Dysphagia final
1/344
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
345 Terms
What are the three branches of CN-V?
Ophthalmic nerve (V1), Maxillary nerve (V2), and Mandibular nerve (V3)
Cranial nerve V
trigeminal nerve
Cranial nerve VII
facial nerve
Cranial nerve IX
glossopharyngeal nerve
Cranial nerve X
vagus nerve
Cranial nerve XI
spinal accessory nerve
Cranial nerve XII
hypoglossal
Write down the three primary branches of the vagus nerve.
Pharyngeal Branch
Superior Laryngeal Nerve
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
What are the pharyngeal branch's sensory and motor innervation
Sensory: oropharynx, laryngopharynx
Motor: all palatal muscles except tensor veli palatini; all pharyngeal muscles except stylopharyngeus
What are the two branches of superior laryngeal nerve? Discuss the sensory and motor innervation of these two branches.
Internal branch: glottal and supraglottal sensation
External branch: cricothyroid (CT) muscle
Discuss the sensory and motor innervation of recurrent laryngeal nerve?
Sensory: subglottic sensation
Motor: all intrinsic laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid muscle
What is the primary function of muscles of mastication?
facilitates mandibular movement
The sensory and motor innervation of muscles of mastication is done by _____
CN-V
The motor innervation of lower facial muscles is done by ____
CN-VII
Which is the primary muscle to contract when you clench the jaw?
Masseter
Which is the primary muscle to contract to increase the buccal tension to hold the food while chewing and sucking?
Buccinator
True/False
There are 4 pairs of intrinsic muscles in the tongue.
True
If a person has damage in bilateral superior longitudinal muscles of tongue, the following will be impaired:
they can't pull the tongue tip upwards
The motor function of tongue is innervated by ____
CN-XII
The function of genioglossus muscle:
retracts the anterior tongue
depresses the entire tongue
protrudes the posterior tongue
**Protrude → push forward
** Retract → pull back
General sensation of tongue (anterior 2/3rds) is innervated by:
CN-V
Taste sensation of tongue (anterior 2/3rds) is innervated by:
CN-VII
General and taste sensation of tongue (posterior 1/3rds) is innervated by:
CN-IX
A person with facial nerve (CN-VII) damage will be seen with:
normal sensation of tongue but impaired taste sensation on anterior 2/3rds
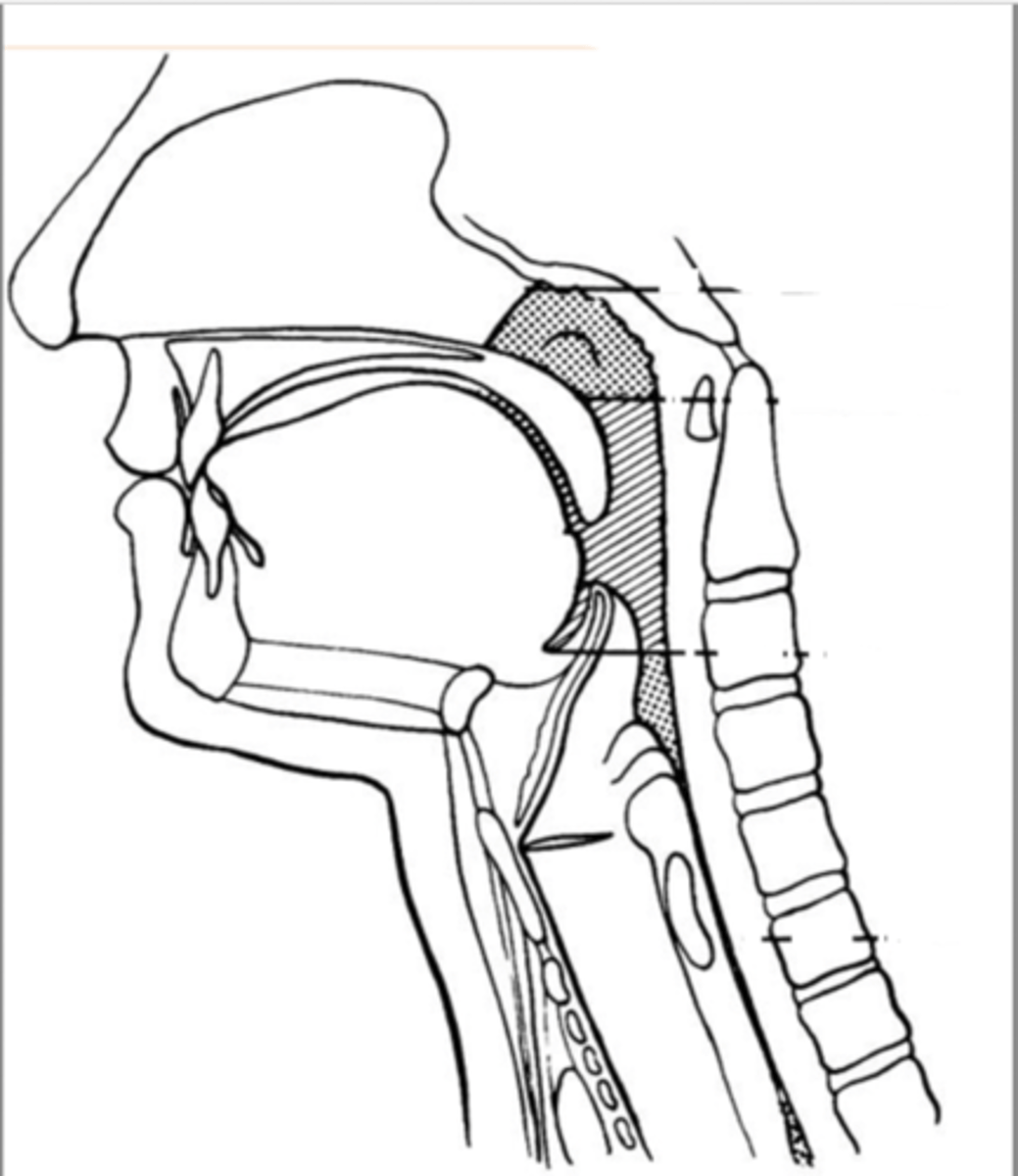
Label Nasopharynx (lateral view)
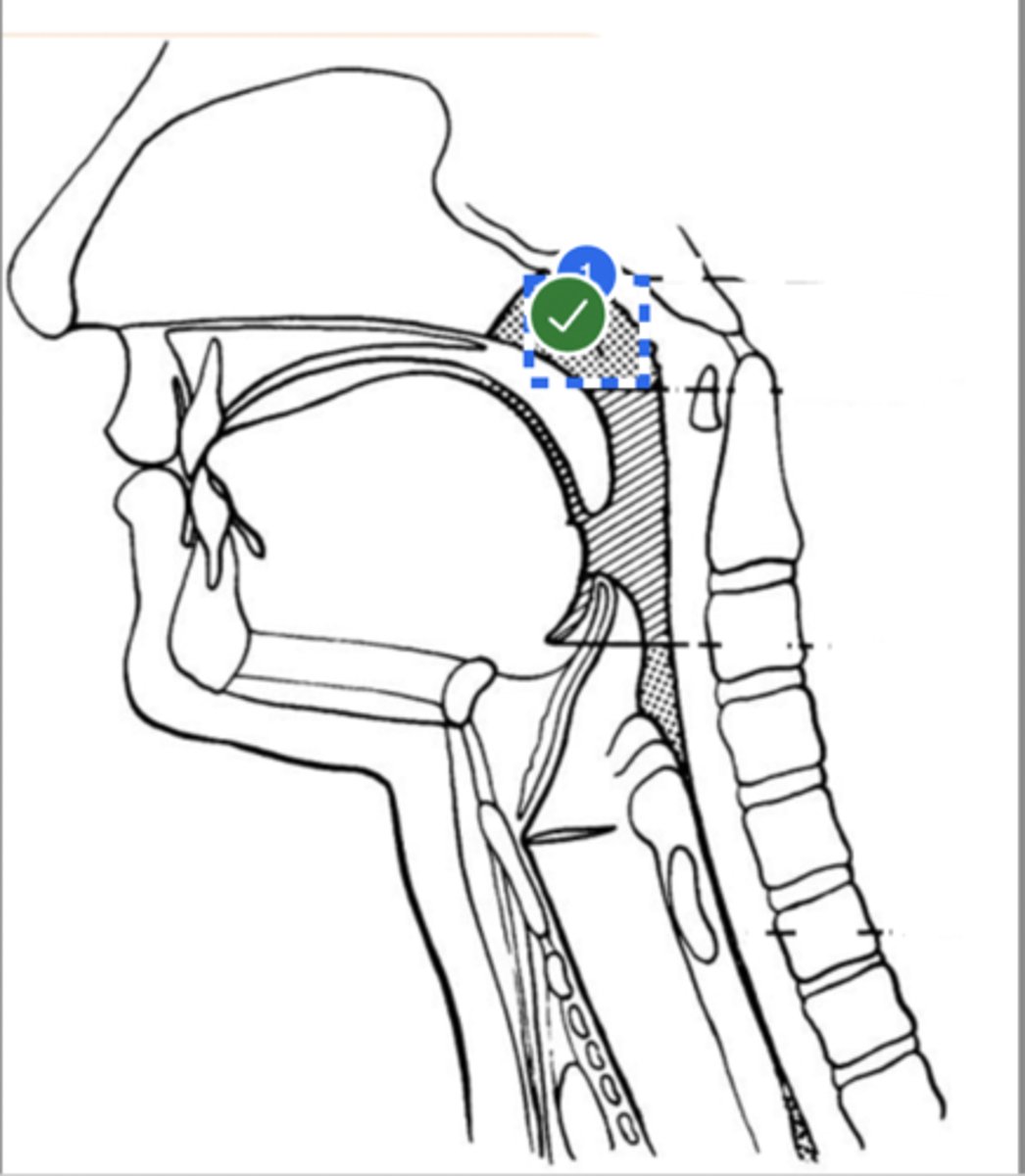
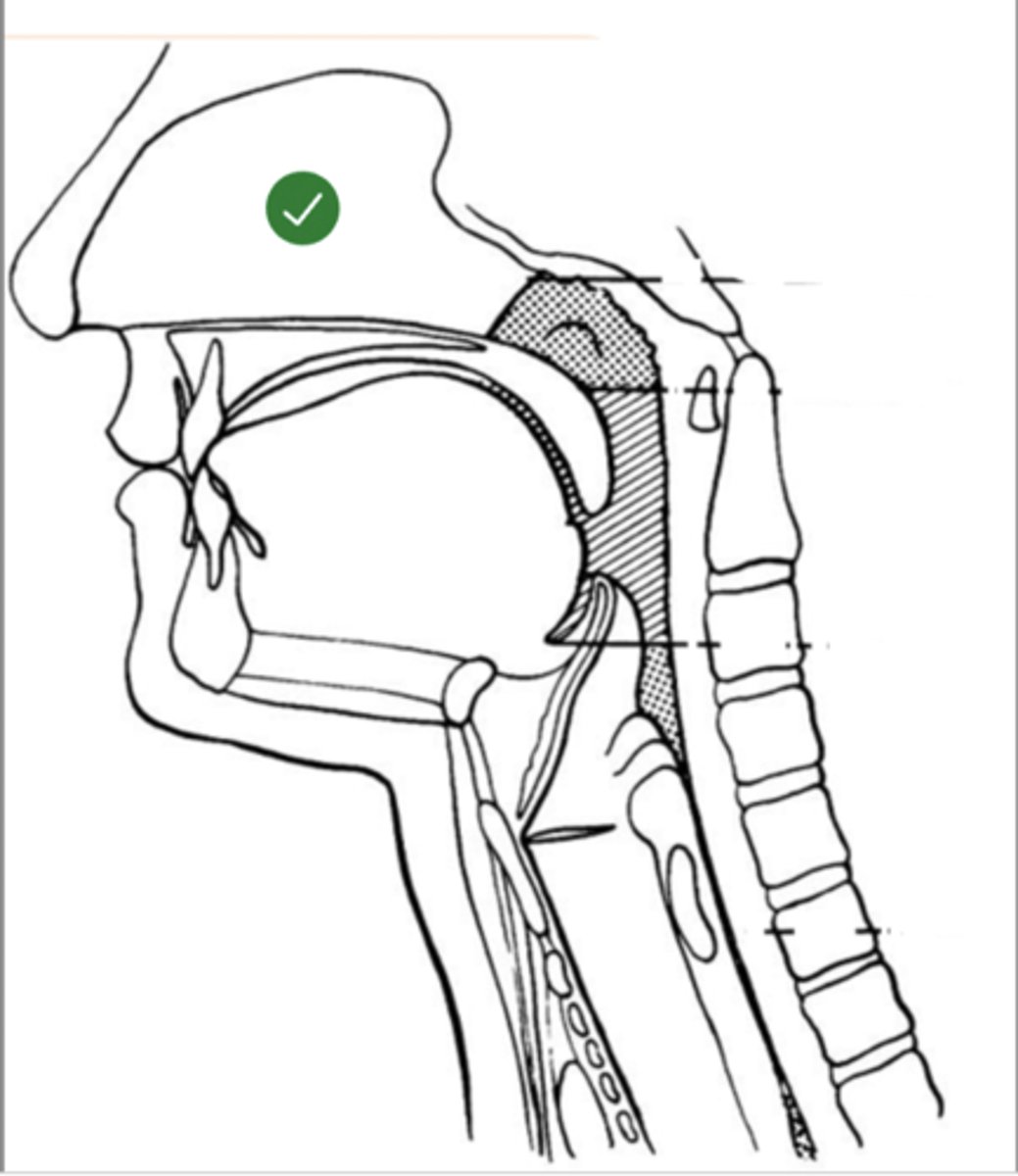
Label Nasal cavity (lateral view)
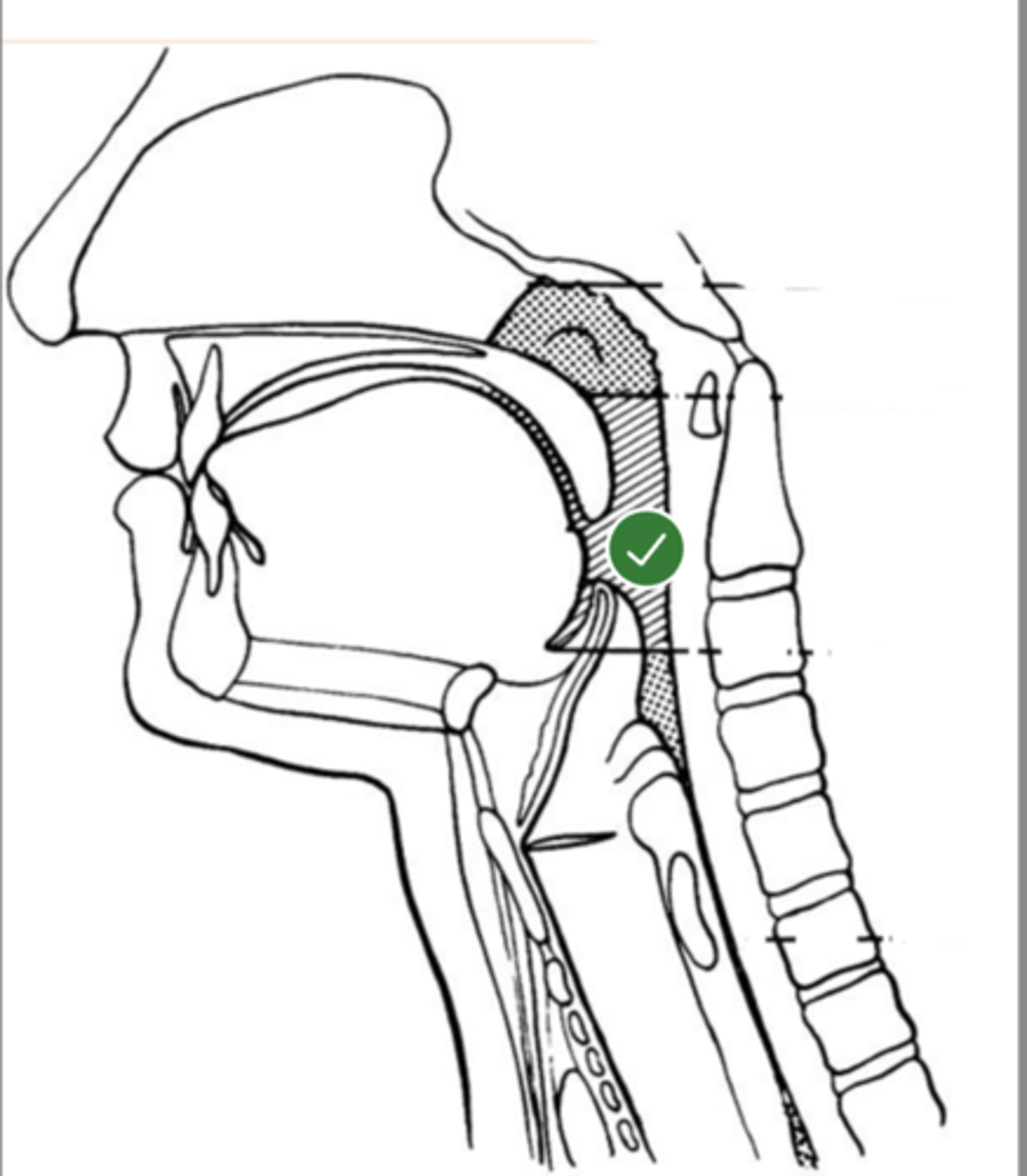
Label oropharynx (lateral view)
Label hypopharynx/ hylolarynx
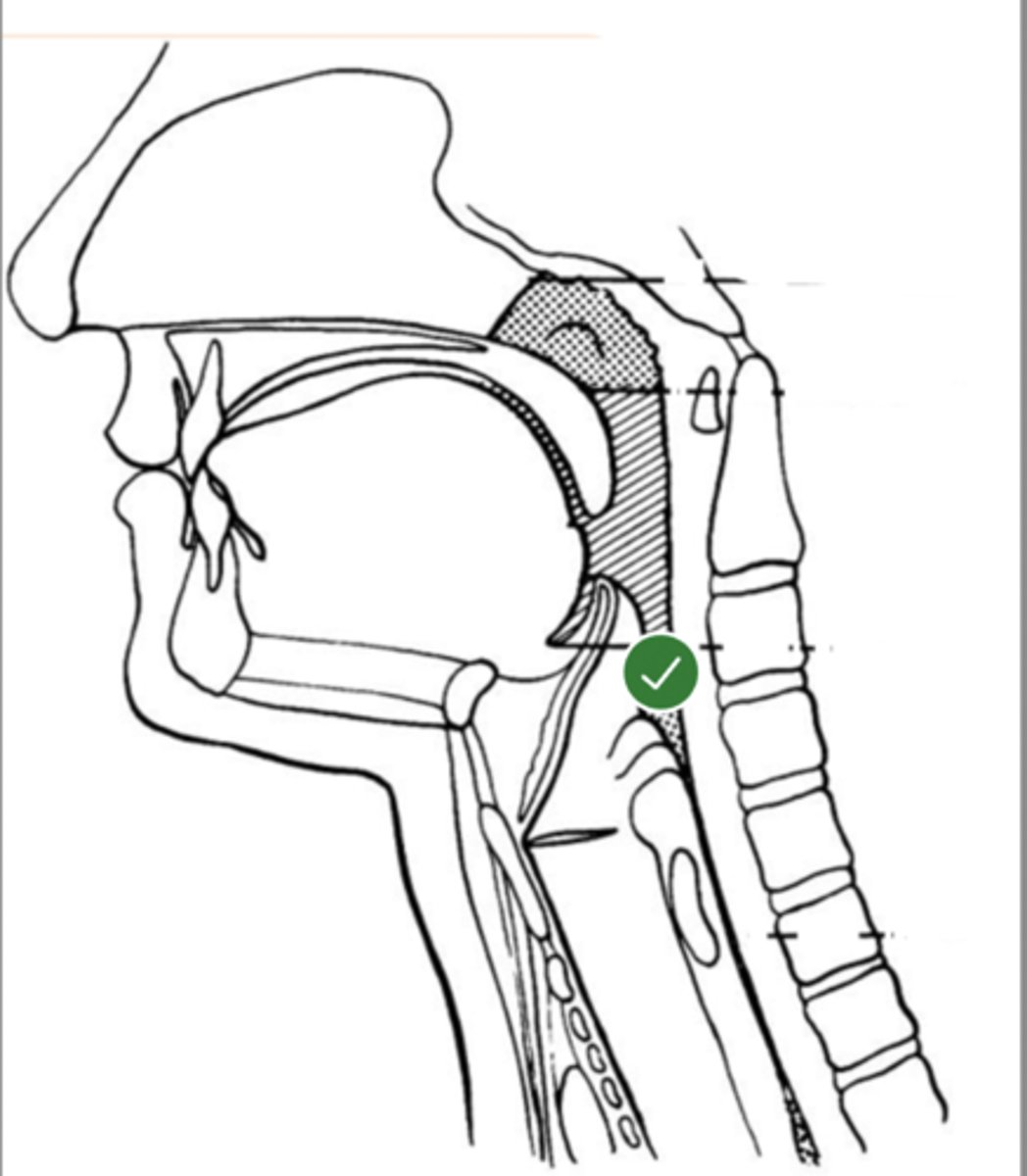
Label tongue (lateral view)
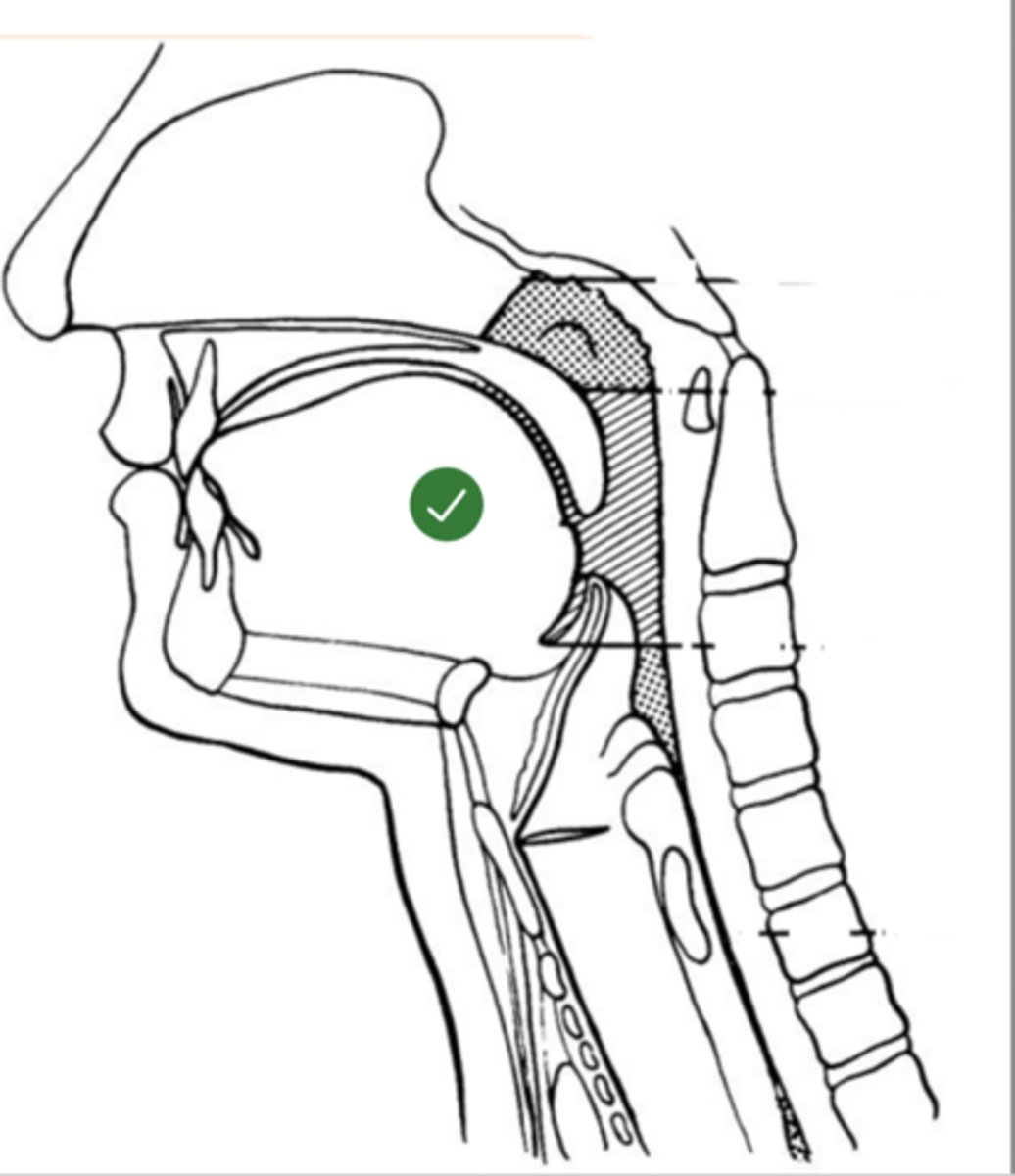
Label soft velum/ palate (lateral view)
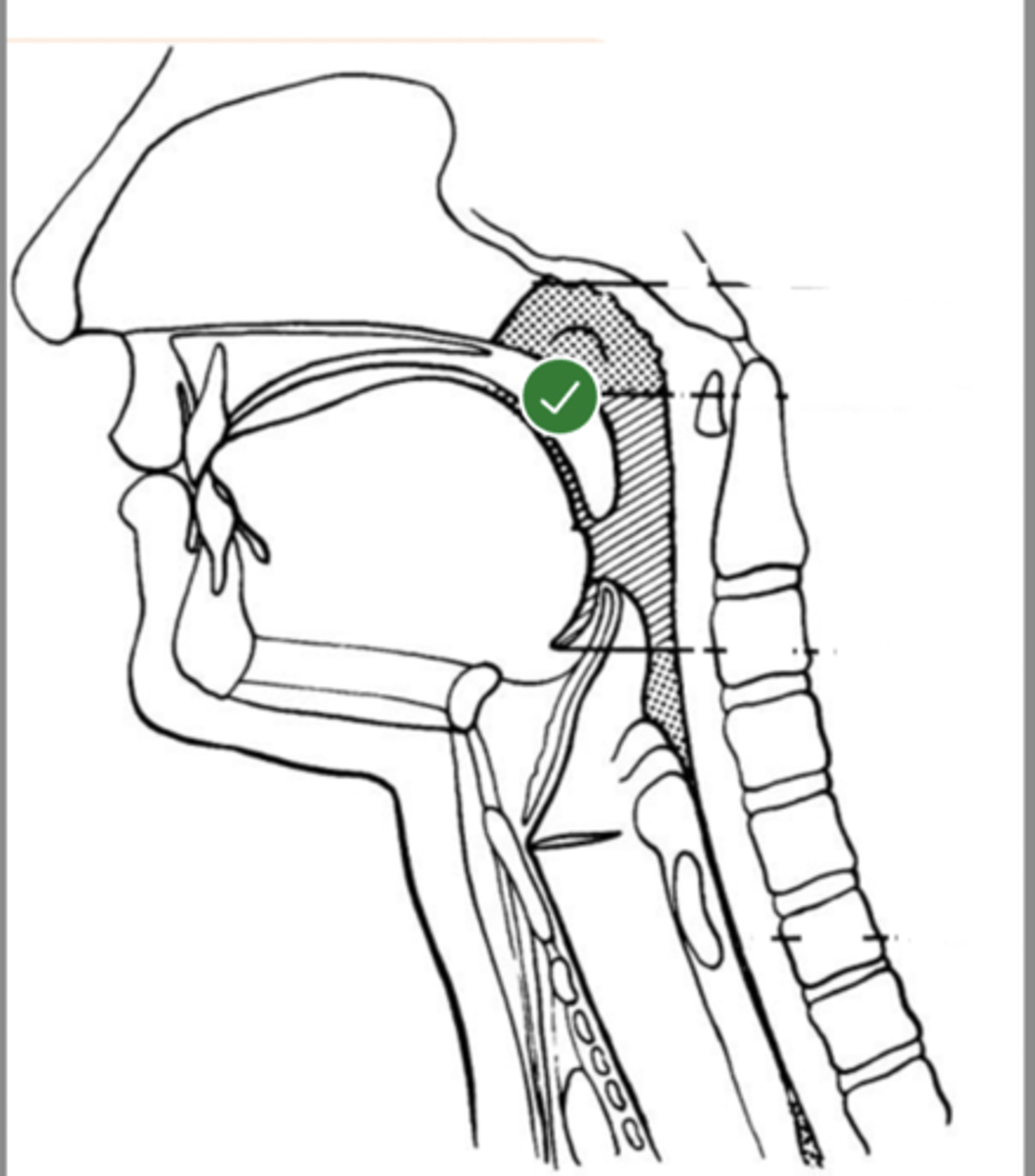
Label hard palate (lateral view)
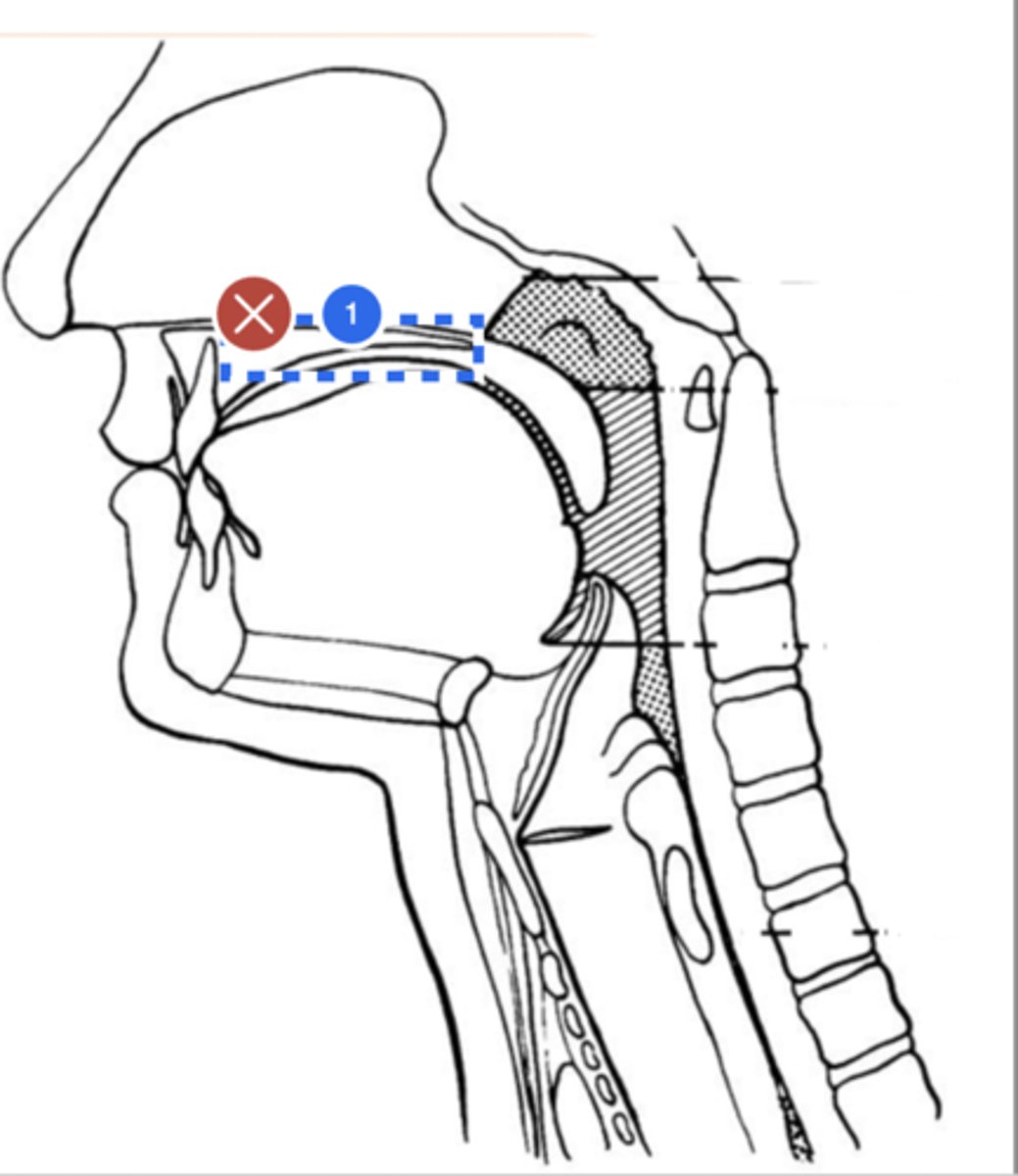
Label mandible (lateral view)

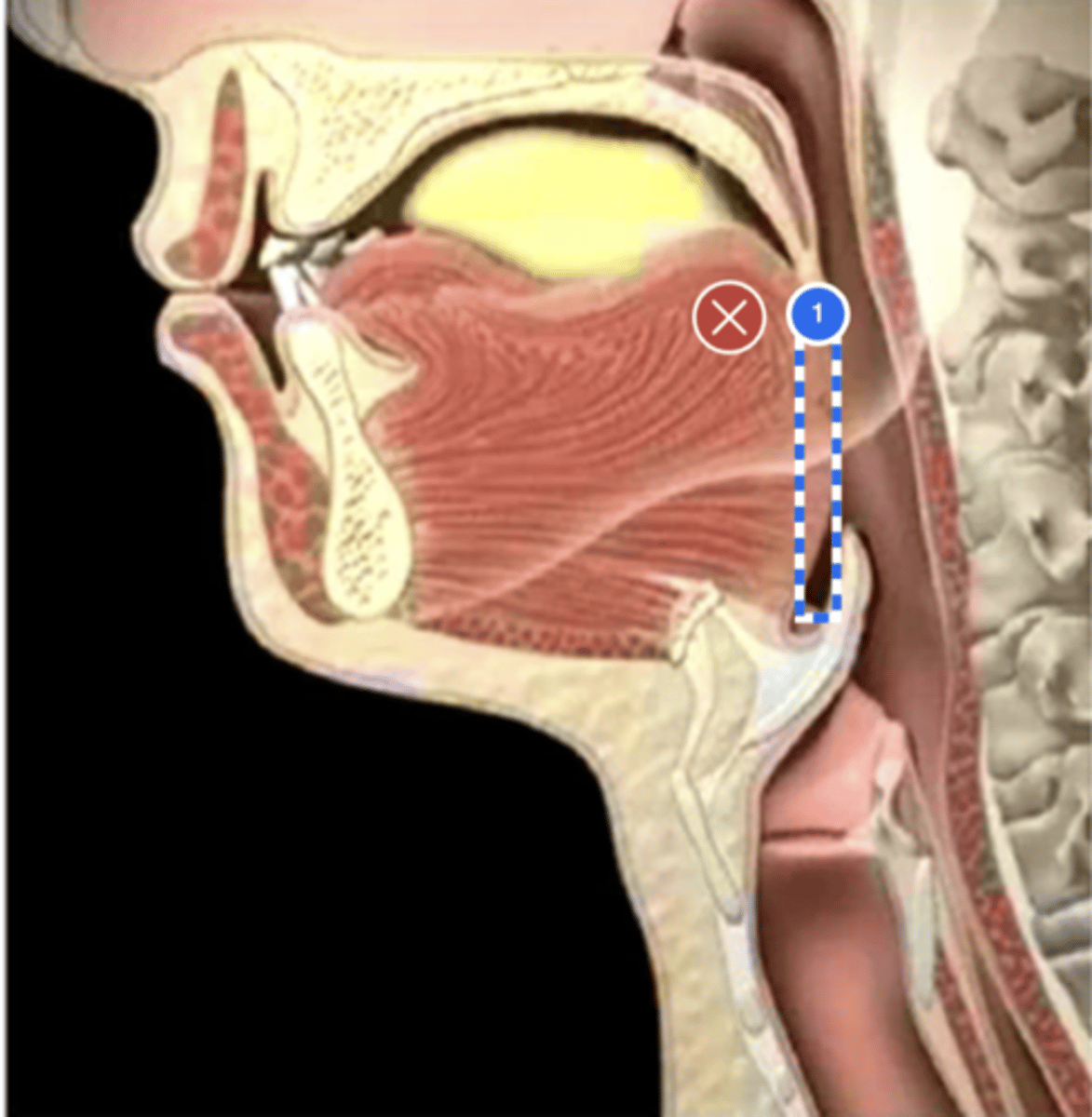
Label base of tongue (lateral view)
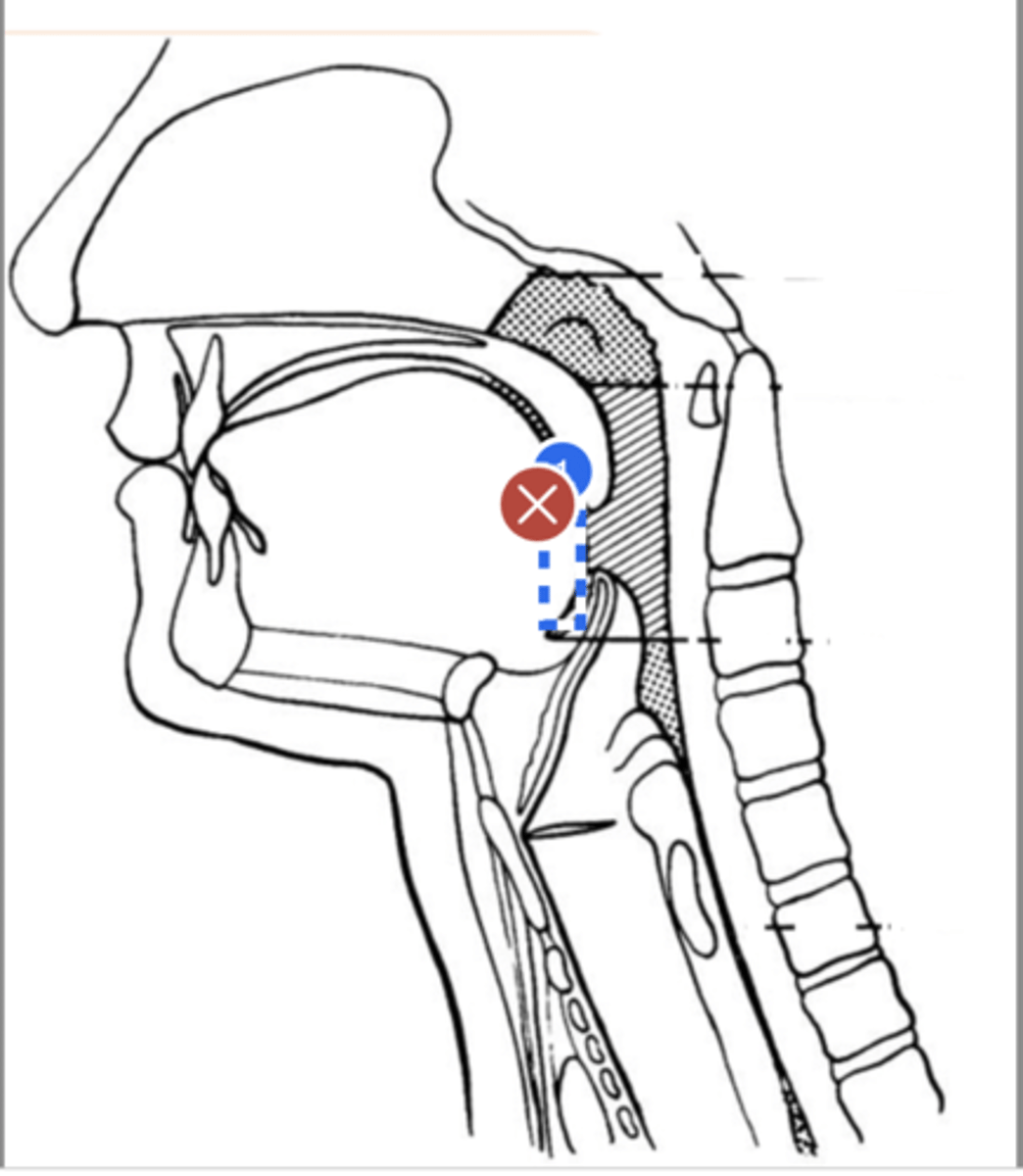
label hyoid bone (lateral view)
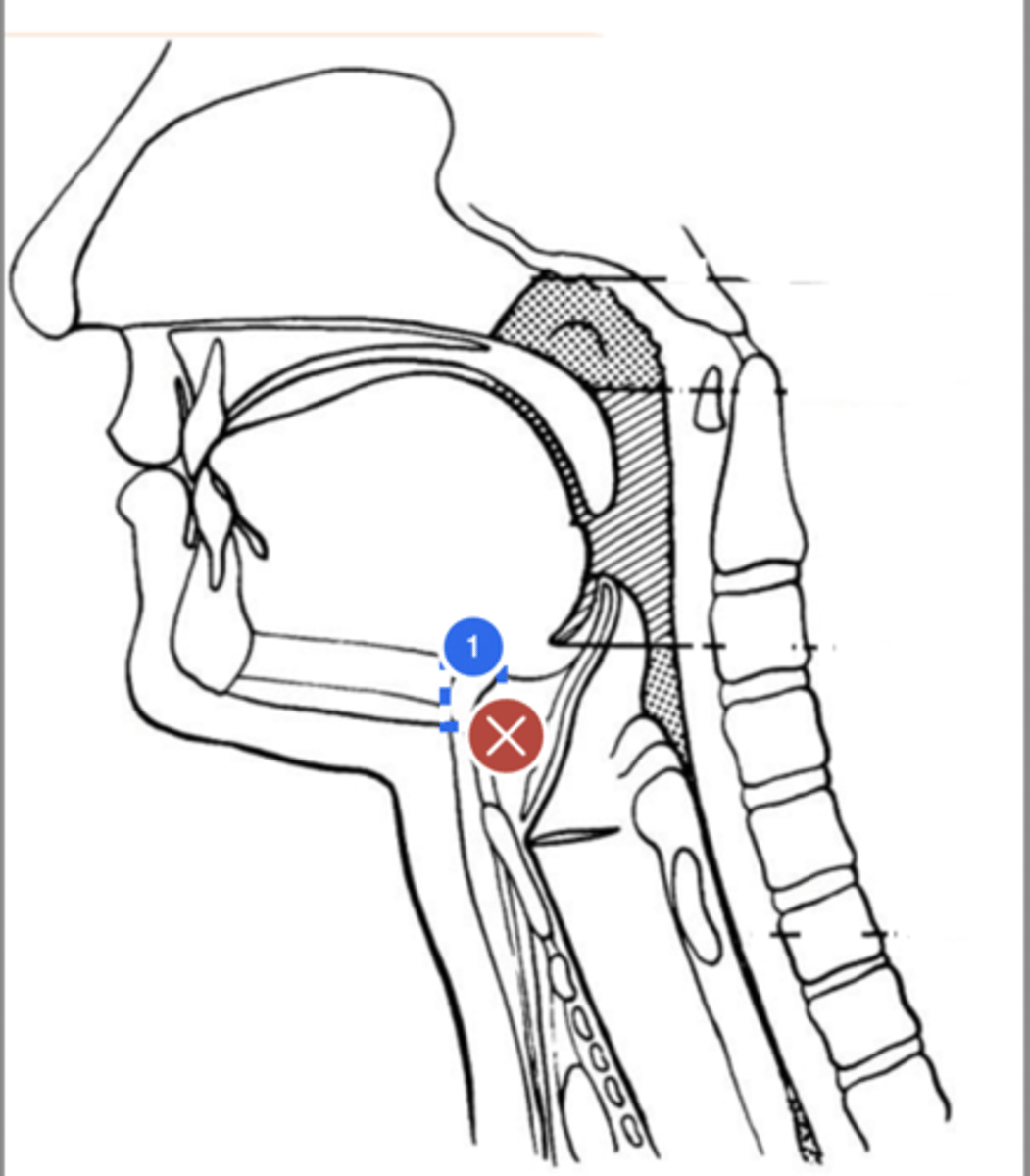
Label epiglottis (lateral view)

label Line of true vocal folds (lateral view)
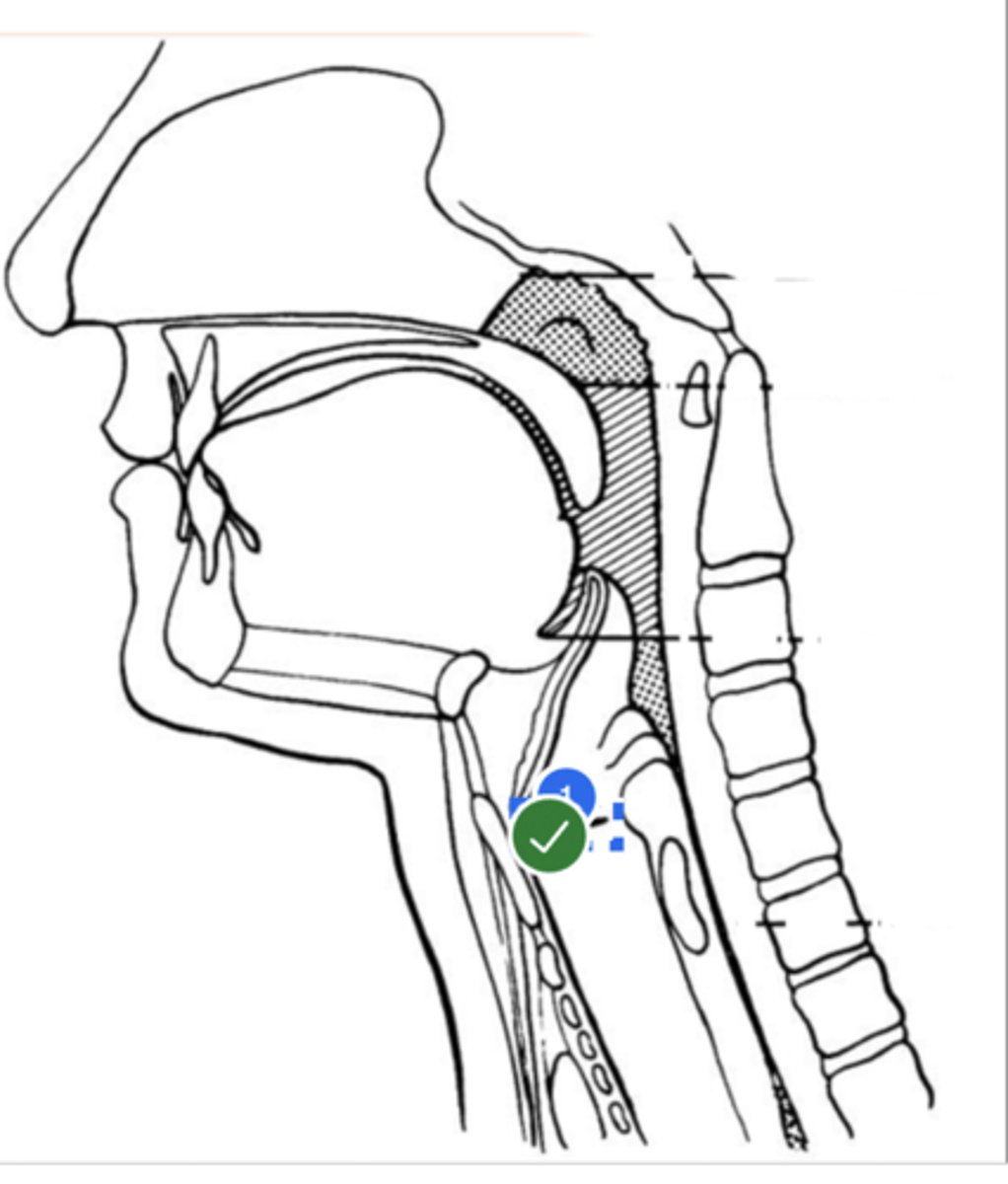
label Thyroid cartilage (anteriorly) (lateral view)
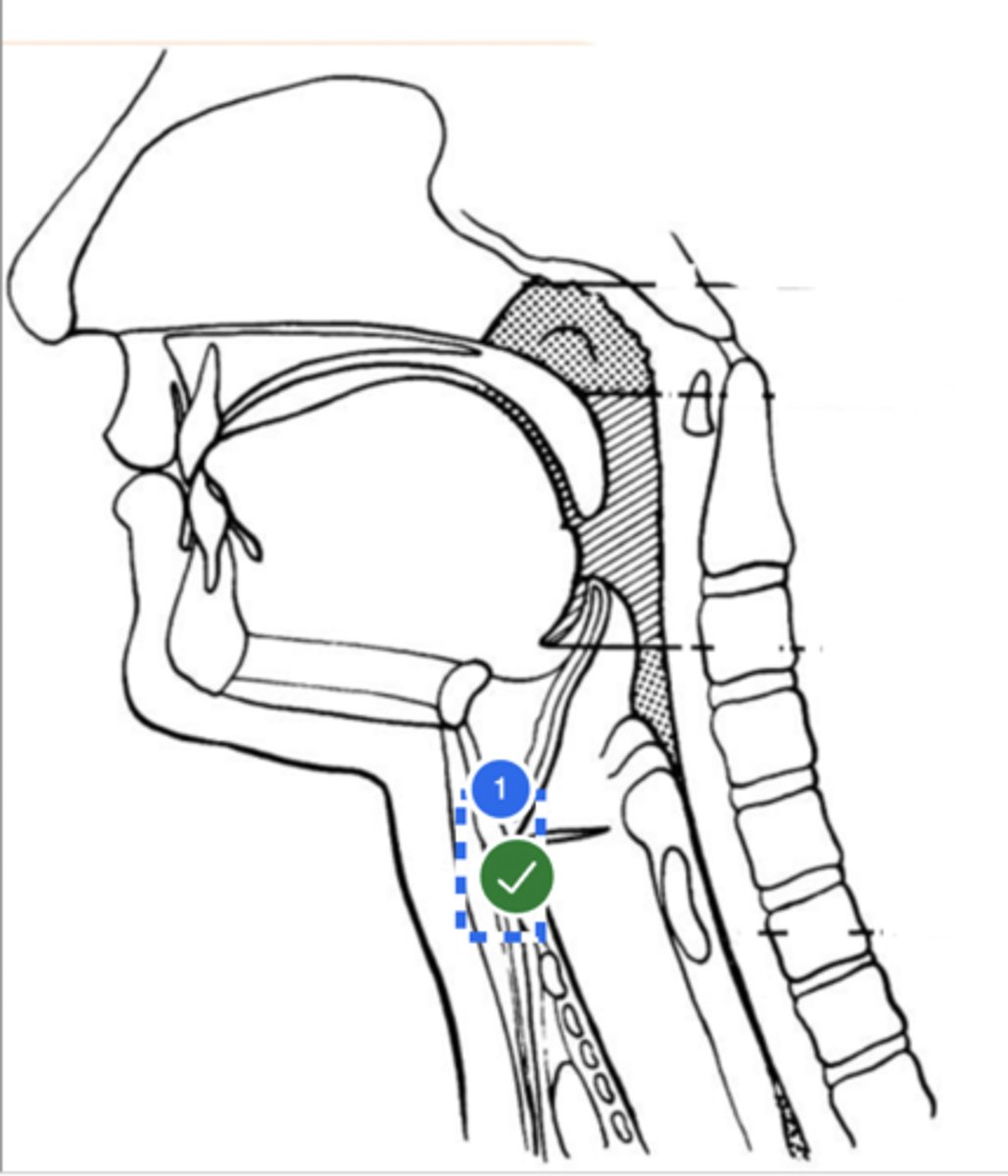
Label posterior cricoid (lateral view)
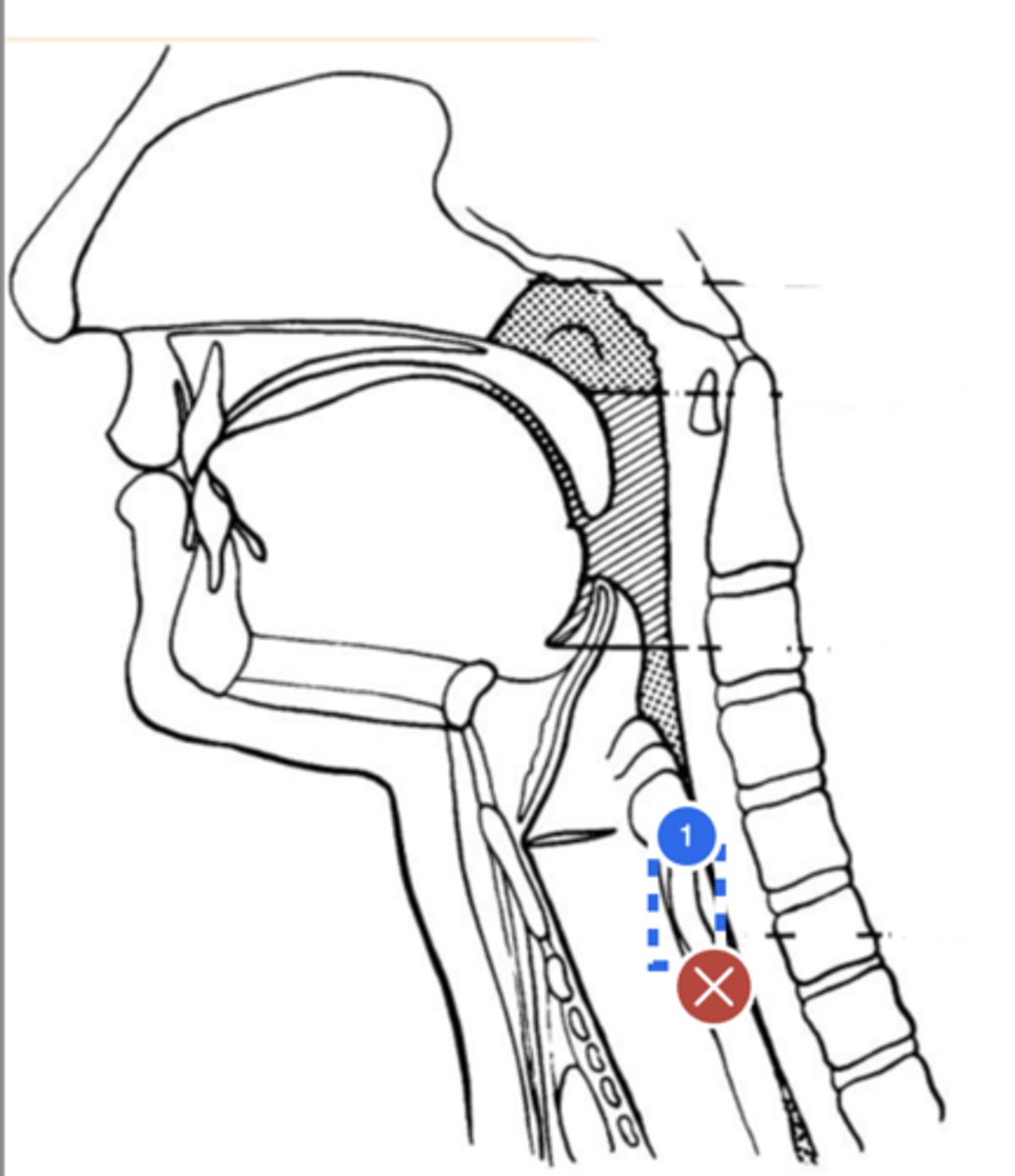
Label esophagus (lateral view)

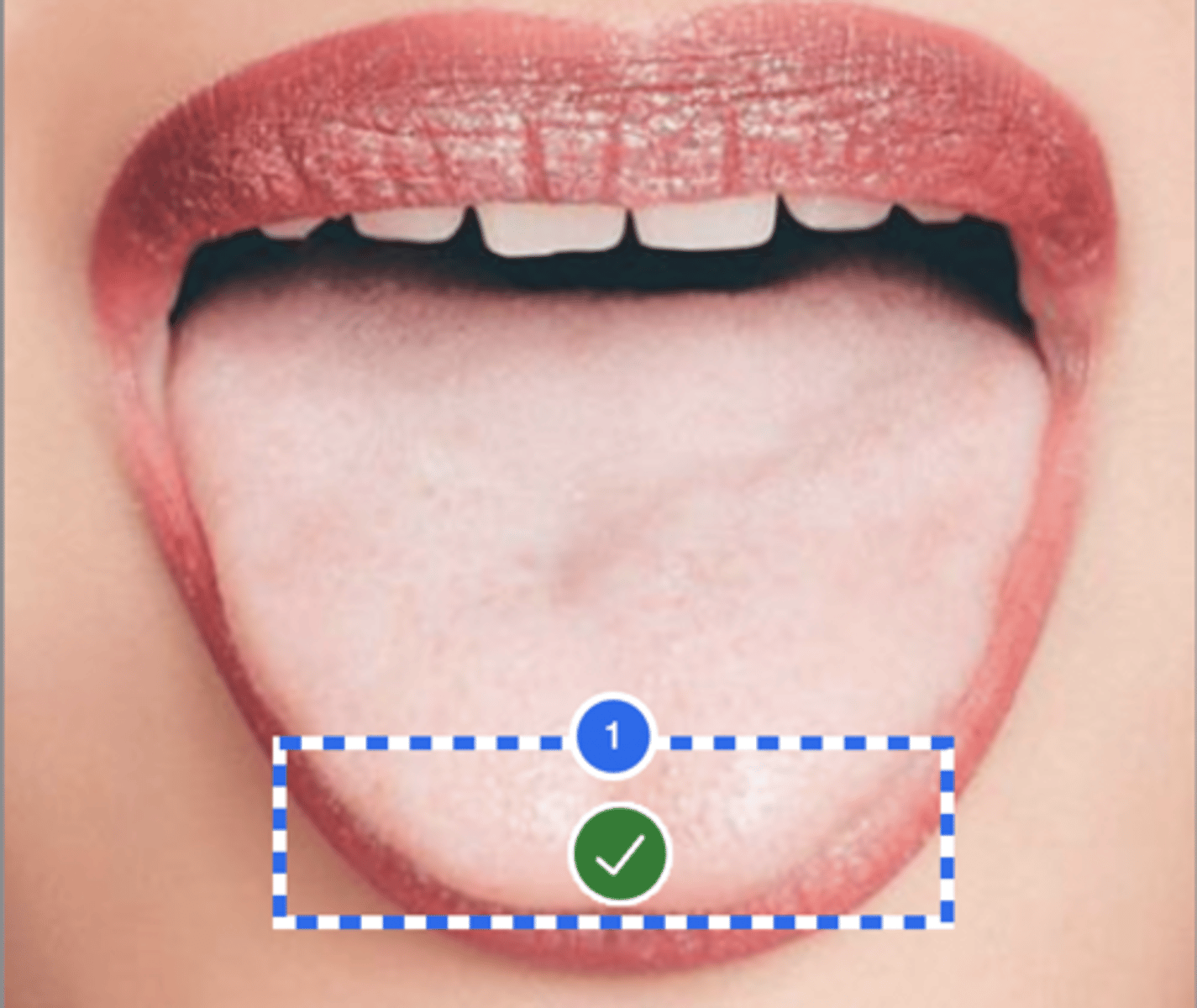
Label tongue tip (anterior view)
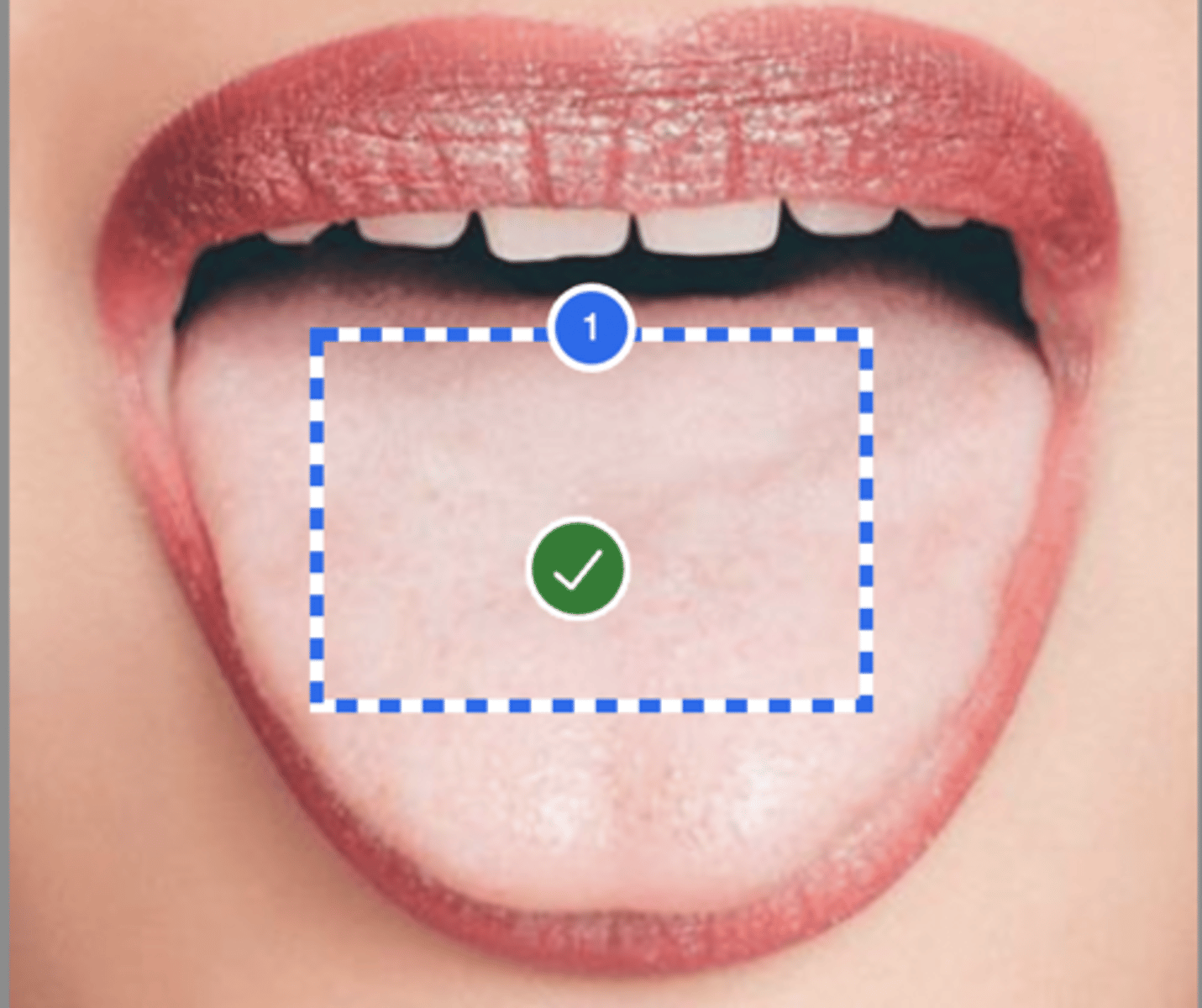
Label tongue blade (Anterior view)
Label floor of mouth
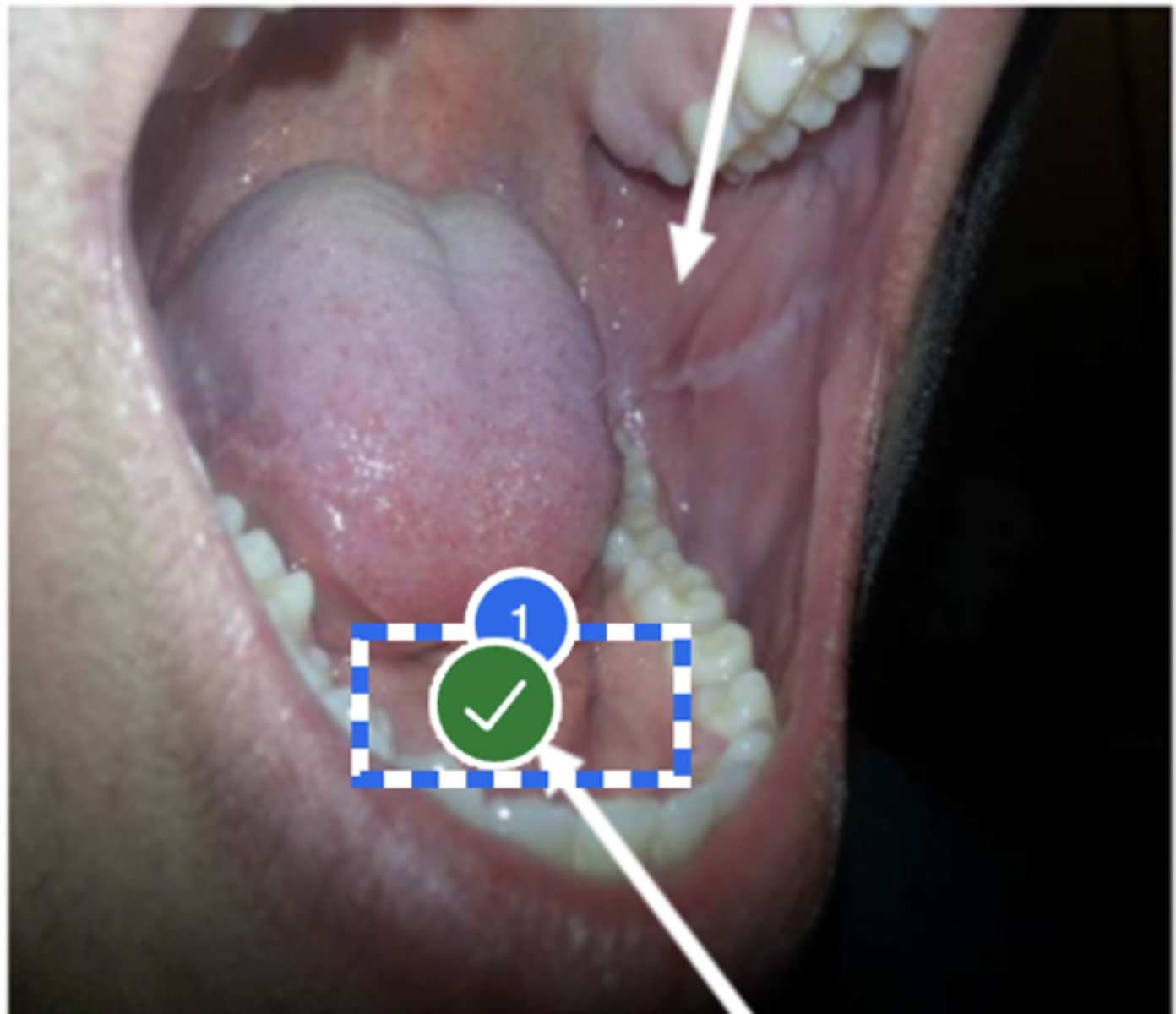
Label buccal cavity
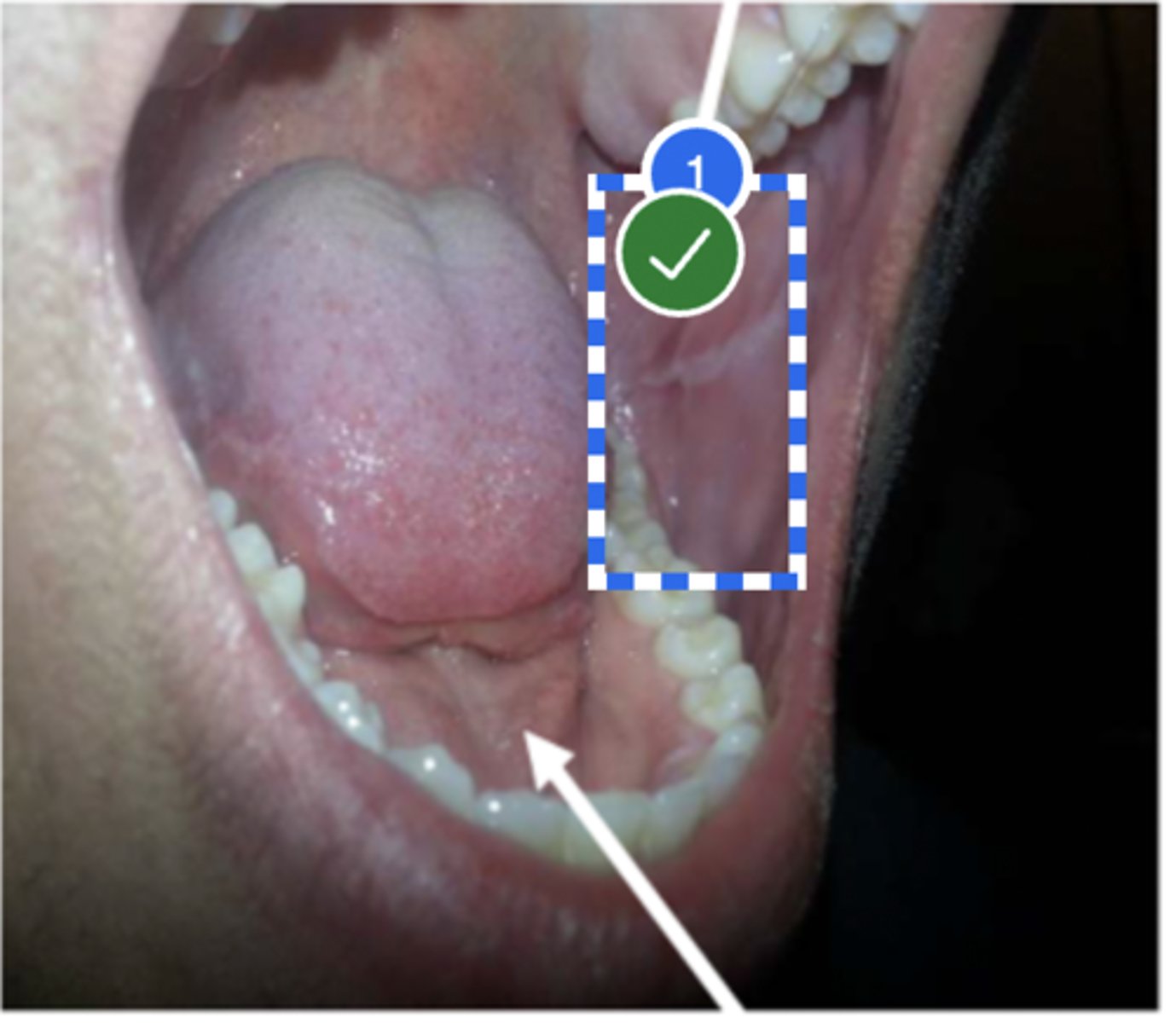
Label base of tongue (lateral view)
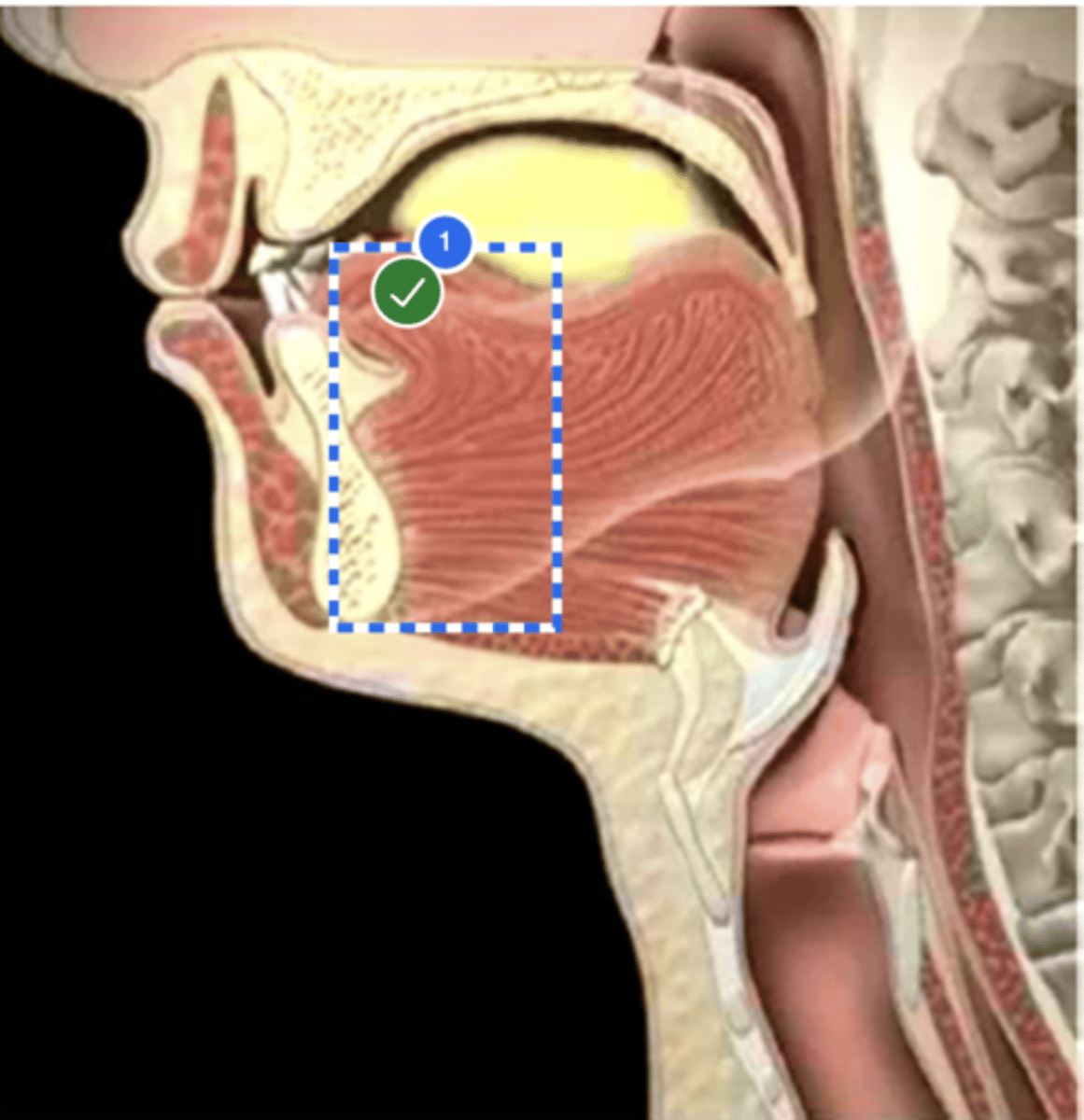
label anterior tongue (lateral view)
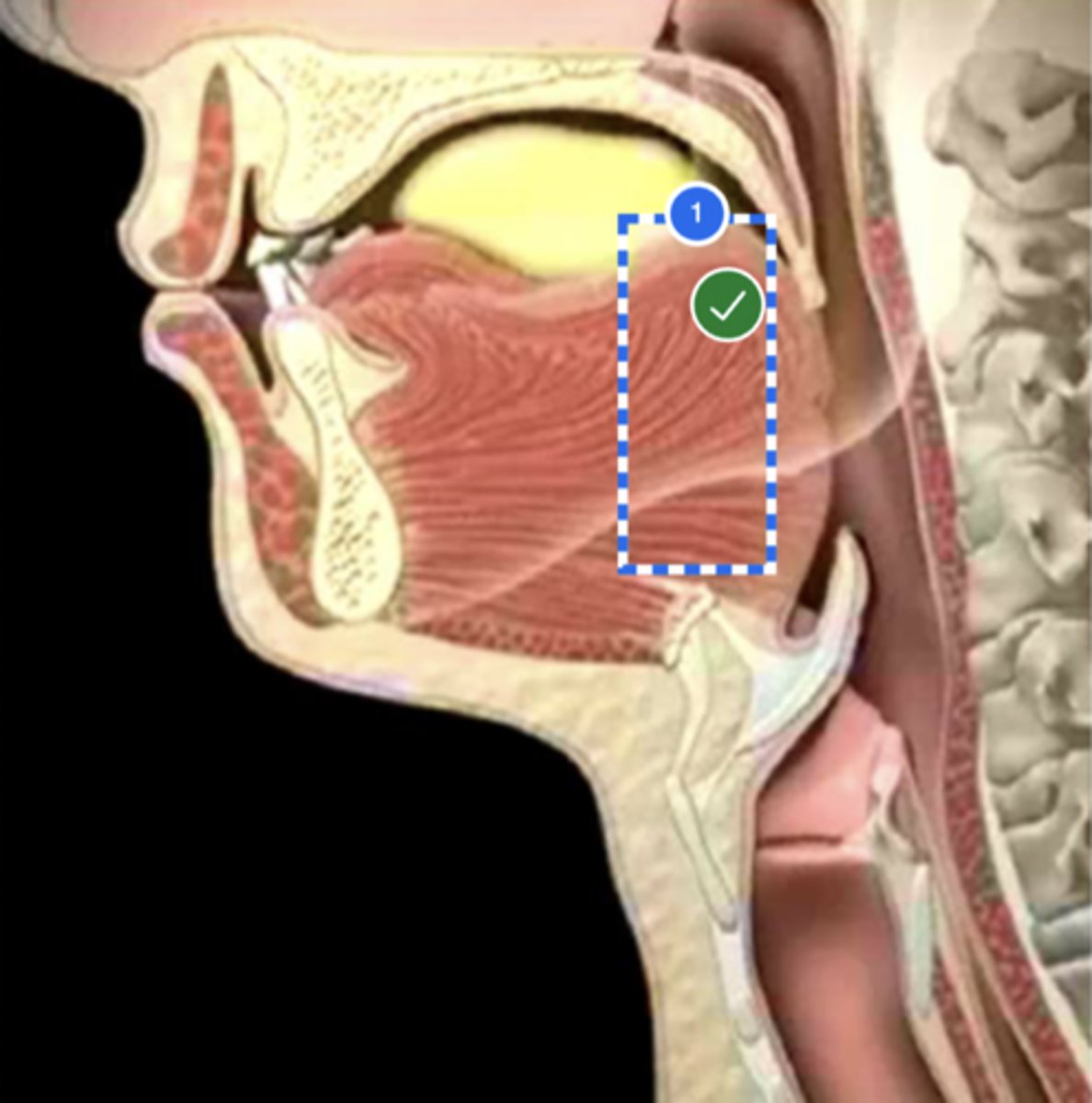
Label posterior/ back of tongue (lateral view)
Label Mandible (lateral view)
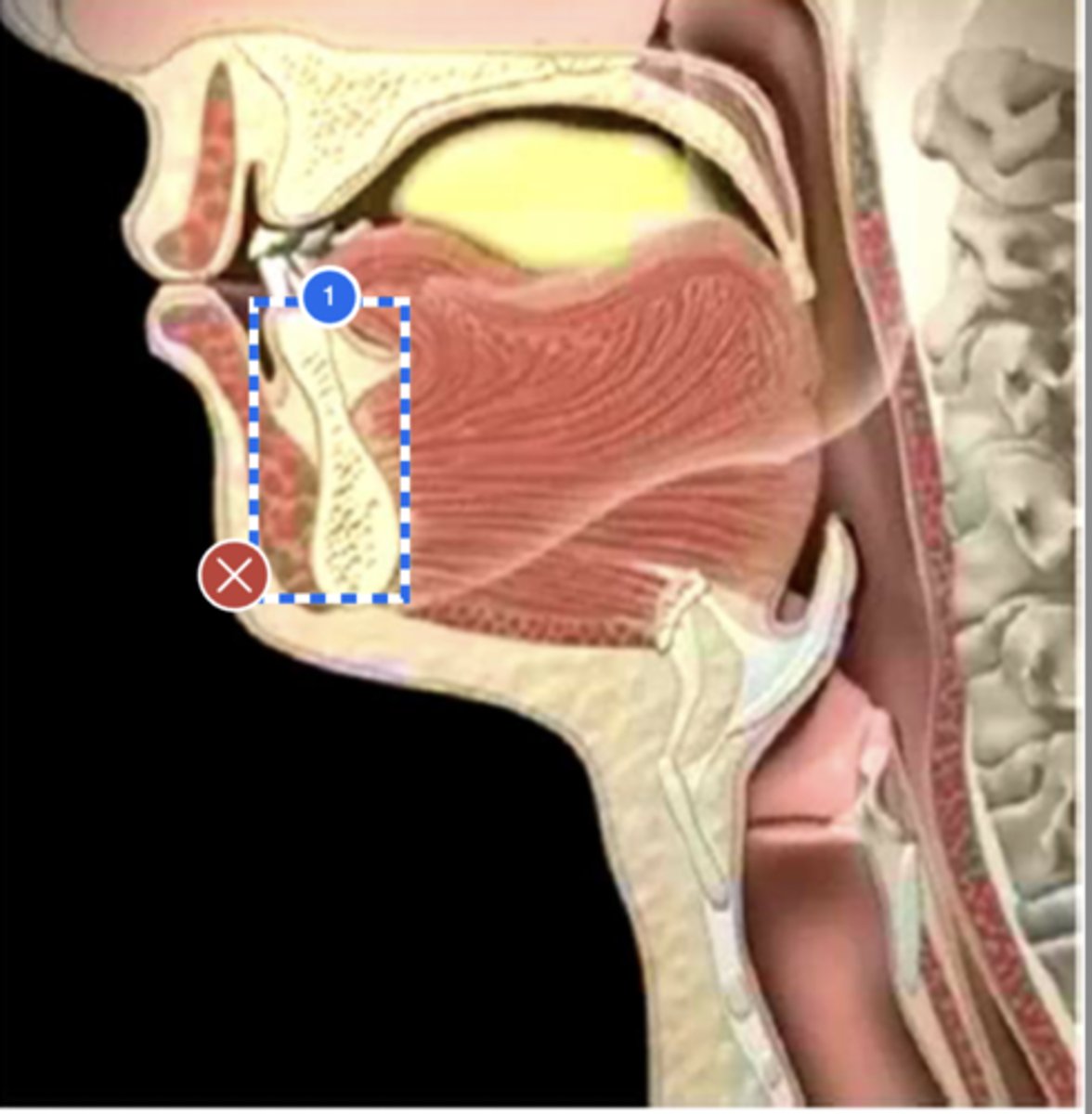
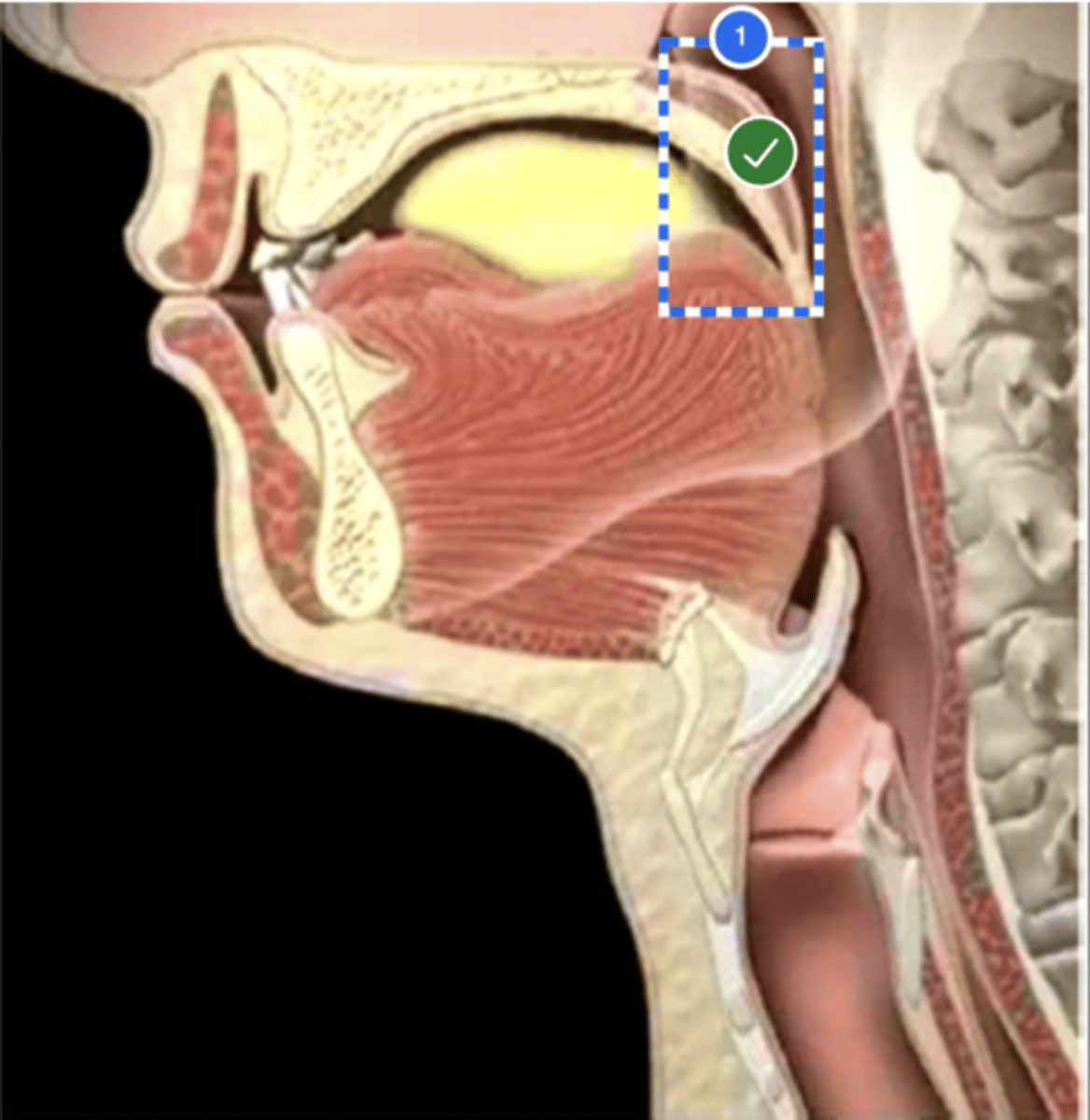
Label velum/ soft palate (lateral view)
Label hyoid bone (lateral view)
Label epiglottis (lateral view)
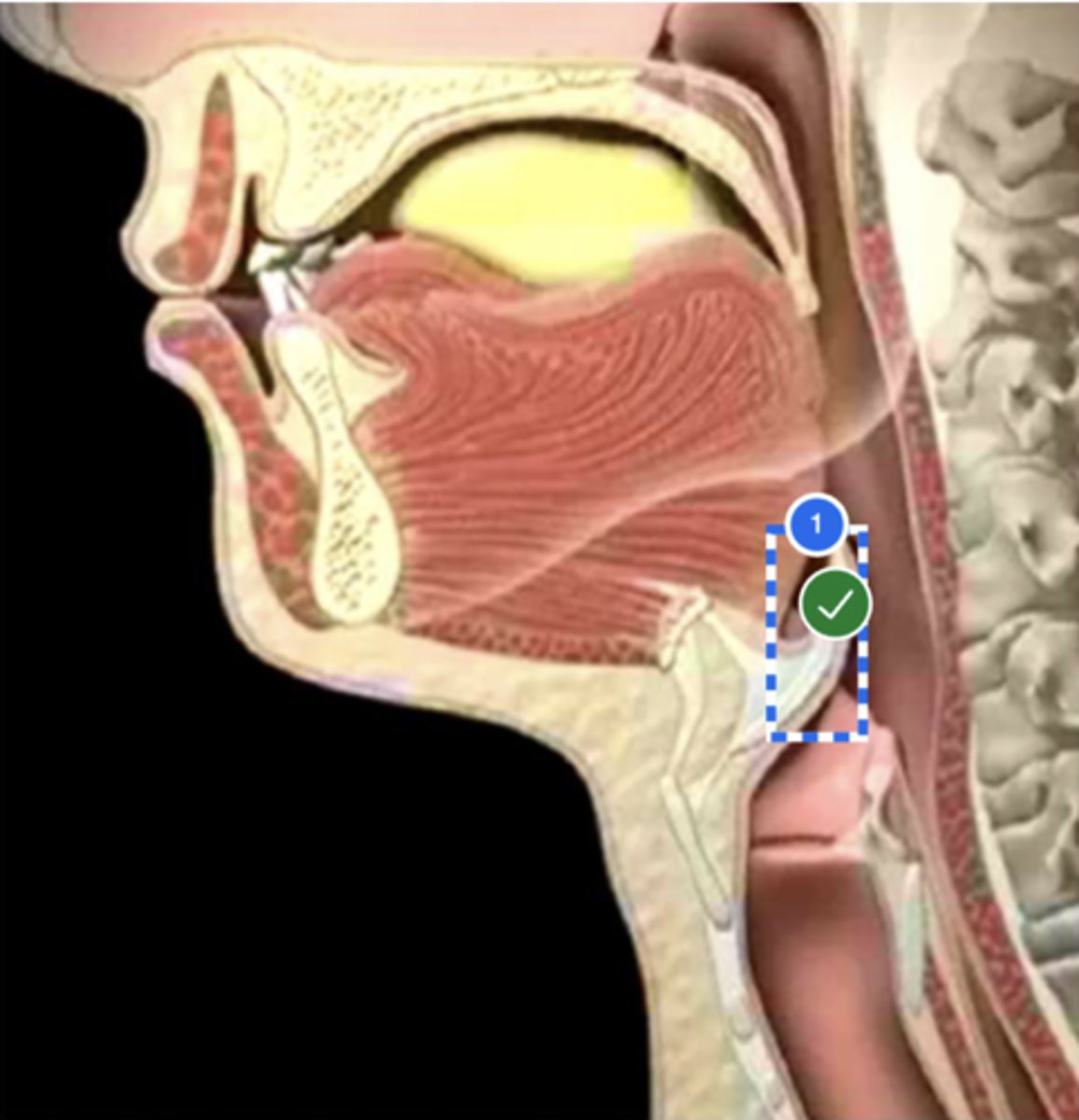
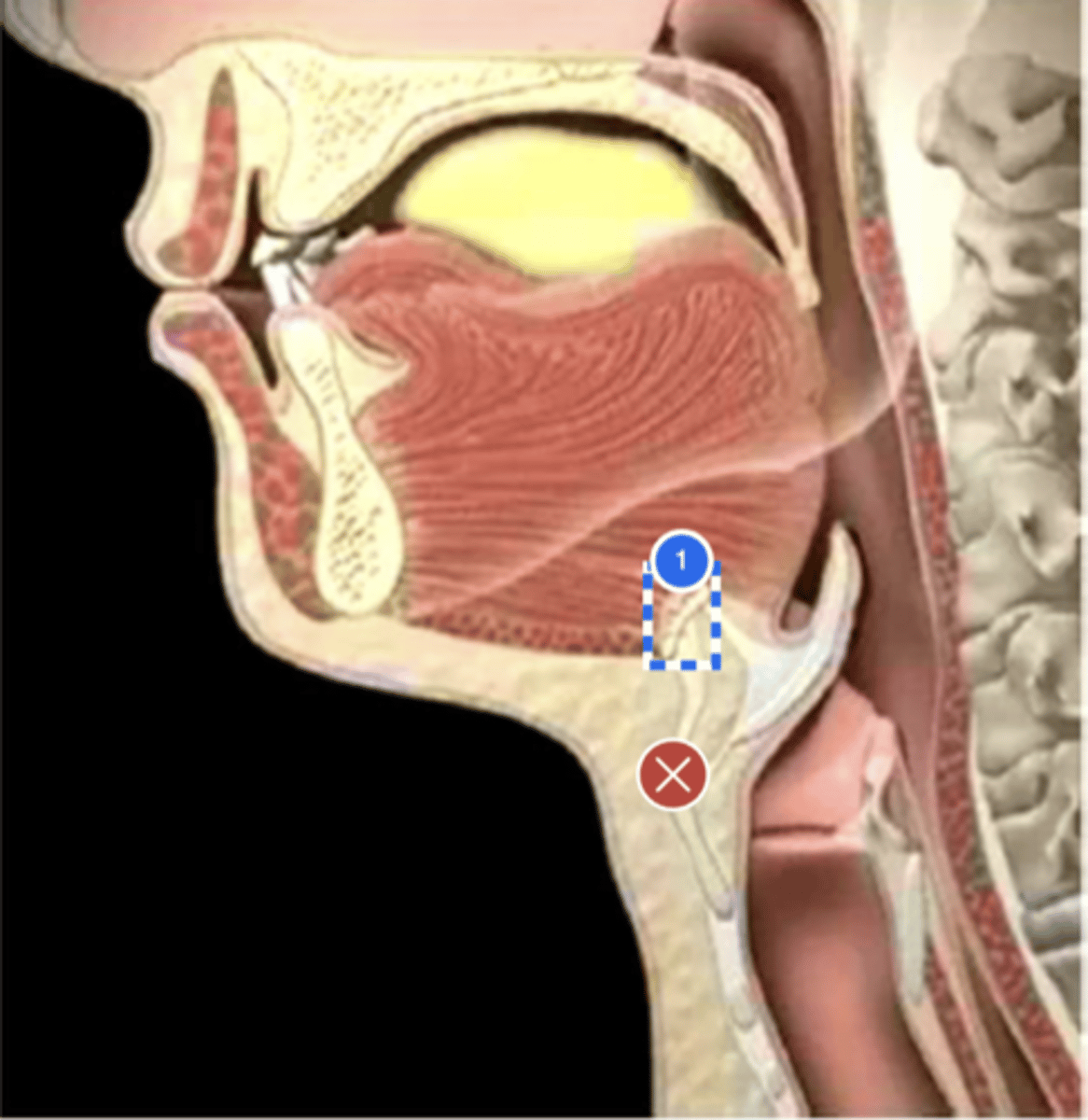
Label thyroid cartilage (lateral view)
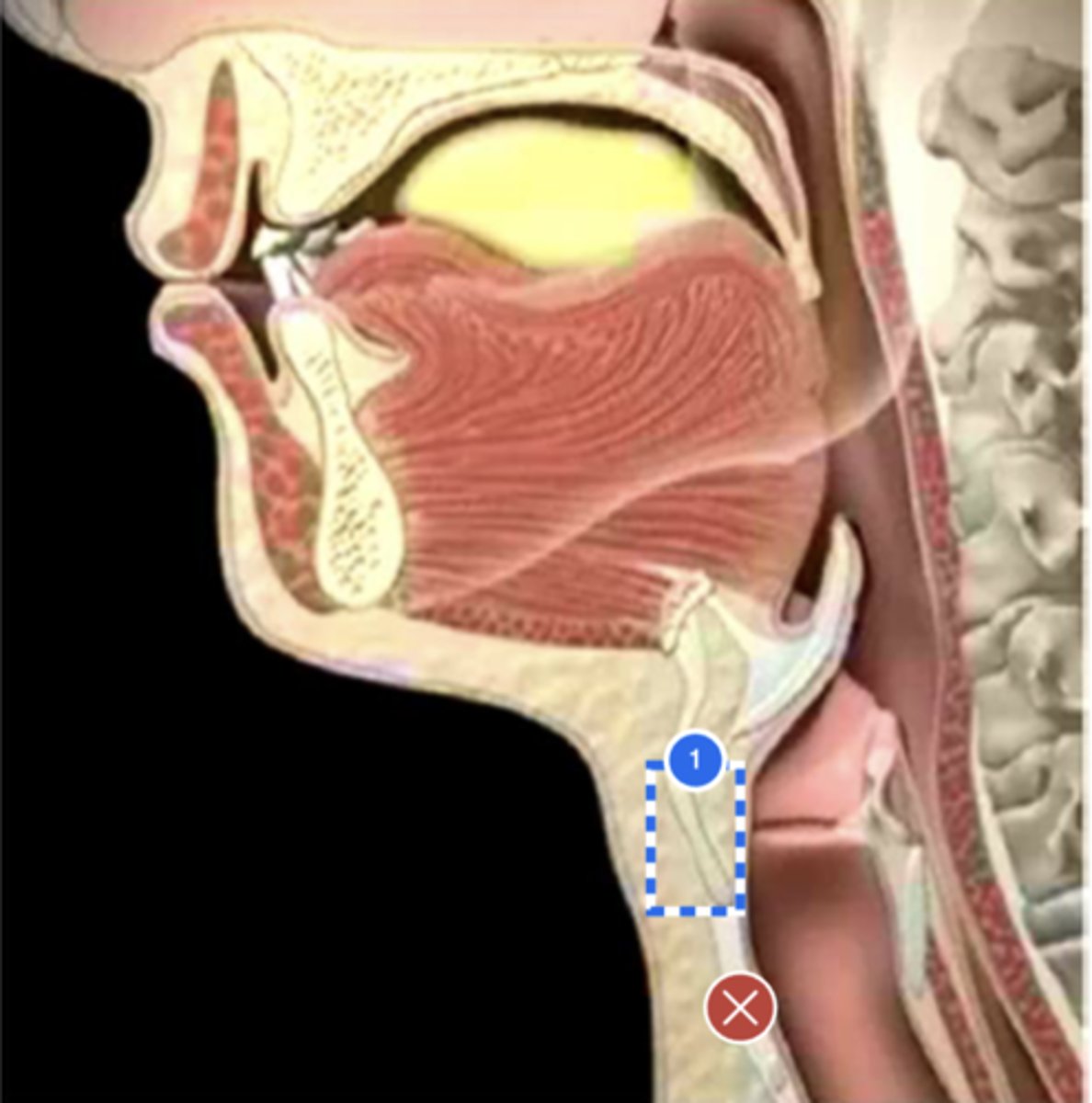
Label posterior cricoid (lateral view)
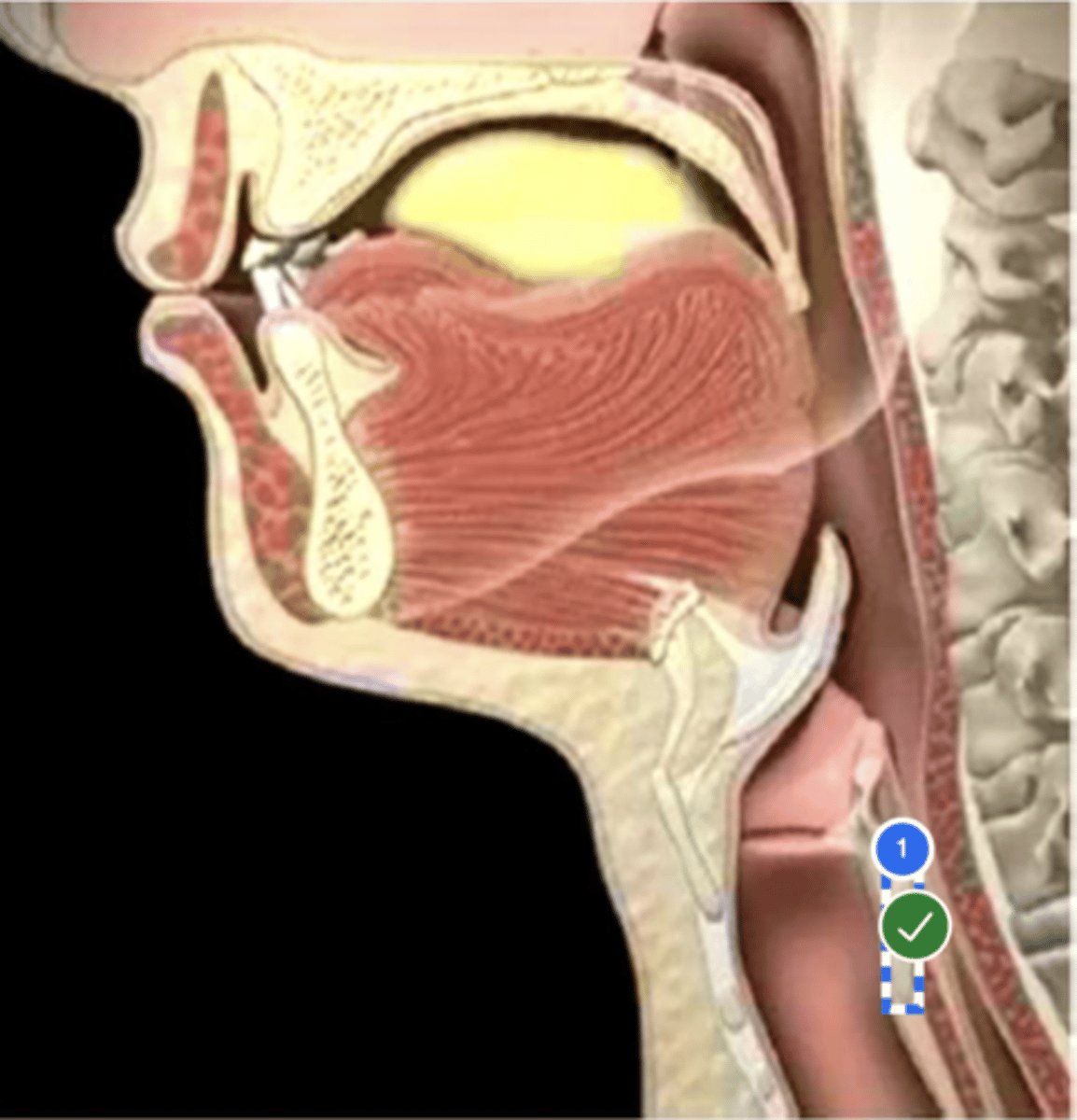
Label trachea (lateral view)
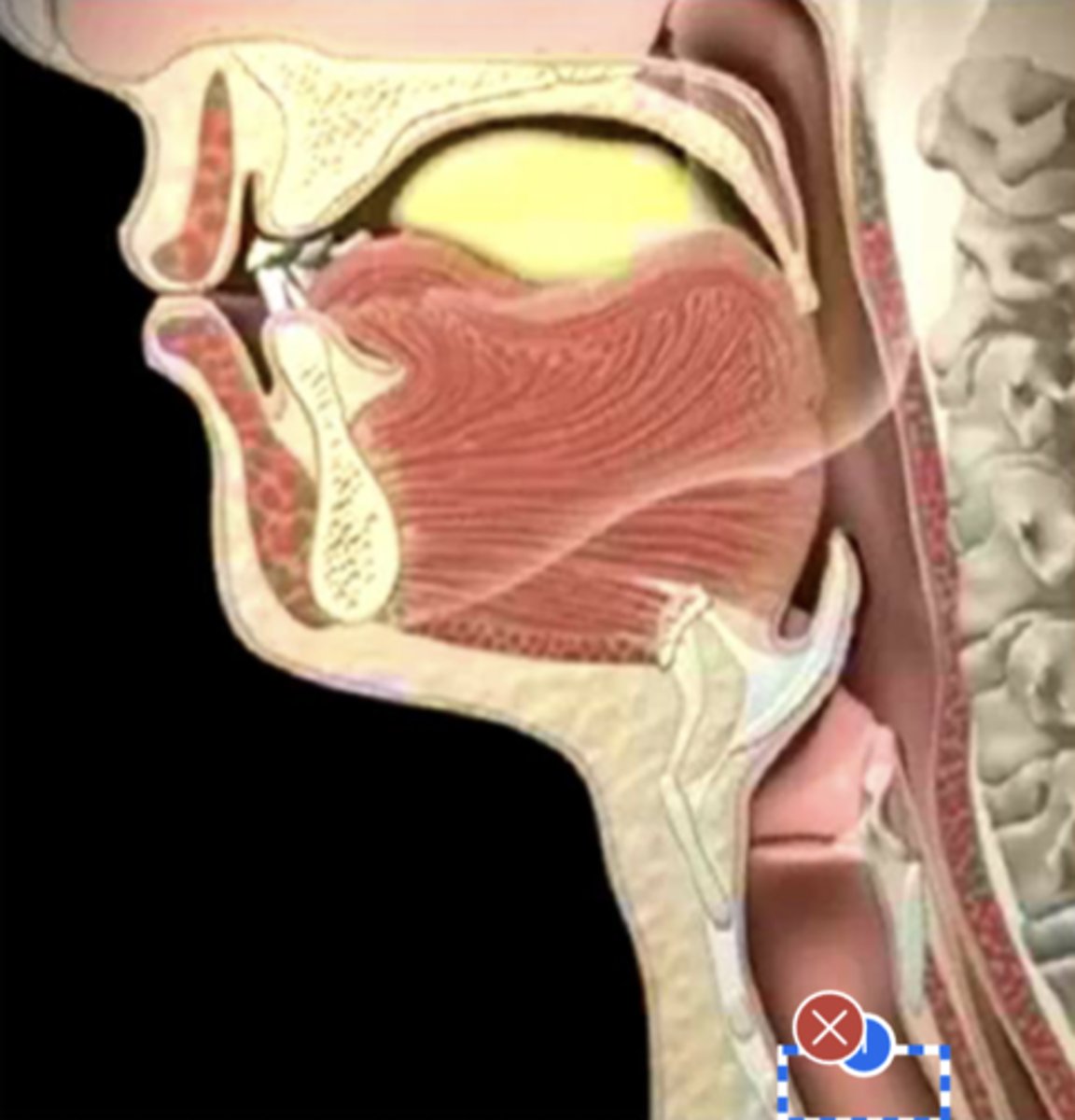
Label upper esophageal sphincter (lateral view)
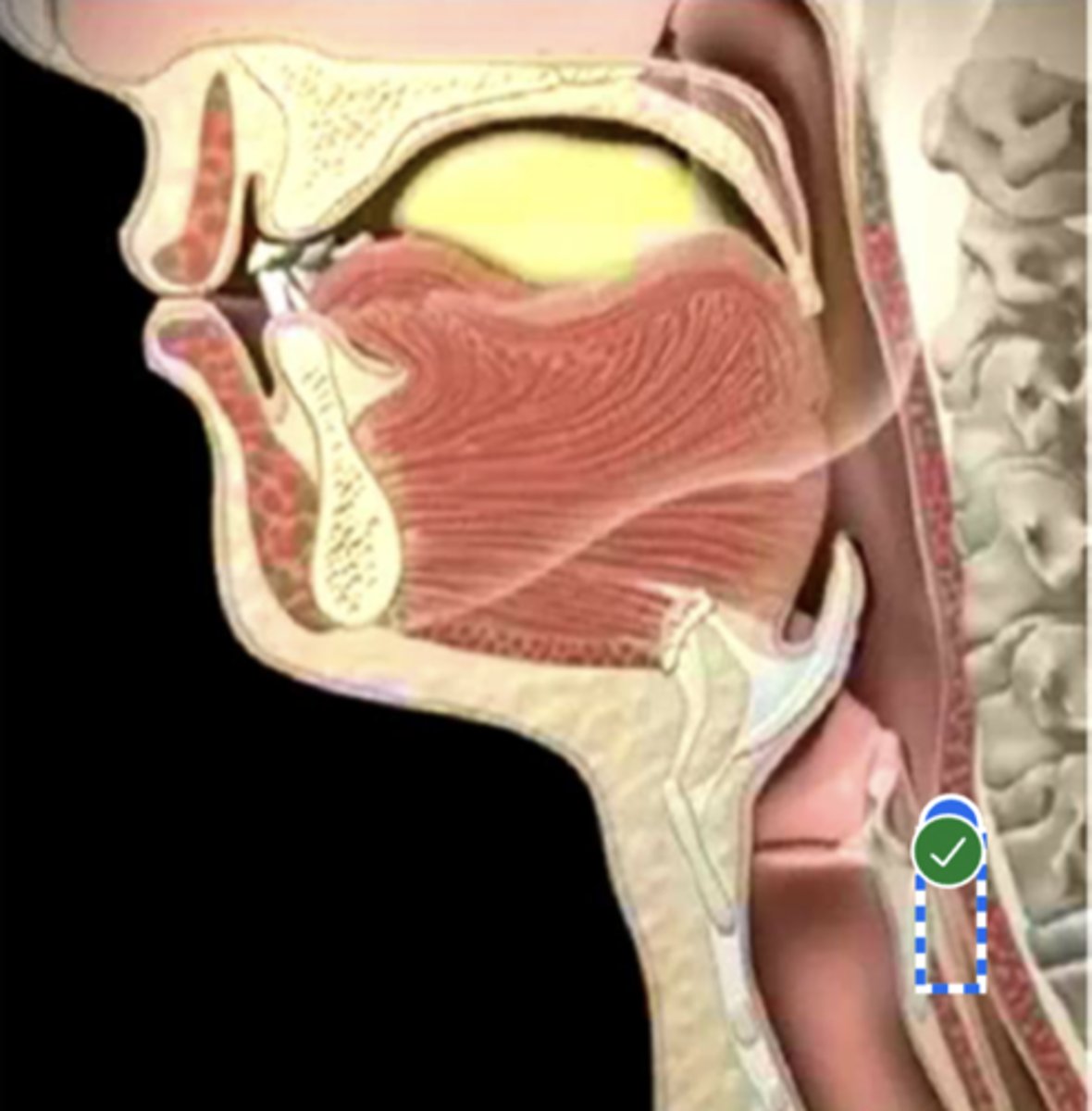
Label esophagus (lateral view)
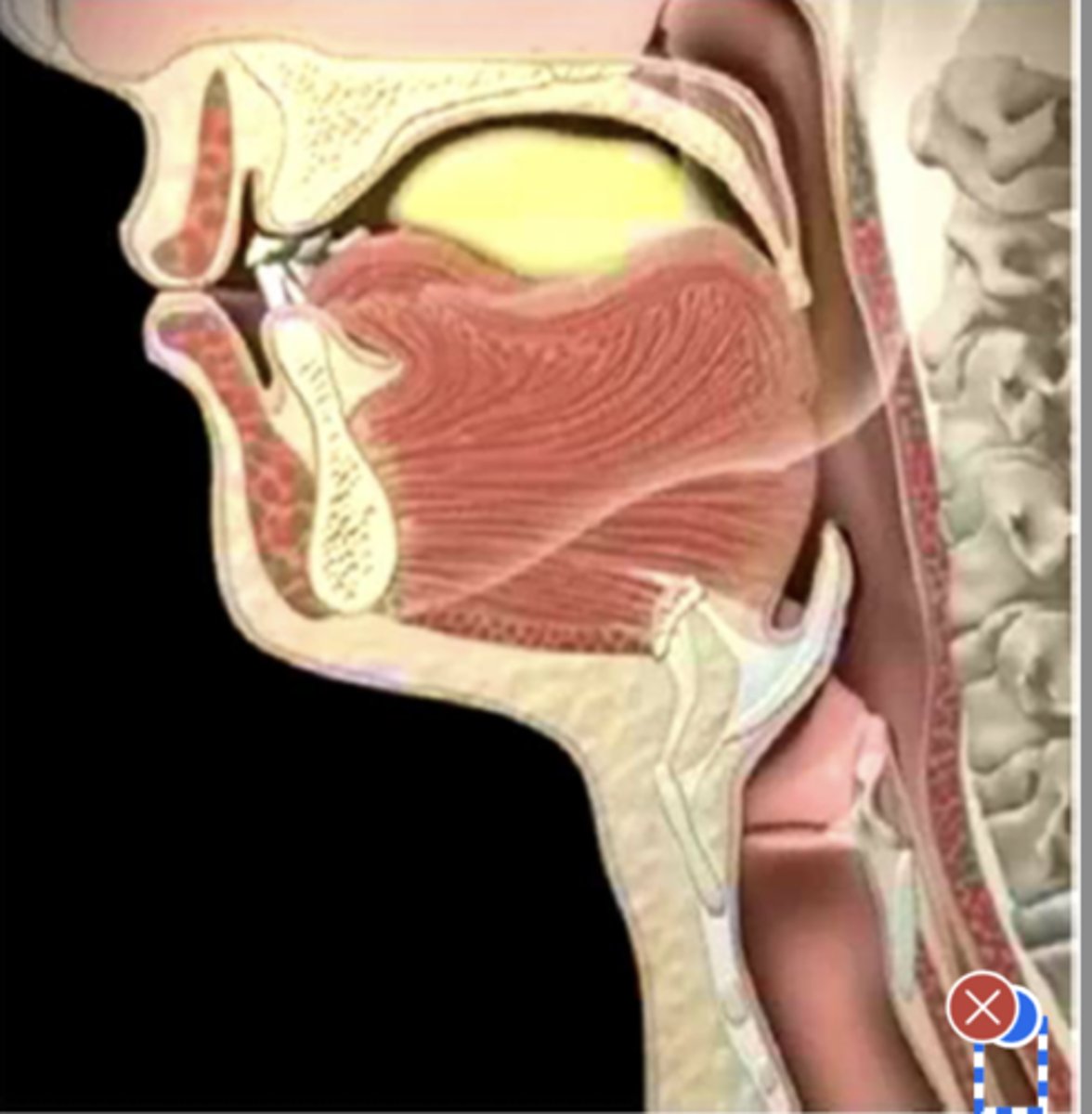
Label posterior pharyngeal wall (lateral view)
Label Right Anterior Faucial Pillar (superior view)
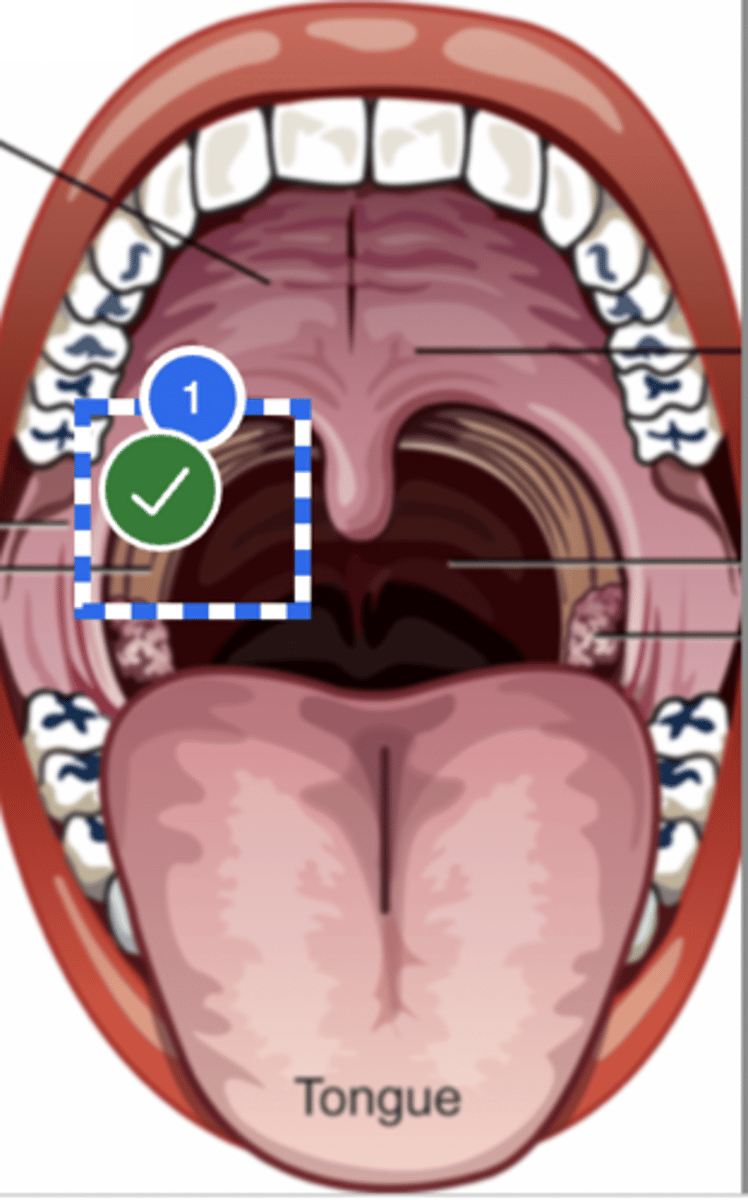
Label uvula (superior view)
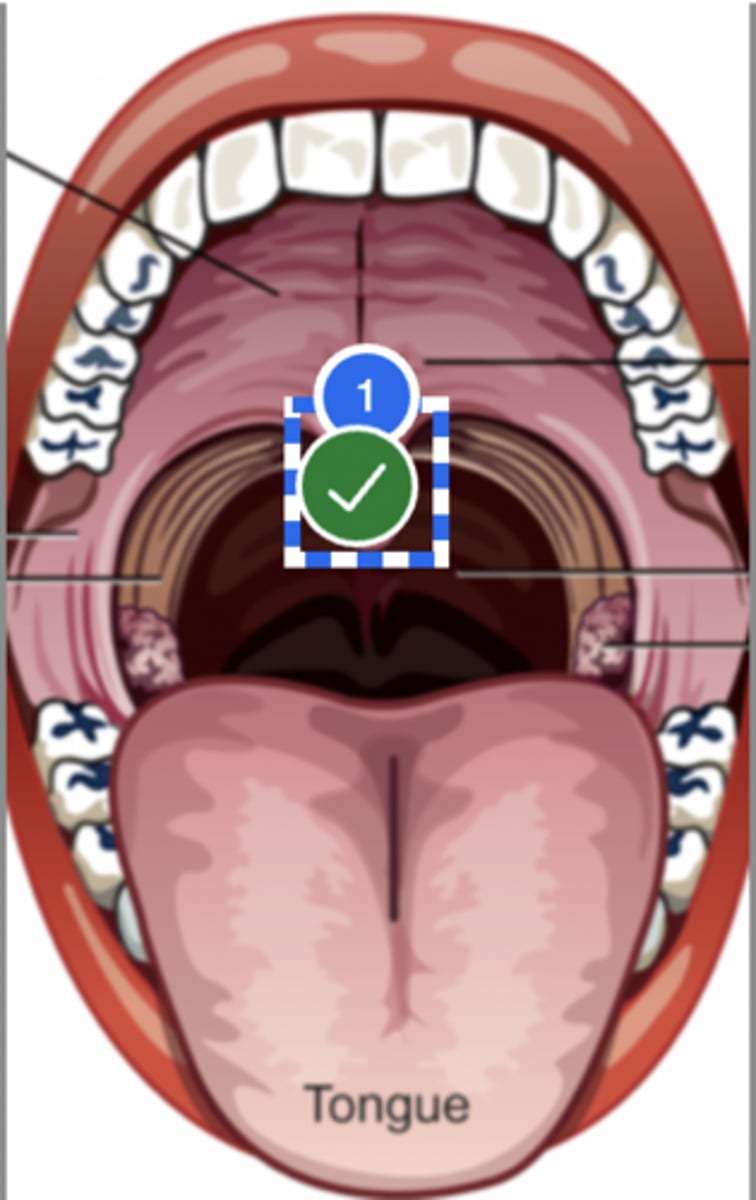
Label palatine tonsil (superior view)
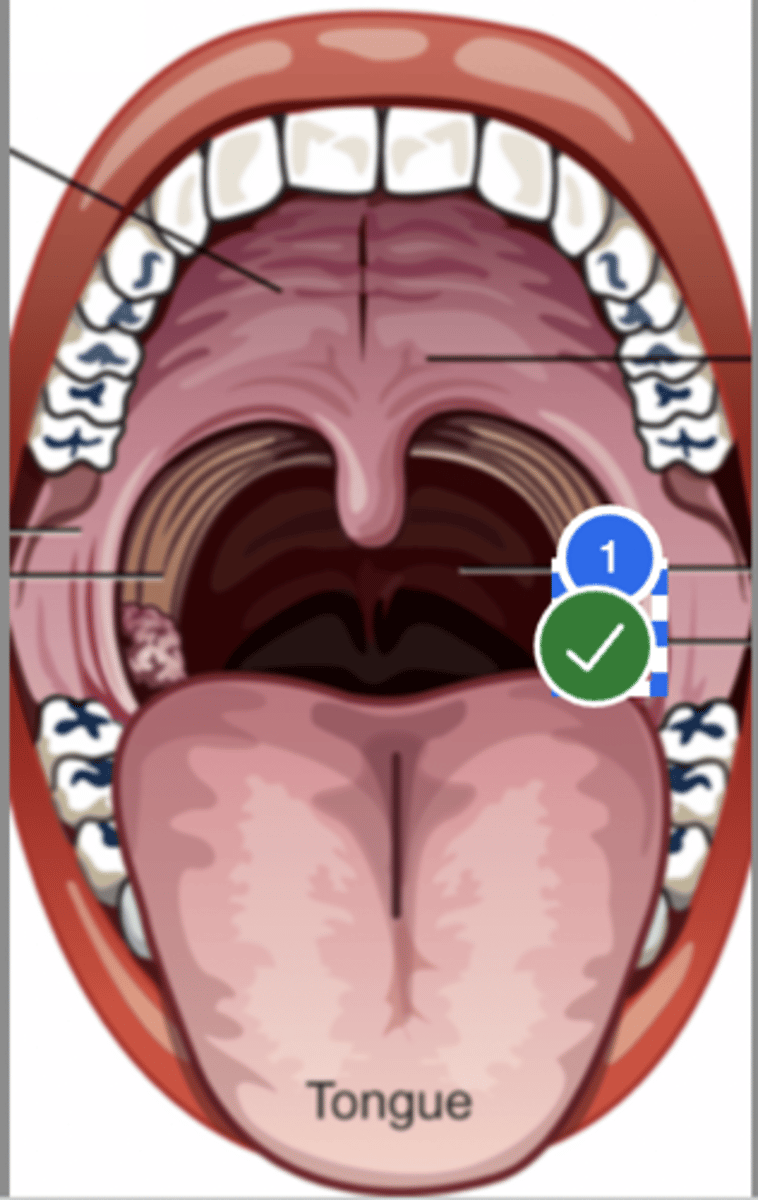
Label left true vocal fold (superior view)
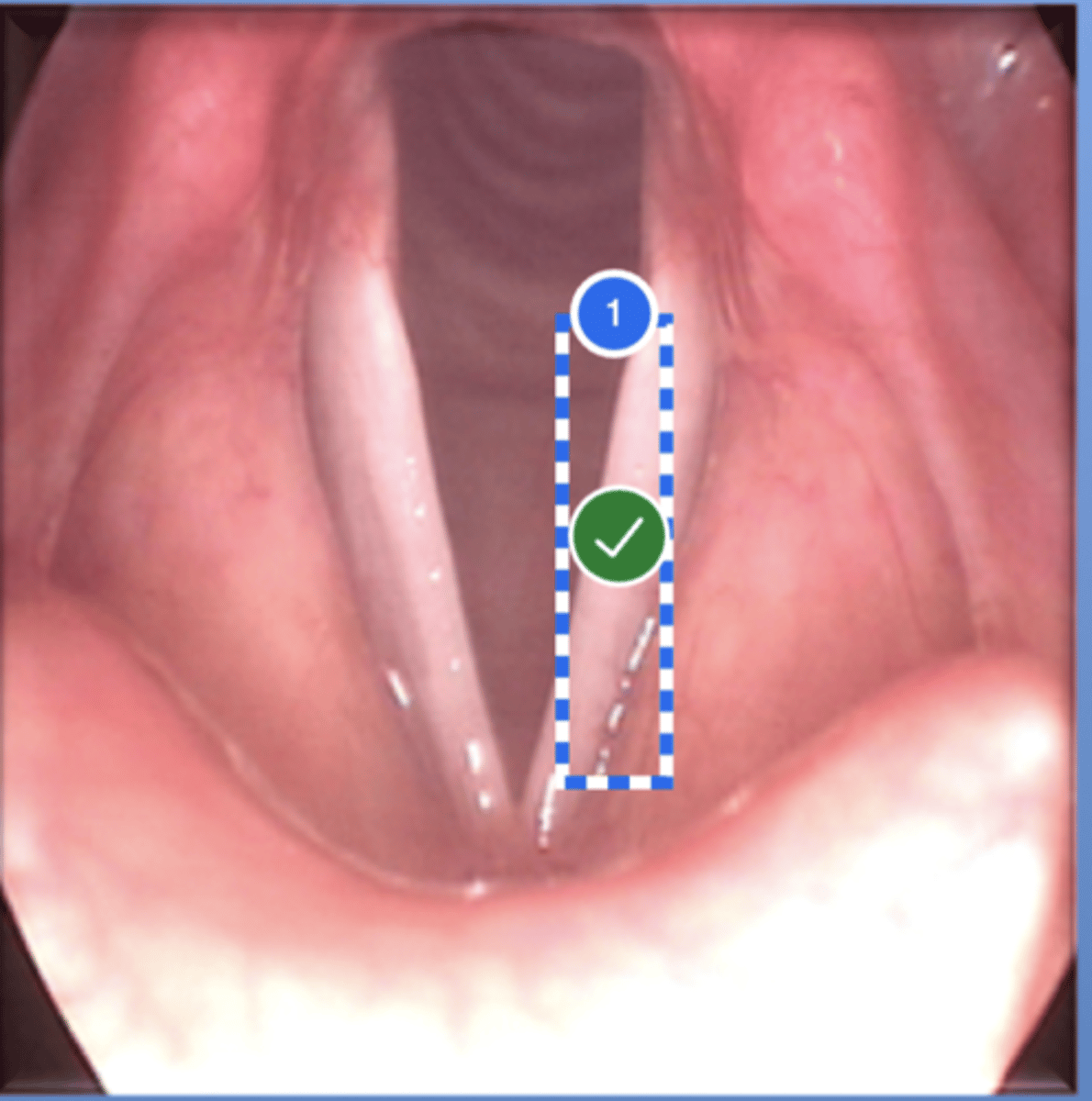
Label right false vocal fold (superior view)
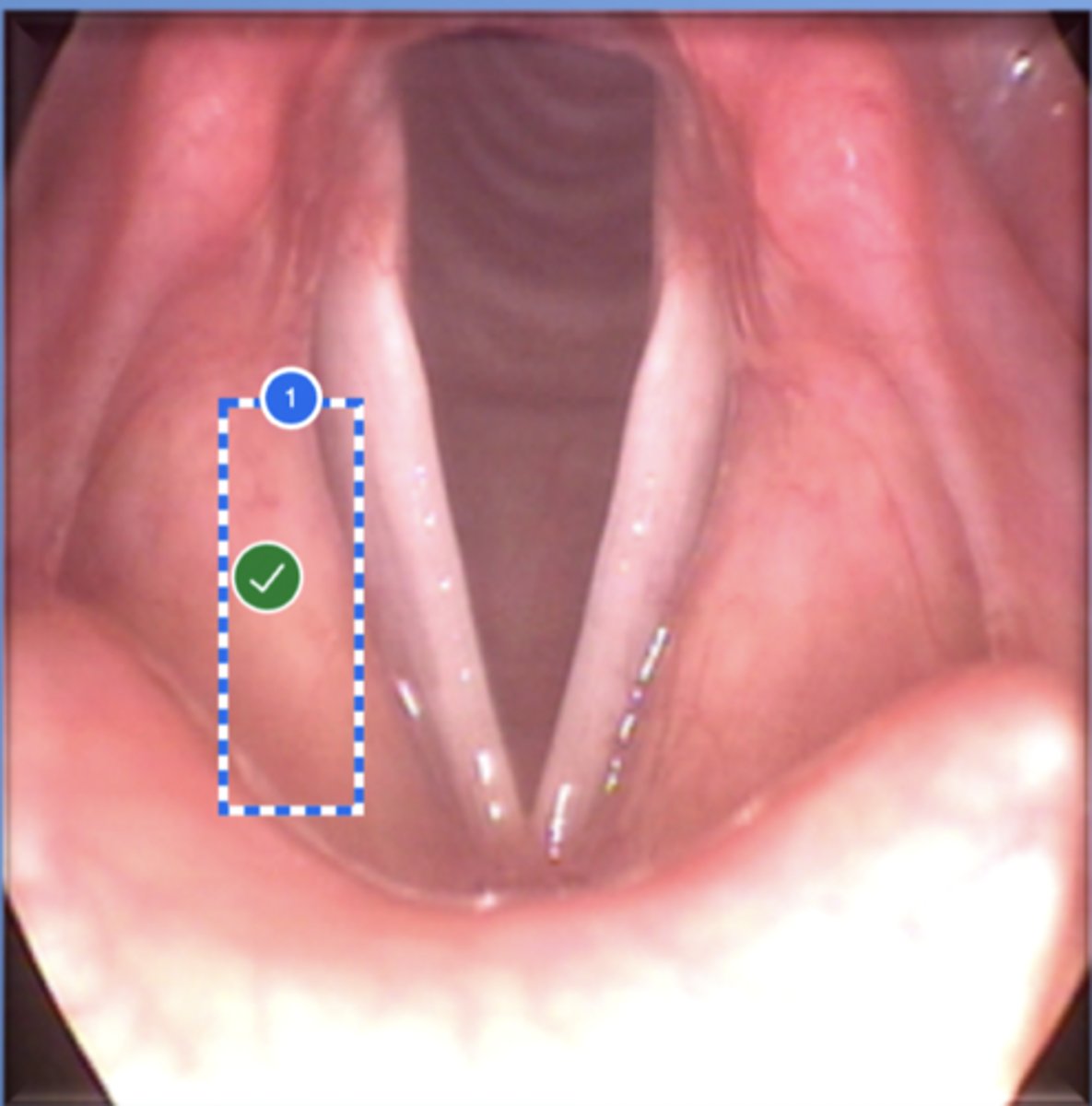
label right arytenoid (superior view)

Label trachea (superior view)
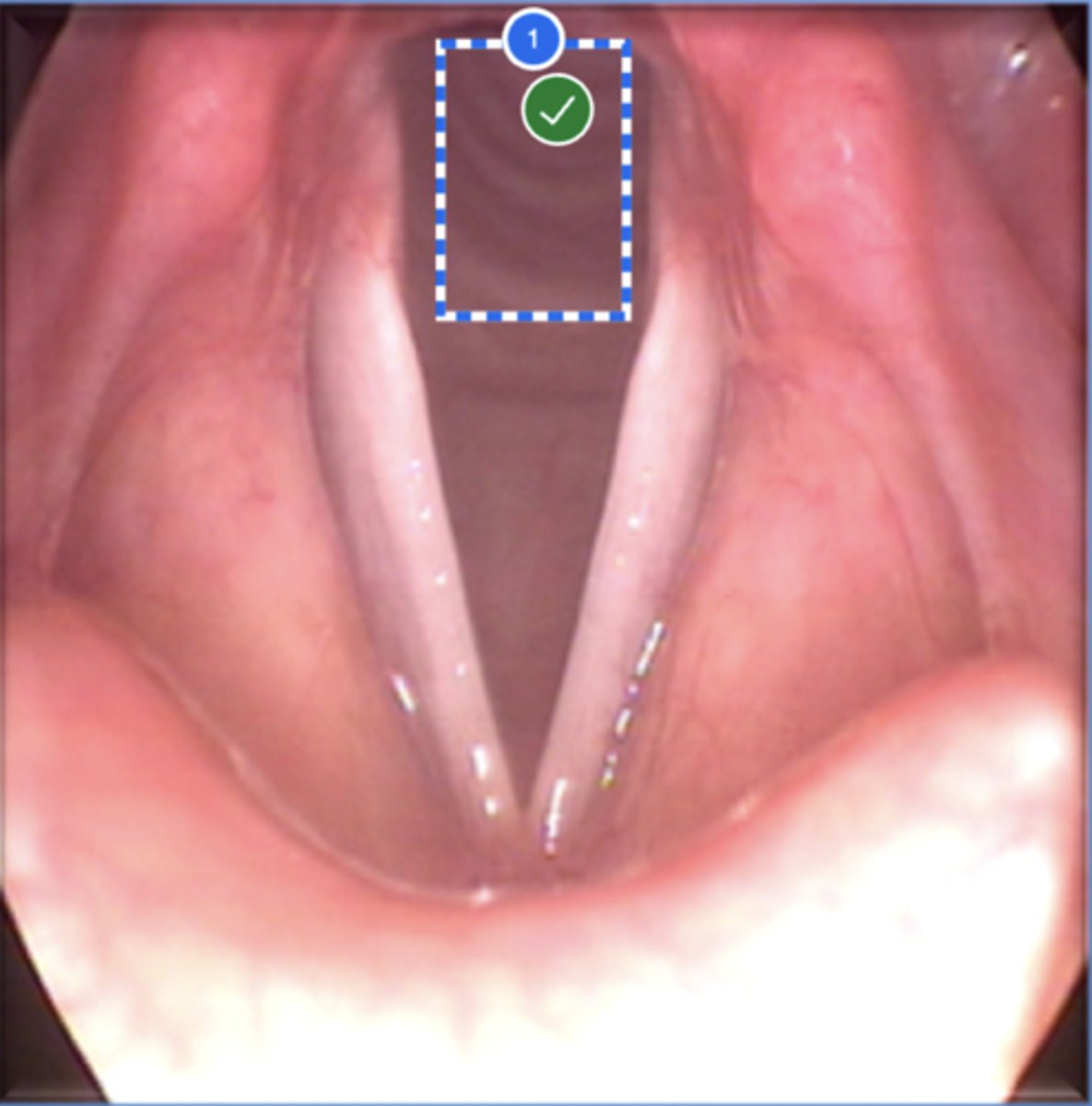
Label epiglottis (superior view)
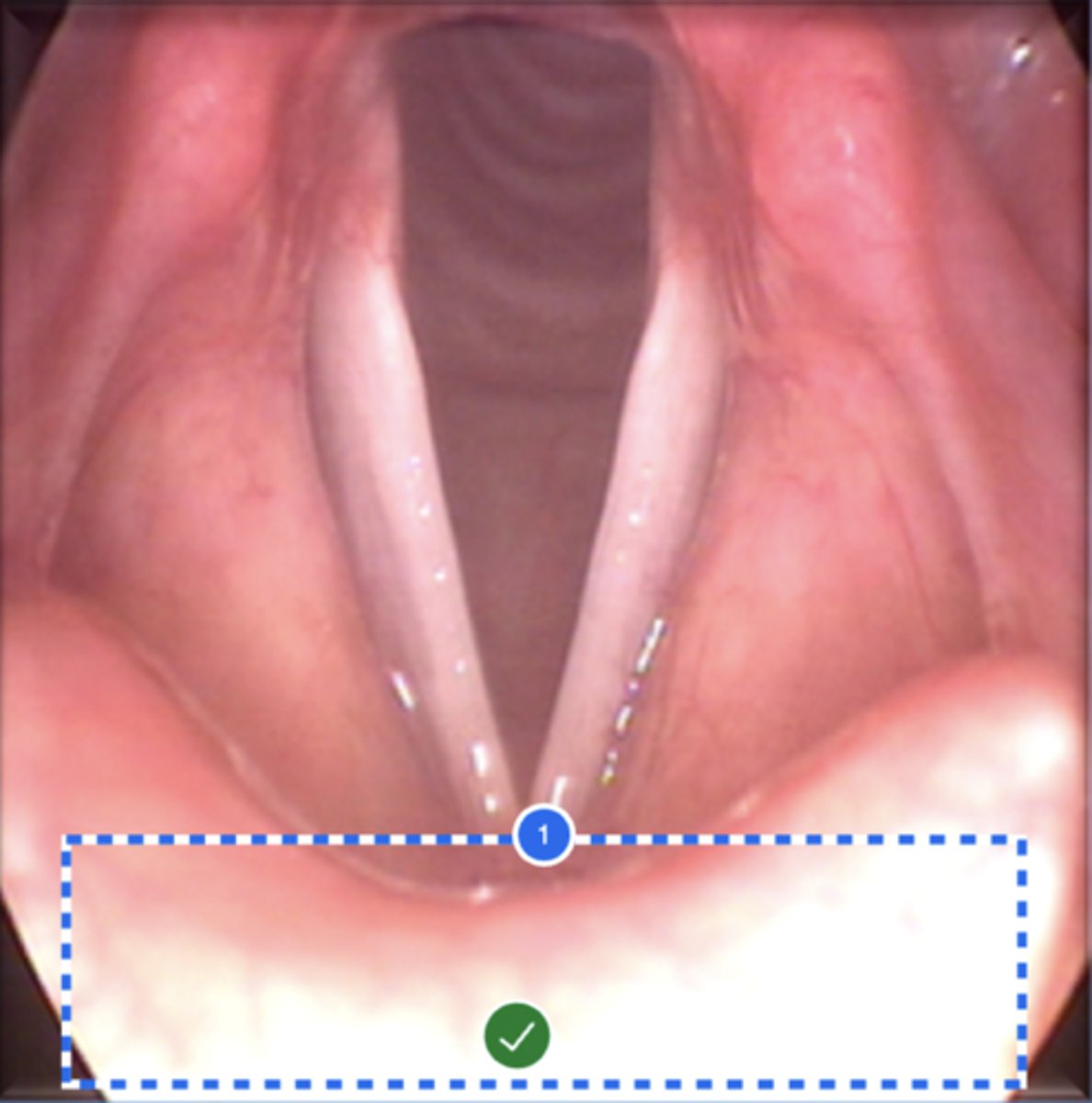
Label left aryepiglottic fold (superior view)
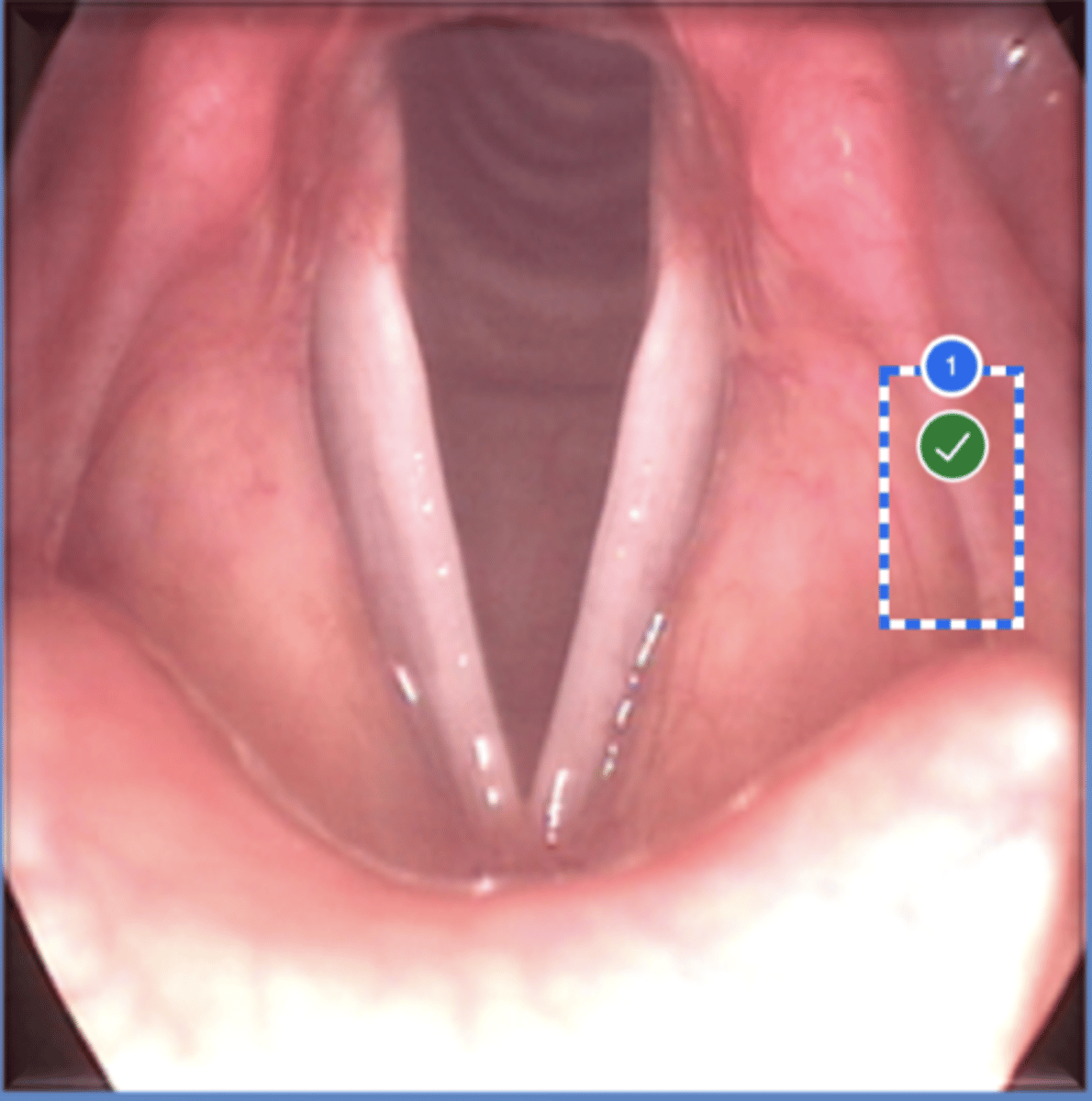
Label laryngral surface of epiglottis (superior view)
Label lingual surface of epiglottis (superior view)
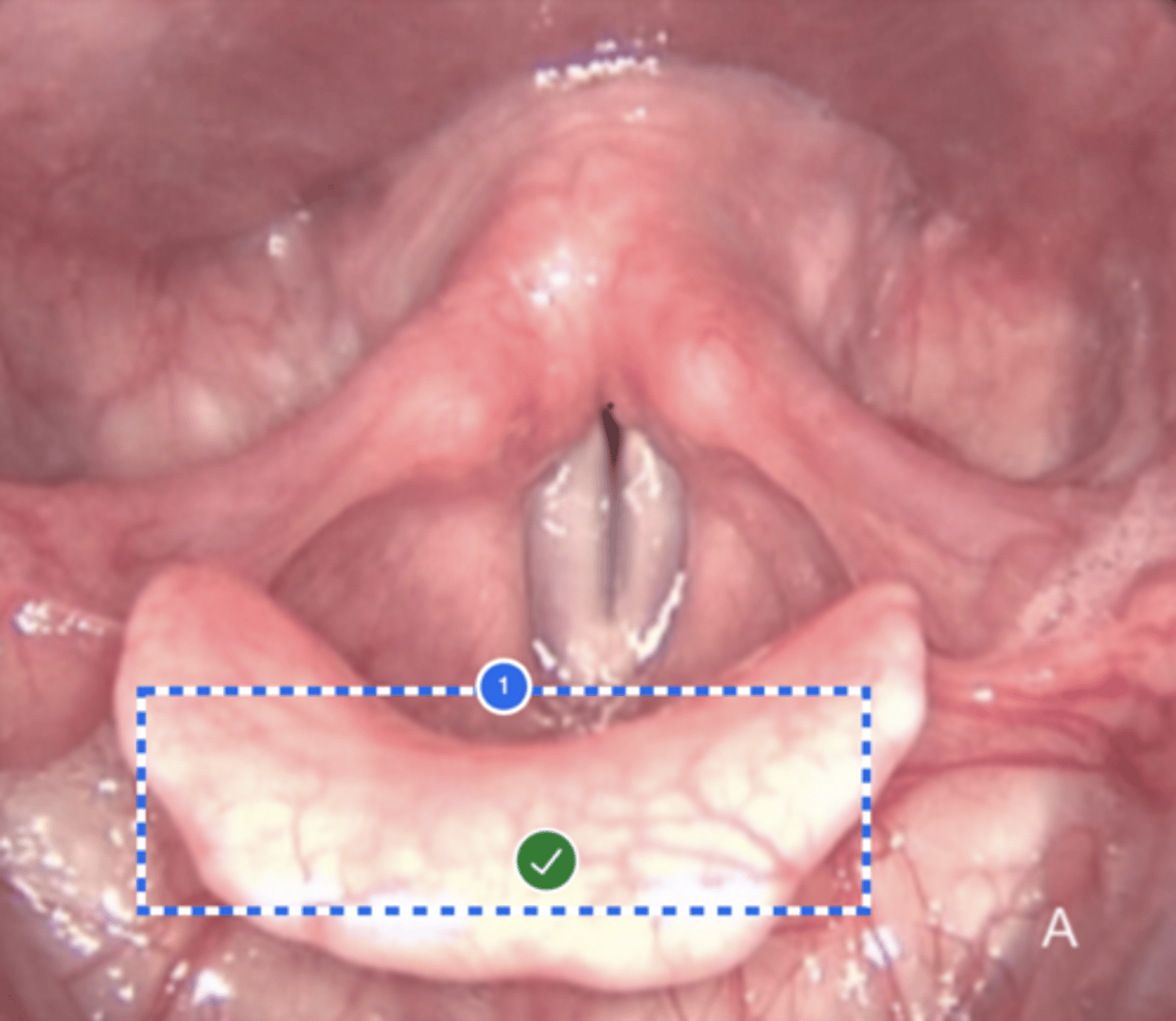
Label base of tongue (superior view)
Label right pyriform sinus (superior view)
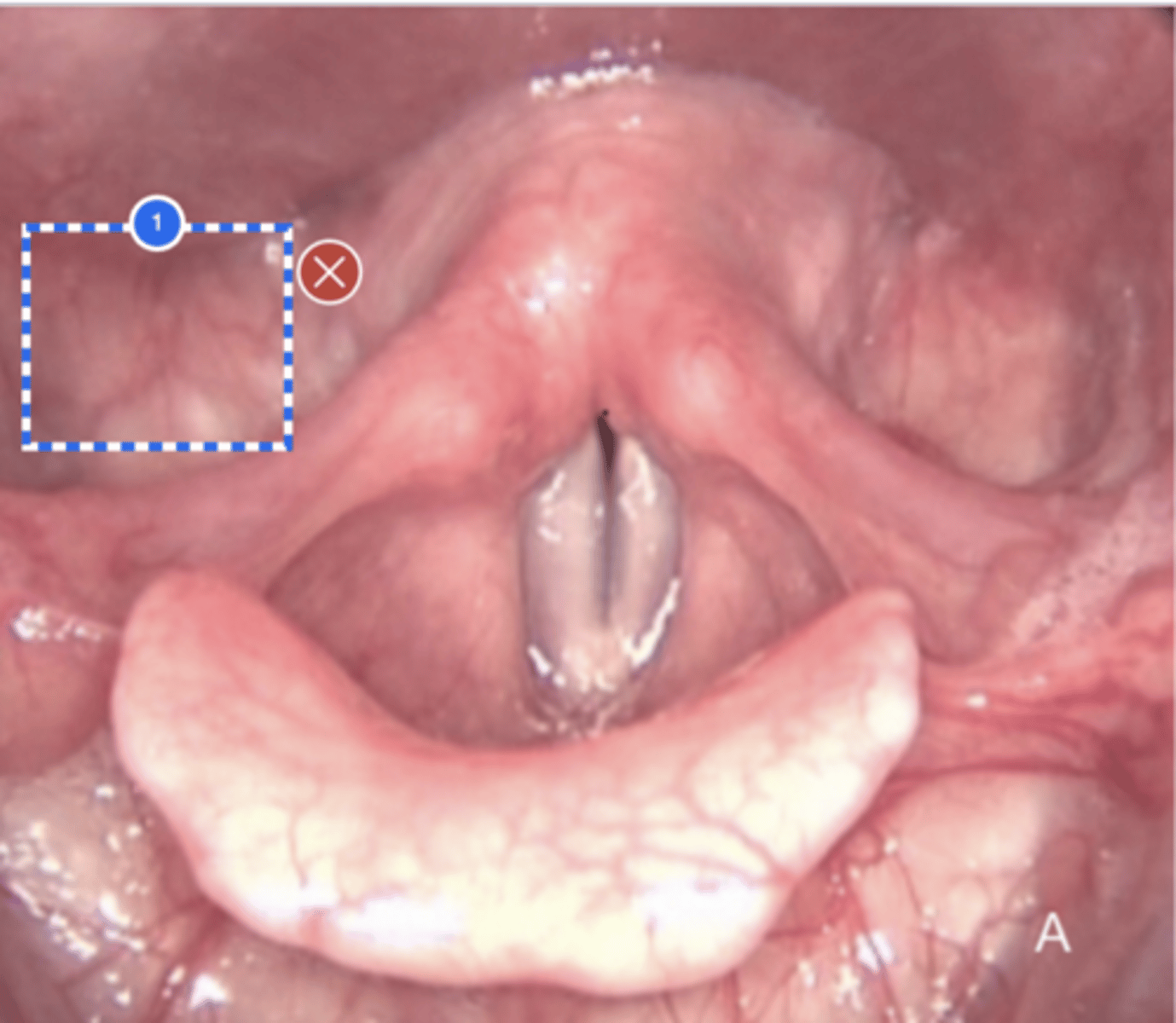
Label upper esophageal sphincter (superior view)
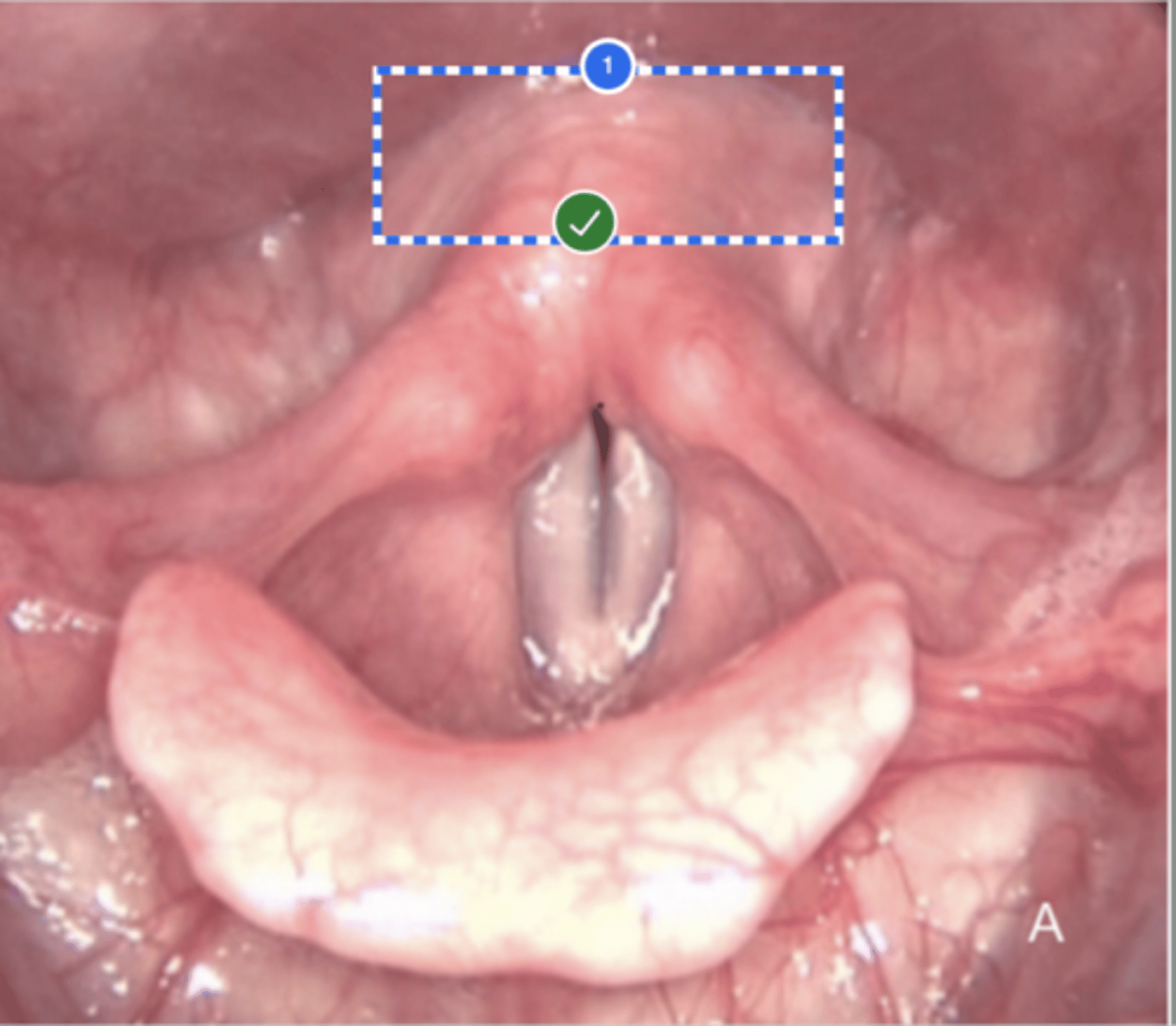
Label right true vf (superior view)
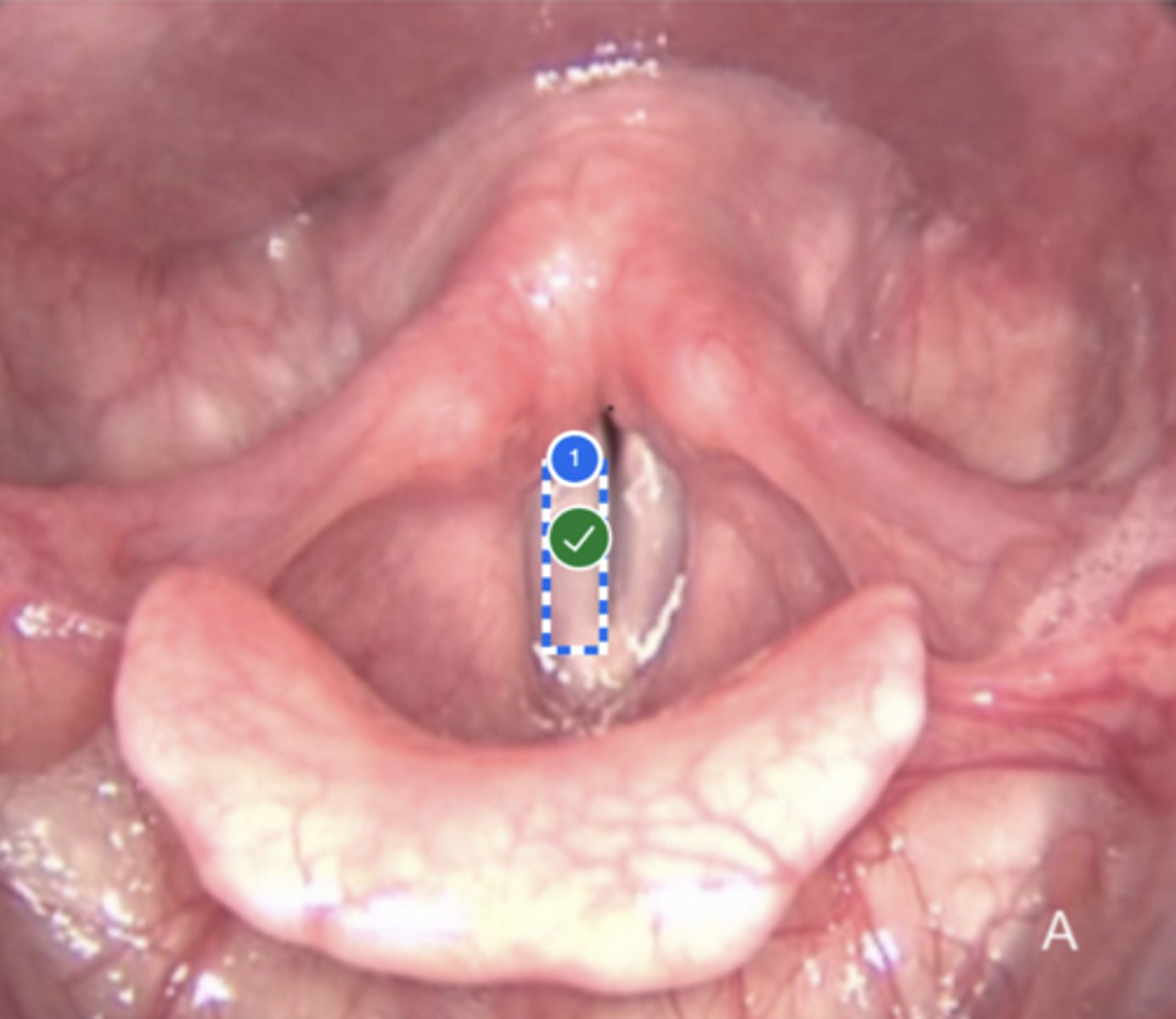
Label hyoid bone (anterior view)
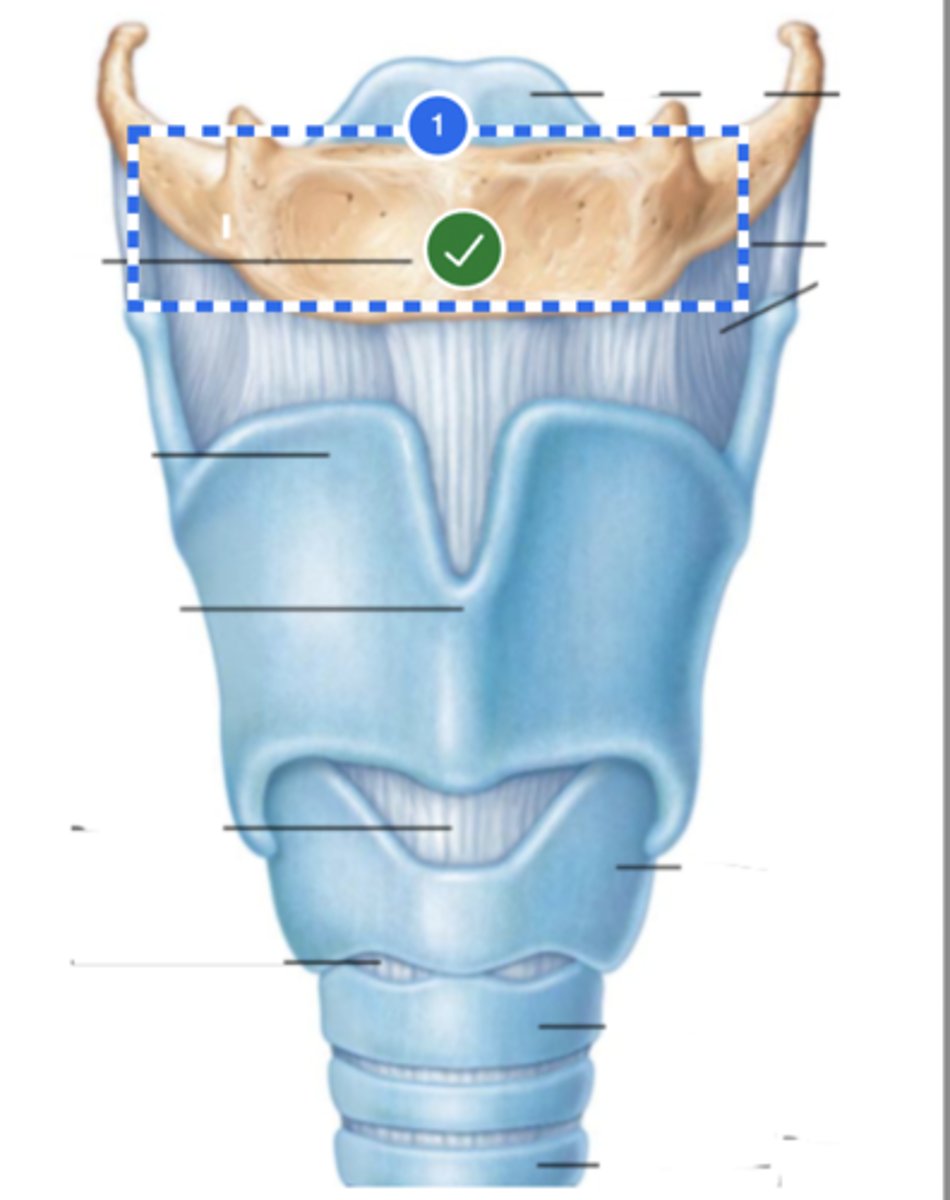
Label epiglottis (anterior view)
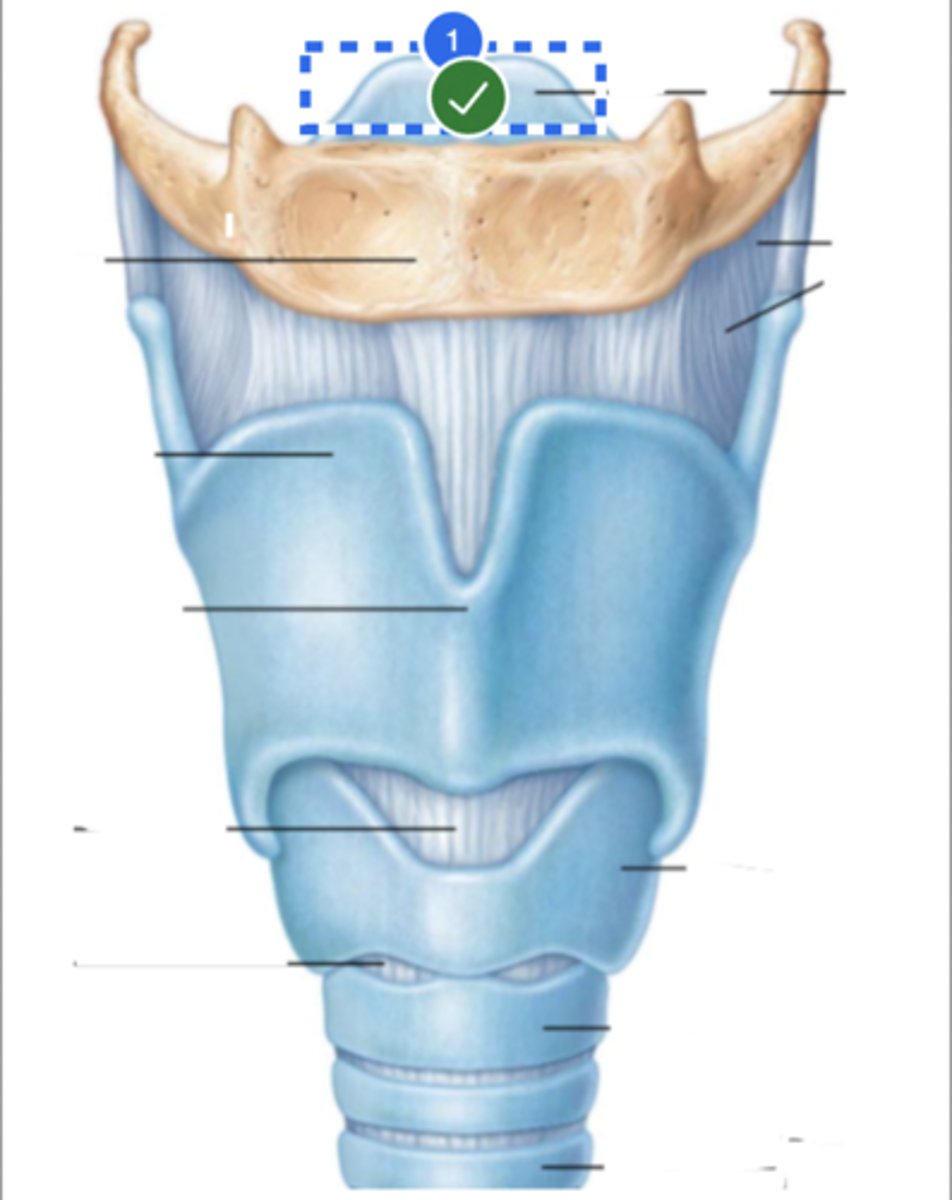
Label Thyroid cartilage (anterior view)

Label cricoid cartilage (anterior view)
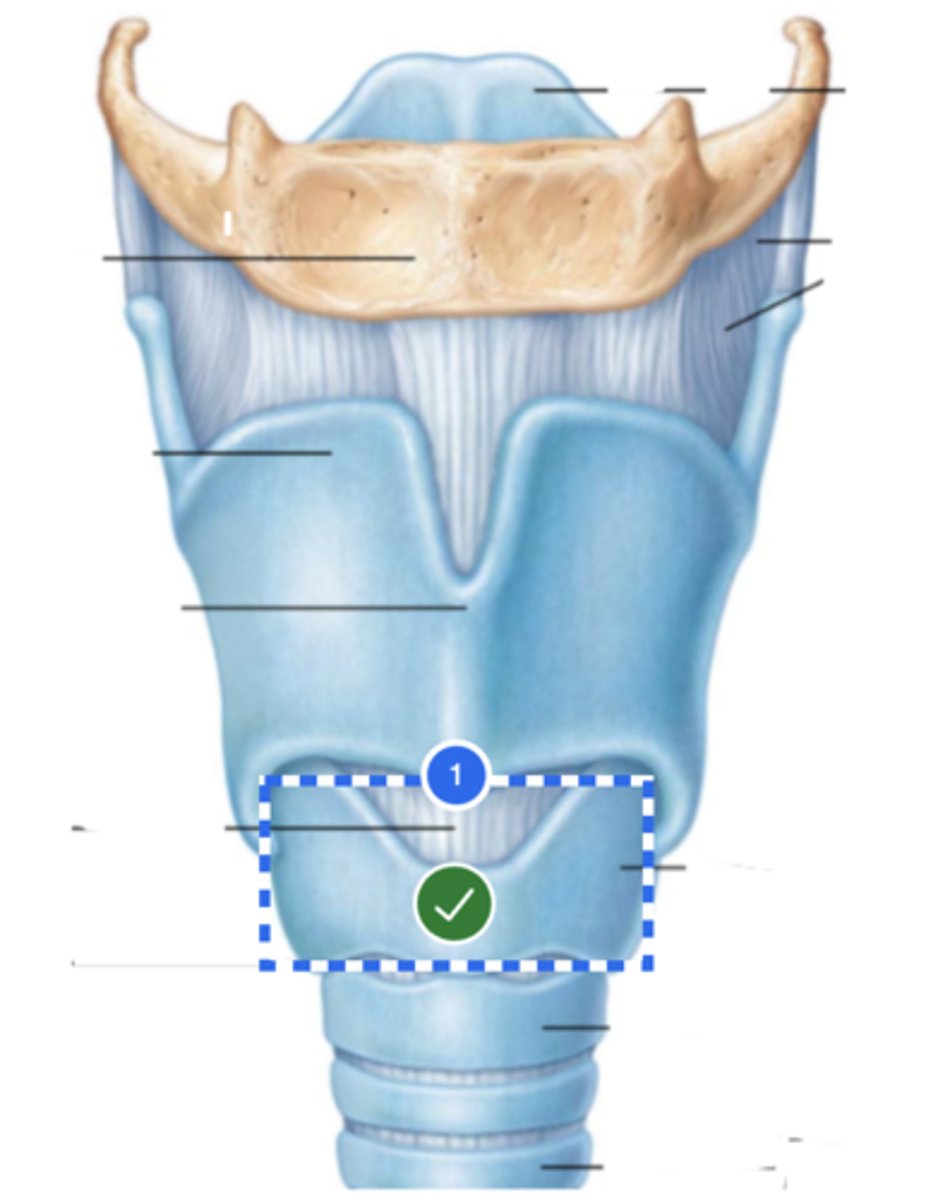
Label 2nd tracheal ring (anterior view)
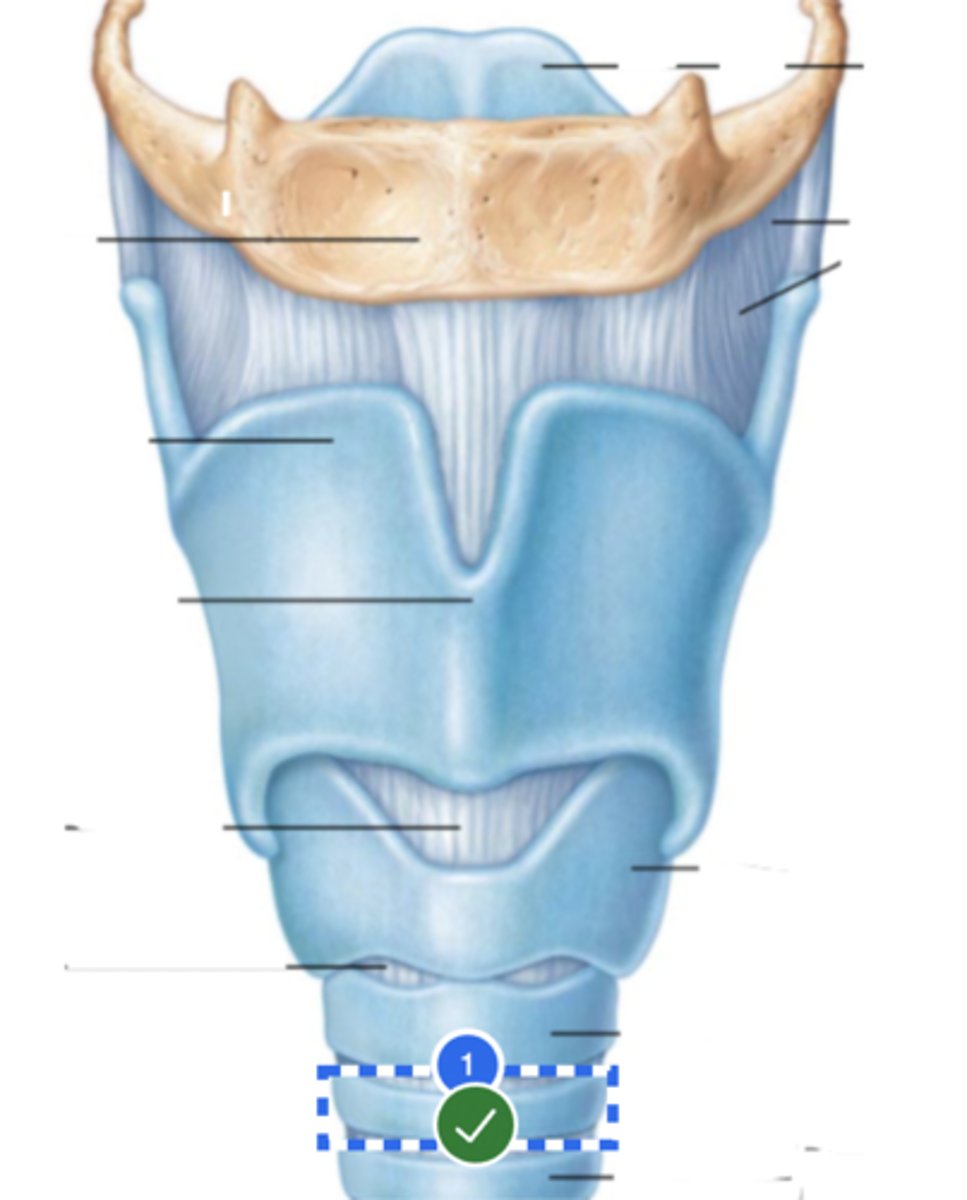
Label left cricothyroid joint (anterior view)

Label Cricoid cartilage (posterior view)
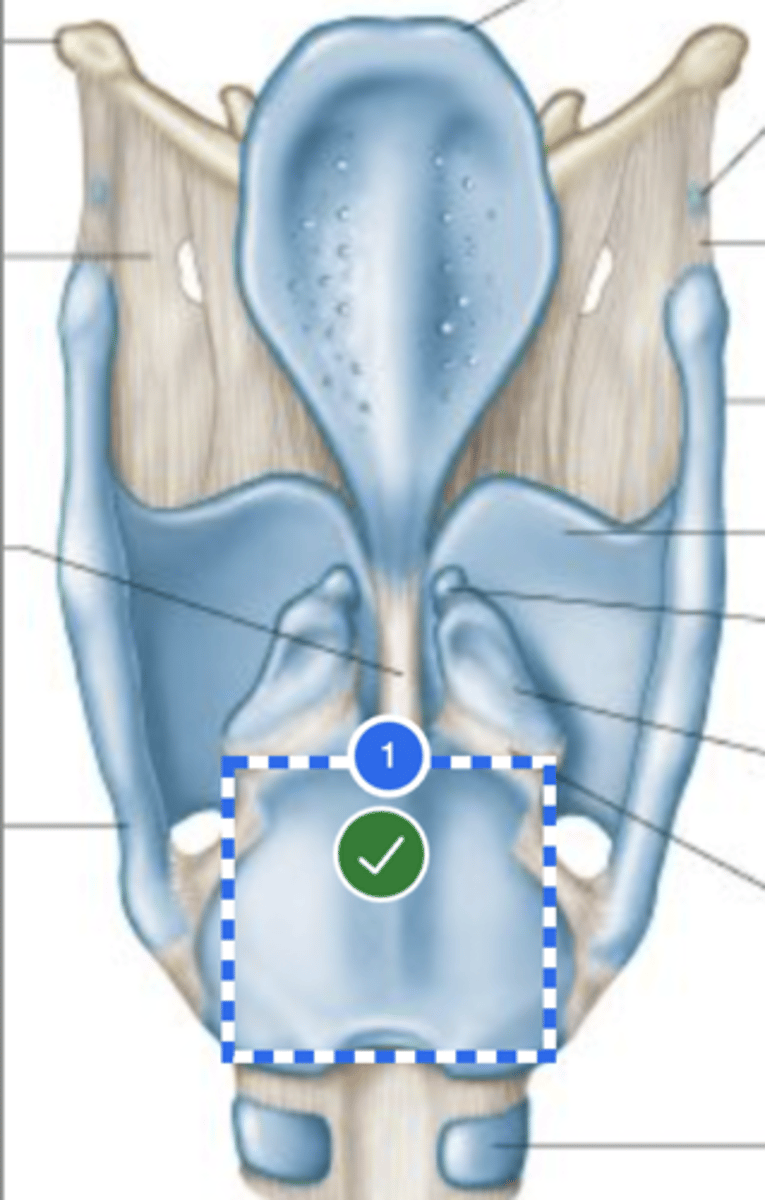
Label Right arytenoid (posterior view)
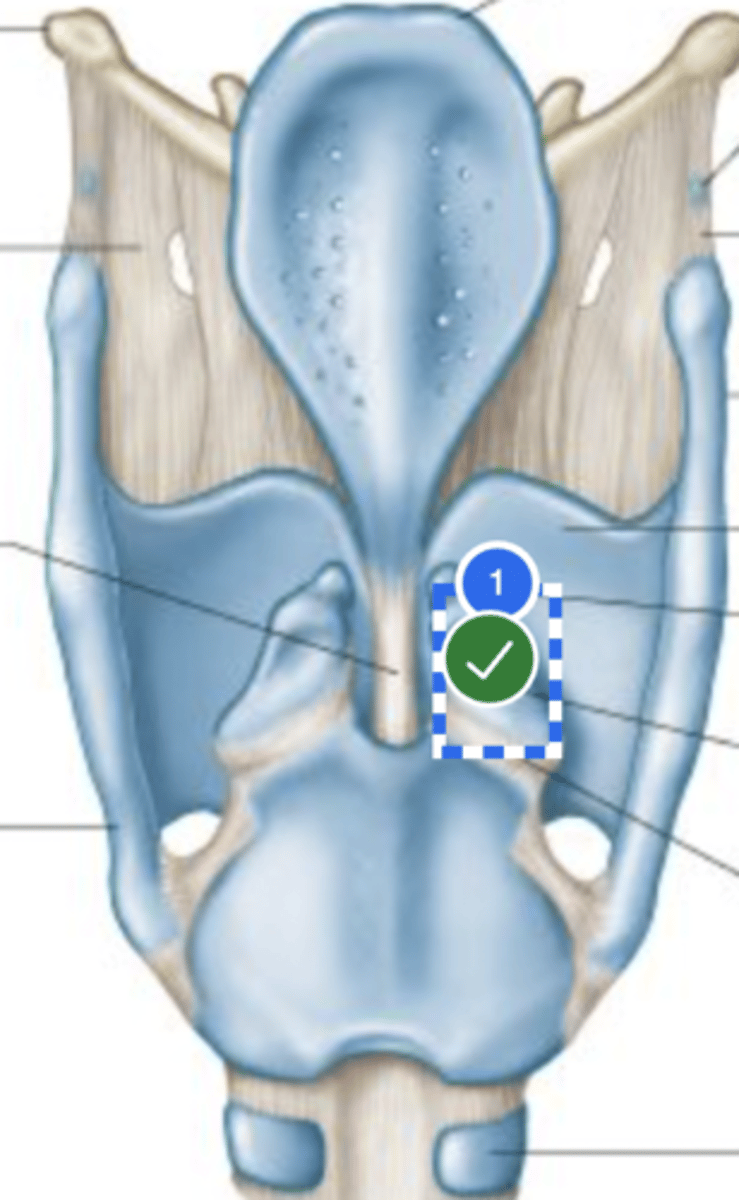
Label Left cricothyroid joint (posterior view)
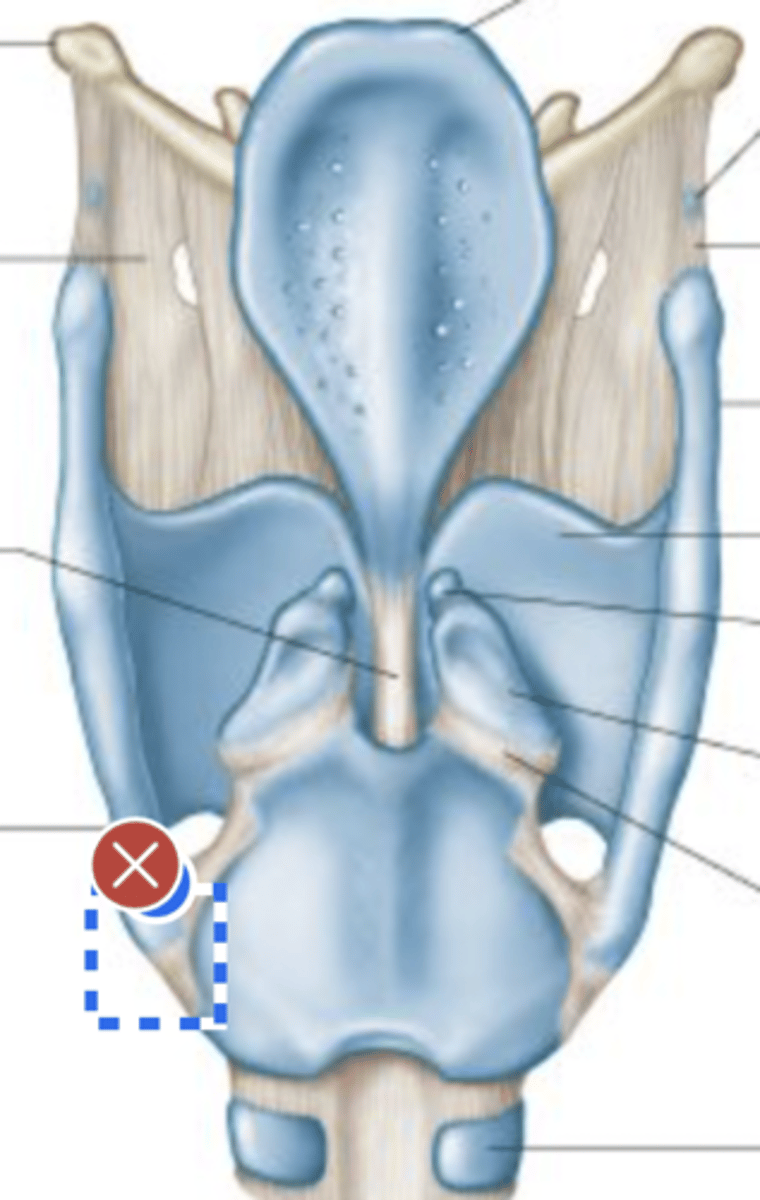
Label Laryngeal surface of epiglottis (posterior view)
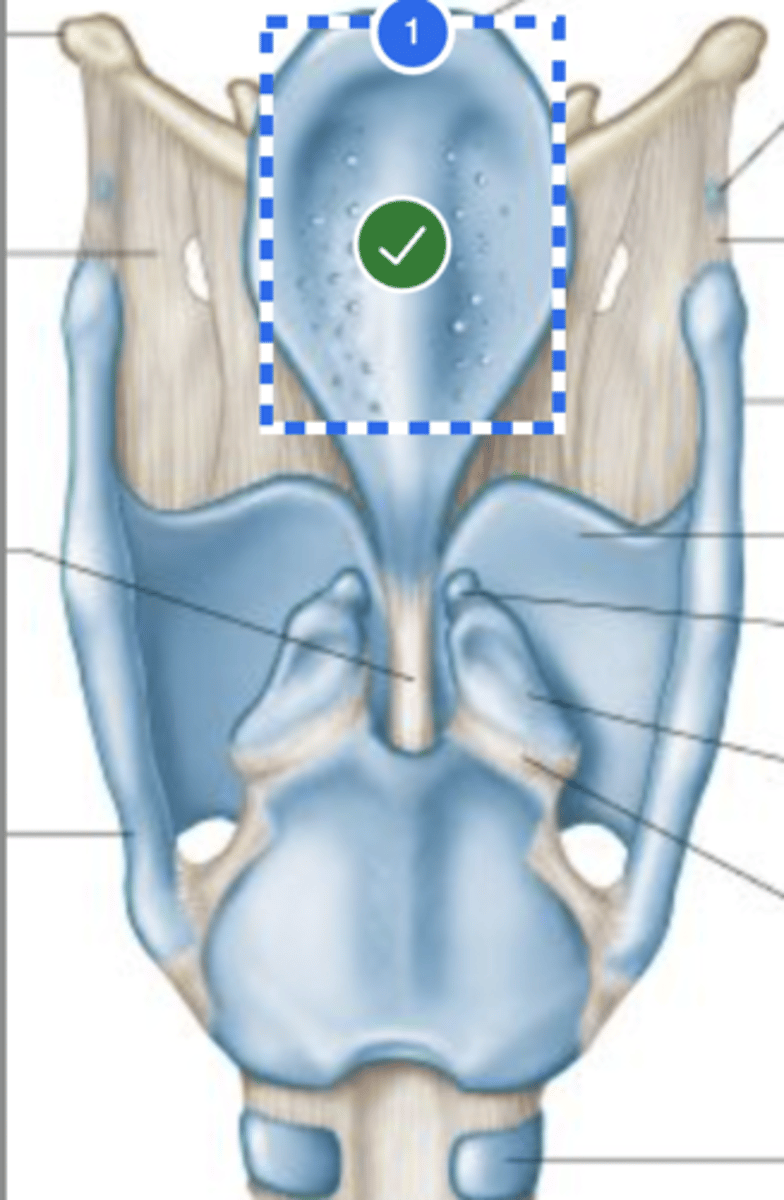
Label 1st tracheal ring (posterior view)
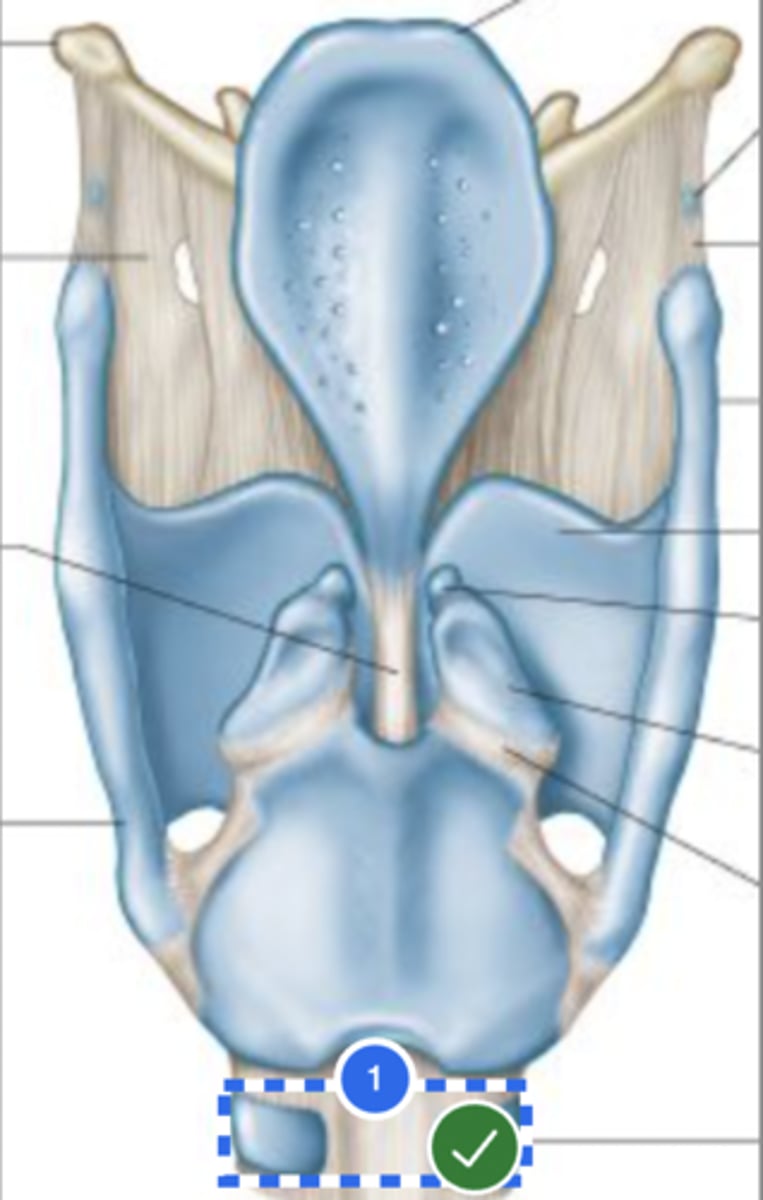
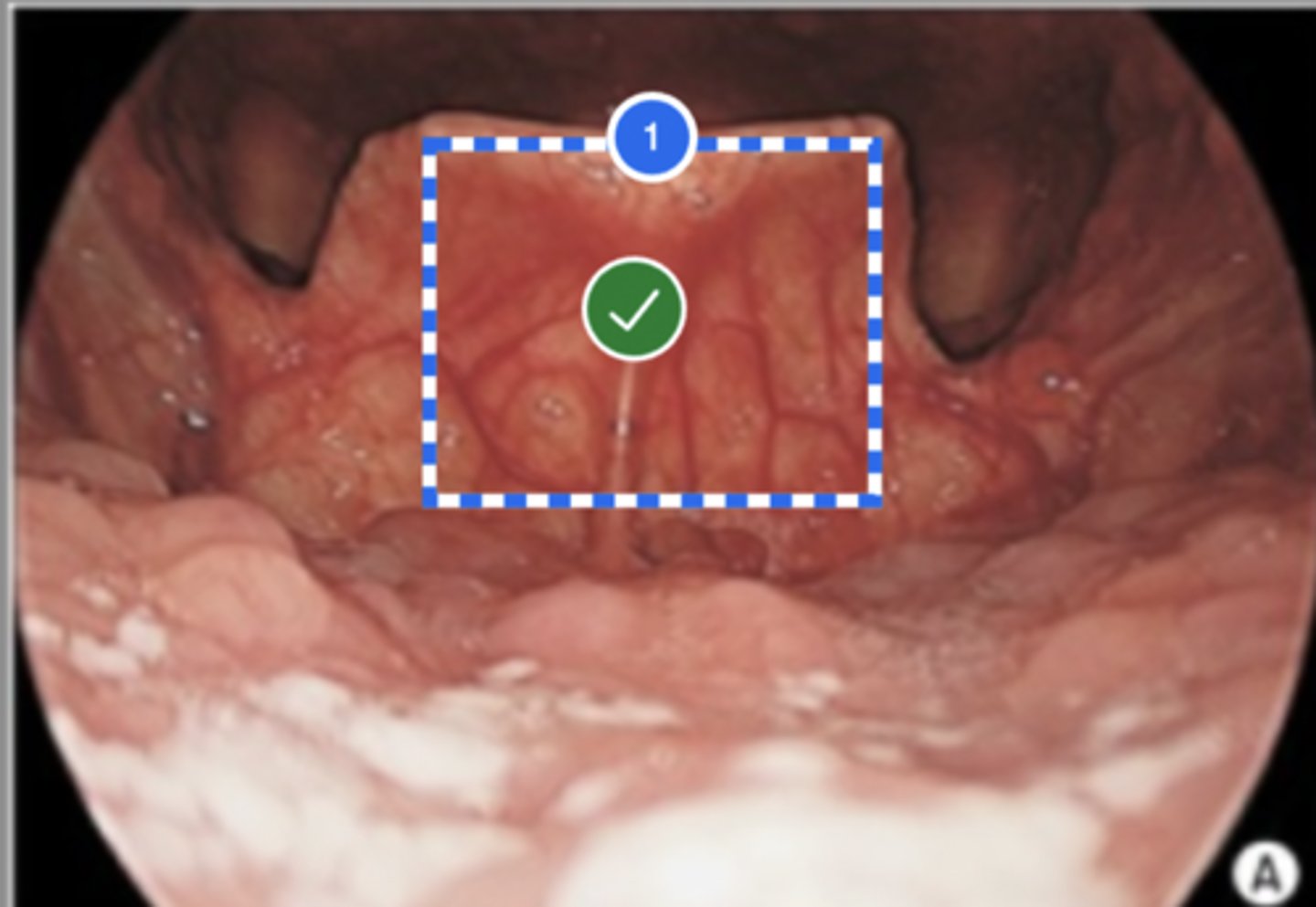
Label Laryngeal surface of epiglottis (superior view)
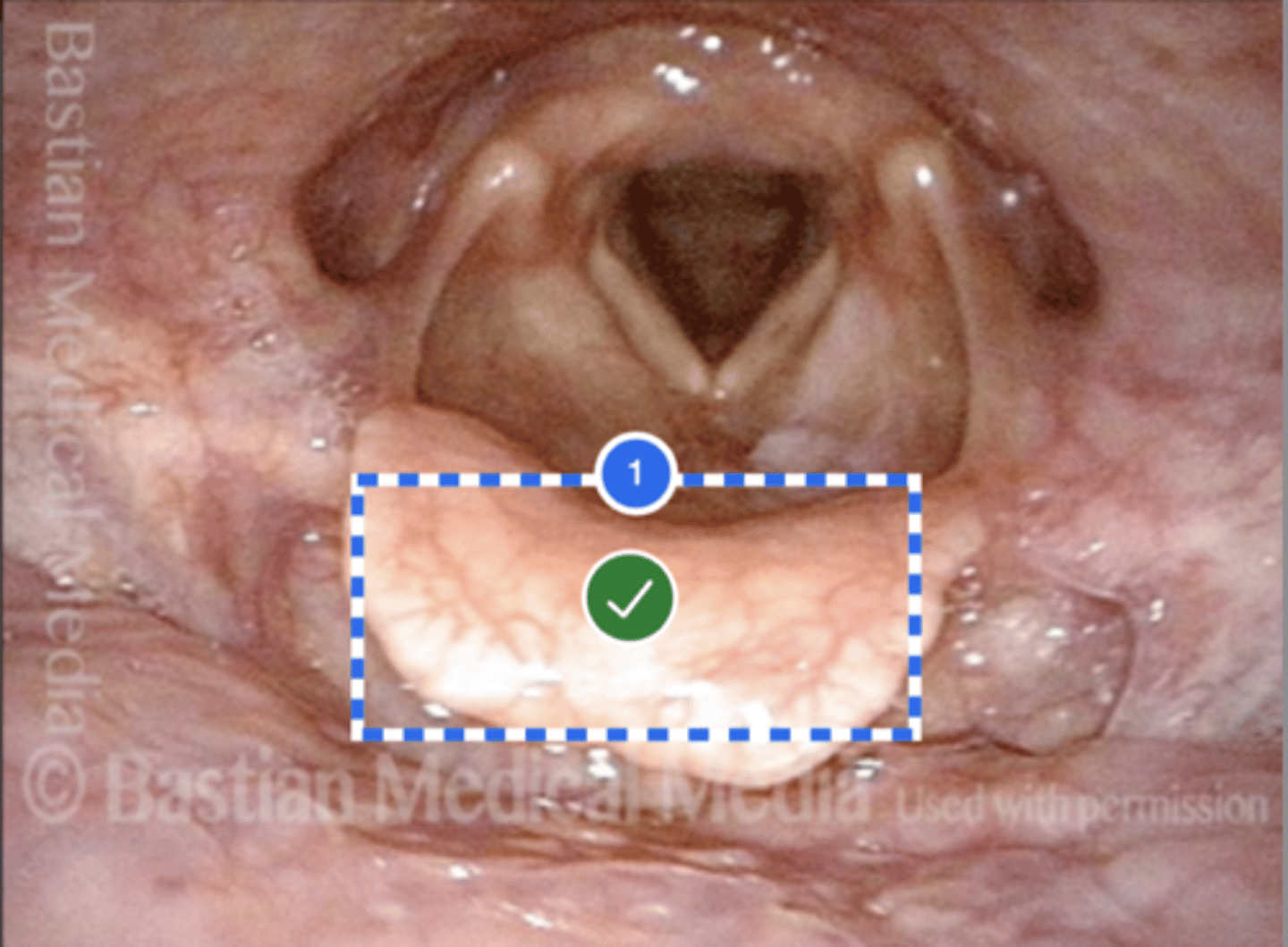
Label (Right) Lateral pharyngeal wall (superior view)
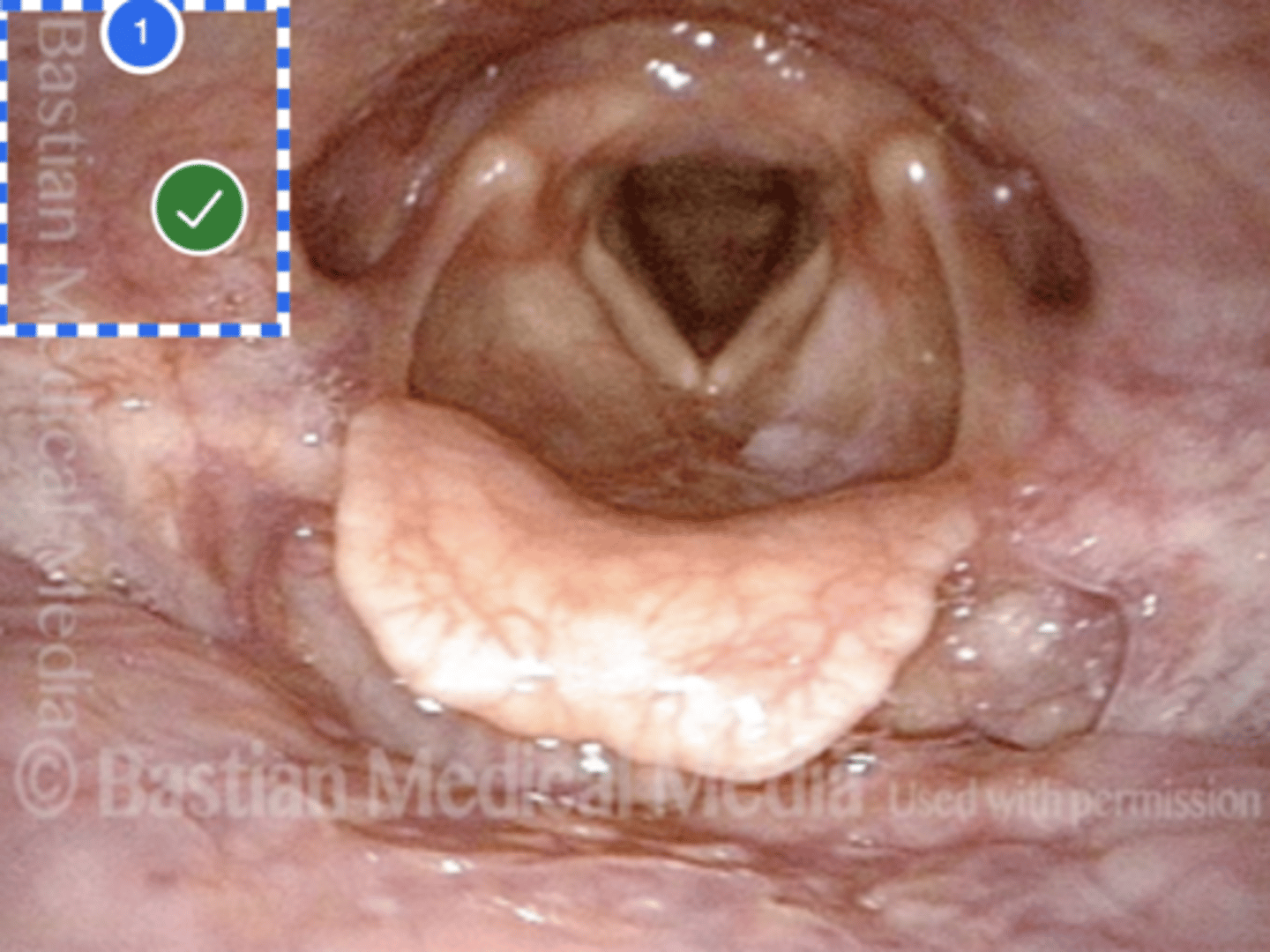
Label Base of tongue (superior view)
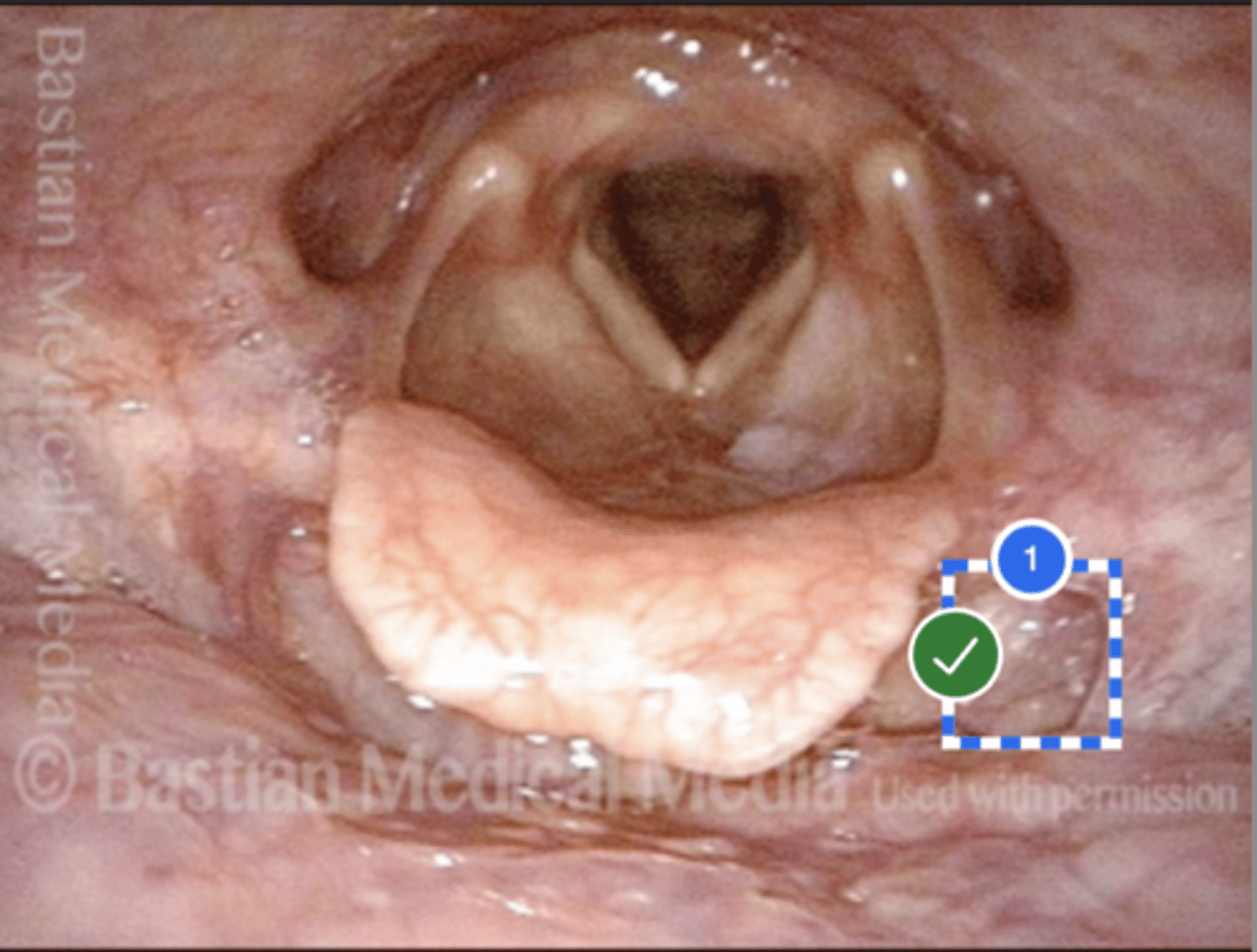
Label left vallecula (superior view)
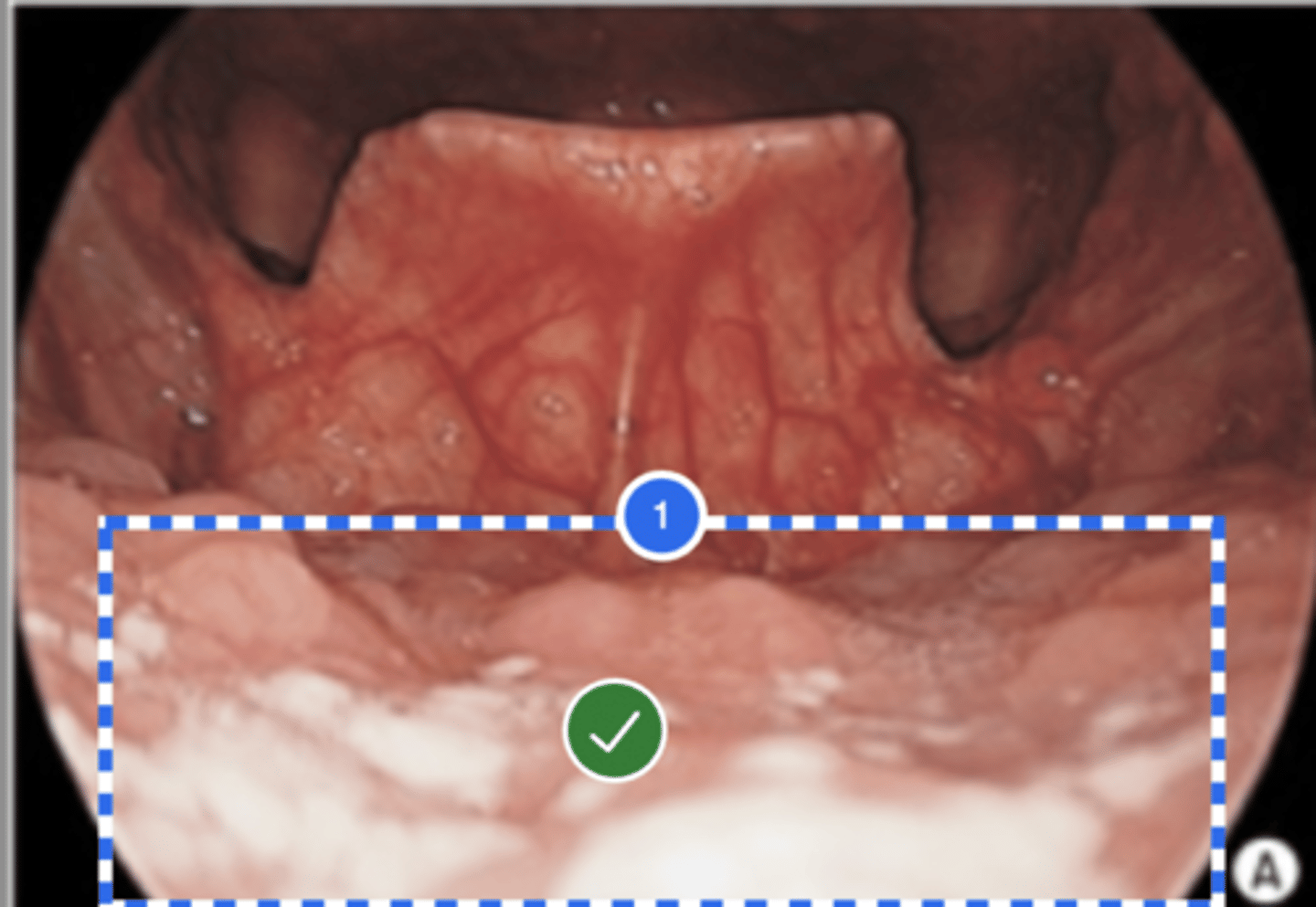
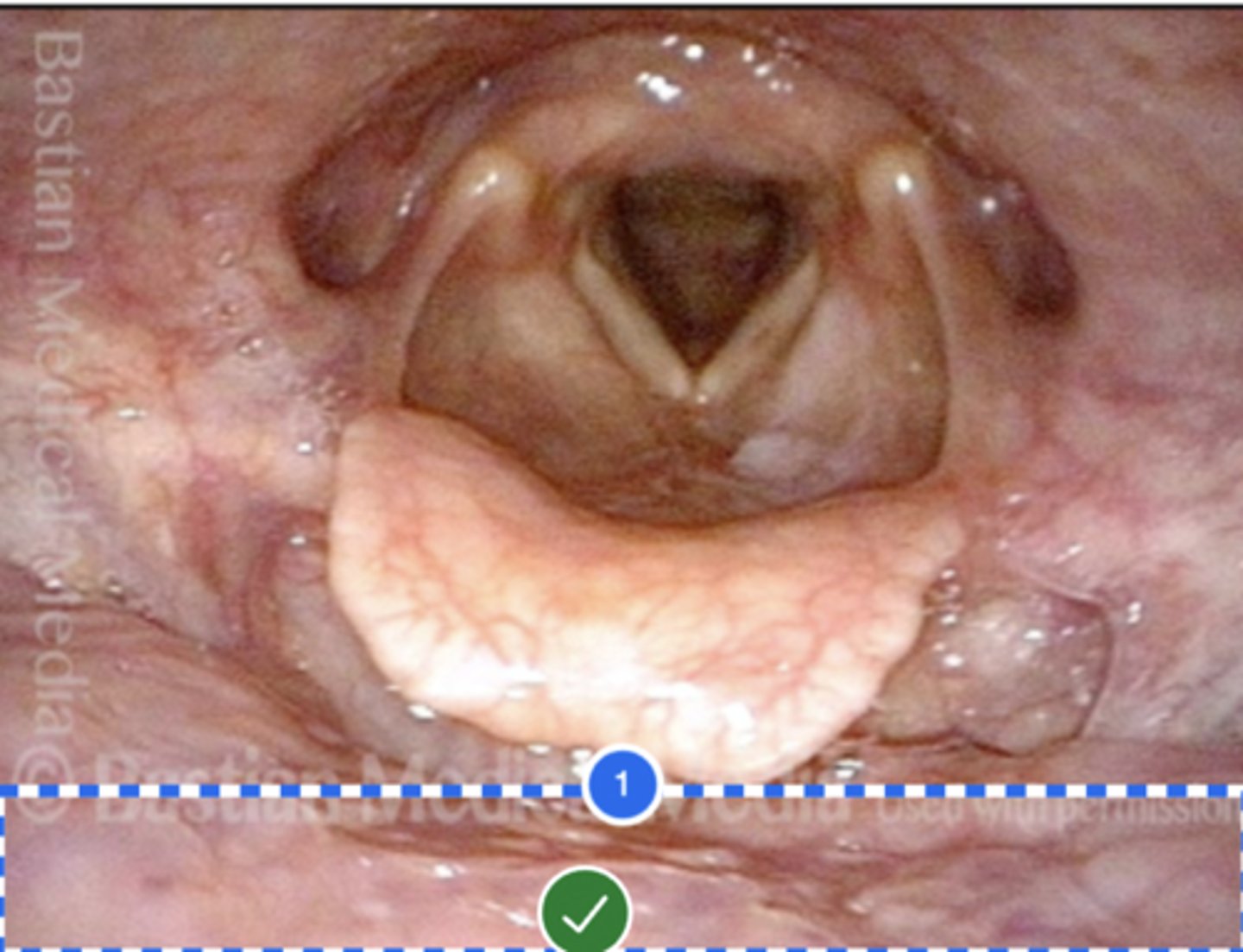
Label Posterior Pharyngeal Wall
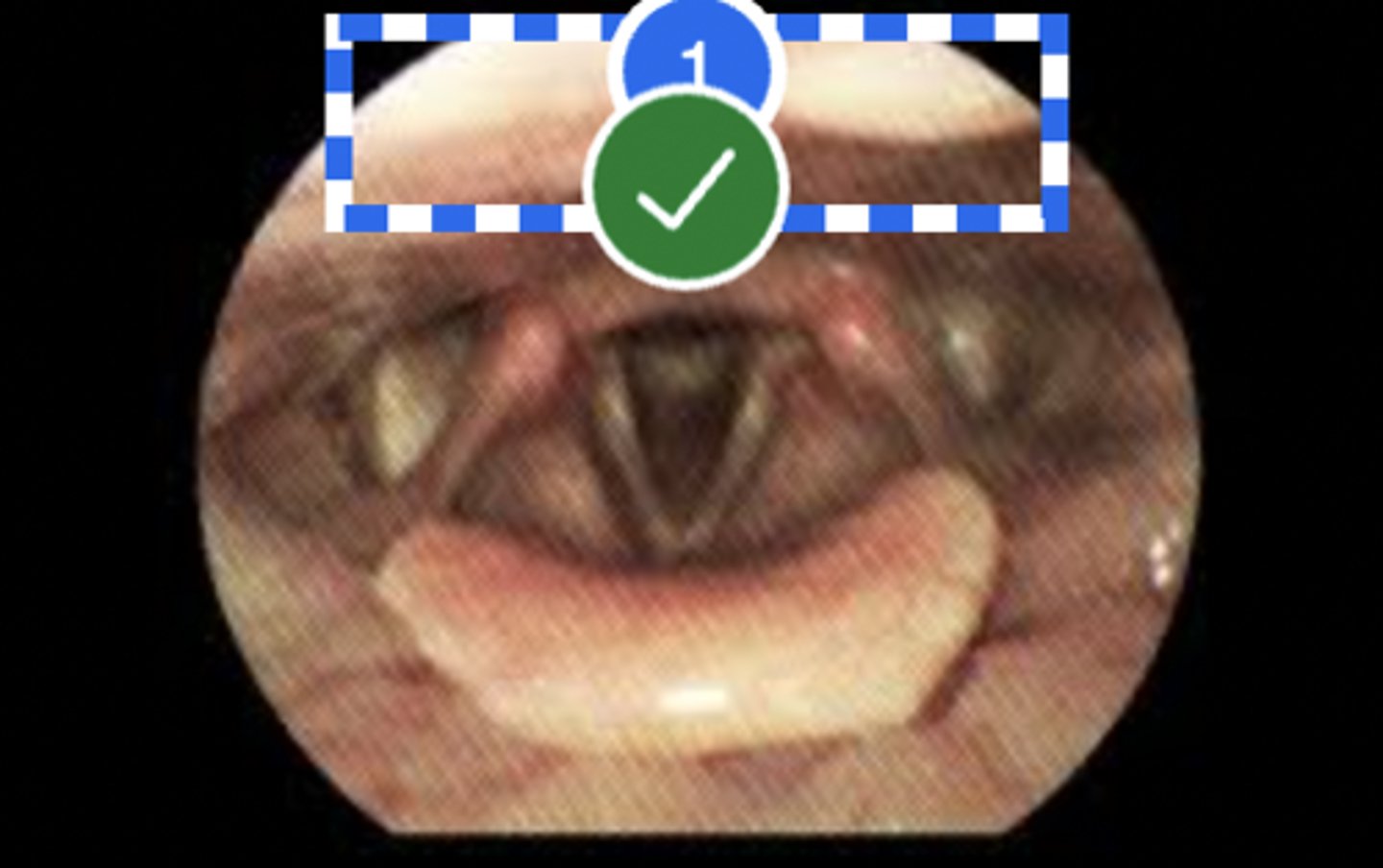
Label Laryngeal surface of epiglottis (superior view)
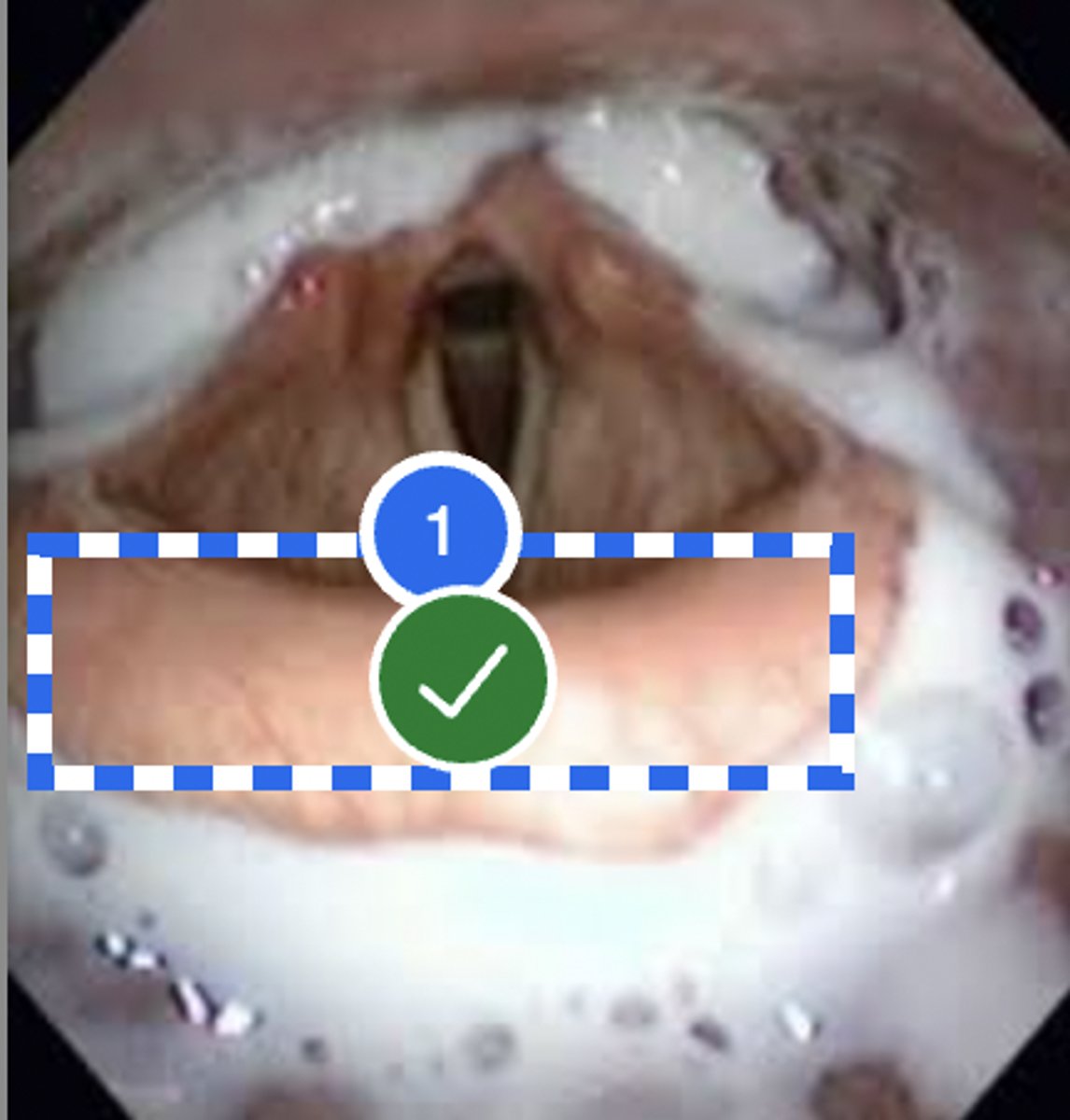
During the oral-mech exam, I gently stroked the patient's posterior 1/3rds of the tongue with a cotton swab dipped in sugar water. But the patient neither sensed the touch nor taste.
Which cranial nerve is affected?
CN-IX
During the oral mech exam, I gently stroked the patient's anterior 2/3rds of the tongue using a sugar water swab. The patient sensed the taste but not the touch.
Which cranial nerve is affected?
CN-V
The primary muscle which helps for velopharyngeal closure during pharyngeal phase is:
Palatopharyngeus (which makes up the posterior faucial arch)
The primary muscle for velar elevation during oral phase:
Palatoglossus (which makes up the anterior faucial arch)
The motor innervation of all palatal muscles is carried by pharyngeal plexus, except ___________ muscle by ______ cranial nerve.
Tensor veli palatini, CN-V
Sensory innervation of palate: CN- ___________
V
Sensory innervation of faucial arches: CN- ______
IX
Muscles of pharynx are:
3 pairs of constrictor muscles: superior, middle, inferior
3 pairs of longitudinal muscles: salpingopharyngeus, palatopharyngeus, stylopharyngeus
I want to show you how both pharyngeal constrictor and longitudinal muscles attached to each other (intertwined).
Answer: Just label anywhere on the constrictors.

See how the middle constrictor muscle runs into______? That is the ________
hyoid bone
--> That is the reason pharyngeal constriction/contraction also assists with hyolaryngeal elevation.
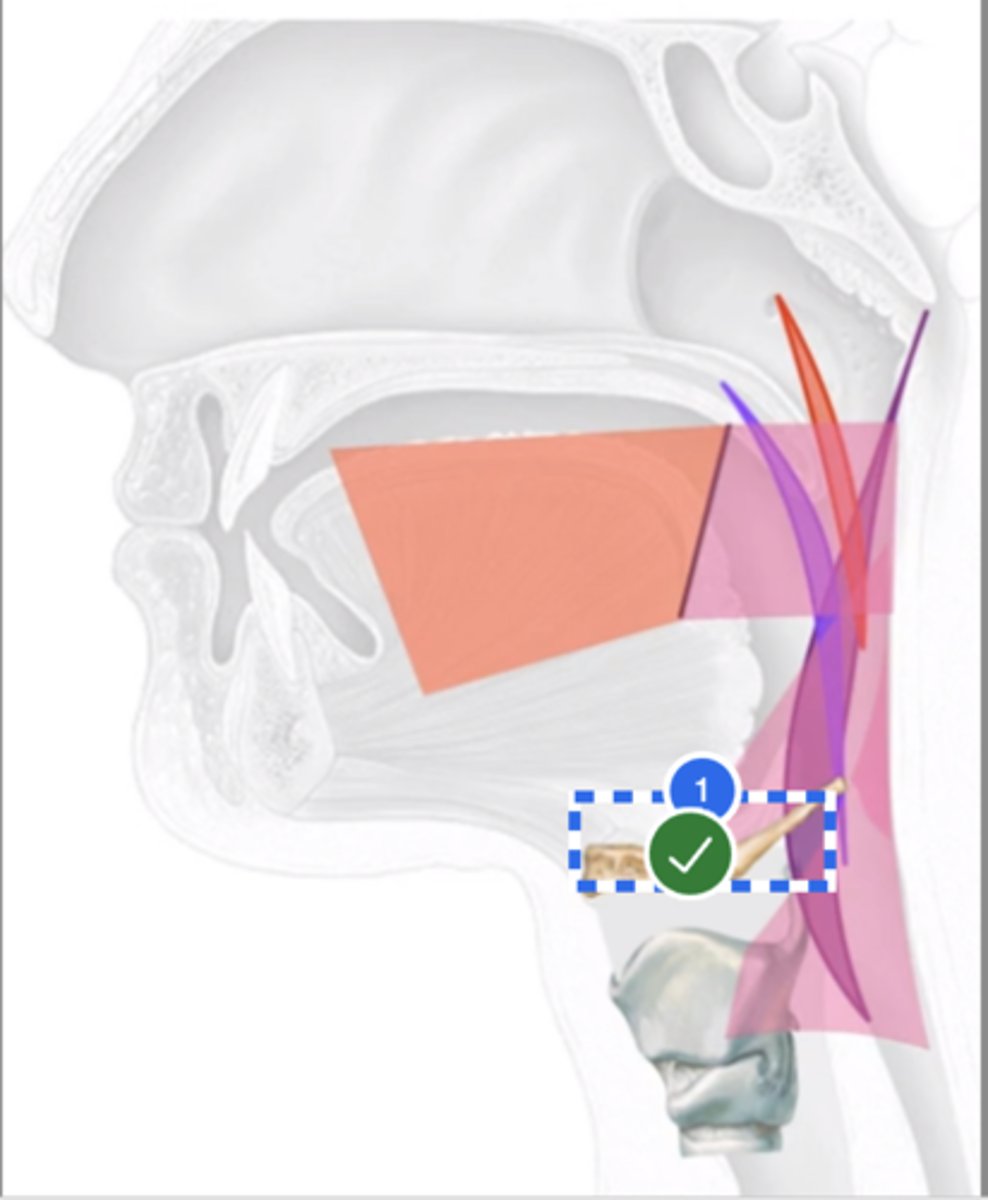
Below is true about pharyngeal muscle function:
1. contraction of pharyngeal constrictor muscles reduce the diameter of pharynx (constriction)
2. contraction of longitudinal pharyngeal muscles shorten the pharynx
3. contraction of pharyngeal constrictor and longitudinal muscles constricts and shortens the pharynx respectively
Sensory innervation of nasopharynx
CN IX