allergies and hypersensitivity
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the most common food allergy in children?
Peanut
Symptoms of a peanut allergy
*gastrointestinal pain
• diarrhea
• nausea
• hives
• Itching or tingling sensation on or around your mouth or throat
• swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat
• respiratory problems, such as shortness of breath and wheezing
• drop in blood pressure
• racing pulse
• confusion
• dizziness
• loss of consciousness
• coronary artery spasms may lead to heart attack
Treatment for an allergic reaction
-Mild reactions can be treated with OTC antihistamines
-Severe reactions require administration of epinephrine (such as an Epi-pen)
What happens when the allergic reaction starts vs when the epinephrine is administered
When you start to have an allergic reaction your blood pressure drops significantly, however whenever the epinephrine is administered your blood pressure starts to increase
Allergen classes
-Prolamin superfamily
-Cupin superfamily
-Profilins
-bet v-1-related proteins
-oleosin
-defensin
when are allergens in food considered major?
Allergens in food are considered major if they are recognized by the serum IgE of greater than 50% of the allergic population
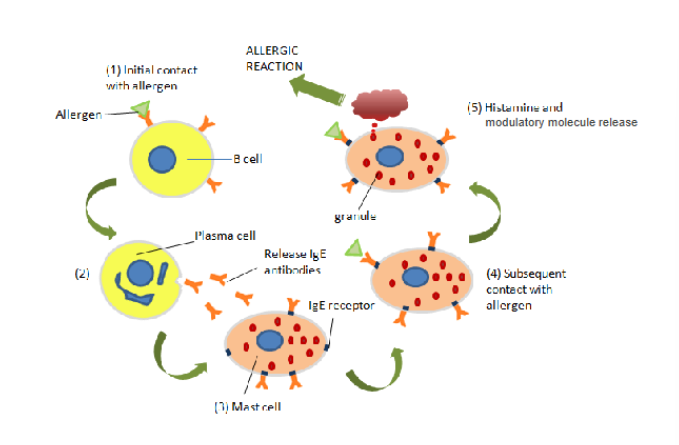
The cause of allergic reaction
• your immune system makes IgE antibodies to the peanut allergens
• these IgE molecules bind to the Fcε receptors on mast cells, sensitizing them
• upon the next exposure to antigen, the antigen binds to and crosslinks the IgE
molecules on the mast cells
• the mast cells degranulate and release histamine and other modulatory molecules
Hypersensitivity reaction 1: IgE mediated
Anaphylaxis
Allergies
Asthma (atopic)
Hypersensitivity reaction 2: antibodies
GPS, Graves disease
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Rheumatic fever
Hypersensitivity reaction 3: Antigen- antibody complex
Glomerulonephritis
Arthus reaction
SLE Serum Sickness
Hypersensitivity reaction 4: T cell Mediated
Dermatitis (contact)
IBD
GVHD
M. Sclerosis
T1DM, TB
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Th1
IgG production (pathogen coating)
Th2
IgE production → binds to mast cells → common allergy symptoms
Th2 vs Th1
If you have more Th2 youre more exposed to antigens, and vise versa
Hygiene hypothesis
This hypothesis proposes that early and frequent exposure to bacterial and other
antigens, such as is common in developing nations, leads to a normal Th1 response, but
that better public hygiene and less infections observed in industrialized nations may lead
to persistence of the Th2 phenotype and thereby increase our risk for developing
allergies
Allergy shots
regular injections over a period of time (generally around three to five years) to stop or reduce allergy attacks. Each shot contains a small amount of the allergens, just enough to stimulate your immune system. Overtime the allergen dose is increased to cause desensitization.
Etokimab
an antibody that inhibits the activity of IL33, which is critical in IgE mediated allergic responses
Hypersensitivity
Body’s response to a particular substance in an exaggerated way
4 types of hypersensitivity
Type 1(allergy/anaphylaxis)
Type 2 (cytotoxic)
Type 3 (immune complex)
Type 4 (Delayed type)
ACID
Immediate vs delayed hypersensivity
Type 1, 2, & 3 are immediate
Type 4 is delayed
immediate is antibody mediated; Delayed is t cell mediated
Immediate happens within 1-3 hours; Delayed happens in 24-72 hours
What is type 1 hypersensitivity triggered by
The interaction of allergens with allergen-specific IgE antibodies that are bound to mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils
When it binds to IgE antibodies, the cells degranulate and release a potent mixture of inflammatory mediators
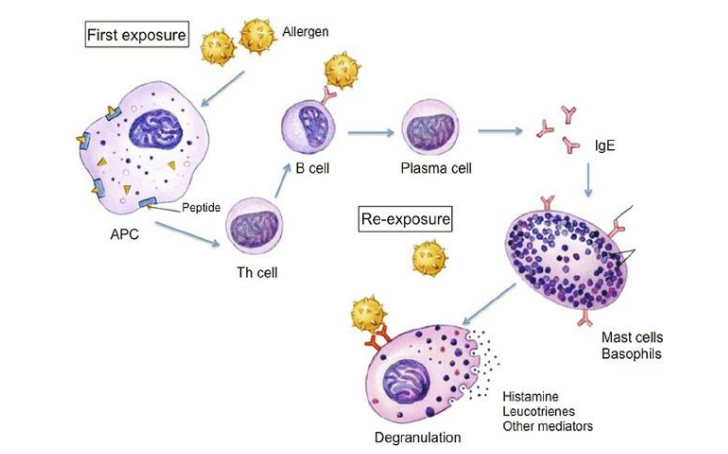
Common type 1 hypersensitivity allergies
skin allergies
hay fever
allergic rhinitis
Asthma
food allergy
First step of hypersensitivity mechanism
first step is sensitization (asymptomatic)
activation of B lymphocytes to produce IgE and sensitization of mast cells
Second step of type 1 hypersensitivity
Subsequent exposure (symptomatic)
-Includes the activation of mast cells, basophils, and degranulation
-clinical manifestations of type 1 reactions result from mediators released during mast cells or basophil degranulation get an increased vascular permeability and inflammatory state
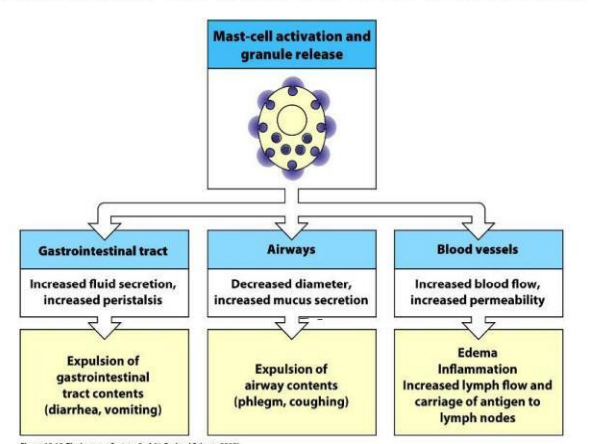
Effect of Mast cell degranulation
Localized reaction of type 1 hypersensitivity
Rashes or blisters in the skin
increased eye and nasal secretions, itching, and sneezing
oropharyngeal mucosal edema
abdominal pain
diarrhea
vomiting
bronchospasm
wheezing