instrumental chap 18 + NMR
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
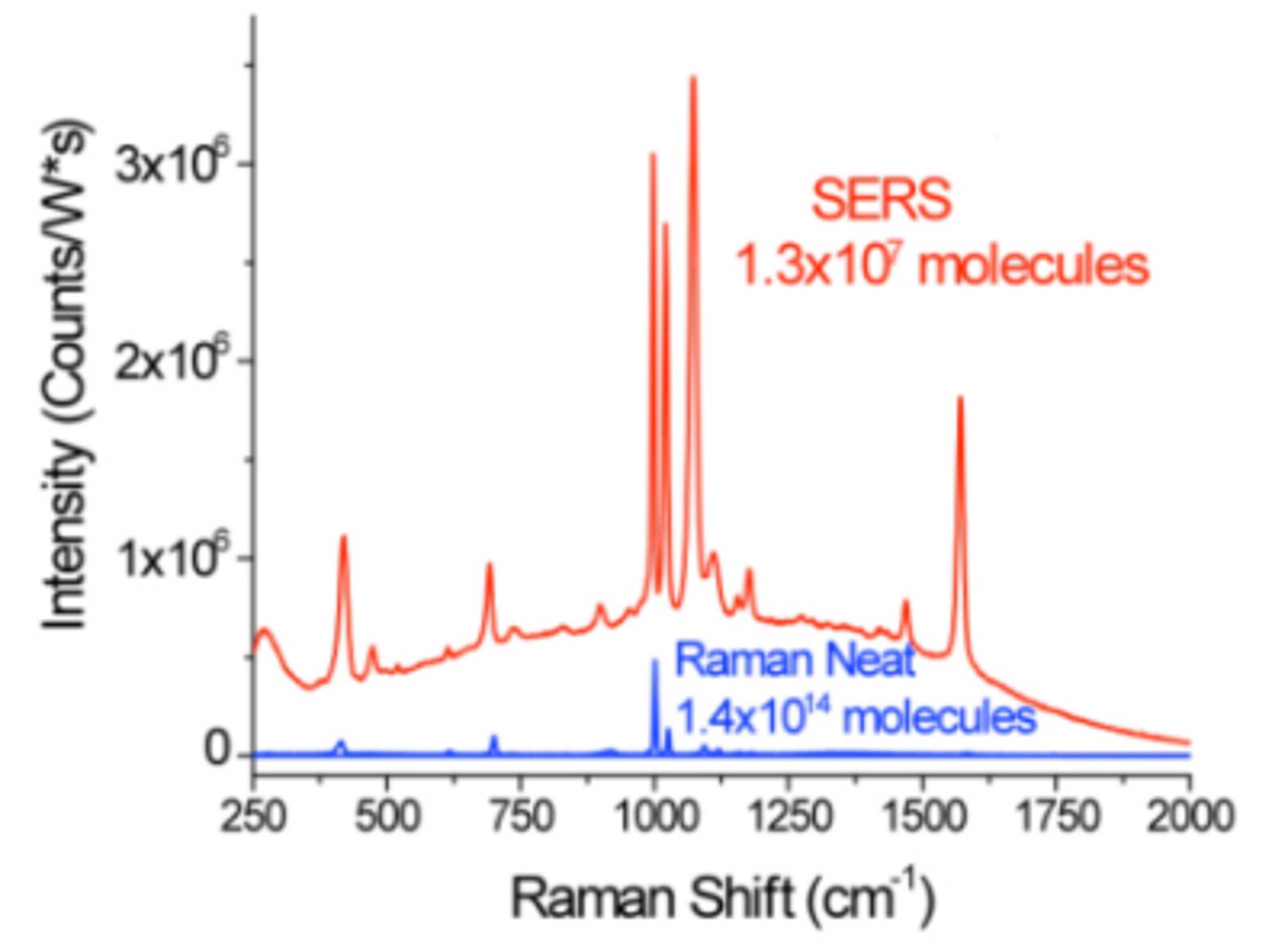
raman spectroscopy
the measurement of the wavelength and intensity of inelastically scattered light from molecules.
wavelength of excitation source
raman shifts are completely independent of
high light throughput, simultaneous measurement of all wavelength, increased scan rate by signal averaging, high precision, reduces fluorescence
FT-Raman advantages
fluorescence and photodecomposition of sample, water absorption
problems with conventional raman
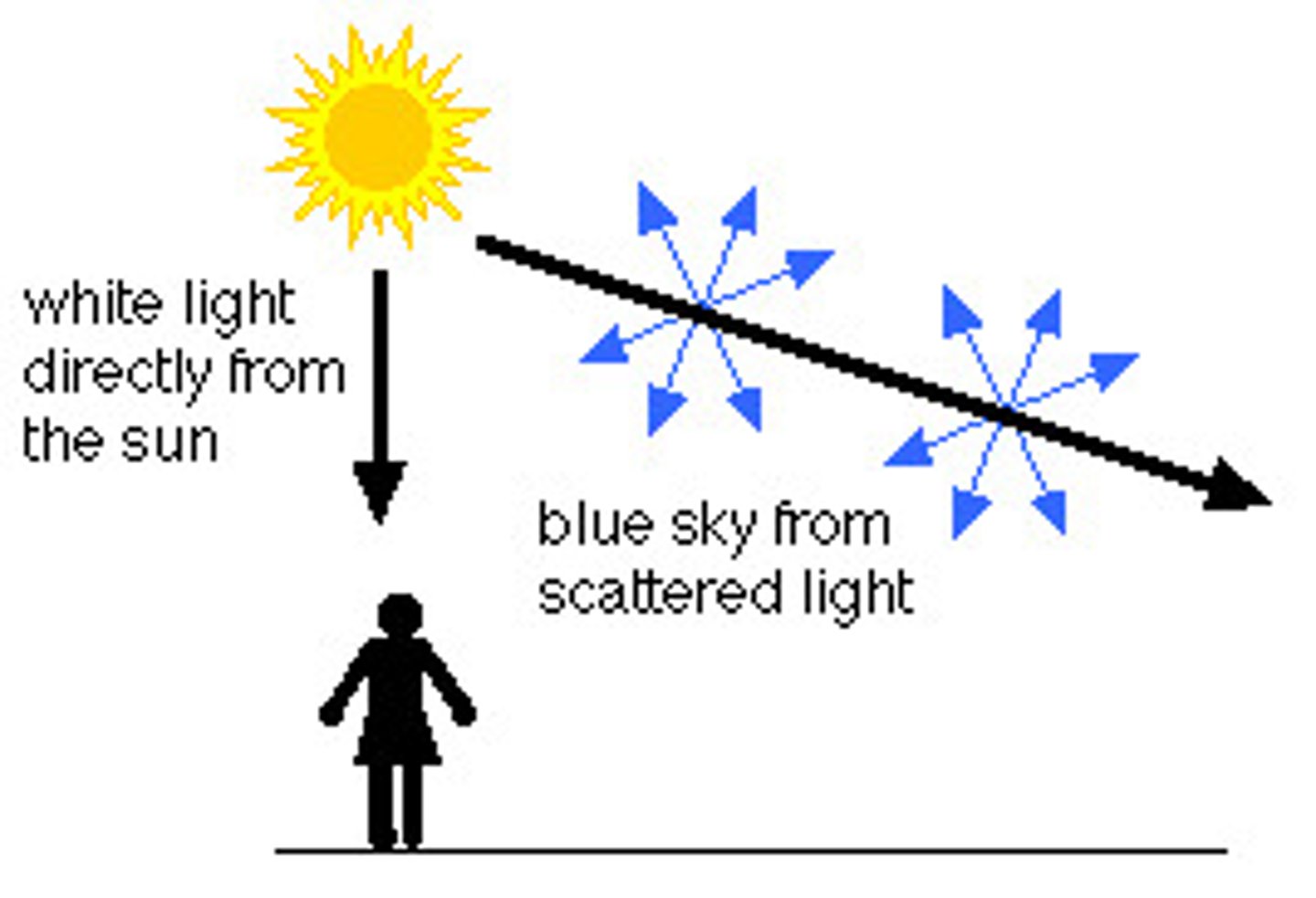
rayleigh scattering
scattering of light caused by atmospheric particles smaller than the wavelength being scattered
raman scattering
scattering of light in which the wavelength of scattered light is changed from that of incident light by an energy corresponding to vibrational energy of the molecule responsible for scattering
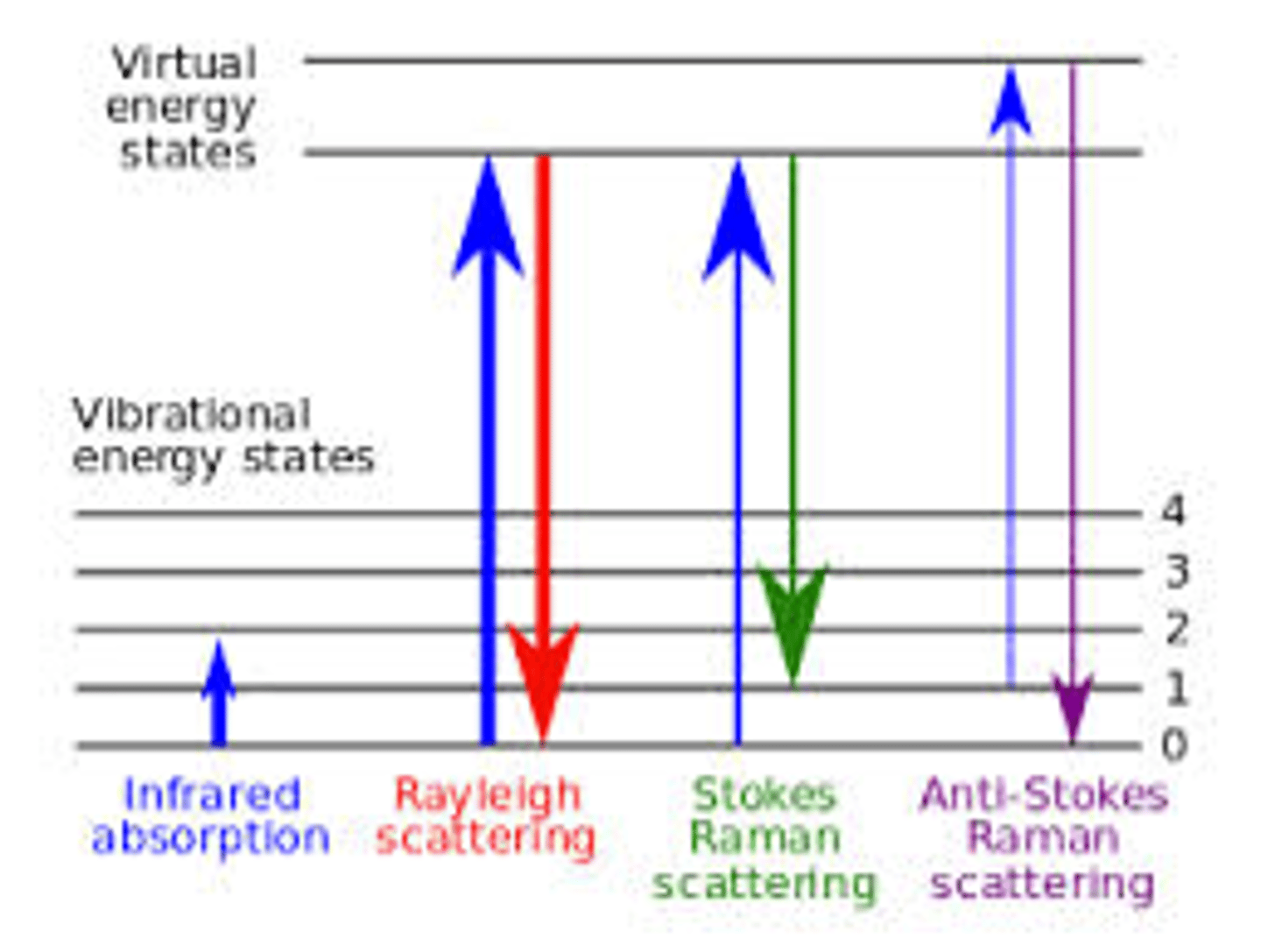
Rayleigh has the same energy as the incident light, Raman is inelastic and the scattered light has a different energy
rayleigh vs raman
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy
Technique used for determining the three-dimensional structure of a protein. It is performed in solution without requiring a protein crystal.
larmor frequency
the specific frequency at which magnetic resonance in a nucleus can be excited and detected, and varies directly with magnetic field strength
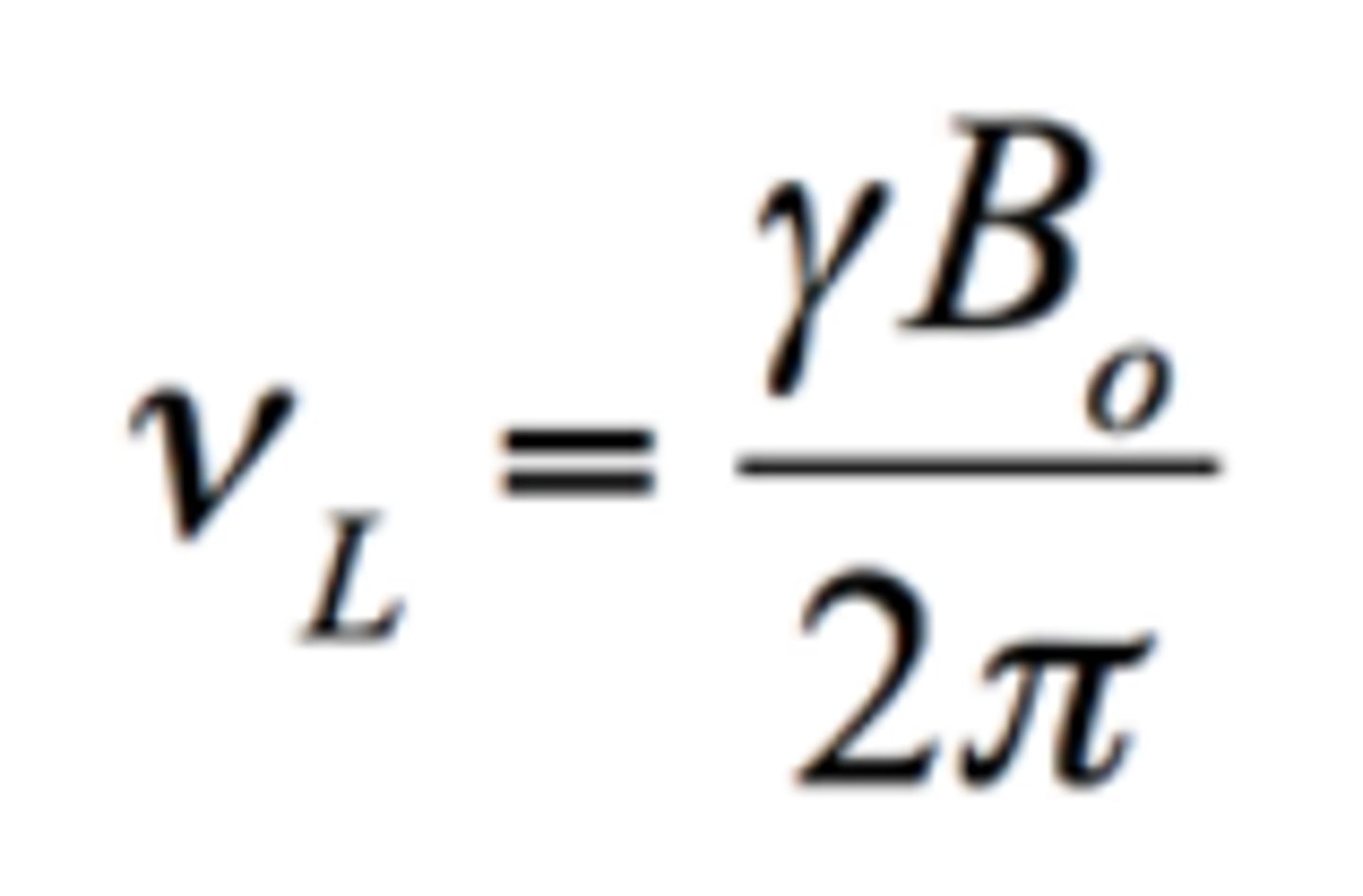
longitudinal relaxation
Return of longitudinal magnetization to its equilibrium value after RF excitation due to the exchange of energy between the nuclear spins and the lattice
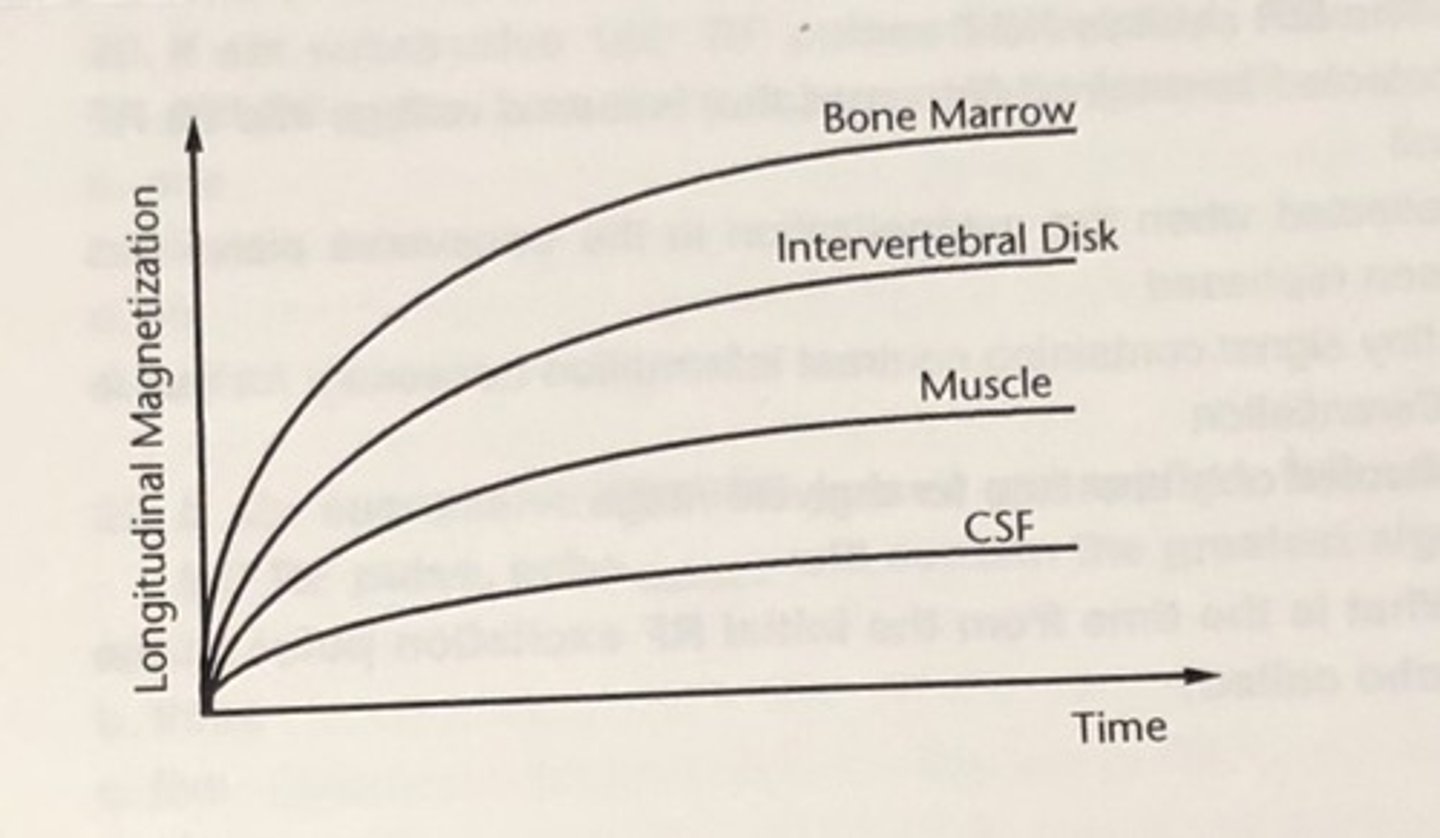
transverse relaxation
decay of transverse magnetization through the loss of phase coherence between precessing spins due to spin exchange; also known as spin-spin relaxation
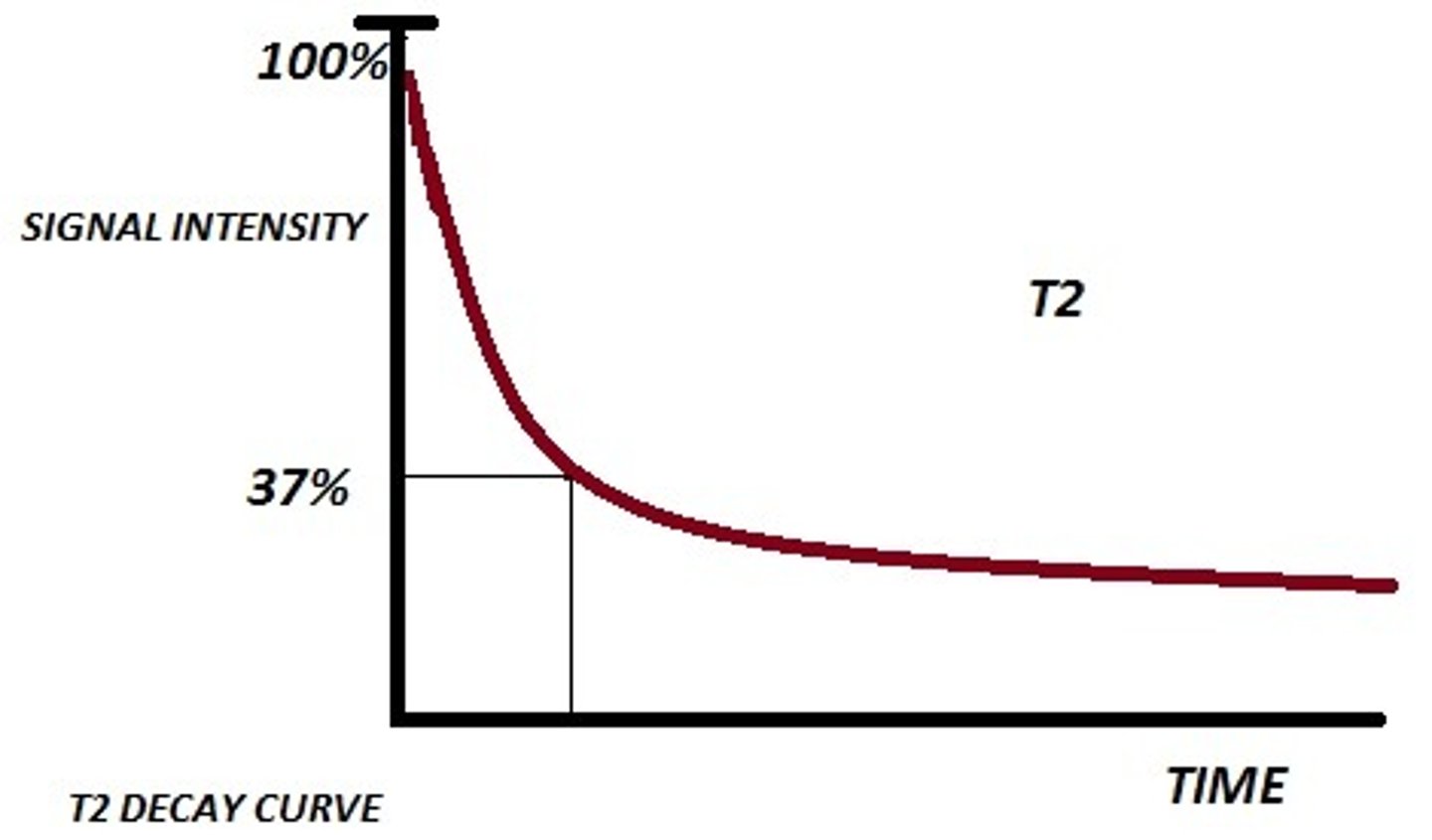
FT NMR
Fourier-transform NMR; a rapid technique for recording NMR spectra in which all magnetic nuclei absorb at the same time.
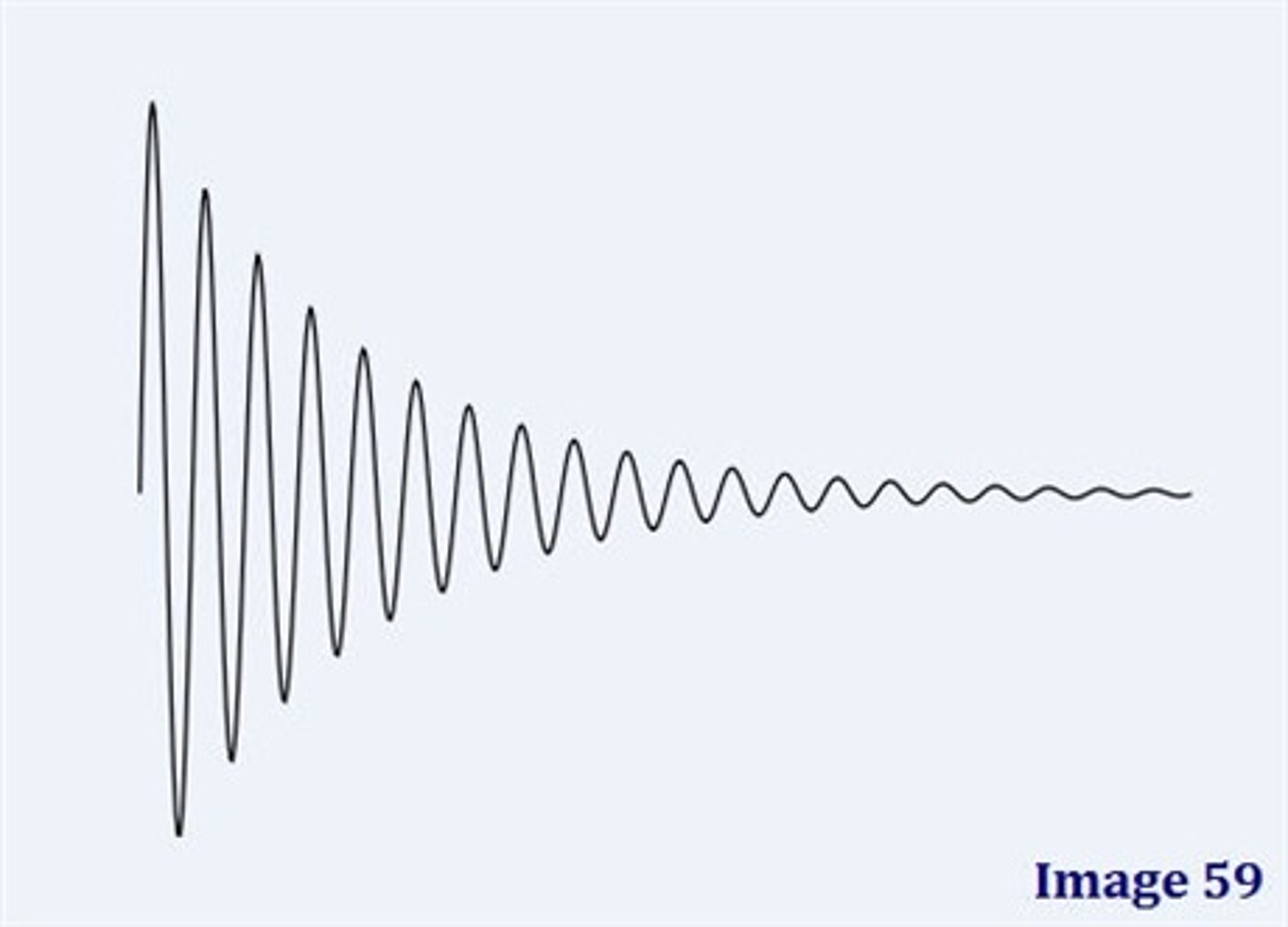
free induction decay
a time-based electrical signal that is detected in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, that is produced by induction from the motion of the magnetic moments of nuclei, that decays with time (T2*), that can be converted to a more conventional frequency-based signal using analysis by Fourier transforms; abbreviated FID
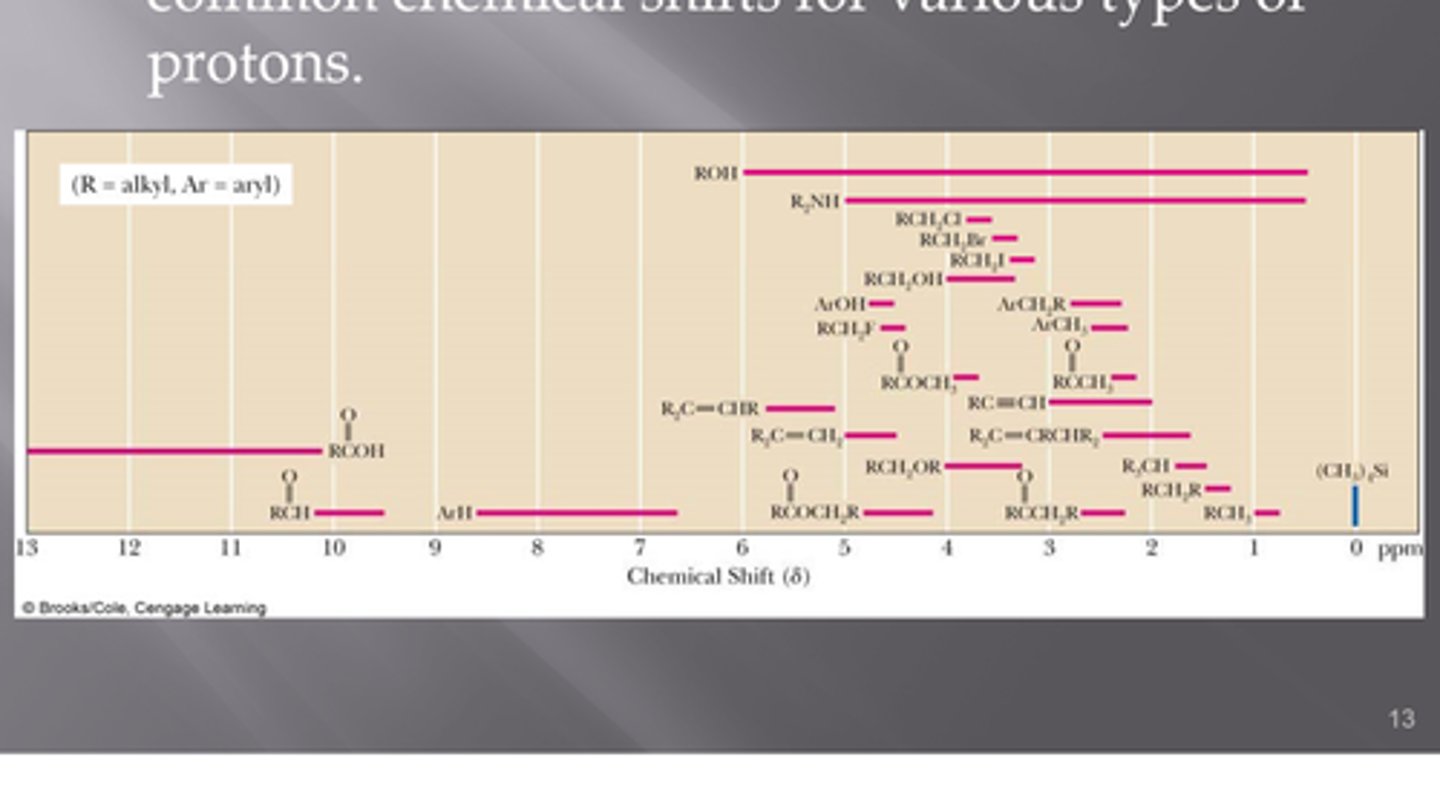
chemical shift
difference between resonance frequency of chemically shifted hydrogens and those on reference compound
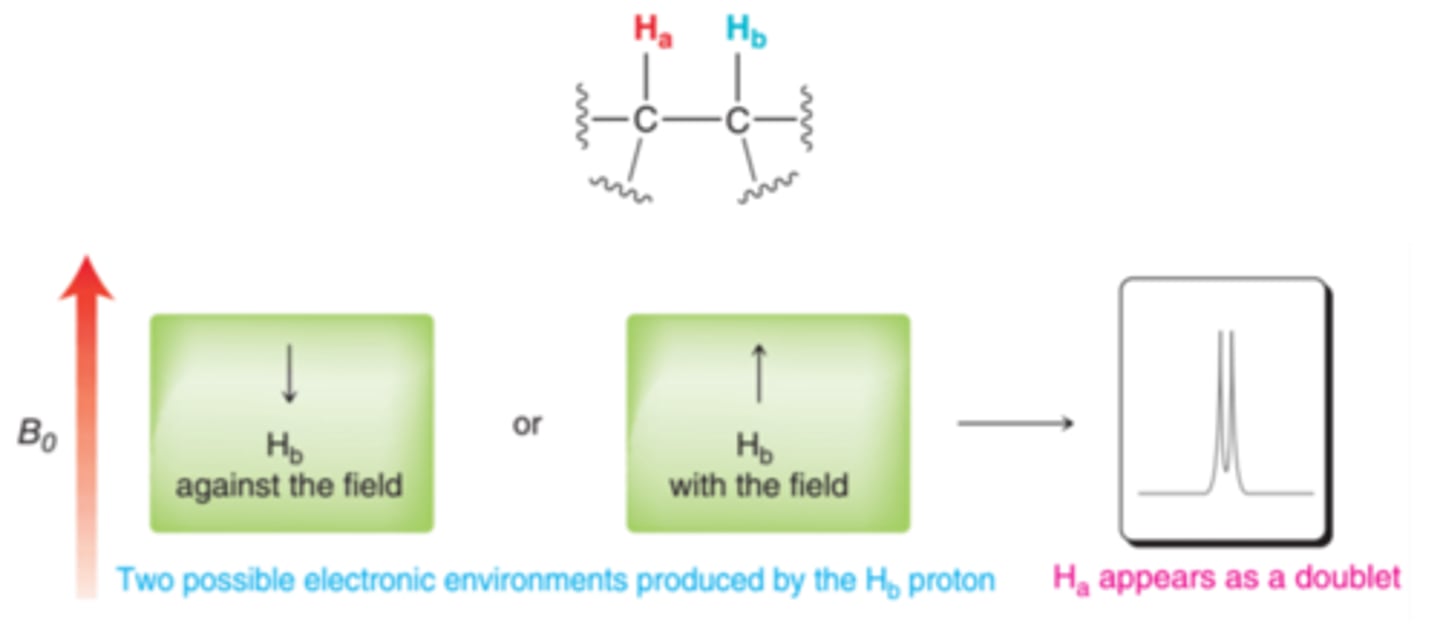
spin-spin splitting
splits into several smaller peaks due to neighboring H that are not chemically equivalent; number of peak splittings is determined by n+1 where n is the number of neighboring H not chemically equivalent
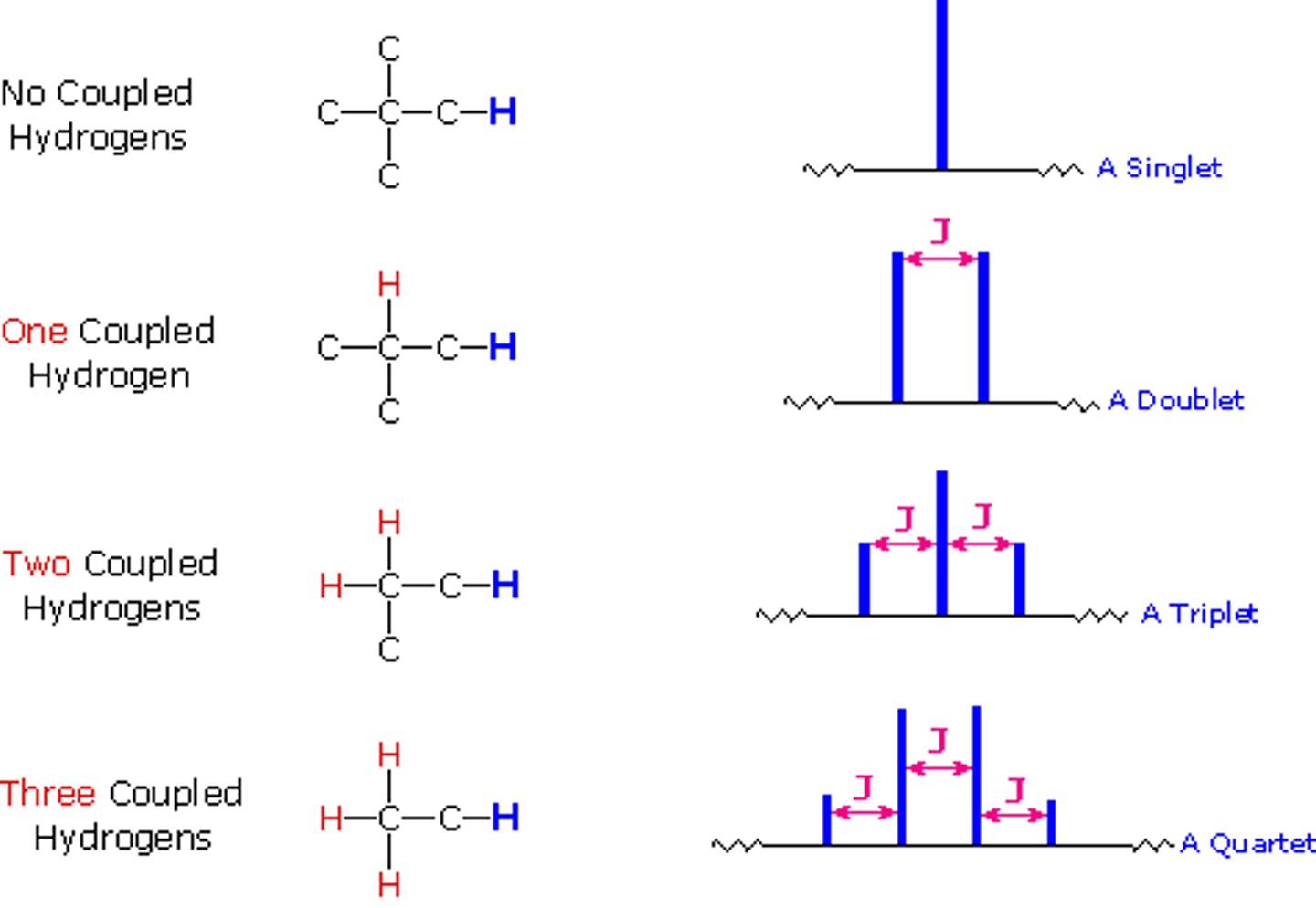
n+1 rule
if a signal is split by N neighboring equivalent protons, it will be split into N+1 peaks
FT-NMR spectrometers
advanced analytical tools that use radiofrequency pulses and Fourier transformation to rapidly analyze molecular structures
superconducting solenoids, measures to compensate for drift and field inhomogeneity
magnet
resolution and sensitivity improves with field strength, spectral interpretation becomes easier
advantanges of using magnet with great strength