part 10: DISPERSION SYSTEM
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Dispersed Systems
Dispersed phase + Dispersion medium
Dispersed phase
Internal or Discontinuous phase
Dispersion medium
External or Continuous phase
Molecular dispersion
Colloidal dispersion
Coarse dispersion
Classification of Dispersed Systems based on Particle Size
< 1nm
Size of Molecular dispersion
1nm - 0.5mcm
Size of Colloidal dispersion
> 0.5mcm
Size of Coarse dispersion
Monophasic
State of Molecular dispersion
Biophasic
State of Colloidal dispersion
Biphasic
State of Coarse dispersion
Invisible in electron microscope
Visibility of Molecular dispersion
Visible in electron microscope
Visibility of Colloidal dispersion
Visible under microscope
Visibility of Coarse dispersion
Molecular dispersion
Pass through ultrafilter and semipermeable membrane
Colloidal dispersion
Pass through filter paper, but no semipermeable membrane
Coarse dispersion
Do not pass through filter paper or semipermeable membrane
Rapid
Diffusion of Molecular dispersion
Slow
Diffusion of Colloidal dispersion
No diffusion
Diffusion of Coarse dispersion
Glucose
Oxygen molecules
Ordinary ions
Example of Molecular dispersion
Colloidal silver solution
Paint
Shaving cream
Example of Colloidal dispersion
Most pharmaceutical emulsions and suspensions
Grains of sand
Red blood cells
Example of Coarse dispersion
Lyophilic colloids
Lyophobic colloids
Association colloids
Types of Colloidal System
Lyophilic colloids
Solvent loving colloids
Thermodynamically stable
Dispersion medium
Water: hydrophilic colloids
Organic molecules
Most lyophilic colloids are ________molecules
Dispersion of Starch
Gum
Protein in water
Example of Lyophilic colloids
Lyophobic colloids
Solvent fearing colloids
Thermodynamically unstable
Dispersion medium
Water: Hydrophobic colloids
Consist of Inorganic particles dispersed in water
Dispersion of gold
Sulfur
Silver iodide in water
Example of Lyophobic colloids
Amphiphilic colloids
Association colloids are also known as?
Association colloids
Formed by the association (self-assemble or associate) of dissolved molecules (surfactants) of a substance to create particles of colloidal dimensions (most commonly termed Micelles)
Critical Micelle Concentration
The concentration of monomer at which micelles form
Aggreation number
The number of monomers that aggregate to form a micelle
Zsigmondy Gold number
Expression of the protective property of colloids
Solid
Liquid
Gas
What are the dispersion phases if the dispersion medium is Solid?
Solidsol
Colloid type if the dispersion medium and dispersion phase is Solid
Pearls
Opal
Example of Solidsol
Solid emulsion
Colloid type if the dispersion medium is Solid and the dispersion phase is Liquid
Cheese
Butter
Example of Solid emulsion
Solid foam
Colloid type if the dispersion medium is Solid and the dispersion phase is Gas
Pumice
Marshmallow
Example of Solid foam
Solid
Liquid
Gas
What are the dispersion phases if the dispersion medium is Liquid?
Sol, Gel
Colloid type if the dispersion medium is Liquid and the dispersion phase is Solid
Jelly
Paint
Example of Sol, Gel
Emulsion
Colloid type if the dispersion medium is Liquid and the dispersion phase is Liquid
Milk
Mayonnaise
Example of Emulsion
Foam
Colloid type if the dispersion medium is Liquid and the dispersion phase is Gas
Whipped cream
Shaving cream
Example of Foam
Solid
Liquid
What are the dispersion phases if the dispersion medium is Gas?
Solid aerosols
Colloid type if the dispersion medium is Gas and the dispersion phase is Solid
Smoke
Dust
Example of Solid aerosols
Liquid aerosols
Colloid type if the dispersion medium is Gas and the dispersion phase is Liquid
Clouds
Mist
Fog
Example of Liquid aerosols
Optical
Kinetic properties
Electrical properties
Properties of Colloids
Optical
Property of Colloids that is useful in obtaining information regarding:
Shape
Size
Structure
Molecular weight of colloids
Tyndall effect
When a beam is passed through a colloidal solution, some of the light may be scattered
Particle size
Shape
Interaction of colloidal materials
Light scattering measurements are used in estimating
Light scattering
Identify the property which is used to determine the molecular weight of colloids
a. Electric properties
b. Fluidity
c. Light scattering
d. Brownian movement
Brownian motion
Diffusion
Sedimentation
Viscosity
Kinetic properties
Brownian motion
Random movement of colloidal particles
Irregular, zigzag pattern movement
Particle size = ↑ particle size = ↓ velocity
Viscosity = ↑ viscosity = ↓ Brownian movement
Factors affecting Brownian motion
Diffusion
Direct result of Brownian movement
Can be expressed by Fick’s law
↓ Particle size = ↑ diffusion
↑ Temperature = ↑ diffusion
↓ Viscosity = ↑ diffusion
Factors affecting Diffusion
Sedimenation
Follows Stoke’s law
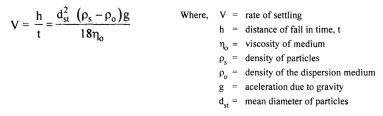
Viscosity
Resistance to flow of a system under applied stress
Shape of the dispersed phase
Spherocolloids - ↓ viscosity
Linear particles - ↑ viscosity
Size of particles
Molecular weight
Affinity of particles to the dispersion medium
Factors affecting Viscosity
Electrical properties
The presence and magnitude, or absence, of a charge on a colloidal particle is an important factor in the stability of colloidal systems
Zeta potential
Nerns’t potential
Electrical properties
Electrokinetic potential
Zeta potential is also known as?
Zeta potential
The difference in potential between the surface of the tightly bound layer (shear plane) and the electroneutral region of the solution
Electrothermodynamic potential
Nerns’t potential is also known as?
Nerns’t potential
Difference in potential between the actual surface and the electroneutral region of the solution
Electrophoresis
Electro-osmosis
Sedimentation potential
Streaming potential
Electrokinetic phenomena
Cataphoresis
Electrophoresis is also known as?
Electrophoresis
The movement of a charged particles through a liquid under the influence of an applied potential difference
Electro-osmosis
The movement of the dispersion medium under the influence of applied potential
Sedimentation potential
Opposite of electrophoresis
Creation of potential when particles undergo sedimentation
Streaming potential
Creation of potential by forcing a liquid to flow through a plug or bed of particles
Colloidal Copper
Colloidal preparation that is used as Cancer treatment
Colloidal Mercury
Colloidal preparation that is used as Syphilis treatment
Colloidal Gold
Colloidal preparation that is used as diagnostic agent for Paresis
Colloidal electrolytes
Colloid that increases solubility, stability and taste of certain compounds in aqueous and oily pharmaceutical preparations
Colloidal Sulfur
Colloidal preparation that is absorbed completely compared to coarsely powdered Sulfur
Sedimentation
This is used to determine the molecular weight of polymers
a. Viscosity
b. Sedimentation
c. Electric properties
d. Brownian movement
True
The velocity of the particles increases with decreasing particle size and increasing the viscosity of the dispersion medium decreases and finally stop the Brownian motion
a. True
b. False
Electric properties
The presence and magnitude, or absence of this on a colloidal particle is an important factor in determining the stability of colloids
a. Light scattering
b. Sedimentation
c. Electric properties
d. Brownian movement