Spermatozoa Transport and Fertilization in Females
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Semen Deposition
Location where semen is introduced into female tract.
Cranial Vagina
Semen deposition site for cows, sheep, dogs.
Cervix
Semen deposition site primarily for pigs.
Cervical Lumen
Semen is delivered into uterus via horse cervix.
Transcervical AI
Semen delivered by bypassing the cervix.
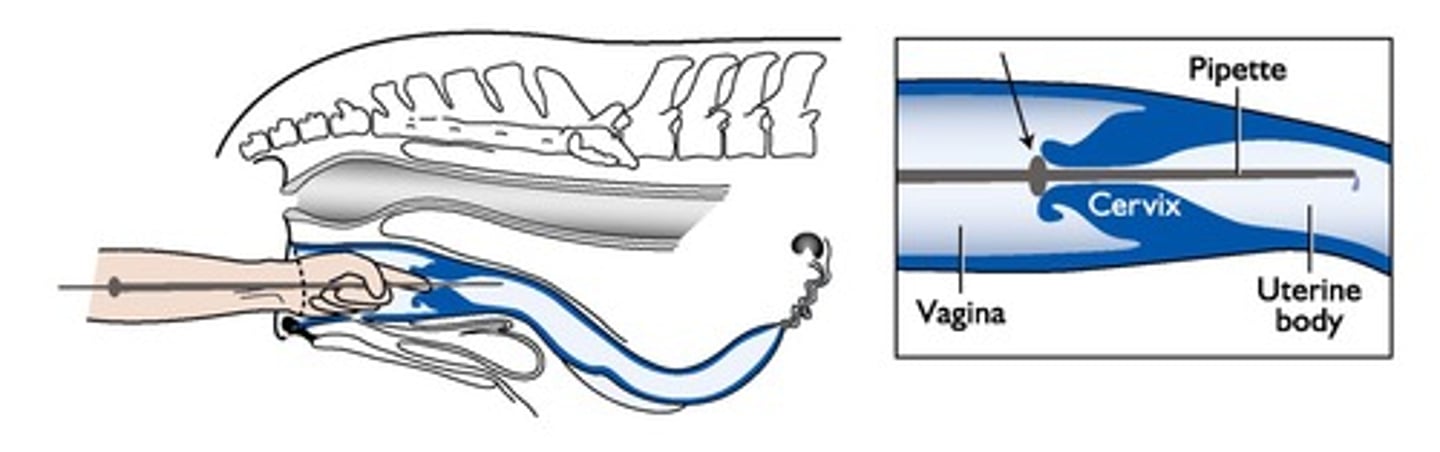
Intracervical AI
Semen positioned within cervix for direct uterine flow.
Semen Volume for Sows
50-80 mL required for optimal conception rates.
Laparoscopic Insemination
Surgical introduction of semen into uterine horns.

Retrograde Transport
Loss of spermatozoa from female tract post-insemination.
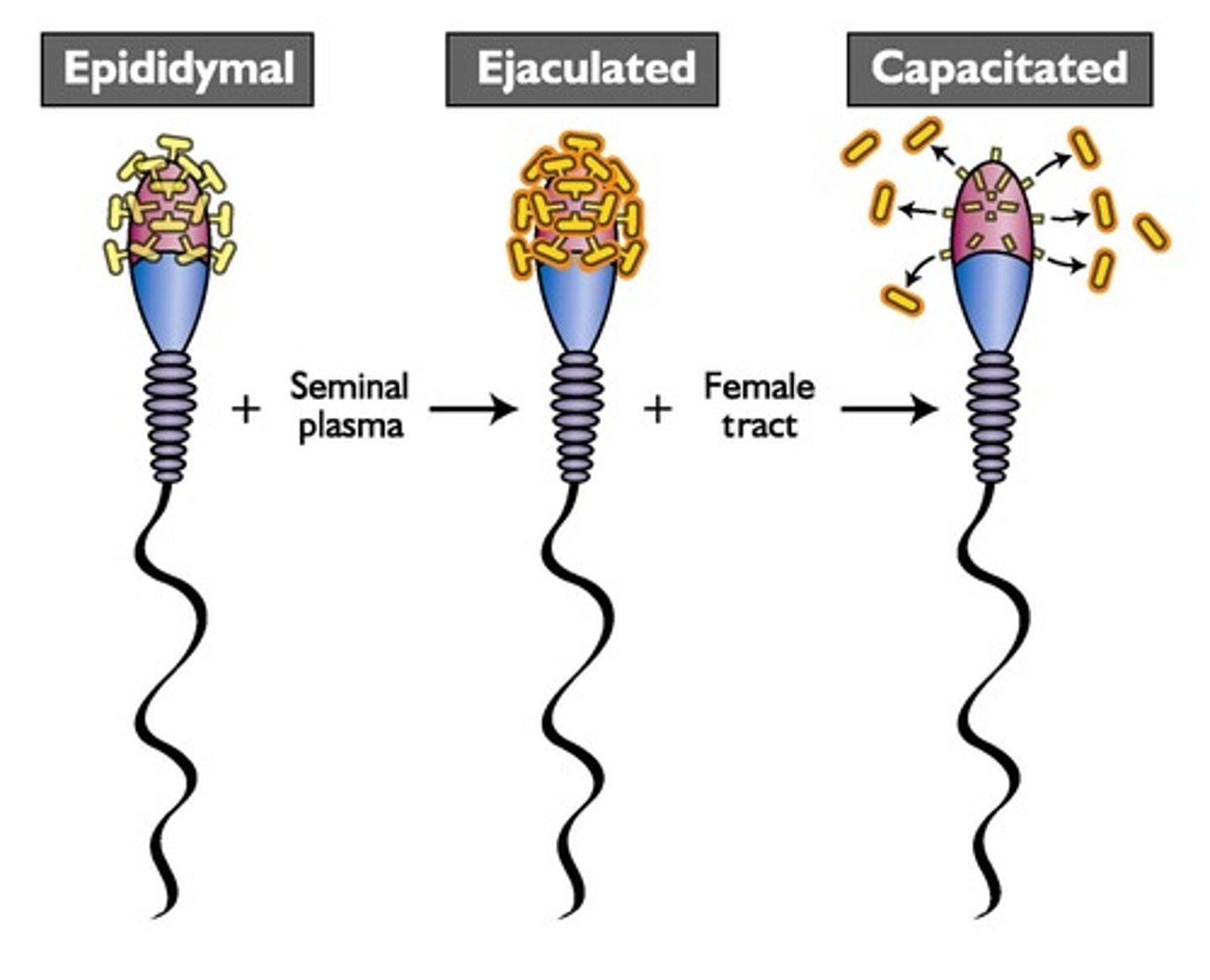
Capacitation
Sperm maturation process necessary for fertilization.
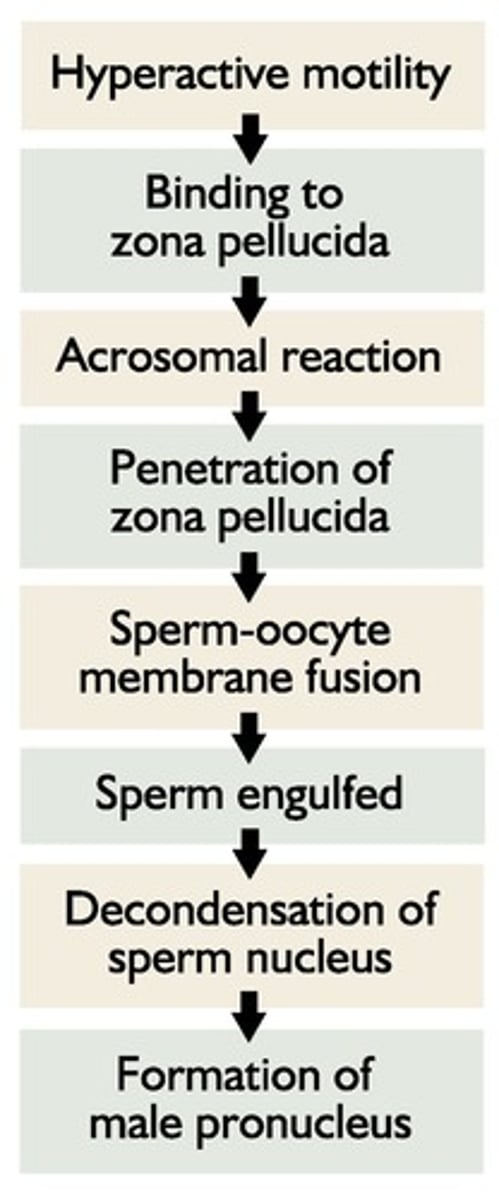
Male Pronucleus Formation
Stage after capacitation leading to fertilization.
Leukocyte Infiltration
Immune response in reproductive tract post-insemination.
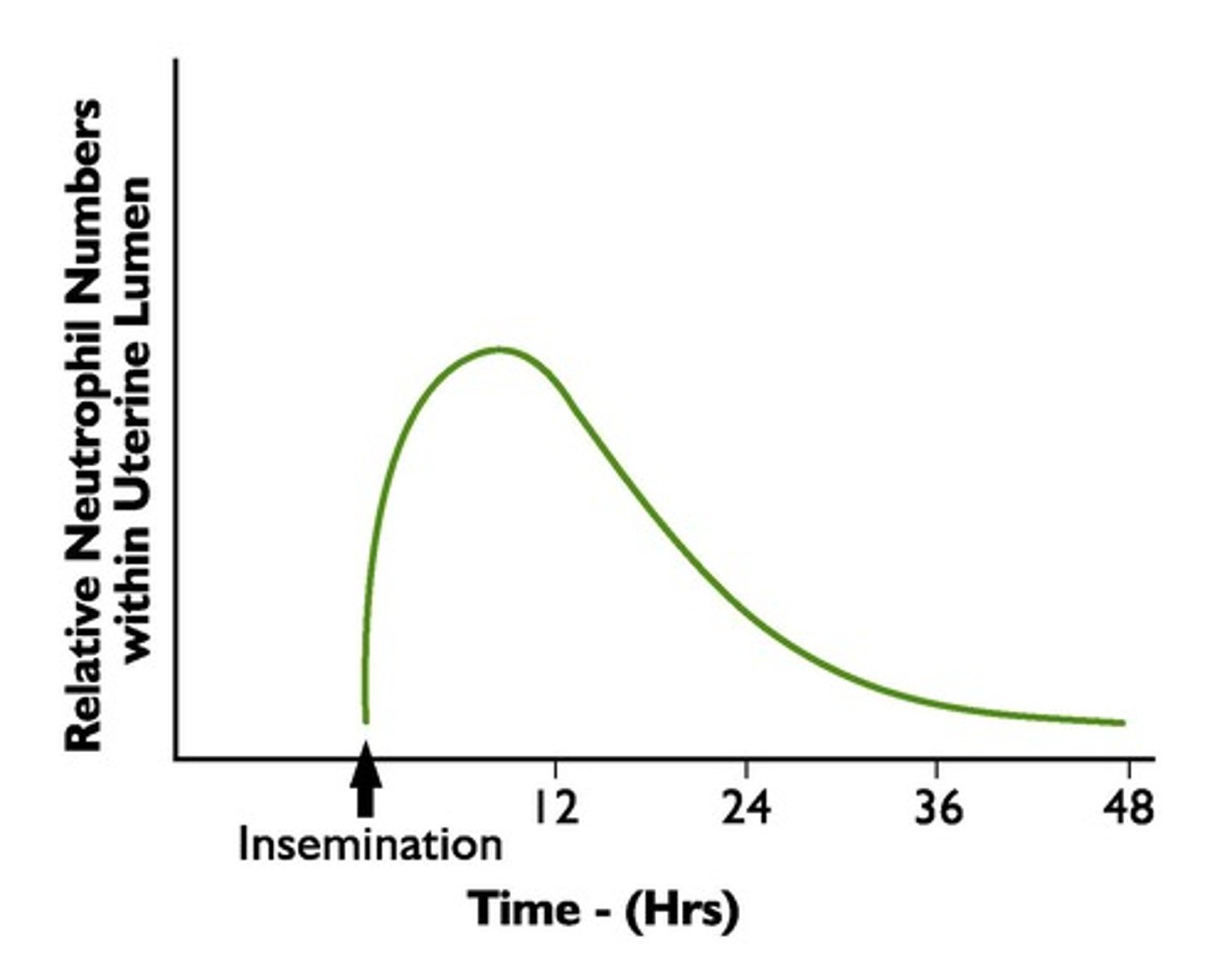
Estradiol Effects
Promotes leukocyte delivery during female estrus.
Genetic Improvement
Using superior sires to enhance offspring quality.
Disease Control
Minimizing disease transmission through artificial insemination.
Record Keeping
Improved tracking of breeding and reproductive data.
Sex-Sorted Semen
Semen separated by sex for targeted breeding.
Insemination Gun Manipulation
Technique for delivering semen into female tract.
Interdigitating Prominences
Cervical structure aiding in sperm retention.
Sperm Loss Percentage
>60% sperm lost within 12 hours post-AI.
Semen Deposited in Uterine Horns
Lower sperm loss compared to cervix deposition.
Artificial Insemination Disadvantages
Requires trained personnel and estrus detection.
Rapid transport phase
Initial sperm movement due to muscularis contractions.
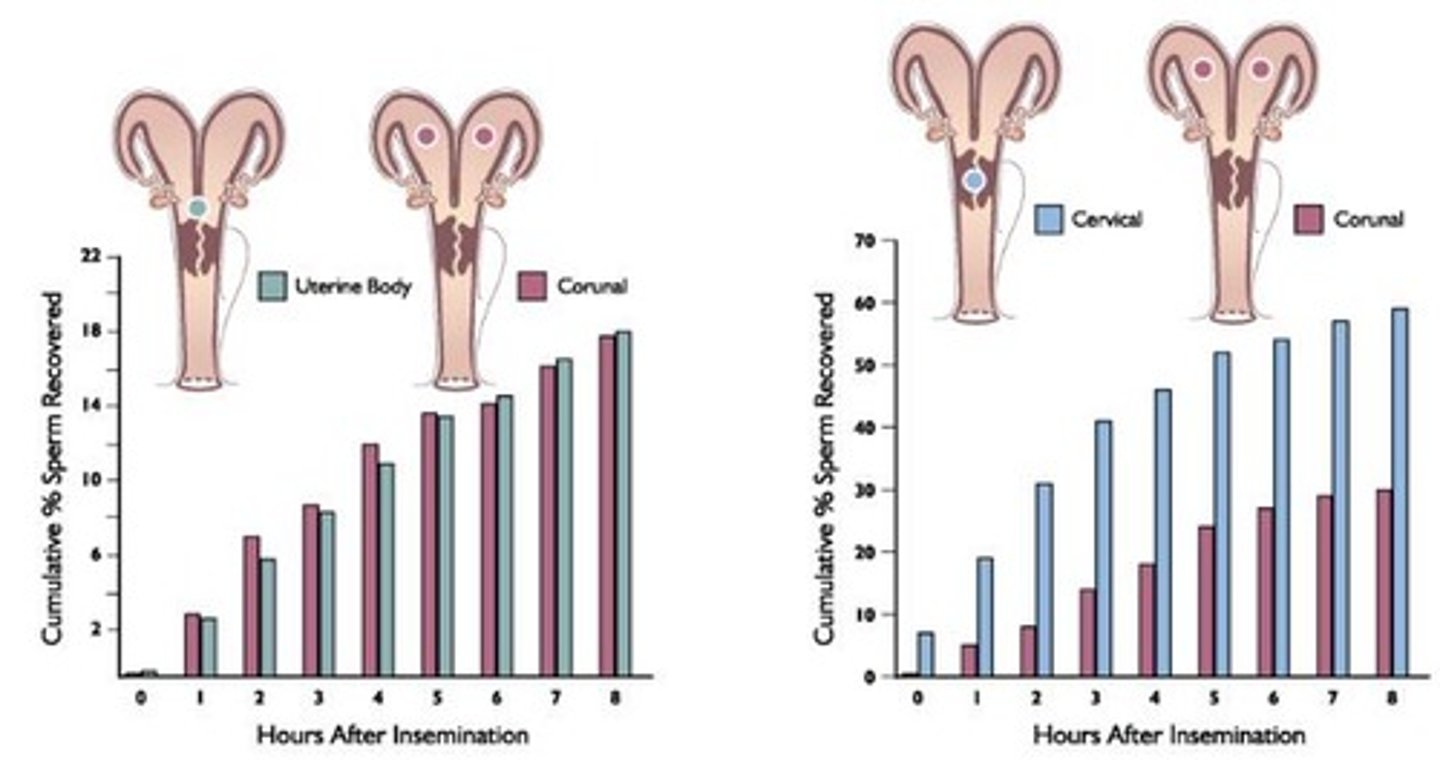
Sustained transport phase
Continuous sperm movement via cervix and isthmus.
Oviducts
Location where sperm can be found shortly after insemination.
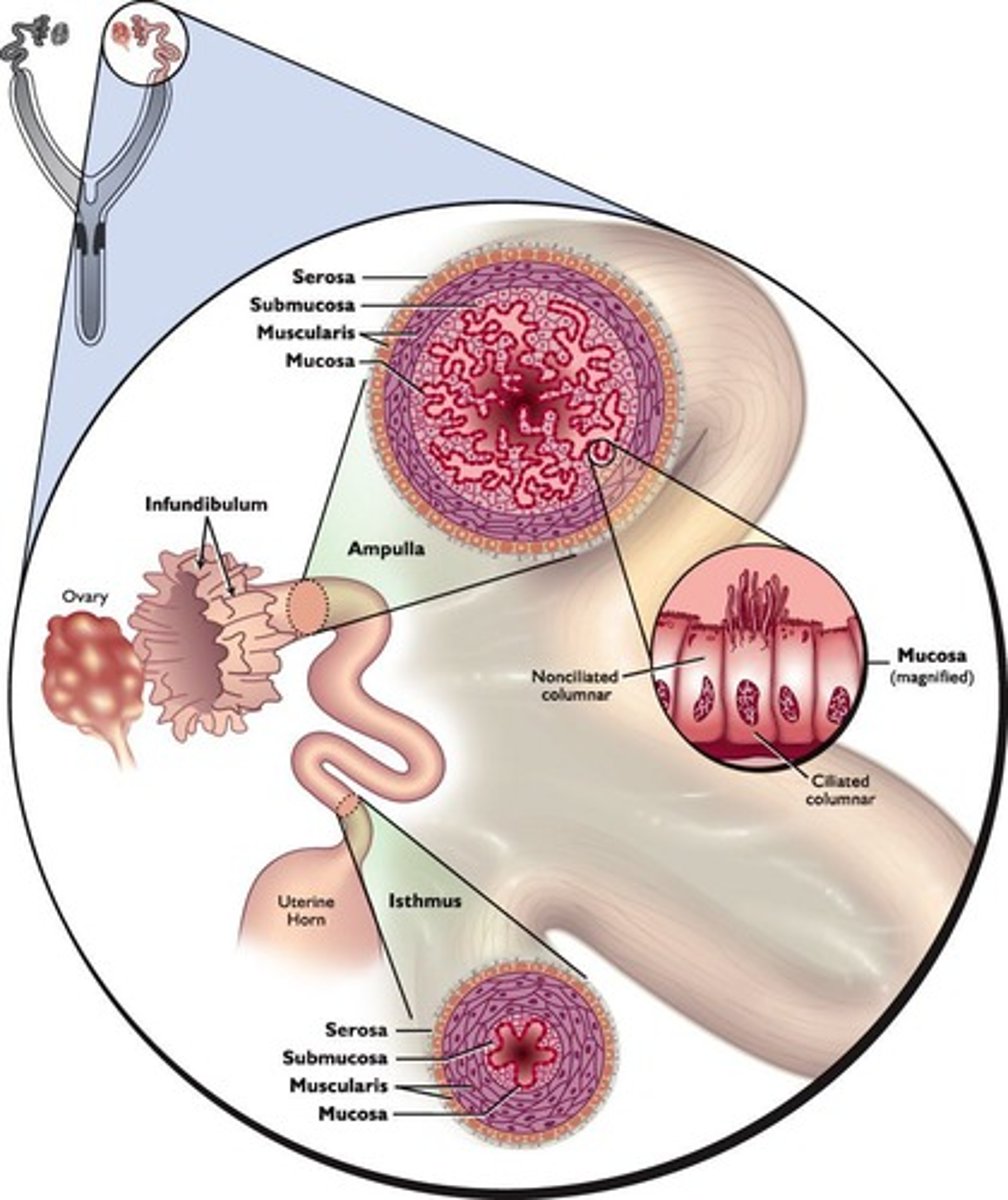
Sperm docking
Attachment to oviductal epithelium enhances sperm viability.
Uterotubal junction
Site where sperm first dock in the oviduct.
Prostaglandins
Compounds in semen that enhance uterine and oviduct tone.
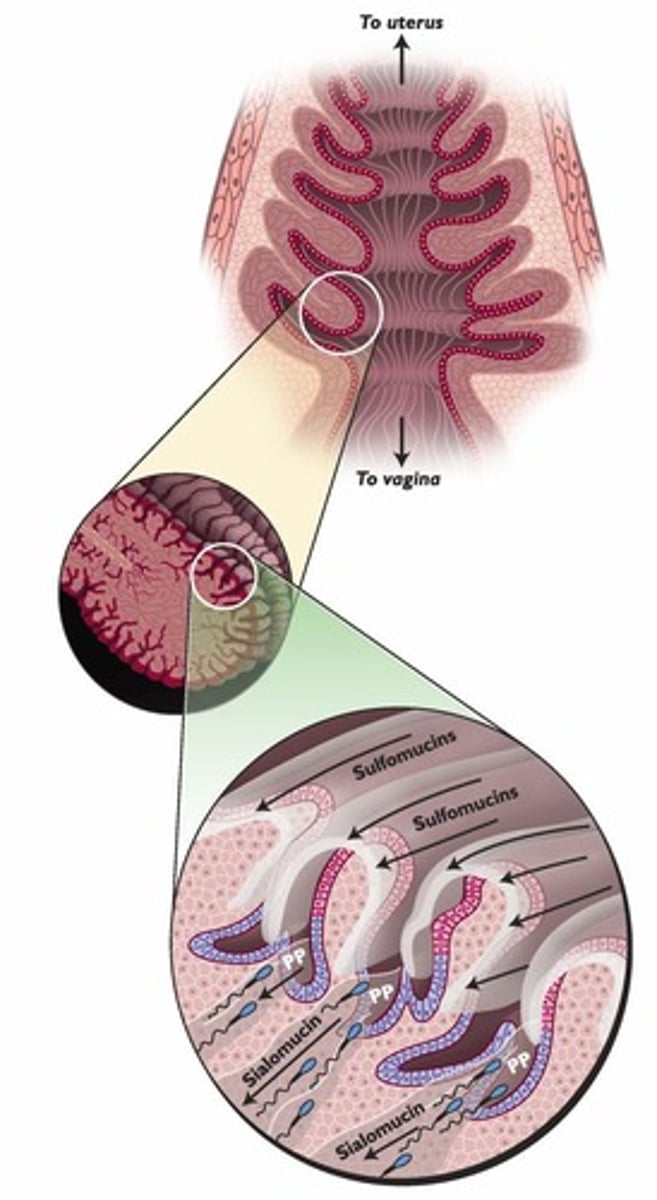
Cervical mucus types
Two mucus types affect sperm passage through cervix.
Sulfomucin
Viscous mucus that washes sperm out of the tract.
Sialomucin
Low viscosity mucus allowing sperm to navigate deeper.
Capacitation
Process enabling sperm to achieve fertilization capability.
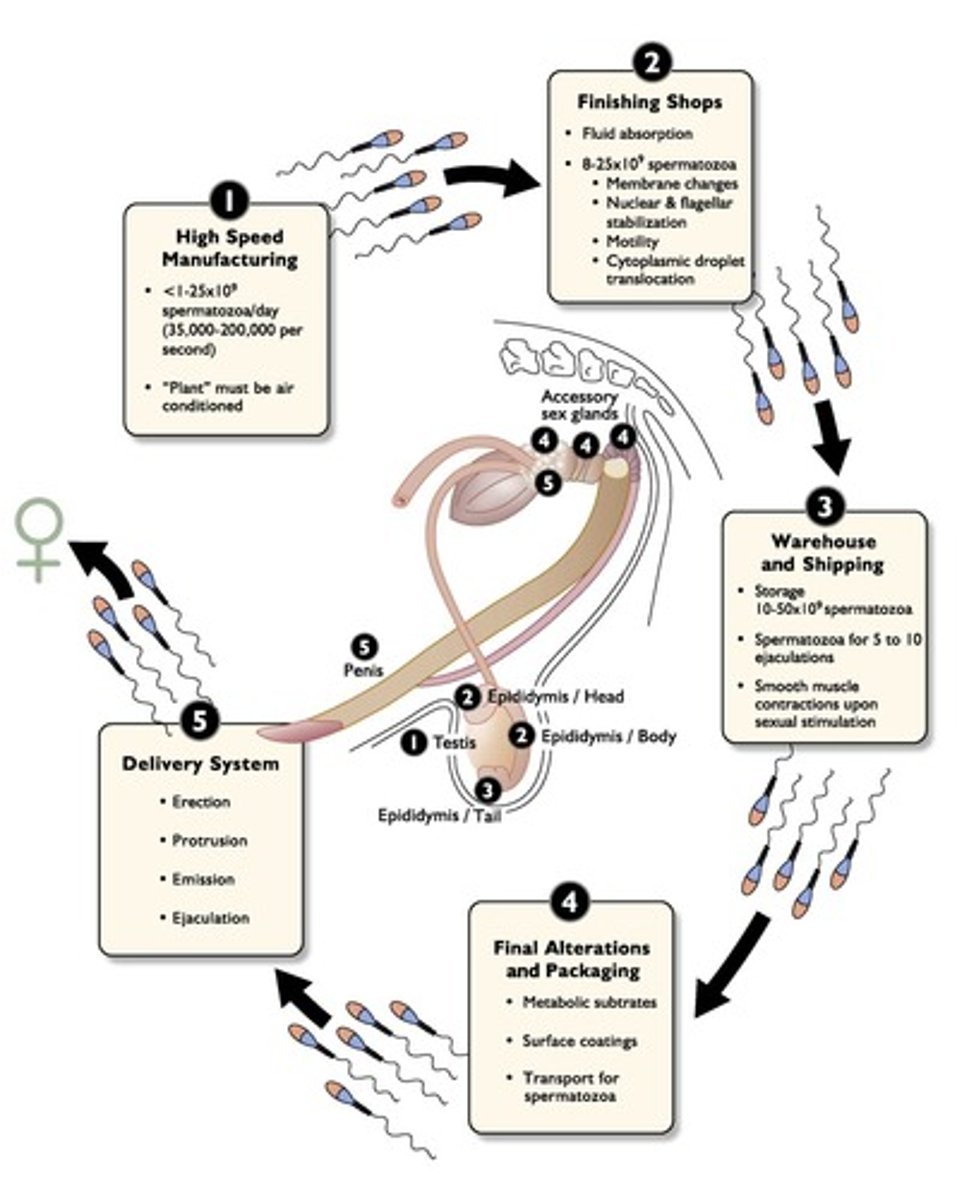
Epididymis
Site where sperm gain maturity before fertilization.
Privileged pathways
Deeper cervical crypts facilitating sperm transport.
Hyperactive motility
Increased motility pattern aiding sperm-oocyte contact.
Zona pellucida
Outer layer of oocyte that sperm must bind to.
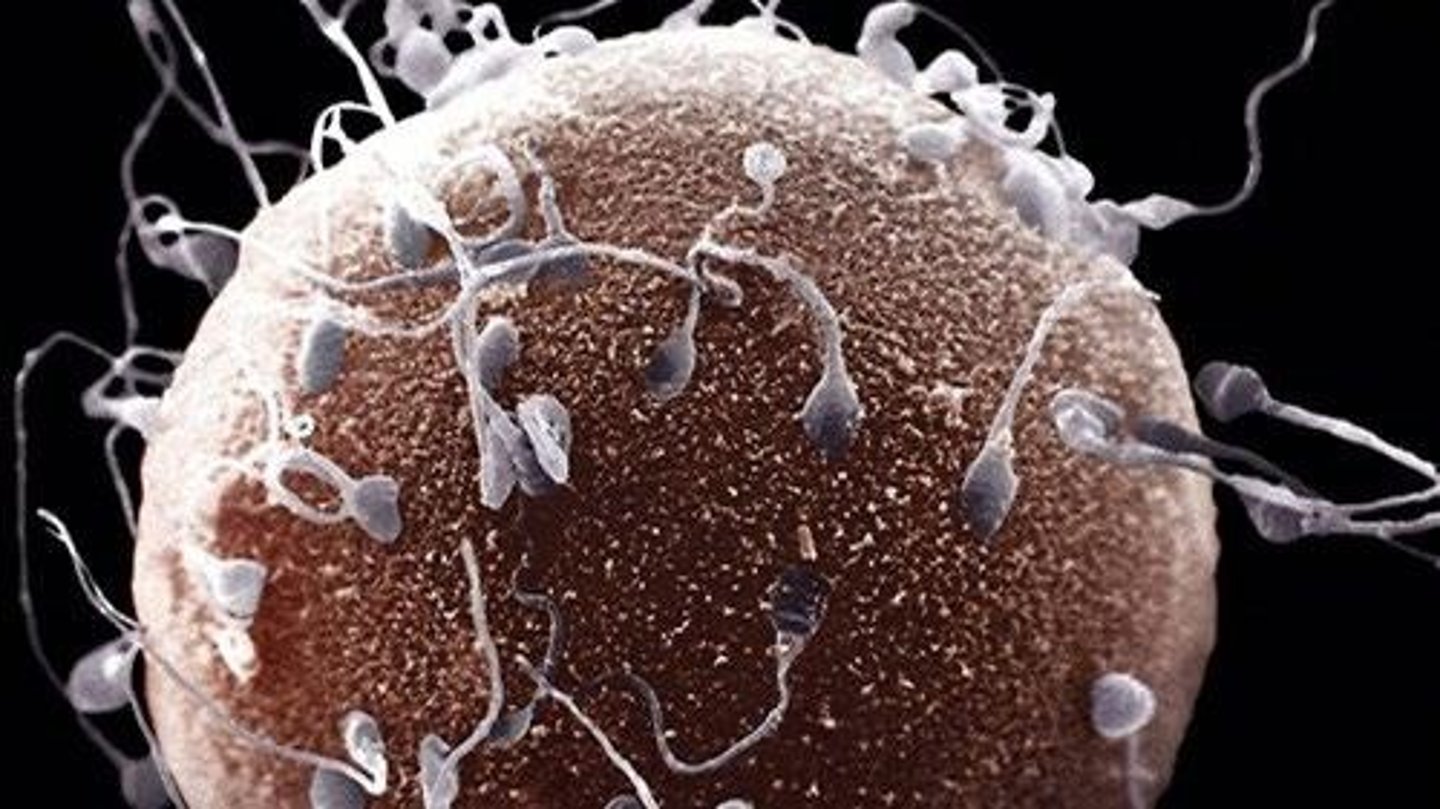
Zona-binding proteins
Proteins on sperm membrane essential for zona binding.
ZP1 and ZP2
Proteins providing structural integrity to zona pellucida.
ZP3
Zona protein that sperm specifically binds to.
Cervical crypts
Grooves in cervix that sperm must navigate.
Insemination
Process of depositing sperm into the female reproductive tract.
Sperm viability
Ability of sperm to survive after insemination.
Fluid secretion
Acts as a vehicle for sperm transport in the tract.
Motility pattern change
Sperm motility alters as capacitation progresses.
Primary zona binding region
Spermatozoa adherence to zona pellucida.
Acrosome reaction promoting region
ZP3 binding initiates acrosomal reaction.
Acrosomal reaction
Fusion of sperm plasma and acrosomal membranes.
Vesiculation
Formation of vesicles during membrane fusion.
Acrosin
Enzyme that hydrolyzes zona proteins.
Perivitelline space
Space between zona pellucida and oocyte membrane.
Fusion protein
Protein enabling sperm-oocyte membrane fusion.
Cortical granules
Granules that release contents post-fusion.
Zona block
Prevents further sperm penetration after fusion.
Polyspermy
Condition of multiple sperm fertilizing an oocyte.
Male pronucleus
Sperm nucleus that decondenses in oocyte.
Syngamy
Fusion of male and female pronuclei.
Zygote
Fertilized egg formed from sperm and oocyte.
Superfecundation
Offspring from multiple sires in one estrus.
Fertile life of sperm
Duration sperm remains fertilizing capable in females.
Bitch sperm lifespan
Fertile for 9-11 days in female tract.
Cow sperm lifespan
Fertile for 1.5-2 days in female tract.
Mare sperm lifespan
Fertile for 4-5 days in female tract.
Woman sperm lifespan
Fertile for 5-6 days in female tract.
Capacitation
Process enabling sperm to fertilize oocyte.
Estrus detection
Critical for timing copulation in agriculture.
Semen deposition sites
Locations where semen is deposited in species.
Sequence of events post-semen deposition
Steps following sperm entry into female tract.