Biology paper 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
How would an endotherm respond to an increase in temperature
dilation of arterioles near the surface of the skin
2
New cards
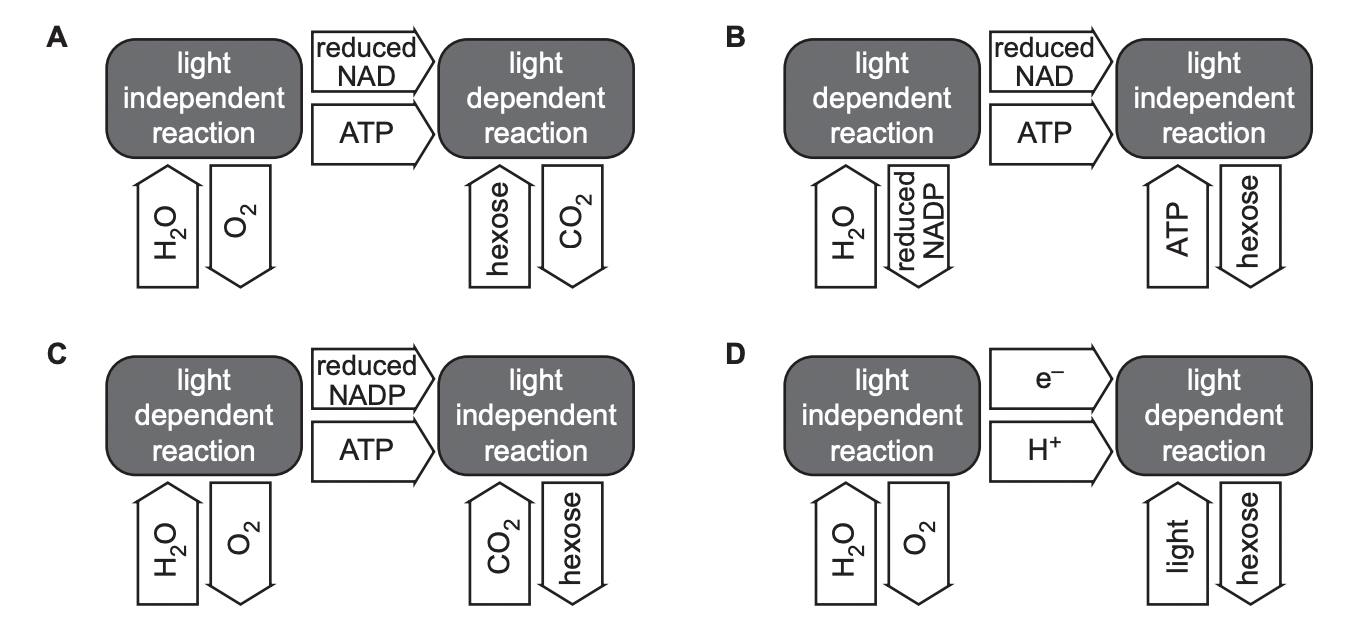
Which diagram correctly summarises photosynthesis
C
3
New cards
Which occurs in the nucleus of a cell
a. synthesis of enzymes
b. synthesis of RNA
c. modification of polypeptides
d. synthesis of carbohydrates
a. synthesis of enzymes
b. synthesis of RNA
c. modification of polypeptides
d. synthesis of carbohydrates
b
4
New cards
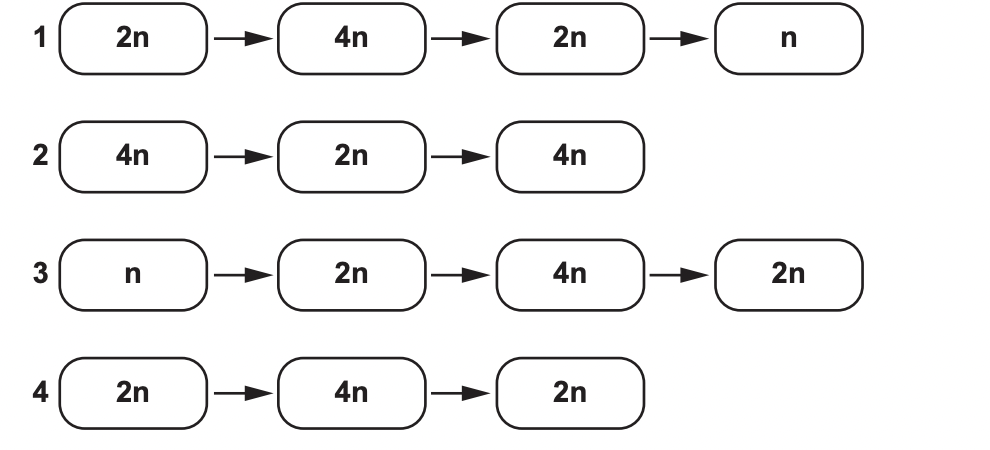
which correctly describes mitosis and meiosis in human cells
4 is mitosis, 1 is meiosis
5
New cards
Which of the following describes a feature of peritoneal dialysis
1. urea and mineral ions pass into the tissue fluid
2. blood is passed over an artificial membrane to remove toxins
3. the patient receives immunosuppressant medication
1. urea and mineral ions pass into the tissue fluid
2. blood is passed over an artificial membrane to remove toxins
3. the patient receives immunosuppressant medication
only 1
6
New cards
describe the way oxygen is transferred into the blood at the gills
blood and water flow in a countercurrent system with a constant conc gradient between them
7
New cards
what makes hCG able to be detected in urine
has a molecular mass of less than 69,000
8
New cards
The hormone ecdysone is synthesised in the prothoracic glands found in the upper thorax of some invertebrates and is released into haemolymph. It is then transported to cells near the surface of the body and causes the loss of the exoskeleton so that a new exoskeleton can form.
Which of the following statements explains how ecdysone is able to act on cells near the surface of the body?
1 Ecdysone is synthesised by specialised neurosecretory cells.
2 Ecdysone is soluble in haemolymph because it is a polar molecule.
3 Ecdysone is complementary to cell surface receptors on cells throughout the body of some invertebrates.
Which of the following statements explains how ecdysone is able to act on cells near the surface of the body?
1 Ecdysone is synthesised by specialised neurosecretory cells.
2 Ecdysone is soluble in haemolymph because it is a polar molecule.
3 Ecdysone is complementary to cell surface receptors on cells throughout the body of some invertebrates.
2 and 3
9
New cards
describe process of adhesion
attraction of water molecules to the impermeable wall of the xylem tissue
10
New cards
Bird droppings are known as guano because they contain a high proportion of guanine. Unlike mammals, birds excrete nitrogenous waste as guanine instead of urea. Guanine is synthesised from ammonia in the liver. The following statements relate to guanine:
1 ammonia is more toxic than guanine
2 urea is more soluble in water than guanine
3 guanine has a high proportion of nitrogen
1 ammonia is more toxic than guanine
2 urea is more soluble in water than guanine
3 guanine has a high proportion of nitrogen
1, 2 and 3
11
New cards
The commercially grown tobacco plant, Nicotiana rustica, has many pests. One such insect pest is Manduca sexta, which causes damage to the stems and leaves of N. rustica.
The tiny wasp Cotesia congregata lays its eggs inside the body of M. sexta. When the larvae develop they feed on the body of the host, eventually killing it.
N. rustica produces a volatile organic compound called volicitin when its leaves are damaged. Volicitin attracts C. congregata at high concentrations.
Why does N. rustica releases volicitin?
The tiny wasp Cotesia congregata lays its eggs inside the body of M. sexta. When the larvae develop they feed on the body of the host, eventually killing it.
N. rustica produces a volatile organic compound called volicitin when its leaves are damaged. Volicitin attracts C. congregata at high concentrations.
Why does N. rustica releases volicitin?
to reduce herbivory in N. rutica
12
New cards
Mistletoe is a plant parasite that lives on the stems of other plants.
It survives by removing water and assimilates from the host plant.
The mistletoe binds to the stem of the host plant and grows a specialised root-like tissue called a haustorium that attaches to different tissues in the stem.
One species of mistletoe, Viscum minimum, contains no chloroplasts.
Why does V. minimum does not need chloroplasts?
It survives by removing water and assimilates from the host plant.
The mistletoe binds to the stem of the host plant and grows a specialised root-like tissue called a haustorium that attaches to different tissues in the stem.
One species of mistletoe, Viscum minimum, contains no chloroplasts.
Why does V. minimum does not need chloroplasts?
the haustorium of V. minimum attaches to sieve tube elements
13
New cards
Many insects such as moths and bumblebees are insulated with scales and hair, and are known as facultative endotherms.
Their metabolism during flight can cause the temperature of the flight muscles to increase 20–30 °C above the external temperature.
(i) Using the information provided, explain why many moths and bumblebees are described as endothermic.
(ii) It is more difficult for moths and bumblebees to maintain their body temperature than for mammals and birds to maintain their body temperature. Explain why.
Their metabolism during flight can cause the temperature of the flight muscles to increase 20–30 °C above the external temperature.
(i) Using the information provided, explain why many moths and bumblebees are described as endothermic.
(ii) It is more difficult for moths and bumblebees to maintain their body temperature than for mammals and birds to maintain their body temperature. Explain why.
(i)
scales and hair help to reduce heat loss
generate heat from respiration
\
(ii)
insects have a larger SA: V ratio
insects have a greater rate of heat loss
mammals and birds have more effective insulation
scales and hair help to reduce heat loss
generate heat from respiration
\
(ii)
insects have a larger SA: V ratio
insects have a greater rate of heat loss
mammals and birds have more effective insulation
14
New cards
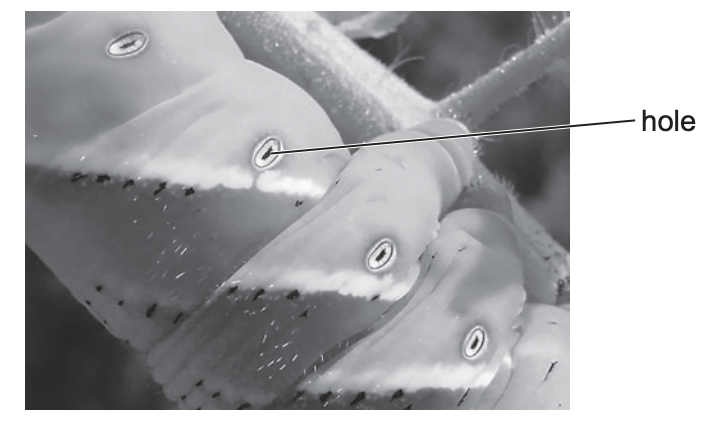
Air is taken into tiny holes along the side of the body of a caterpillar
\
name these holes
\
name these holes
spiracles
15
New cards
Fluid is found in the tubes responsible for gaseous exchange in insects. Name this fluid.
tracheal fluid
16
New cards
Outline the reasons why insects and other animals need well-developed transport systems
1. high metabolic demands
2. need rapid oxygen supply
3. diffusion not sufficient
4. to maintain steep diffusion gradients
5. SA:V ratio is low
17
New cards
What guidelines should a student follow to ensure their diagram is presented clearly and accurately
1. large size
2. title
3. labels outside diagram
4. label lines should not cross over others
5. no shading
6. state magnification
7. correct proportion
8. use plain paper
9. continuous lines
10. use a sharp pencil
11. use ruled label lines
12. include a scale bar
18
New cards
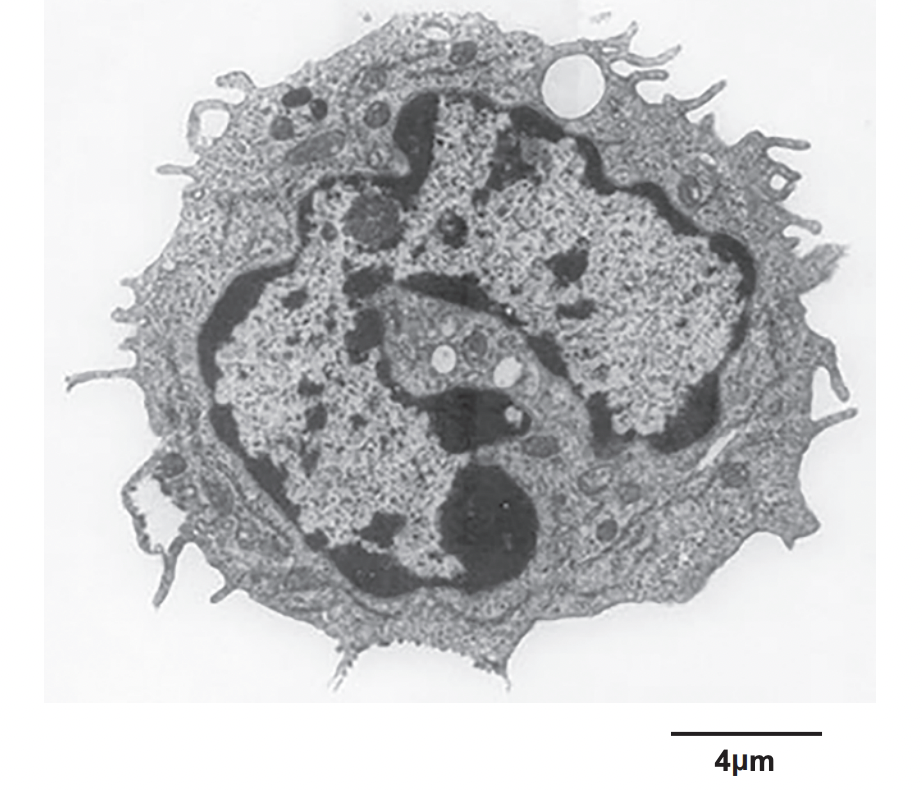
what type of microscope has been used to obtain this image
TEM
* 2D image
* internal details visible
* organelles visible
* high magnification
* high resolution
* 2D image
* internal details visible
* organelles visible
* high magnification
* high resolution
19
New cards
Light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature are all limiting factors in photosynthesis.
Explain what is meant by a limiting factor.
Explain what is meant by a limiting factor.
factor will determine the rate, when at lower/ sub-optimal level
20
New cards
Water can fill air spaces in the soil surrounding the roots. This prevents oxygen from reaching root hair cells. Using your knowledge of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, explain why overwatering can kill plants.
Aerobic respiration
* no oxygen so no aerobic respiration takes place
* no link reaction/ krebs cycle/ ETC/ oxidative phosphorylation
* no oxygen to act as the final electron acceptor
\
Anaerobic respiration
* only anaerobic respiration can occur
* only glycolysis occurs
* alcoholic fermentation occurs
* NAD regenerated
* pyruvate to ethanal to ethanol
* only 2 ATP
\
Consequences for plant
* ethanol is toxic
* alcoholic fermentation is irreversible
* less ATP produced
* less active transport
* root hair cells cannot take up mineral ions by active transport
* so plant cannot make proteins
* cannot generate water potential gradient
* water cannot be absorbed
* less photosynthesis
* no oxygen so no aerobic respiration takes place
* no link reaction/ krebs cycle/ ETC/ oxidative phosphorylation
* no oxygen to act as the final electron acceptor
\
Anaerobic respiration
* only anaerobic respiration can occur
* only glycolysis occurs
* alcoholic fermentation occurs
* NAD regenerated
* pyruvate to ethanal to ethanol
* only 2 ATP
\
Consequences for plant
* ethanol is toxic
* alcoholic fermentation is irreversible
* less ATP produced
* less active transport
* root hair cells cannot take up mineral ions by active transport
* so plant cannot make proteins
* cannot generate water potential gradient
* water cannot be absorbed
* less photosynthesis
21
New cards
Explain why water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with nitrate ions
water is polar
nitrate ions is charged
hydrogen bonds form between H on water and O on nitrate
nitrate ions is charged
hydrogen bonds form between H on water and O on nitrate
22
New cards
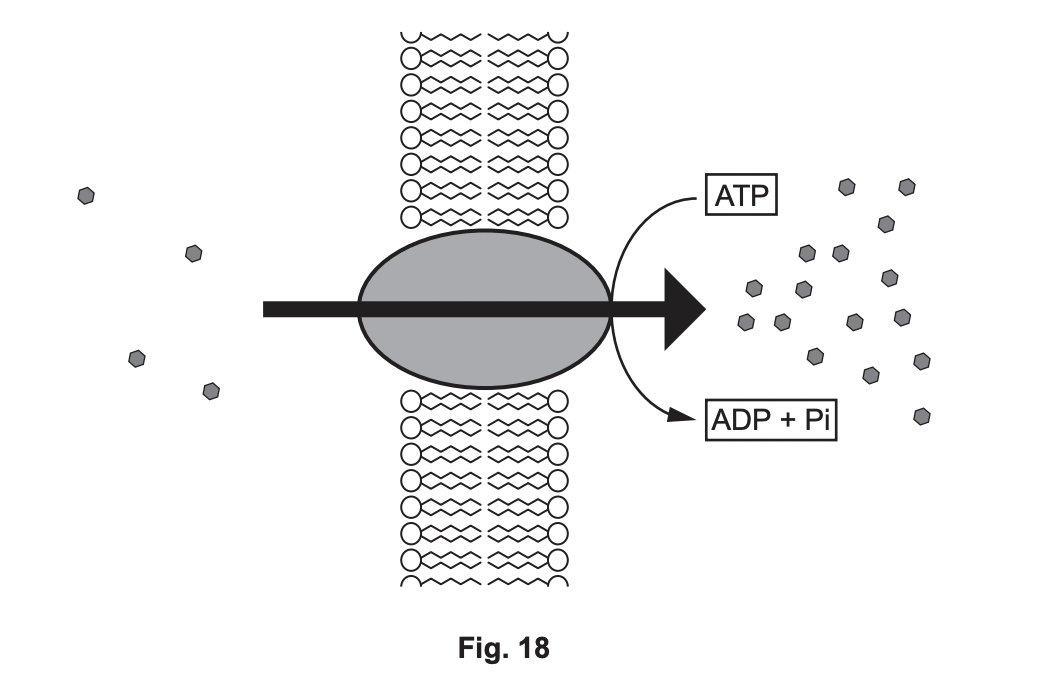
shows a process that occurs in the cell surface membrane of the endodermis in the root.
explain how the events shown in the diagram cause water to enter the endodermis
explain how the events shown in the diagram cause water to enter the endodermis
solutes enter against conc gradient
reduces water potential of endodermal cells
water moves by osmis
reduces water potential of endodermal cells
water moves by osmis
23
New cards
why is a plant leaf described as an organ
organ is a collection of tissues that carry out a role
\
leaves have epidermis, phloem, xylem, mesophyll
to carry out photosynthesis
\
leaves have epidermis, phloem, xylem, mesophyll
to carry out photosynthesis
24
New cards
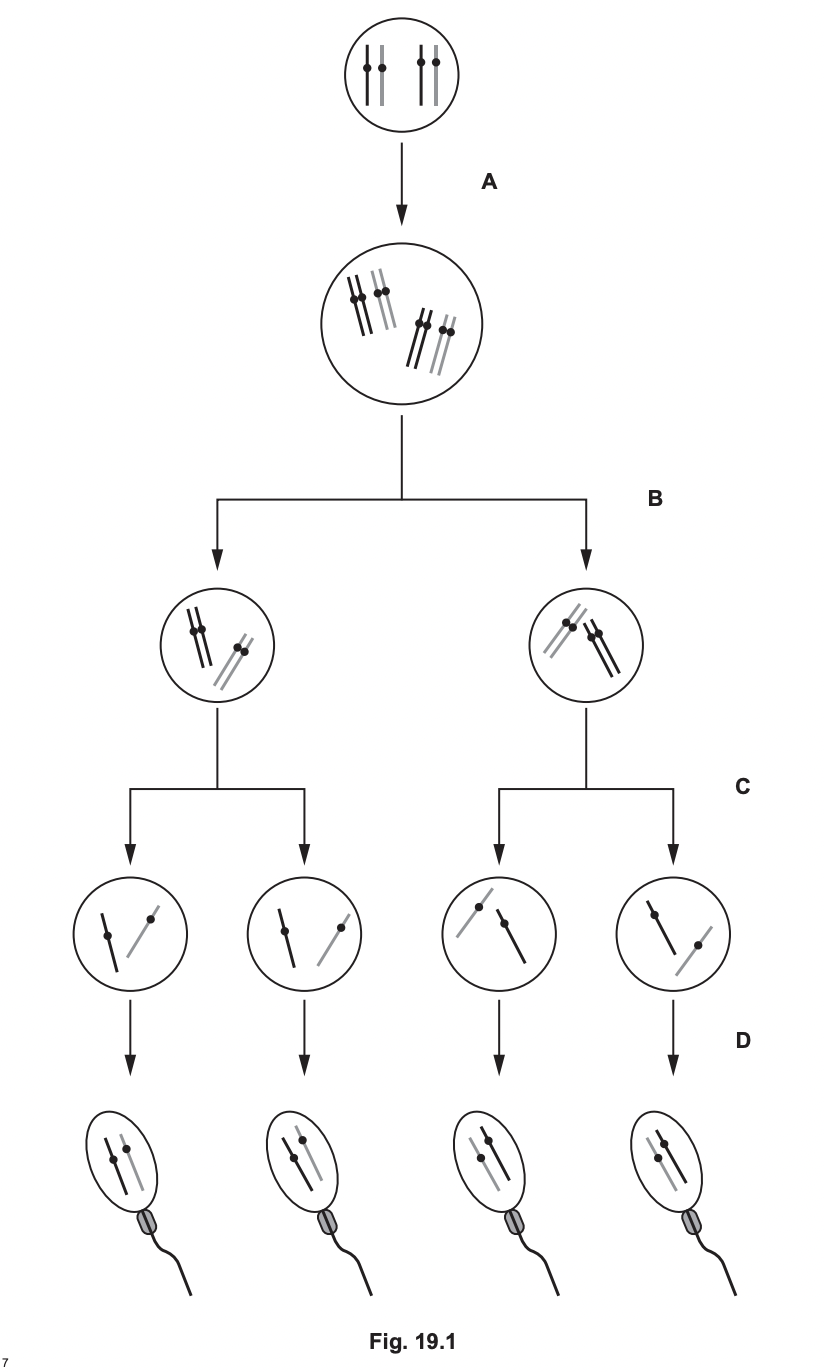
Sperm cells in animals are formed by spermatogenesis.
Metaphase 1 occurs at
telophase 2 occurs at
anaphase 1 occurs at
Metaphase 1 occurs at
telophase 2 occurs at
anaphase 1 occurs at
b
c
b
c
b
25
New cards
Nucleic acids are made from ........................................ monomers. Phosphodiester bonds form between the monomers. They consist of a ........................................ group between the ........................................ molecules, forming the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. In DNA, hydrogen bonding between the two antiparallel ........................................ causes the characteristic double helix shape.
nucleotide
phosphate
pentose
strands
phosphate
pentose
strands
26
New cards
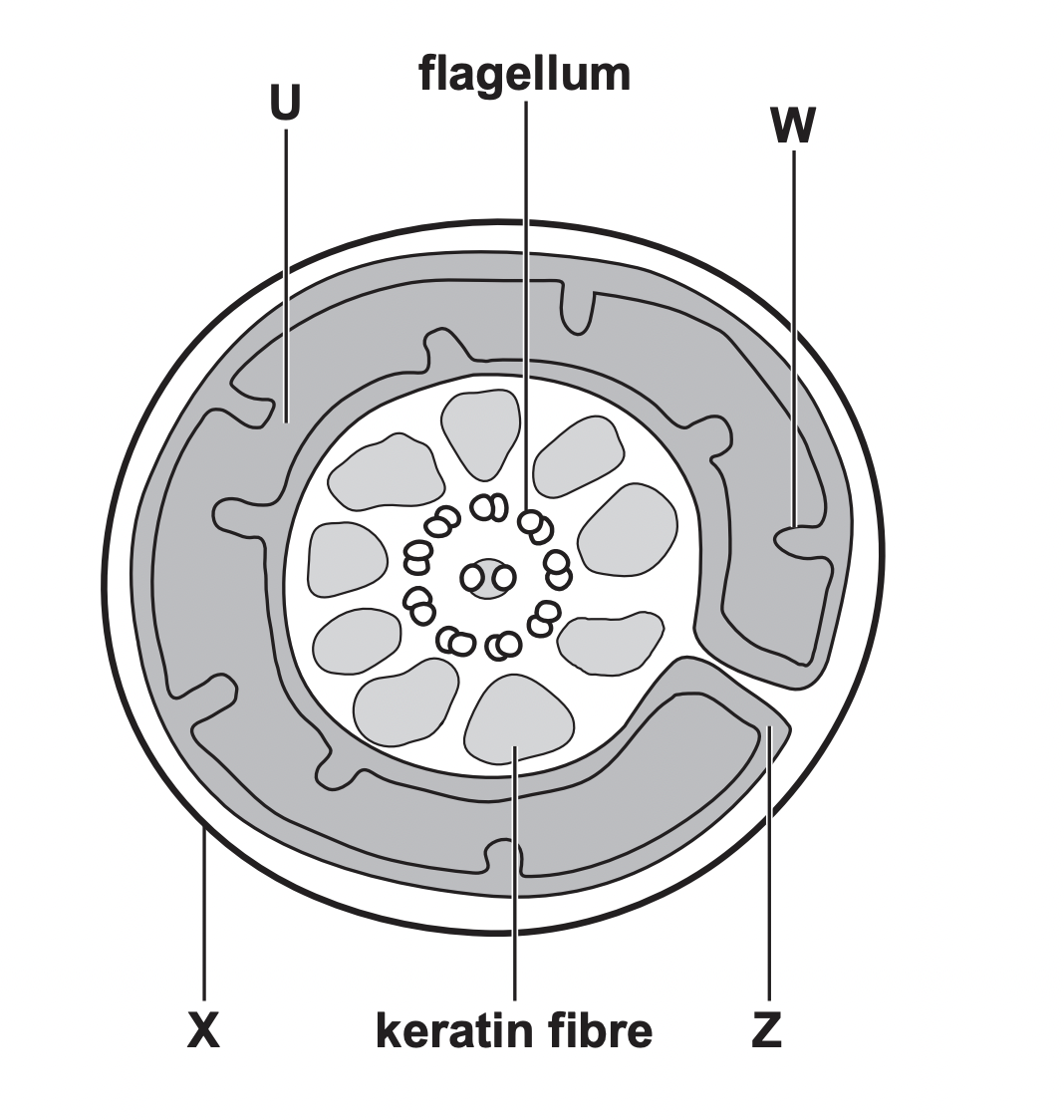
image shows a transverse section of a sperm cell. the mitochondria of sperm cells form a spiral around the central flagellum
identify U, W ,Z
identify U, W ,Z
u- matrix
w- cristae/ inner mitochondrial matrix
z- inter-membrane space
w- cristae/ inner mitochondrial matrix
z- inter-membrane space
27
New cards
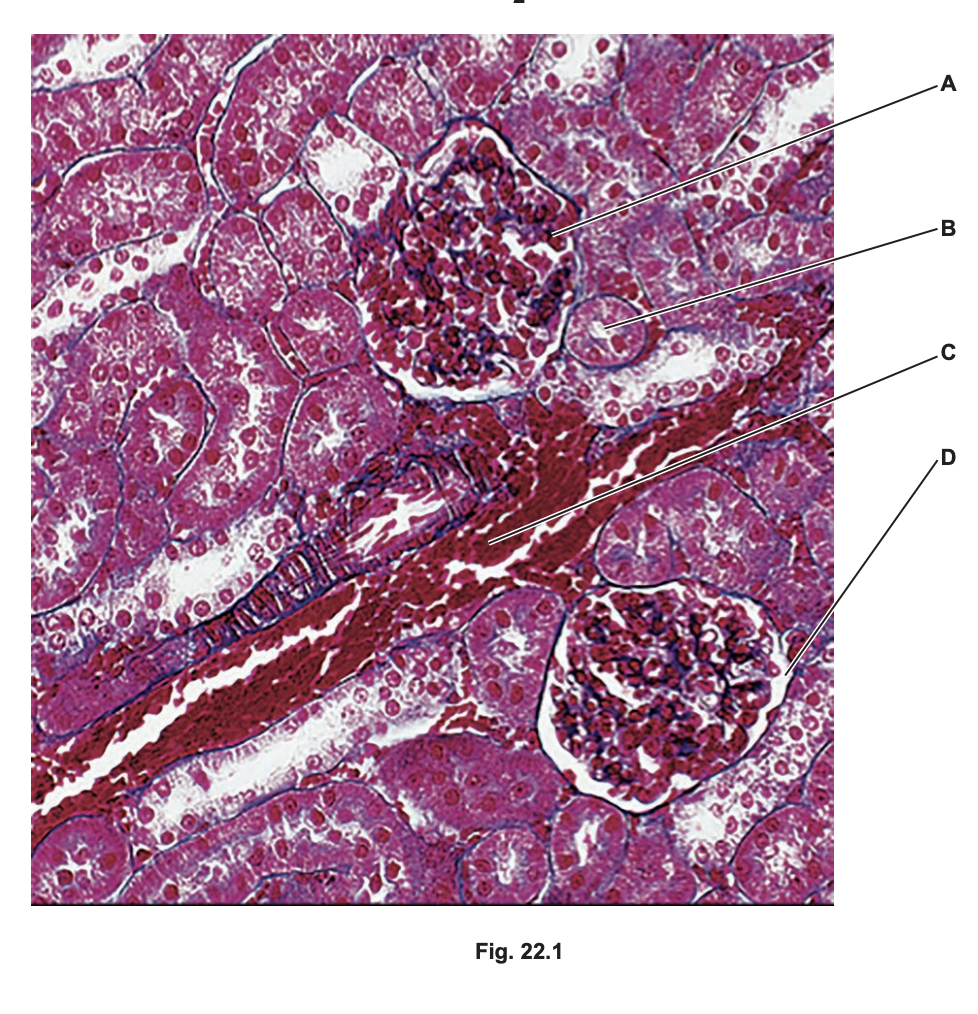
Cross section of part of the cortex of a mammalian kidney
which letter identifies the region with the highest hydrostatic pressure
which two letters identify regions that do not contain plasma proteins
which letter identifies the region with the highest hydrostatic pressure
which two letters identify regions that do not contain plasma proteins
A
\
B,D
\
B,D
28
New cards
Compare the processes occuring in the proximal and distal convoluted tubules
S1 Both use active transport
S2 both use co-transport
S3 Both involve selective reabsorption
S4 both involve the use of sodium ions
\
D1 DCT involves use of calcium ions
D2 co transport in DCT uses ions only
D3 PCT involves ions and molecules (glucose, amino acids)
S2 both use co-transport
S3 Both involve selective reabsorption
S4 both involve the use of sodium ions
\
D1 DCT involves use of calcium ions
D2 co transport in DCT uses ions only
D3 PCT involves ions and molecules (glucose, amino acids)
29
New cards
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is a disease of the kidney that affects the regulation of water potential in the blood. One cause is lithium poisoning. Lithium ions enter the kidney tubules through sodium channels.
This prevents the cells of the collecting duct from responding to ADH in the blood.
State and explain one symptom you would expect to observe as a result of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
This prevents the cells of the collecting duct from responding to ADH in the blood.
State and explain one symptom you would expect to observe as a result of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
high volume of urine
fewer aquaporins in the plasma membrane of the collecting ducts
fewer aquaporins in the plasma membrane of the collecting ducts
30
New cards
Fig. 22.2 shows a podocyte from the kidney. The many gaps between the microscopic
processes form fenestrations in the Bowman’s capsule.
Why are podocytes unable to undergo mitosis
processes form fenestrations in the Bowman’s capsule.
Why are podocytes unable to undergo mitosis
1. have already differentiated
2. are in resting phase
3. shape is too irregular
4. cytoskeleton cannot form
5. if mitosis occurred it would alter the number/ size of the gaps and fenestrations
6. and could alter ultrafiltration (e.g., changes composition of filtrate)
31
New cards
What features of adult stem cells make them suitable for regeneration of tissues in the kidney?
1. multipotent
2. able to become any cell type within the kidney
32
New cards
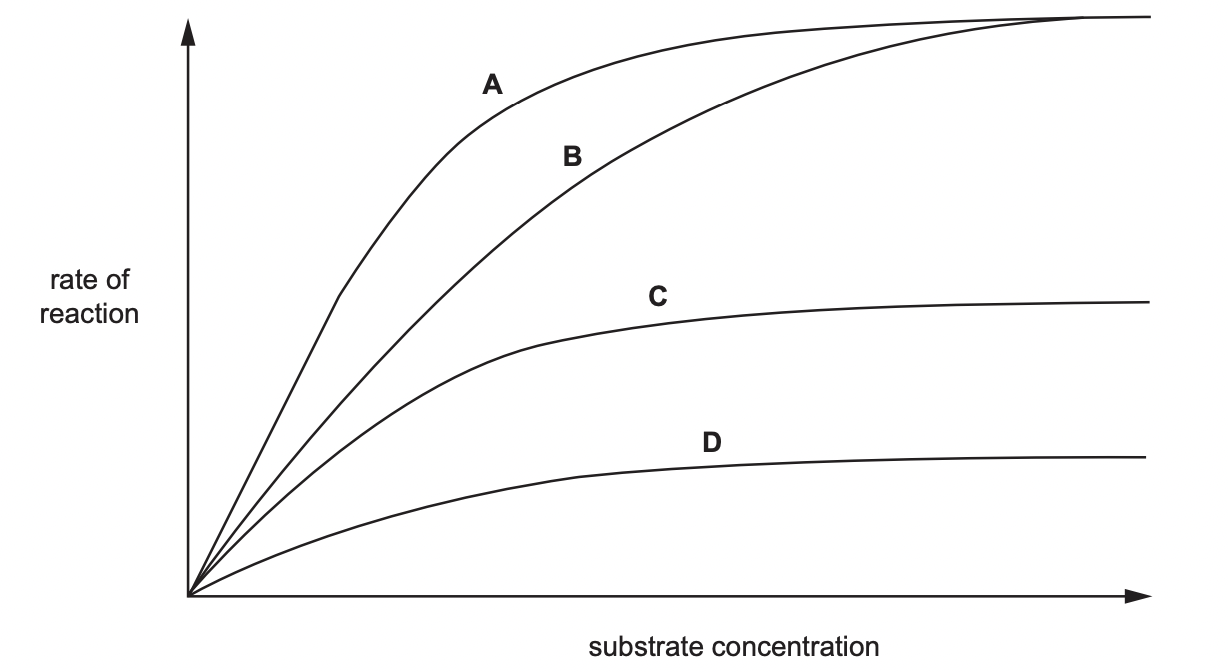
Which shows the ROR with a fixed quantity of competitive inhibitor
B
33
New cards
Why does diastole follow systole in the mammalian heart
cardiac muscle takes a short time to repolarize after being stimulated
34
New cards
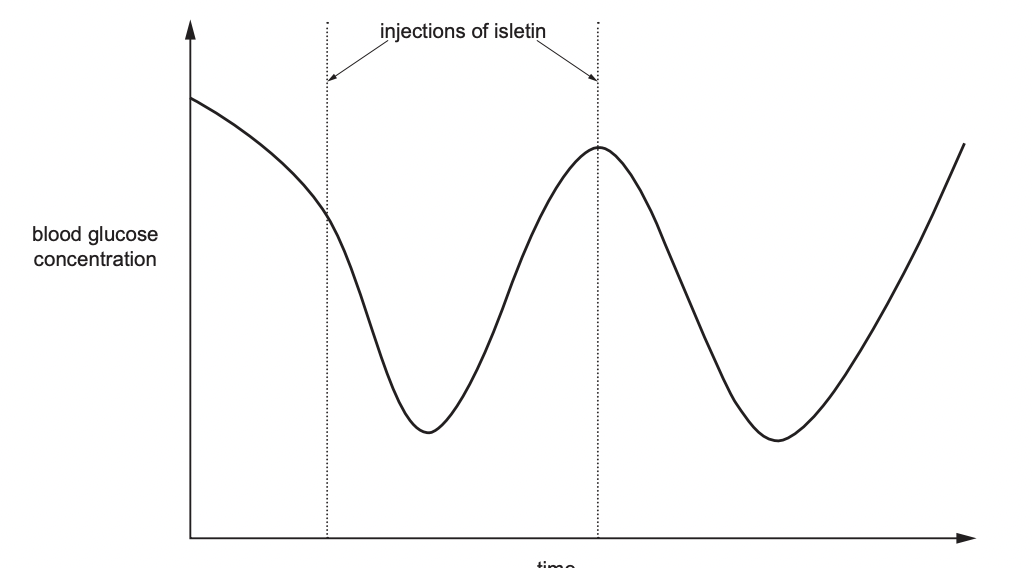
Banting and Best pioneered experiments into the functions of the pancreas. In one experiment, they removed the pancreas of dogs. Shortly afterwards, the dogs developed the symptoms of diabetes.
• Banting ground up the removed pancreas to produce an extract.
• He called the extract “isletin”.
• The isletin was then injected into dogs that had had their pancreas removed.
• He then tested the blood glucose concentration.
\
What explains these results
• Banting ground up the removed pancreas to produce an extract.
• He called the extract “isletin”.
• The isletin was then injected into dogs that had had their pancreas removed.
• He then tested the blood glucose concentration.
\
What explains these results
Iselin reduces BG conc
the effects of isletin are short-lived
the effects of isletin are short-lived
35
New cards
What is a similarity in thw way ATP is made in respiration and photosynthesis
both involve proton gradients
36
New cards
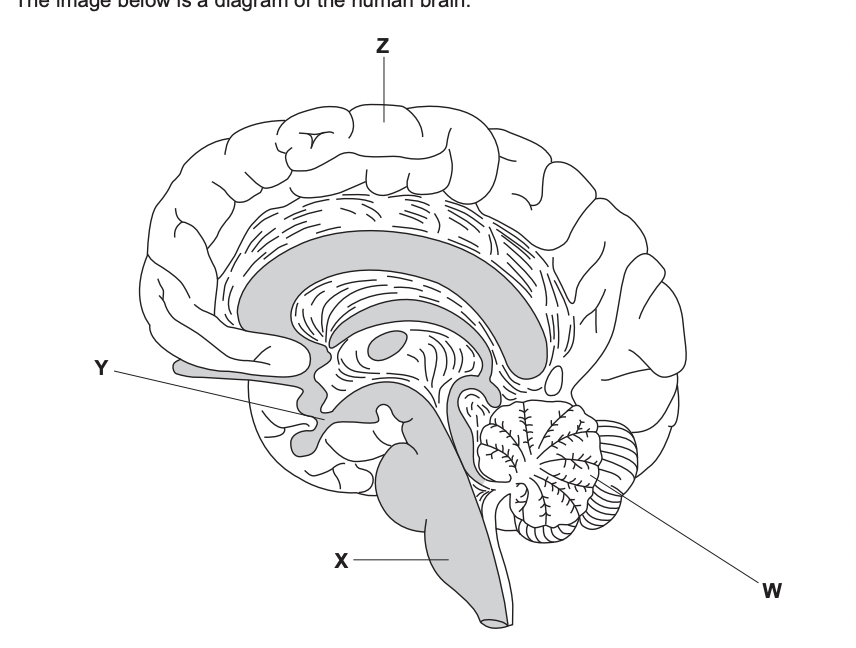
Which regions would be involved in learning to play an instrument
W and Z
37
New cards
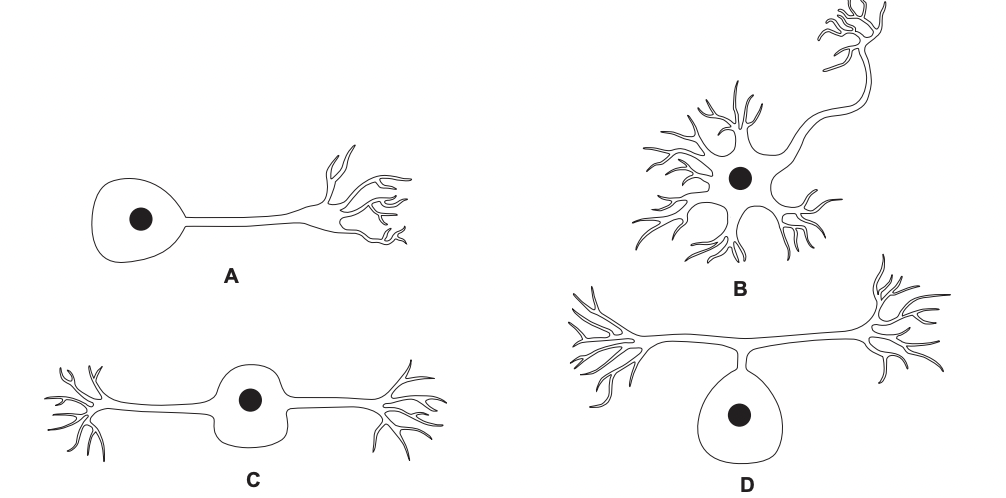
Which shows a sensory neurone
D
38
New cards
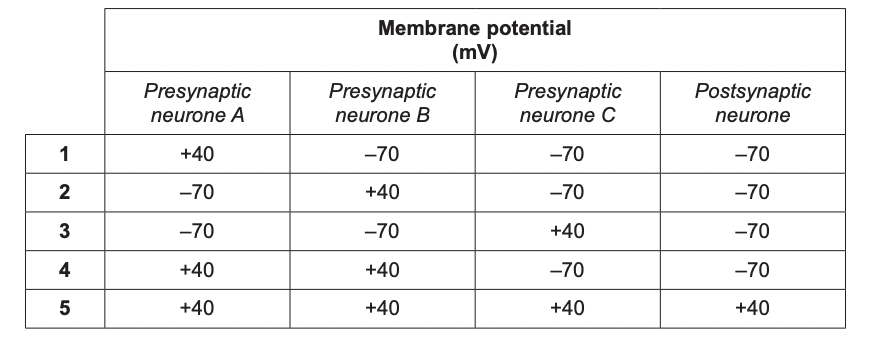
The table below shows the membrane potentials of different neurones at a cholinergic synapse. The data were recorded on five separate occasions, as shown in the five rows.
What explains this data
What explains this data
spatial summation
39
New cards
The drug metoprolol prevents stimulation of the post-synaptic receptors in the sympathetic nervous system
what could this drug be used to treat
1. muscle fatigue
2. tachycardia
3. high BP
what could this drug be used to treat
1. muscle fatigue
2. tachycardia
3. high BP
tachy cardia and high BP
40
New cards
Gestational diabetes is a medical condition that affects pregnant women. It results in high levels of glucose in the blood, even though the woman produces normal levels of insulin.
(i) Gestational diabetes is most similar to which other type of diabetes?
(ii) Suggest two ways a woman with gestational diabetes can manage her condition.
(i) Gestational diabetes is most similar to which other type of diabetes?
(ii) Suggest two ways a woman with gestational diabetes can manage her condition.
(i) Type two
* insulin is still produced
* beta cells still working
* liver cells no longer respond to insulin
* if it was type I then women would not produce normal levels of insulin
\
(ii)
* low carbohydrate diet
* exercise
* manage weigh
* drugs to control glucose levels
* insulin is still produced
* beta cells still working
* liver cells no longer respond to insulin
* if it was type I then women would not produce normal levels of insulin
\
(ii)
* low carbohydrate diet
* exercise
* manage weigh
* drugs to control glucose levels
41
New cards
Skeletal muscle is one of the main tissues where glucose is removed from the blood in response to insulin. Name the other tissue.
liver
42
New cards
Explain why glucose is required for the contraction of skeletal muscle.
* as respiratory substrate
* to produce ATP
* ATP needed for breaking cross-bridges between myosin and actin
* ATP hydrolysed to ADP and Pi to reset myosin heads
* ATP for active transport of calcium ions into sarcoplasmic reticulum
* to produce ATP
* ATP needed for breaking cross-bridges between myosin and actin
* ATP hydrolysed to ADP and Pi to reset myosin heads
* ATP for active transport of calcium ions into sarcoplasmic reticulum
43
New cards
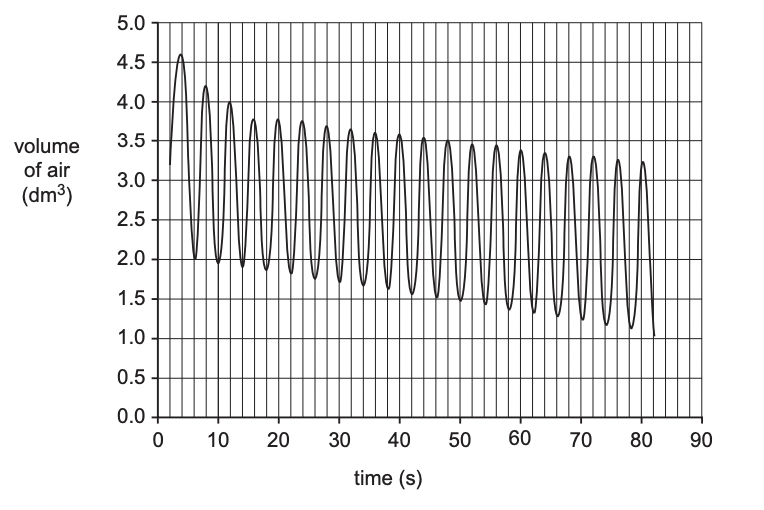
During late pregnancy, women find ventilation more difficult, as the developing foetus reduces the volume of the thorax. This can lead to tiredness and difficulty breathing.
A student used a spirometer to measure ventilation in a woman who was 36 weeks pregnant.
Fig. 16.1 shows the trace produced.
\
Mean oxygen uptake rate at rest in women is around 0.020 dm3 s–1.
Using these data, the student made the following conclusion: My data show that being pregnant reduces rate of oxygen uptake by up to 20%.
Evaluate this claim, using the data in Fig. 16.1.
A student used a spirometer to measure ventilation in a woman who was 36 weeks pregnant.
Fig. 16.1 shows the trace produced.
\
Mean oxygen uptake rate at rest in women is around 0.020 dm3 s–1.
Using these data, the student made the following conclusion: My data show that being pregnant reduces rate of oxygen uptake by up to 20%.
Evaluate this claim, using the data in Fig. 16.1.
* calculated rate of oxygen uptake between 0.010 and 0.018
* calculated reduction rate of oxygen uptake between 10-50%
\
* claim is correct
* mean uptake 0.020
\
* one women reading is not enough
* being 36 weeks pregnant is not representative of whole pregnancy
* calculated reduction rate of oxygen uptake between 10-50%
\
* claim is correct
* mean uptake 0.020
\
* one women reading is not enough
* being 36 weeks pregnant is not representative of whole pregnancy
44
New cards
Chromista are photosynthetic protoctists that live in water. Chromista are different from other photosynthetic organisms because they contain the pigment chlorophyll c. Chlorophyll c is not found in plants.
(i) Outline the importance of photosynthetic pigments in photosynthesis
(i) Outline the importance of photosynthetic pigments in photosynthesis
* pigments absorb light
* electrons promoted to higher energy level
* accessory pigments pass energy to reaction centres
* primary pigments become oxidised
* for light dependent reaction
* electrons promoted to higher energy level
* accessory pigments pass energy to reaction centres
* primary pigments become oxidised
* for light dependent reaction
45
New cards
The wavelengths of light absorbed by chlorophyll c are different from those wavelengths absorbed by chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
Suggest why Chromista need pigments that are different from those of other photosynthetic organisms.
Suggest why Chromista need pigments that are different from those of other photosynthetic organisms.
* they have to absorb shorter wavelengths of light
* some wavelengths don’t reach them
* some wavelengths don’t reach them
46
New cards
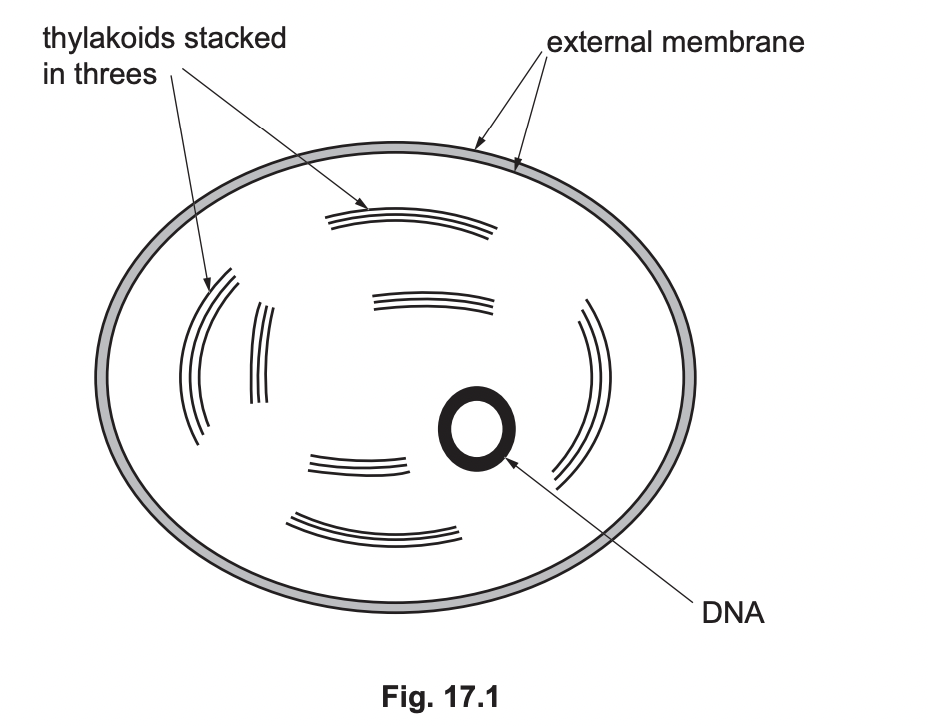
Outline the structural differences between the Chromista chloroplast in Fig. 17.1 and the chloroplasts found in flowering plants.
* chromista has fewer thylakoids
* chromista has no intergranal lamellae
* plants have thylakoids in groups of more than three
* plants have starch grains
* chromista has no intergranal lamellae
* plants have thylakoids in groups of more than three
* plants have starch grains
47
New cards
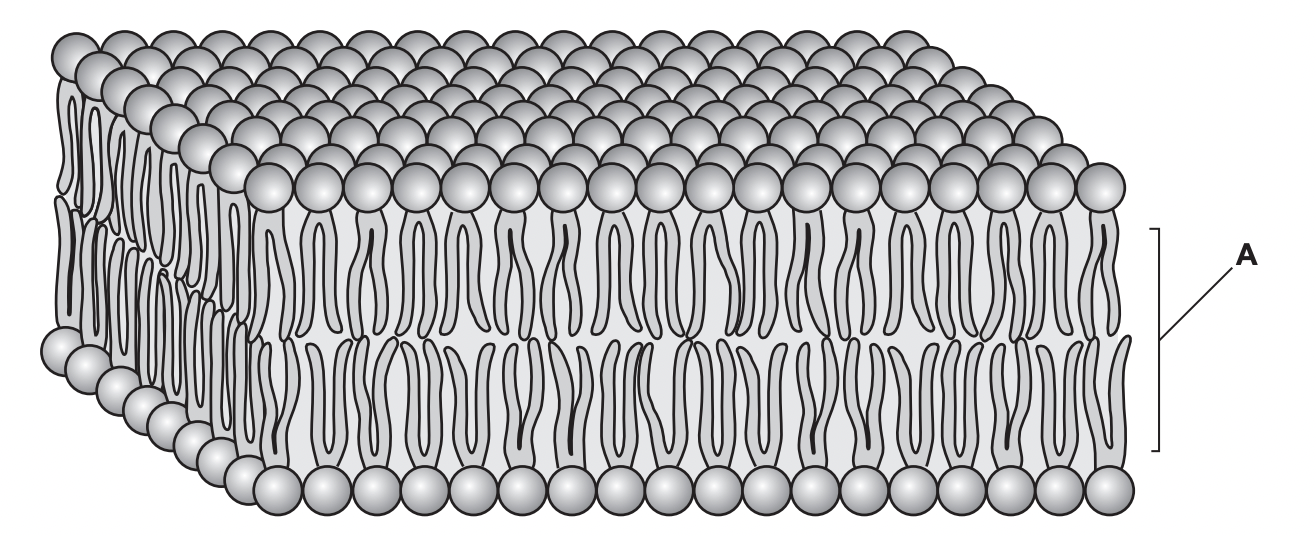
Diagram is apart of the plasma membrane of a Chromista cell.
State and explain how region A contributes to stability of the plasma membrane
State and explain how region A contributes to stability of the plasma membrane
Property
hydrophobic fatty acid tails
Explanation
helps form bilayer
\
property
contains cholesterol
explanation
regulates fluidity
hydrophobic fatty acid tails
Explanation
helps form bilayer
\
property
contains cholesterol
explanation
regulates fluidity
48
New cards
Outline the role of membranes within cells
compartmentalisation
sites of chemical reactions
provide attachment sites for enzymes
allow formation of conc gradient
sites of chemical reactions
provide attachment sites for enzymes
allow formation of conc gradient
49
New cards
Plants lose water by transpiration. The rate of transpiration varies between different species of plant. The rate of transpiration can be measured using a potometer. Plan an investigation into the rate of transpiration in two species of plant that would allow valid data to be collected. Details of how to set up a potometer are not required.
* movement of bubble in potometer
* timing distance travelled by bubble
* repeating investigation with two different plant species
* repetition to gain replicates
* calculation of mean
* statistical test
\
* temp, humidity, light, wind, SA of leaves
* how controlled
* timing distance travelled by bubble
* repeating investigation with two different plant species
* repetition to gain replicates
* calculation of mean
* statistical test
\
* temp, humidity, light, wind, SA of leaves
* how controlled
50
New cards
Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer of β-glucose. Give three properties of cellulose that make it suitable as the basis of plant cell walls
1. insoluble
2. unreactive
3. high tensile strength
4. flexible
5. can form hydrogen bonds with neighbouring chains
51
New cards
Cellulose cannot be digested by animals. Some mammals have bacteria in their stomachs that produce enzymes that can digest cellulose. Explain whether the action of these enzymes is intracellular or extracellular.
extracellular
\
takes place outside of cells
\
takes place outside of cells
52
New cards
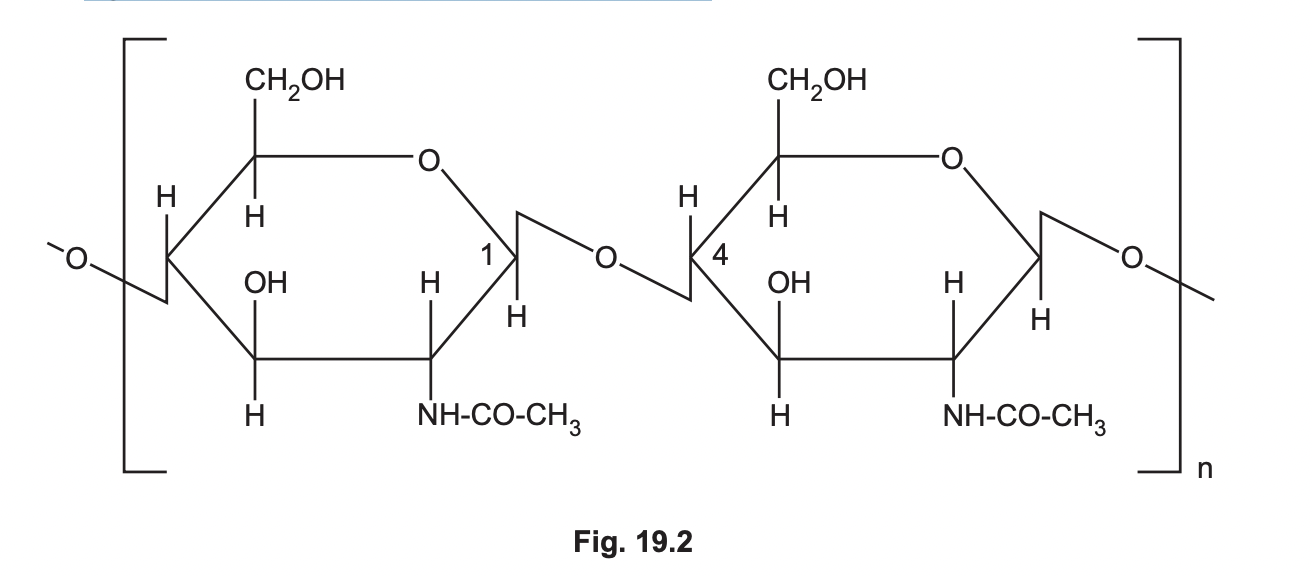
Chitin is a polysaccharide found in insects. It is used to form the hard outer casing of their bodies. Fig. 19.2 shows the chemical structure of chitin.
describe 2 similarities and 2 differences between structures of chitin and glycogen
describe 2 similarities and 2 differences between structures of chitin and glycogen
S
* Both polymers
* have 6 carbons
* have 1-4 glycosidic bonds
\
D
* chitin as beta-glycosidic bonds
* chitin contains N
* no 1-6 glycosidic bonds in chitin
* no branching in chitin
* Both polymers
* have 6 carbons
* have 1-4 glycosidic bonds
\
D
* chitin as beta-glycosidic bonds
* chitin contains N
* no 1-6 glycosidic bonds in chitin
* no branching in chitin
53
New cards
\* Insects use glucose to generate ATP. Outline the processes involved in the generation of ATP through chemiosmosis.
* occurs in mitochondria
* involves inner membrane and matrix
* involves movement of hydrogen across membrane
* use of enzyme ATP synthase
* hydrogen ions pumped out of matrix across membrane into intermembrane space
* proton gradient created
* H+ ions pass through hydrophilic transmembrane protein
* cristae
* ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP +Pi
* H+ ions move from area of high conc to low coonc
* some H+ ions leak back into matrix
* involves inner membrane and matrix
* involves movement of hydrogen across membrane
* use of enzyme ATP synthase
* hydrogen ions pumped out of matrix across membrane into intermembrane space
* proton gradient created
* H+ ions pass through hydrophilic transmembrane protein
* cristae
* ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP +Pi
* H+ ions move from area of high conc to low coonc
* some H+ ions leak back into matrix
54
New cards
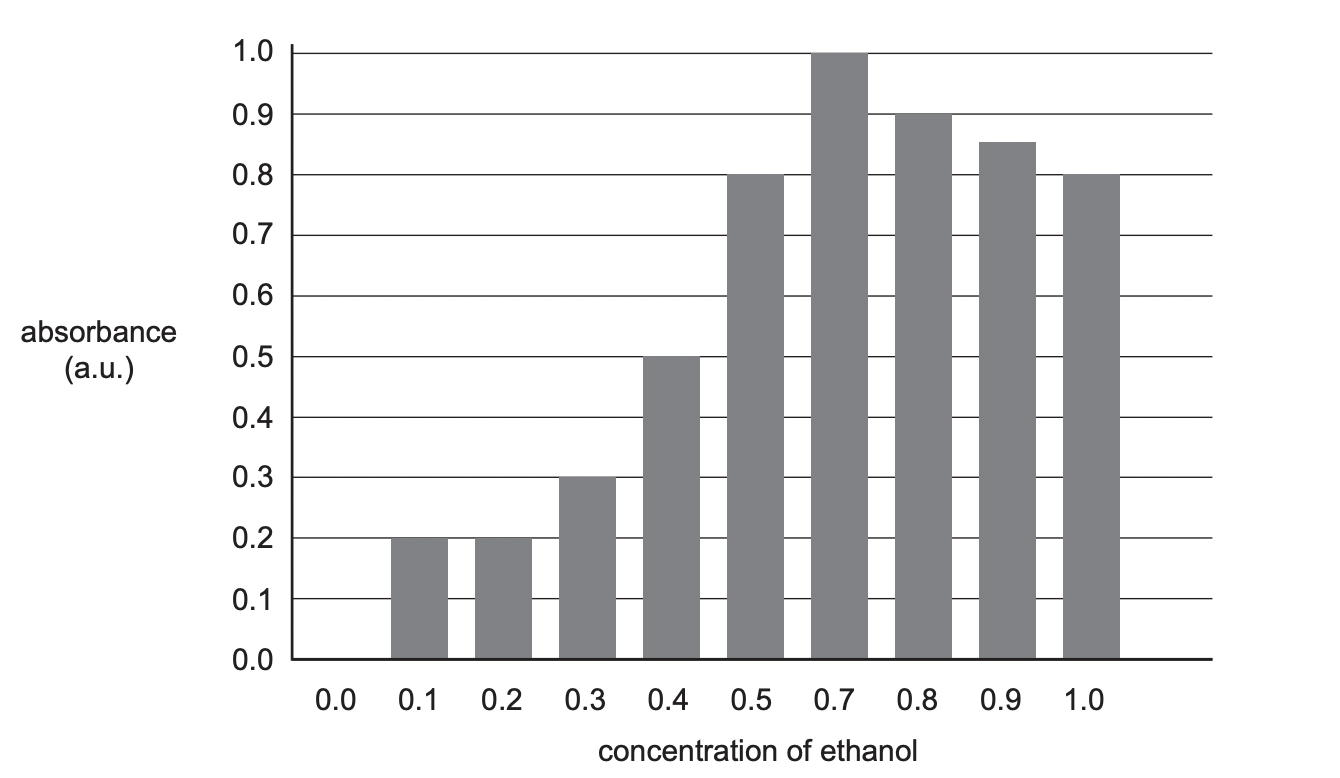
Make three criticisms of the way the student has displayed these results
* x axis has no units
* should be a line graph as continuous data
* x axis has incorrect scale
* no title
* should be a line graph as continuous data
* x axis has incorrect scale
* no title
55
New cards
Explain how carrying out replicates could improve an investigation
calculate mean
allows anomalies to be identified
improves repeatability
allows statistical test to be completed
allows anomalies to be identified
improves repeatability
allows statistical test to be completed
56
New cards
The greater blue-ringed octopus, Hapalochlaena lunulata, is one of the most venomous of all animals. Its bite contains tetrodotoxin (TTX), a neurotoxin that can cause paralysis and death within minutes.
(i) The following information has been discovered about the effects of TTX on nerve cells: •
TTX binds to the external surface of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels in the axon membrane.
• Binding of TTX changes the tertiary structure of the channel.
• This means the channel cannot open.
Using the information provided, explain how TTX affects the activity of neurones.
(i) The following information has been discovered about the effects of TTX on nerve cells: •
TTX binds to the external surface of the voltage-gated sodium ion channels in the axon membrane.
• Binding of TTX changes the tertiary structure of the channel.
• This means the channel cannot open.
Using the information provided, explain how TTX affects the activity of neurones.
* sodium ions cannot enter
* no depolarisation of the membrane
* prevents action potential being generated
* impulse not conducted along axon
* no release of neurotransmitter
* no depolarisation of the membrane
* prevents action potential being generated
* impulse not conducted along axon
* no release of neurotransmitter
57
New cards
A common cause of death from TTX poisoning is suffocation (not getting enough oxygen) as a result of paralysis of the diaphragm.
Explain how paralysis of the diaphragm could lead to suffocation
Explain how paralysis of the diaphragm could lead to suffocation
* no increase in vol of thorax
* no change in pressure of thorax
* no air drawn into lungs
* no change in pressure of thorax
* no air drawn into lungs
58
New cards
TTX is also known to reduce the speed of conduction in the Purkyne fibres of the heart. Suggest and explain what effect this would have on the heart rate.
slows heart rate
* slows transmission of impulse from AVN to ventricles
* slows ventricular systole
* longer delay before ventricular contraction
* increases time heart is in diastole
* slows transmission of impulse from AVN to ventricles
* slows ventricular systole
* longer delay before ventricular contraction
* increases time heart is in diastole
59
New cards
Why is transmission of action potentials along the axon slower in the absence of saltatory conduction?
no nodes of ranvier
shorter local currents
whole axon needs to be depolarised
shorter local currents
whole axon needs to be depolarised
60
New cards
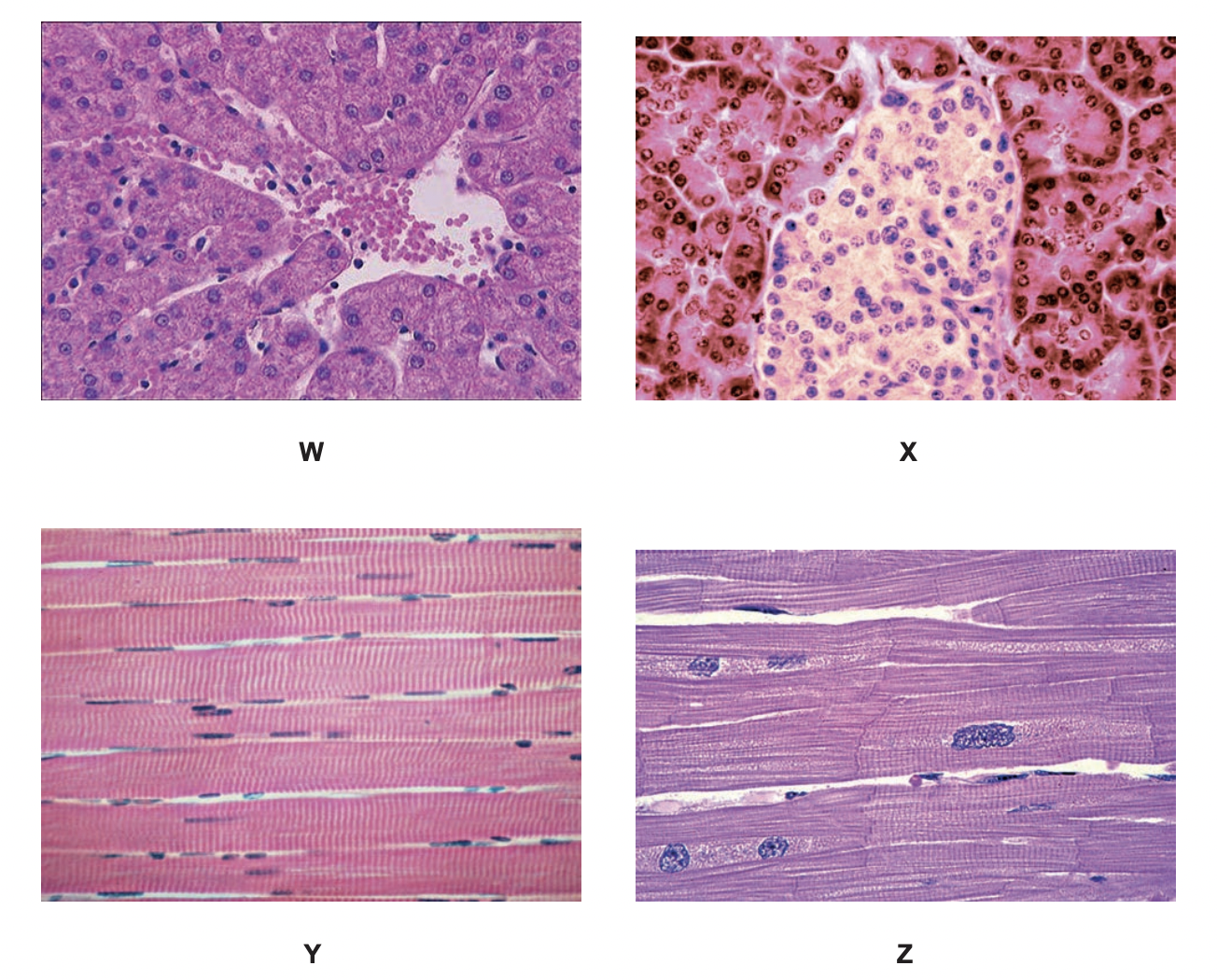
identify tissues W, X, Y
W- Liver
X- Pancreas
Y- Skeletal
X- Pancreas
Y- Skeletal
61
New cards
When the heart rate is too low the level of carboxylic acid in the blood becomes higher than normal. The vagus nerve sends action potentials to the AVN to increase the contraction rate of the heart muscle. The baroreceptors in the walls of the blood vessels then detect that the pH of the blood is normal, so heart rate can return to resting.
The endocrine system can also change heart rate. Release of the hormone adrenaline from the adrenal medulla causes the smooth muscle of the heart to contract more frequently.
\
Identify any mistakes
The endocrine system can also change heart rate. Release of the hormone adrenaline from the adrenal medulla causes the smooth muscle of the heart to contract more frequently.
\
Identify any mistakes
* carboxylic acid should be carbonic acid
* vagus nerve should be accelerator/ sympathetic nerve
* AVN should be SAn
* baroreceptors should be chemoreceptors
* smooth muscle should be cardiac muscle
* vagus nerve should be accelerator/ sympathetic nerve
* AVN should be SAn
* baroreceptors should be chemoreceptors
* smooth muscle should be cardiac muscle
62
New cards
Describe a reflex response a 3-year-old child would make to an object moving towards their eyes and explain the advantage of this response
* shutting of the eyes
* involuntary
* prevents damage to eyes
* involuntary
* prevents damage to eyes
63
New cards
Why are stem cells a potential source of treatment for arthritis
stem cells allow the regeneration of a variety of tissue types
64
New cards
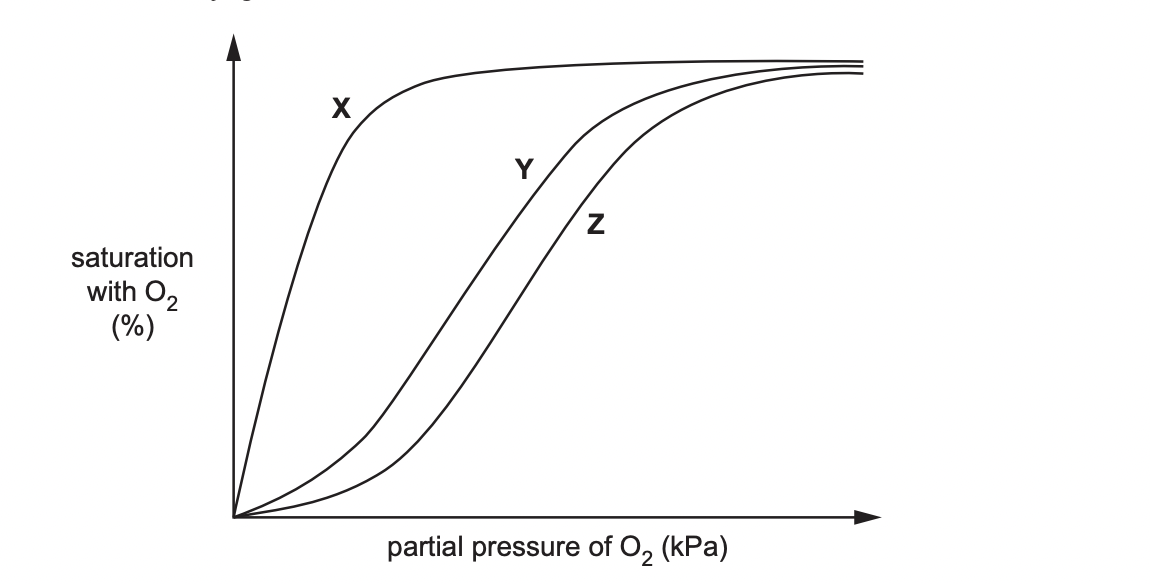
Myoglobin is a protein found in muscle. Myoglobin has a very high affinity for oxygen at most partial pressures of oxygen.
The figure below shows dissociation curves for • adult haemoglobin • fetal haemoglobin • myoglobin.
\
identify X, Y, Z
The figure below shows dissociation curves for • adult haemoglobin • fetal haemoglobin • myoglobin.
\
identify X, Y, Z
X, Myoglobin
Y, Fetal haemoglobin
Z, Adult haemoglobin
Y, Fetal haemoglobin
Z, Adult haemoglobin
65
New cards
Describe hematopoietic stem cells
Multipotent not pluripotent
66
New cards
Why can meristems can differentiate into xylem vessels in plant
meristems are living and unspecialised
67
New cards
Auxin is synthesised in cells at the ....................... of the shoot. Auxin causes the cells to ....................... on one side, so the stem bends. Scientists originally thought auxin was ....................... by light but this was disproved by the fact that plants growing in the dark and plants growing in unilateral light had ....................... auxin levels.
tip
elongate
destroyed
similar
elongate
destroyed
similar
68
New cards
8 A scientist tested a plant suffering from water stress. The plant was found to have high levels of abscisic acid (ABA) in its tissues. What explains this observation
ABA stimulates stomatal closing
69
New cards
What is evidence for geotropism
roots grow downwards
70
New cards
Many trees drop their leaves in the autumn
Which of the following plant hormones is/are thought to be involved in the control of leaf drop?
Which of the following plant hormones is/are thought to be involved in the control of leaf drop?
Auxin
Ethene
Ethene
71
New cards
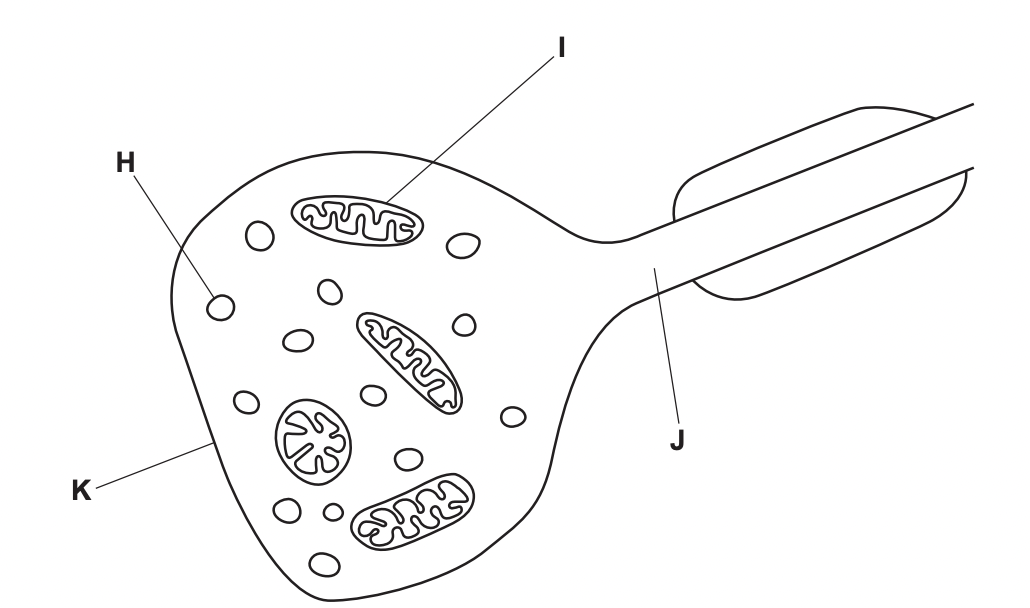
Label H, I, J, K
H: Vesicle containing neurotransmitter
I: Mitochondrion
J: Axon
K: Presynaptic membrane
\
I: Mitochondrion
J: Axon
K: Presynaptic membrane
\
72
New cards
Damage to the hypothalamus results in lower water potential of the blood, what explains these observation
Fewer water channels are inserted into the CSM of the collecting duct
73
New cards
Collagen is found in tendons. What makes collagen suitable for this role
strong
flexible
insoluble
flexible
insoluble
74
New cards
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic prokaryotes. A scientist exposed cyanobacteria to light of different colours and intensities and made the following observations:
• Most cyanobacteria are blue in colour.
• At low light intensities, glucose production in cyanobacteria is low.
• When light intensity reaches a certain level the rate of glucose production in cyanobacteria stops increasing.
What correctly explains these observations?
• Most cyanobacteria are blue in colour.
• At low light intensities, glucose production in cyanobacteria is low.
• When light intensity reaches a certain level the rate of glucose production in cyanobacteria stops increasing.
What correctly explains these observations?
the pigments in the cyanobacteria absorb red light and light intensity is a limiting factor for the rate of photosynthesis
75
New cards
The hormone aldosterone is produced by the adrenal cortex. Excess production of aldosterone can result in high blood pressure.
The following statements describe processes that occur as a result of aldosterone secretion:
1 Na+/K+ pumps in the collecting duct of the kidney move three Na+ ions into the blood and two K+ ions out of the blood.
2 Cl − ions enter the blood to maintain electrochemical balance.
3 H+ ions enter cells lining the kidney tubules.
Which of the above statements explain(s) why excess aldosterone production can result in high blood pressure?
The following statements describe processes that occur as a result of aldosterone secretion:
1 Na+/K+ pumps in the collecting duct of the kidney move three Na+ ions into the blood and two K+ ions out of the blood.
2 Cl − ions enter the blood to maintain electrochemical balance.
3 H+ ions enter cells lining the kidney tubules.
Which of the above statements explain(s) why excess aldosterone production can result in high blood pressure?
Only 1 and 2
76
New cards
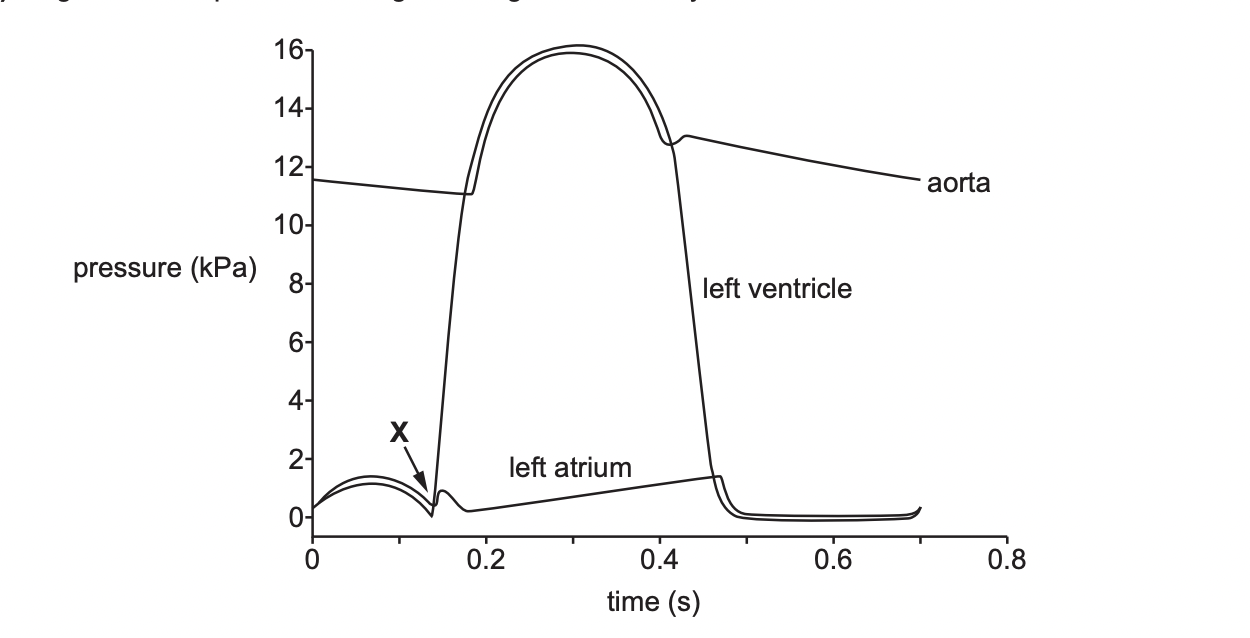
Compare the changes in pressure in the LV with the changes in pressure with the LA
* similar increase and decrease in pressure between 0-0.15s
* steeper rise in ventricle
* bigger increase in ventricle pressure
* at 0.15s atrial pressure has small rise and fall, but ventricular is increasing
* from 0.3s ventricular pressure decreases but atrial pressure still increasing
* from 0.5 no change in pressure in both
* steeper rise in ventricle
* bigger increase in ventricle pressure
* at 0.15s atrial pressure has small rise and fall, but ventricular is increasing
* from 0.3s ventricular pressure decreases but atrial pressure still increasing
* from 0.5 no change in pressure in both
77
New cards
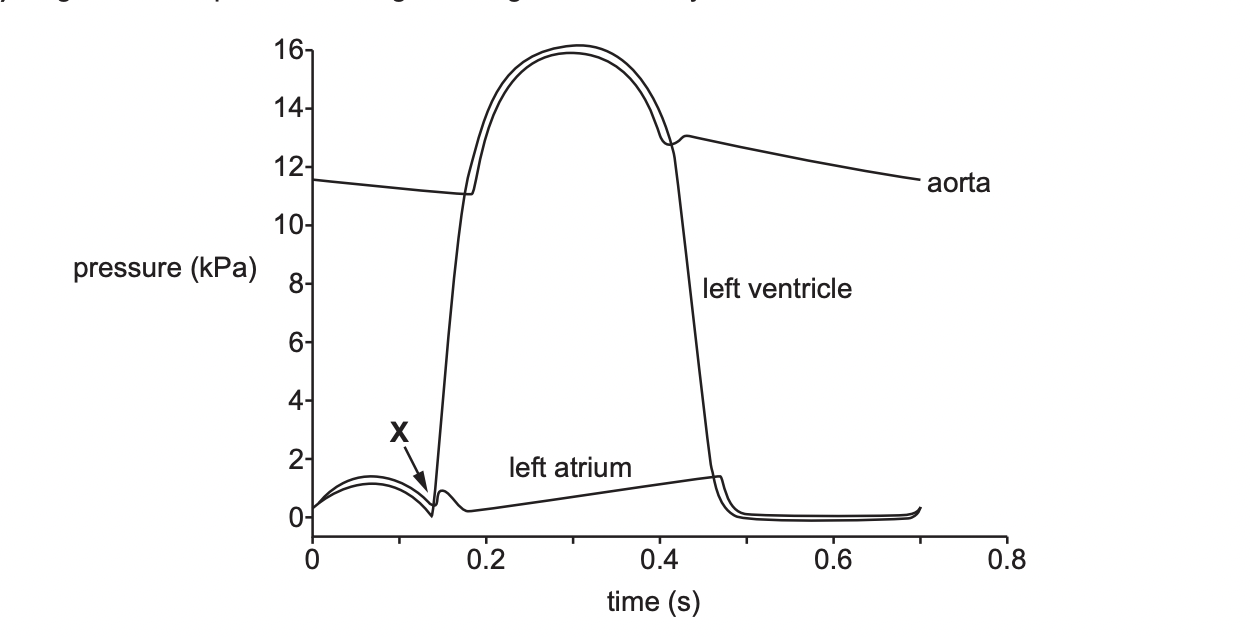
Calculate heart rate of this individual
86 bpm
78
New cards
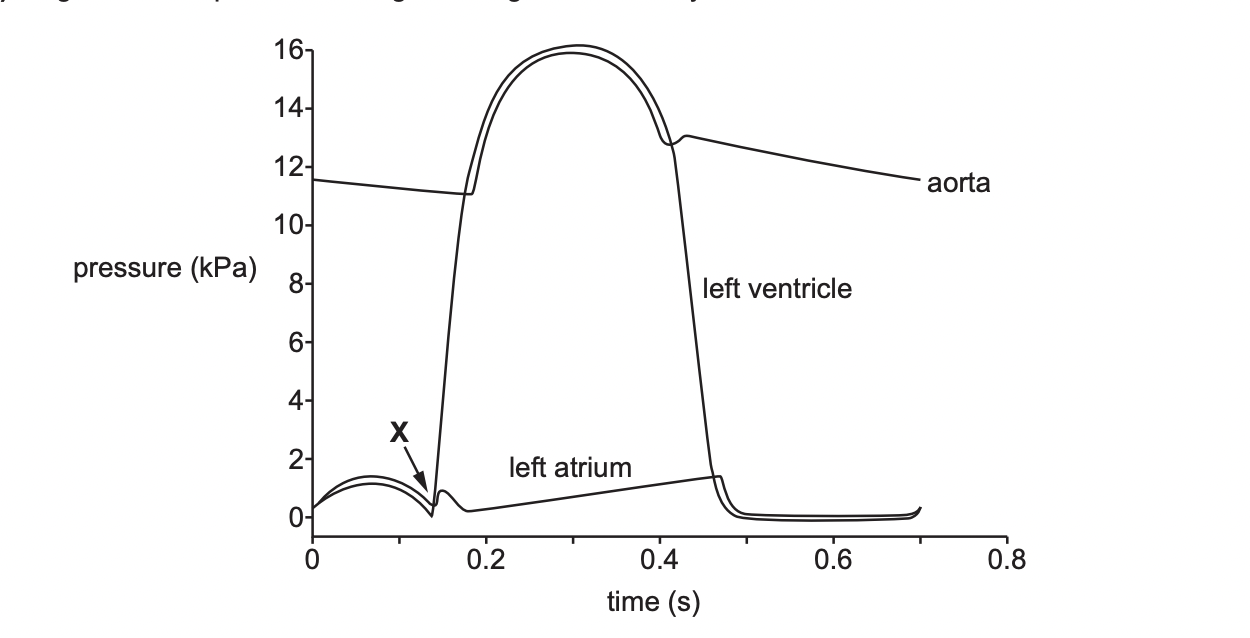
Name valve that closes point X
atrioventricular
79
New cards
)Brown fat is a type of tissue. Brown fat has a higher need for oxygen because fat cells in this tissue carry out aerobic respiration at a higher rate than fat cells in other tissues.
Suggest which organelle is present in higher numbers in brown fat cells than in other fat cells.
Suggest which organelle is present in higher numbers in brown fat cells than in other fat cells.
Mitochodria
80
New cards
Gibberellin causes stem elongation in plants
Gibberellin causes an increase in the distance between the leaves on the stem, which is known as internodal length
Explain why gibberellin is classed as a plant hormone
Gibberellin causes an increase in the distance between the leaves on the stem, which is known as internodal length
Explain why gibberellin is classed as a plant hormone
1. chemical messenger
2. produced in one part of the plant but has effects in other
3. affects activity of target cells
4. long-lasting
5. wide-spread effect
81
New cards
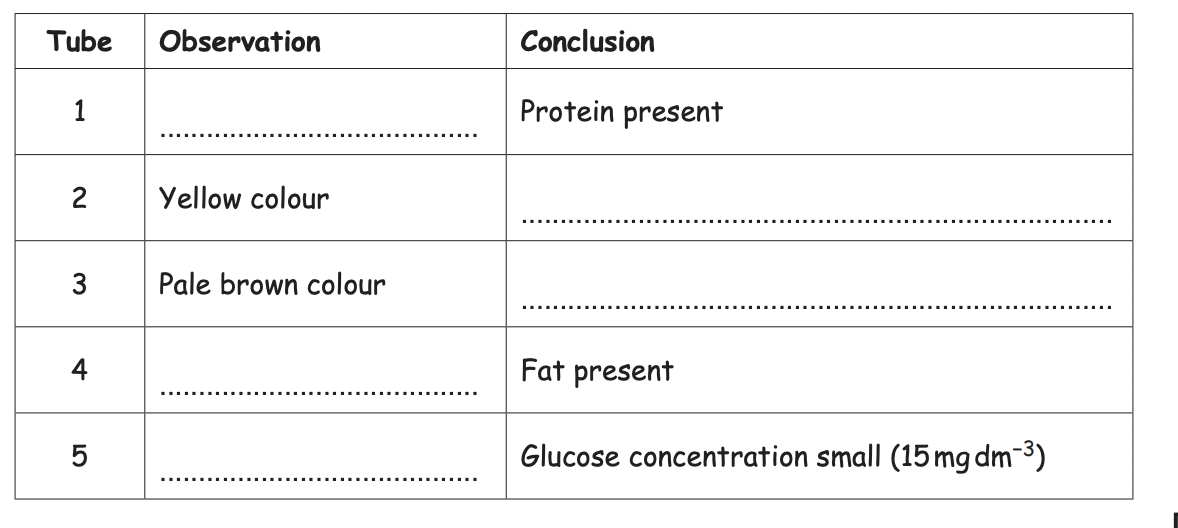
Complete the table
1. purple
2. reducing sugar
3. no starch
4. forms white suspension/emulsion
5. pink
82
New cards
Why does the use of a colorimeter improve the students experiment
* quantitative
* not subjective
* not subjective
83
New cards
Mammals and fish both need circulatory systems to transport oxygen to respiring tissues. They have different circulatory systems because they have different oxygen requirements.
(a)\* Compare and contrast the circulatory systems of mammals and fish.
(a)\* Compare and contrast the circulatory systems of mammals and fish.
FISH
* Single circulation
* one atrium and 1 ventricle
* blood passes through 2 sets of capillaries
* blood pressure is lower
* less efficient at transporting
* fulfils needs as fish are cold blooded
\
MAMMAL
* Double circulation
* two atria and 2 ventricles
* blood passes through
* blood maintained at higher pressure
* 2 circulation with different pressures
* more efficient at transporting oxygen
* fulfils needs as mammals need to maintain a constant body temperature
* Single circulation
* one atrium and 1 ventricle
* blood passes through 2 sets of capillaries
* blood pressure is lower
* less efficient at transporting
* fulfils needs as fish are cold blooded
\
MAMMAL
* Double circulation
* two atria and 2 ventricles
* blood passes through
* blood maintained at higher pressure
* 2 circulation with different pressures
* more efficient at transporting oxygen
* fulfils needs as mammals need to maintain a constant body temperature
84
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter in mammals. Studies have suggested that it also functions as a hormone in some invertebrate species, such as squid.
When ACh comes into contact with specialised cells in squid skin, it causes them to change colour. These colour changes allow the squid to communicate and to camouflage itself.
ACh is made by cells in the centre of the squid’s body.
Explain how it is possible for ACh to have an effect on cells in the skin of the squid.
When ACh comes into contact with specialised cells in squid skin, it causes them to change colour. These colour changes allow the squid to communicate and to camouflage itself.
ACh is made by cells in the centre of the squid’s body.
Explain how it is possible for ACh to have an effect on cells in the skin of the squid.
secreted into / travels in ,
blood binds to receptors on (skin) cell (surface)
detail of response inside cell(s)
blood binds to receptors on (skin) cell (surface)
detail of response inside cell(s)
85
New cards
Squid blood contains a blue oxygen-carrying protein called haemocyanin.
High partial pressures of carbon dioxide reduce the affinity for oxygen of haemocyanin.
Suggest a mechanism by which carbon dioxide could reduce the affinity for oxygen of haemocyanin.
High partial pressures of carbon dioxide reduce the affinity for oxygen of haemocyanin.
Suggest a mechanism by which carbon dioxide could reduce the affinity for oxygen of haemocyanin.
* CO2 forms carbonic acid
* haemocyanin acts as a buffer
* H+ causes change in tertiary structure of hemocyanin
* haemocyanin acts as a buffer
* H+ causes change in tertiary structure of hemocyanin
86
New cards
Vascularisation occurs in bodybuilders because blood vessels are pushed to the surface by increased muscle mass. They can also become more visible due to reduced body fat and dehydration.
(a) Explain why the visible blood vessels are likely to be veins.
(a) Explain why the visible blood vessels are likely to be veins.
* have thin walls so valves will bulge
* large lumen as contains large vol of blood
* found closer to the surface of the skin than arteries
* large lumen as contains large vol of blood
* found closer to the surface of the skin than arteries
87
New cards
Some bodybuilders use anabolic steroids to increase their muscle mass.
Suggest why anabolic steroids are effective when applied to the surface of the skin.
Suggest why anabolic steroids are effective when applied to the surface of the skin.
1. large surface area for absorption
2. skin has network of capillaries
3. steroids are lipid soluble
4. so can cross phospholipid bilayer
88
New cards
Rubredoxin is known as a conjugated protein.
Use Fig. 20.1 to explain what is meant by the term conjugated protein.
Use Fig. 20.1 to explain what is meant by the term conjugated protein.
* contains non-protein groups
* has prosthetic group
* prosthetic group is Fe
* prosthetic group attached by covalent bond
* has prosthetic group
* prosthetic group is Fe
* prosthetic group attached by covalent bond
89
New cards
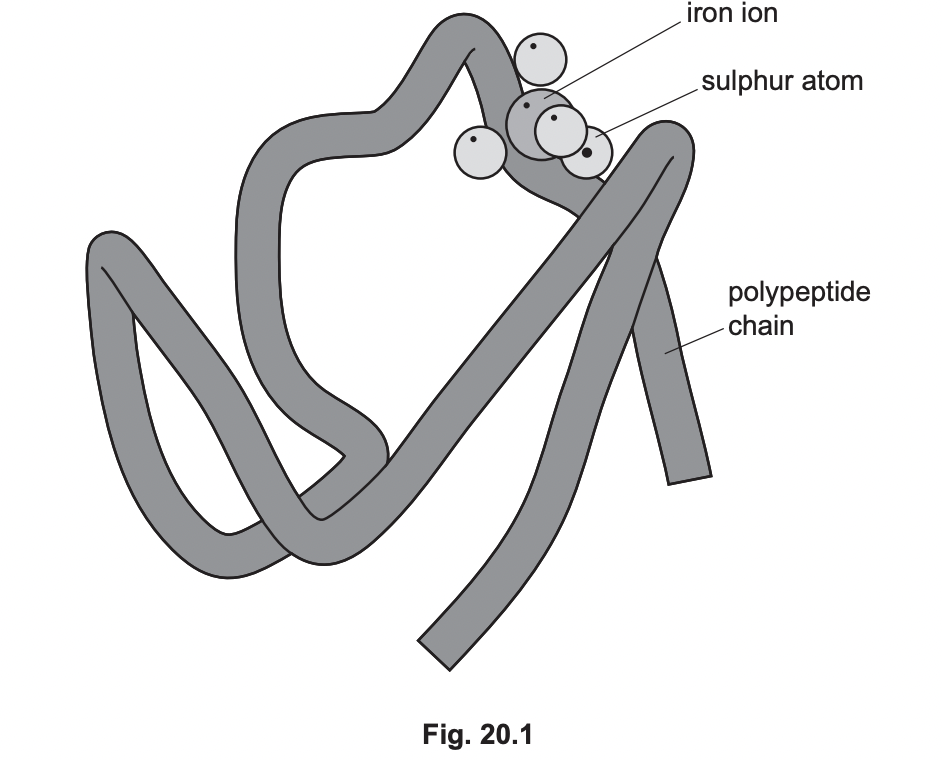
Using the information provided about rubredoxin, state two similarities between the structures of rubredoxin and haemoglobin.
* contains polypeptide chains
* have sulphur atoms
* have prosthetic groups
* contain iron ions
* have sulphur atoms
* have prosthetic groups
* contain iron ions
90
New cards
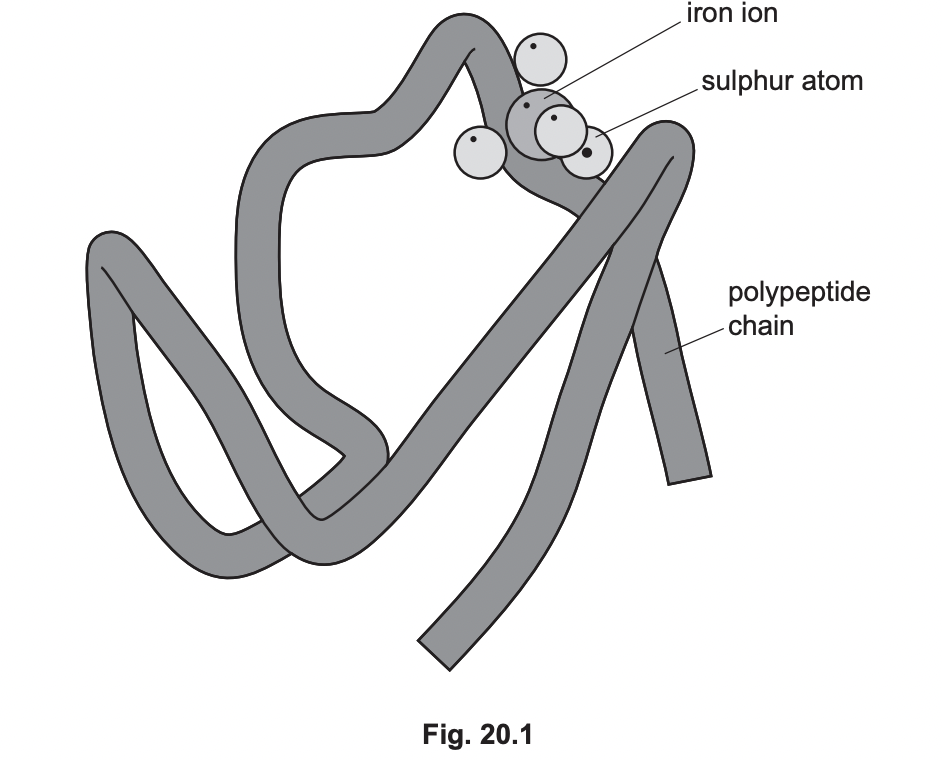
Using the information provided about rubredoxin, state two other differences between the structures of rubredoxin and haemoglobin.
1. hemoglobin is larger molecule
2. haemoglobin has quaternary structure
3. haemoglobin has more than one prosthetic group
4. haemoglobin contains haem groups
91
New cards
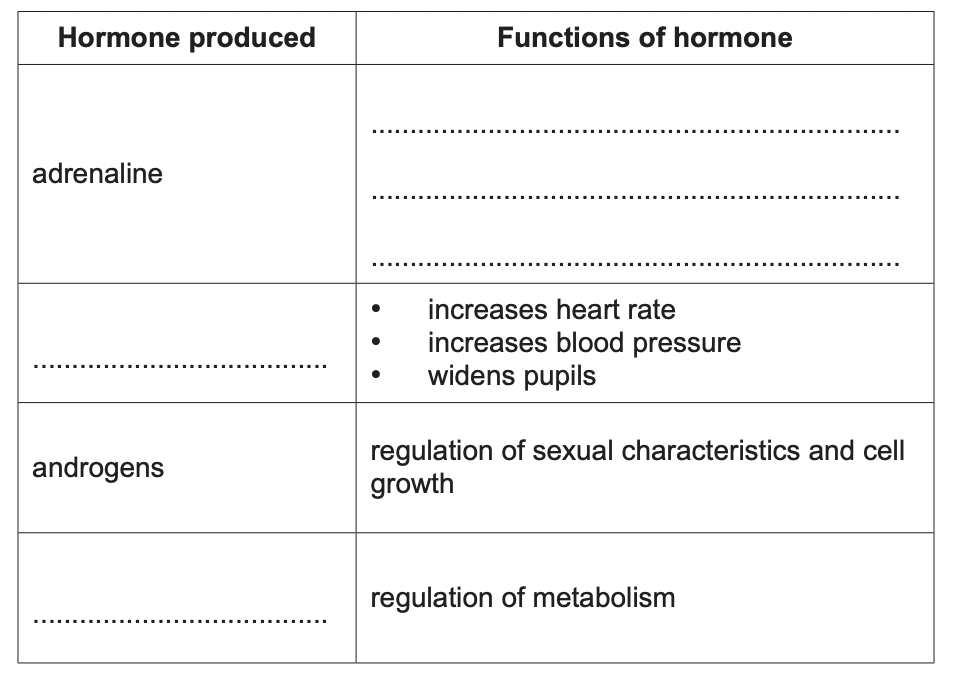
complete table
1. increases heart rate, increases blood flow to muscles, increases blood glucose level
2. noradrenaline
3. cortisol
92
New cards
name of the region of the adrenal gland that secretes adrenaline.
adrenal medulla
93
New cards
Suggest why reduced heart rate is sometimes seen in people who are very aerobically fit.
increased stroke volume / AW
increased volume of ventricle (chamber)
increased , thickness / strength , of heart muscle
increased volume of ventricle (chamber)
increased , thickness / strength , of heart muscle
94
New cards
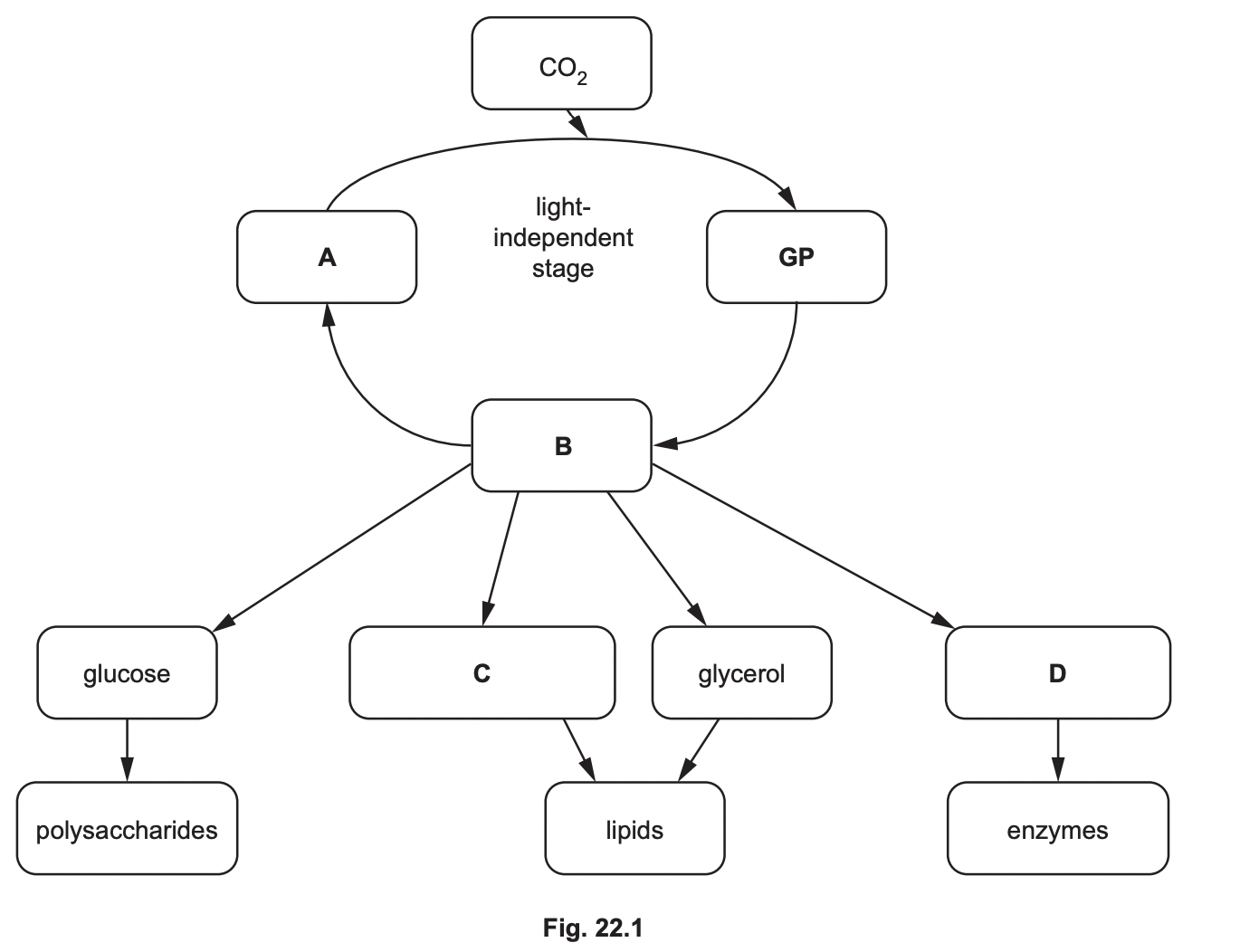
Identify A, B, C, D
A: RuBP
B: TP
C: Fatty acid
D: amino acids
B: TP
C: Fatty acid
D: amino acids
95
New cards
The light-independent stage of photosynthesis used to be referred to as the ‘dark reaction’.
(i) Explain why this is both an accurate and an inaccurate way to describe the light independent stage
(i) Explain why this is both an accurate and an inaccurate way to describe the light independent stage
does not require photons
\
needs ATP produced in light-dependent stage
\
needs ATP produced in light-dependent stage
96
New cards
Name the enzyme responsible for fixing CO2 in the light-independent stage
ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase
97
New cards
The scientist then investigated the effect of auxin on P. pusillus stems.
The growing tips of stems were removed and the stems were placed in solutions containing different concentrations of auxin.
The scientist analysed the results and determined the following relationship:
The higher the concentration of auxin in the solution, the fewer side shoots grew on the P. pusillus stems.
(i) Explain why this relationship occurs in P. pusillus stems.
The growing tips of stems were removed and the stems were placed in solutions containing different concentrations of auxin.
The scientist analysed the results and determined the following relationship:
The higher the concentration of auxin in the solution, the fewer side shoots grew on the P. pusillus stems.
(i) Explain why this relationship occurs in P. pusillus stems.
auxin causes apical dominance
98
New cards
Give two examples of the commercial uses of auxin.
1. rooting powder
2. tissue culture
3. weed killers
4. production of seedless fruit
5. promotes fruit ripening
99
New cards
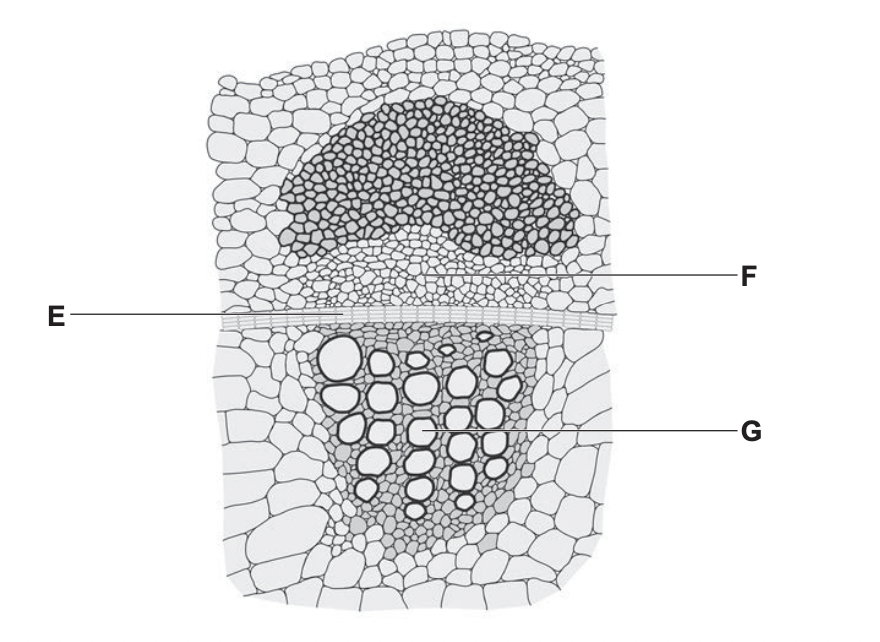
Name of tissue E
Function of Tissue F
Function of tissue G
Function of Tissue F
Function of tissue G
CAMBIUM
TRANSPORT OF ASSIMILATES
TRANSPORT OF WATER
TRANSPORT OF ASSIMILATES
TRANSPORT OF WATER
100
New cards
Large multicellular animals need a transport system for oxygen and carbon dioxide. Large multicellular plants do not need a transport system for oxygen and carbon dioxide, explain these observations
Plant cells have a low metabolic rate