Web Filtering
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Web Filter Activation
FortiGate looks for the HTTP GET request to collect URL information and perform web filtering
In HTTP, the domain name and URL are separate parts
If you filter by domain, sometimes it blocks too much so you want to be specific and block by URL
Flow-Based Inspection
Default
Examines the files as they passes through FortiGate, original traffic is not altered and therefore advanced features that modify content such as safe search enforcement are not supported
Advantages: The user sees a faster response time for HTTP requests and less chance of a time-out error caused by the server at the other end responding slowly
Disadvantages: Not all security features are available and fewer actions are available depending on the website categorisation
Proxy-Based Inspection
Transparent proxy because at the IP layer, FortiGate is not the destination address but FortiGate does intercept the traffic
FortiGate buffers traffic and examines it as a whole, before determining an action, examining more points of data
The proxy analyses the headers and may change the headers such as HTTP host and URL for web filtering
If a security profile decides to block, the proxy can send a replacement message adding latency to the overall transmission speed
SSL Certificate Inspection
With this method, FortiGate doesn’t decrypt or inspect encrypted traffic and only the initial unencrypted SSL handshake
If the SNI field exists, FortiGate uses it to obtain the FQDN to rate the site, and if not, it gets from the CN field of the server certificate
In some cases, the CN server name might not match the requested FQDN
SSL certificate inspection only works with web filtering, because the full payload does not need to be inspected
FortiGuard Category Filter
Rather than block or allow websites individually, it looks at the category rated on a website and takes action based on the category
This is a live service that requires an active contract, validating the connections to the FortiGuard network
FortiGate reports a rating error for every rating request made
In addition, by default, FortiGate blocks web pages that return a rating error but this can be changed
You can configure FortiManager to act as a local FortiGuard server, so you must download the databases to FortiManager and configure FortiGate to validate the categories against FortiManager instead of FortiGuard
You can enable the FortiGuard category filtering on the web filter profile and it can be customisable
The default actions are Allow, Monitor, Block, Warning and Authenticate
Monitor allows access and logs it as well and can configure a quota in proxy-based inspection
Quota
Allow daily access for a specific length of time or bandwidth
Once the daily quota is reached, traffic is blocked
Can be applied to Monitor, Warning and Authenticate
Only in proxy-based inspection
Warning and Authenticate
Warning
Informs users that the requested website is not allowed by the internet policies, however, the ability to continue is given
You can customise the warning interval, such as the time for it to display the message again
Authenticate
Blocks the requested websites unless the user provides credentials
FortiGate supports local and remote authentication using LDAP, RADIUS and so on for web filtering authentication
To do this, define Users and Groups first
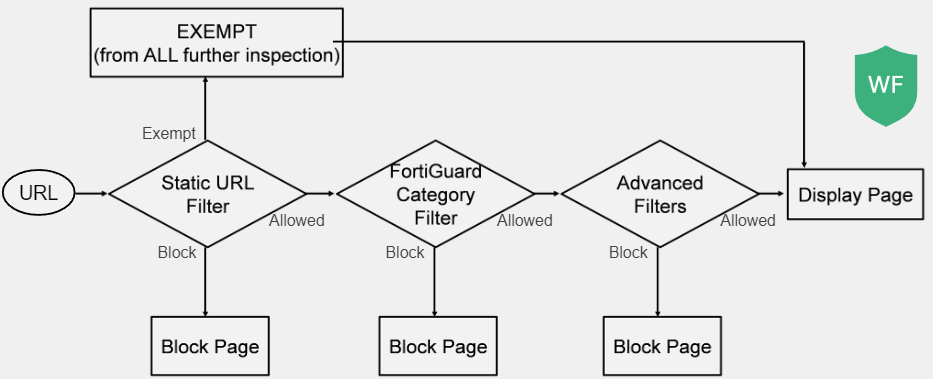
Configure URL Filter
Static URL filtering is another web filter feature, for more granularity
Configured URLs here are checked from top to bottom against the visited websites and perform a configured action
Exempt: Allows the traffic to bypass all inspections
Block: Denies the attempt and users receive a message
Allow: Permits access, but is passed to the remaining security operations
Monitor: Allows the traffic while creating log entries and is still subject to all other inspections
To find the exact match, there are 3 pattern types: Simple, Regular Expressions and Wildcard
HTTP Inspection Order
1. Local Static URL filter
2. FortiGuard category filter
3. Advanced Filters
If there is no match, FortiGate goes to the next step
FortiGuard Connection Troubleshooting
Verify the connection to the FortiGuard servers in the CLI, looking at the ones you can connect to as well as: Weight, RTT, Flags, TZ, FortiGuard-requests, Curr Lost and Total Lost
By default, FortiGate is configured to enforce the use of HTTPS port 443 to perform live filtering with FortiGuard or FortiManager
By disabling the FortiGuard anycast setting on the CLI, other ports and protocols are available such as UDP ports 443, 53 or 8888
Enable Web Filter cache to reduce requests to FortiGate reducing the amount of time to establish a rating and memory lookup is quicker
Web Filter Troubleshooting Issues
Make sure that the SSL inspection field includes at least one profile with and SSL certification inspection method
Make sure that the correct web filter profile is applied to the firewall policy
Verify the inspection mode setting with the feature set in the corresponding web filter profile
Web Filter Log
Use to confirm the correct configuration and web filtering behaviour
You can also view the raw log data by clicking the download icon at the top of the GUI, which gives you a plain text file in a syslog format