Blood Vessel Circuits and Structures ch13
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover the essential vocabulary related to blood vessel circuits, structures, and functions, serving as a study aid for understanding the cardiovascular system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Pulmonary circuit
Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the left atrium.
Systemic circuit
Transports oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body and returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart.
Capillaries
Microscopic vessels connecting arteries and veins, facilitating nutrient and gas exchange.
Tunica intima
The innermost layer of arteries and veins; includes endothelial lining and connective tissue.
Tunica media
Middle layer of arteries and veins; contains smooth muscle layers controlling vessel diameter.
Tunica externa
The outer layer of arteries and veins; provides structural support and anchorage.
Elastic arteries
Large arteries that stretch and recoil to help maintain blood pressure.
Muscular arteries
Medium-sized arteries that distribute blood to organs and muscles.
Arterioles
Small arteries that regulate blood flow and pressure through smooth muscle contraction.
Large veins
Veins that have all three tunics and a thick tunica externa, like the vena cavae.
Medium-sized veins
Veins with a thinner tunica media and a thick tunica externa.
Venules
Smallest veins that collect blood from capillaries.
Blood flow pattern
The path blood takes through the circulatory system: arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins → heart.
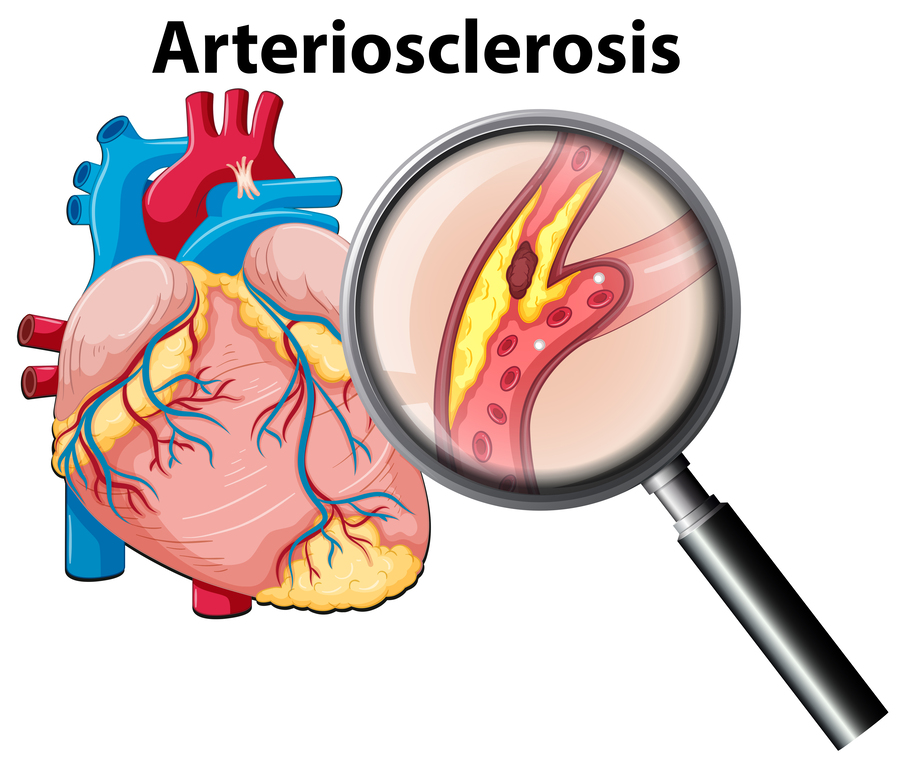
Arteriosclerosis
Thickening and hardening of arterial walls, a major cause of cardiovascular diseases.
Atherosclerosis
A specific type of arteriosclerosis characterized by fatty deposits in artery walls.

Atherosclerotic plaques
Fatty masses that restrict blood flow in arteries, leading to cardiovascular issues.
Capillary bed
A network of capillaries connecting arterioles to venules.
Metarteriole
The initial part of a capillary bed that contains smooth muscle to regulate flow.
Precapillary sphincter
A ring of smooth muscle that controls blood flow into capillary beds.
Vasomotion
Rhythmic contraction and relaxation of precapillary sphincters.
Arteriovenous anastomosis
A direct connection between an arteriole and a venule that bypasses capillaries.
Venous pressure
Pressure in veins, which is significantly lower than in arteries.
Valves in veins
Folds of tunica intima that prevent backflow and ensure one-way blood flow.
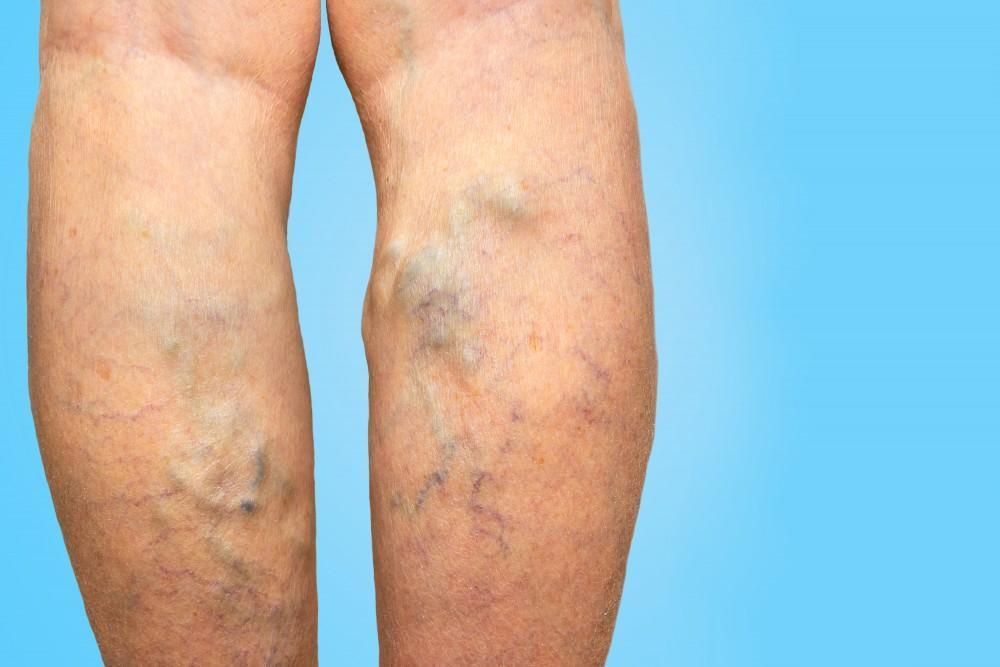
Varicose veins
Dilated veins resulting from valve failure and blood pooling.
Venoconstriction
Sympathetic response that reduces vein diameter to maintain arterial blood volume.
Blood reservoirs
Organs and tissues that store large volumes of blood, primarily the liver and bone marrow.
Superior vena cava
The large vein that collects deoxygenated blood from the upper body and returns it to the heart.
Inferior vena cava
The large vein that collects deoxygenated blood from the lower body and returns it to the heart.
Vasomotor center
Part of the brain that regulates blood vessel diameter and venoconstriction.
Right/left symmetry
A pattern of blood vessel organization where vessels are matched on both sides of the body.
Blood vessel anastomoses
Connections between blood vessels that provide alternative routes for blood flow.
Elastic membrane
A layer found in arteries that gives them the ability to stretch.
Smooth muscle layers
Muscle layers in blood vessel walls that control diameter and blood flow.
Coronary artery disease
A disease caused by atherosclerosis affecting the arteries supplying blood to the heart.
Stroke
Interruption of blood supply to the brain, often as a complication of arteriosclerosis.
Gas exchange
Process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs.
Nutrient exchange
The transfer of nutrients from the blood via capillaries into tissues.
Aorta
The largest artery in the body, from which systemic circulation originates.
Capillary walls
Only one cell thick, allowing for efficient diffusion and exchange.
Endothelium
The thin layer of cells lining the blood vessels.
Skeletal muscle contraction
Aids venous return by compressing veins and propelling blood toward the heart.
Mean arterial pressure
Average arterial pressure in a single cardiac cycle.
Autonomic nervous system
Part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary functions including blood vessel control.
Blood flow regulation
Controlled by smooth muscle contraction in the blood vessel walls.
Endothelial lining
The thin layer of cells that line the interior of blood vessels.
Vessel stability
Support provided by surrounding connective tissues and structural layers of blood vessels.
Blood circulation
Continuous movement of blood throughout the body via closed circulatory system.
Oxygenated blood
Blood rich in oxygen, delivered from the lungs to the body.
Deoxygenated blood
Blood low in oxygen, returning from the body to the heart.
Gas exchange sites
Locations where oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange occurs, primarily in the lungs.
High blood pressure
A risk factor for atherosclerosis characterized by elevated pressure in arteries.
Thick tunica externa
The outermost layer of veins, providing support and structure.
Interstitium
Space between cells that interstitial fluid occupies for nutrient and waste exchange.