Psychology 2e Chapter 3
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Biopsychology
How biological mechanisms underlie behavior
Theory of evolution
The organisms that are better suited for their environment will survive and reproduce, while those that are poorly suited for their environment will die off.
Chromosome
Long strand of genetic information known as DNA.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Helix-shaped molecule made of nucleotide base pairs.
In each chromosome, sequences of DNA make up genes
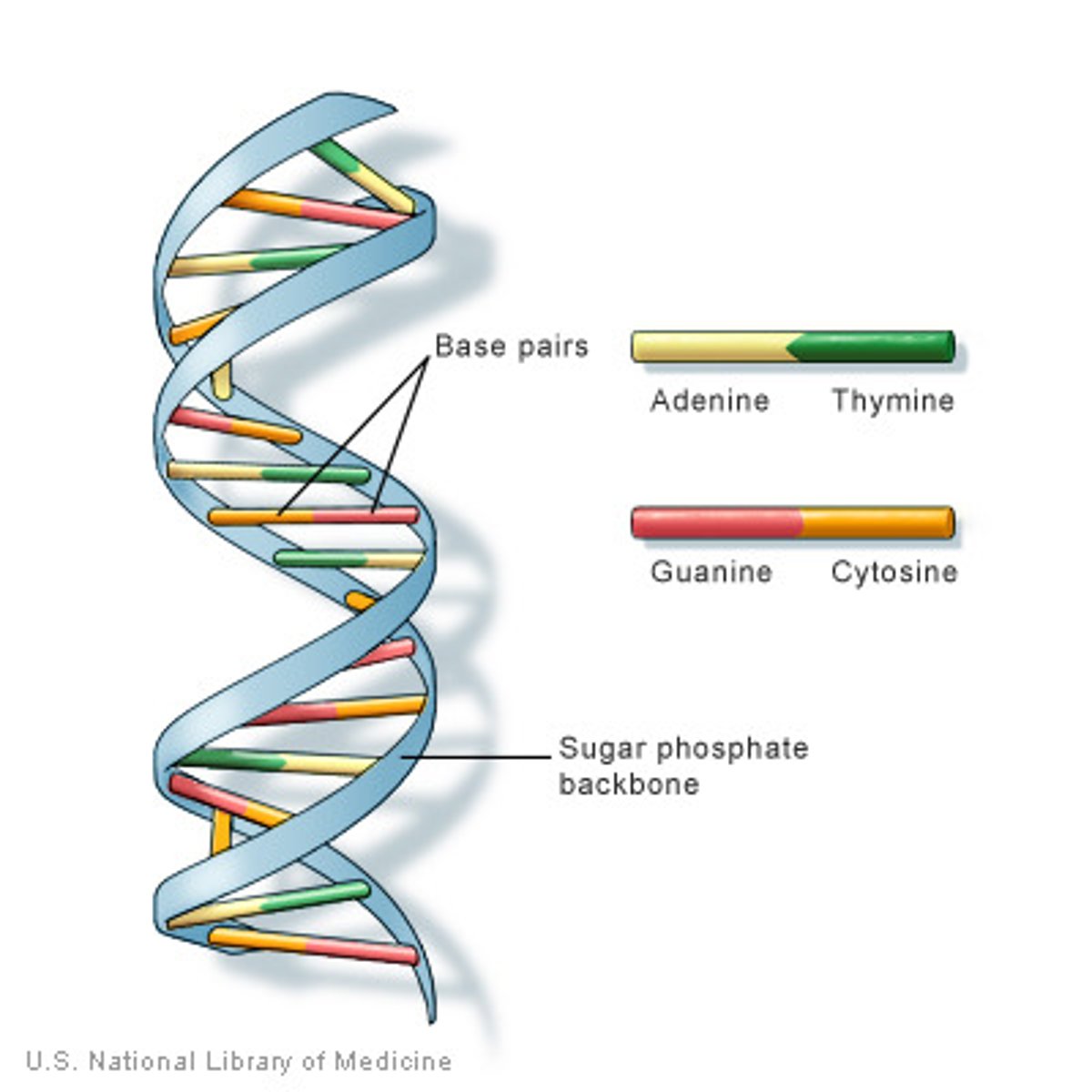
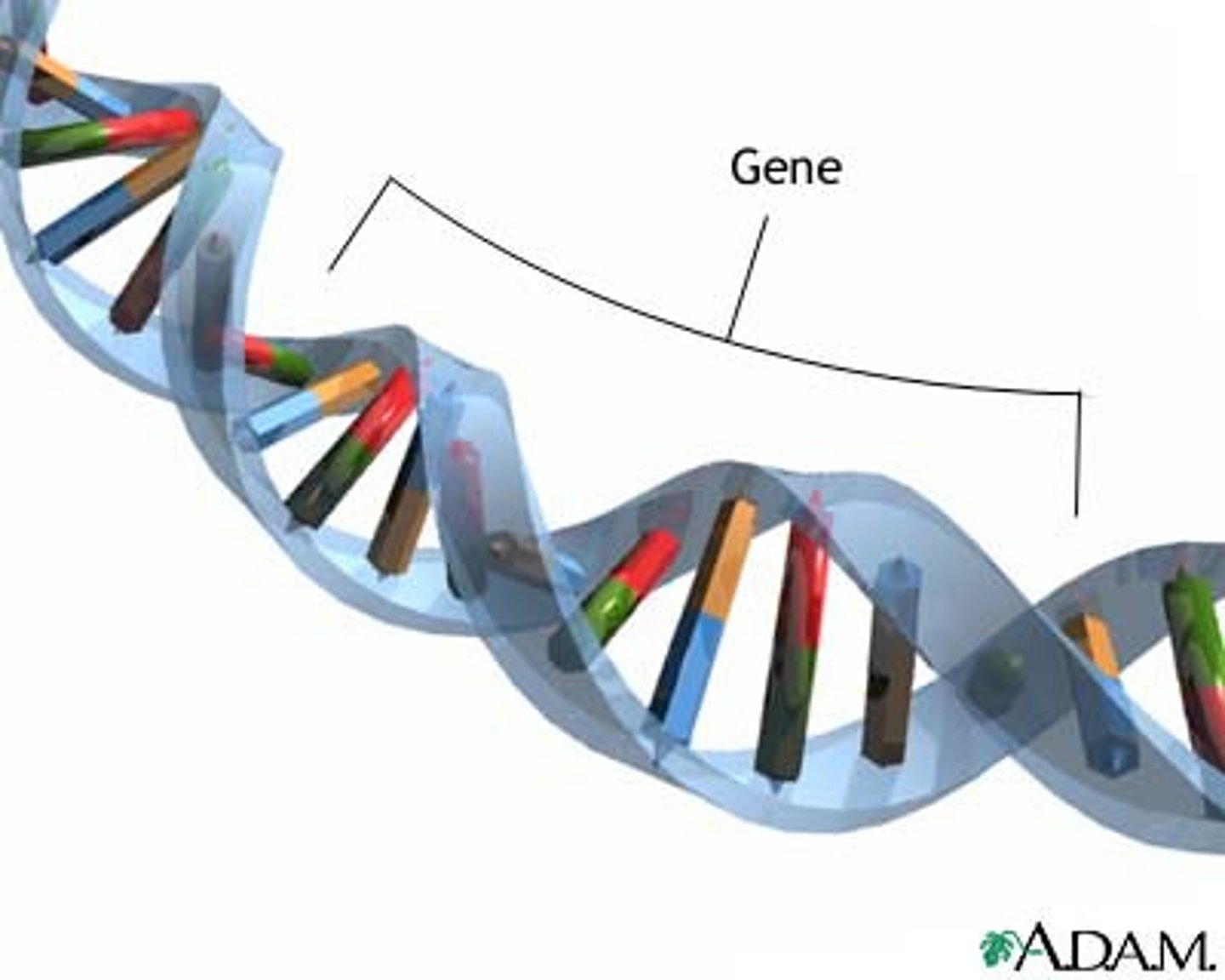
Gene
Sequence of DNA that controls or partially controls physical characteristics known as traits (eye color, hair color etc).
Range of reaction
Genes set the boundaries within which we can
operate, and our environment interacts with the genes to determine where in that
range we will fall.

Genetic environmental correlation
Genes affect our environment, and our environment influences the expression of our genes.
Epigenetics
Study of gene-environment interactions
Evolutionary Psychology
How behaviors and cognitive processes have evolved over time through inherited traits
Glial (or glia) cells
Help neurons line up closely with each other to allow
neuronal communication, provide insulation to neurons, transport nutrients and
waste products, and mediate immune responses.
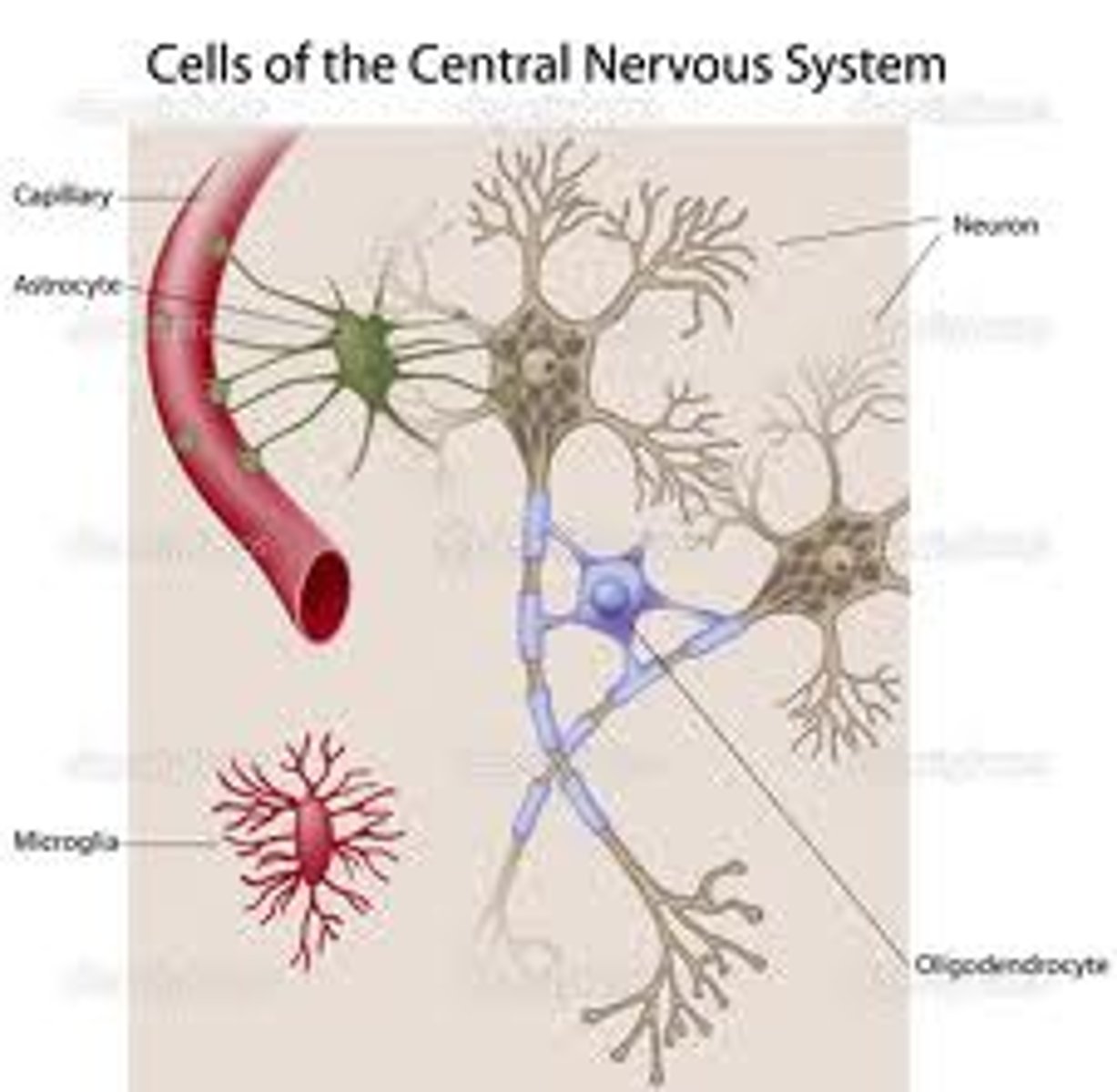
Neurons
Serve as interconnected information processors.
Semipermeable membrane
A neuron's outer surface allows smaller molecules and molecules without an electrical charge to pass through it while stopping larger or highly charged molecules.
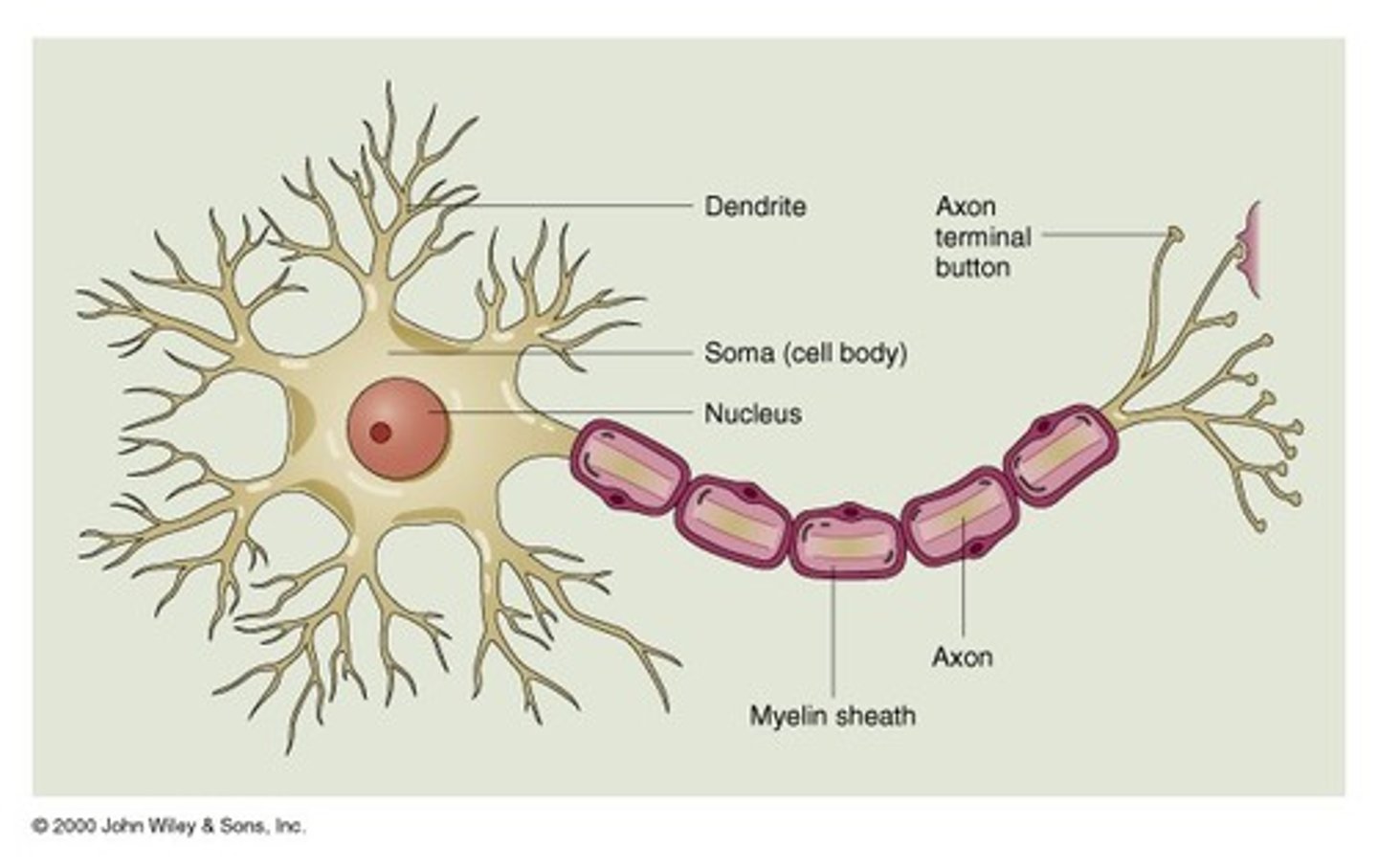
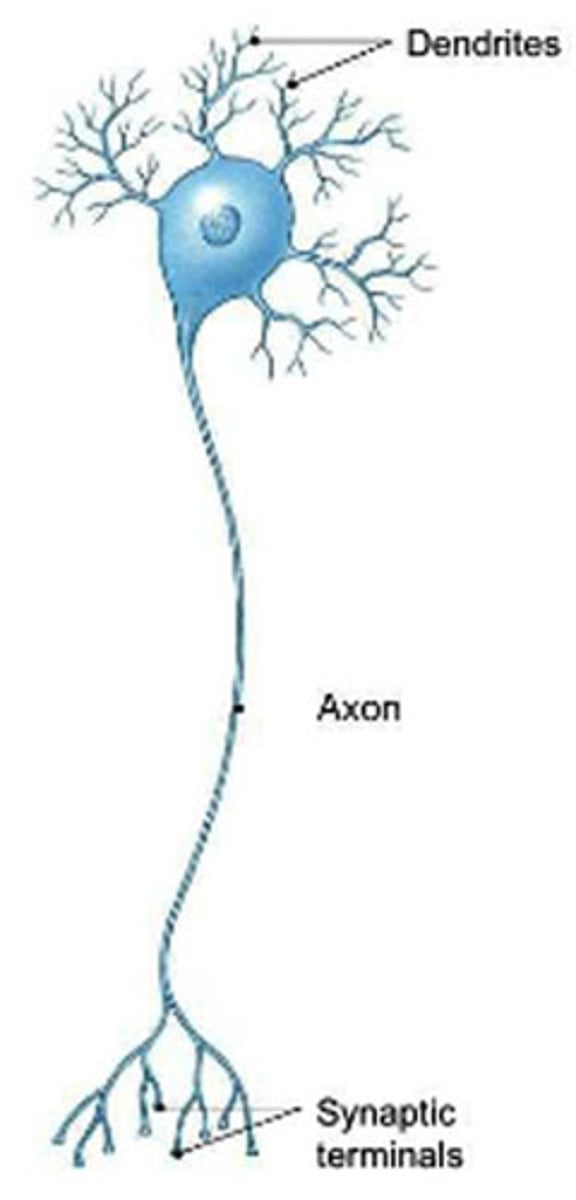
Soma
Cell body, where nucleus of neuron is located
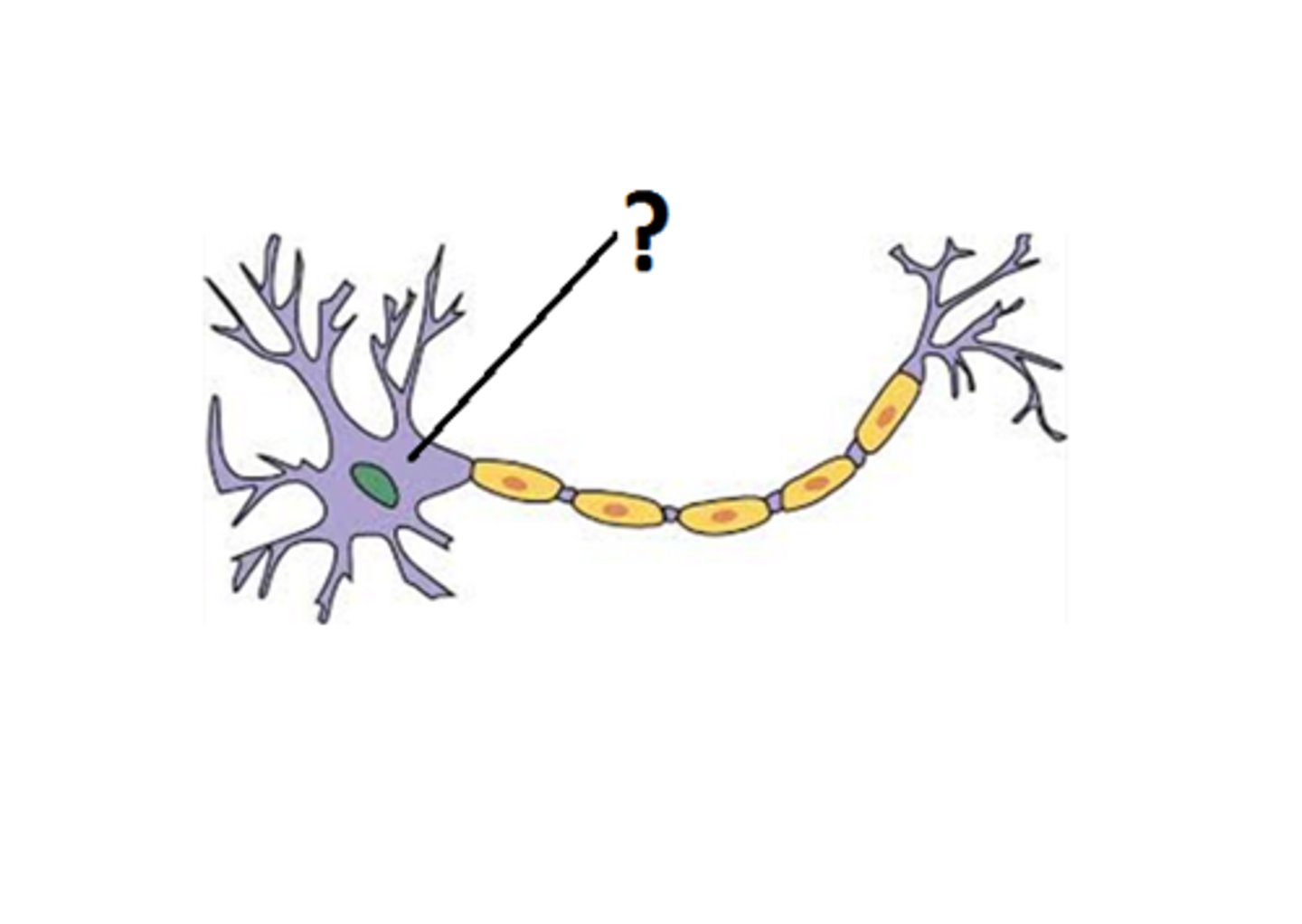
Dendrites
Branching extensions, serve as input sites where signals are received from other neurons
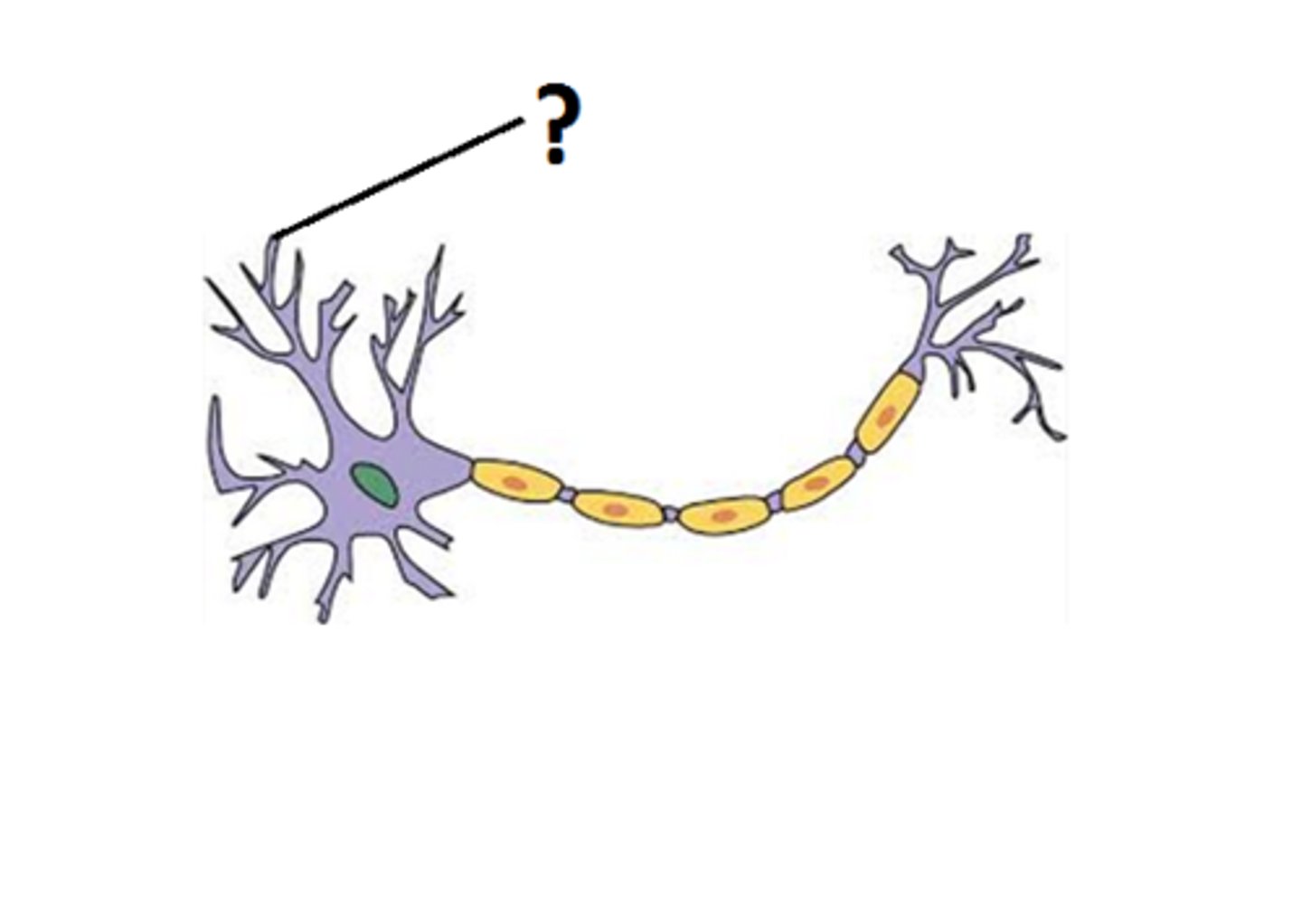
Axon
Tunnel through which signals are transmitted electrically across the soma and down a major extension. Axons range in length from a fraction of an inch to several feet.
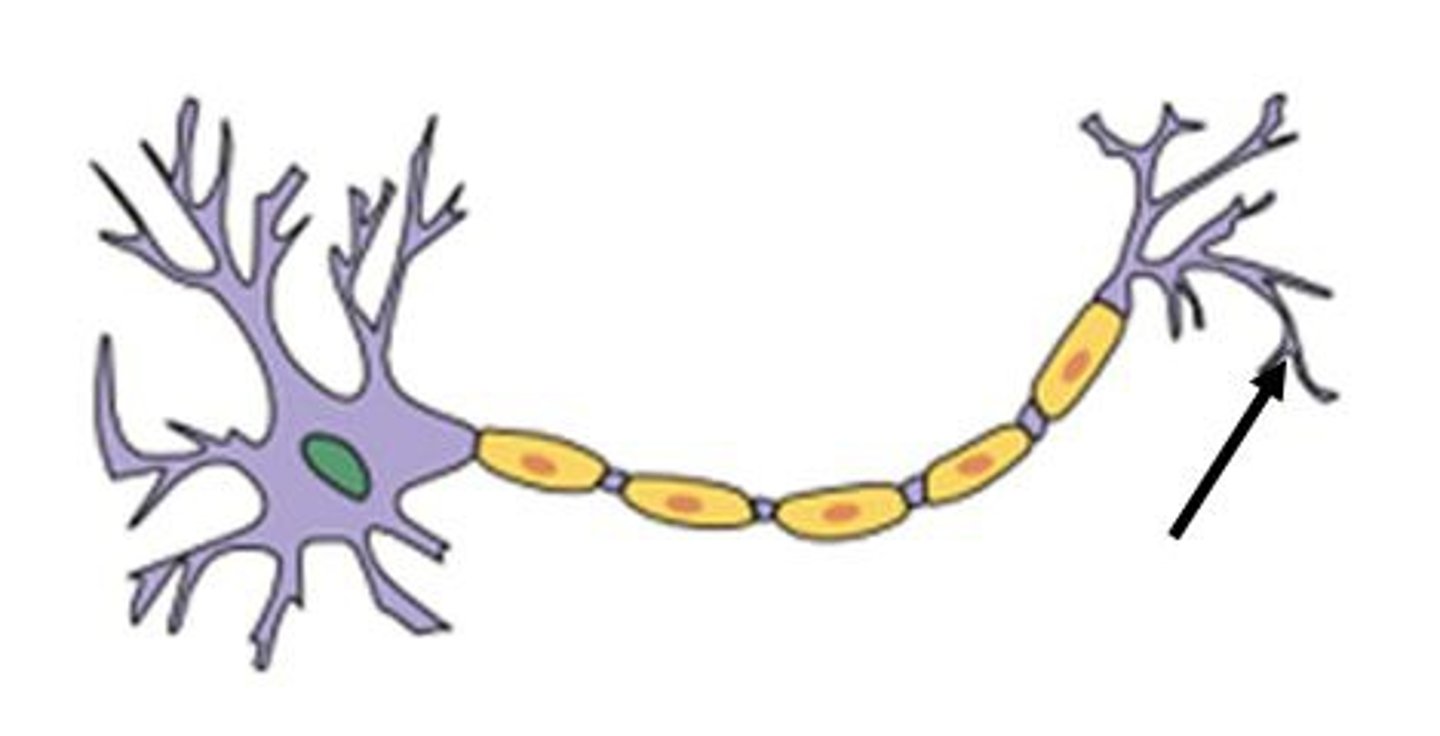
Terminal buttons
Located at the end of the neuron and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons. Contain synaptic vesicles that house neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers of the nervous system.
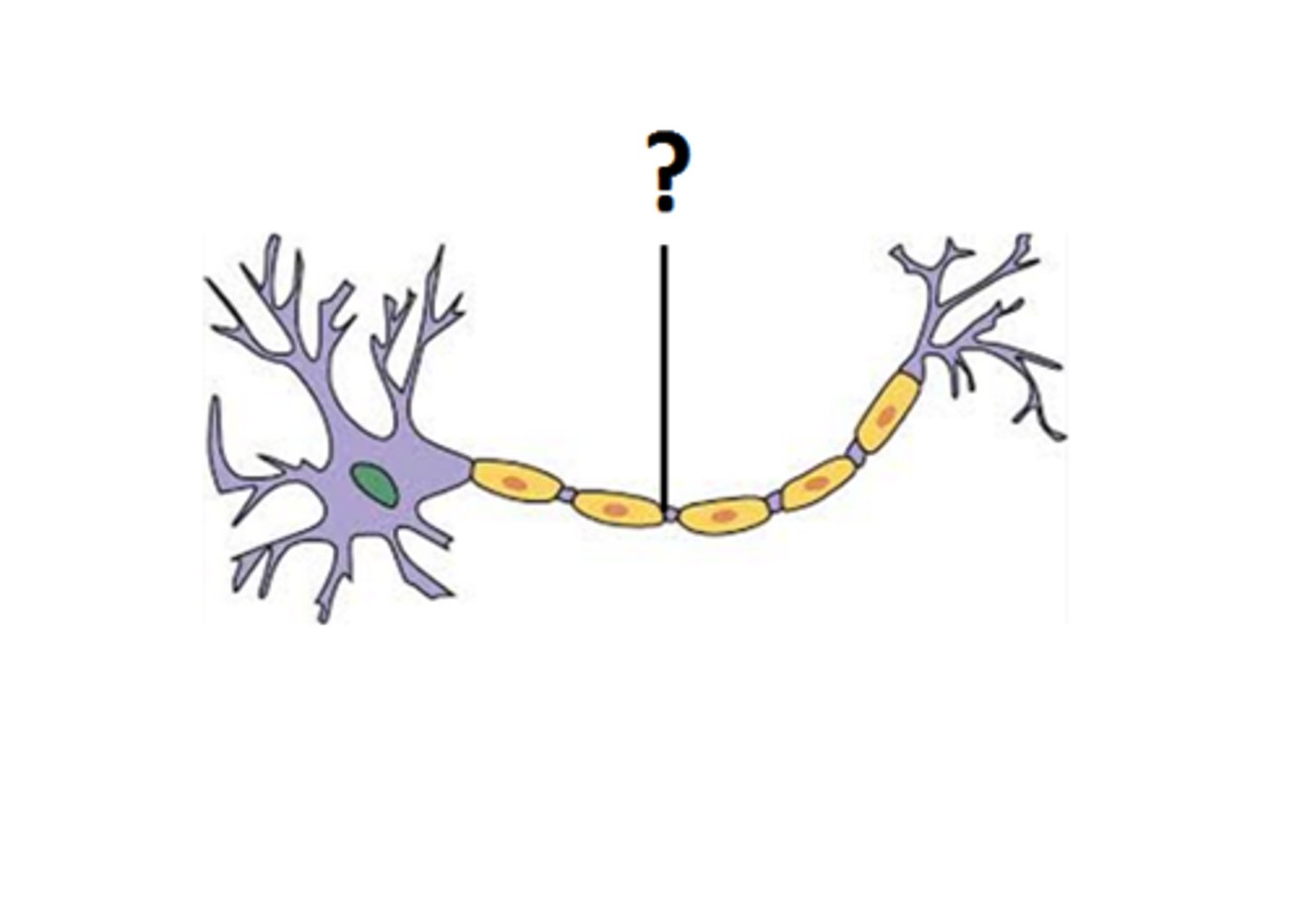
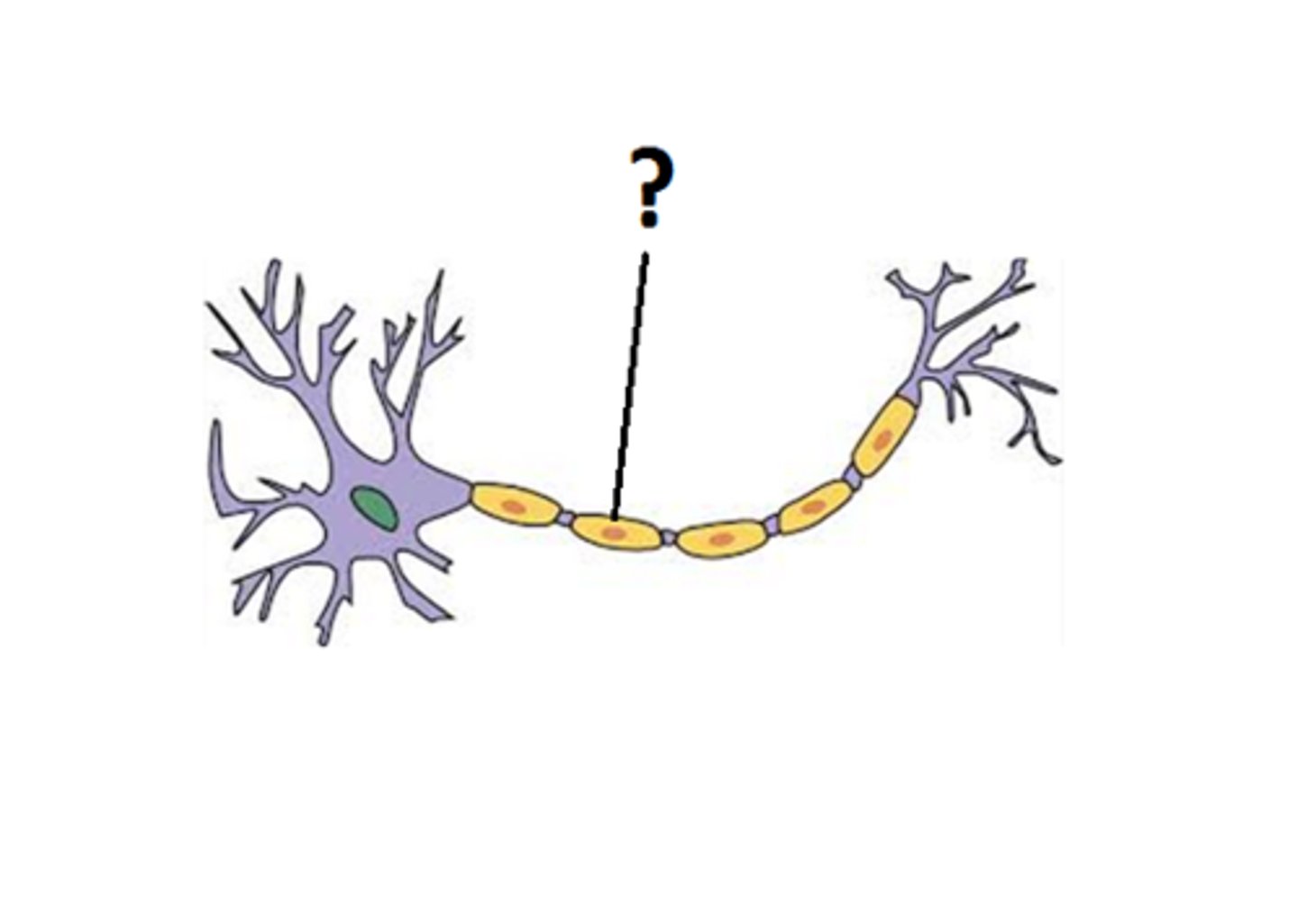
Myelin sheath
Glial cells form a fatty substance known as the myelin sheath, which coats the axon and acts as an insulator, increasing the speed at which the signal travels. The myelin sheath is not continuous and there are small gaps that occur down the length of the axon. These gaps in the myelin sheath are known as the Nodes of Ranvier. The myelin sheath is crucial for the normal operation of the neurons within the nervous system: the loss of the insulation it provides can be detrimental to normal function.
Synaptic cleft
Small space between two neurons and is an important site where communication between neurons occurs.
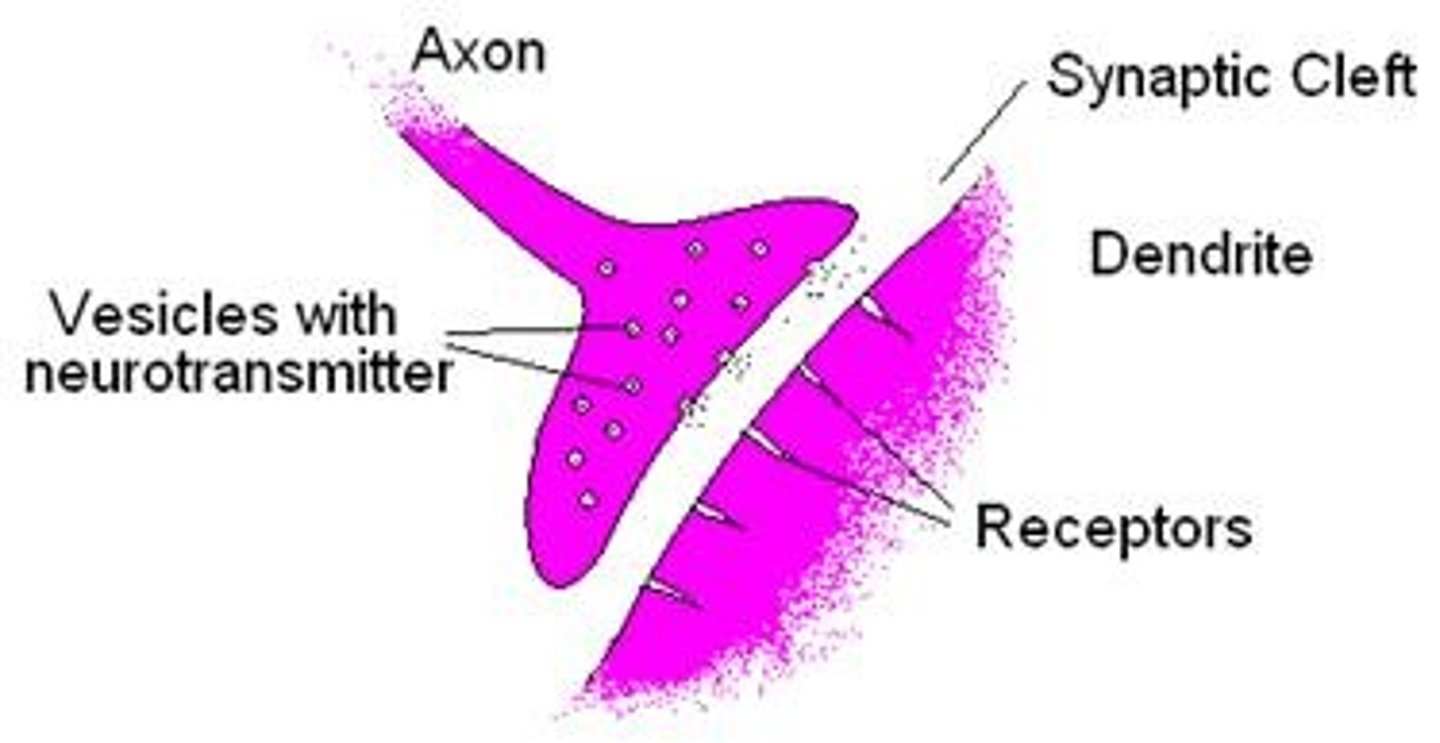
Neuron Receptors
Proteins on the cell surface where neurotransmitters attach, vary in shape, with different shapes "matching" different neurotransmitters.
Membrane Potential
The neuronal membrane keeps these two fluids separate—a critical role because the electrical signal that passes through the neuron depends on the intra- and extracellular fluids being electrically different. This difference in charge across the membrane, called the membrane potential, provides energy for the signal.
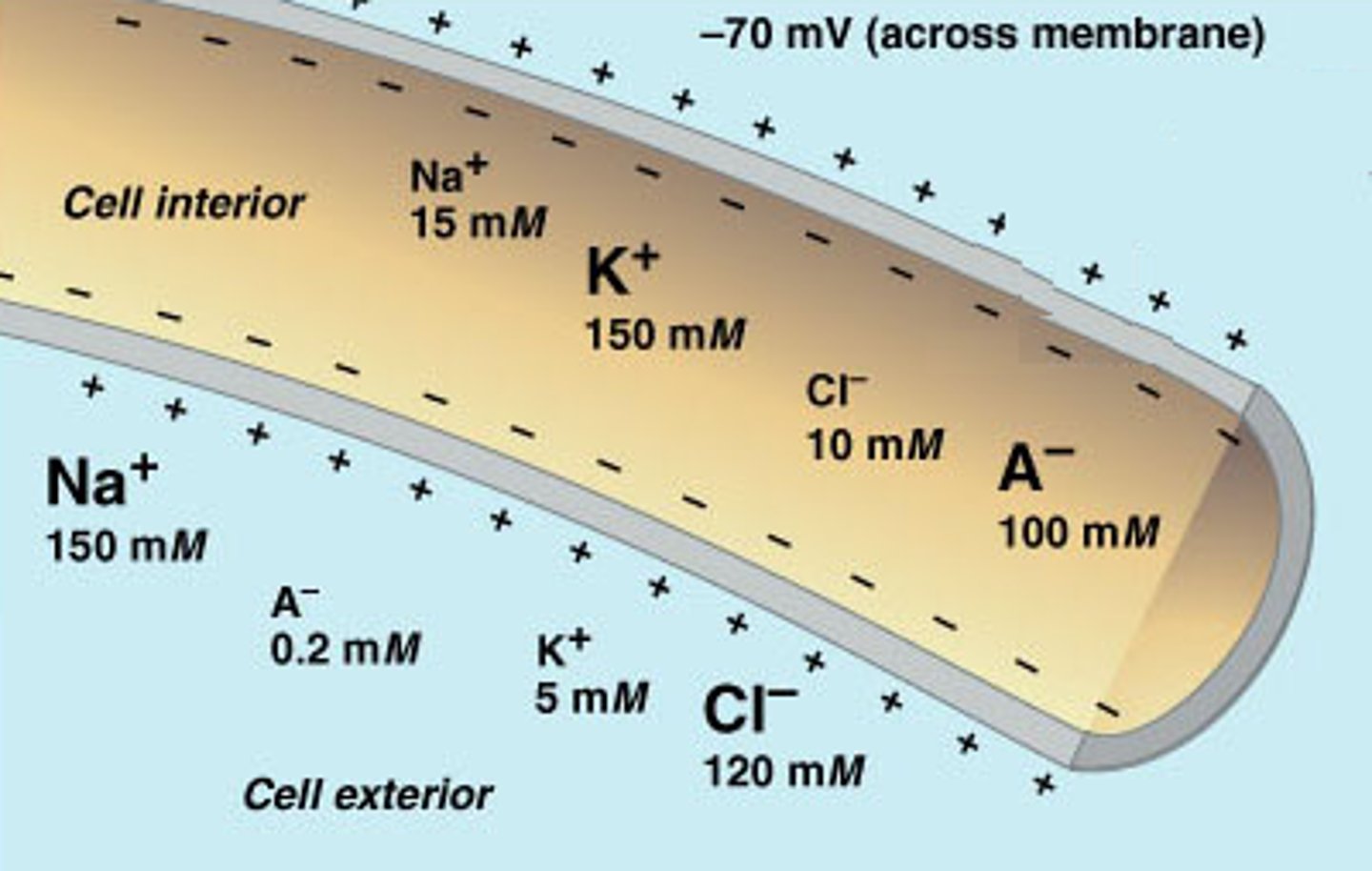
Resting Potential
Between signals, the neuron membrane's potential is held in a state of readiness
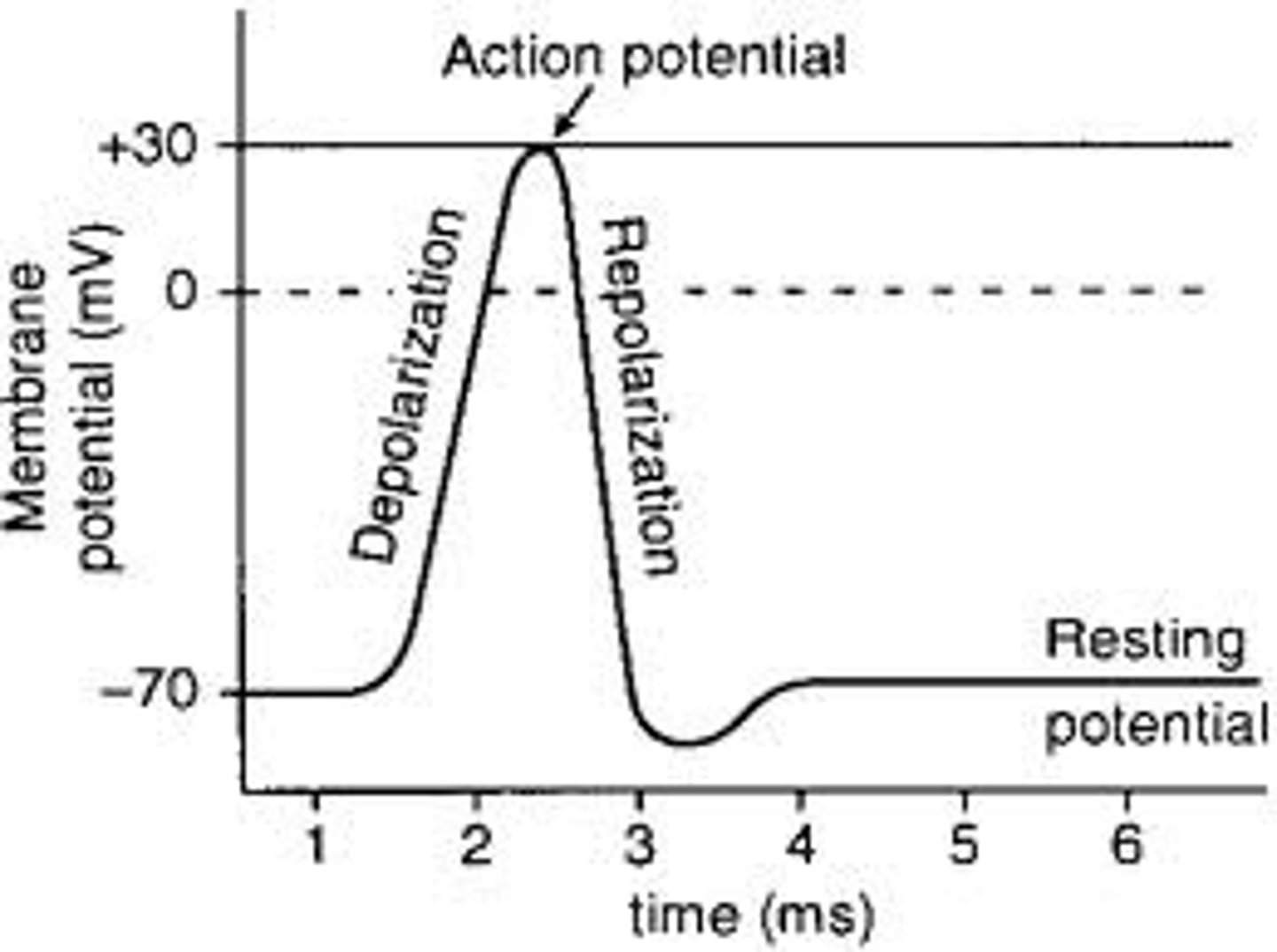
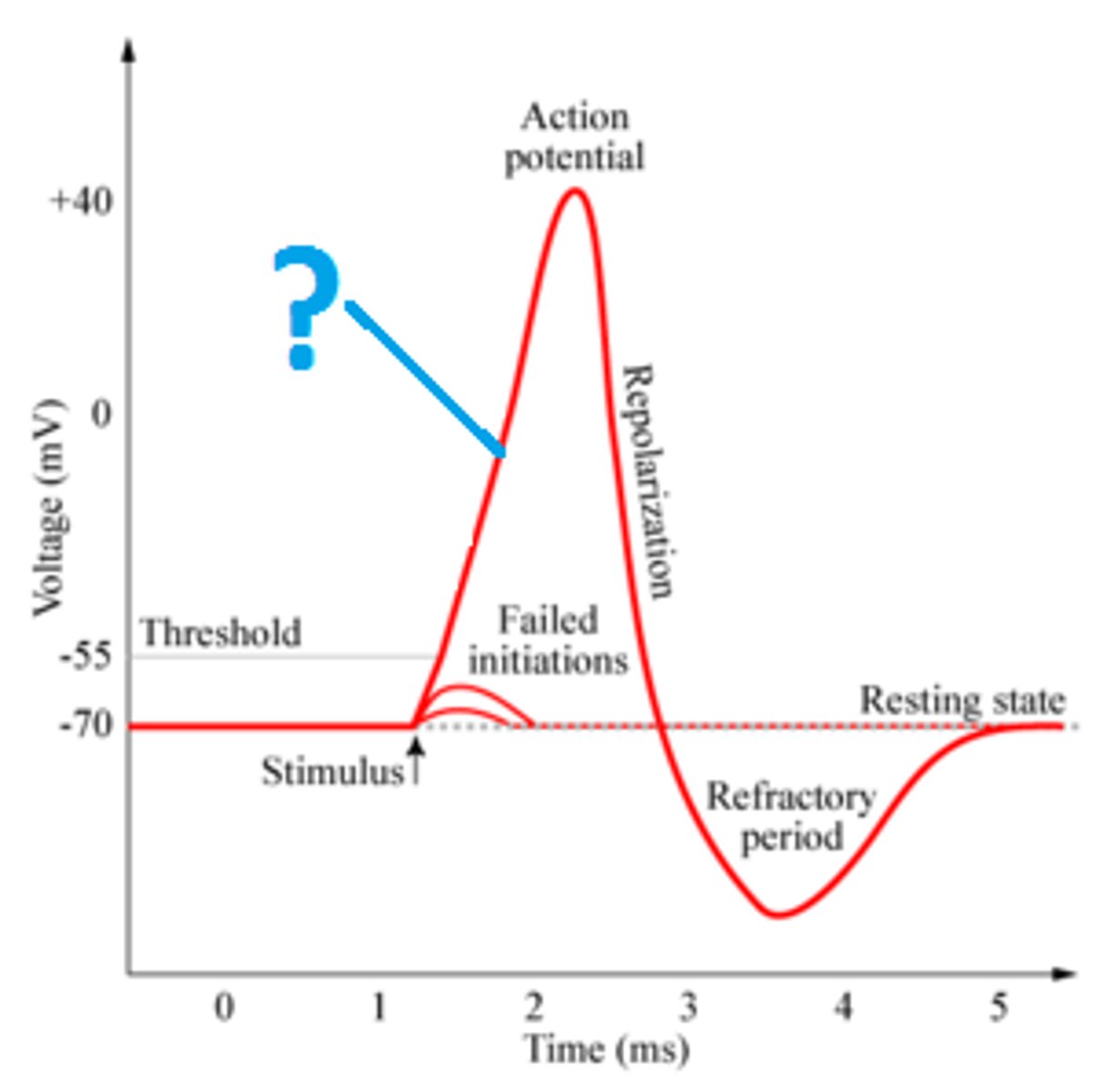
Threshold of excitation
If that charge reaches a certain level, called the threshold of excitation, the neuron becomes active and the action potential begins. If the level of charge reaches the threshold of excitation an action potential
will occur. Ion channels open causing Na+ to rush into the cell and the inside to momentarily become more positive.
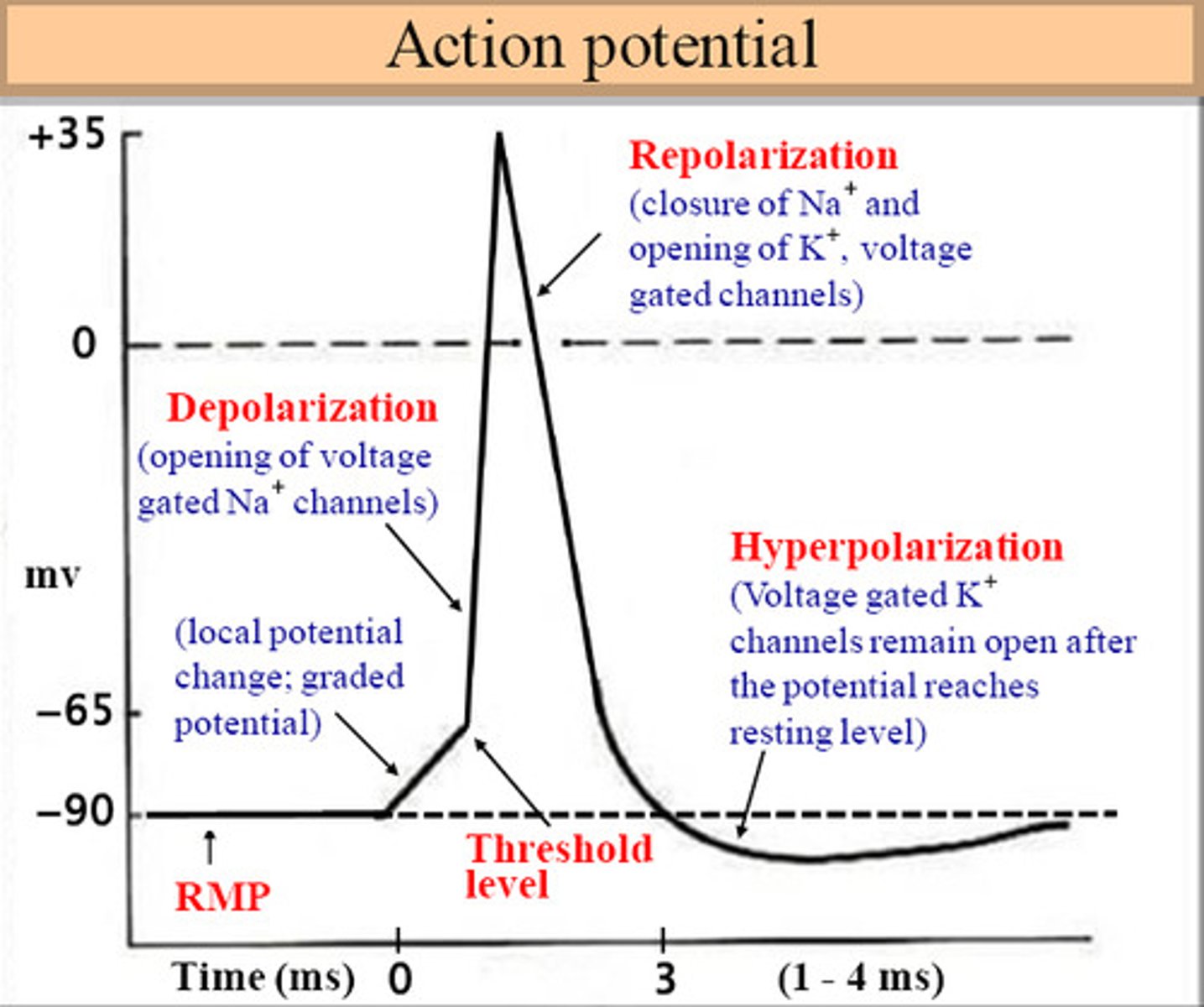
Action Potential
Neurotransmitters from nearby neurons attach to receptors on dendrites causing the membrane potential to change. The electrical signal then typically moves from the cell body down the axon to the axon terminals. The electrical signal moves down the axon with the impulses jumping in a leapfrog fashion between the Nodes of Ranvier.
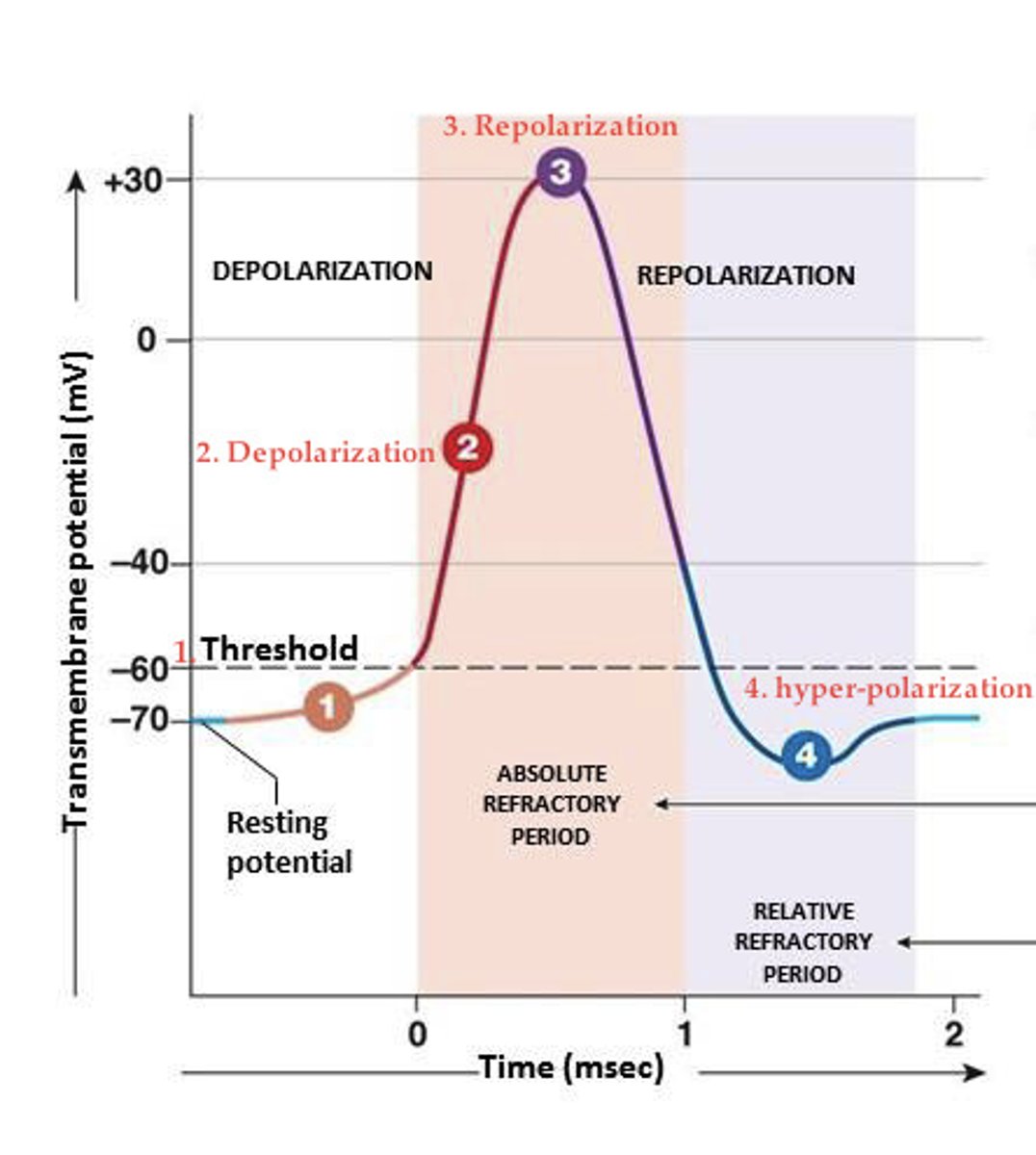
Depolarization
Membrane potential becomes less negative making the neuron more likely to fire (excitation).
Hyperpolarization
Membrane potential becomes more negative making the neuron less likely to fire (inhibition).
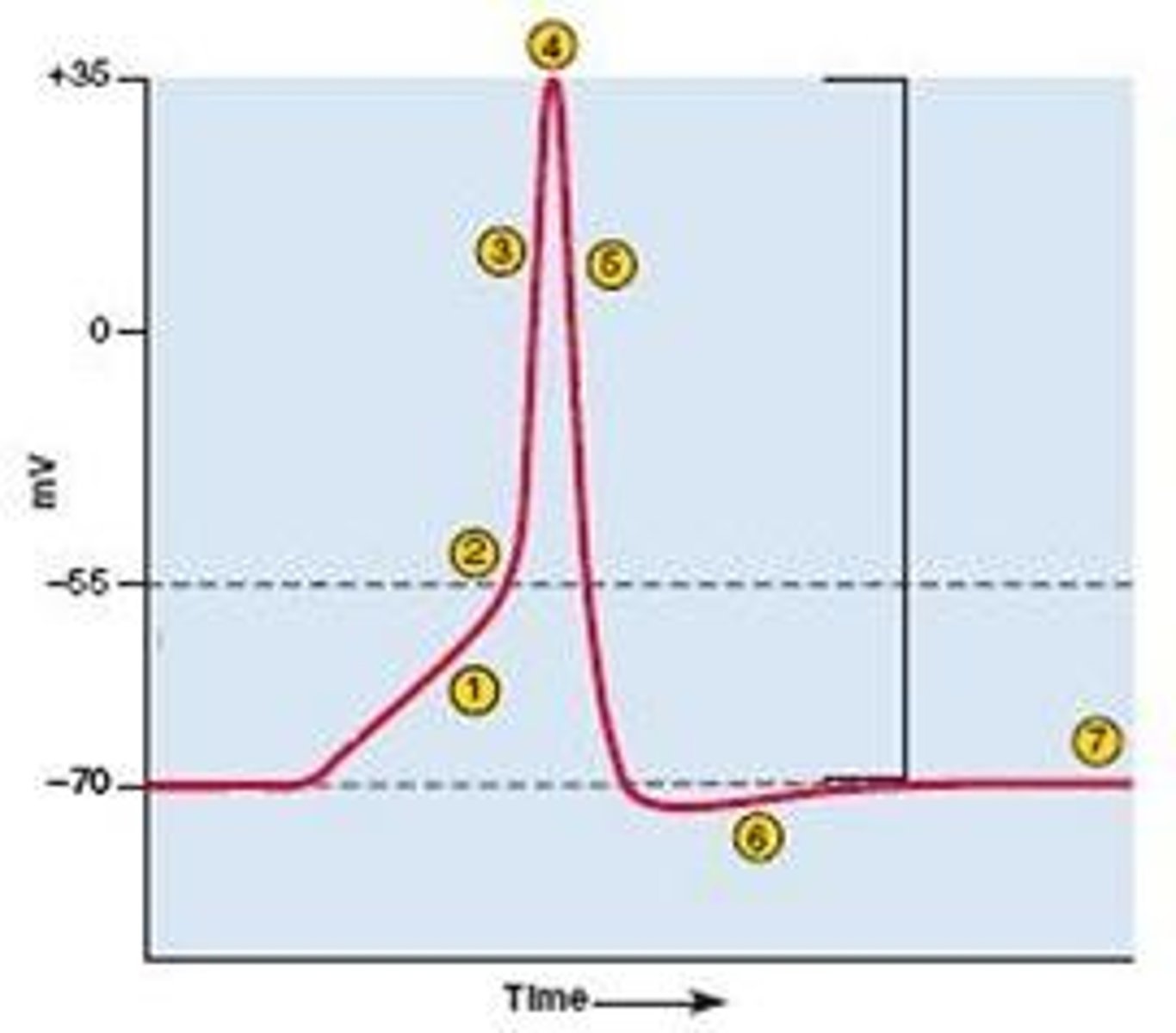
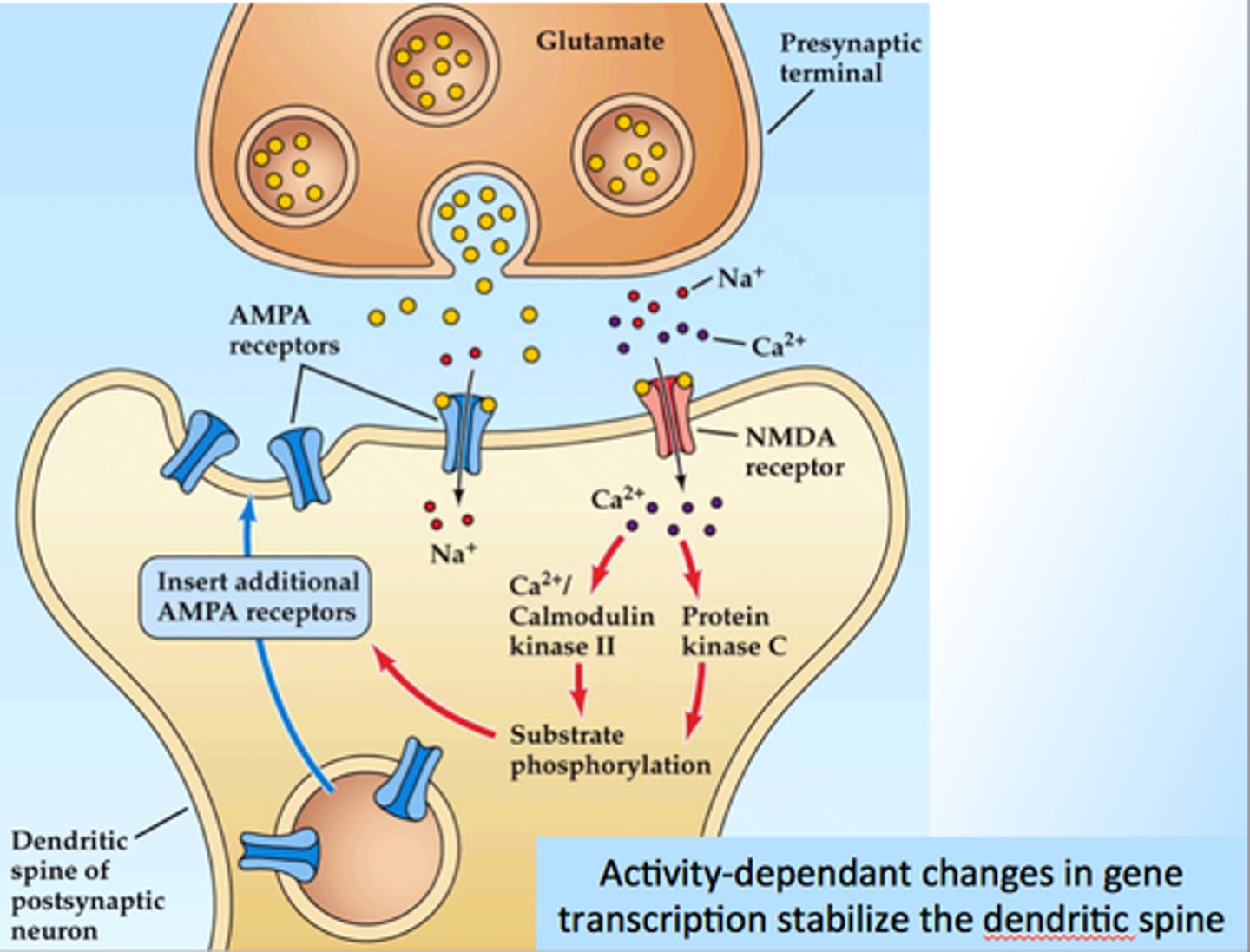
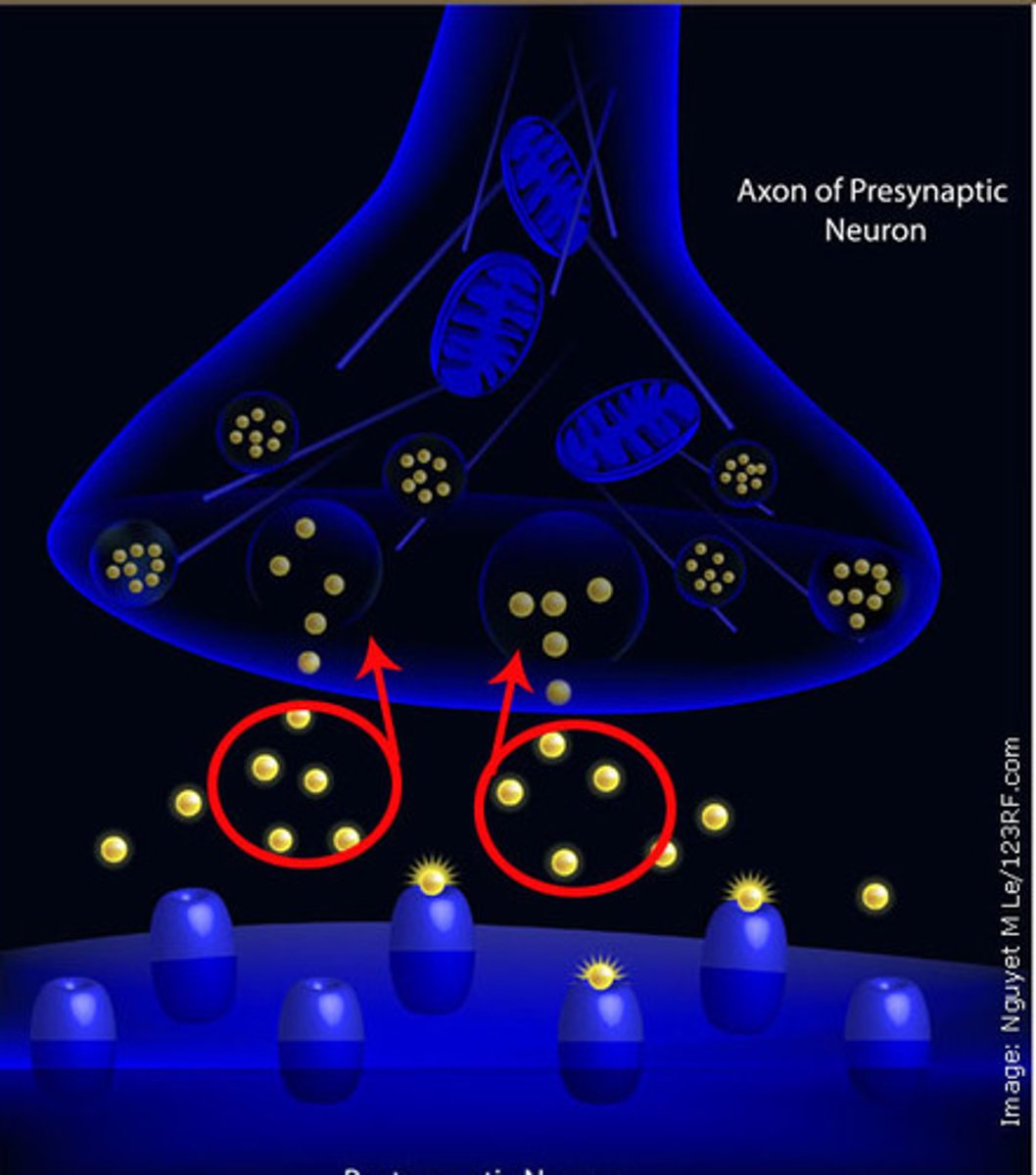
Reuptake
Once the signal is delivered, excess neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft drift away, are broken down into inactive fragments, or are reabsorbed. Reuptake involves the neurotransmitter being pumped back into the neuron that released it, in order to clear the synapse.
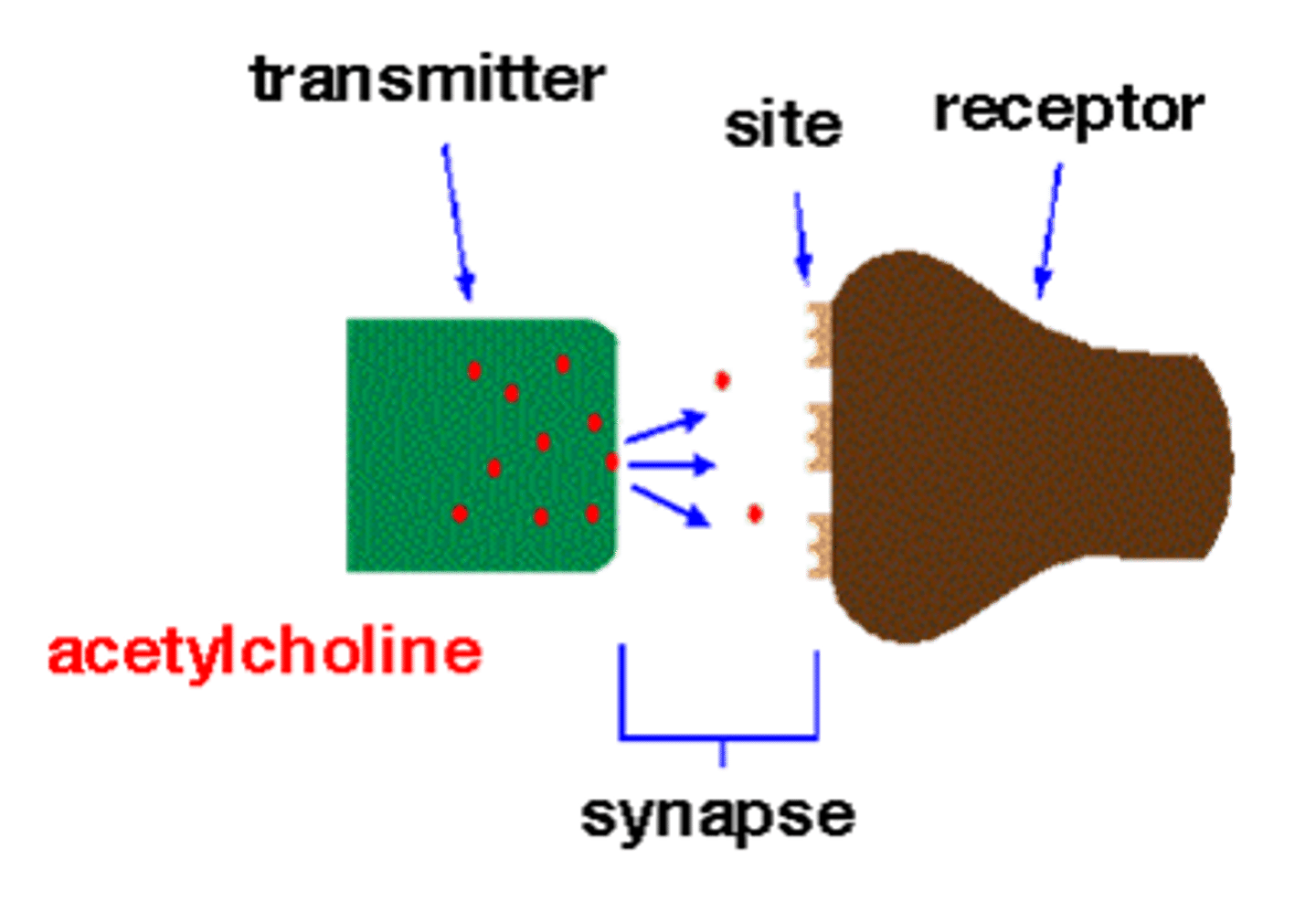
Acetylcholine
Muscle action, memory= Increased arousal, enhanced cognition

Beta-endophin
Pain, pleasure=Decreased anxiety, decreased tension

Dopamine
Mood, sleep, learning=Increased pleasure, suppressed appetite

Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Brain function, sleep=Decreased anxiety, decreased tension

Glutamate
Memory, learning=Increased learning, enhanced memory

Norepinephrine
Heart, intestines, alertness=Increased arousal, suppressed appetite

Serotonin
Mood, sleep=Modulated mood, suppressed appetite
Psychotropic medication
Drugs that treat psychiatric symptoms by restoring neurotransmitter balance
Agonist
Drug that mimics or strengthens the effects of a neurotransmitter.
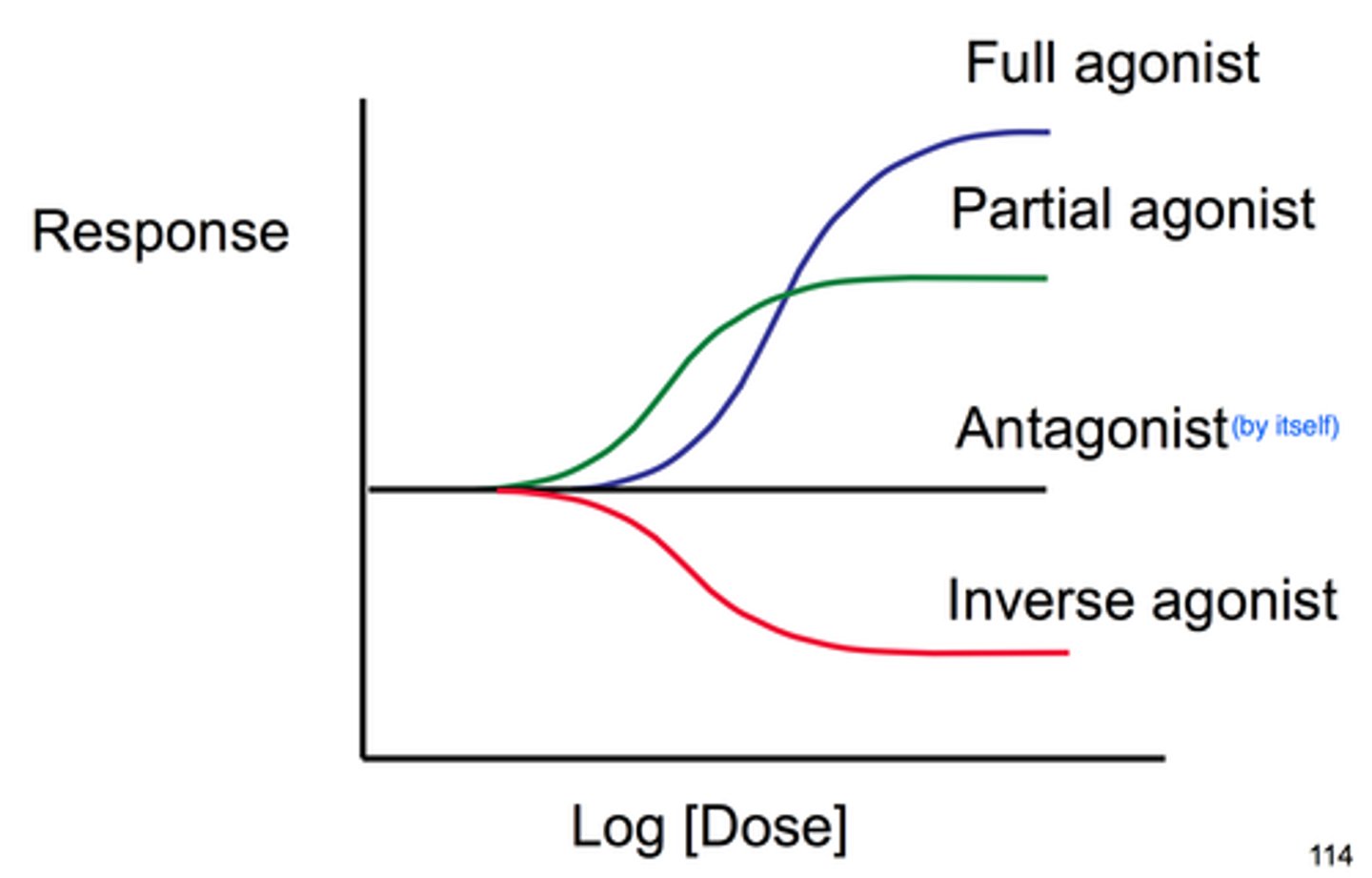
Antagonist
Drug that blocks or impedes the normal activity of a given neurotransmitter.

Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The peripheral nervous system is made up of thick bundles of axons, called nerves, carrying messages back and forth between the CNS and the muscles, organs, and senses in the periphery of the body (i.e., everything outside the CNS). The PNS has two major subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
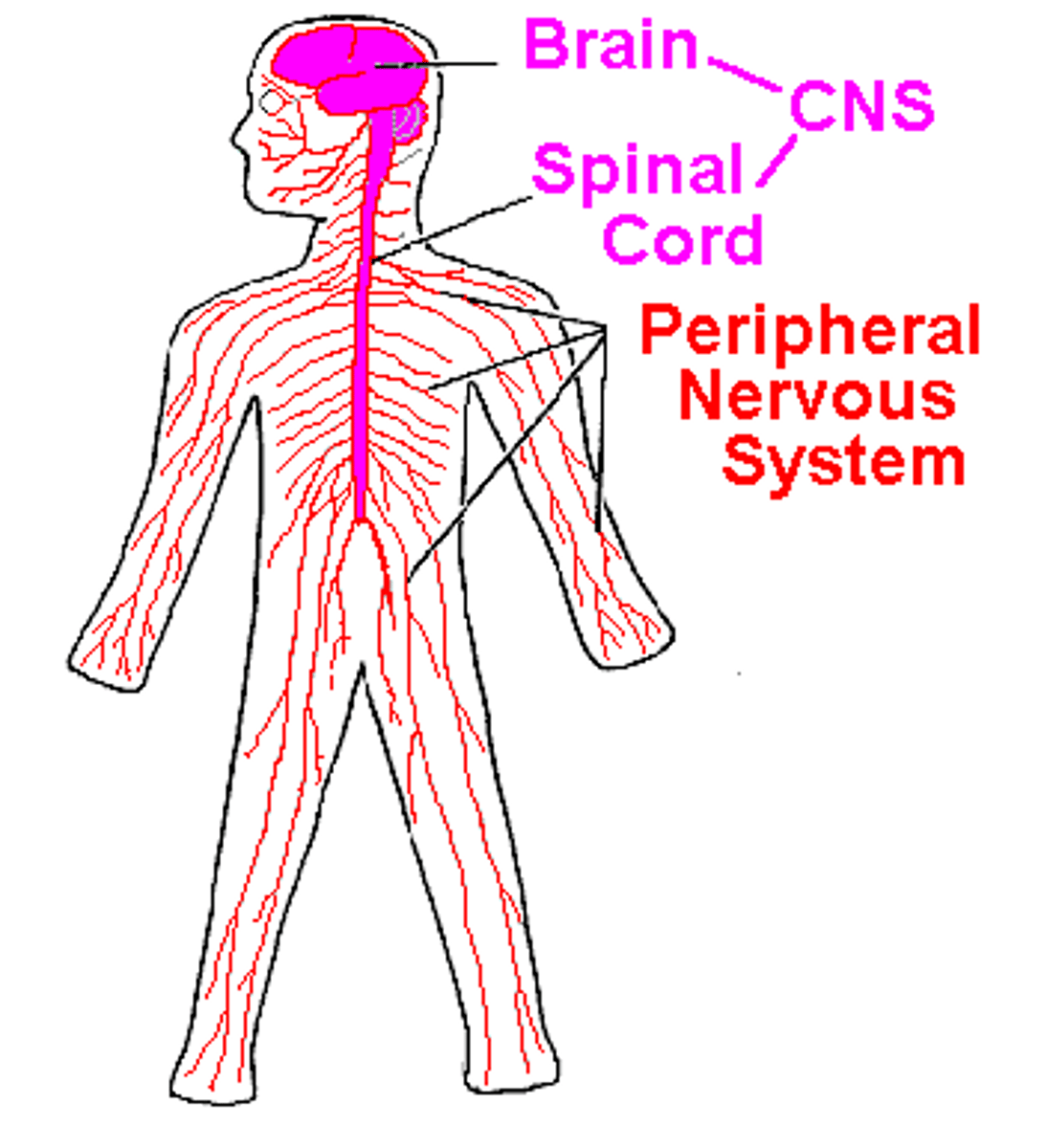
Central nervous system (CNS)
The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord; the PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
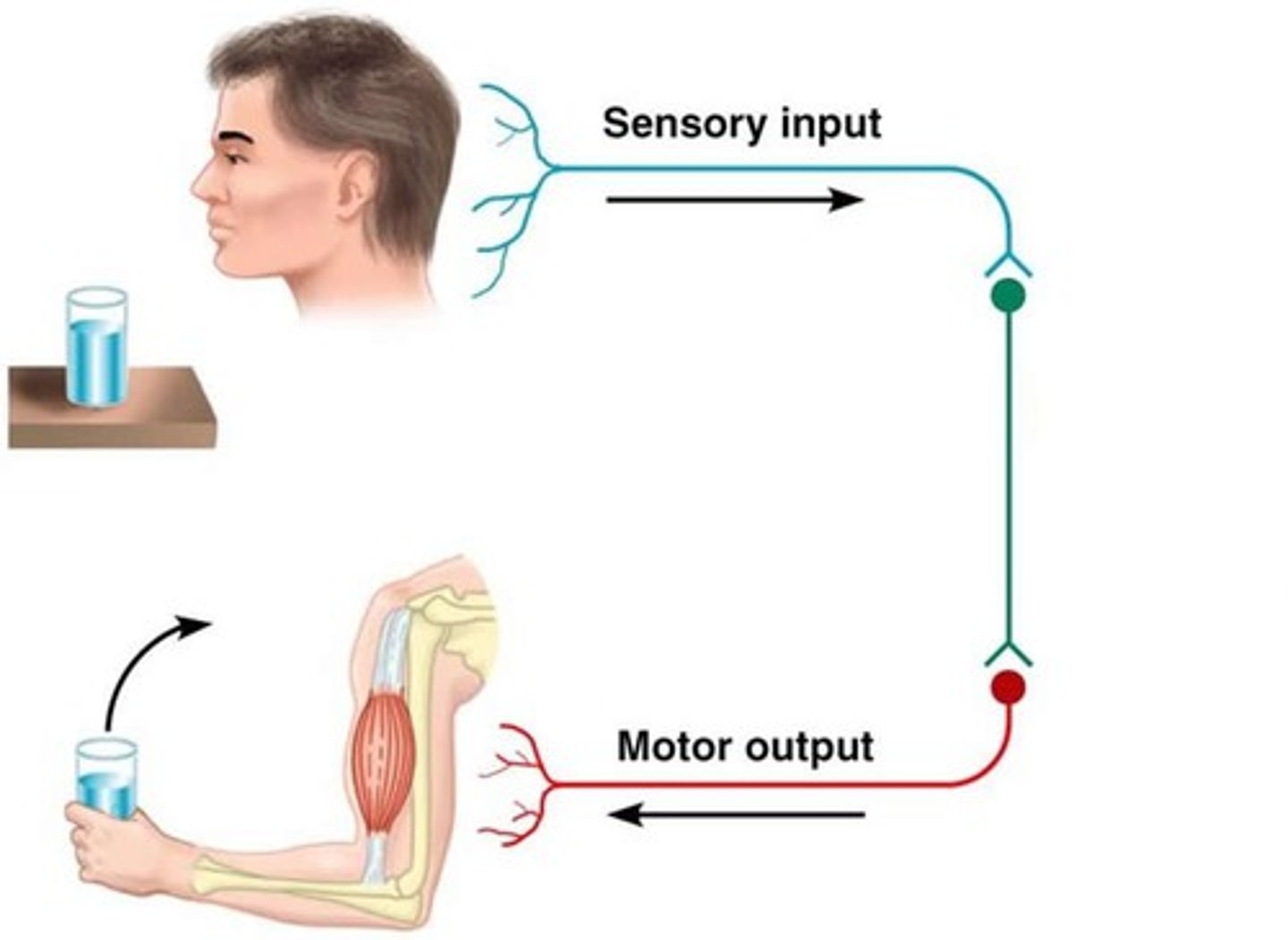
Somatic nervous system
Relays sensory and motor information to and from the CNS
Autonomic nervous system
Controls our internal organs and glands and can be divided into the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic nervous systems.
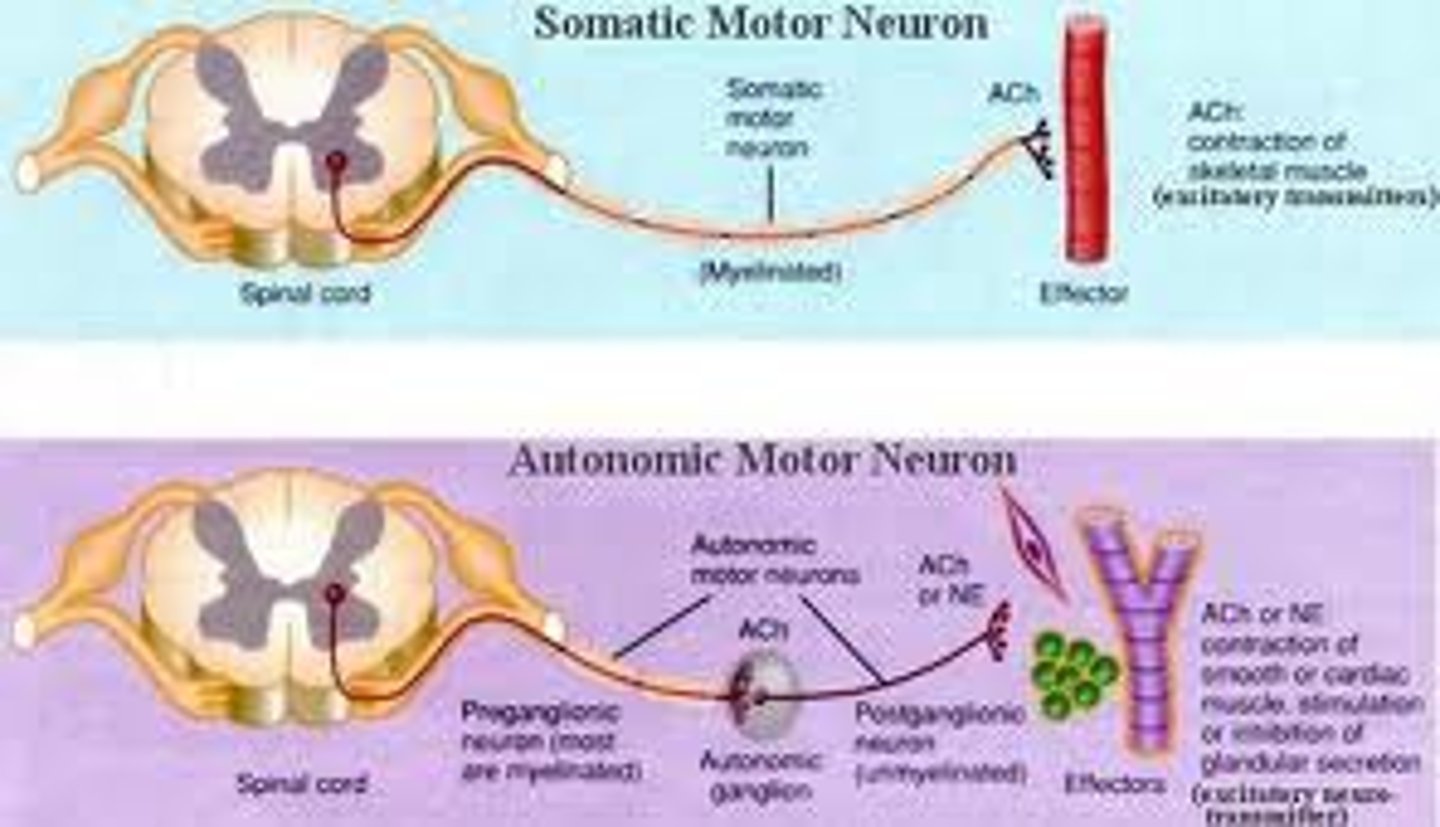
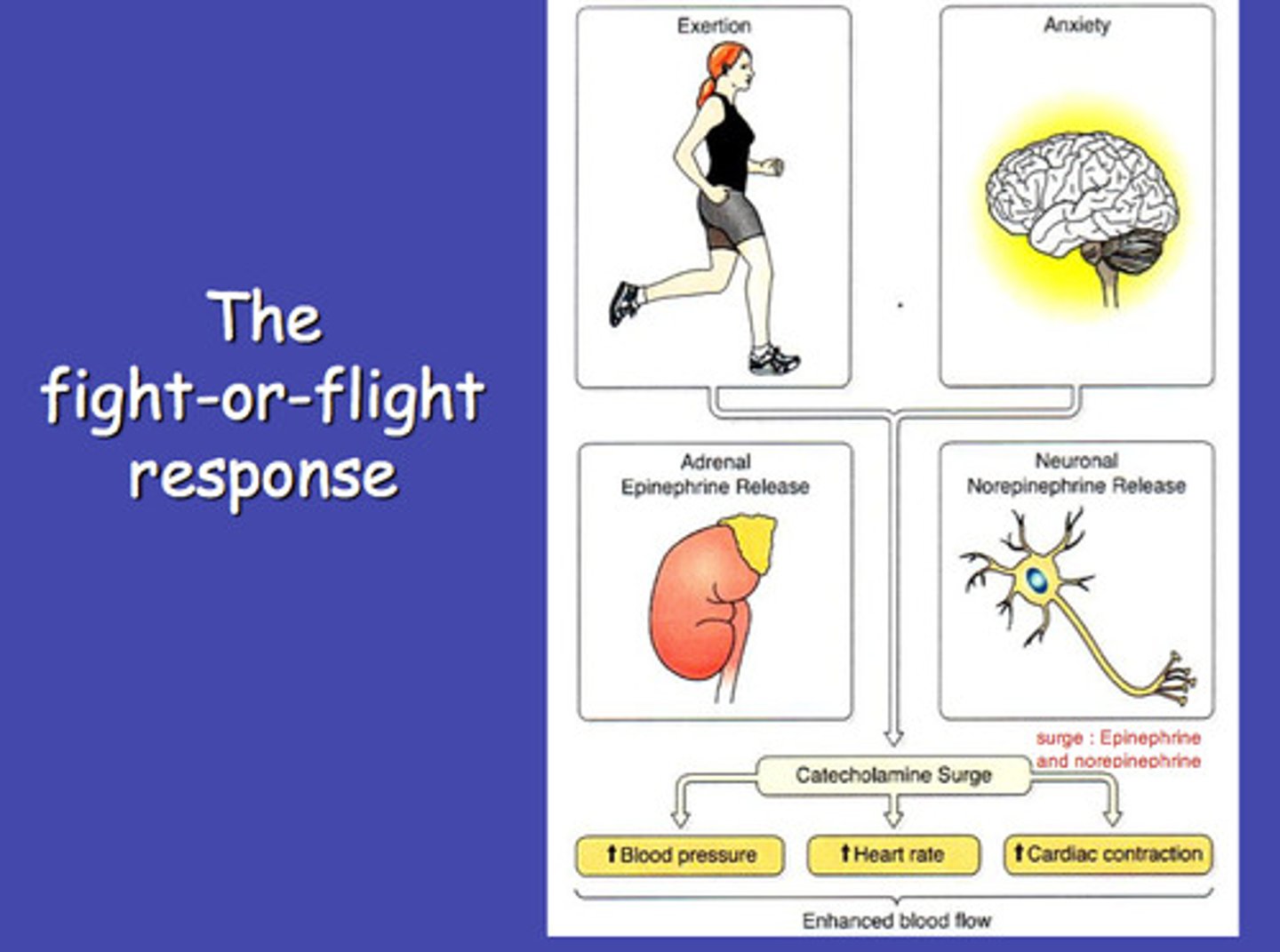
Sympathetic nervous system
Involved in stress-related activities and functions; prepares us for fight or flight. Fight or flight response - activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, allowing access to energy reserves and heightened sensory capacity so that we might fight off a given threat or run away to safety.
Parasympathetic nervous system
Associated with routine, day-to-day operations of the body under relaxed conditions.Rest and restore response - relaxes the body after fight or flight (aka rest and digest)

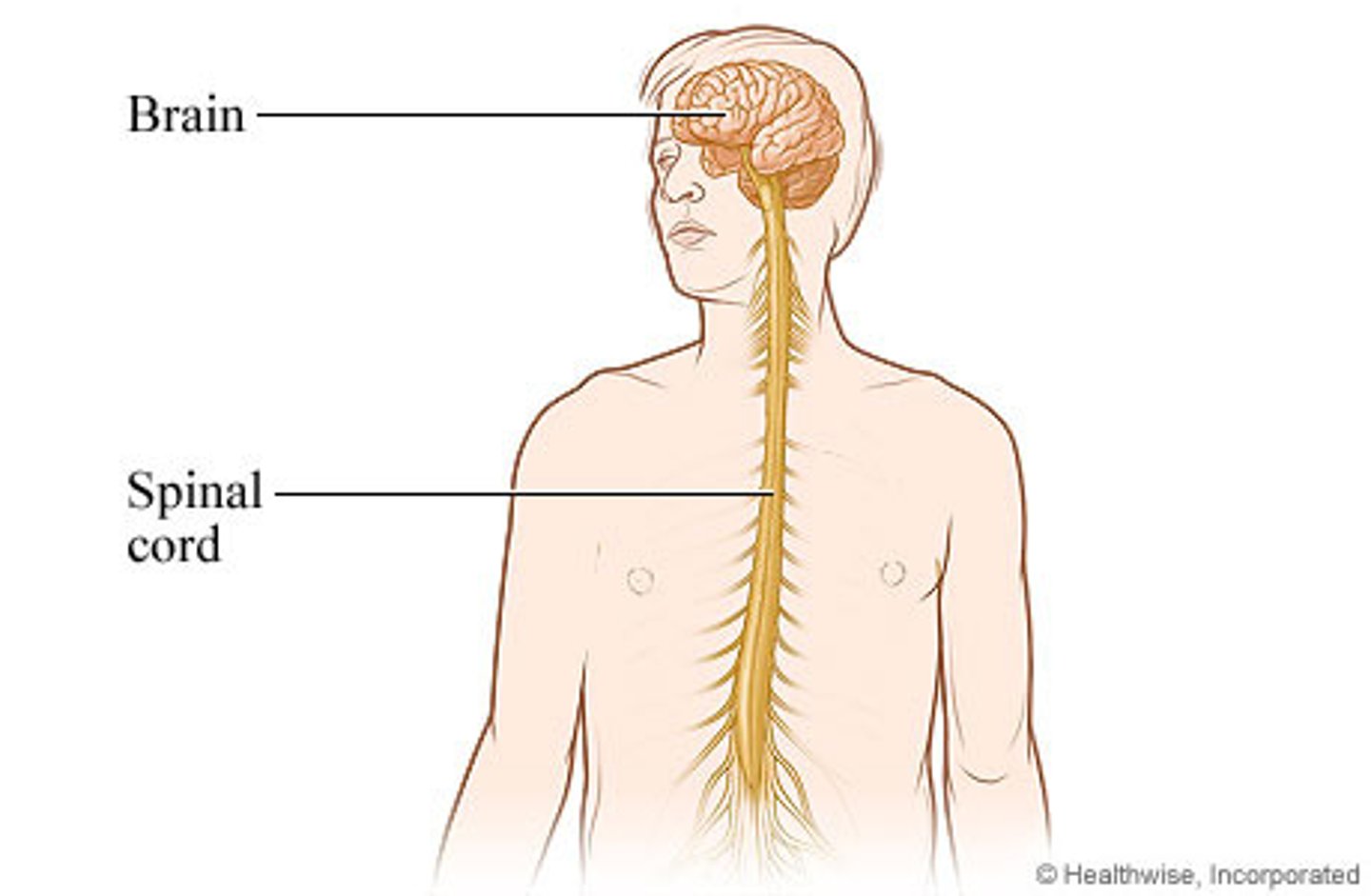
Brain
Comprised of billions of interconnected neurons and glia. - Bilateral (two-sided). - Can be separated into distinct lobes but all areas interact with one another.
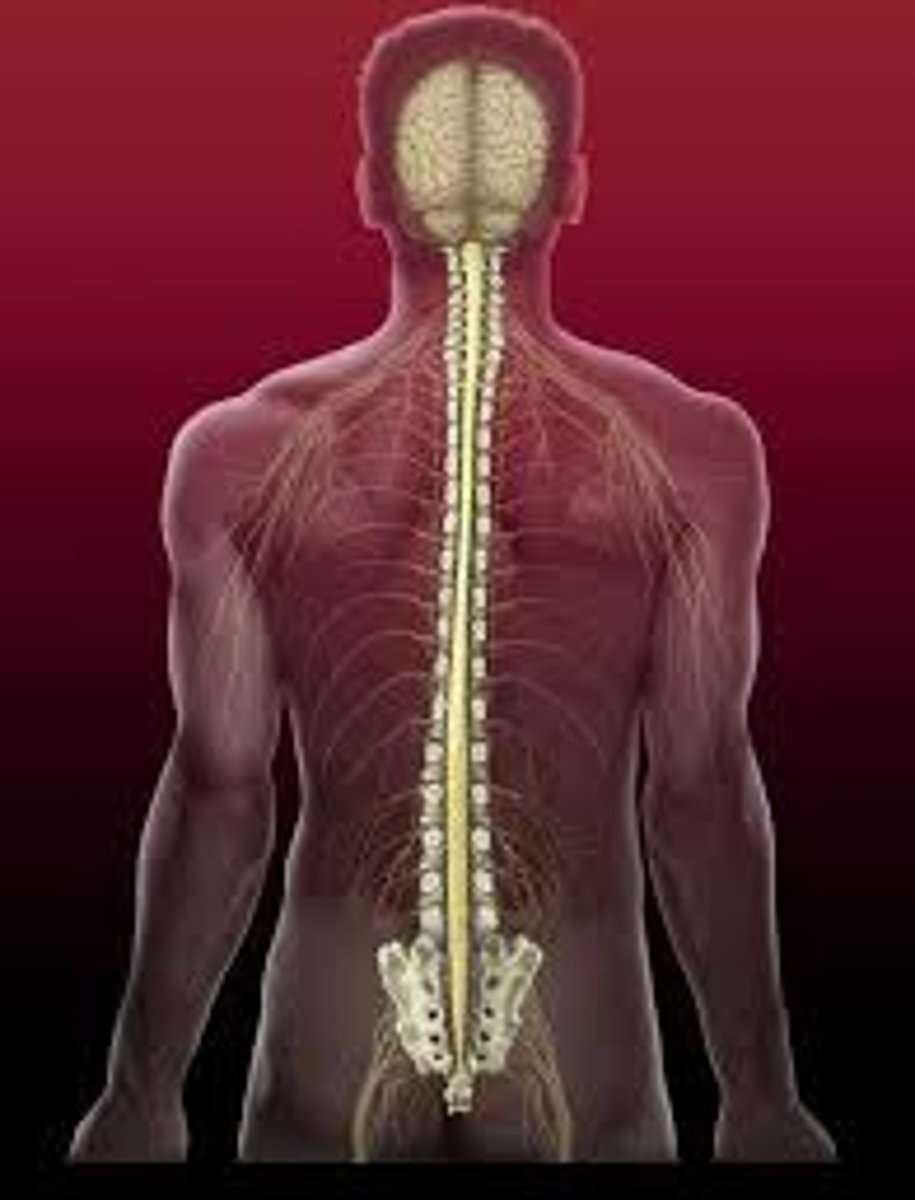
Spinal Cord
Delivers messages to and from the brain. - Has its own system of reflexes. - The top merges with the brain stem and the bottom ends just below the ribs - Functionally organized into 30 segments, each connected to a specific part of the body through the PNS. - Sensory nerves bring messages in and up to the brain; motor nerves send messages out to the muscles and organs. - In moments of survival, automatic reflexes allow motor commands to be initiated without sending signals from sensory nerves to the brain first, allowing for very quick reactions.
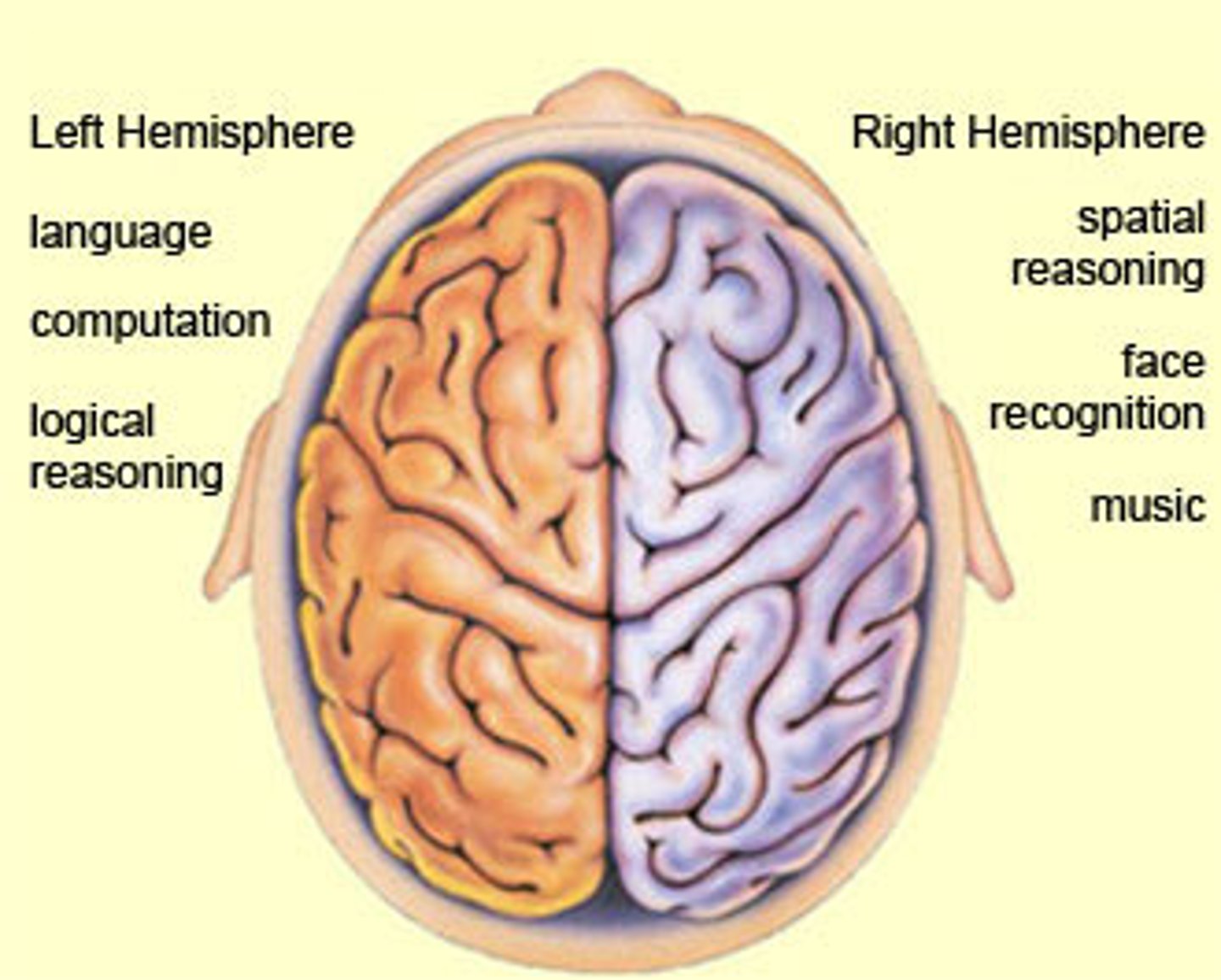
Lateralization
Concept that each hemisphere of the brain is associated with specialized functions. - The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body. - The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body.
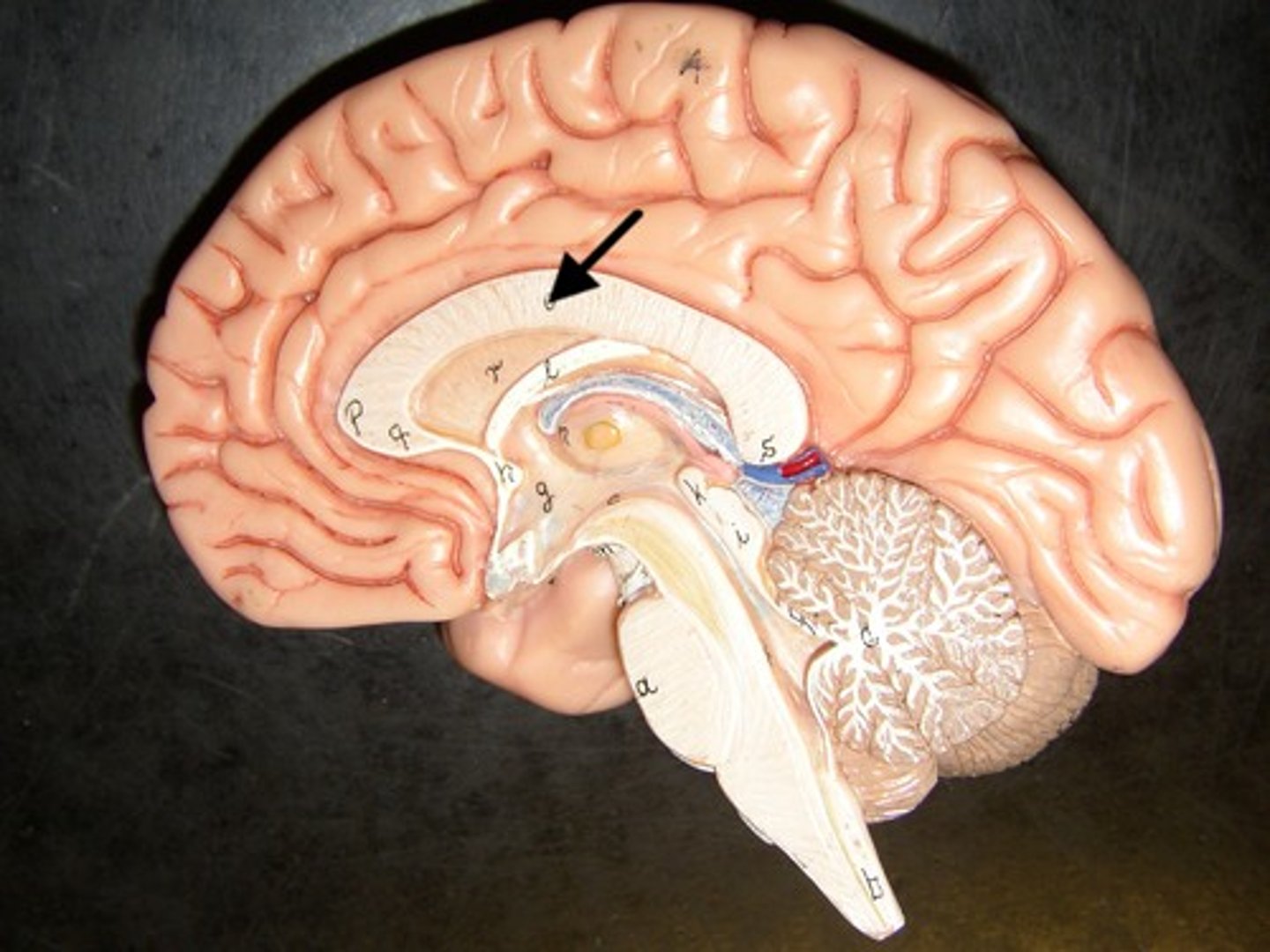
Corpus Callosum
The two hemispheres are connected by a thick band of neural fibers known as the corpus callosum, consisting of about 200 million axons. The corpus callosum allows the two hemispheres to communicate with each other and allows for information being processed on one side of the brain to be shared with the other side.
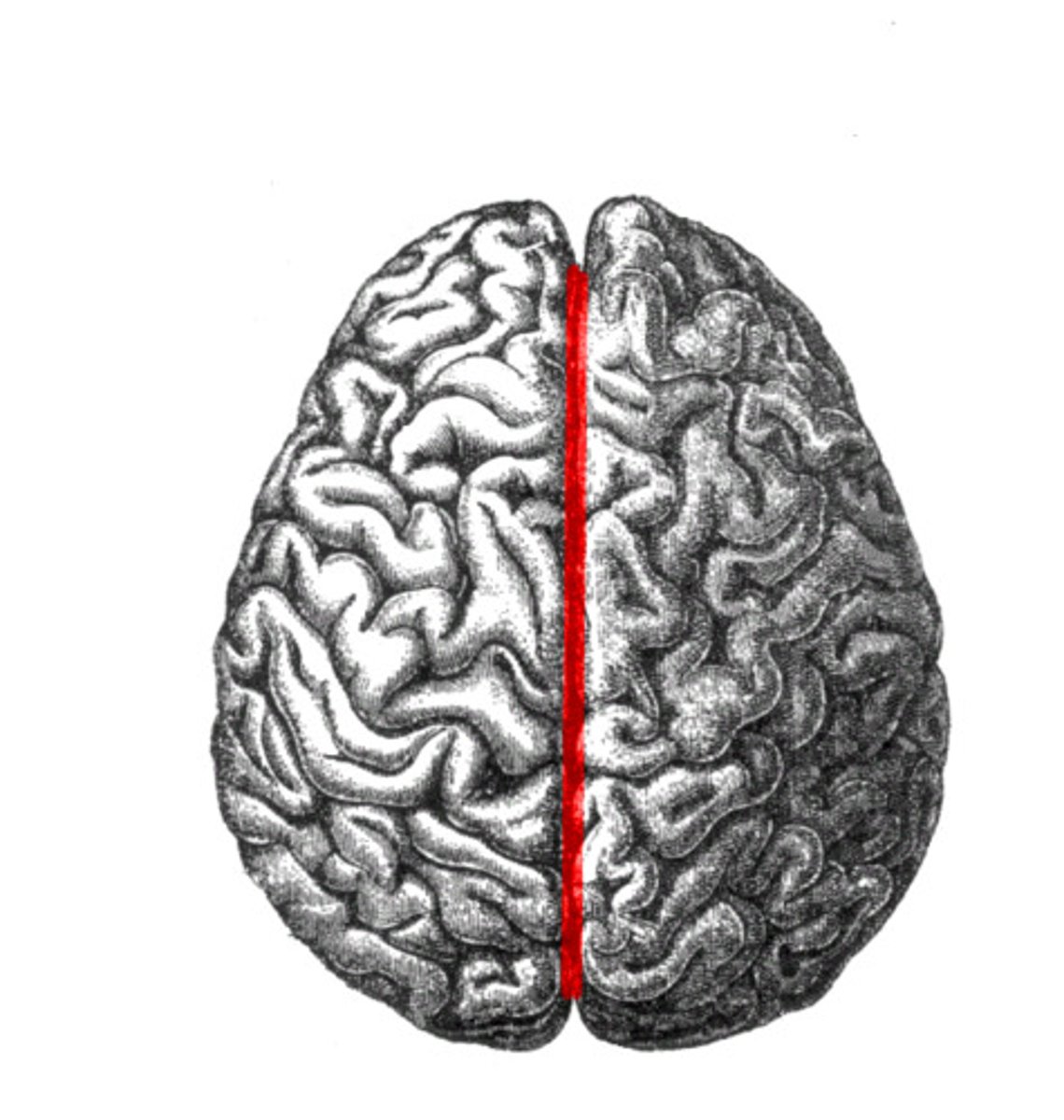
Longitudinal fissure
Deep groove that separates the brain into two halves or hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere.
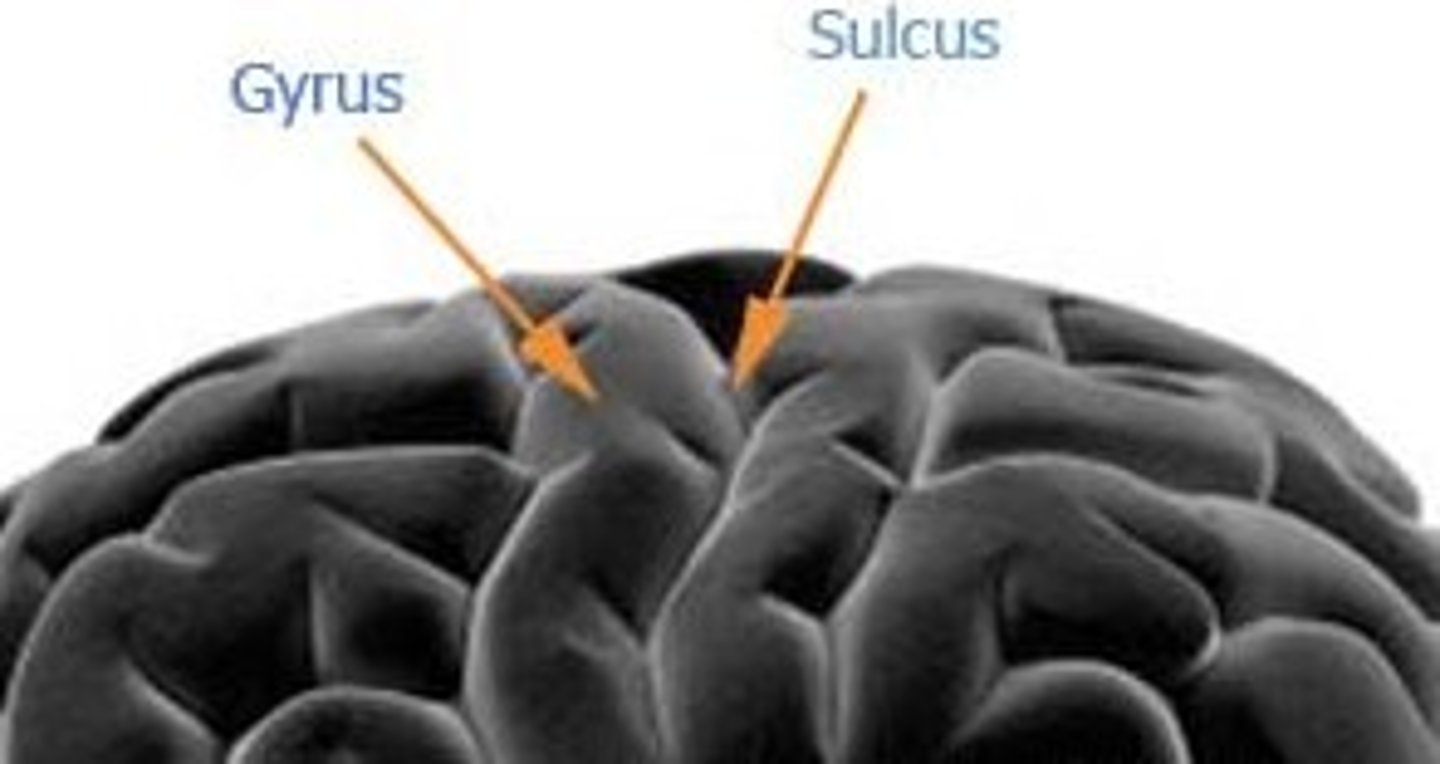
Gyri and Sulci
The ridges and grooves of the cerebral cortex
Forebrain, midbrain & hindbrain
The brain and its parts can be divided into three main categories: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain
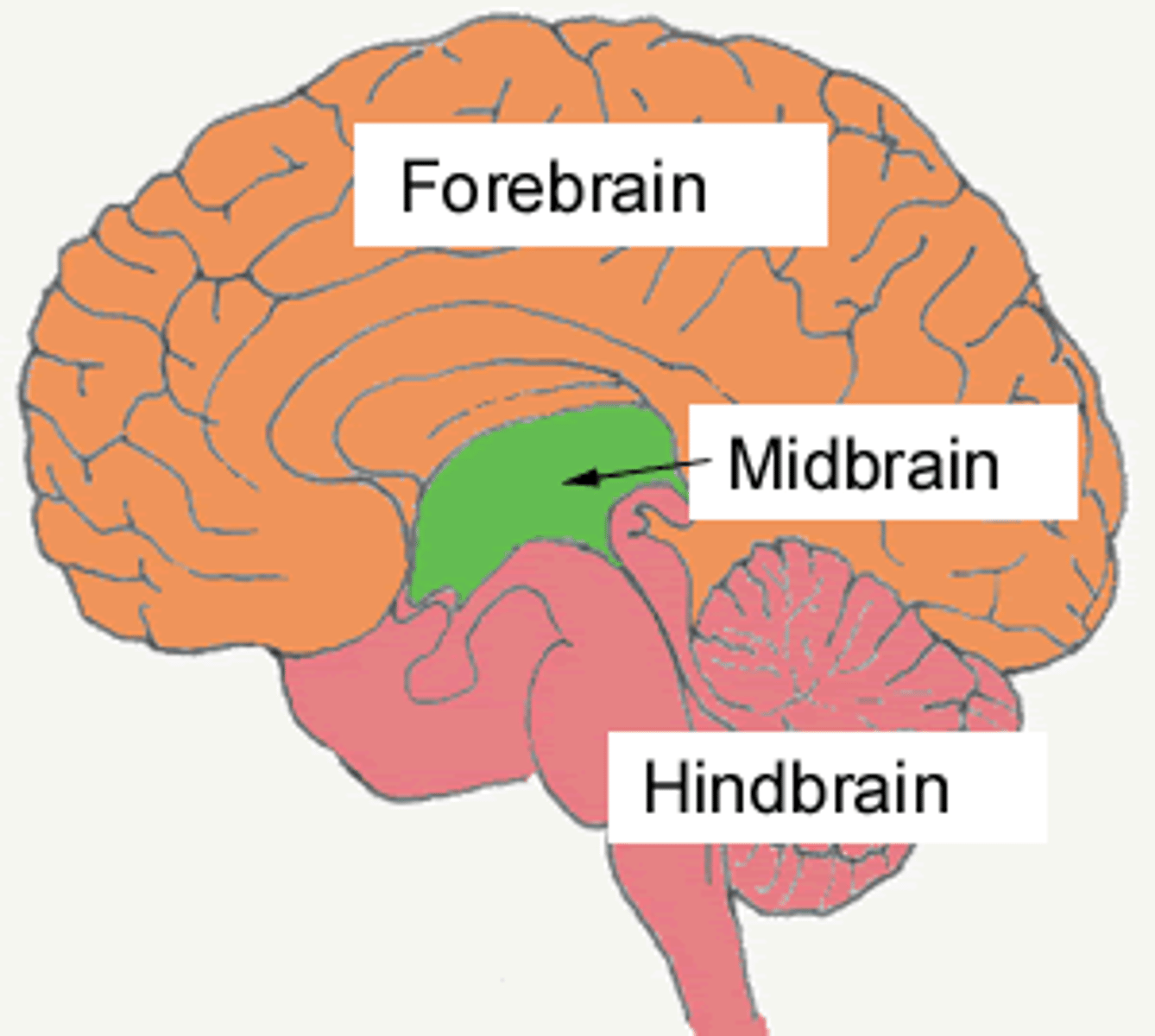
Forebrain structures
The forebrain is the largest part of the brain
The cerebral cortex - higher level processes
Thalamus - sensory relay
Hypothalamus - homeostasis
Pituitary gland - master gland of the endocrine system Limbic system - emotion and memory circuit
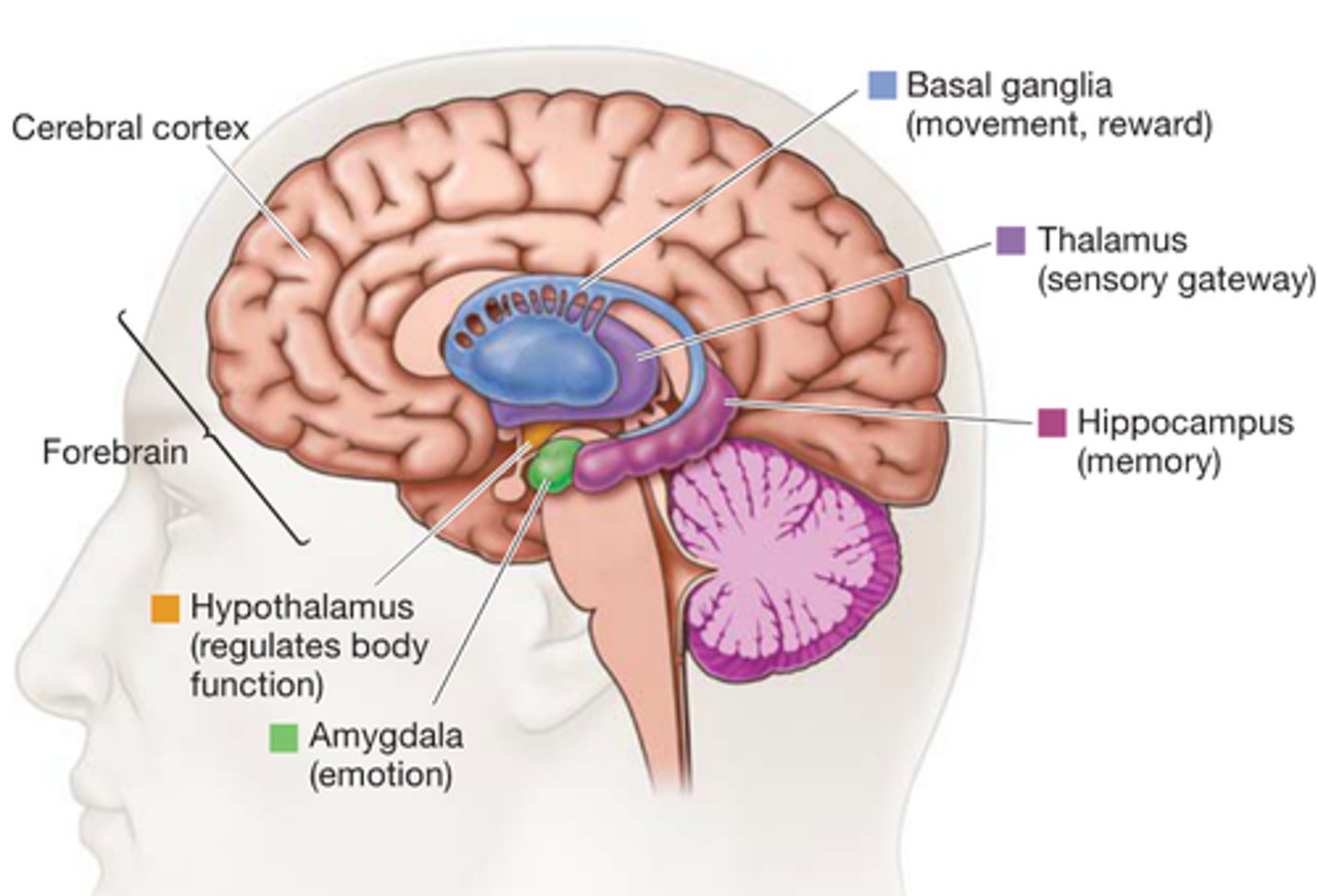
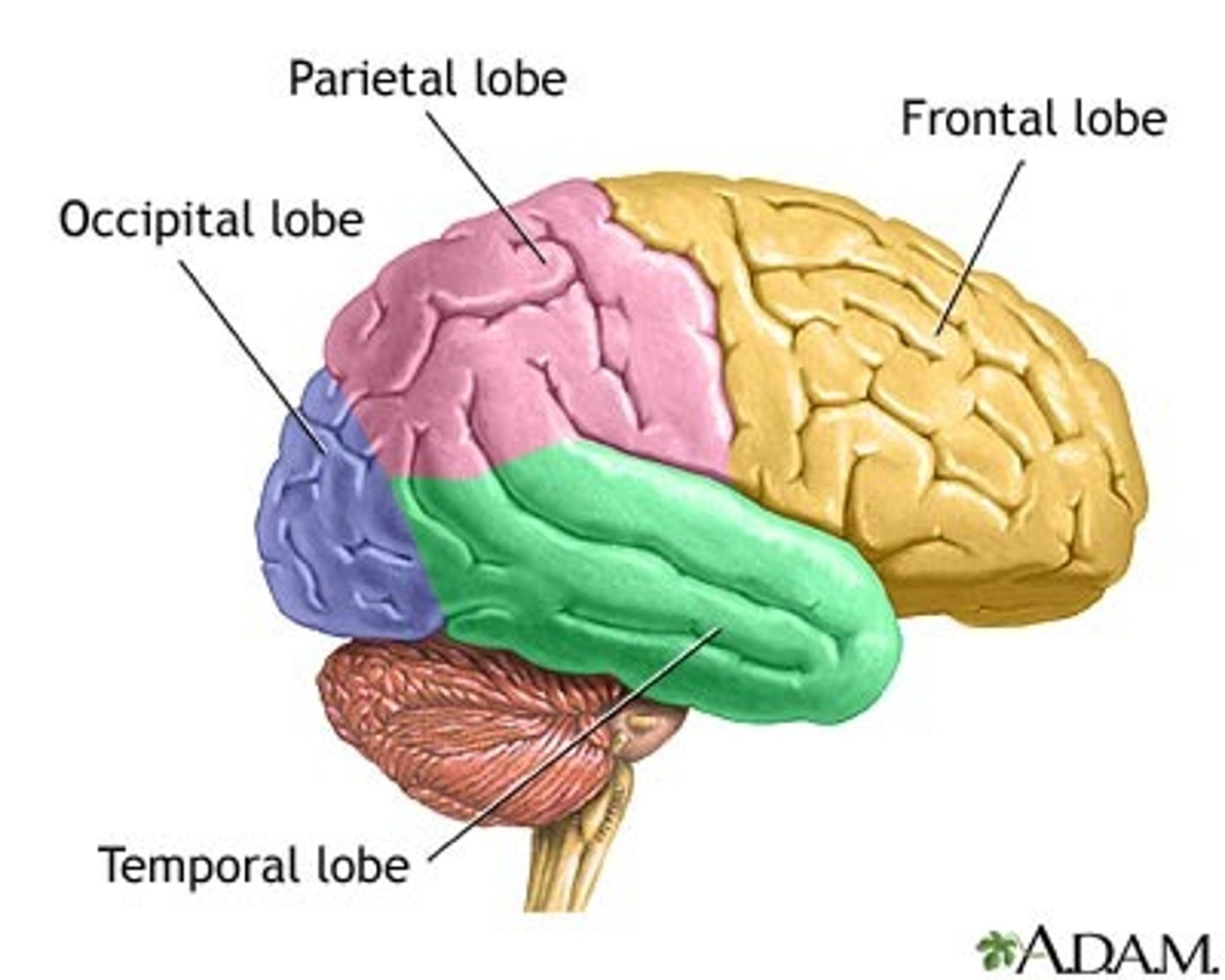
Cerebral cortex
Surface of the brain that is associated with out highest mental capabilities such as consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language and memory. It can be broken up into four lobes, each with a different function.
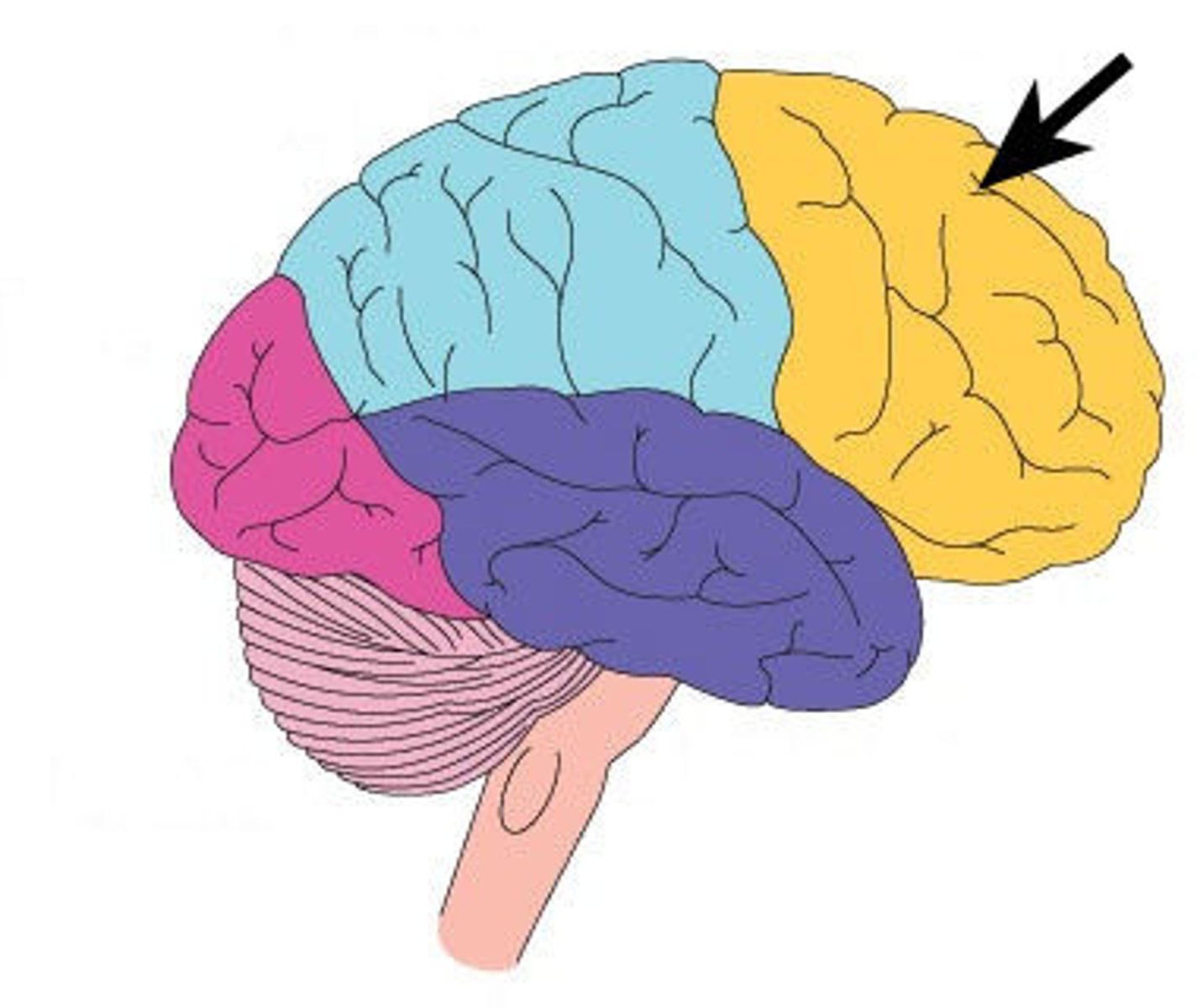
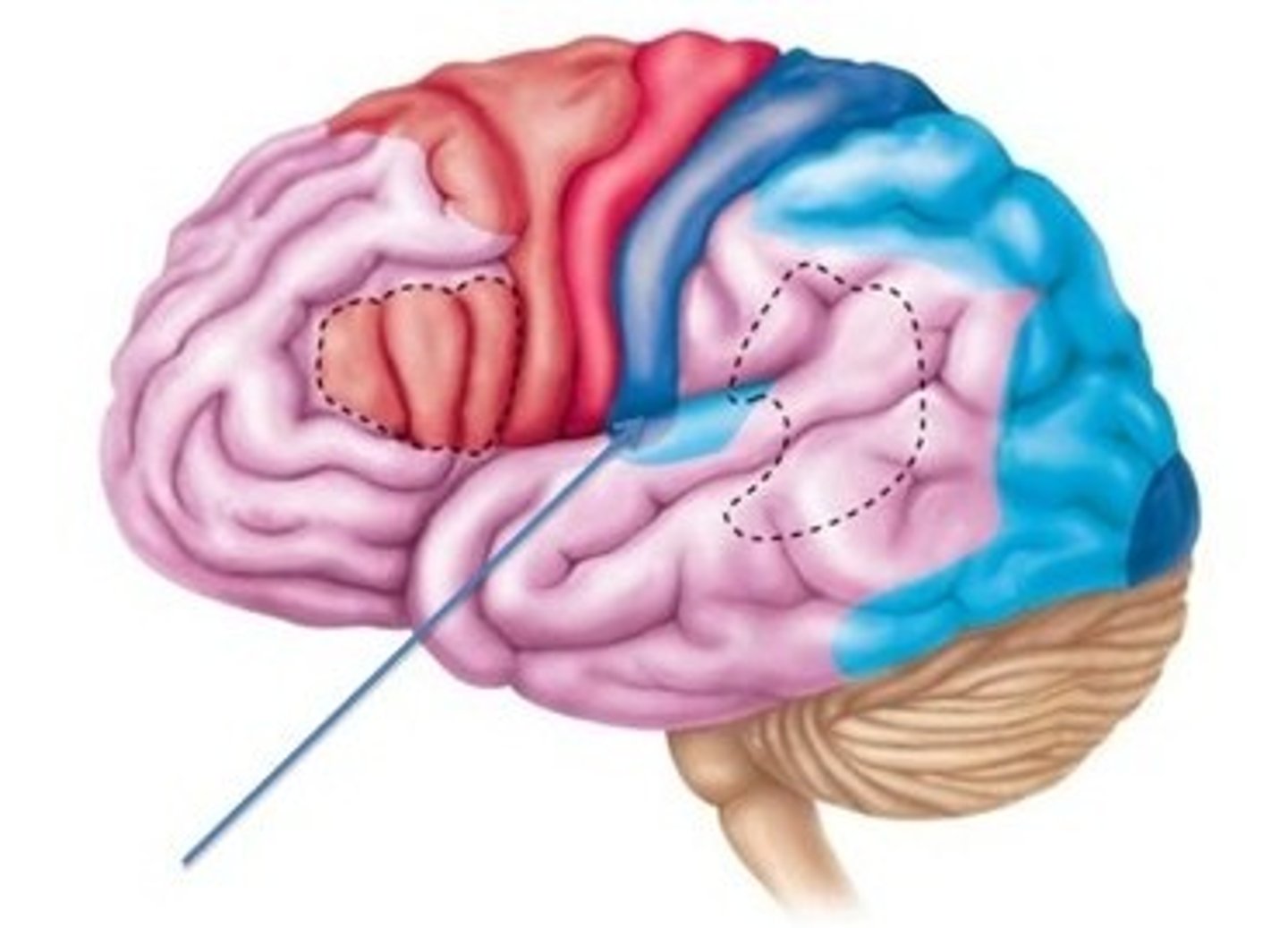
Frontal Lobe
Involved in executive functioning (planning, organization, judgement, attention, reasoning), motor control, emotion, and language.
It contains:
The Motor cortex - strip of cortex involved in planning and coordinating movement.
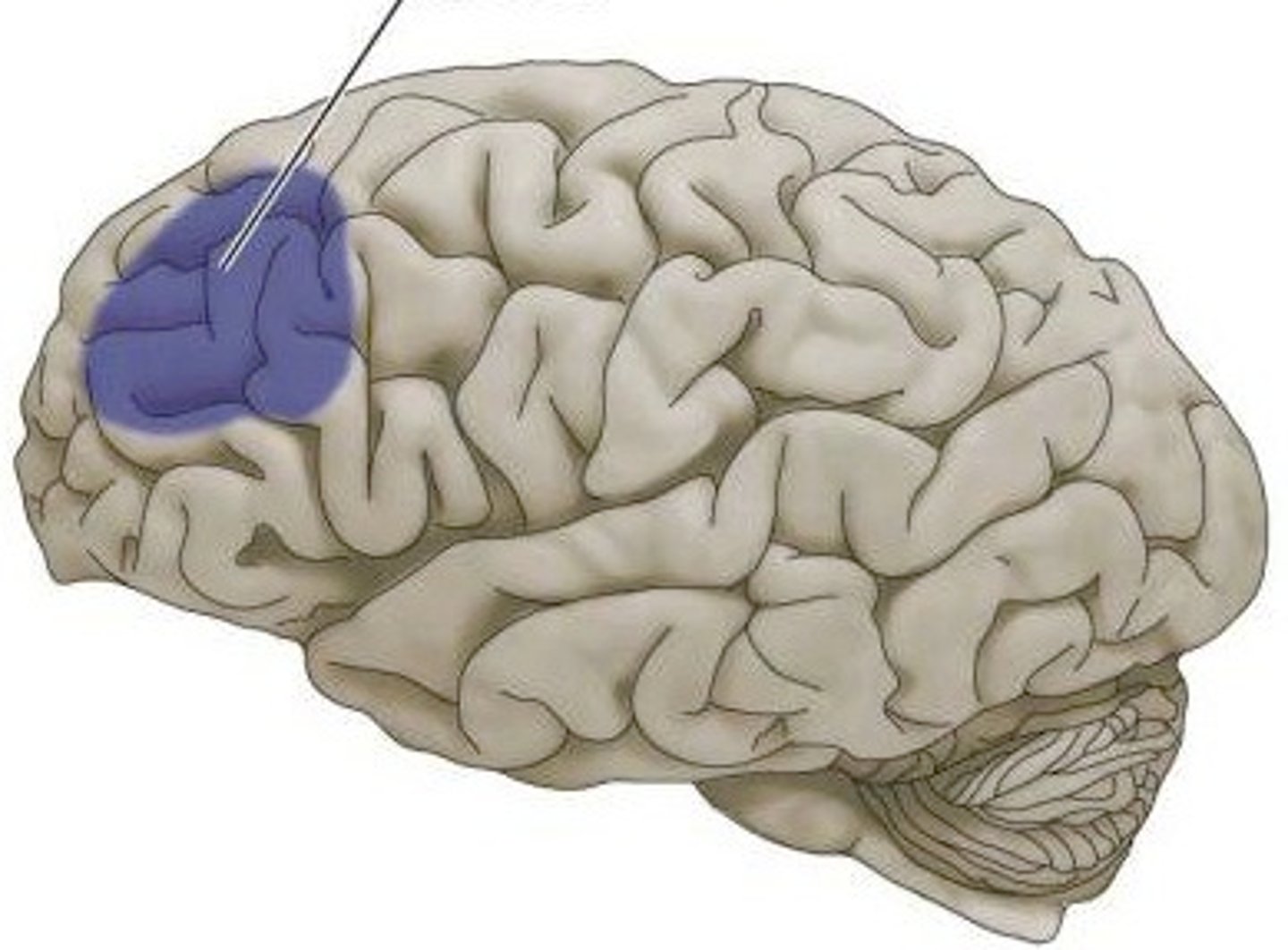
The Prefrontal cortex - responsible for higher-level cognitive functioning.
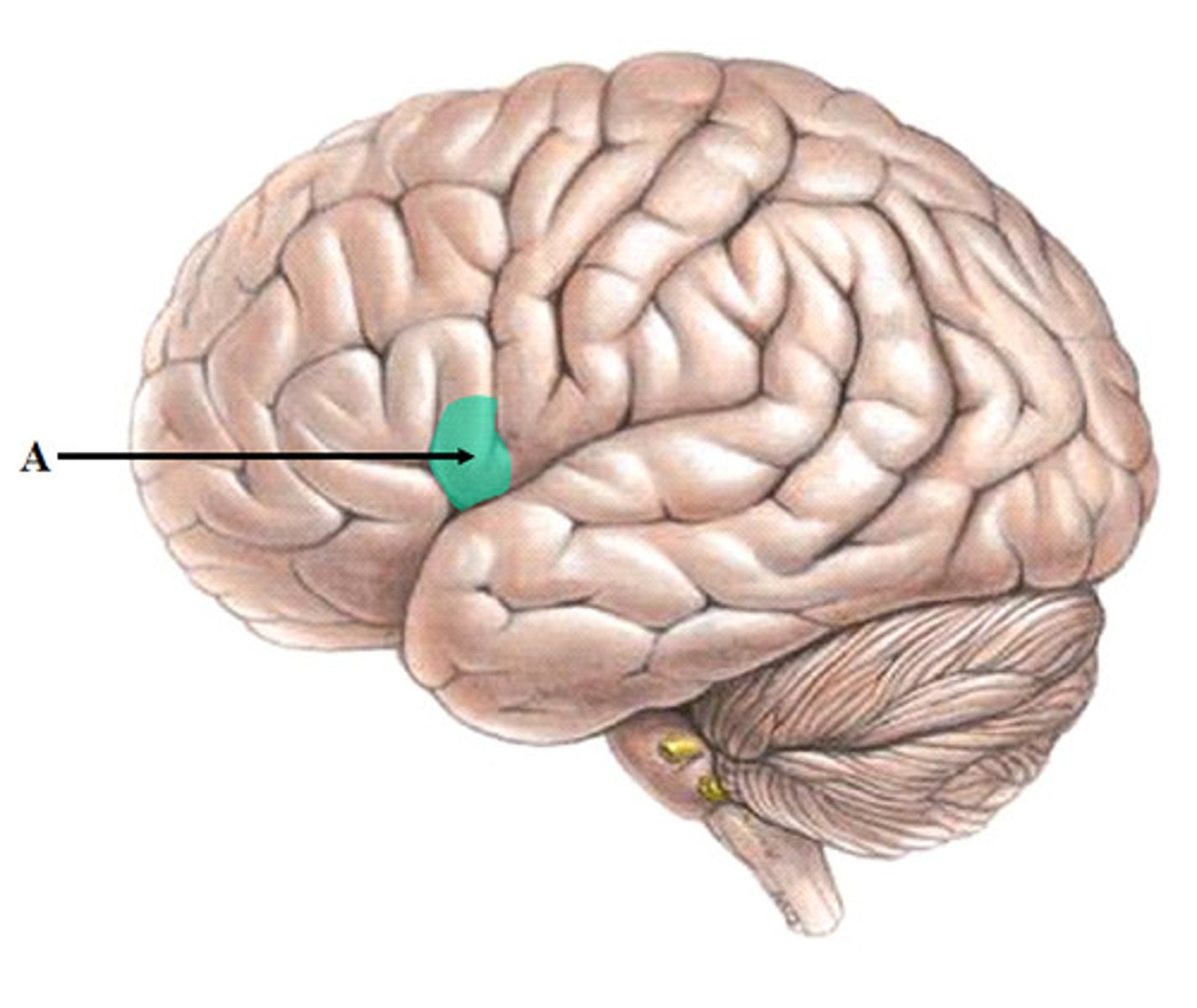
Broca's area - region in the left hemisphere that is essential for language production.
- Damage to Broca's area leads to difficulties producing language.
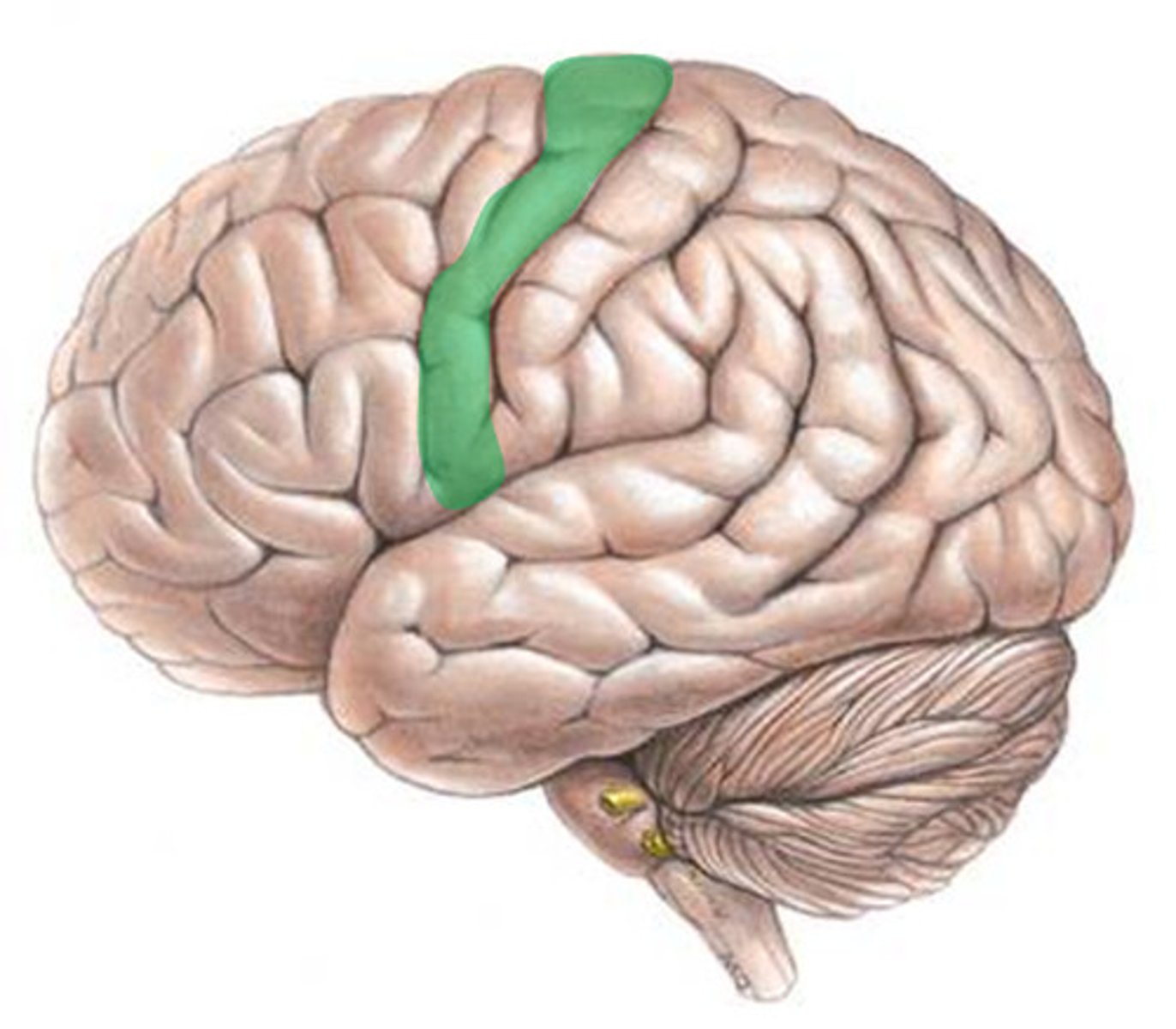
Motor Cortex
An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
Prefrontal Cortex
Part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
Broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
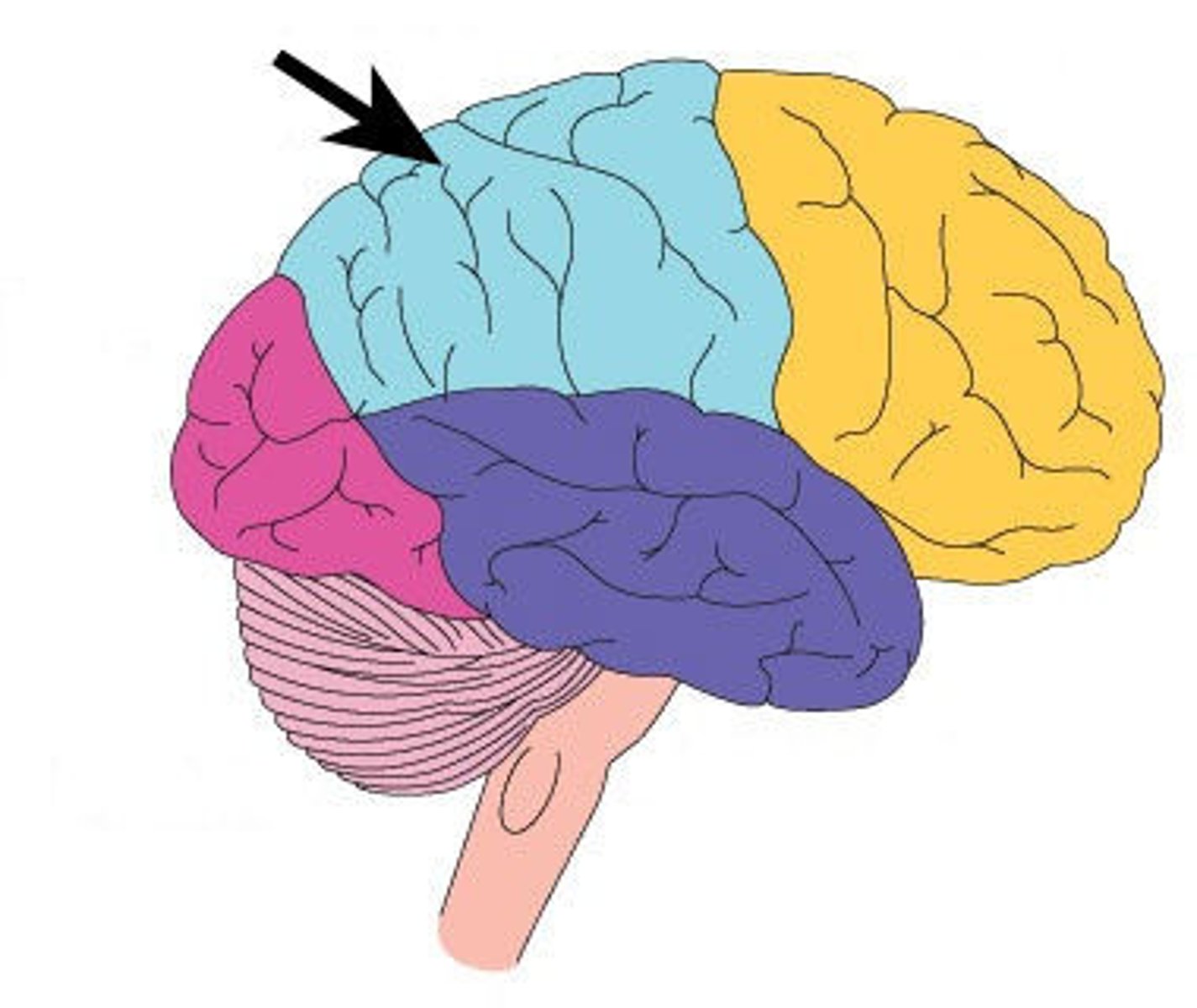
The parietal lobe
Involved in processing various sensory and perceptual information. Contains the primary somatosensory cortex.
Somatosensory cortex
Essential for processing sensory information from across the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain. - Organized topographically.
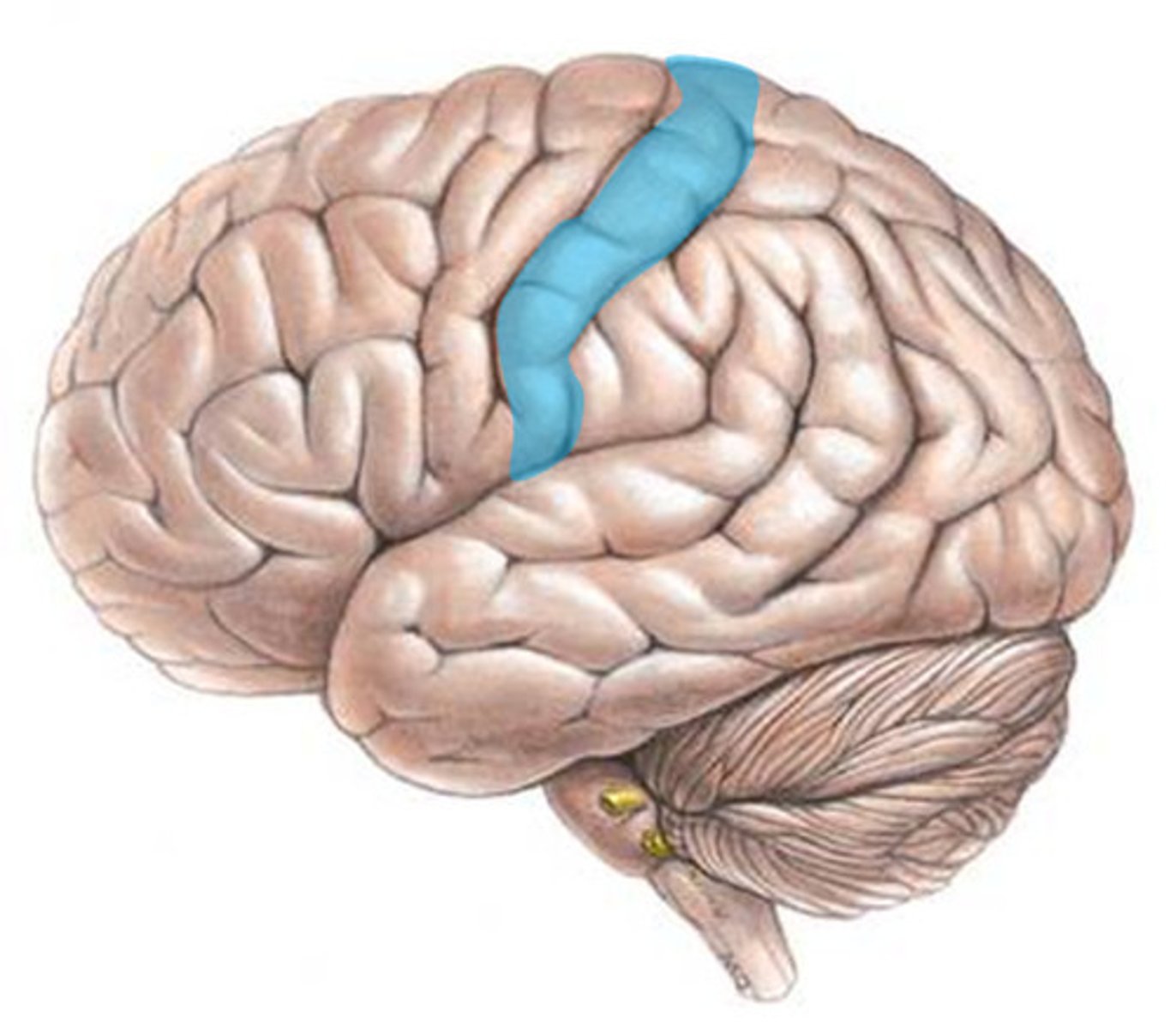
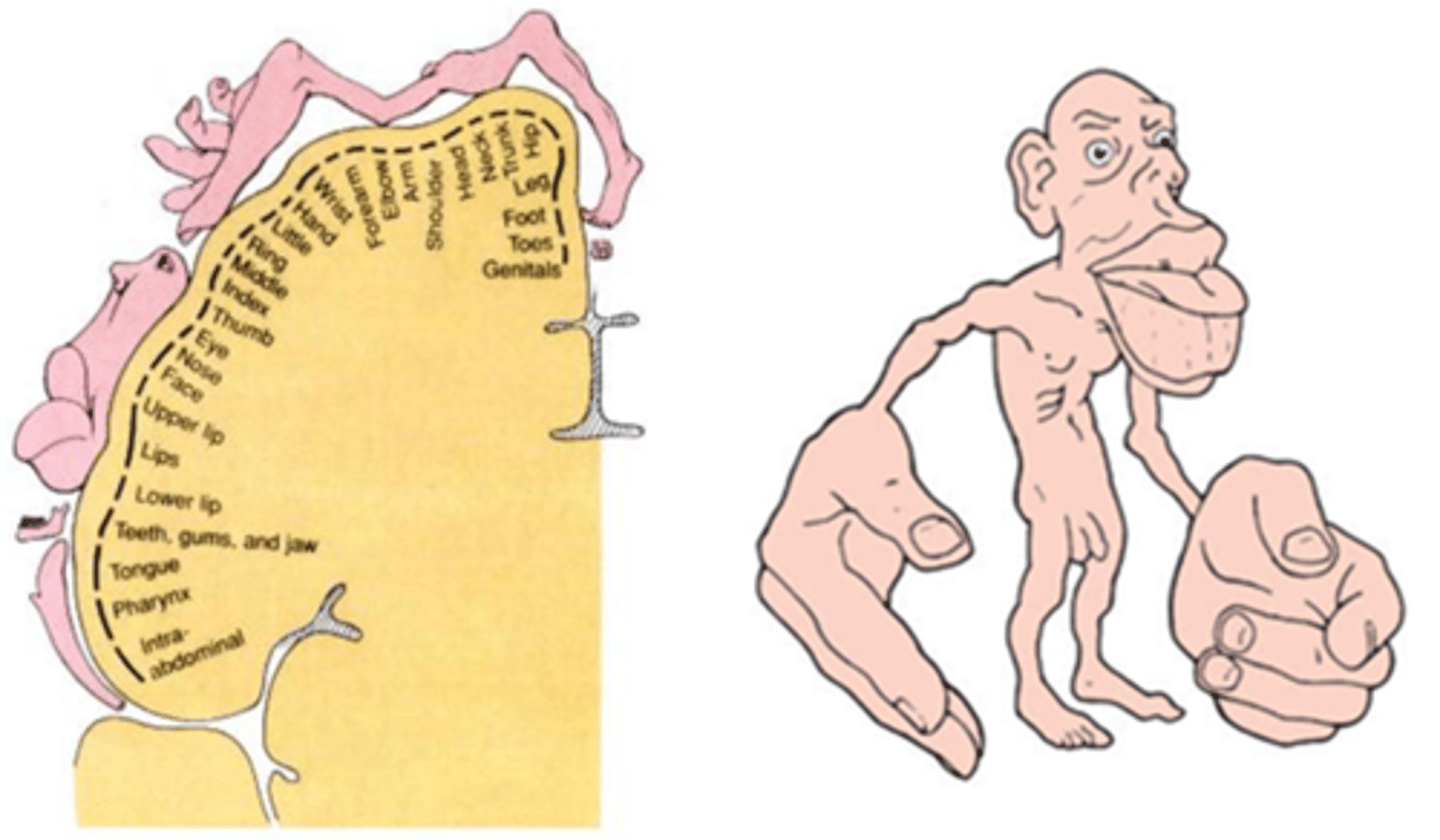
Homunculus
A maplike representation of regions of the body in the brain
The temporal lobe
Associated with hearing, memory, emotion and some aspects of language. Located on the side of the head (near the temples). It contains:
The Auditory cortex - strip of cortex in the temporal lobe that is responsible for processing auditory information.
Wernicke's area - important for speech comprehension. - Damage to Wernicke's area results in difficulty understanding language.
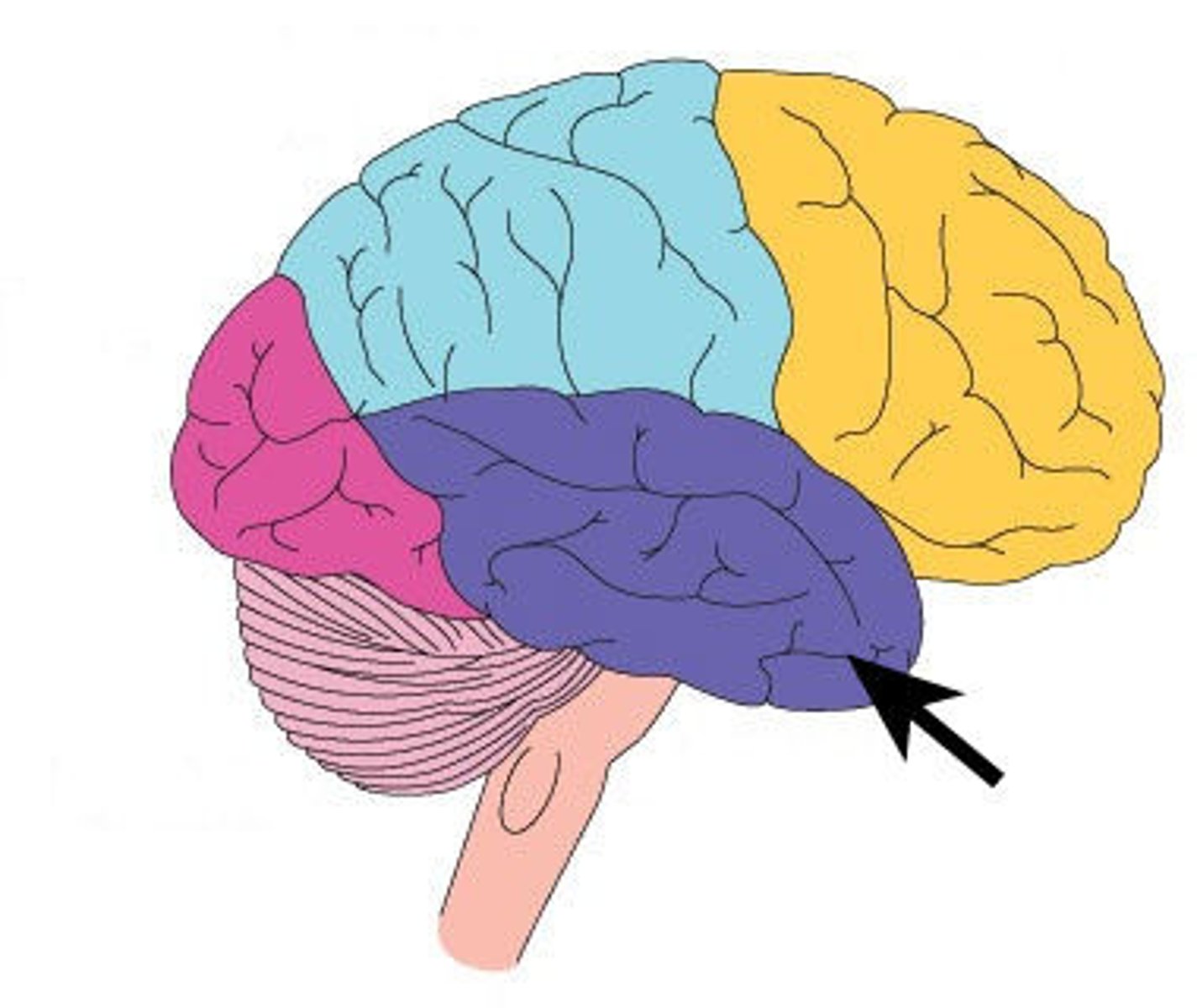
The Auditory cortex
The area of the temporal lobe responsible for processing sound information
Wernicke's area
Important for speech comprehension.
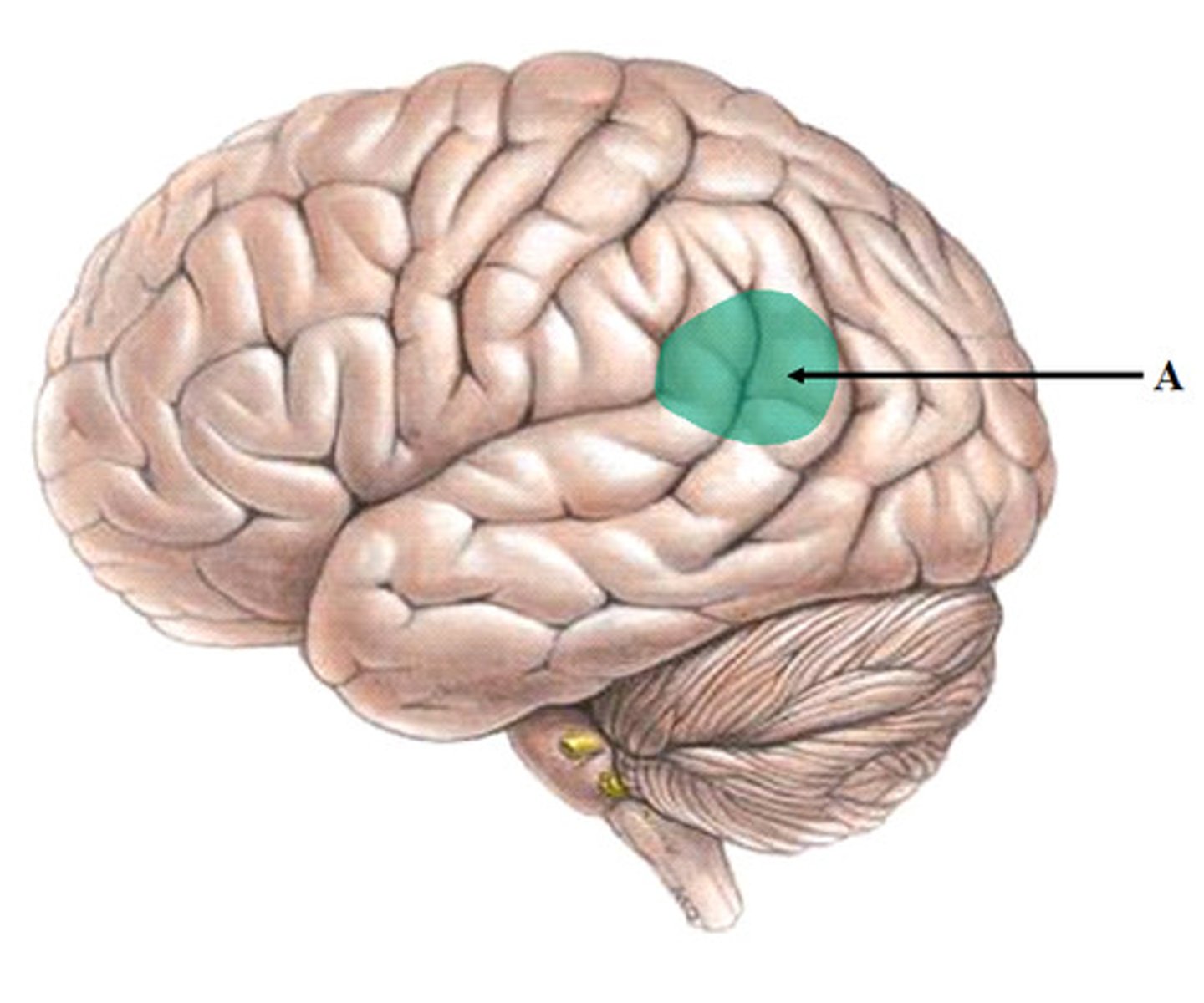
The occipital lobe
Associated with visual processing. Contains the primary visual cortex which is responsible for interpreting incoming visual information. Organized retinotopically.
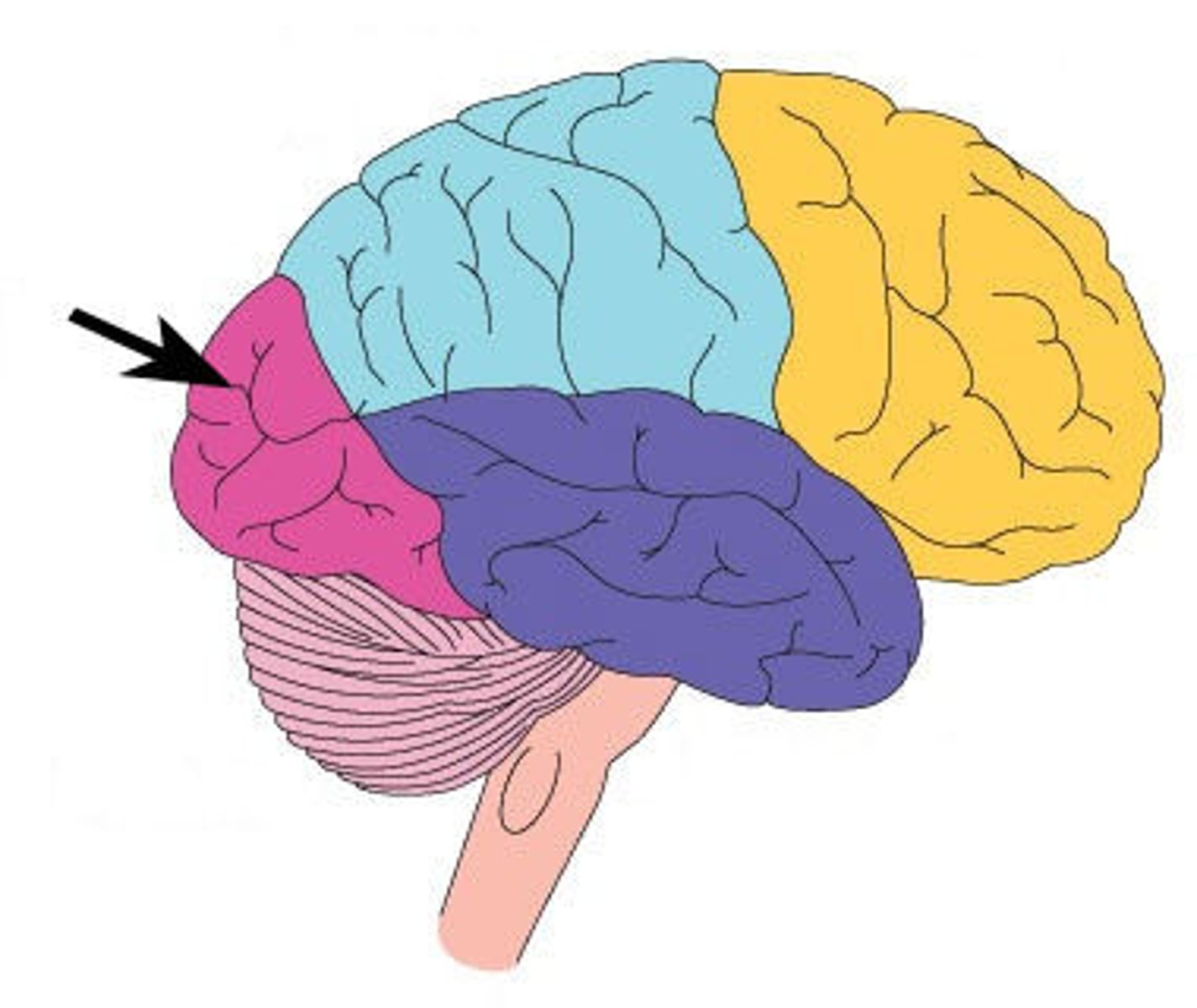
The thalamus
The brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
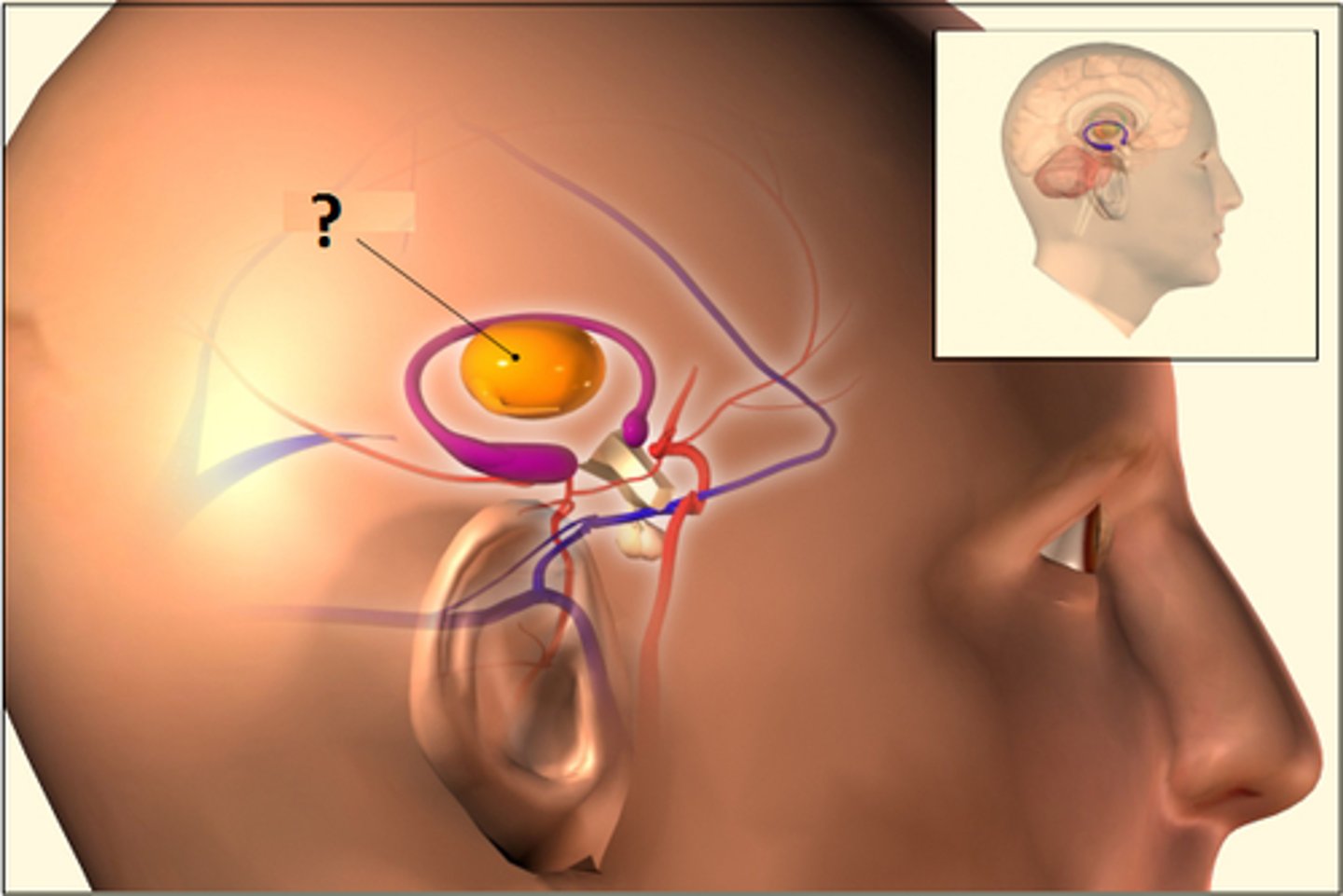
Limbic System
Neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives
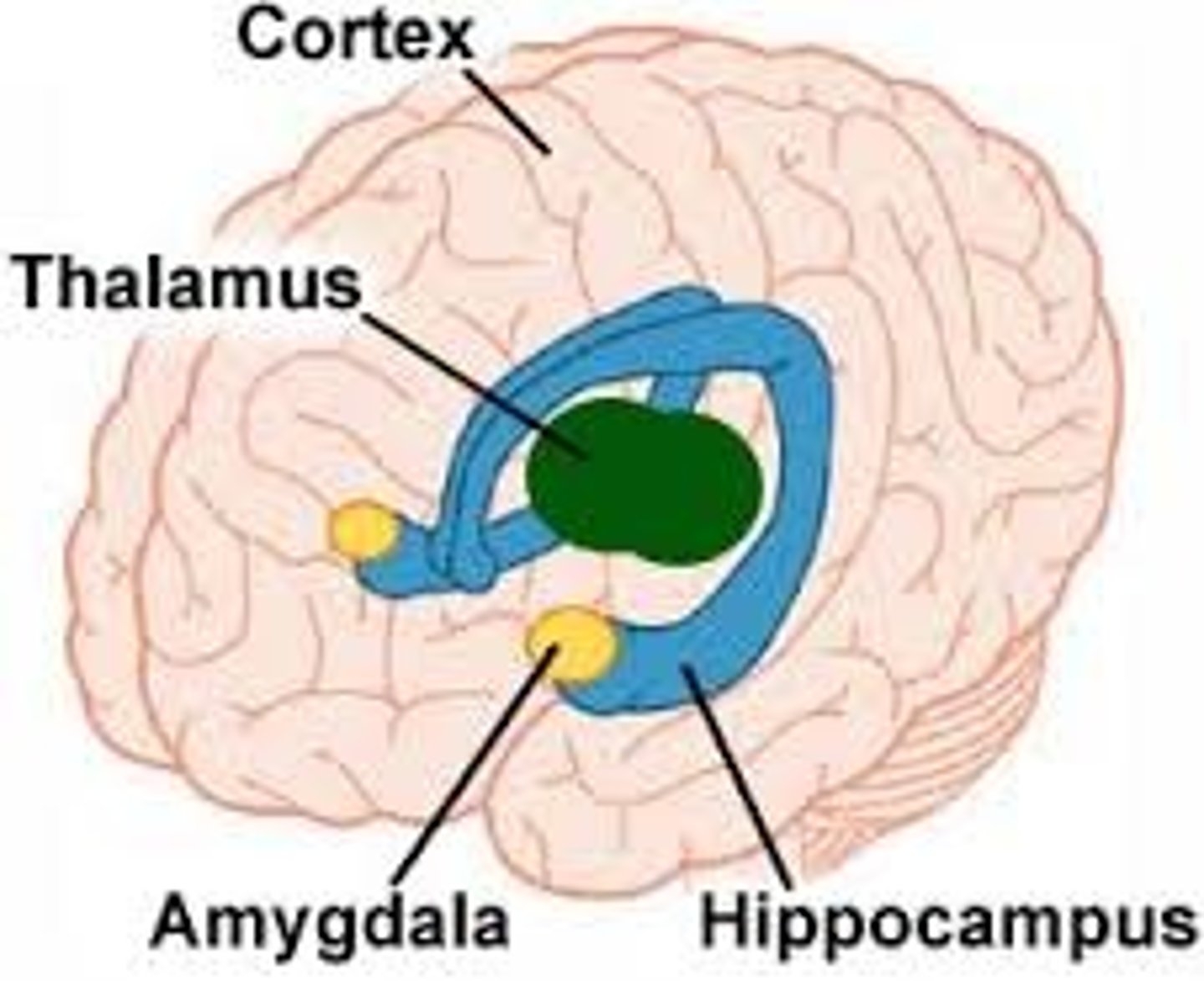
Amygdala
Involved in our experience of emotion and tying emotional meaning to our memories. Involved in processing fear.

Hippocampus
Structure associated with learning and memory (in particular spatial memory).
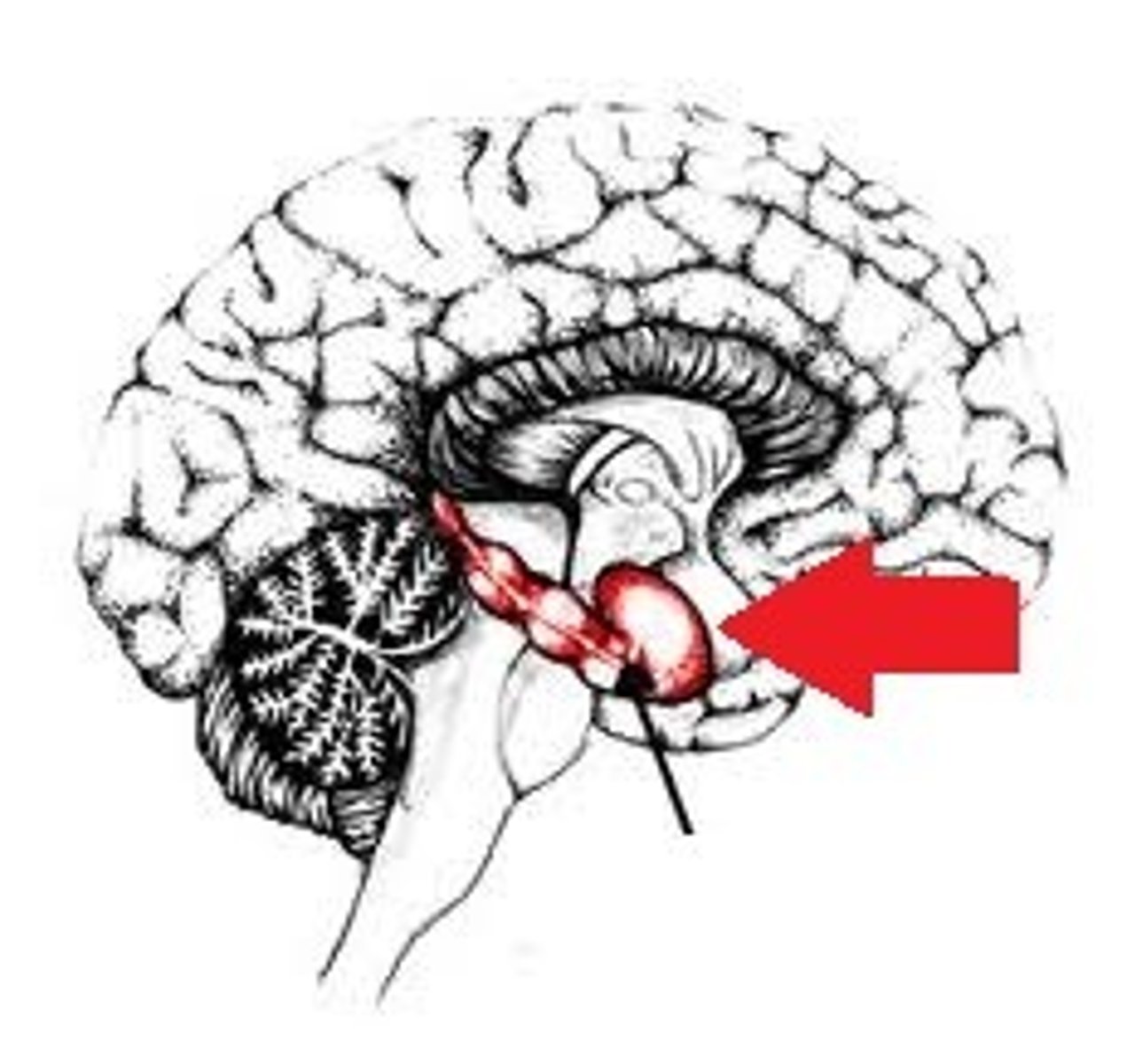
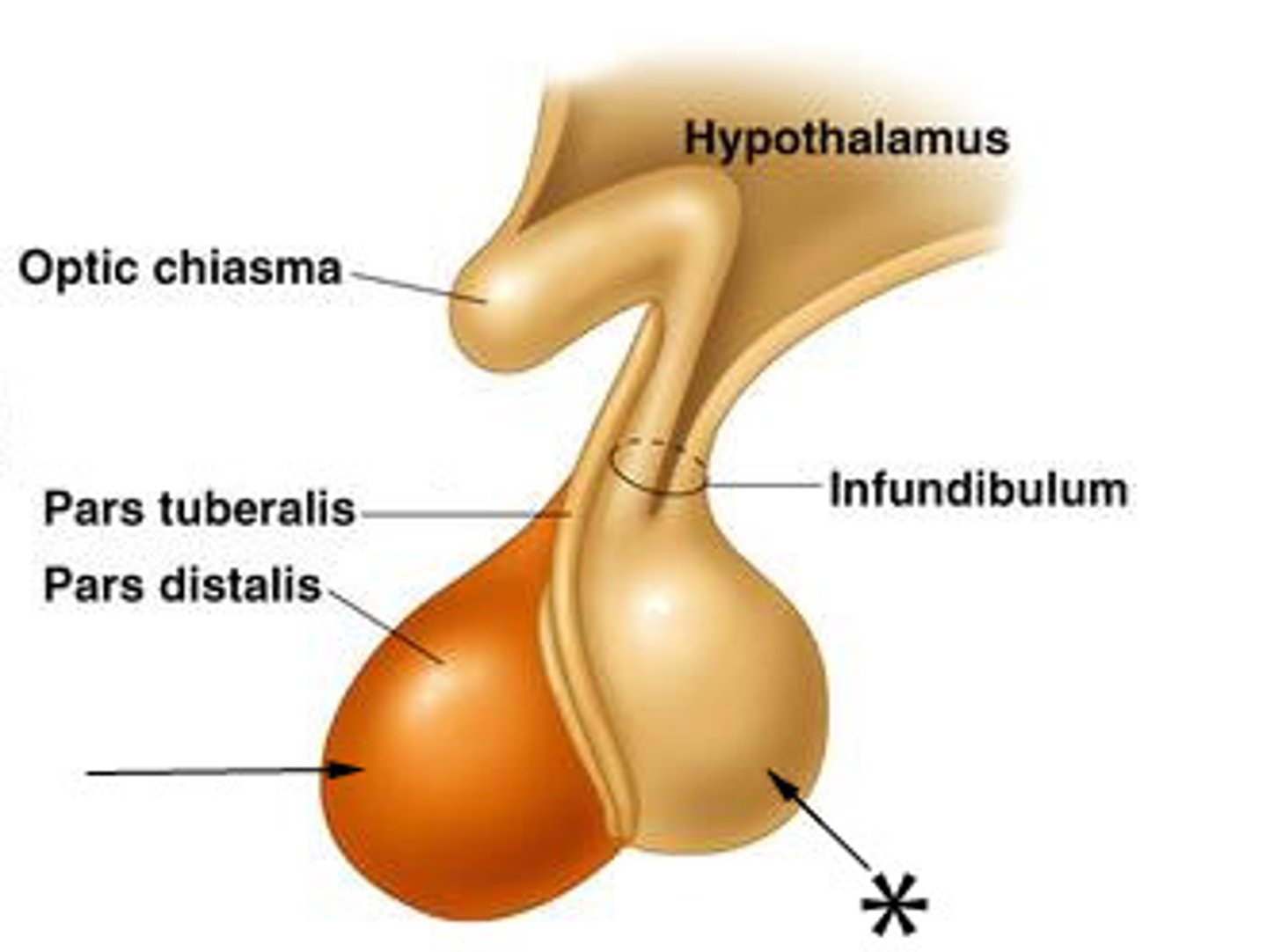
Hypothalamus
Regulates homeostatic processes including body temperature, appetite and blood pressure.
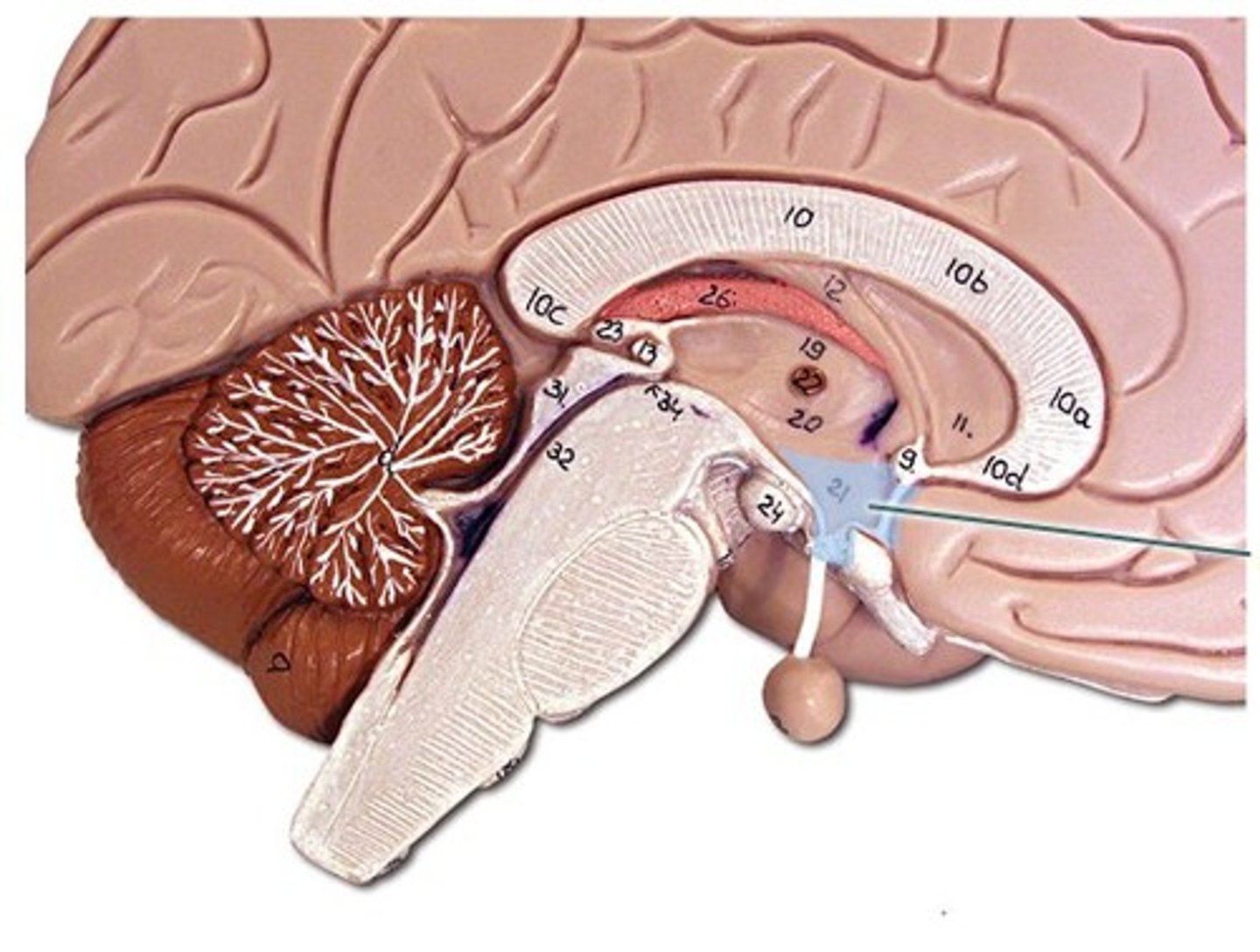
Reticular formation
Important in regulating the sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor activity.

Substantia Nigra
Where dopamine is produced; involved in control of movement.

Ventral tegmental area (VTA)
Where dopamine is produced; associated with mood, reward, and addiction. Degeneration of the Substantia Nigra and VTA is involved in Parkinson's disease.

Medulla
Controls automated processes like breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate.
Pons
Connects the brain and the spinal cord; involved in regulating brain activity during sleep.

Cerebellum
Controls our balance, coordination, movement, and motor skills, and it is thought to be important in processing some types of memory. These 3 structures combined are known as the brain stem.

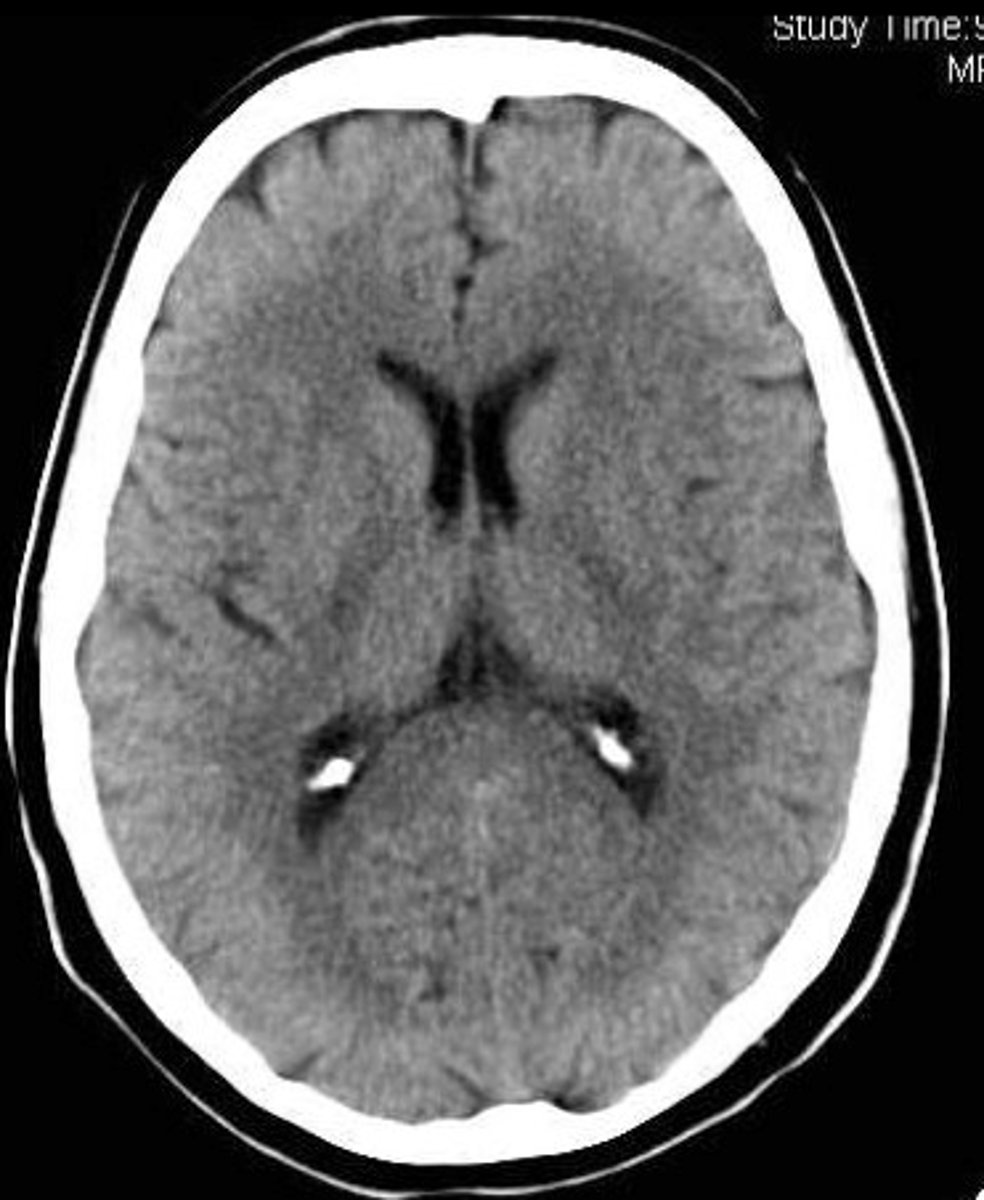
CT scan
Involves x-rays and creates an image through x-rays passing through varied densities within the brain.
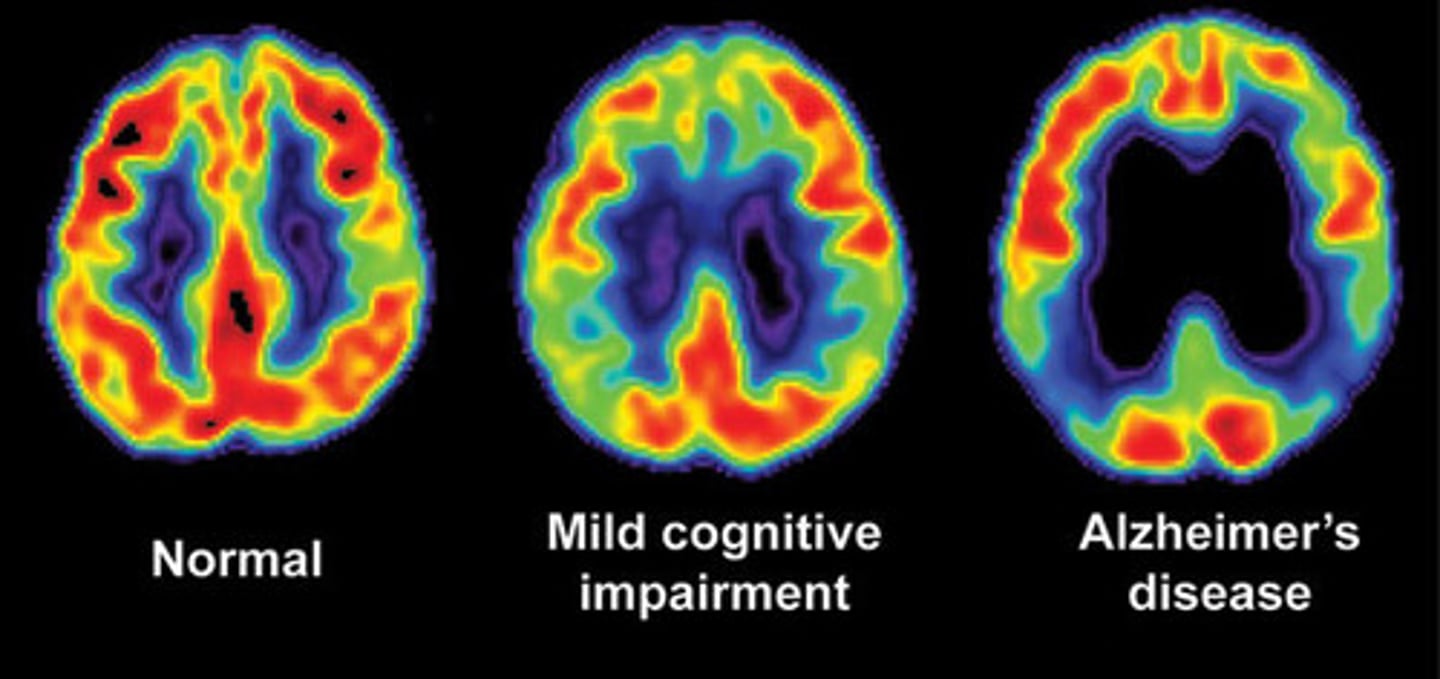
PET scan
Involves injecting individuals with a mildly radioactive substance and monitoring changes in blood flow to different regions of the brain. A PET scan is helpful for showing activity in different parts of the brain.
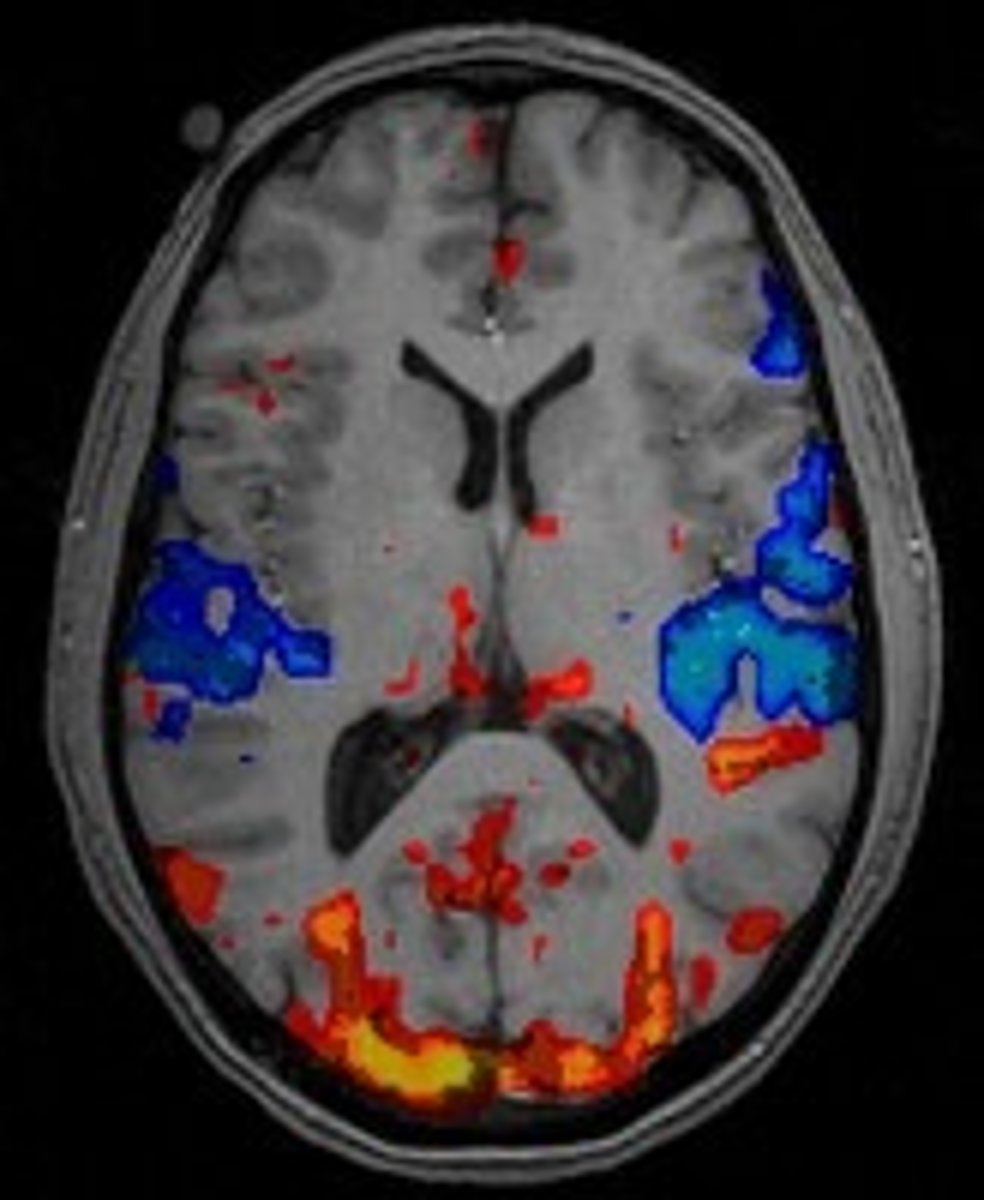
MRI and fMRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - magnetic fields used to produce a picture of the tissue being imaged.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) - MRI that show changes in metabolic activity over time.
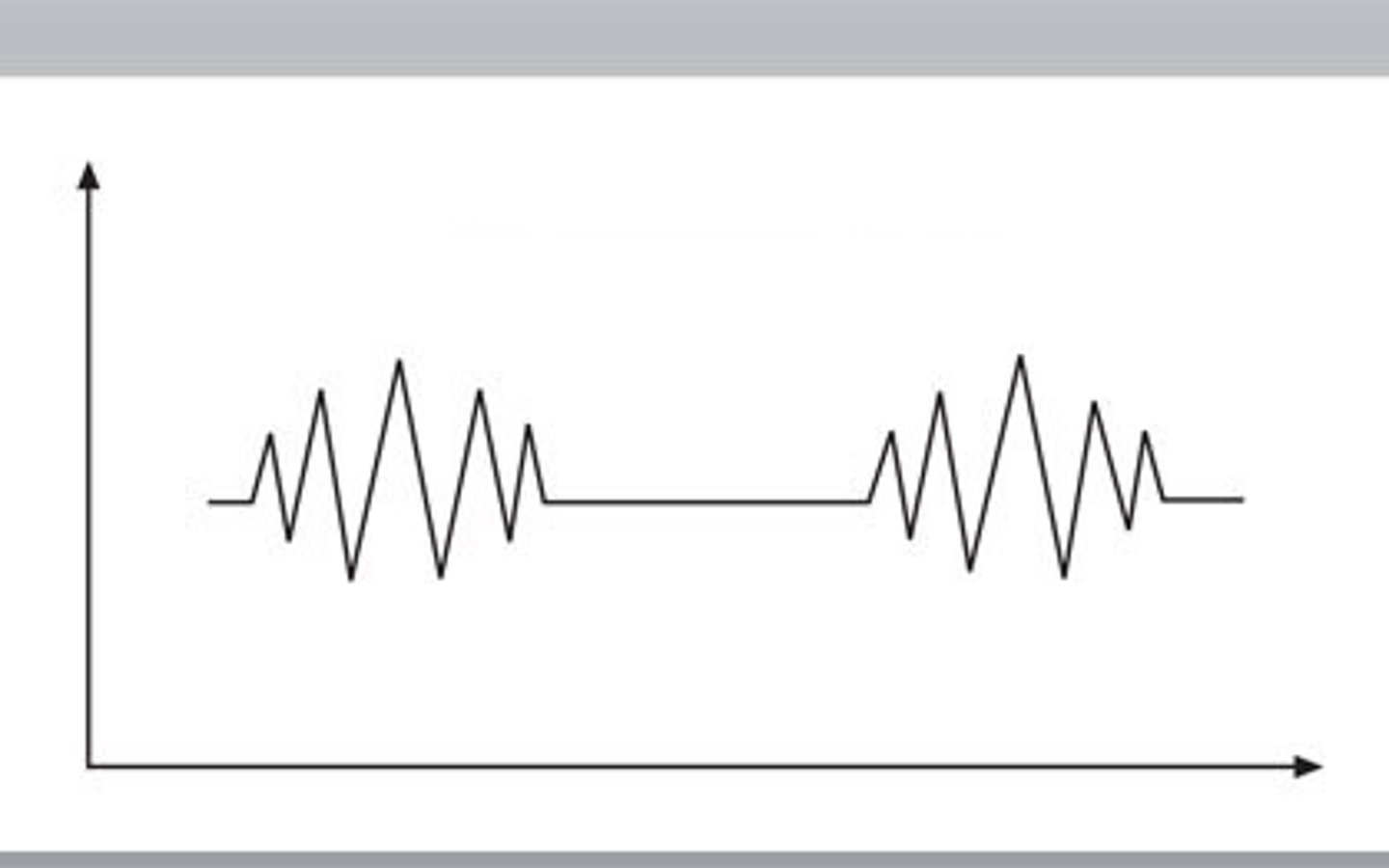
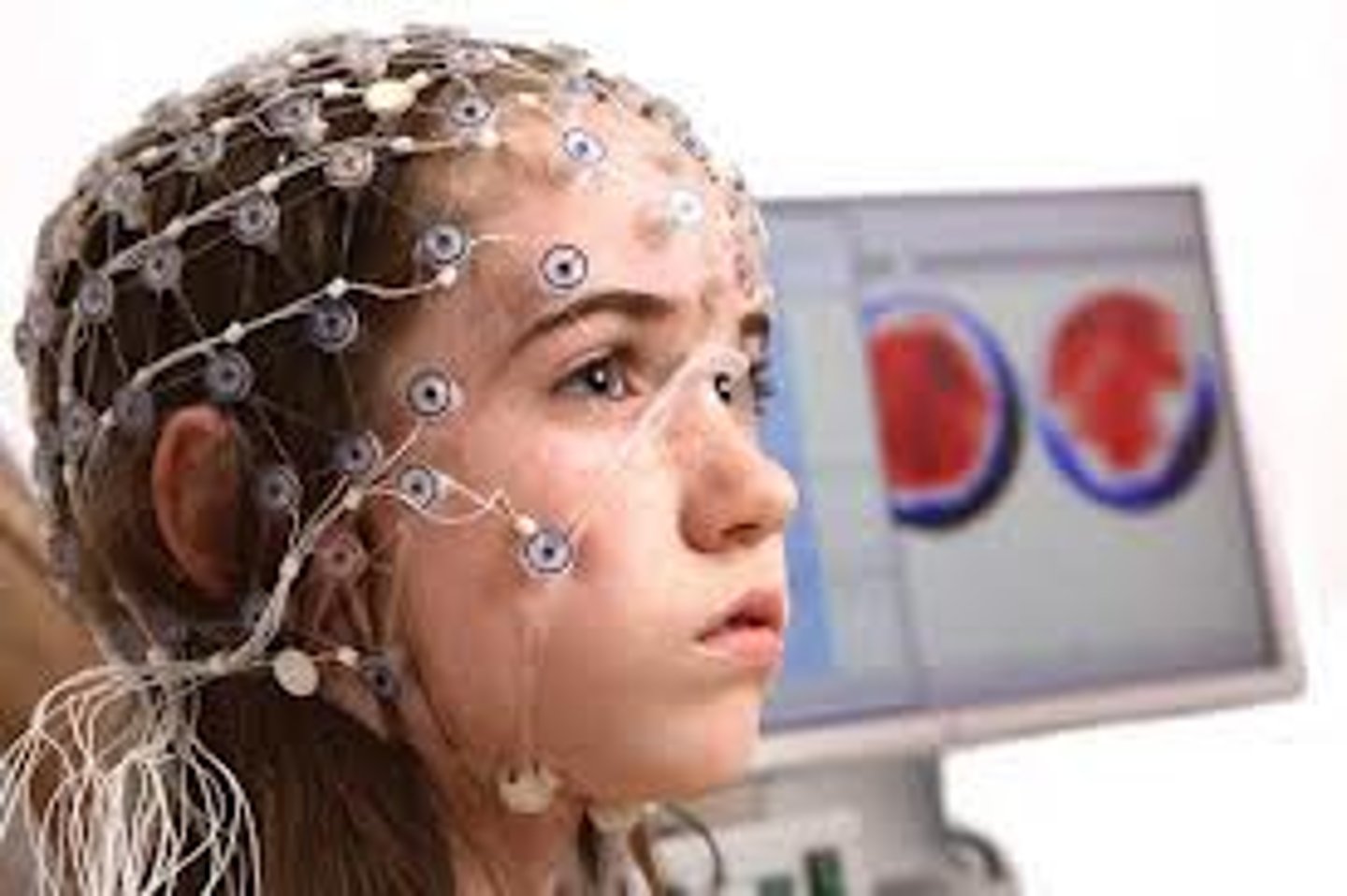
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Involves recording the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes on the scalp.
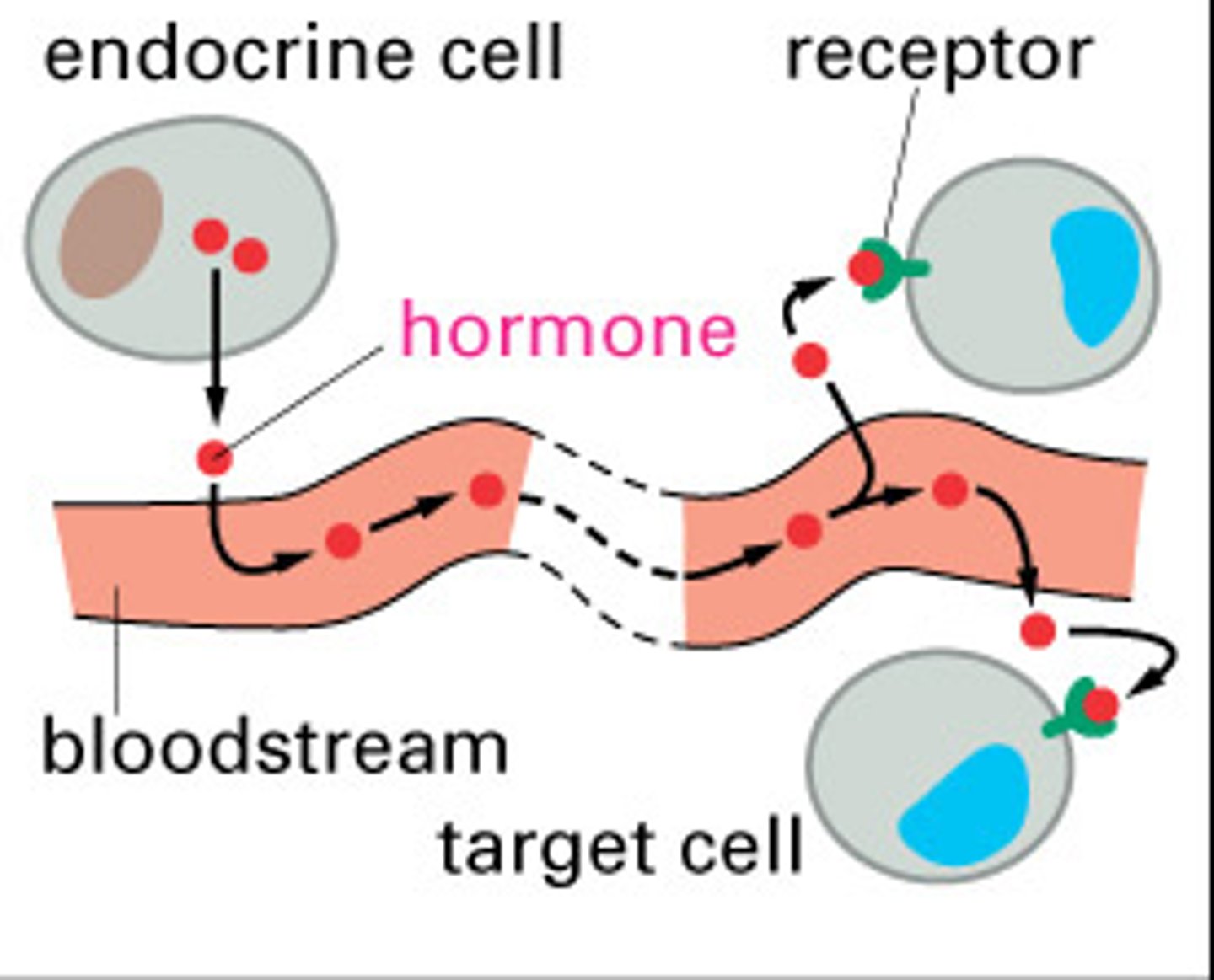
The endocrine system
A series of glands that produce hormones to regulate normal body functions.The Hypothalamus links the nervous system and endocrine system by controlling the pituitary gland.
Pituitary gland
Serves as the master gland, controlling the secretions of all other glands.
Thyroid
Secretes Thyroxine which regulates growth, metabolism and appetite

Adrenal gland
Secretes hormones involved in the stress response.

Gonad
Secretes sex hormones, which are important for successful reproduction, and regulate sexual motivation and behavior.
Pancreas
Secretes hormones that regulate blood sugar.