Genetics Exam 2
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Tetrad stage
occurs during prophase I of meiosis, when homologous chromosomes pair up and form a structure called a tetrad (consisting of four chromatids)
Tetrad
group of 4 chromatids formed when 2 homologous chromosomes align closely
Synapsis
the alignment essential for genetic recombination
linkage
The condition in which genes are present on the same chromosome, causing them to be inherited as a unit, provided that they are not separated by crossing over during meiosis
True
True or False: The chromosome is the unit of transmission during meiosis, NOT the gene
Recombination
crossing over or reshuffling of alleles (always occurs in the tetrad stage)
Frequency of Crossing Over between any 2 loci
= the distance between them (map units)
Recombinant/Crossover gametes
new allele combinations created from crossing over
Non-crossover gametes
2 chromatids not involved in crossing over
Complete linkage produces only…
Parental gametes
Complete linkage Ratio
1:2:1
(Usually observed only when genes are very close together and the number of progeny is relatively small)
Test Cross with F1 produces…
1:1 ration of thin brown and heavy, red flies
Linkage Group
each chromosome represents 1 linkage group
Thomas Hunt Morgan
discovered genetic linkage and recombination
Most offspring showed parental traits when…
When crossing females with mutant yellow body (y) and white eye (w) alleles with wild-type males
Discovery of Crossing Over
Morgan proposed that homologous chromosomes form chiasmata during meiosis, where genetic exchange (crossing over) occurs
Morgan concluded…
• Genes are arranged linearly on chromosomes.
• The likelihood of crossing over depends on the distance between genes: closer genes recombine less frequently.
Sturtevant
• Sturtevant defined 1 map unit (mu) = 1% recombination.
• He created the first genetic map, later expanded to include five X-linked genes.
• He and Calvin Bridges also showed that autosomal genes exhibit linkage and crossing over.
Close loci
less likely to recombine
Distant loci
more likely to recombine
Morgan and Sturtevant’s work confirmed…
the chromosomal theory of inheritance
Theoretically… when two linked genes are more than 50 mu apart…
a crossover is expected to occur between them in 100 percent of tetrads
-each tetrad would yield equal proportions of the four gametes
To calculate the crossover percent…
product rule is used
The gene in the middle
found by comparing DCO to parental types, it’s the only gene that switches
Finding map distance between genes
Requires you to add up SCOs and DCOs that include two genes to find map unit between those 2
Determining Gene Order
Assuming any one of the three orders, first determine the arrangement of alleles along each homolog of the heterozygous parent giving rise to noncrossover and crossover gametes (the female in our example).
Determine whether a double-crossover event occurring within that arrangement will produce the observed double-crossover phenotypes. Remember that these phenotypes occur least frequently and are easily identified.
If this order does not produce the predicted phenotypes, try each of the other two orders. One must work!
The farther apart two genes are…
the greater the probability that undetected crossovers will occur
Most accurate maps are constructed when…
Genes are close together
Interference
the phenomenon through which a crossover event in one region of the chromosome inhibits a second event in nearby regions, causes this reduction.
-describes the extent to which a crossover in one region of a chromosome influences the occurrence of a crossover in an adjacent region of the chromosome and is quantified by calculating the coefficient of coincidence (C).
Coefficient of Coincidence
Observed DCO/Expected DCO
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) and Microsatellites
the earliest examples of DNA markers
Bacteriophages
viruses that use bacteria as their hosts
Minimal medium
organic carbon source, variety of ions/organic salts
-bacteria that synthesize all essential organic compounds (amino acids, purines, pyrimidines, vitamins, and fatty acids) grow on these mediums=prototroph
Auxotroph
bacteria that loses the ability to synthesize one or more organic compounds through mutation
Prototroph
bacteria that synthesizes all needed organic compounds
3 processes of genetic recombination in Bacteria
conjugation, transformation, transduction
Vertical gene transfer
when genetic information occurs between generations of the same species
Horizontal Gene Transfer
transfer between unrelated cells
Conjugation
a process by which genetic information from one bacterium is transferred to and recombined with that of another bacterium
F+ Cells (F+ = fertility)
donate parts of chromosome
F- cells
recipient bacteria that receive the donor chromosome material and recombine it with part of their own chromosome
Hfr cells
-special class of F+ cells
-exhibit high frequency of recombination
Interrupted Mating Technique
allows you to determine the order of genes transferred
-used for mapping in time units
Plasmids (ex. F. factor)
autonomously replicating DNA molecules found in the bacterial cytoplasm, sometimes containing unique genes conferring antibiotic resistance as well as the genes necessary for plasmid transfer during conjugation.
Transformation
small pieces of extracellular DNA are taken up by a living bacterium, potentially leading to a stable genetic change in the recipient cell
-another mechanism for recombining genetic information in some bacteria
competence
the transient state or condition during which the cell can bind and internalize exogenous DNA molecules, making transformation possible.
Bacteriophage T4
-E. coli host
-intricate structure
-DNA encased in icosahedral protein coat
-head connected to a complex tail structure consisting of a collar
-base plate of 15 proteins
Plaque Assay
way to study how bacteriophages reproduce in host cell
Transduction
Virally mediated bacterial recombination. Also used to describe the transfer of eukaryotic genes mediated by a retrovirus.
For a molecule to serve as genetic material it must possess 4 main characteristics:
-replication
-storage of information
-expression of information (central dogma)
-variation by mutation
Proteins
initially favored to serve as the genetic material
Griffith Experiment
-concluded that heat-killed IIIS bacteria somehow converted live avirulent IIRcells into virulent IIIS cells
-called the process transformation
The Hershey-Chase Experiment
-E. coli bacteria
-T2 bacteriophage
-composed of protein coat and DNA core
-goal was to determine whether DNA or protein carries the genetic instructions for viral replication
-DNA carried the genetic info
Retroviruses
replicate by using RNA as a template for the synthesis of a complementary DNA molecule (reverse transcriptase)
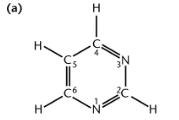
Pyrimidine Ring
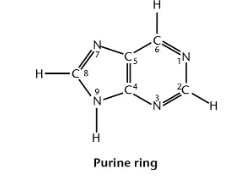
Purine Ring
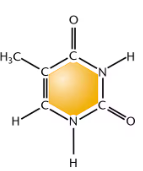
Cytosine
Uracil
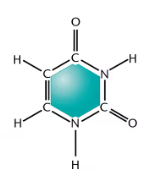
Thymine
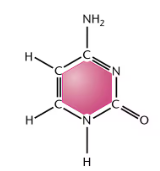
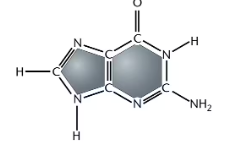
Guanine
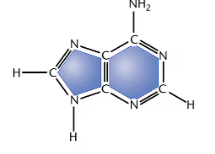
Adenine
Ribose
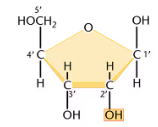
Deoxyribose
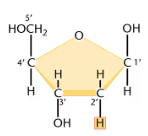
Nucleoside
nucleotide without phosphate group
Phosphodiester bonds
covalent bonds
create the backbone of nucleic acid molecules
The phosphate group connects two sugar molecules in adjacent nucleotides
DNA consists of one ___ strand and one ____ strand
old;new (semiconservative)
Indirect evidence that DNA is the genetic material
-DNA is sequestered in the nucleus, protein is found everywhere in the cell
-DNA content of haploid cells is consistently approximately half that of diploid
-UV light is most mutagenic at of wavelength f 260nm at which nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, strongly absorb
Direct evidence that DNA is the genetic material
-Recombinant DNA molecules can confer heritable information responsible for a product of a gene
-Genomics has shown that differences in DNA sequences can explain specific traits and heritable disorders
When calculating number of double crossovers…
Use product law for gene map units then multiply by number of progeny
Calculating DCO with interference
Interference=1-C
C= observed DCO/expected DCP