Microbial Cell Structure and Function Study Guide (Ch.3, 4.1, 4.2)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
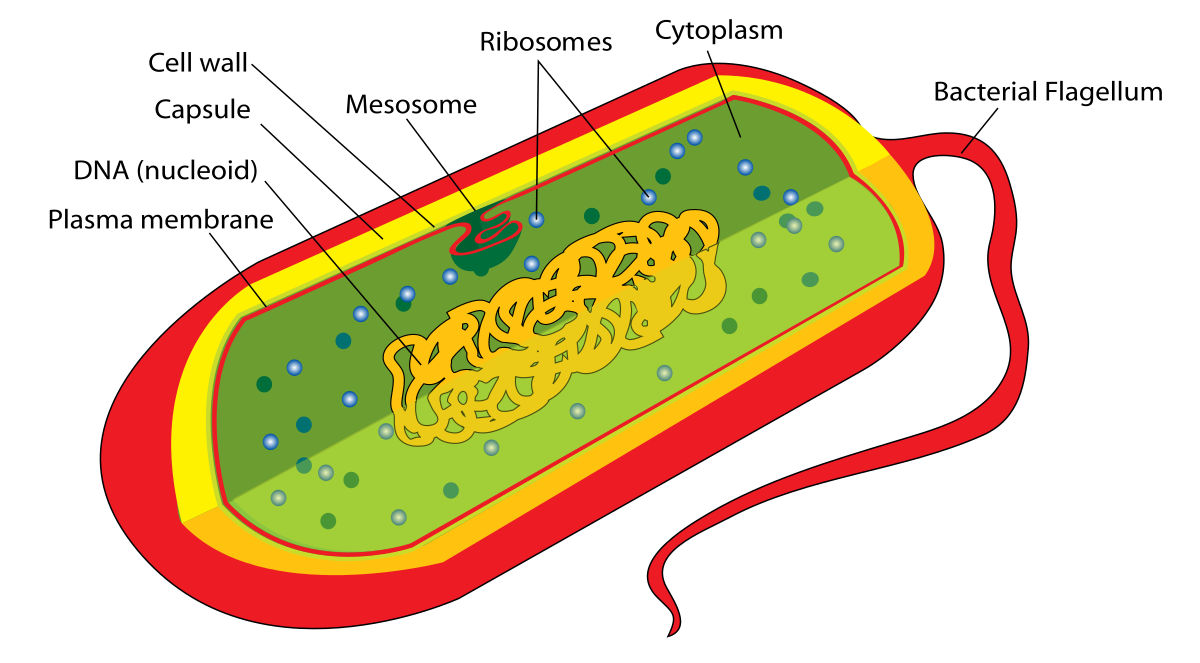
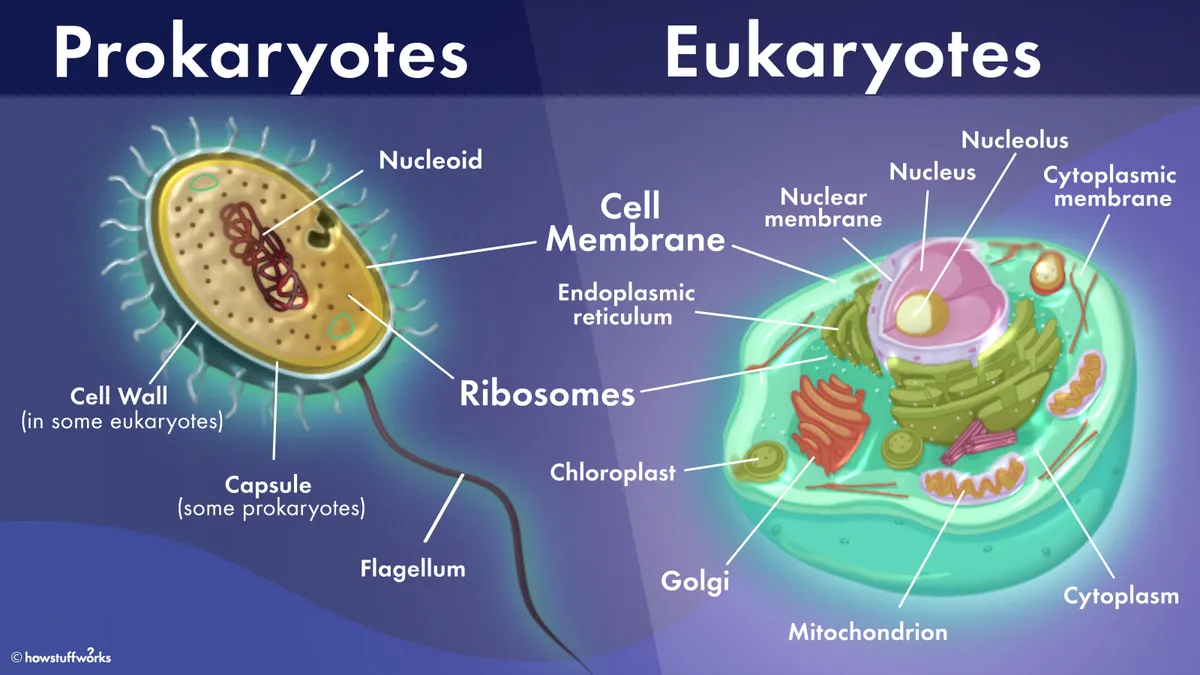
What is a prokaryote?
A simple, single-celled organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus and specialized organelles.
Prokaryotes fall under which domains?
Bacteria and Archaea, these microorganisms store their genetic material within the nucleoid.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Asexually through binary fission; one cell divides into two identical cells
What is a eukaryote?
An organism whose cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus that houses DNA as well specialized membrane-bound organelles
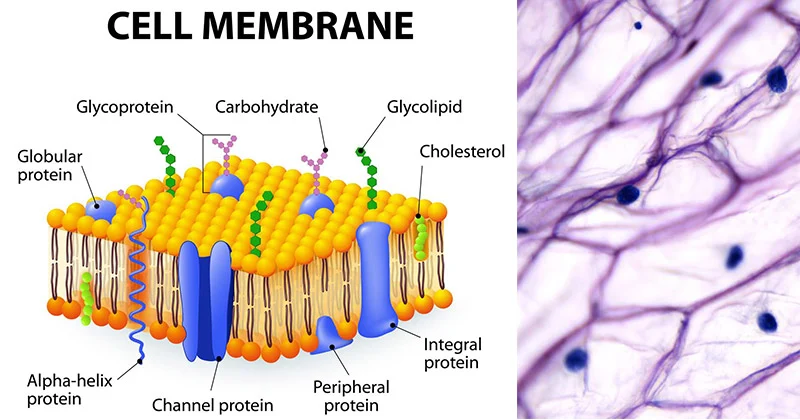
What is the cytoplasmic membrane?
Flexible and semipermeable lipid bilayer that separates a cell’s interior from the outside environment
What is the function of the cytoplasmic membrane (plasma membrane)?
It protects the cell, regulates the transport of nutrients and waste, and facilitates signaling.
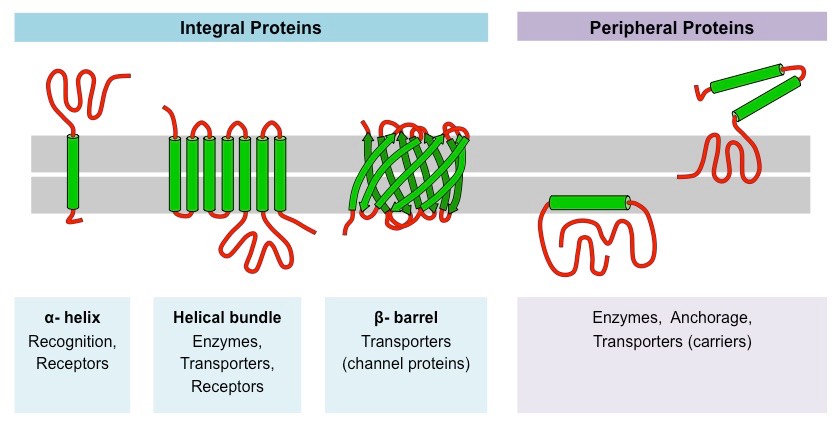
What is a integral membrane protein?
Proteins are permanently embedded within the cell’s lipid bilayer (partially or fully), crucial for transport, signaling, and cell structure by connecting the cell’s interior with outside environment.
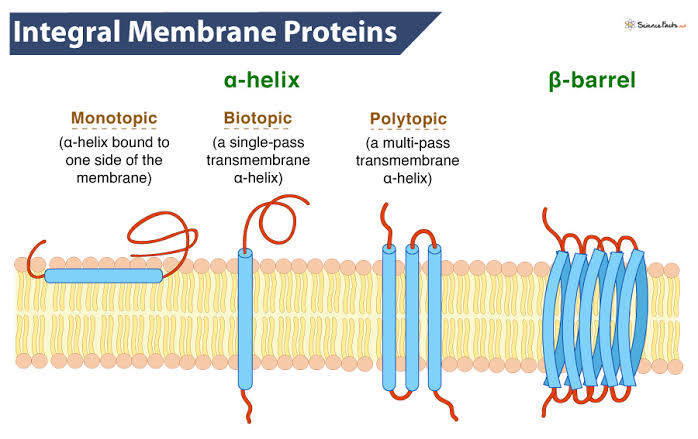
What is the structure of integral membrane proteins and what is the purpose of this structure?
Integral membrane proteins have hydrophobic amino acid residues that interact with the fatty core of the membrane, allowing them to function as channels, receptors, pumps, and enzymes, facilitating movement and communication
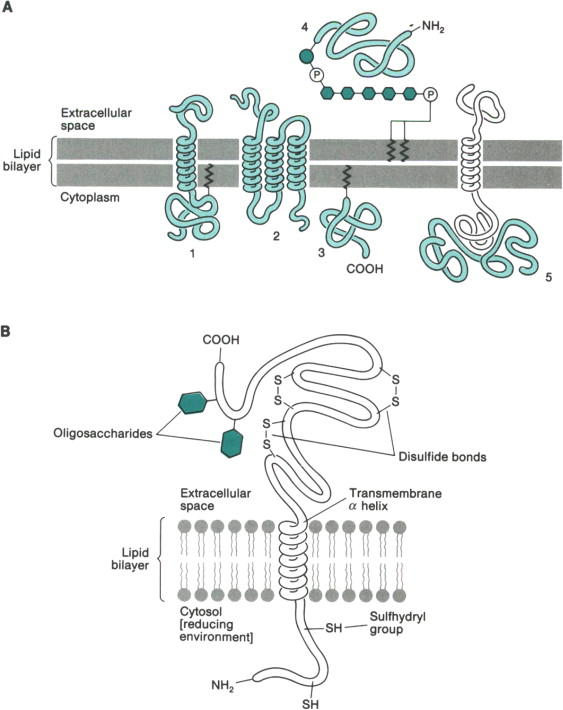
What is a peripheral membrane protein?
Proteins loosely attached to the cell’s lipid bilayer membrane’s surface via non-covalent bonds, sticking to integral proteins or lipid heads, but not in the hydrophobic core
What is the function of peripheral membrane proteins?
Peripheral proteins function is to signal, provide cytoskeleton support, catalyze surface reactions (enzyme), and assist in vesicle trafficking

Cytochrome c in the electron transport chain is an example of what type of protein?
Peripheral membrane protein
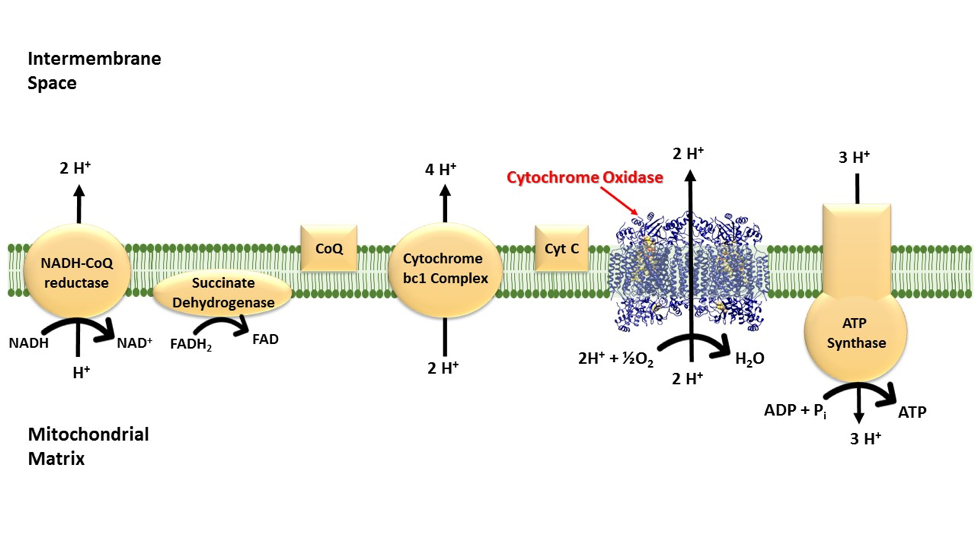
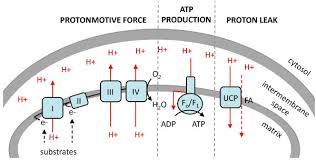
What is the proton motive force (PMF)?
An electrochemical gradient of protons across a membrane that stores E to perform cellular work (ATP synthesis). Generated by electron transport chains, it acts like a battery, combing pH and charge difference
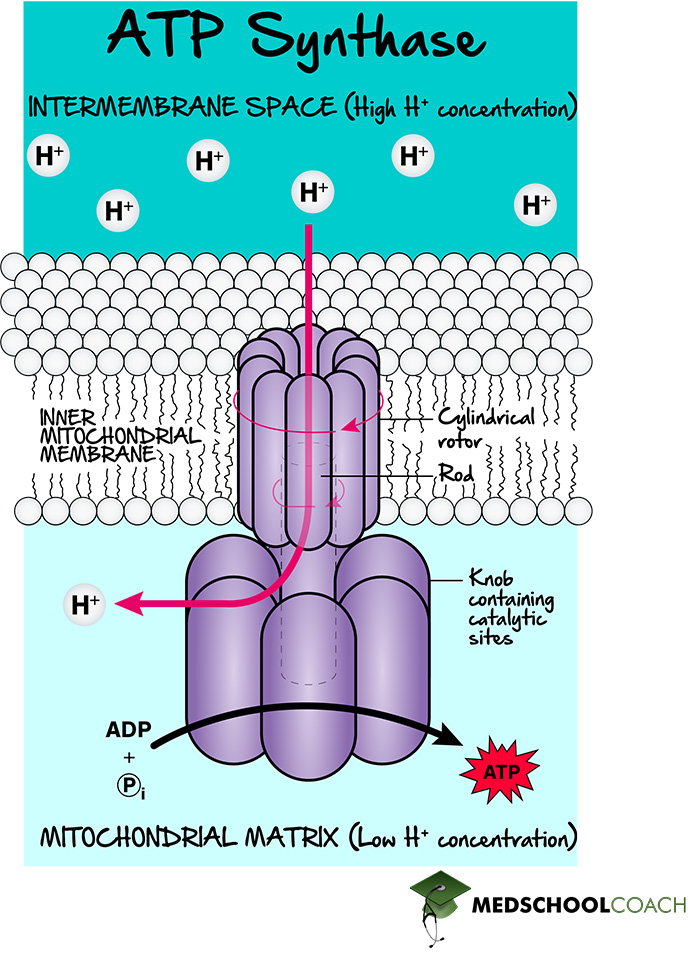
What is the function of the PMF?
This gradient represents potential energy that drives the synthesis of ATP through the enzyme ATP synthase as protons flow back across the membrane. Essential for life allowing cells to convert energy from food or sunlight into usable, storable chemical E
What are porins?
Porins are a major class of water-filled, beta-barrel transmembrane proteins channels
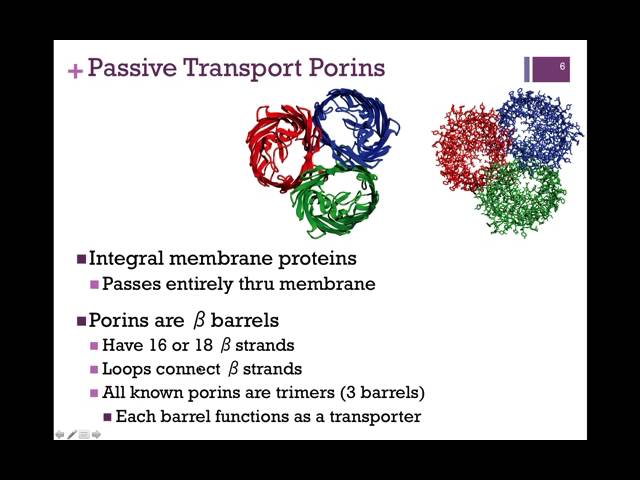
Porins are trimers. What does this mean?
Porins contain three identical subunits to form large passive pores
Where are porins located?
Porins are primarily located on the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, mitochondrial outer membranes, and eukaryotic plasma membranes.
What is the function of porins?
Porins allow passive transport (molecules move with concentration gradient), essential for nutrient uptake and metabolic exchange
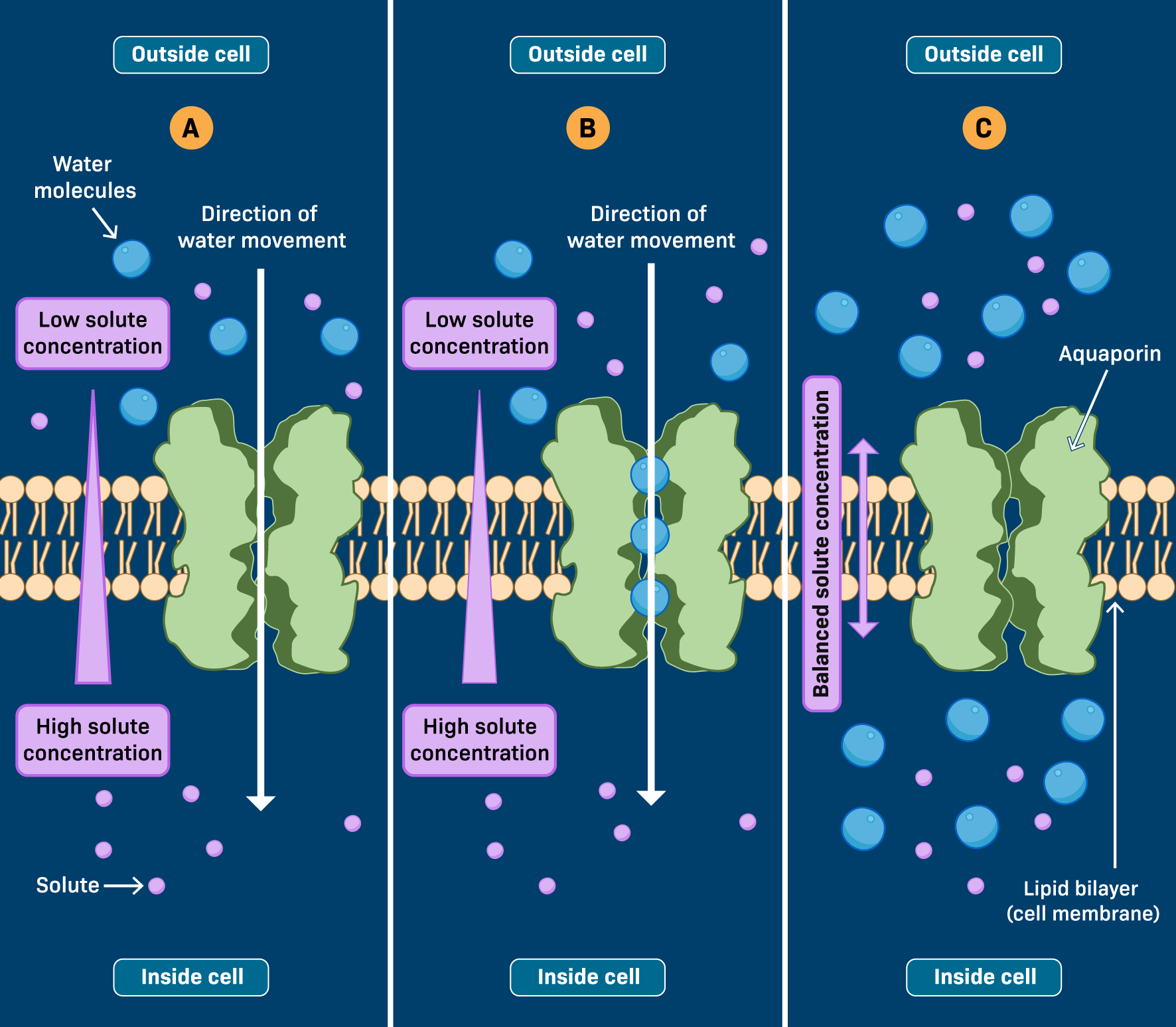
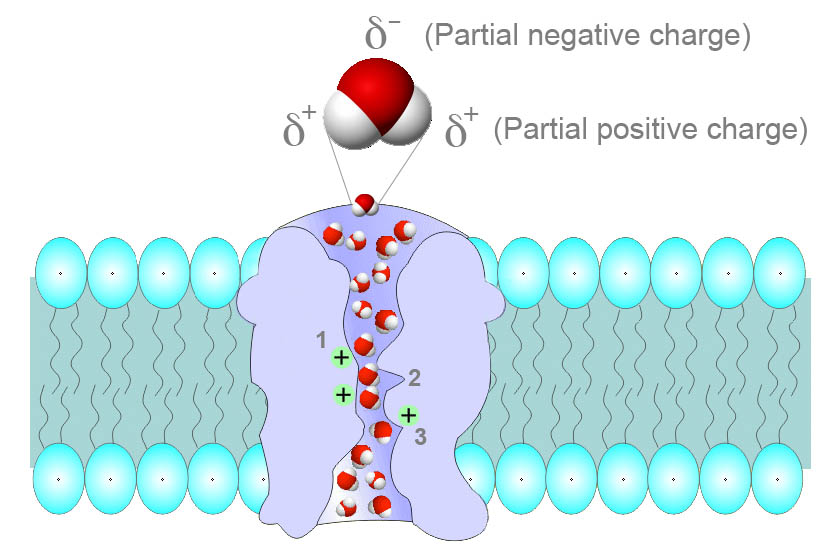
What are aquaporins?
AKA “water channels” they are specialized integral membrane proteins that facilitate the rapid, passive movement of water molecules across biological membranes.
What are transporters?
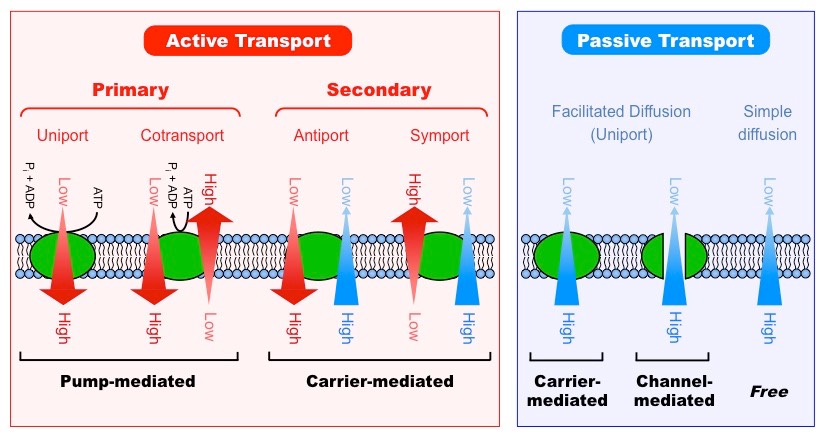
Transporters are specialized proteins that facilitate the movement of ions and molecules across the lipid bilayer. Can be passive or active.
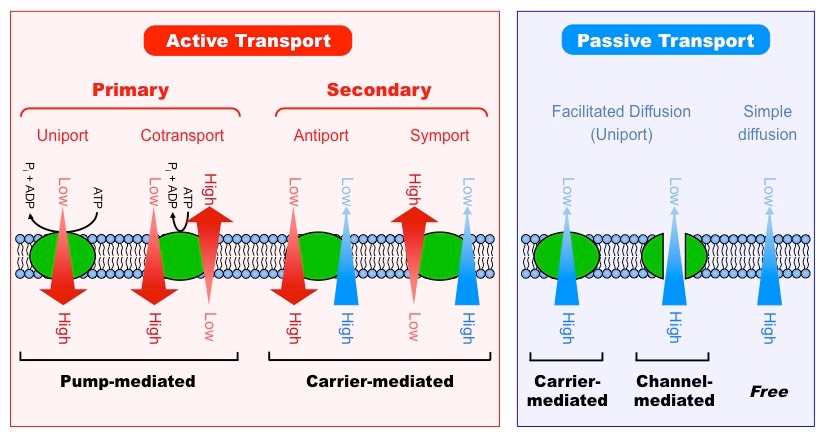
What are the different types of transporters within the cell membrane?
Channel proteins (passive)
Carrier proteins (3 types)(passive/active)
Pumps (active)
ABC Transporters (active)
What are the 3 types of carrier proteins?
Uniporters (passive)
Symporters (secondary active)
Antiporters (active)
What are channel proteins and their purpose?
Proteins that form hydrophilic pores that allows solutes (mostly ions) to pass through the membrane down their concentration gradient (aquaporins, ion channels)
What are carrier proteins and their purpose?
Proteins that bind to a specific molecule (polar molecules, ions, aa, glucose, nucleotides), cauing a conformational change that moves the solutes across the membrane
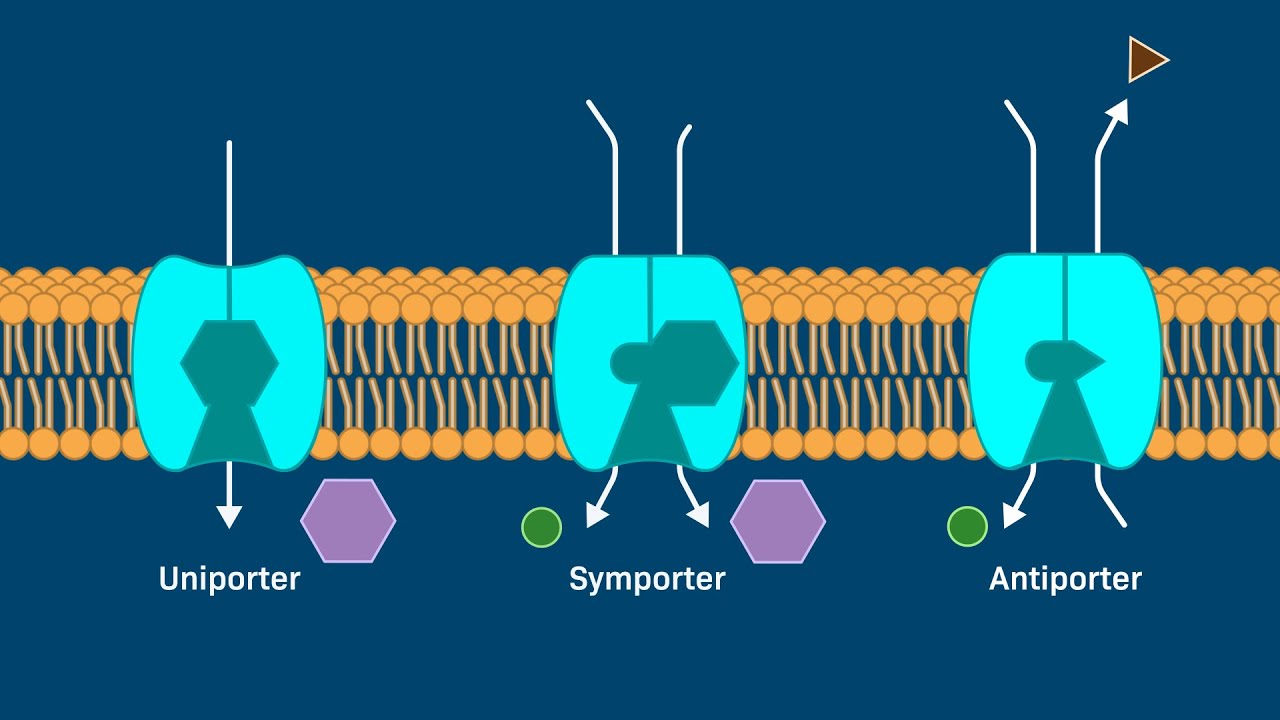
What is the function of a uniporter?
Facilitates diffusion of a single substance down its gradient
What is the function of a symporter?
Secondary active transporter that moves two substance in the same direction
What is the function of a antiporter?
Secondary active transport moving two substances in opposite directions
What are transporter pumps and their purpose?
Proteins that use energy (ATP or ion gradients) to move solutes against a concentration gradient.
What are ABC transporters and their purpose?
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) are active transporters directly use ATP to move various substrates across the cell membrane
Within bacteria’s cell membrane, they are filled with hopanoids/hopanes. What are they and what is the function?
Hopanoids are condense phospholipids that stabilize the cell membrane, regulate fluidity, increase membrane viscosity, and decrease permeability dependent upon conditions.
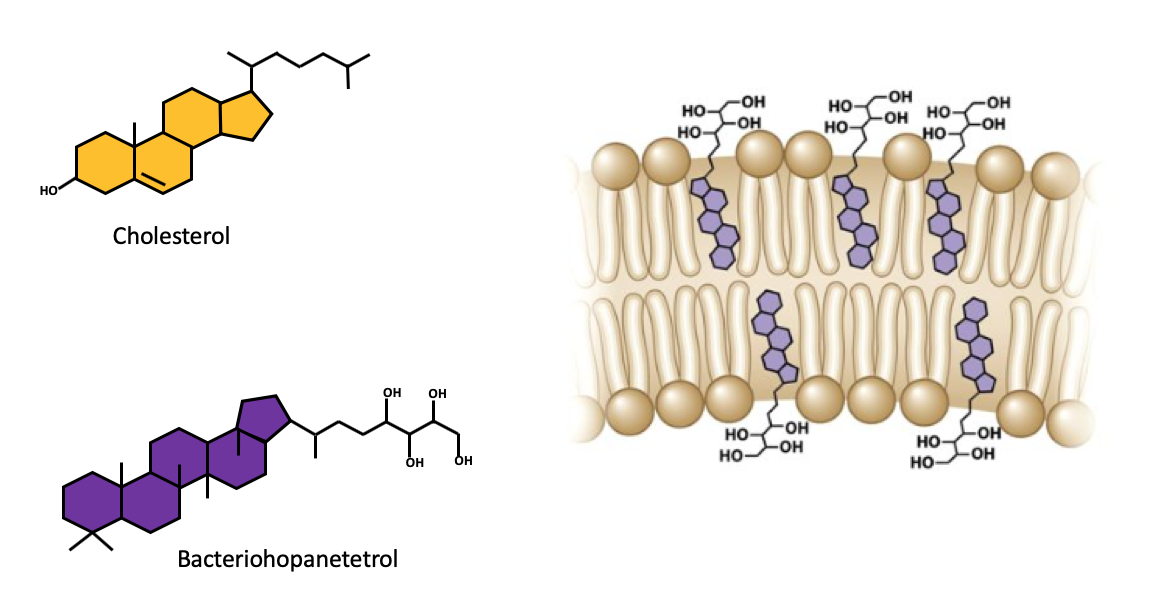
How do hopanoids interact with lipids?
They can covalently bind to lipid A, enhancing stability of the outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria
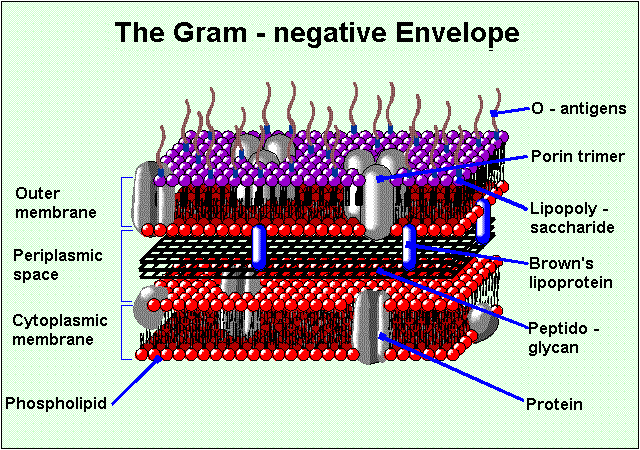
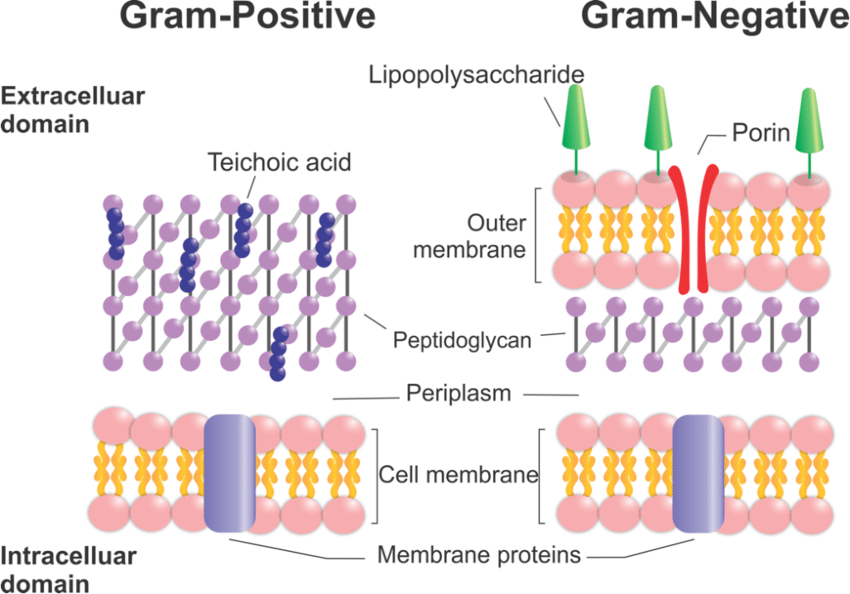
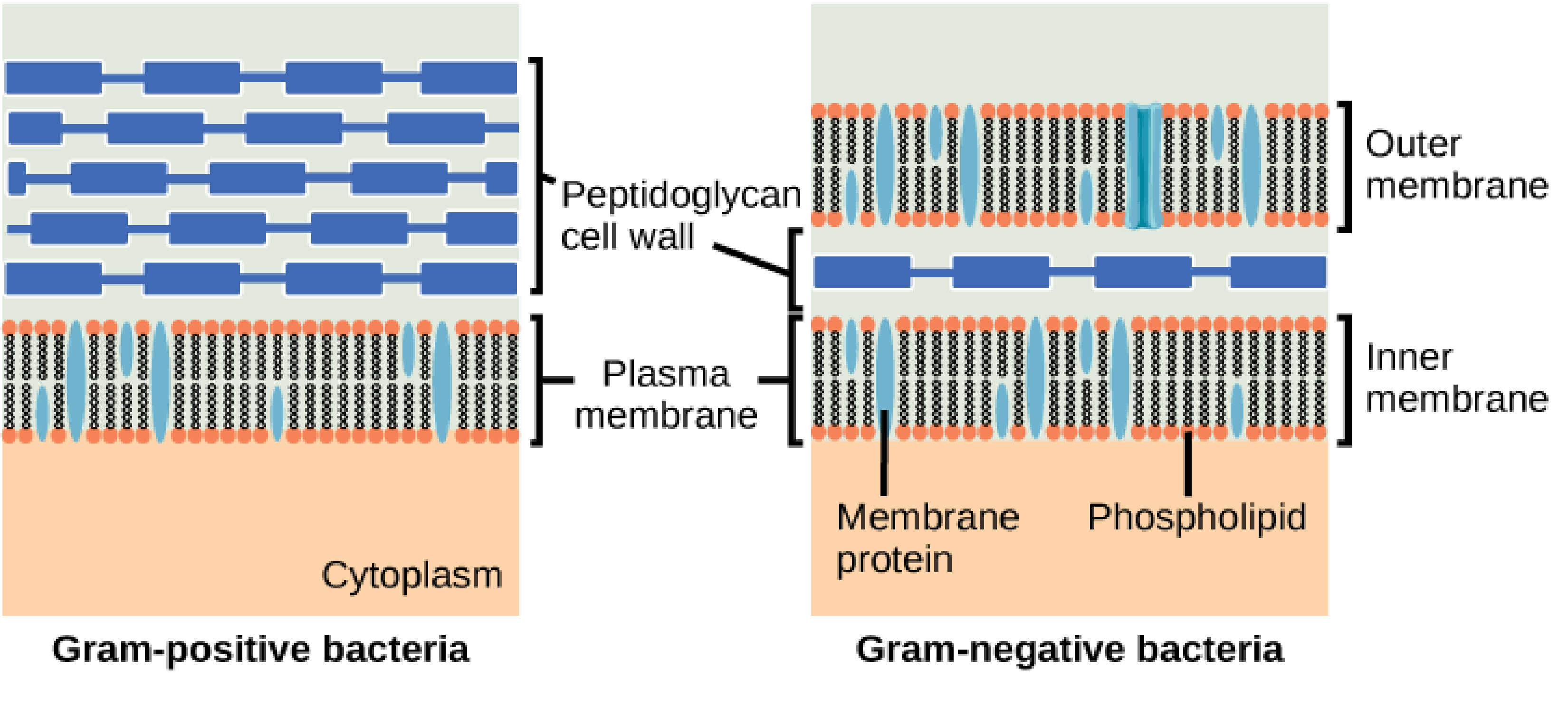
What is the bacterial cell envelope?
A protective, multilayered structure that surrounds cytoplasm, consisting of the plasma membrane, peptidoglycan cell wall, and an outer membrane (gram-neg only)
What are the two types of bacterial cell envelopes?
Gram-Positive and Gram-negative
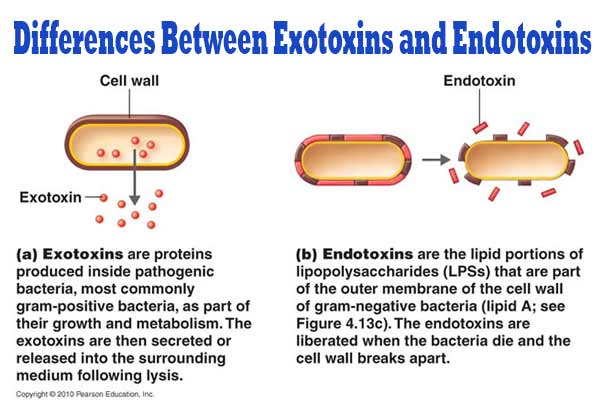
What is lysis of the bacterial cell envelope?
The rupture of the cell wall and plasma membrane, resulting in the release of internal components and cell death
How do antibiotics cause lysis?
Antibiotics can inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis, weakening the peptidoglycan layer and pressure forces the membrane to rupture
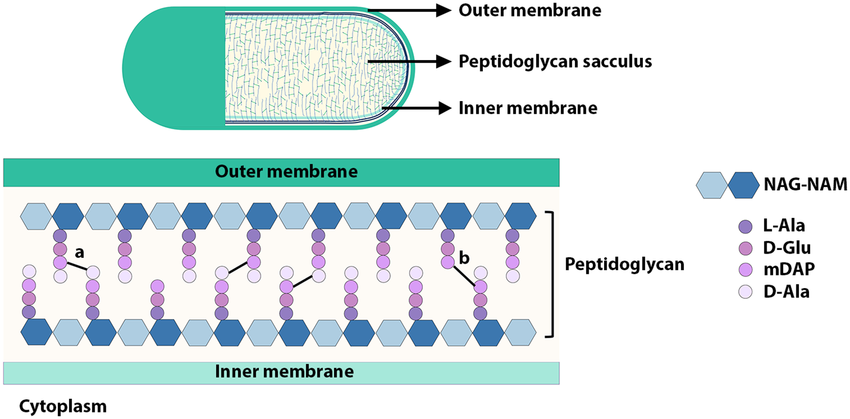
What is the bacterial cell envelope sacculus?
A rigid, bag-shaped exoskeleton composed of peptidoglycan (murein) that completely surrounds that cytoplasmic membrane. It is a mesh work of linear glycine strands cross-linked by short peptides.
What is the purpose of sacculus within the bacterial cell envelope?
Crucial for withstanding high osmotic pressure (prevents lysis), maintaining cell shape, and serves as a scaffolding anchoring to the outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria
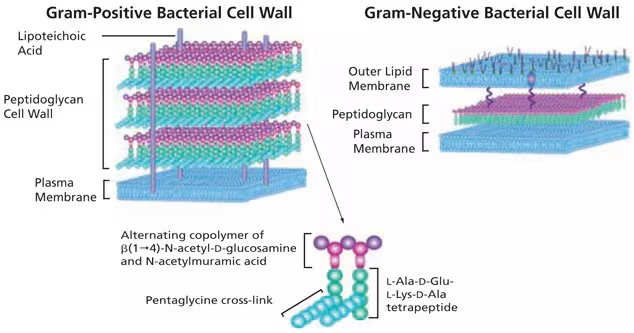
What is peptidoglycan?
Peptidoglycan (murein) is a mesh-like polymer composed of alternating sugars (NAG, NAM) cross-linked by peptide chains.
What is the purpose of peptidoglycan?
Forms a protective, rigid sacculus around the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane to maintain cell shape and resist high internal osmotic pressure
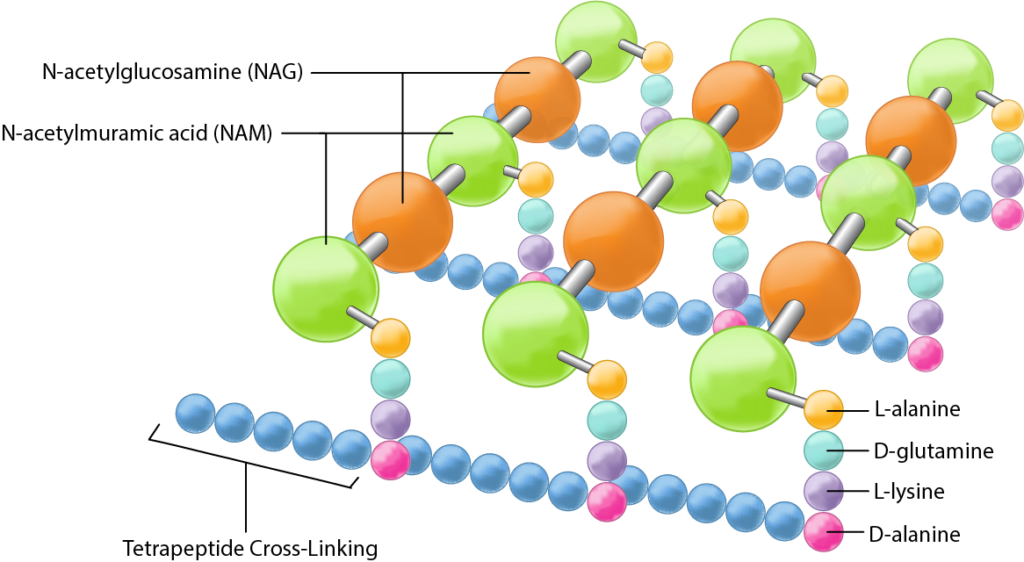
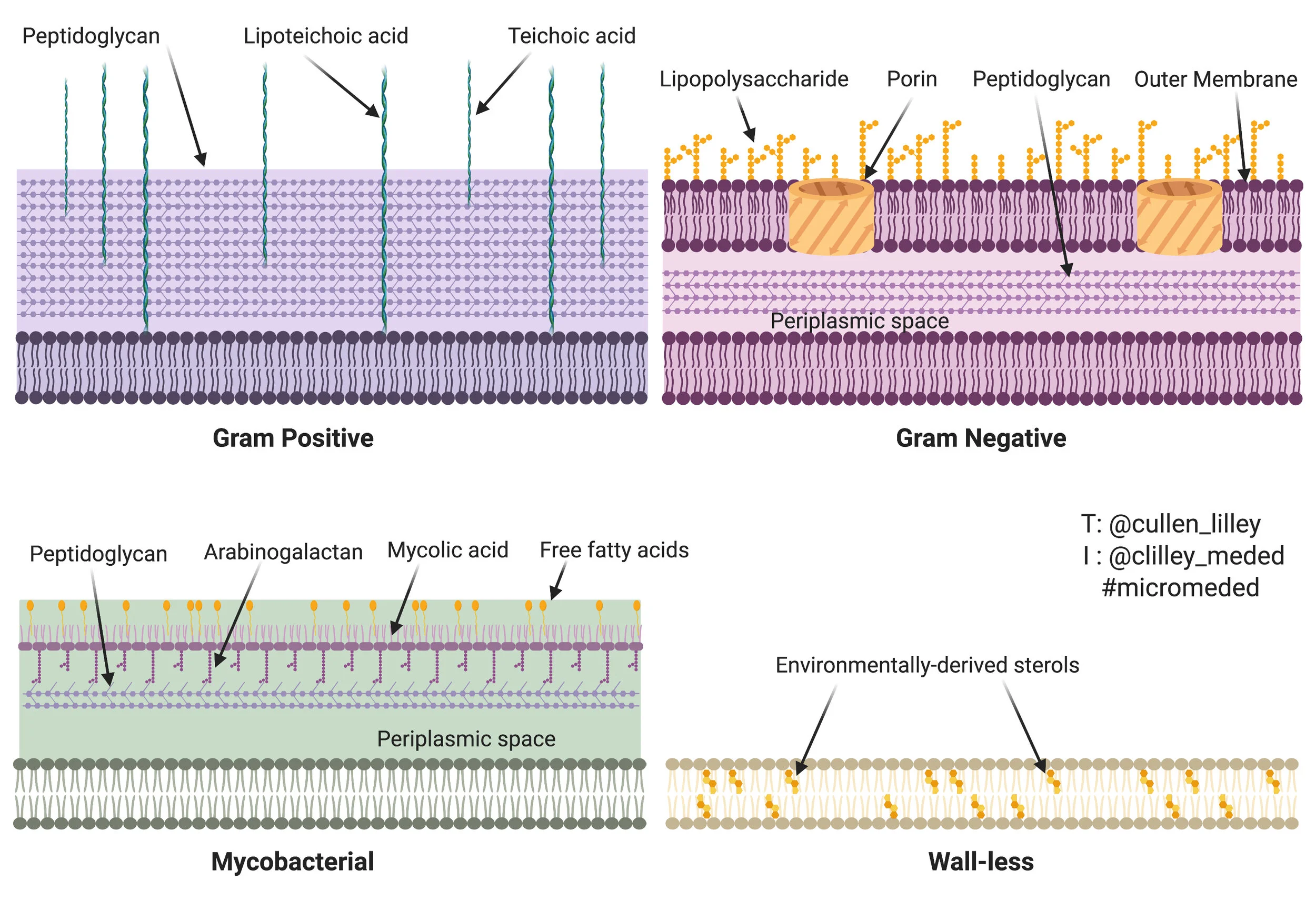
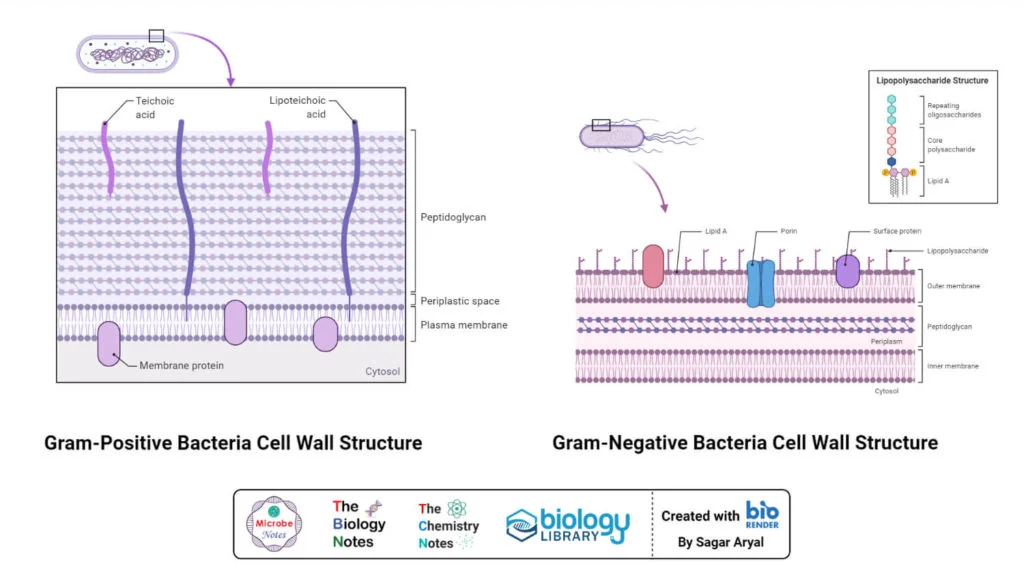
What is gram-positive bacteria?
Microorganisms characterized by a thick, multi-layered peptidoglycan cell wall that retains crystal violet stain, appearing purple.
What are teichoic acids in gram-positive bacteria?
Essential, negatively charged (polyanionic) glycopolymers found within the thick peptidoglycan cell wall
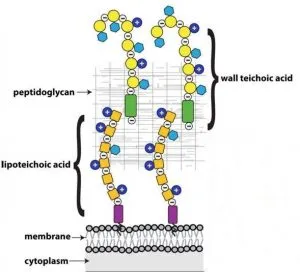
What is the function of teichoic acids in the gram-positive cell envelope?
Maintain cell envelope: regulate autolysins (enzymes that break down peptidoglycan), cell division, and maintain shape
Protect against environmental substances
May bind to host cells to initiate infection

What are gram-negative bacteria?
Microorganisms characterized by a thin peptidoglycan cell wall in between an inner cytoplasmic membrane and bacterial outer membrane. They appear pink since they do not retain stain due to a rich lipid outer membrane
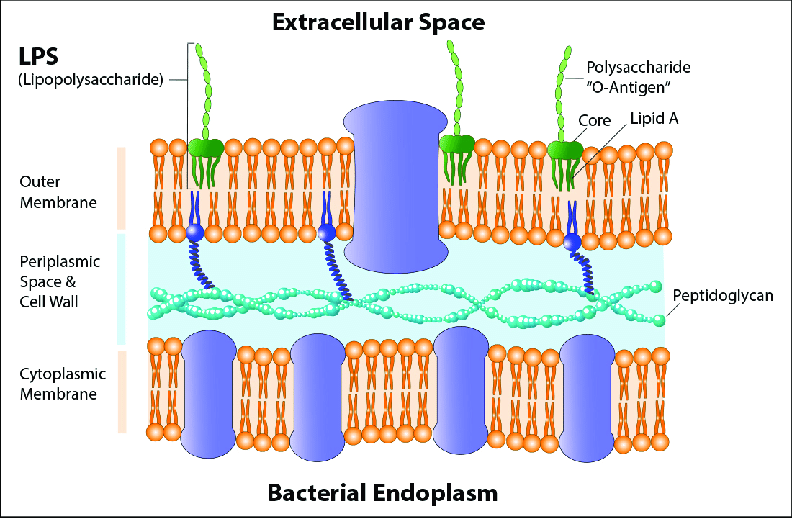
What is LPS within gram-negative bacteria?
Lipopolysaccharide is a glycolipid composed of a hydrophobic lipid A region, a oligosaccharide core, and a O-antigen chain
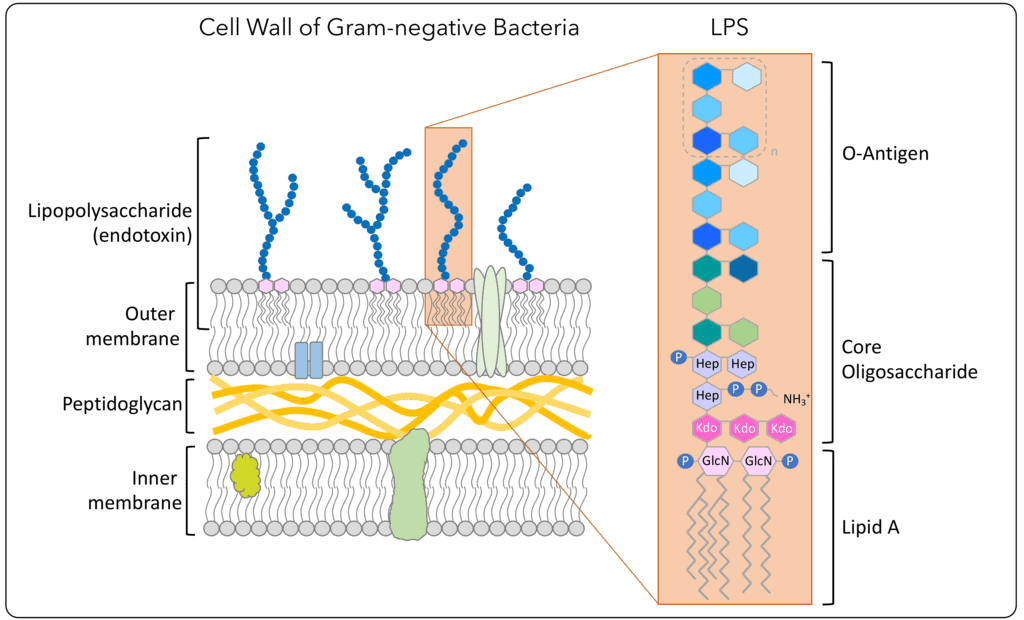
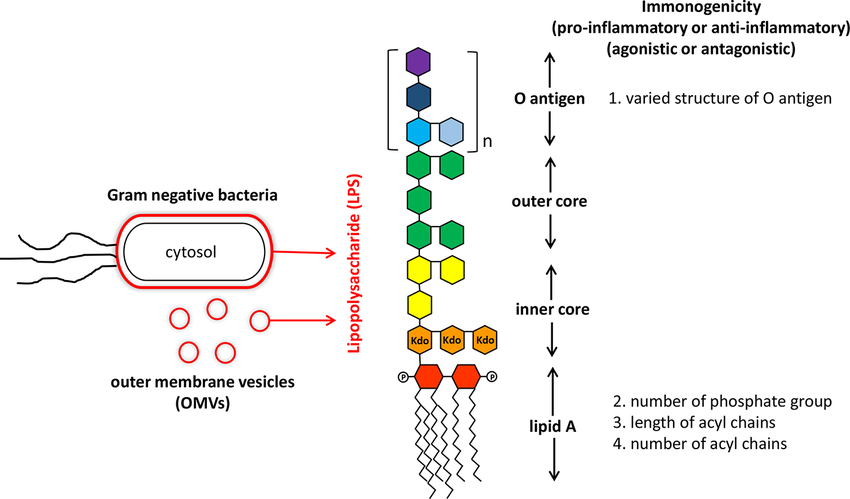
Why is gram-negative LPS known to be an endotoxin?
It triggers severe immune responses (septic shock, fevers, inflammation) when released upon bacterial cell death or during division, primarily due to its lipid A component
What is the function of LPS?
Provides structural integrity, protects against bile salts/antibiotics, and allows bacteria to adhere to surfaces
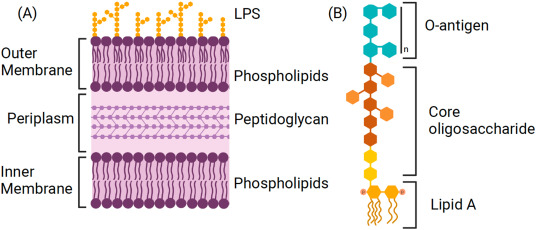
What is periplasm?
A gel-like matrix that holds the thin peptidoglycan layer, nutrient-binding and transport proteins, and chaperons. It is located within the periplasmic space, separating the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer membrane bilayers
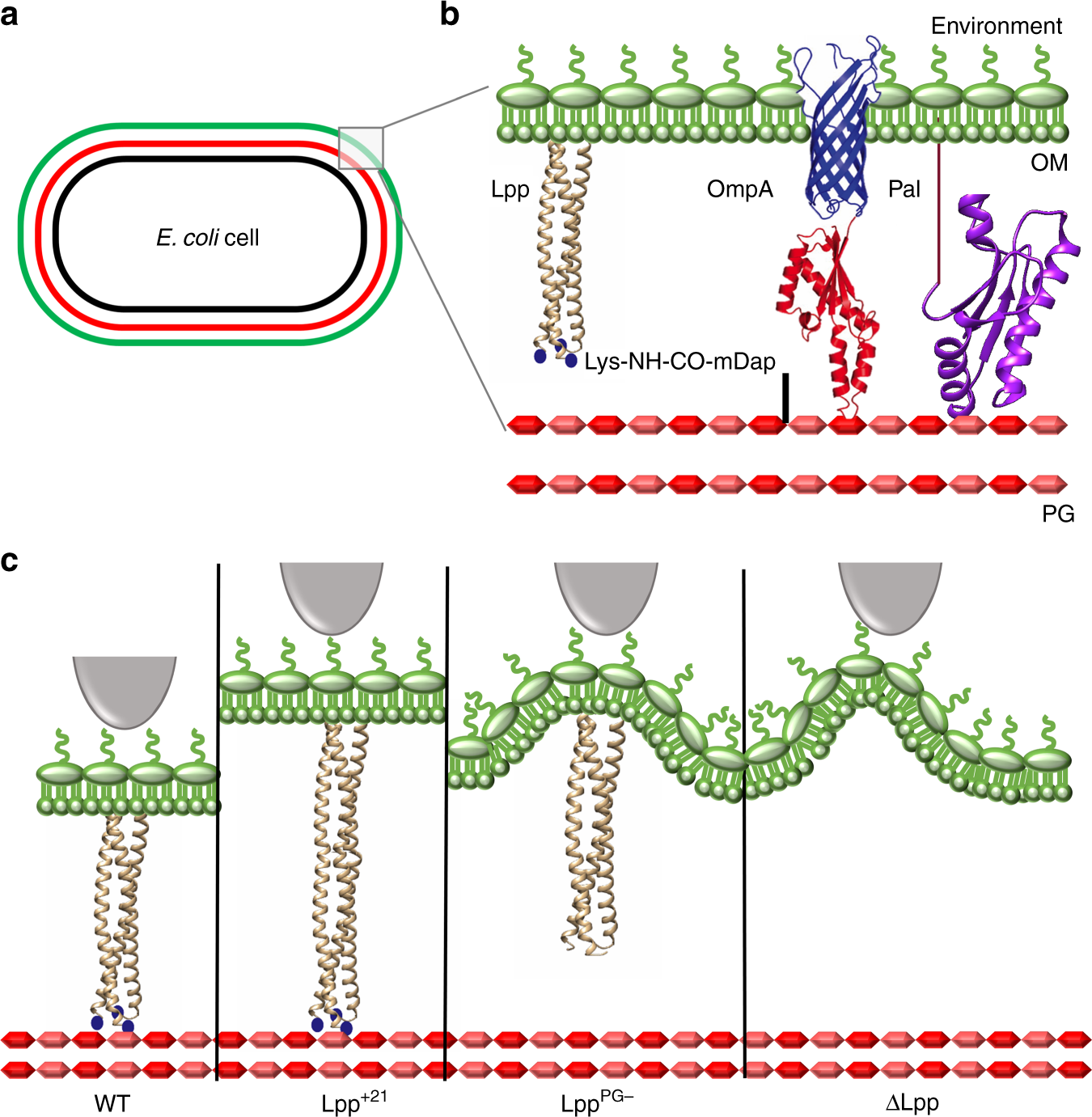
What is murein lipoprotein (Lpp) in gram-negative bacteria?
The most abundant protein in the outer membrane. It anchors the outer membrane to the peptidoglycan layer, providing critical structural integrity, maintaining the cell envelope
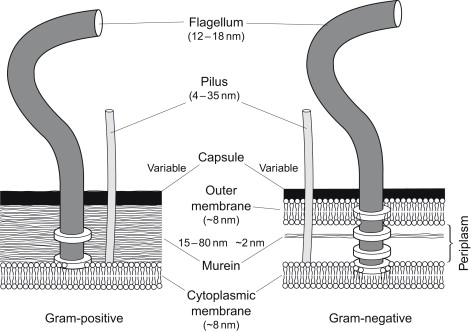
What is a capsule?
A protective gel-like layer, primarily composed of polysaccharides (sugars), surrounding the cell wall of bacteria. It acts as a virulence factor, enabling pathogens to evade host immune defenses, adhere to surfaces, resist dehydration, and protect against toxins
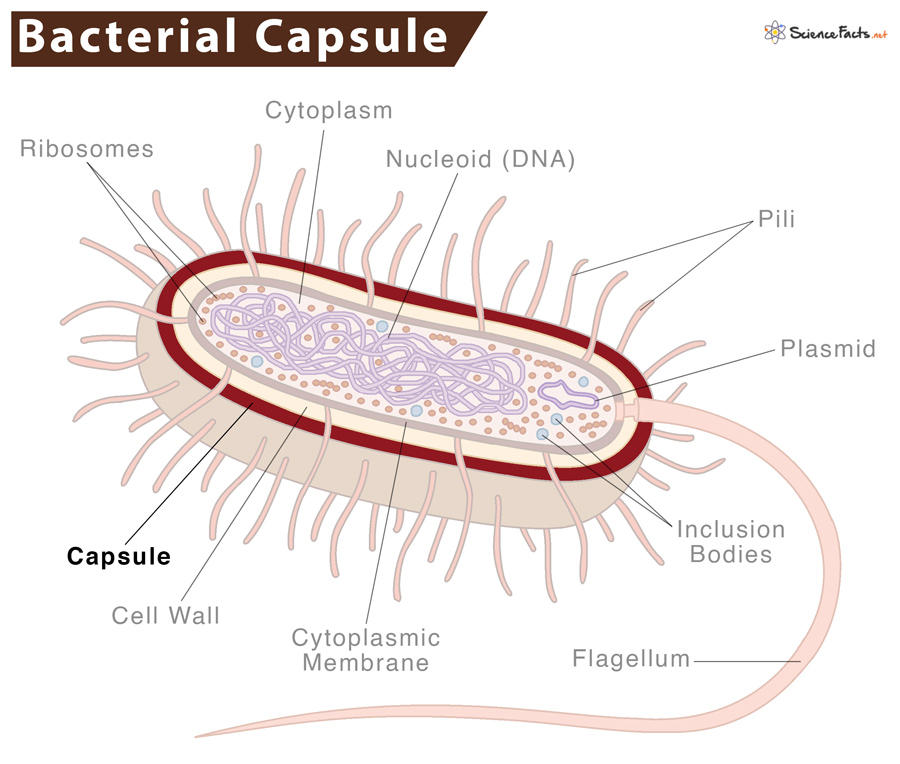
What is the function of the bacterial structures?
Protection: barrier against environmental hazards such as drying out and bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria)
Immune evasion: Masks surface antigens, preventing WBC from destroying bacteria
Adhesion: Attachs to surfaces and colonize, essential for biofilm formation
What are fimbriae?
Primarily on the surface on gram-negative bacteria, they are thin appendages composed of polymerized pilin proteins
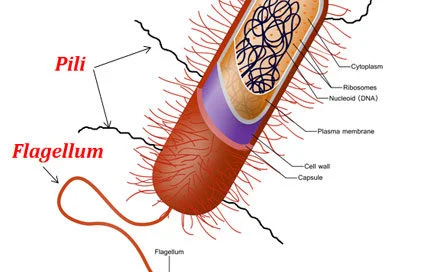
What is the function of fimbriae?
Act as adhesions, allowing bacteria to anchor to host cells, tissues, or surfaces. They are crucial for colonization and infection, playing a key role in bacterial pathogenesis and biofilm formation
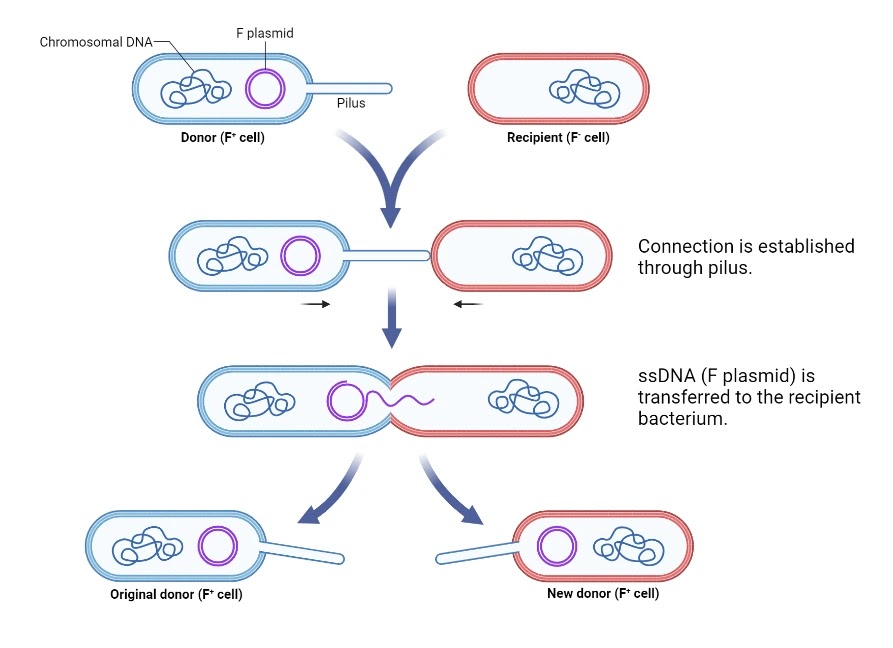
What are pili?
Thin, hair-like appendages found on the surface of bacteria, primarily gram-negative, they function in adhesion to host tissues, biofilm formation, DNA transfer (conjugation) and twitching motility
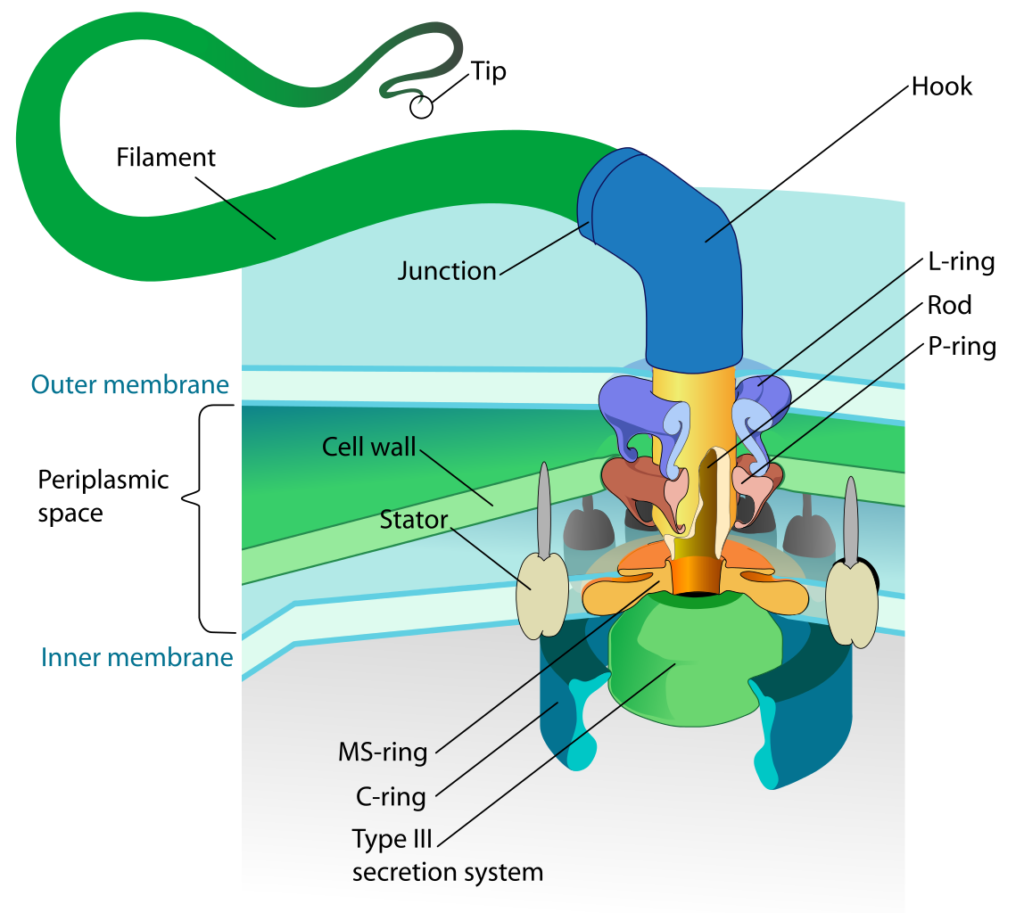
What are flagella? Function?
Long, hair-like appendages on bacteria that function as propellers to enable motility and movement through liquid or surface environments. Powered through proton or sodium-motive force. They also assist in initial stages of colonization.

What is chemotaxis?
Process in which bacteria sense chemical gradients and bias their movement toward attractants (nutrients) or away from repellents (toxins). Bacteria utilize their flagella in this process.
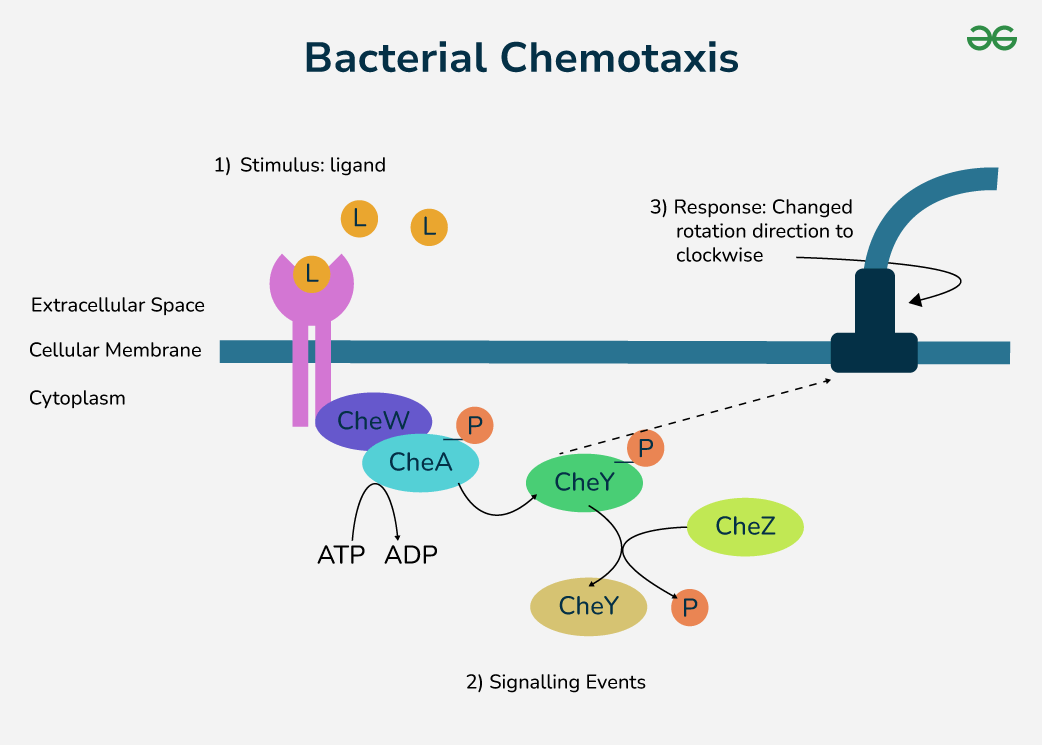
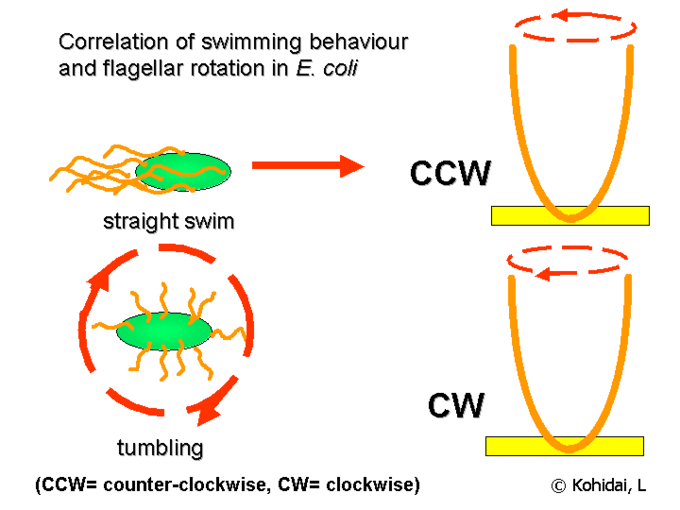
During chemotaxis, what happens when bacteria “runs” v.s “tumbles”?
Runs: flagella rotates counterclockwise wise for straight “runs”
Tumbles: Flagella rotates clockwise to “tumble” and enable movement
What is an endospore?
Highly resistant, dormant structures formed inside certain bacteria (only gram-positive) as a survival mechanism against harsh environmental conditions like heat, radiation, and starvation
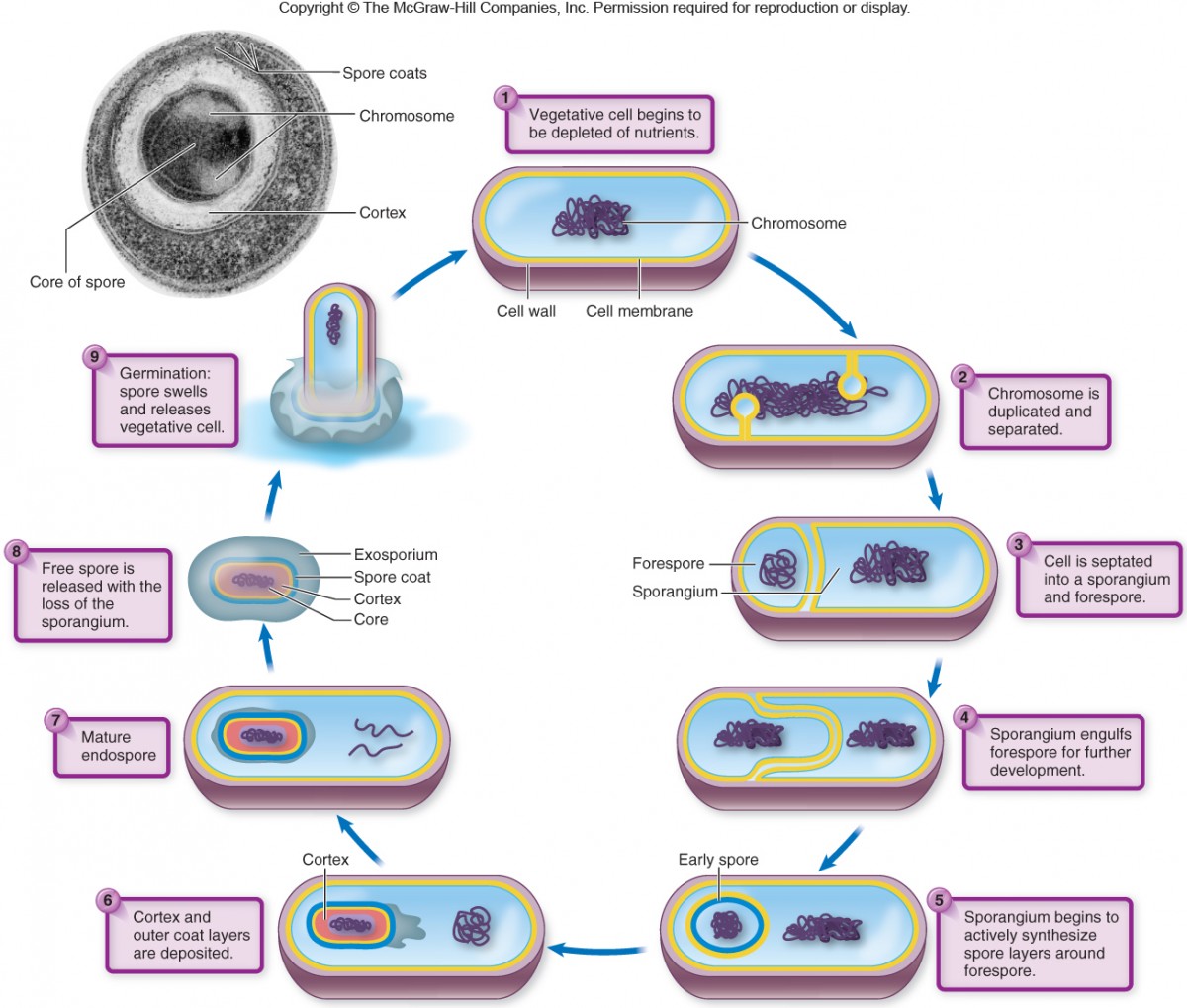
What is the structure of an endospore?
They contain the bacterium’s DNA, ribosomes, and dipicolinic acid, protected by multiple layers: a core, inner membrane, germ cell wall, cortex, spore coat, and sometimes an exosporium
When do bacterial endospores form?
They form in response to nutrient depletion
What does it mean for a cell to be vegetative?
Metabolically active, living form cells (bacteria/fungi) as opposed to dormant endospores. They consume nutrients, produce toxins, and divide asexually. They are susceptible to environmental stress but crucial for maintaining and expanding the organisms body
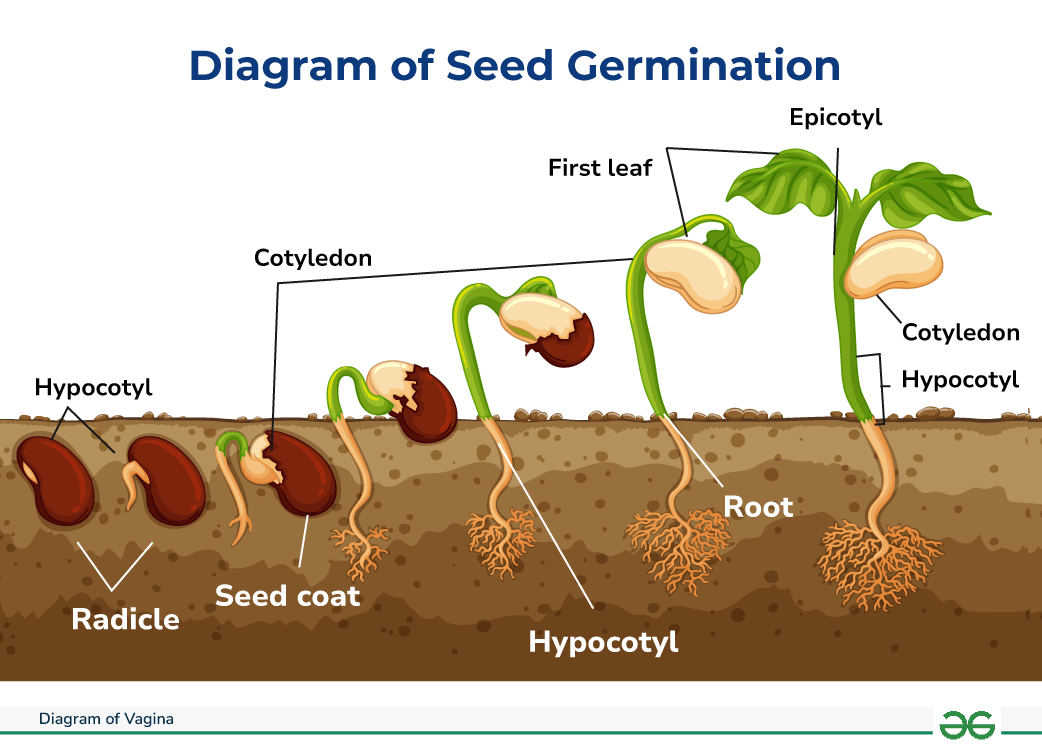
What is germination?
Process where a plant embryo inside a seed begins to grow and sprout into a seedling, starting its life cycle by emerging from the seed coat, typically after a period of dormancy , triggered by favorable conditions such as water, warmth, and oxygen
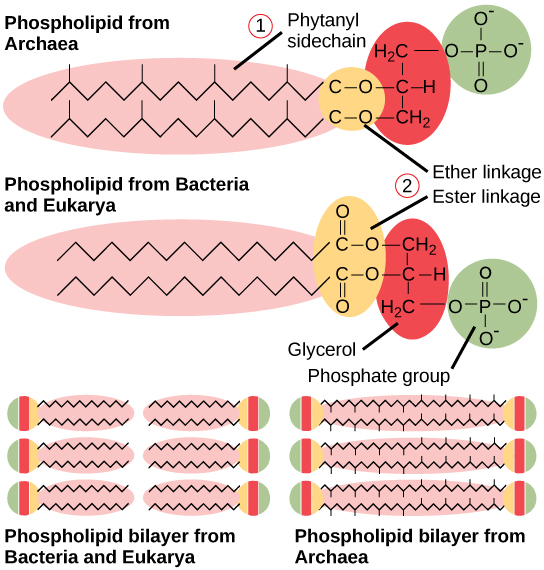
How do archaea cells differ from bacterial cells?
Archaea differ since they lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls, contain ether-linked membrane lipids (often monolayers) instead of ester-linked belayers, and have distinct genetic machinery closer to eukaryotes.
Archaea thrive in extreme environments, do not cause diseases, and use unique energy sources
Bacteria: ester-linked membranes, peptidoglycan walls, and form endospores
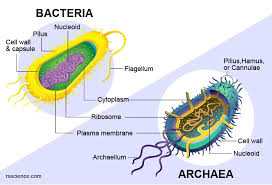
What are the ways in which archaea reproduce?
Fission, budding, and fragmentation
What are ways in which bacteria reproduce?
Fission and spore formation
How do specialized structures such as flagellum, pili, and capsules allow bacteria to survive in a given environment?
They facilitate movement (nutrients or escaping toxins), attachment (adhesion to surfaces and host cels), and protection (against dehydration and immune system phagocytosis).