Lecture 13: SC Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the function of the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus?
The Circadian rhythm
Recieve input from ipRGC [intrinsically photosensitive RGC]
What is the Circadian rhythm?
24 hr fluctations of biological processes
What is a topographic map in the superior coliculus?
Axons from RGCs in both eyes that are activated by the same object in the
visual field converge onto the same neurons in the SC
What is the layered structure in the SC?
Sensory neurons directly synapse onto motor neurons to control
movements, such as gaze and saccades.
What is in the Anterior (left & up) corner
Superficial layers
What is in the posterior (right & down) corner?
Visual,
Auditory,
Somatosensory input
Motor output
What is in the anterior / posterior (left & down) corner?
Intermediate & deep layers
What is in the posterior / anterior ( right & up) corner?
visual input
What is the purpose of the cortical visual subsytems?
They are required to consciously perceive objects
How do the the Cortical Visual Subsystems move information?
Retina — LGN [Lateral Geniculate Nucleus] — [Visual Cortex]
V1-V2-V3, V4,, V5
How does Blindsight work in moving information?
DOES NOT GO TO [ LGN or visual cortex]
Retina to SC (superior colliculus). Can track/avoid objects subconsciously
Retina to SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus) circadian rhythm intact
Where does Blindsight signals from the retina NOT go?
Lateral Geniculate nucleus LGN —v1-v2-v3,v4,v5
The Receptive Field size in the Peripheral & RGC type?
Convergence of Synaptic Input
Large Receptive Field
M (Magno)-type
The Receptive Field size in the Central & RGC type?
No or Less Convergence of Synaptic Input
Small Receptive Field
P (Parvo)-type
What are v3 and v4 used for?
Movement
What is V4 used for?
Color
What is the Inferotemporal Cortex (IT) used for?
Complex Objects
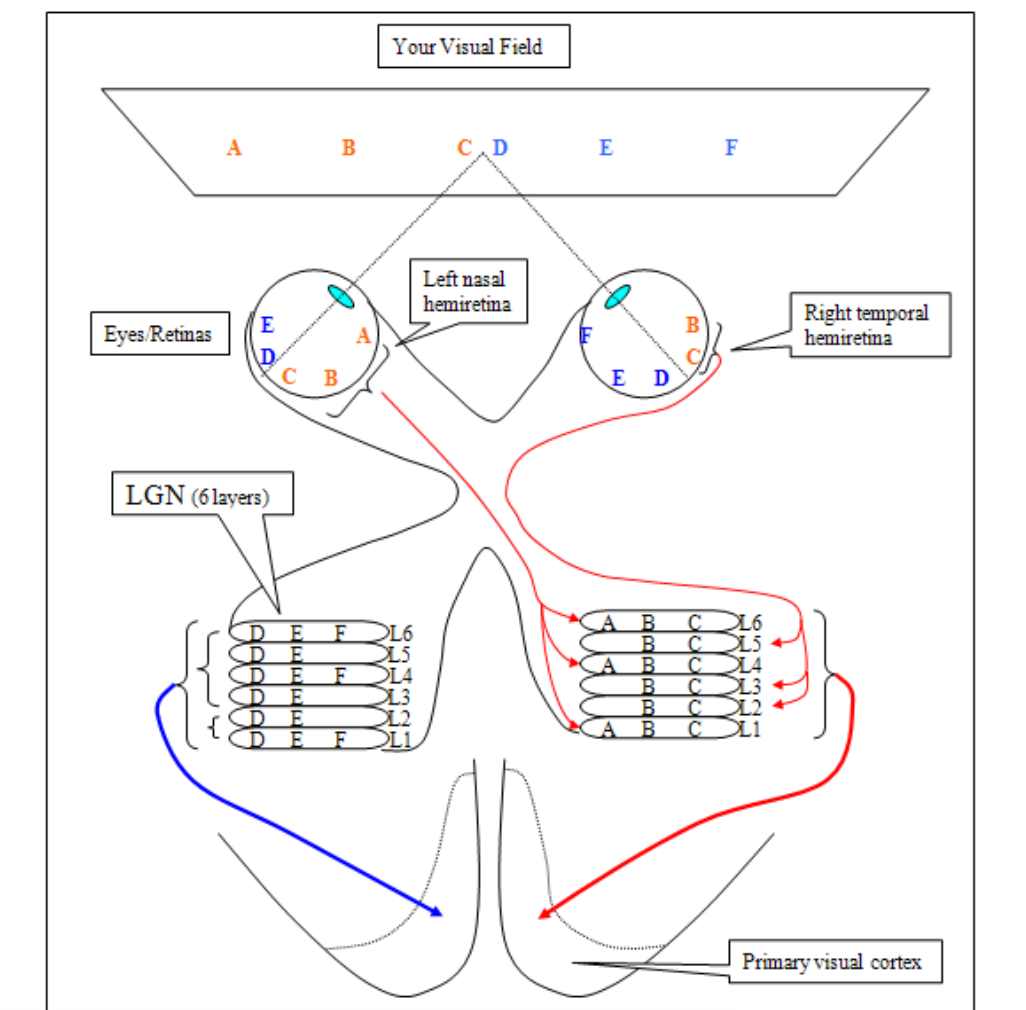
How many layers make up the LGN?
6
What do layers 1 and 2 contain?
Magnocellular
Larger cells
What do layers 3 to 6 contain?
Parvocellular
smaller cells
What does each layer receive input from?
One Eye
The Retinal Inputs to LGN Layers
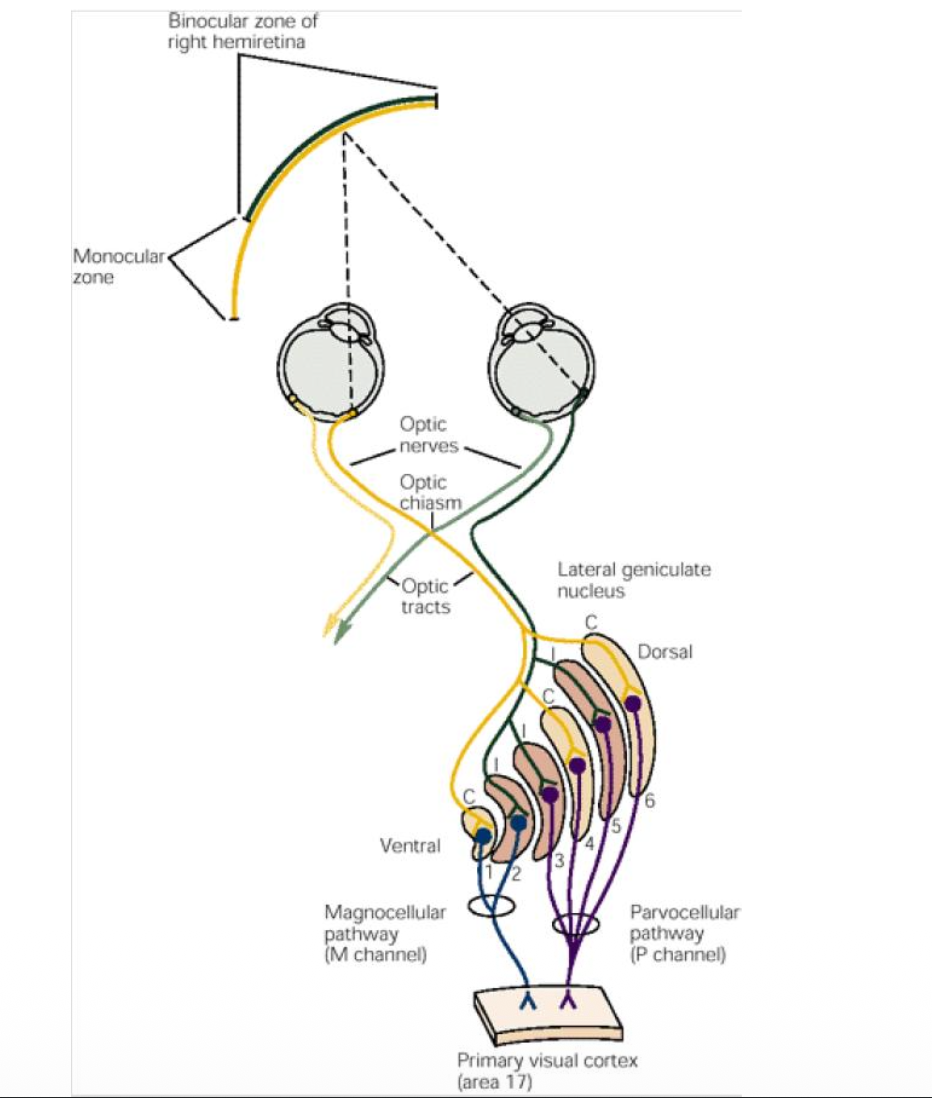
More descriptive Retinal Inputs to LGN layers