Classes of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Fast-twitch fibers
Muscle fibers with high myosin ATPase activity and proceed rapidly through crossbridge cycles.
Location of Fast-twitch fibers
in muscles that must move body parts rapidly, such as those that move the eyeballs
Slow-twitch fibers
Fibers with low myosin ATPase activity and proceed through crossbridge cycles more slowly.
Location of Slow-twitch fibers
in muscles that require slow, sustained contractions, such as the postural muscles of the back.
Type I fibers (Slow oxidative fibers, red muscle)
slow-twitch fibers that are small to intermediate in diameter, contract more slowly and less forcefully than other fibers, but they can maintain extended periods of contraction. This ability requires the continual generation of large quantities of ATP via oxidative catabolism; for this reason
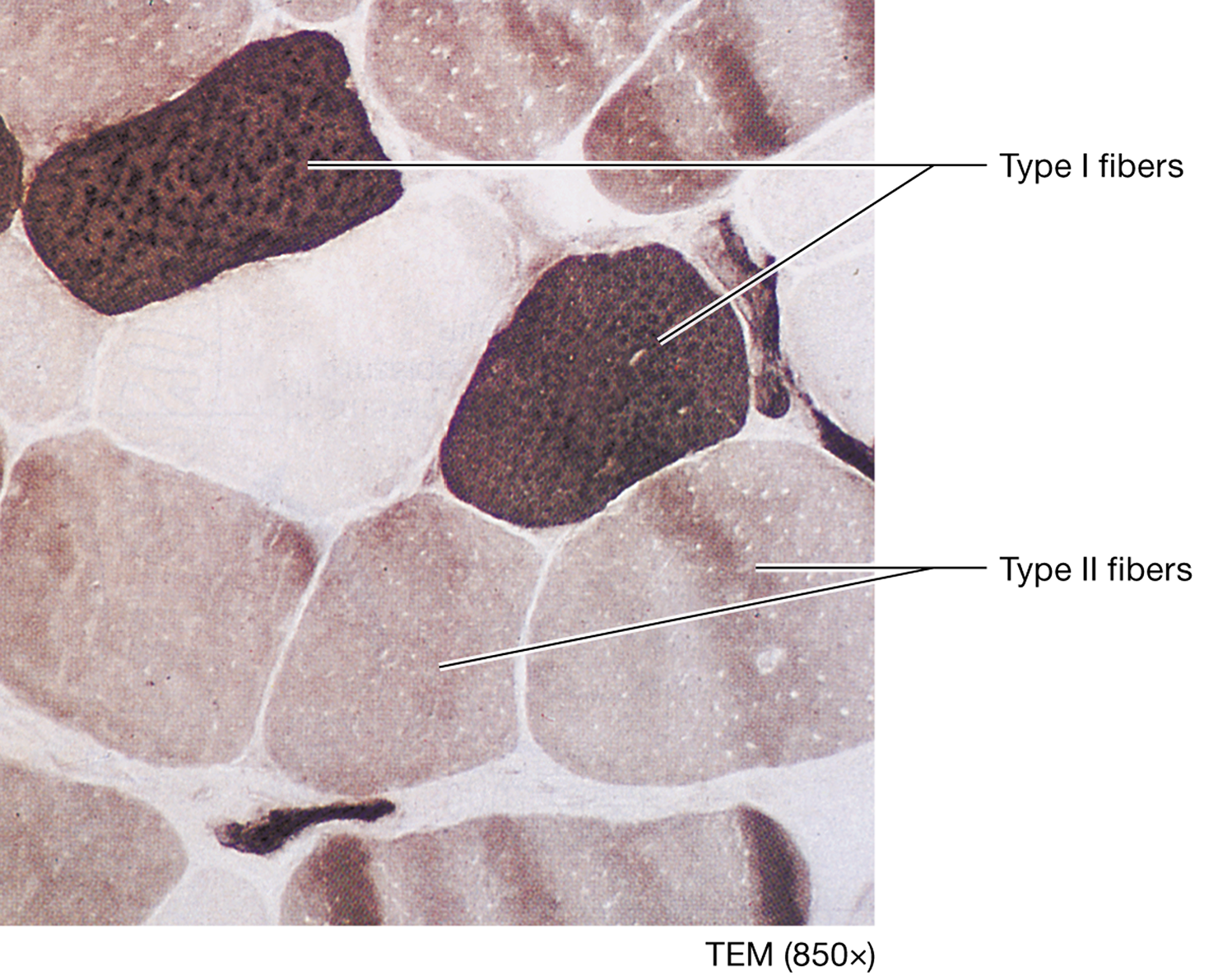
How do Type I fibers support oxidative catabolism?
contract more slowly and less forcefully than other fibers, but they can maintain extended periods of contraction. This ability requires the continual generation of large quantities of ATP via oxidative catabolism; for this reason
Type II fibers (white muscle)
fast-twitch fibers that are often larger in diameter and contract more rapidly than type I fibers, but they are quickly fatigued, rely more heavily on glycolytic energy sources, and they have less myoglobin, fewer mitochondria, and a less extensive blood supply than type I fibers
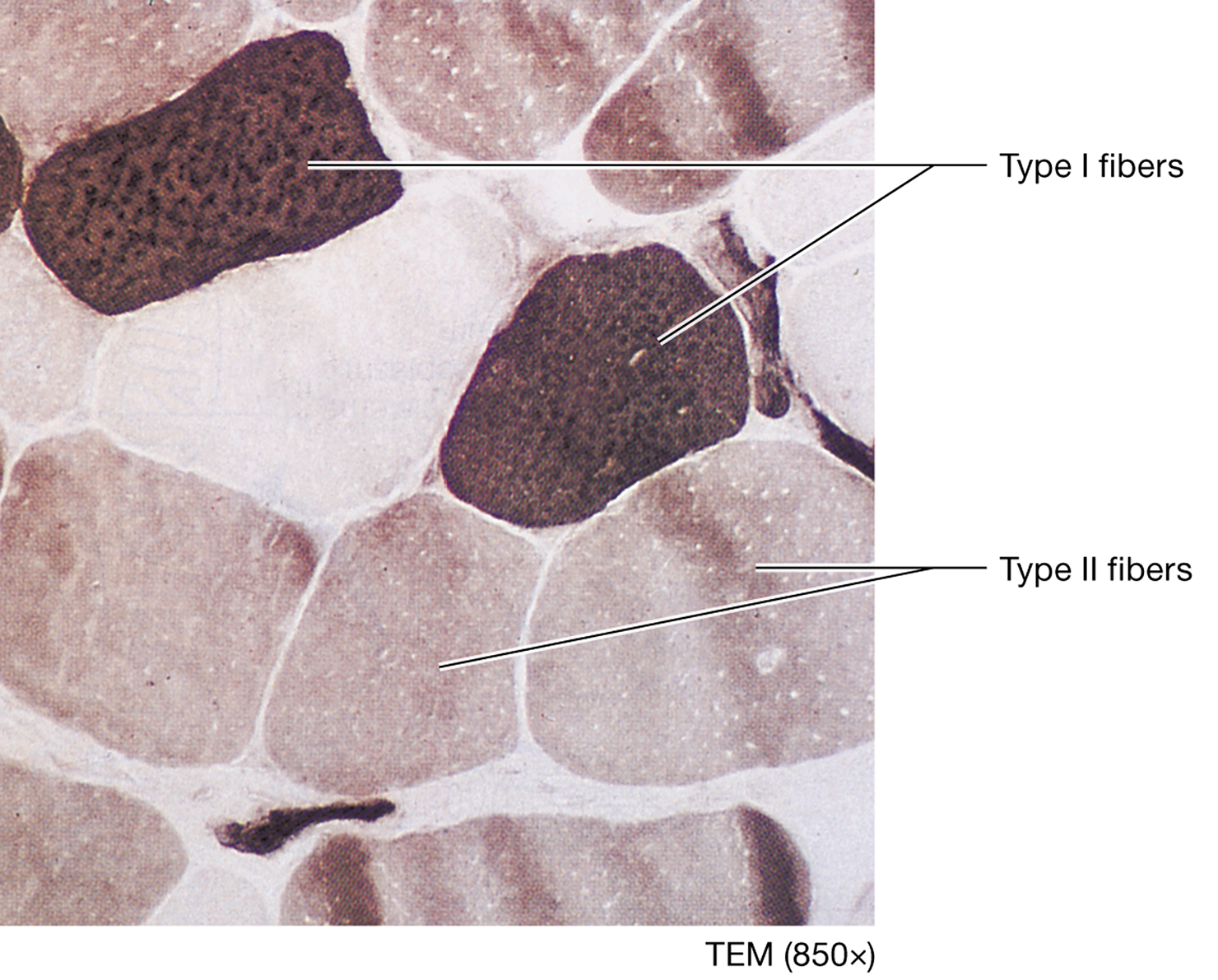
Types of Type II fibers
Fast oxidative glycolytic (IIa)
Fast glycolytic (IIx)
Fast oxidative glycolytic (IIa)
have progressively faster, stronger twitches and rely increasingly on glycolytic energy sources
Fast glycolytic (IIx)
has extremely fast, powerful twitches and using glycolytic catabolism almost exclusively