Comprehensive Cell Signaling, Hormones, and Plant Responses in Biology
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Autocrine Signaling
Self signaling, send out a ligand and same cell receives it.
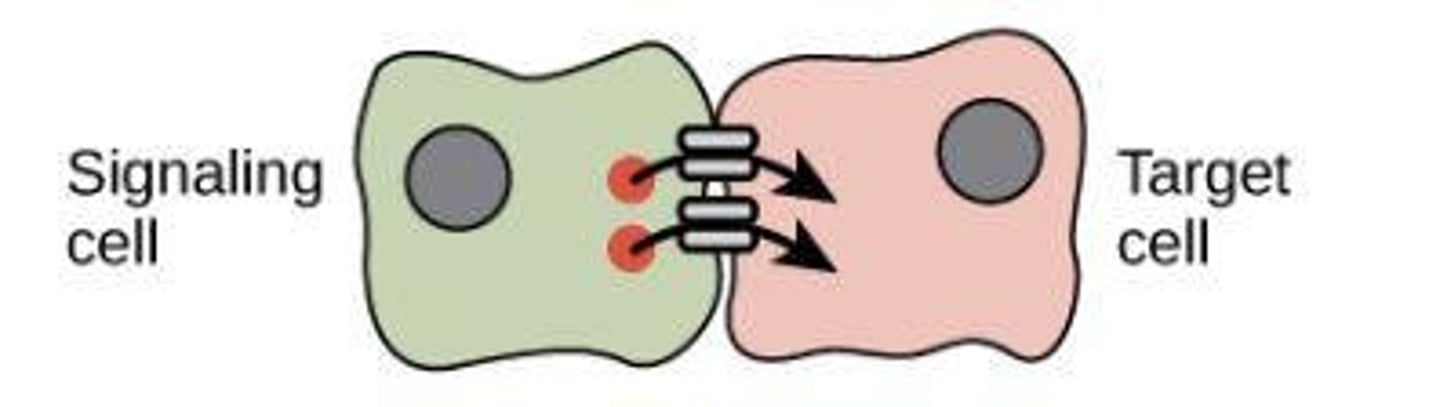
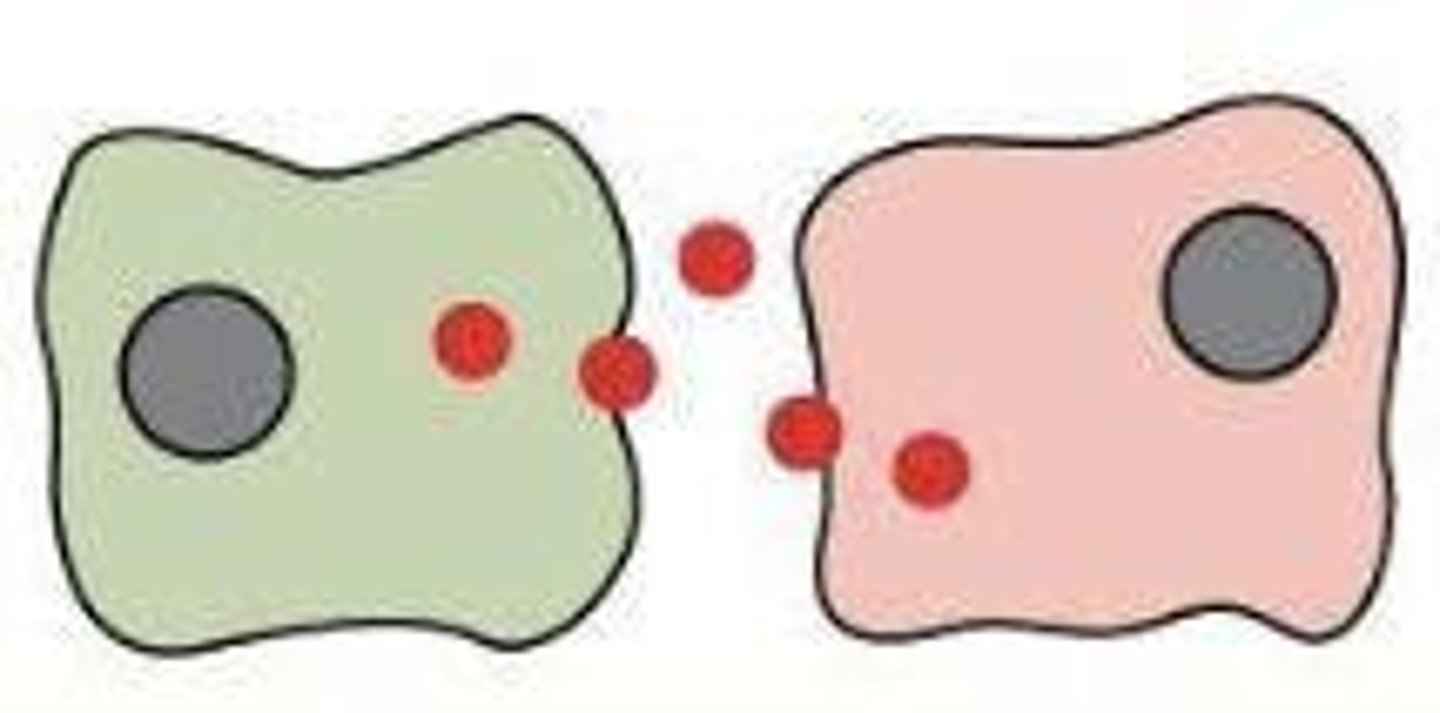
Paracrine Signaling
Cell releases molecule and it impacts a neighboring cell (no contact). Ex: chemical synapse between two neurons.
Endocrine Signaling
Cell releases molecule into blood stream and it impacts target cells farther away. Ex: Neuroendocrine neuron releases a signal molecule into blood stream and impacts target farther away.
Pheromone
Signal released from one individual into the environment to act on another individual.
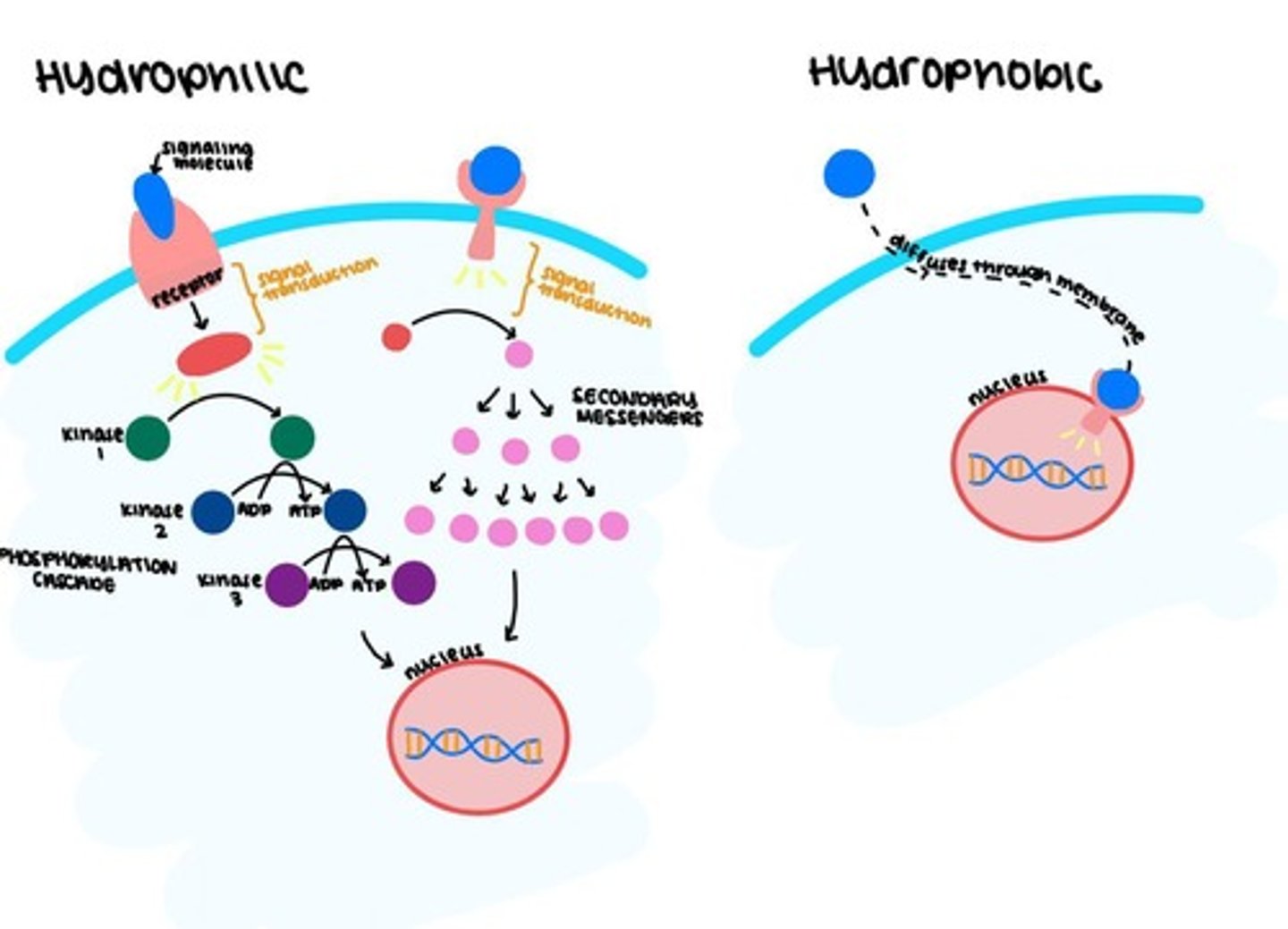
Hydrophobic
Binds intracellularly.
Hydrophilic
Bind to cell surface.
Steroid hormone
Small ring structure made from cholesterol; no signal transduction.
Peptide hormone
Small protein; initiates signaling pathway; has indirect impact.
Gas hormone
Binds intracellularly; gas that can act as a ligand; no signal transduction; direct impact on gene transcription.
Amino Acid-derived hormone
Bind to cell surface; modified AA have an amine group; initiates signaling pathway; has indirect impact.
Signal Transduction
The process by which a cell responds to signals from its environment.
Positive Feedback Loop
A process that enhances or amplifies changes; tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state.
Negative Feedback Loop
A process that counteracts changes; tends to stabilize a system.
Crosstalk
Interactions between different signaling pathways that can complicate the signaling process.
Quorum Sensing
The regulation of gene expression in response to fluctuations in cell-population density.
Transduction Example A
A hormone diffuses through the cell membrane and binds to an intracellular receptor that then moves to the nucleus.
Transduction Example B
A hormone binds to a cell surface receptor, triggering the release of second messengers that activate intracellular proteins.
Transduction Example C
A sensory receptor cell converts photon energy into an electrical signal that alters ion channel activity.
Impact of Destroyed Receptors
If all cell membrane receptors in a human cell are completely destroyed, small, nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules like steroid hormones would still be able to signal the cell.
Corticosteroid Hormone Signaling
If you were to block all cell surface receptors, the hormone cannot bind to an external receptor so the pathway is terminated.
Corticosteroid hormone
A nonpolar hormone that passes through the cell membrane as it is a steroid hormone, allowing signaling pathways to continue normally.
Hormone signaling pathway
The series of steps that a hormone undergoes to elicit a response in a target cell.
Hydrophobic (Nonpolar)
Refers to molecules that do not interact well with water and can pass through cell membranes.
Hydrophilic (Polar)
Refers to molecules that interact well with water and typically cannot pass through cell membranes without assistance.
Phosphorylation cascade
A chain reaction in which a series of proteins are phosphorylated, leading to a cellular response.
Secondary messengers
Molecules that relay signals received at receptors on the cell surface to target molecules inside the cell.
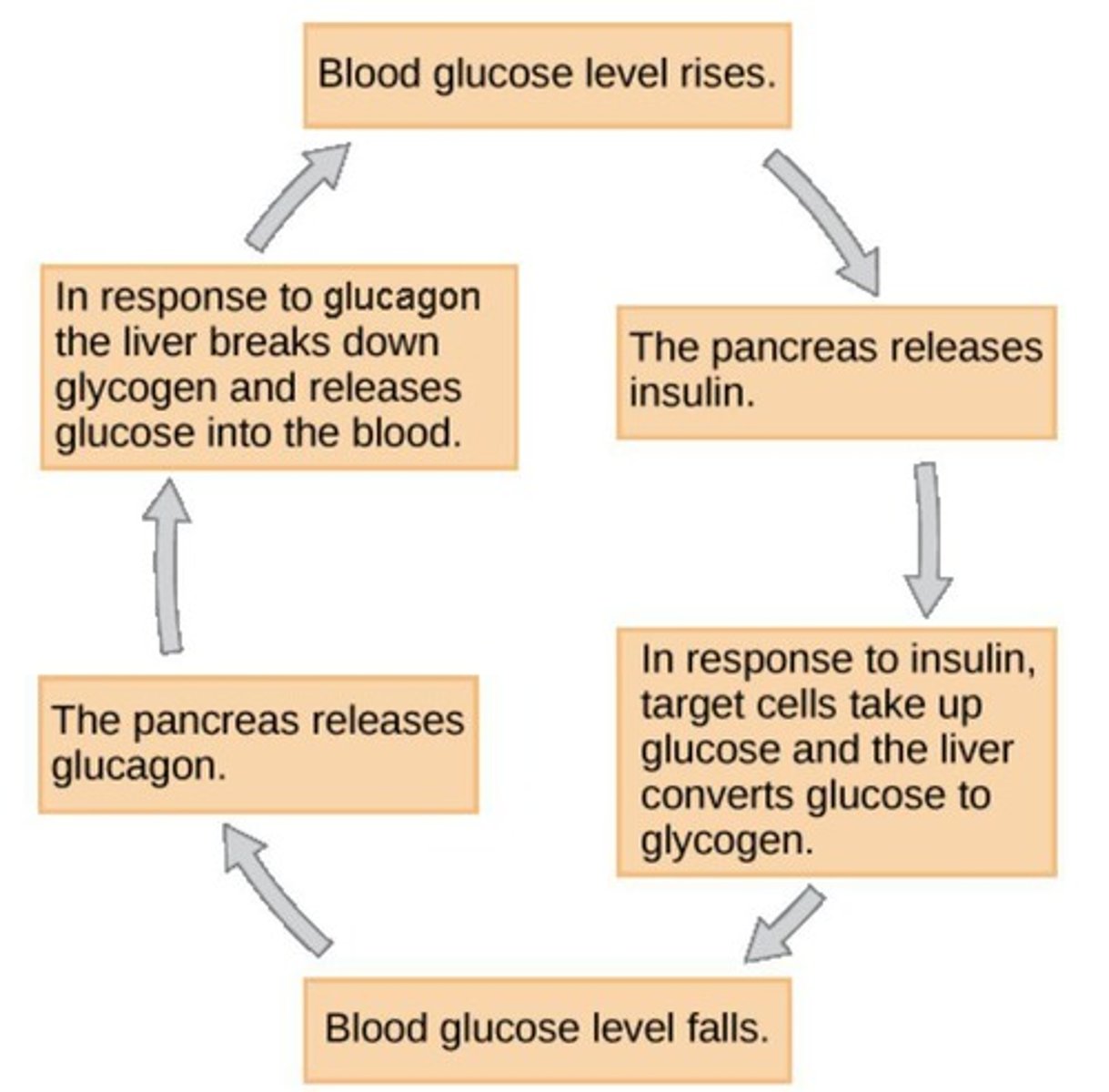
Glucagon
A hormone released by the pancreas that signals the liver to break down glycogen into glucose when blood glucose levels drop.
Feedback loop
A system where the output of a process influences its own input.
Cell membrane receptor
A receptor located on the cell membrane that binds to polar hormones to facilitate signal transduction.
Intracellular receptor
A receptor located inside the cell that binds to nonpolar hormones, allowing them to bypass the cell membrane.
Conformation change
A structural alteration in a protein that occurs upon binding of a hormone, allowing it to perform its function.
Amplification
The process by which a small signal is converted into a larger response through multiple steps.
Hormone ligand types
Categories of hormones based on their polarity and the type of receptors they bind to.
Peptide/Amino Acid (Polar)
Hormones that bind to cell membrane receptors to facilitate signal transduction.
Steroid (Nonpolar)
Hormones that bind to intracellular receptors, bypassing the cell membrane.
Blood glucose regulation
The process by which the body maintains stable blood sugar levels through hormonal responses.
Feedforward regulation
A response that occurs in anticipation of a future change.
Activated system
A system that has undergone a change due to hormone binding, leading to a cellular response.
Target proteins
Proteins that are affected by secondary messengers or phosphorylation cascades in response to hormone signaling.
Oxytocin
A hormone that stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth, which triggers the release of more oxytocin, increasing contractions further.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
A hormone that signals the ovaries or testes to produce another hormone, such as estrogen or testosterone.
Adrenaline
A hormone that causes liver cells to release glucose and dilates blood vessels in skeletal muscle.
Biofilms
Protective layers formed by bacteria in response to quorum sensing.
Bioluminescence
The ability of certain organisms to produce light, often as a group response to quorum sensing.
Virulence
The ability of bacteria to attack a host, which can be influenced by quorum sensing.
Major glands involved in hormone synthesis
Includes the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, gonads, and adrenal glands.
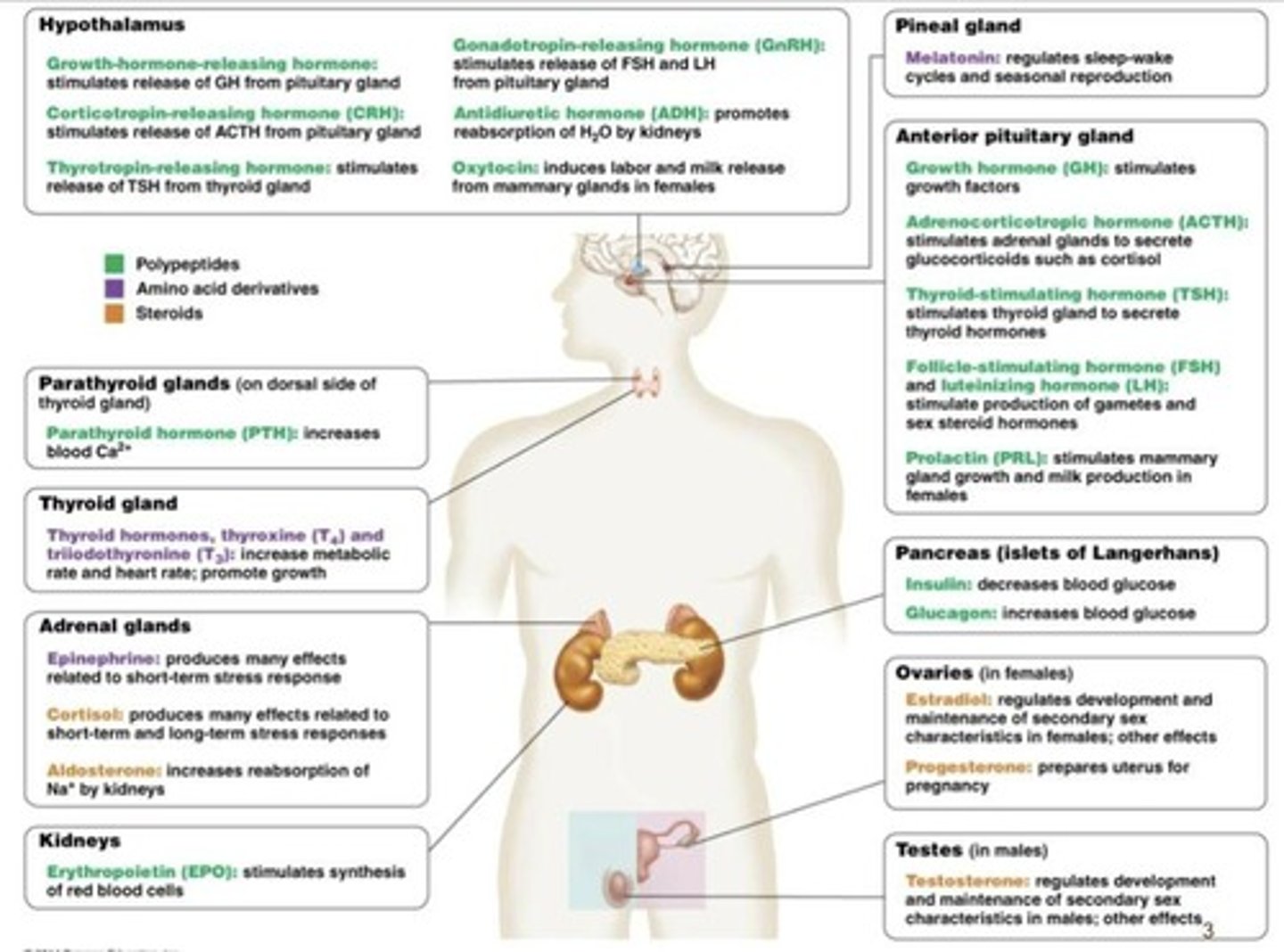
Functions of hormones
The roles played by hormones produced by major glands in the body.
Hormone pathway
The sequence of events involving hormones that lead to a physiological response, such as blood glucose regulation.
Metamorphosis
A biological process where an organism undergoes significant change in form, often regulated by hormones.
Stress response
The physiological changes that occur in an animal in reaction to stress, often involving hormone pathways.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Produced by the anterior pituitary, it plays a role in reproductive processes.
Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH)
Produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary, it regulates water balance.
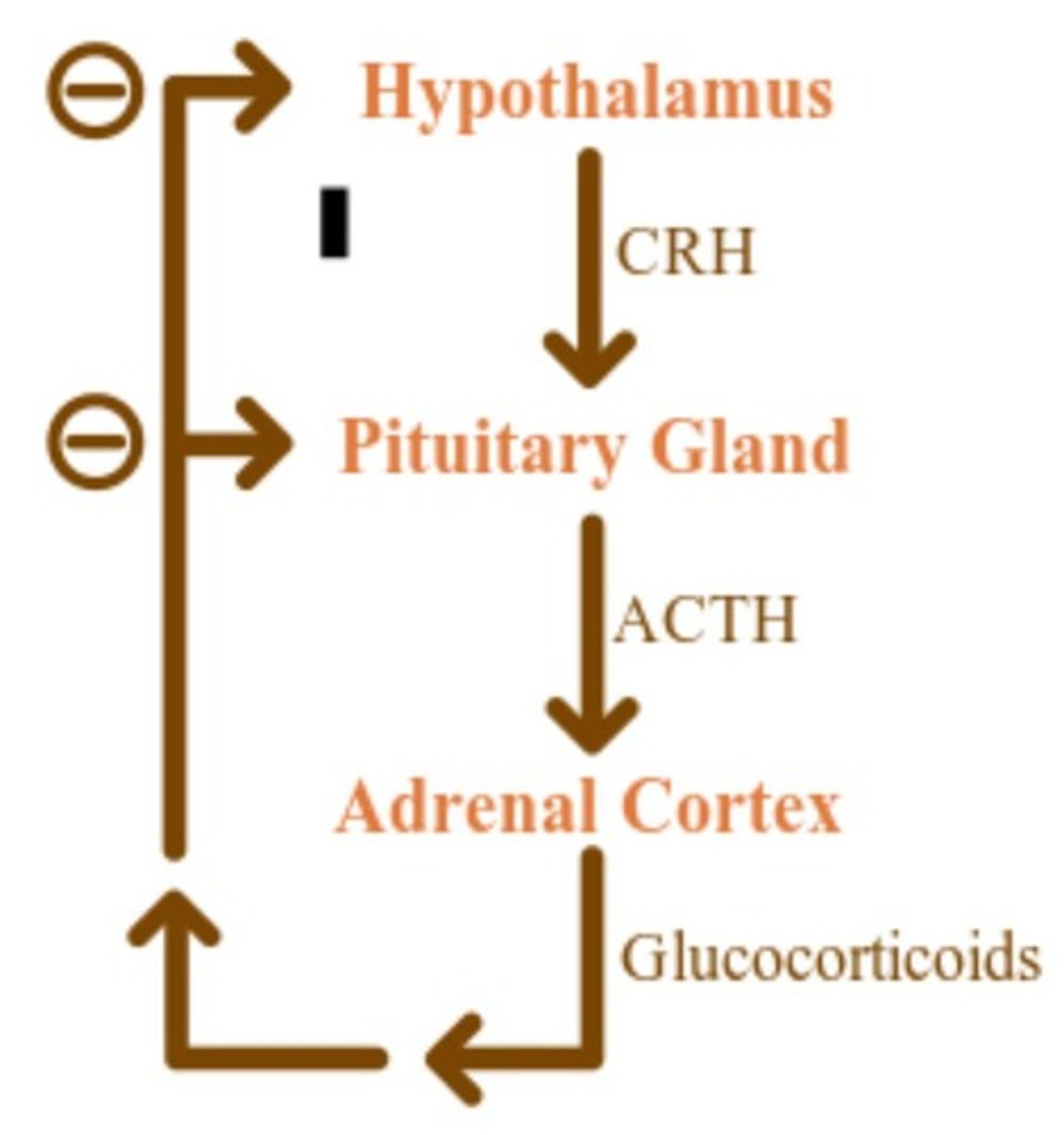
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Produced by the anterior pituitary, it stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol.
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Produced by the anterior pituitary, it stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4.
Prolactin (PRL)
Produced by the anterior pituitary, it promotes milk production in mammals.
Endorphins
Known as the 'Feel-Good Hormone', they are produced by the anterior pituitary and help relieve pain.
Growth Hormones (GH)
Produced by the anterior pituitary, it stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
Thyroid
Located in the neck, it produces T3 and T4, which promote growth and metabolism.
Adrenal Cortex
Part of the adrenal glands that produces aldosterone and cortisol, related to long-term stress response.
Aldosterone
A mineralocorticoid produced by the adrenal cortex that increases salt reabsorption to regulate water balance.
Cortisol
A glucocorticoid produced by the adrenal cortex that increases blood glucose levels by stimulating gluconeogenesis.
Adrenal Medulla
Releases epinephrine, responsible for short-term stress response (Fight-or-Flight).
Pancreas
Produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood glucose levels by the synthesis and breakdown of glycogen.
Gonads
Responsible for the production of sex steroids in ovaries and testes.
Metamorphosis Trigger
High JH and ecdysone release triggers metamorphosis, while low levels of these hormones also play a role.
Short-term Stress Response
Involves the release of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla, triggering fight-or-flight responses.
Long-term Stress Response
Involves the adrenal cortex releasing cortisol, leading to effects such as suppressed immune function.
FALSE
This is a negative feedback loop because when T3 and T4 levels are high, they are inhibiting TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormones) and TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) secretion.
Glucose
Sugar our body uses for energy.
Insulin
Lowers blood glucose, released when glucose levels are too high, made by beta cells.
Insulin processes
Enhances glucose uptake/utilization, increases glucose transport into certain cells, stimulates glucose conversion to glycogen (liver) and fat in adipose cells, synthesis of proteins.
Glucagon process
Stimulates breakdown of glycogen to glucose, adipose cells to release fatty acids, absorption of amino acids from blood to convert to glucose (liver).
Blood Glucose Conditions
Diabetes Mellitus: Low insulin production or low insulin sensitivity in tissues → prevents glucose uptake therefore high blood glucose.
Diabetes Mellitus effects
Can lead to nerve damage in eyes and body tissue, kidney and cardiovascular damage.
Hypoglycemia
Too much insulin → low blood glucose levels.
Hypoglycemia effects
Can lead to not enough glucose to cells therefore muscle weakness and sometimes unconsciousness or death.
Juvenile hormone
Maintains larval stage of animal, secreted by corpus allatum.
Prothoracicotropic hormone
Signals prothoracic gland to secrete ecdysone.
Ecdysone
Can promote molting/metamorphosis but depends on JH levels.
Ecdysone + Low JH
Metamorphosis into adult.
Ecdysone + High JH
Molts into next larval phase.
Thyroxine (T4)
Made in thyroid gland, affects protein synthesis, basal metabolic rate, energy metabolism.
Triiodothyronine (T3)
In vertebrates like frogs, triggers development of new structures.
Human Growth Hormone (hGH)
Made in anterior pituitary, regulates IGF, calcium absorption, increases protein synthesis and glucose circulation.
Insect generation mutation
An insect generation has a mutation in which they never stop producing high levels of the juvenile hormone.
Insect fate with high juvenile hormone
The insect will never reach full maturity.
Epinephrine
A hormone also known as adrenaline that prepares the body for energy bursts.
Norepinephrine
A hormone also known as noradrenaline that prepares the body for energy bursts.
Glucocorticoid
A type of hormone, such as cortisol, that is involved in long-term stress response.
Mineralocorticoid
A type of hormone, such as aldosterone, that promotes water and sodium retention.
Auxin
A plant hormone responsible for cell elongation and inhibiting abscission.
Cytokinin
A plant hormone that promotes cell division in growing roots, embryos, and fruits.
Gibberellin
A plant hormone that promotes shoot elongation, seed germination, and fruit maturation.
Abscisic Acid (ABA)
A plant hormone that responds to stress by causing leaf abscission and closing stomata.
Ethylene
A plant hormone involved in fruit ripening and aging processes.
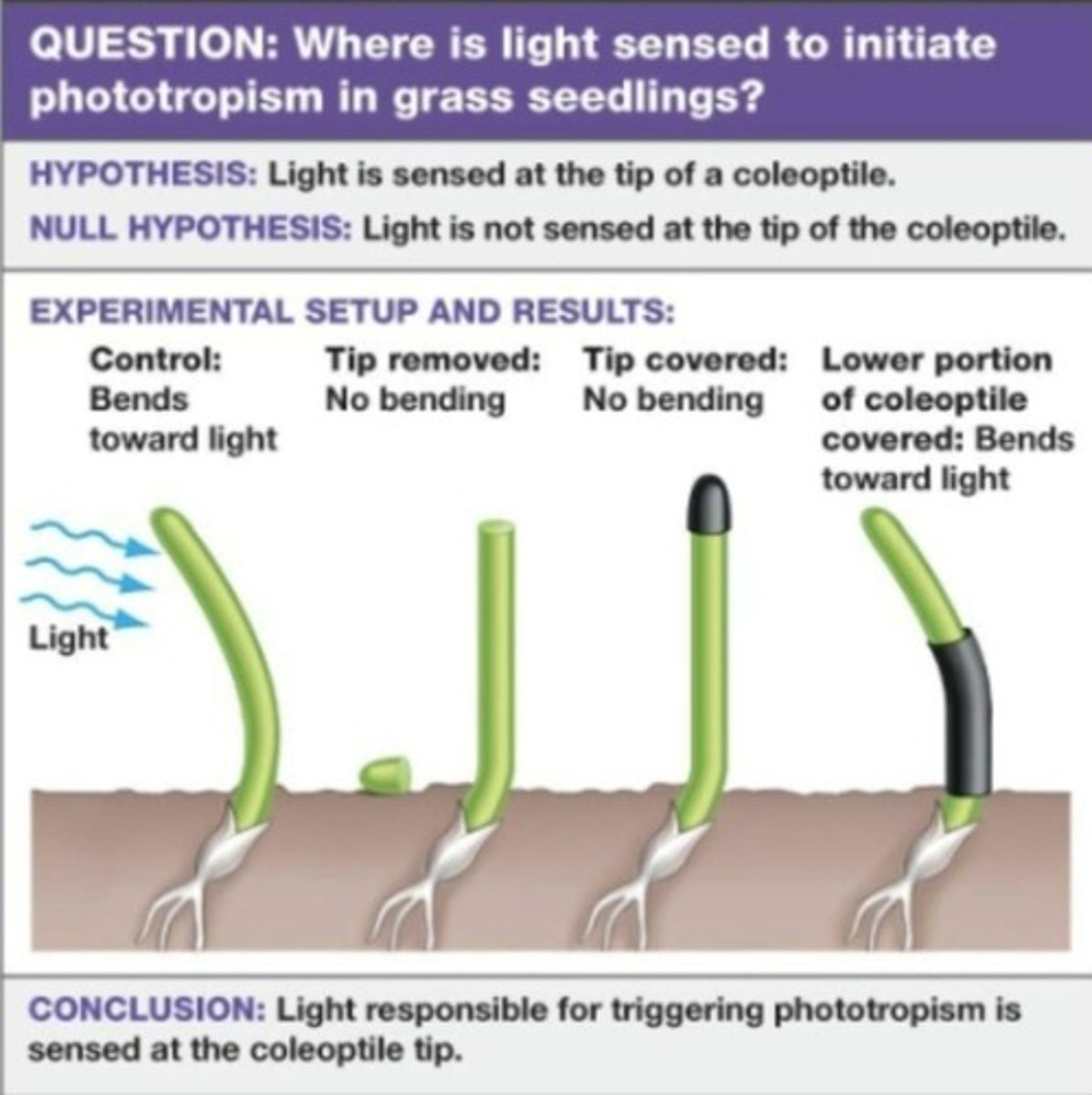
Phototropism
A plant behavior that involves growth towards light.
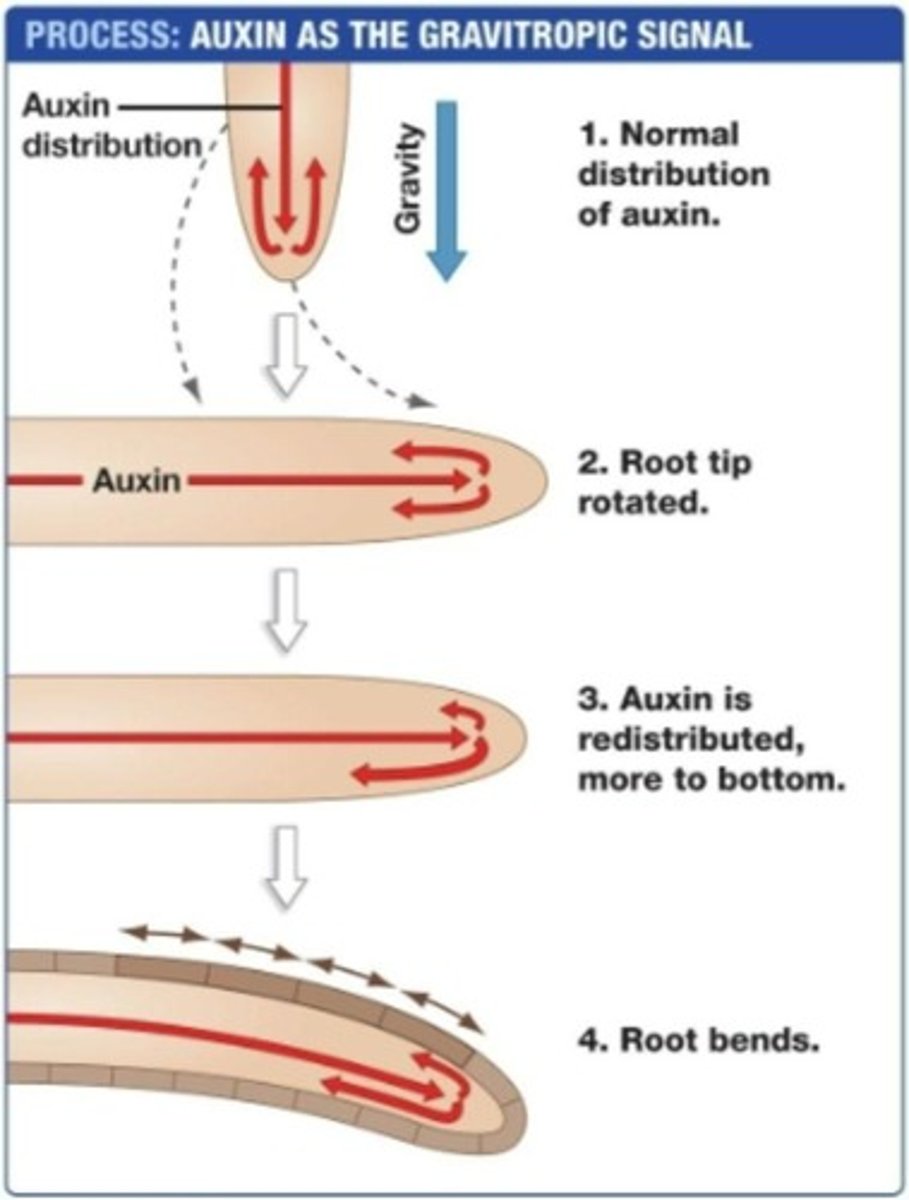
Gravitropism
A plant behavior that involves growth in response to gravity.
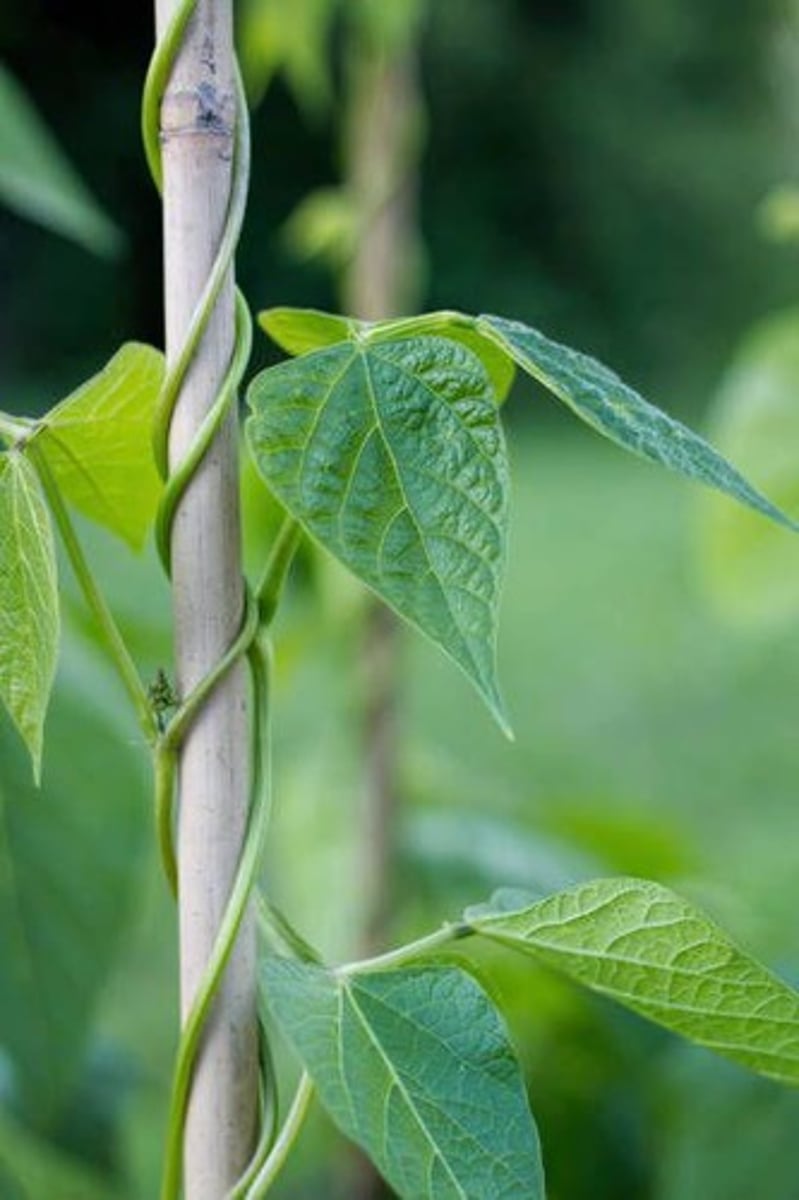
Thigmotropism
A plant behavior that involves growth in response to touch.

Dormancy
A state in which seeds or buds remain inactive until conditions are favorable.
Stomatal closing
A response in plants to conserve water during stress.