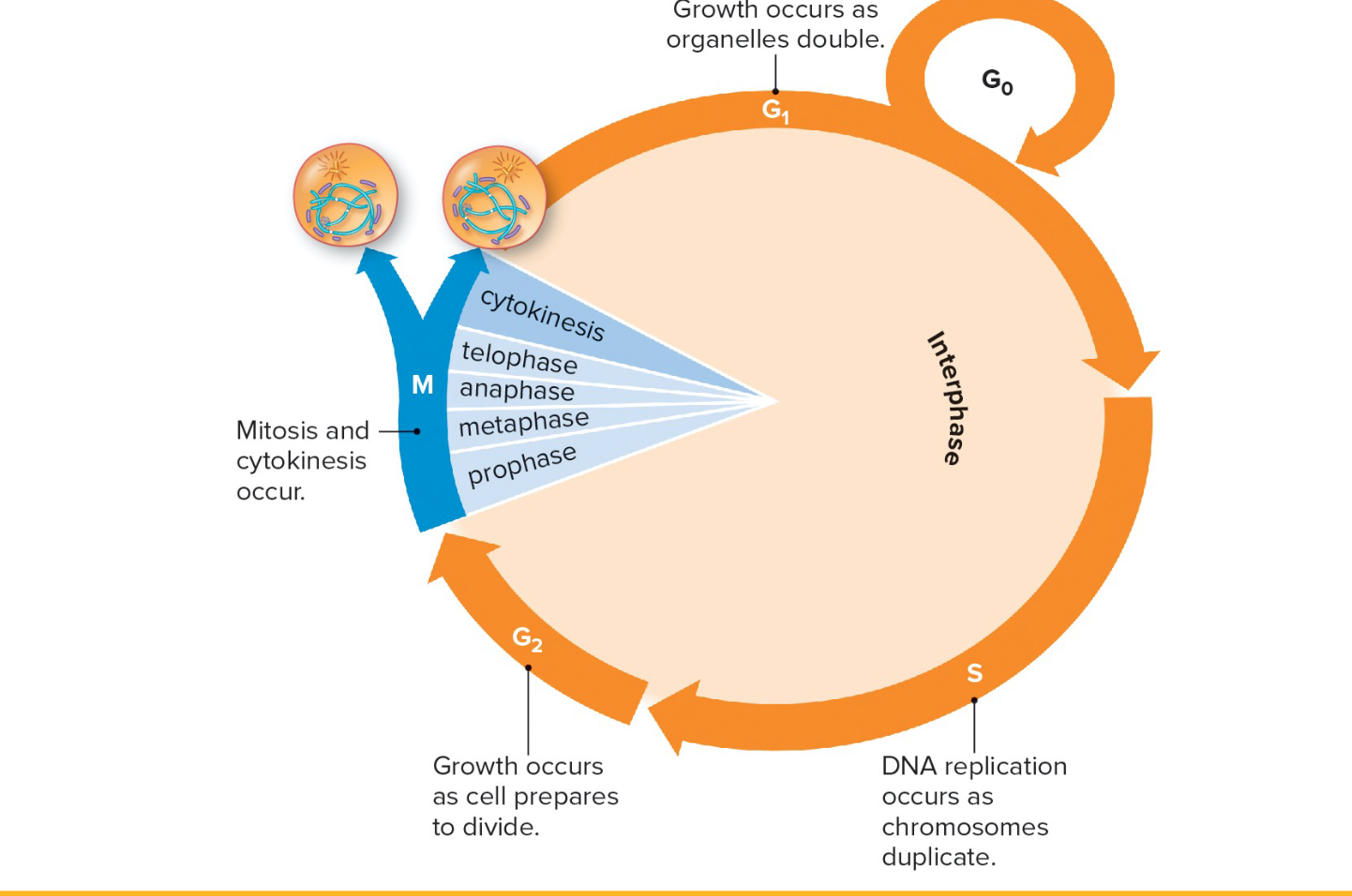
Cell cycle.
Duplicated chromosomes are made up of sister chromatids joined at the____
centromere.
Interphase stages
G1
S- DNA synthesis
G2
G1 stage
Cell doubles organelles
S-DNA synthesis
Results in each chromosome being composed of 2 sister chromatids
G2 stage
Extends to onset of mitosis
synthesizes proteins needed for cell division.
Daughter nuclei
genetically identical to each other
Spindle
pulls chromatids apart.
Made of microtubules
Prophase
chromosomes are visible
condensed pairs
Metaphase
equatorial plate
(Middle)
Anaphase
chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles of cell
(apart)
Telophase
two distinct cells
Cell division occurs in ___ phase
Mitotic phase.
Division of nucleus is
Mitosis
Creates two identical daughter nuclei.
Division of cytoplasm
Cytokinesis
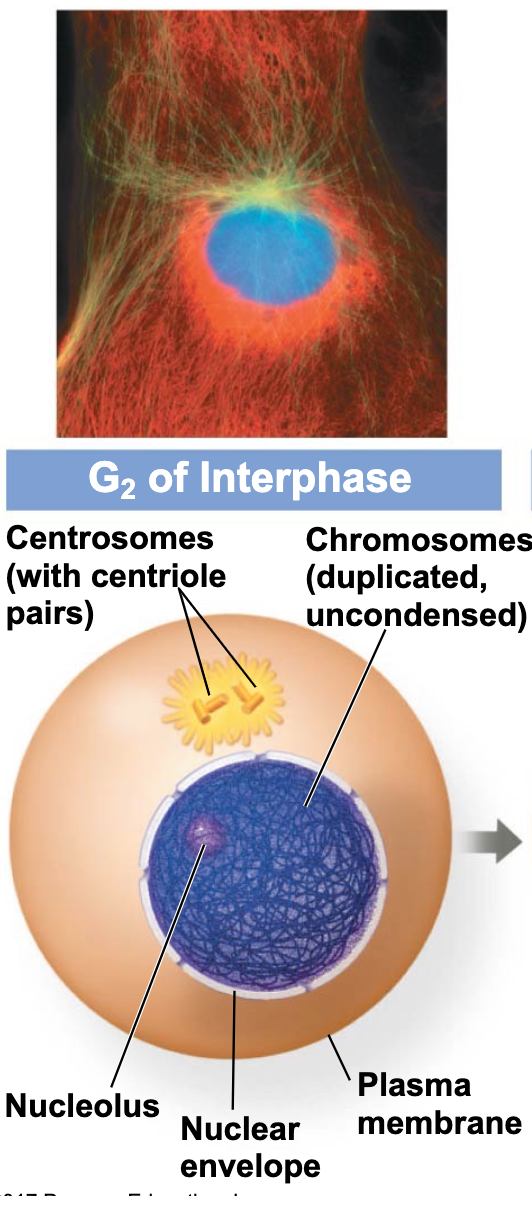
Image of G2 interphase
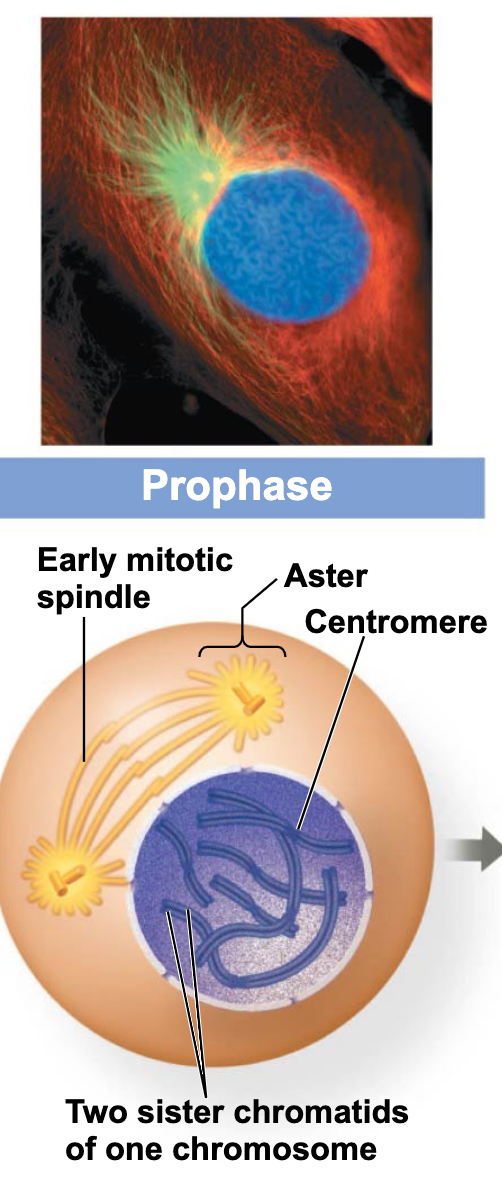
Prosphase
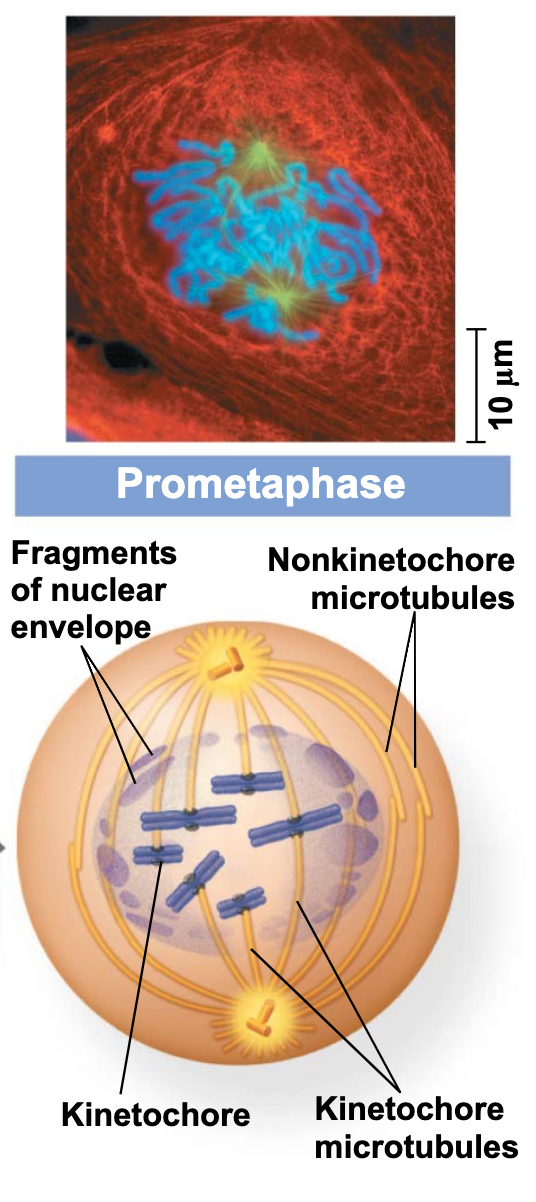
Prometaphase.
Although mitosis is divided into phases…
it is a continuous process
Plants have centrosomes but…
lack centrioles
Cell membrane in plants…
form from center outward along a cell plate
Cell membrane in animals forms through a
Cleavage furrow..
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells
ridged call wall
cell plate
Check points
G1 checkpoint
G2 checkpoint
Mitotic stage checkpoint (M)
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
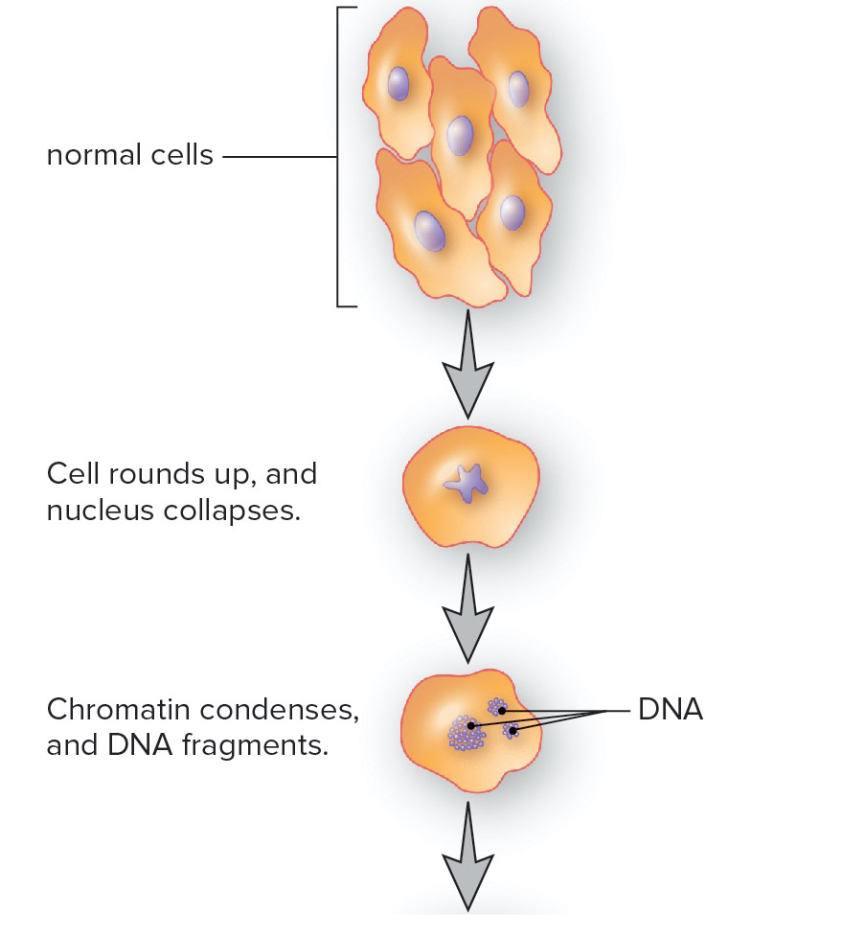
Apoptosis
Cell Cycle and Cancer
regulated by signals that inhibit or promote
cell cycle.
Cancer Cells
Undergo metastasis
Benign
Malignant
G1 checkpoint
Apoptosis can occur is DNA damage cannot be repaired
G2 checkpoint
Mitosis will NOT occur if DNA has replicated
Mitotic Stage Check point (M)
Mitosis stops until chromosomes are properly aligned
Benign
in a capsule
Malignant
invasive and may spread
Cell cycle and cancer
cell cycle is regulated by signals that inhibit or promote cell cycle
Signal
a molecule that stimulates or inhibits an event
external signals
come from outside the cell
Internal signals
come from inside the cell