unit 3- Early Modern Era Economic Transformations
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What luxury commodities were in high demand in Europe but could only be acquired from Asia?
Spices, porcelain, and silk
What two groups held a monopoly control on the overland trade to Europe in goods from Asia?
Muslim empires control the middle east- and the overland trade (silk road). Made it to where it costed a fortune to obtain items that were very high in demand.
What happens to prices when demand is high, but supply is low?
Prices go up
How did religious beliefs play a role in the rationale of European exploration?
Catholic Europeans were deeply committed to spreading Catholicism around the word.
What Muslim empire was putting the most pressure on Christian Europe?
Ottomans
Who were three religious reformers that had created problems for the Catholic Church?
John Wycliffe (England), John Hus (bohemia burned at the stake), Martin Luther
How did the political structure of Europe in the early modern era lead to competition for overseas exploration?
Rivalries existed at a national level for power, wealth, prestige, and fame. For one nation to win other must necessarily lose/ pushes all of Europeans leaders to try to get in the front of the line- often with an armed conflict.
What European nation led the early stages of the exploration era?
Portugal
What explorer, working for Portugal, made the first successful voyage to India?
Vasco Da Gama
What kind of “empire” did Portugal build? Explain how it is different from traditional empires
Trading post empire… never fully controlled the territory but controlled the shipping and trade through the areas by establishing fortified bases at several important locations.
What strategically significant places did Portugal control as part of its expansion.
Mabasa (east Africa), Hormuz (entrance to the persian gulf), Goa (west coast of India), Malacca (southeast Asia *most important one because it is where the spices came from), Malacca, Macu
What was the “cartaz?”
a license that Portugal required all ships passing through their waters to purchase
Why did Portugal’s influence fade after 1600?
Small nation limited population and resources didn’t have the gold/silver from Americas that Spain did.
What European nations challenged Portugal for control of trade in Asia
Spain and the Dutch
Where did Spain establish a significant colony in Asia? Philippines Why was it important?
It was close to China and spice islands of Indonesia; it was not controlled by a single government making it easy to take over.
What explorer’s voyage was the basis for Spain’s claim on the Philippines?
Magellan’s voyage
What religious group did Spain come into contact with in its efforts to colonize the Philippines?
Islam
What two European nations set up joint-stock companies called “…East India Trading Companies
the Dutch (from holland) and the English (British)
What is a “joint-stock” company?
Private shareholders bought a stake and pooled their money, then government of England and holland gave them charters with unique powers
What special rights did England and Holland give to their East India Trading Companies?
Could raise private armies/ navies, make war in the name of their home country, could govern foreign people.
Where did the Dutch East India Company focus its efforts?
Islands of Indonesia
Where did the English East India Company focus its efforts?
India
What large, powerful empire did the English encounter in India?
Mughals Empire
What was Japan’s first response to the arrival of Europeans on their shores?
Allowed some early Portuguese traders and missionaries in the country.
What was Japan’s first response to the arrival of Europeans on their shores? WHY?
Only allowed them there for long enough to figure out what weapons and useful technologies they had
How did the Shogun dramatically change Japan’s actions toward Europeans?
Kicked out the Portuguese traders and banned all missionaries. Repression of Christianity was brutal.
Who were the “daimyo?”
regional nobility that had been fighting for control using their private armies of samurai
What precious metal formed the basis of the world economy by 1600?
sliver
Why was silver especially sought after in China during this time?
A new tax was put on their people and had to be paid in sliver
Where was the silver discovery that led to much of Spain’s wealth during this time?
In the Andes mountain at Potosi
Why was Spain especially well-positioned to supply the demand for silver?
They were able to supply 85% of sliver since they had colonies in the Americas
How did the role of the Philippines in world trade grow as the importance of silver grew?
They occupied the Philippines which allowed them to exchange sliver for the products of china.
What was the standard Spanish coin?
Piece of 8
How did the need for silver transform China’s economy?
Led to an increased specialization and commercialization of the Chinese economy, had a number of effect many of them damaging to the environment of china
Why did the influx of silver wealth not lead to lasting prosperity in Spain?
Pursued military and political ambitions- spending fortunes, led to inflation, economy crashed when the abundance of sliver across the world led to a substantial drop int eh value of sliver.
What was referred to as “soft gold?
Fur
Why was fur in short supply in Europe by 1500?
Most fur being animals had been hunted to dwindling numbers
How had the “Little Ice Age” impacted demand for furs
Drove up the demand and prices for fur
In what two parts of the world did the fur hunt take place in this era?
North America, and Siberia
Where did the French do most of their fur hunting activity?
St. Lawrence valley and the Mississippi River valley.
Where did the English do most of their fur hunting activity?
Hudson Bay region (Canada)
How were native Americans and the natives of Siberia utilized in the fur hunt
Created a new economy for the Indian of North America. Traded them useful things such as copper pots, knives, cloth, guns, and alcohol
What significant negative impacts did the fur trade have on native American cultures?
Diseases, loss of traditional skills/ crafts (gunpowder weapons>bows and arrows, copper pots>wooden things, cotton clothes> leathers), introduction of alcohol (Bing drinking violence and addiction)
What significant negative impacts did the fur trade have on the environment of North America?
Led to the near extinction of beaver, led to damage to water habitats as the beavers were not filling their ecological niche, many wetlands los and other species were affected.
How did the Russian government forcibly encourage the taking of more fur-bearing animals in Siberia?
Imposed a tax payable in furs on every able bodies’ male in Siberia.
What are three common characteristics to most examples of slavery in history?
Slaves were property, slaves generally were used for manual labor or domestic tasks, slaves were vulnerable to abuse (sexual, physical, etc.)
What gender slaves were preferred in Islamic empires?
women
What gender slaves were preferred in Islamic empires… WHAT RATIO
2:1
What gender slaves were preferred in Islamic empires… FOR WHAT REASON
For household servants
Where did the Muslim empires maintain trans-Saharan slave trading networks?
Across the Sahara in both west Africa and East Africa
The production of what commodity led to more European involvement in slavery?
sugar
What European nation was first responsible for the transportation of slaves from Africa?
portuguese
What role did the Pope play in advancing the use of slave labor
Signed off on the practice finding Spain and Portugal the right to “enslave Saracens (Muslims), pagans and any other unbelievers
Approximately how many Africans were captured to be slaves?
12.5 million
How many survived the passage and actually were enslaved in the Americas
10.5 million
How did each of the following factors play a role in the choice of Africans as slaves: Proximity
Europeans were in need of labor and the large population of Africa was nearby
How did each of the following factors play a role in the choice of Africans as slaves: Biology
Africans were somewhat immune to most tropical and European diseases
How did each of the following factors play a role in the choice of Africans as slaves: Religion
were not Christian by definition not worthy of equal treatment- pope had basically said so
How did each of the following factors play a role in the choice of Africans as slaves: practicality
most were skilled farmer (work they were needed for in the Americas), could be acquired for goods Europeans had guns clothing other manufactured items
What is meant by “chattel slavery?”
African slaves used as breeding stock for children to be sold
How did the Europeans go about acquiring slaves from Africa?
Africans were willing to sell other africans into slavery. Captured slaves would be brought to coast to trading bases then the Europeans would take them on their ships.
What was the Middle Passage?
Ship ride to the Americas. Slaves were crammed into small spaces. Physically and psychologically tortuous many committed suicide
What was the African Diaspora?
Led to major population of their descendants in every nation in the western hemisphere (Haiti became a nation through a slave revolt, Africans outnumbered European immigrants until the 19th century)
How did the importation of Africans to North and South American impact the culture of those places?
Brought their religion, music, and food
How did the depopulation of Africa (especially of men) impact the social/cultural life of Africa’s remaining people?
Women were less likely to be able to marry causing women taking on non-traditional roles in their society
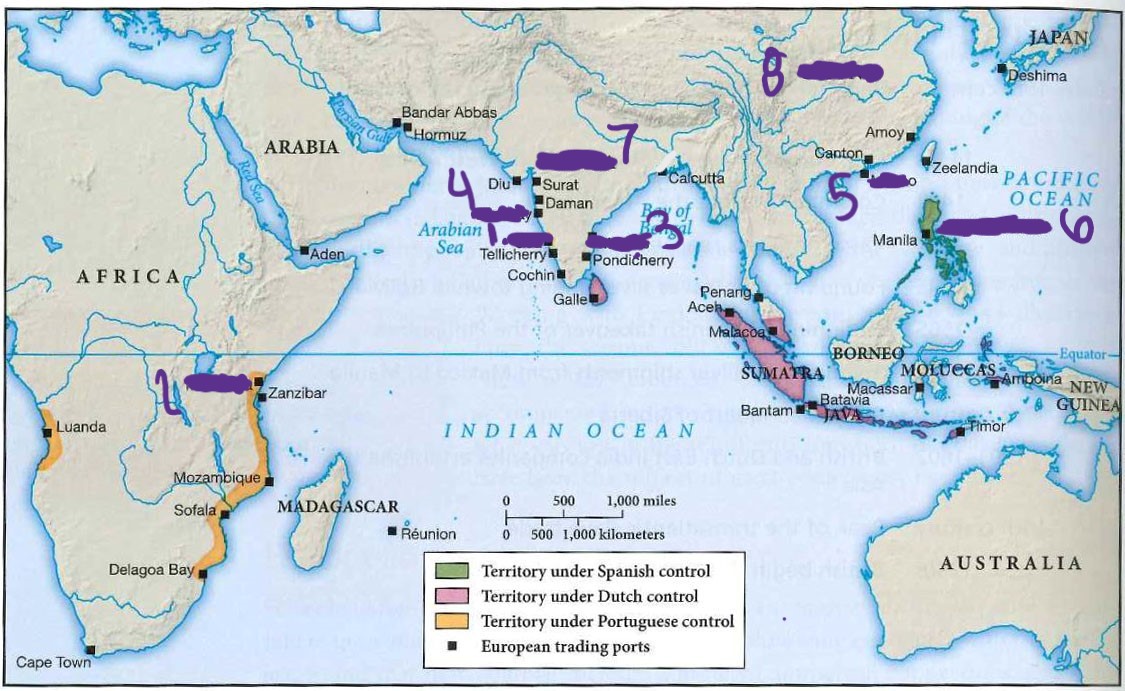
what is 1.
Goa
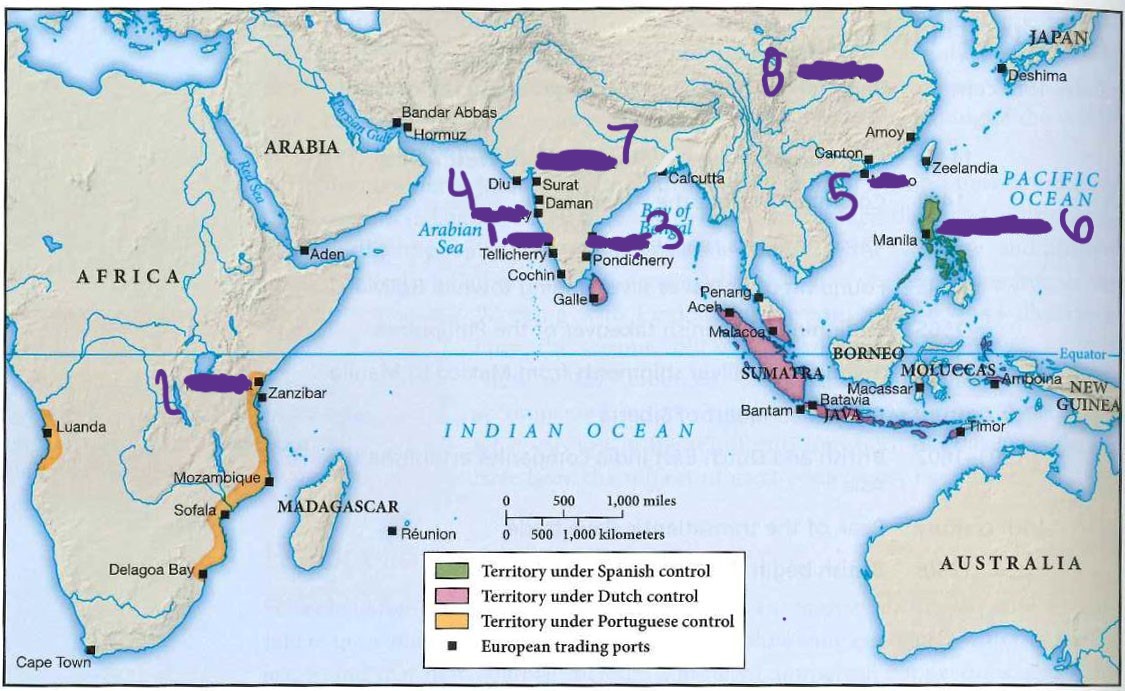
what is 2
Mombasa
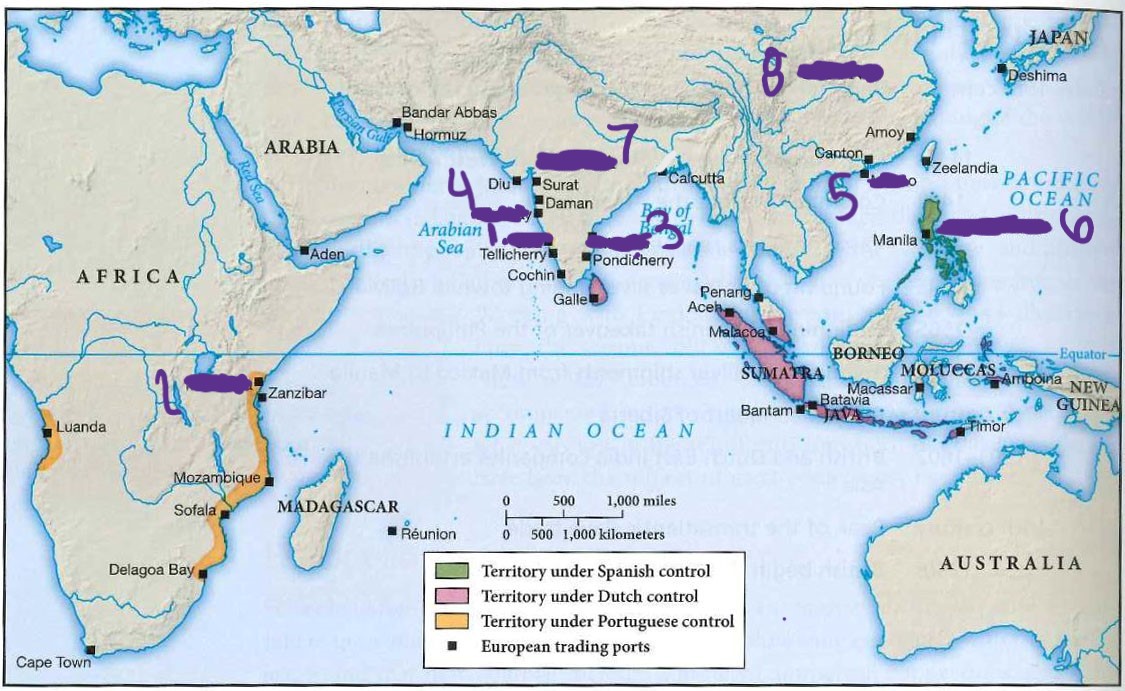
what is 3
madras
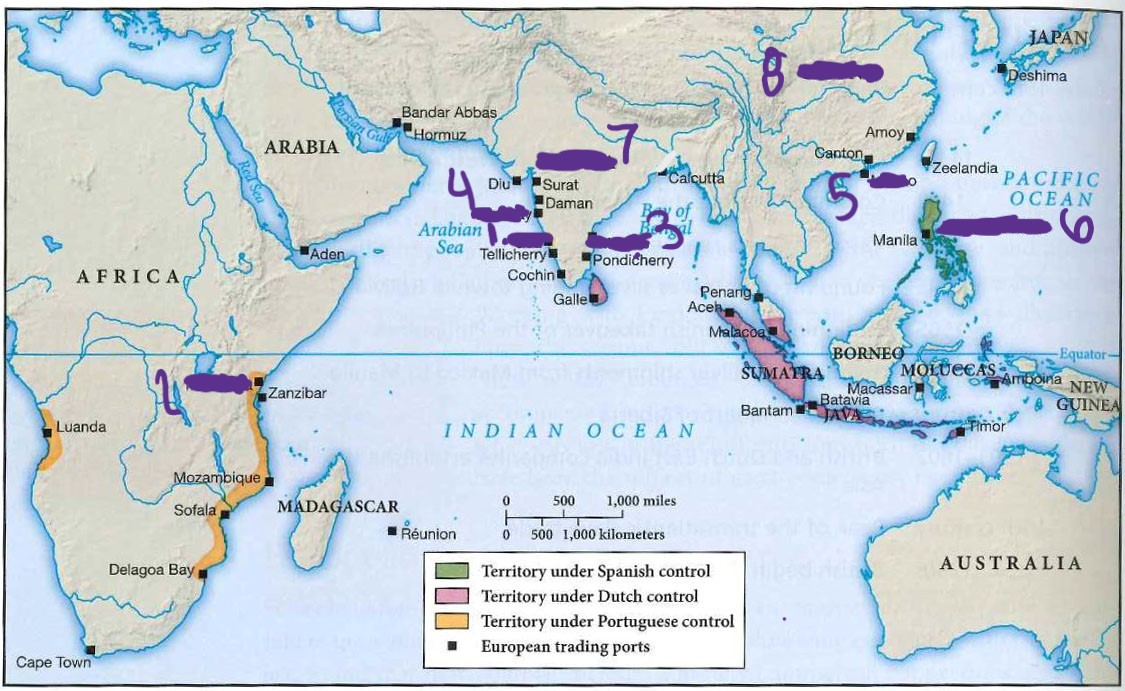
what is 4
bombay
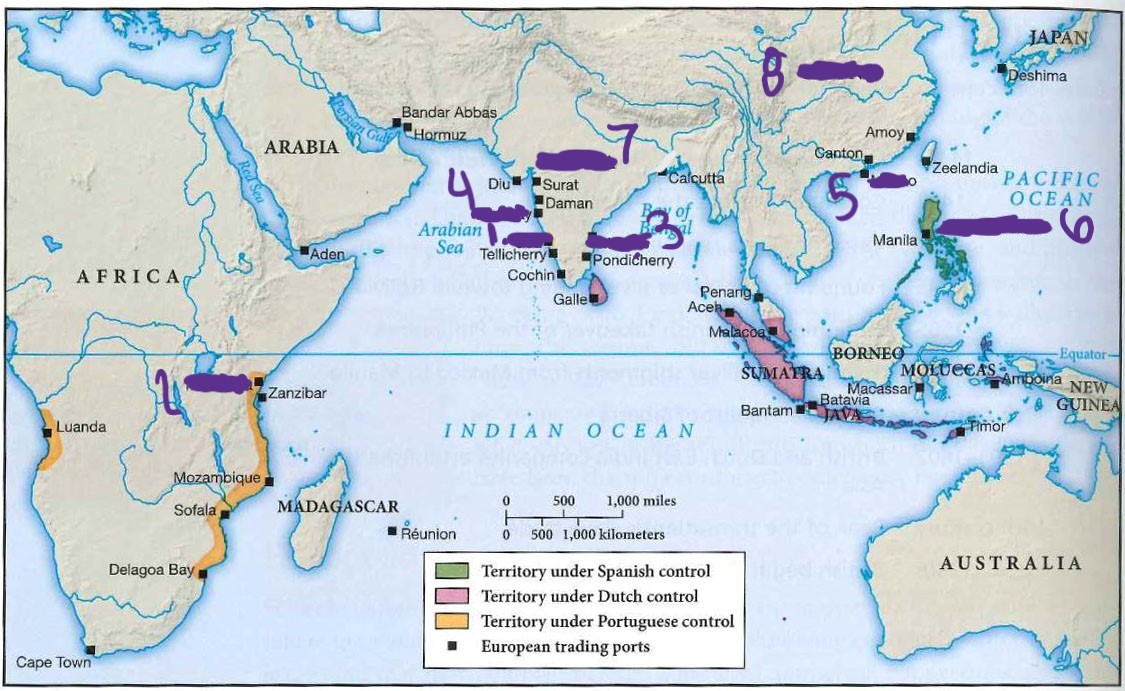
what is 5
mocao
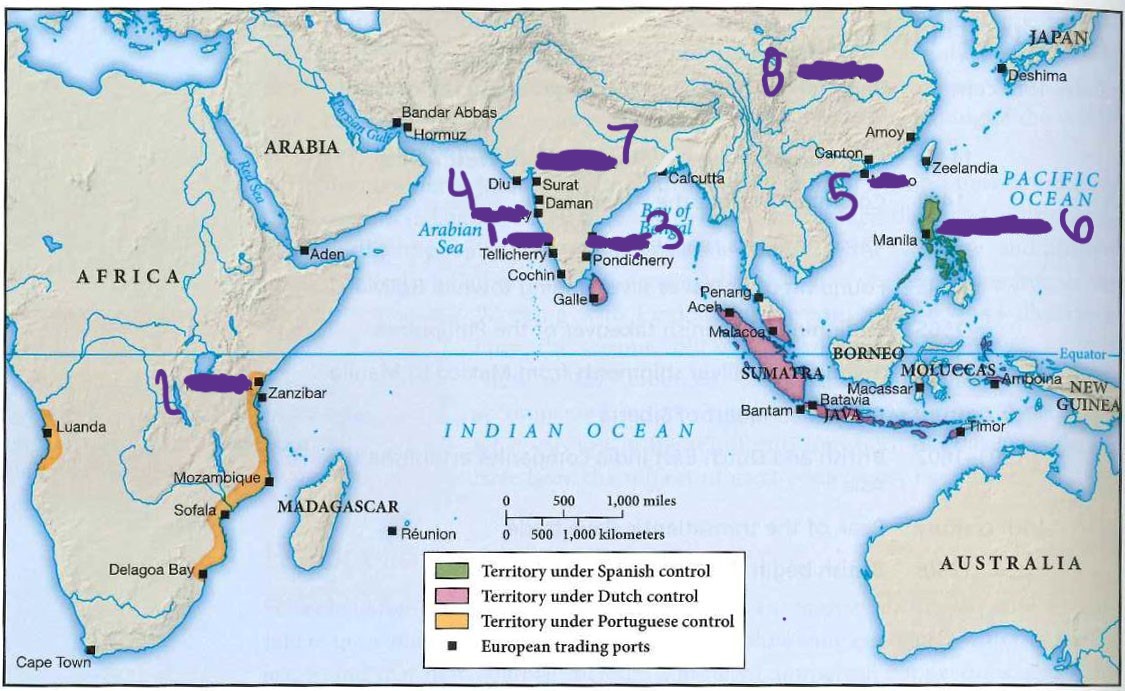
what is 6
Philippines
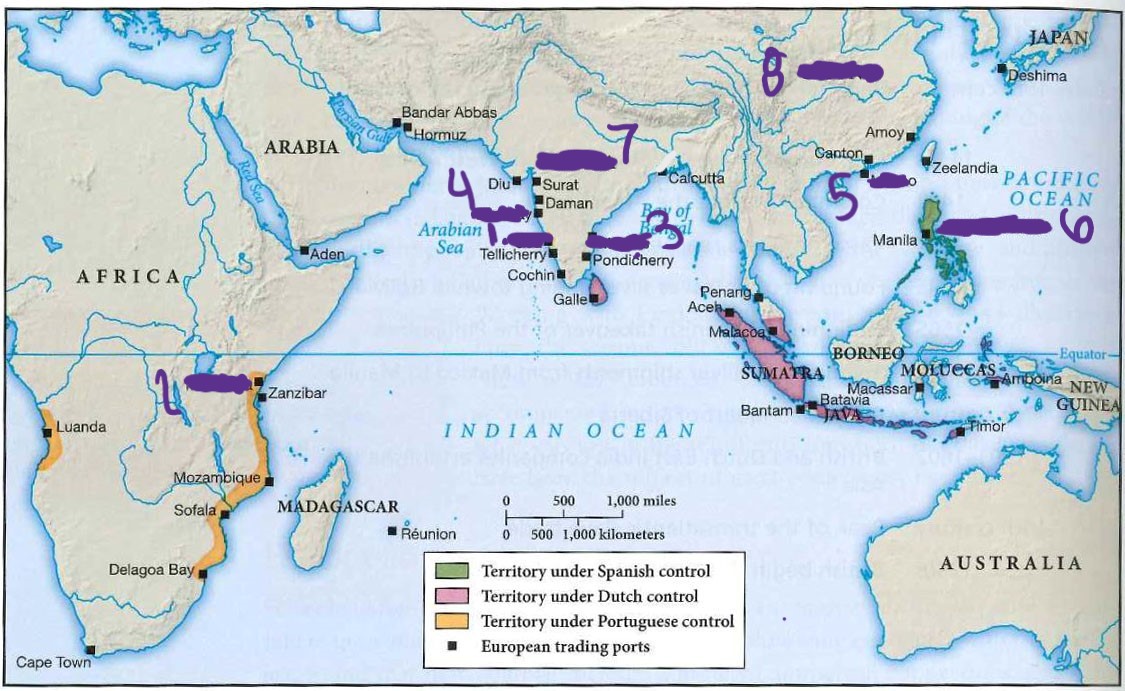
what is 7
india
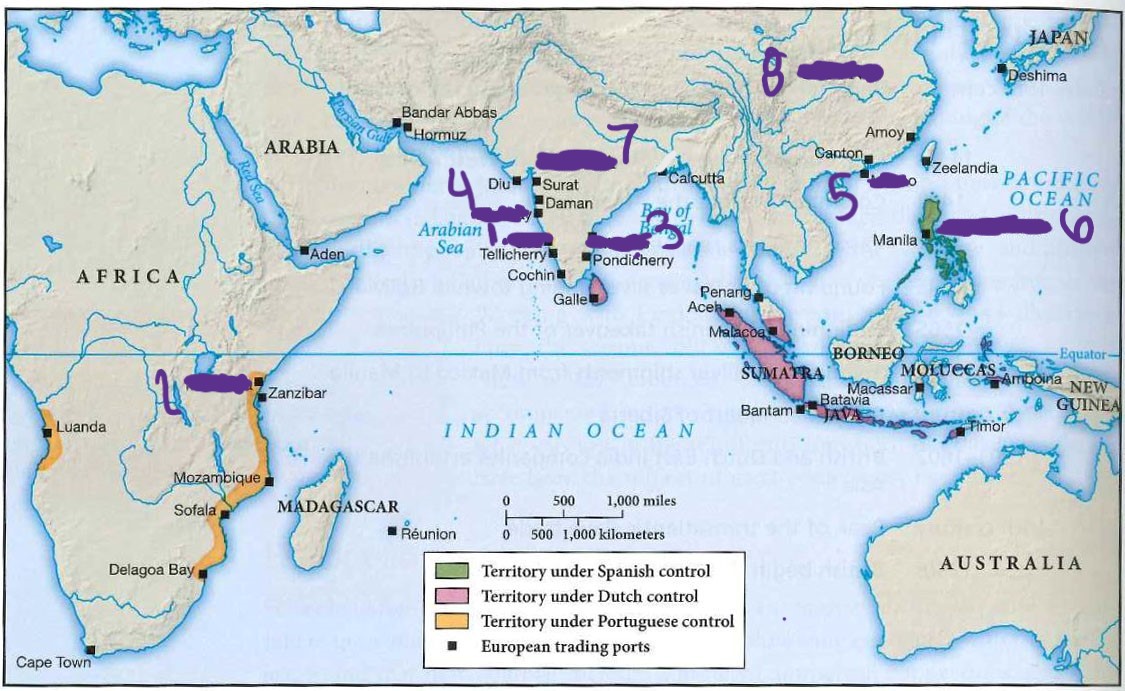
what is 8
china
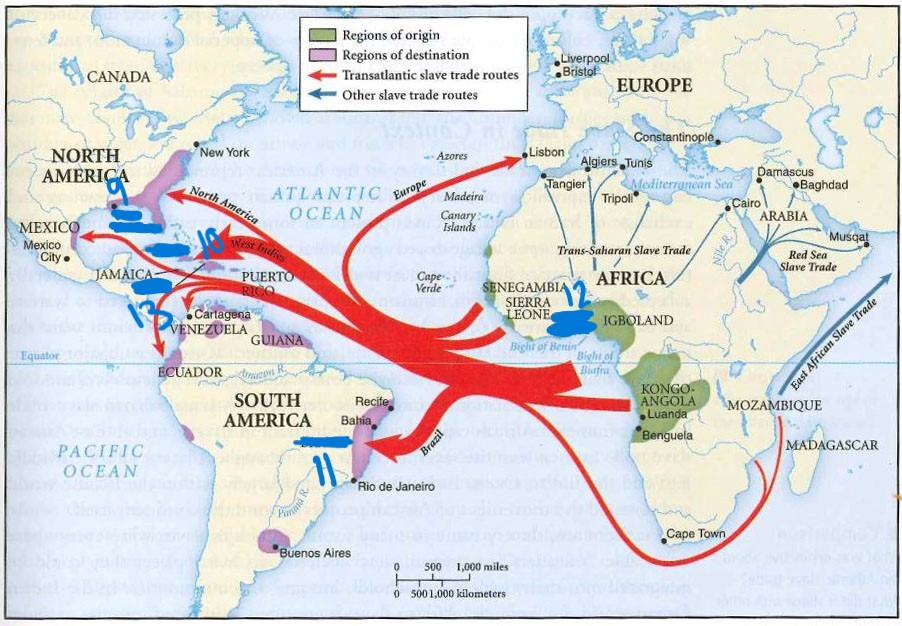
what is 9
new Orleans
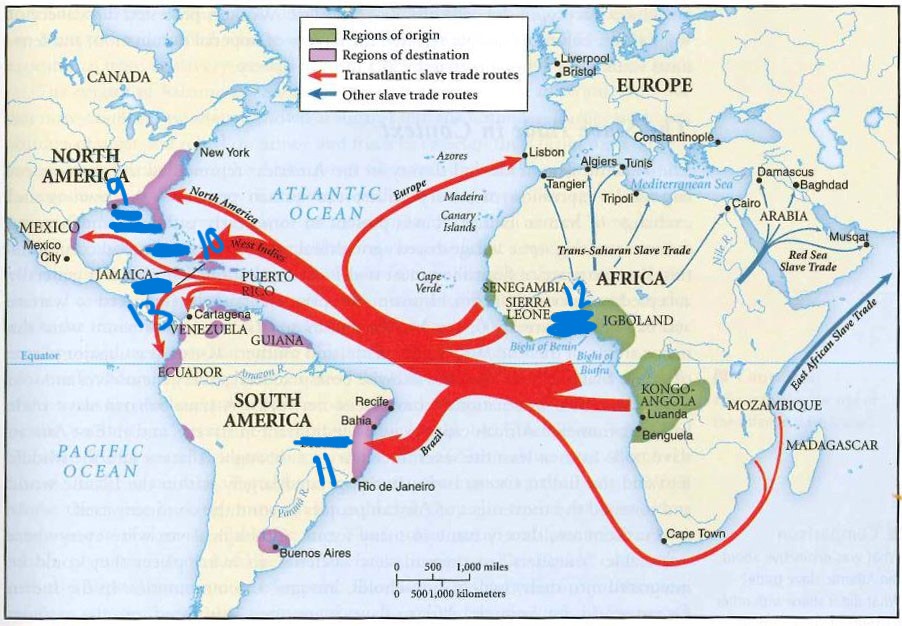
what is 10
cuba
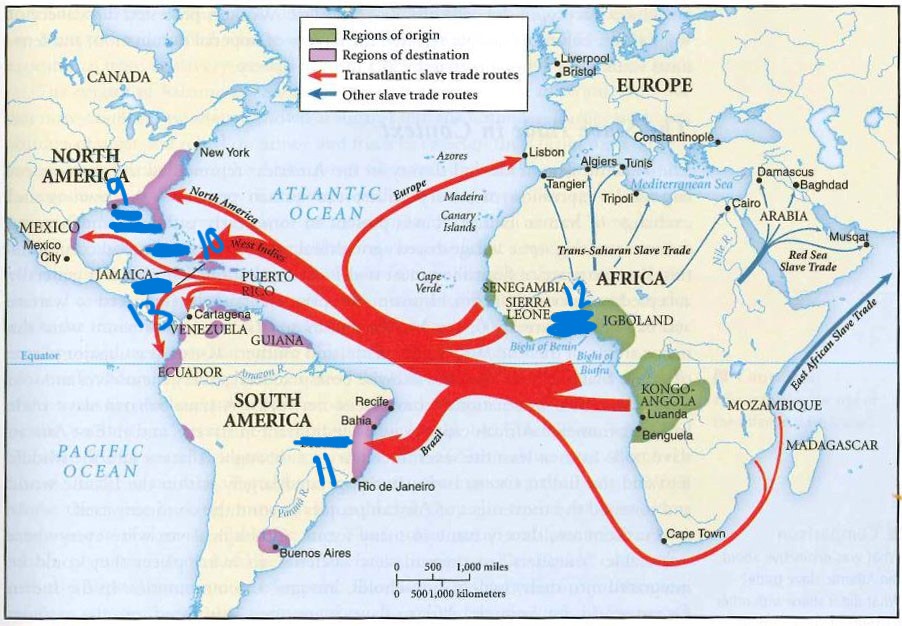
what is 11
brazil
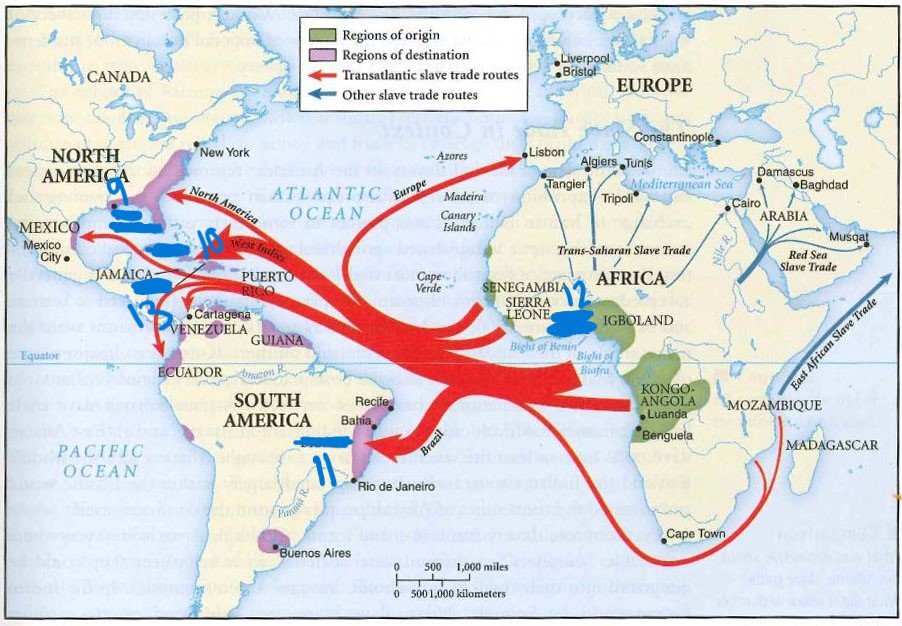
what is 12
gold coast
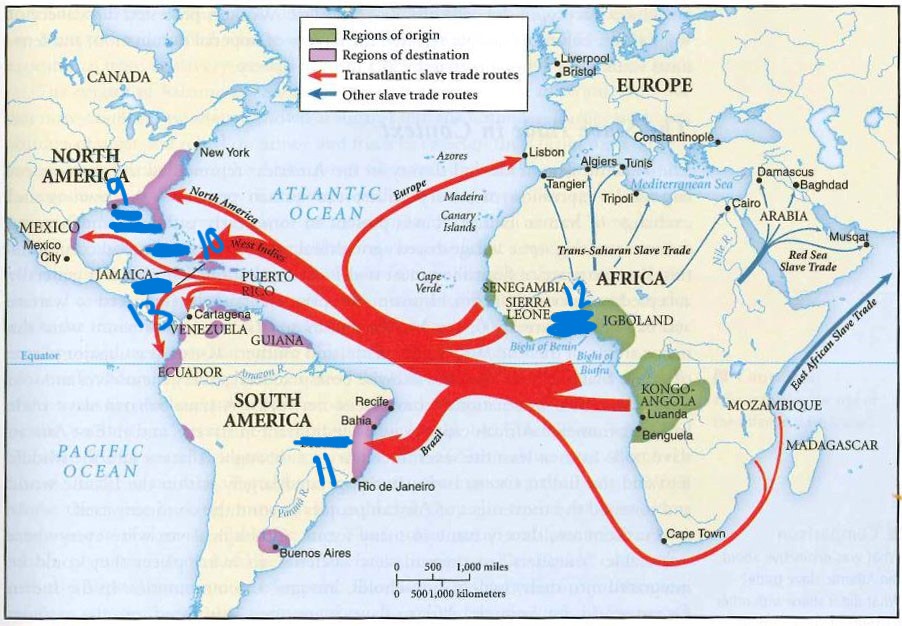
what is 13
haiti
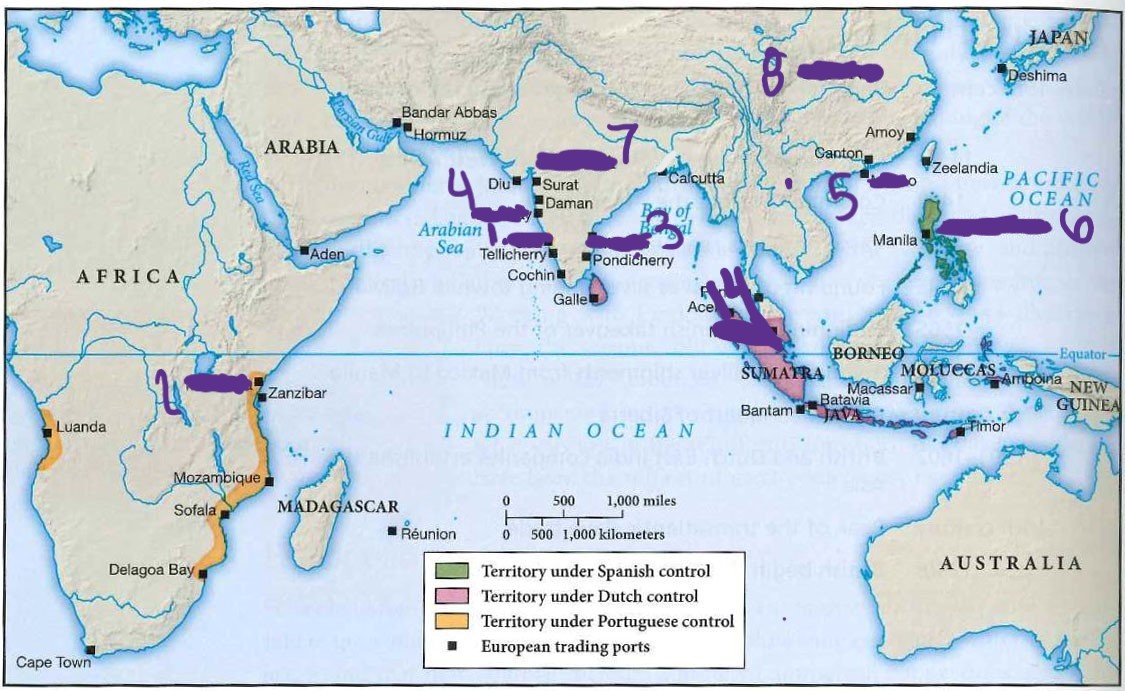
what is 14
malacca
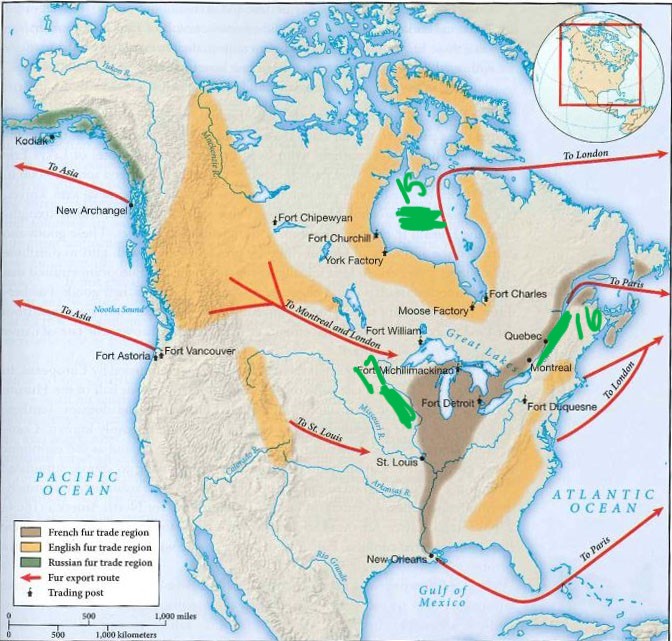
what is 15
hudson bay
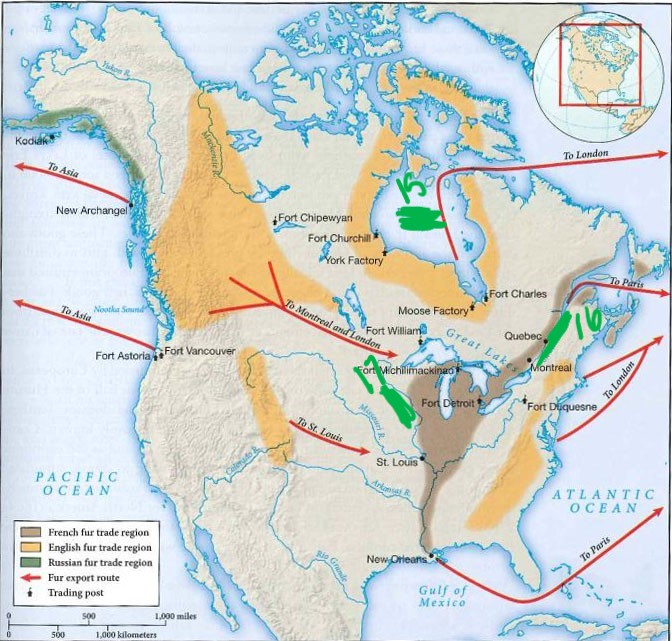
what is 16
St. Lawrence
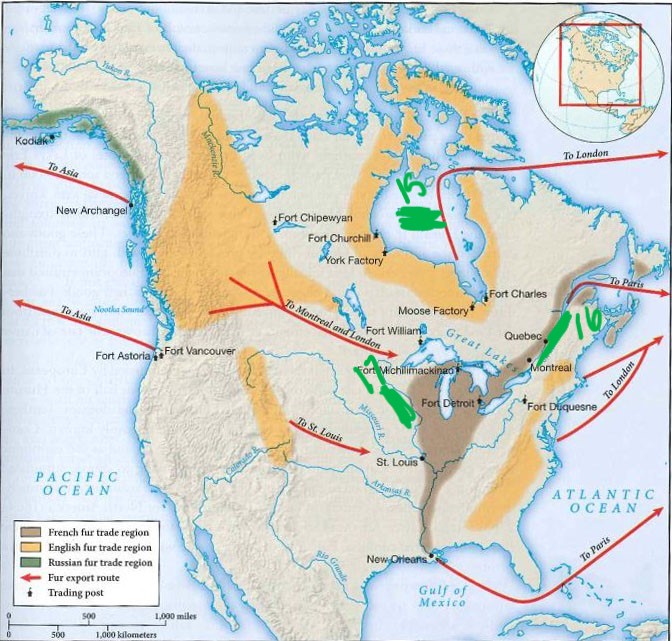
what is 17
Mississippi river