Cardiac muscle
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
heart
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
how is cardiac like the skeletal?
Ca2+ → troponin → more tropomyosin → so myosin binds → actin
how is cardiac muscle like fatty acids
oxidative metabolism
many mitochondria
describe heart myosin
cardiac myosin
10 times slower than skeletal
how is the heart self-starting
pacemaker
does the heart have recruitment, tetany, or fatigue
no, it is pacemaker
what kind of channels does the heart have
gap junctions
prevent recruitment
what is technically the pacemaker
sino-atrial (SA) node

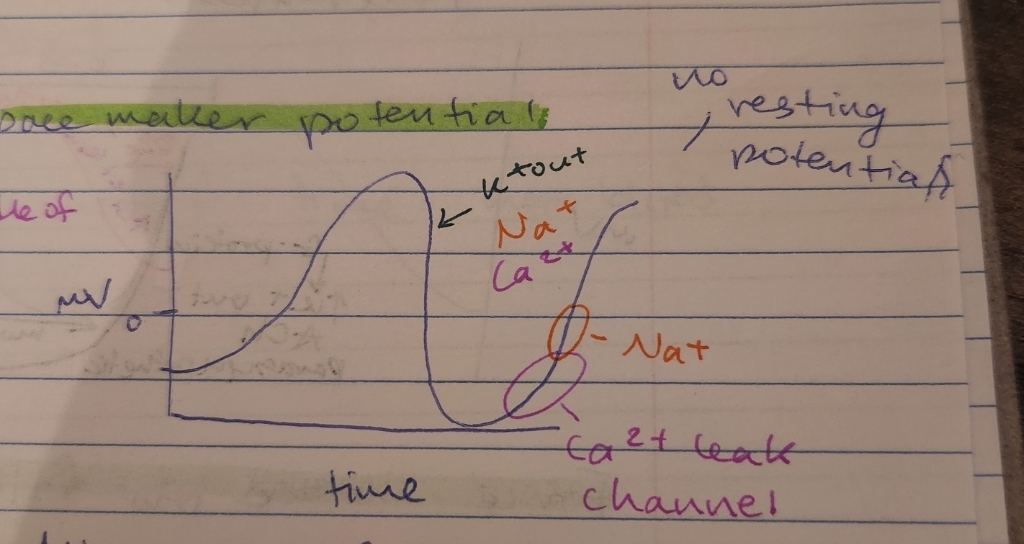
describe the pacemaker potential
(graph)
all or none, every cell is excited to contract every time
graph goes down, K+ out
graph goes up, Ca2+ (leak) and Na+ go in
no resting potential
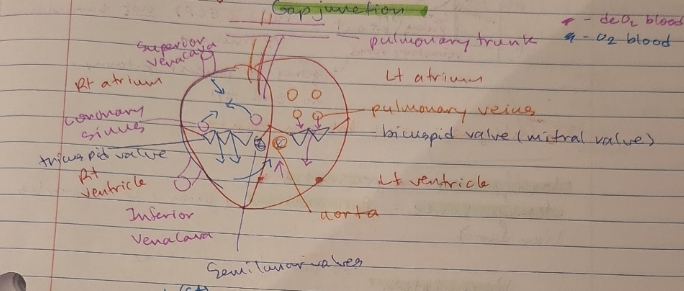
what are the steps of the pacemaker, heart conduction system
SA node (pacemaker potential) → atrial muscle → AV node → bundle of His → Bundle of branches → Purkinjie fibers → ventricle muscle
cardiac muscle cell potential
(graph)
Na+ goes into cell
Ca2+ goes into cell
Ca2+ for contraction, comes from extra cellular fluid (ECF) not sarcoplasmic recticulum
K+ goes out, Ca2+ plateau = refractory period
prevent tetany, no 2nd AP

where does the Ca2+ come from
the extra cellular fluid (NOT sarcoplasmic recticulum)
what does the refractory period prevent
tetany, no 2nd AP
does the heart fatigue
no it rests between beats
what changes the heart rate
the pacemaker
what changes the heart force
the fill volume (every cell works harder)
what is the pacemaker BPM
75 beats per min
0.8sec
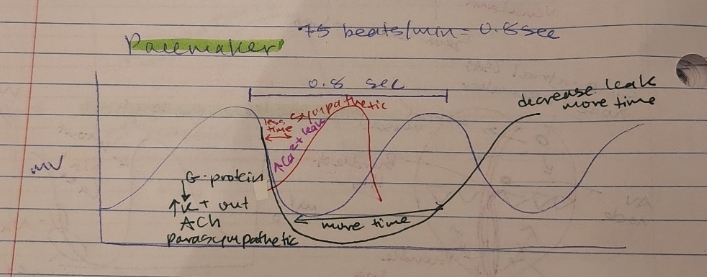
decrease leak equals
more time in between beats
G-protein down, more K+ out
AcH
parasympathetic
during sympathetic, the force vs time would
have more BPM
less time in between beats
lots ok Ca2+ leak
what is frank-starling law of the heart
at end diastalsis, volume increases, the force of heart beat increases

diastolic is
rest time of the heart
systolic is
contraction time of the heart
EDV is?
End Diastolic Volume
max fill of heart just before contraction (intrinsic mechanism)

when the volume goes up what happens to sarcomere
stretch increases
what happens when theres more blood to the heart
sympathetic
exercise
relax/slow down means more fill time, and more blood
“in vivo” means
beats 25-43 BPM, CN X (vagus nerve)
basal parasympathetic
pacemaker
“in vitro” means
45-60 BPM
pacemaker
in humans SA is about ~
100 BMP 70-80
basal sympathetic