Unit 1 - Error, 1.1, 1.4, 2.1
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Causes of error
imperfections in apparatus
imperfections in methodology
judgements made by humans
Random Uncertainty
cannot be avoided
degree of error
sort of solved by doing many trials and averaging data
Analog uncertainly
by eye measures
half the smallest division available
Digital Uncertainty
measured by equipment
uncertainty is 1 of the smallest digit
Absolute uncertainty
the uncertainty associated with a given measurement
Relative uncertainty
absolute uncertainty / volume or substance
Adding and Subtracting Uncertainties
the absolute uncertainties are added
Multiplying and dividing
relative uncertainties added
Percent error
(experimental-theoretical)/(theoretical)
Systematic errors
consistent bias that always changes the outcome
Mole
1 mole =6.02×1023
energy
the ability to preform work or produce heat
Atomic theory
All matter is comprised of atoms and matter can neither be created nor destroyed
Elementary substances
contain atoms of a single element
Chemical Compounds
contain atoms of two or more elements bound together
Filtration
mixture is pored through a paper filter or other porous material
Dissolution
mixture is added to water or an organic solvent
crystallization
mixture dissolved in hot water, solution then left to cool down, crystals formed
Sublimation
when a solid substance turns directly into a gas (skips melting phase)
Deposition
When gases turn directly into solids (no liquid phase)
Endothermic process
system absorbs heat from suroundings
exothermic process
System releases heat into the surroundings
Temperature
the measure of the average kinetic energy
0 degrees C
273.15 Kelvin
Relative Molecular mass
the ratio of the mass of a molecule to 1/12 of a Carbon-12 molecule
hydrates
compounds in which water molecules form coordinated bonds with ions
Molar Mass (M)
M= mass/moles
Molecular formula
shows the actual number of atoms of each element in the molecule of that substance
Empirical formula
shows the simplest ratio (integers) of atoms of the different elements
Percent composition
elemental composition in percent by mass
Solutions
homogenous mixtures of two or more substances
Solvent
what the liquid/dissolver is
Solute
what is being dissolved (salt)
Molar Concentration (AKA Molarity)
the ratio of the amount of solute to the volume of the solution
M= grams/volume in dm3
Stock solutions
Standard solutions
can be stored and dilluted
Avagadro’s Law
the volume of two reacting gases under the same conditions is proportional to the amounts
v1/n1 = V2/n2
Assumptions of the ideal gas model
all gas molecules are in constant random motion
collisions between molecules are perfectly elastic (no energy is lost)
the volume occupied by gas molecules is negligible compared to the volume of the container they occupy
there are not Intermolecular Forces (wont condense into a liquid)
the kinetic energy of the molecules is directly proportional to the temperature in kelvin
Boyle’s Law
pressure and volume are inversely related
P1V1=P2V2
KE decr. and IMF’s form
Effect of low temp. on the ideal gas model
relation between pressure and volume no longer inverse
Effect of high pressure on the ideal gas model
Combined gas law
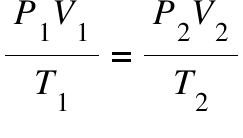
Ideal gas law
PV=nRT
ideal gas constant
8.31 JK mol
Percent yield
experimental/theoretical *100
Common practices of Green Chemistry
aqueous or solvent-free
renewable starting materials
mid reaction conditions
efficient catalysts
utilization of any byproducts formed
Atom economy
the measure of the efficiency of a reaction
= (molar mass of desired)/(total mass of reaction) * 100%