Yr 10 - Movement Analysis
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers: biomechanics levers, applying knowledge of levers to sporting actions, movement terminology, body planes and axe, how the human machine causes movement, muscle structure and slow and fast twitch muscle fibres
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Name the 14 types of synovial joint movements
flexion and extension
adduction and abduction
circumduction and rotation
supination and pronation
depression and elevation
inversion and eversion
plantar flexion and dorsi flexion
Define adduction
movement towards the body’s midline
define abduction
movement away from the body’s midline
define flexion
decrease the angle of a joint
define extension
increase the angle of a joint
define pronation
palms down
define supination
palms up
define elevation
movement upwards/superiorly
define depression
movement downwards/inferiorly
define rotation
turning a structure around it’s long axis
define circumduction
circular motion
define eversion
moving ankle outward
define inversion
moving ankle inward
define plantar flexion
depressing the foot (pointing the toes)
define dorsi flexion
pulling the toes up to the shin
What are the 8 locations for the location of the body?
Superior & inferior
Medial & lateral
Posterior & anterior
Proximal & distal
Define proximal and distal
proximal: towards the origin of limb
distal: further away from the origin of limb
Define medial and lateral
medial: towards the midline of body
lateral: away from the midline
define superior and inferiror
superior: above or nearer the head
inferior: below or further away from the head
define anterior and posterior
anterior: towards the front of the body
posterior: towards the back of the body
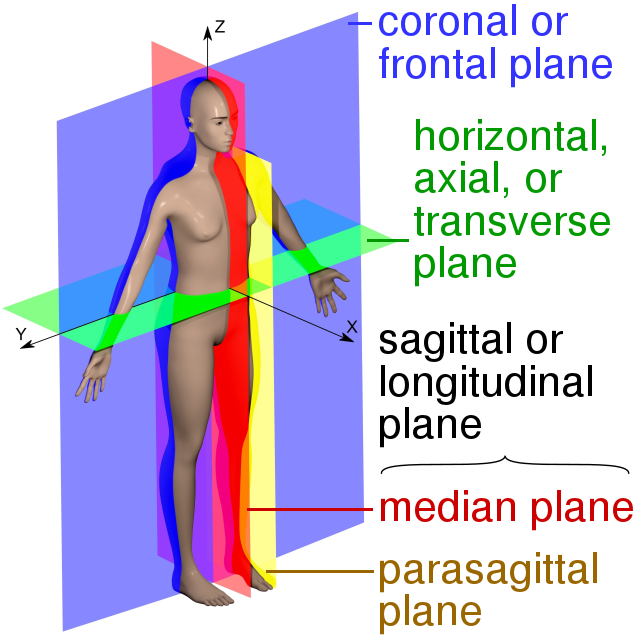
What are the 3 planes of the body
1) Sagittal (cuts the body left to right)
2) Frontal (cuts the body from the back)
3) Traverse (cuts the body from top to bottom)
→ planes cut the body in centre of gravity
What are the muscle contractions:
Isotonic - muscle length changes
1) Concentric - muscle shortens
2) Eccentric - muscle lengthens
Isometric - muscle length stays the same
Define antagonistic pair/reciprocal inhibition
2 muscles that work with each other to facilitate movement
Agonist is the prime mover, responsible for the movement (contracts)
Agonistic muscle opposes the movement (relaxes).
Define scalar
Measurement with only 1 size (length, volume, area, mass)
Define vector
Measurement that includes both size and direction (acceleration, velocity, momentum)
Define distance
How far an object travels (scalar)
Define force
Mass x acceration (vector)
Define speed
distance moved per unit of time (vector)
Define velocity
speed in a given direction (vector)
Define displacement
the change of postion of object (diff of SP and EP) (vector)
Define acceleration
rate body changes it’s velocity (vector)
Define momentum
measure amount of motion possessed by a moving body (vector)
mass x velocity
Define impulse
product of the force applied to an object or body, and the duration it is applied for
force x time (vector)
In a lever class, what is the lever, fulcrum, load and effort
Lever: bone
Fulcrum: joint
Load: force applied to the body (such as body weight or dumbbell)
Effort: muscles that moves the force
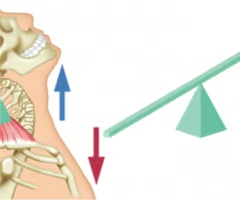
First lever class
Fulcrum between force and effort
force: fulcrum: effort
such as: tilting the head up
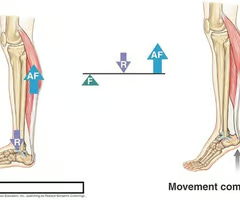
second lever class
load between the fulcrum and effort
fulcrum: load: effort
such as: lifting the heel (plantar flexion)
overcome resistance better than generating speed
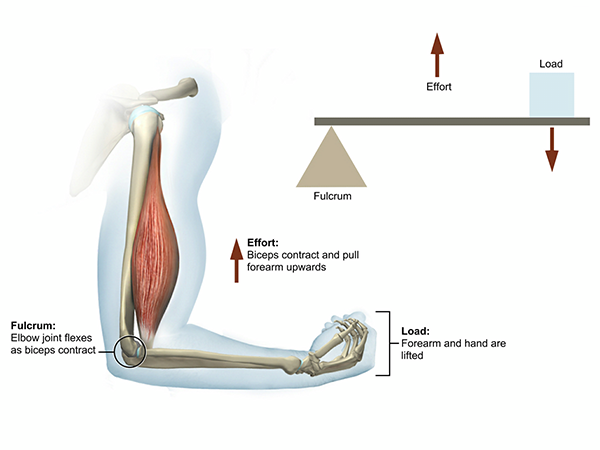
third lever class
effort in the middle
fulcrum: effort: load
such as: bicep curl
most common
increase speed and full range of movement
What is mechanical advantage?
ratio of input:output of force
if input force creates greater output force there is MA
What are the 3 factors that impact projectile motion?
1) Height of release (higher the more distance - more time spent in air)
2) Angle of release (optimal angle usually 45)
3) Speed of release (how fast object is released (muscle force))
What are the factors that impact projectile movement during motion/flight?
1) gravity - decreases height
2) spin - change height, direction (move to least air pressure)
3) air resistance - affect by SA, type, speed and mass of ball
What is articular cartilage?
thin white layer of cartilage around the end of bones
reduce friction to protect bones
absorb shock
limits movement for structural support
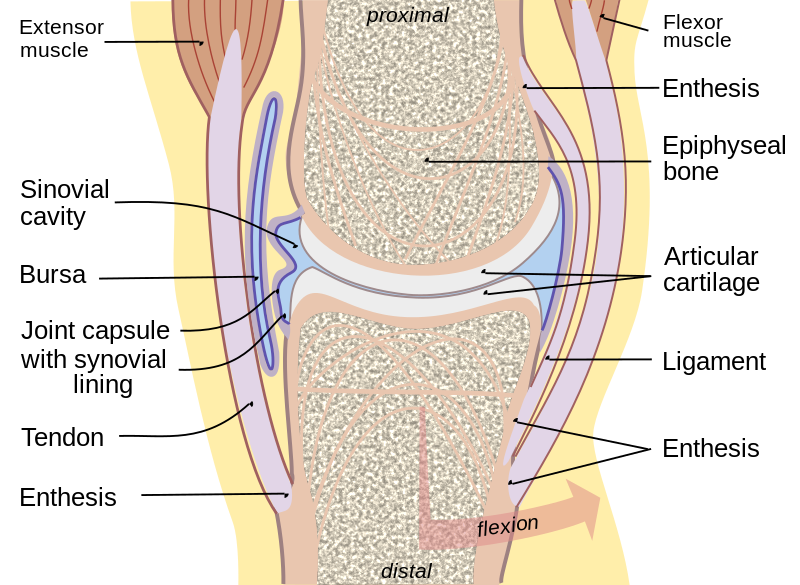
What is synovial fluid?
liquid coats and lubricates articular cartilage
prevents friction of the articular cartilage during movement
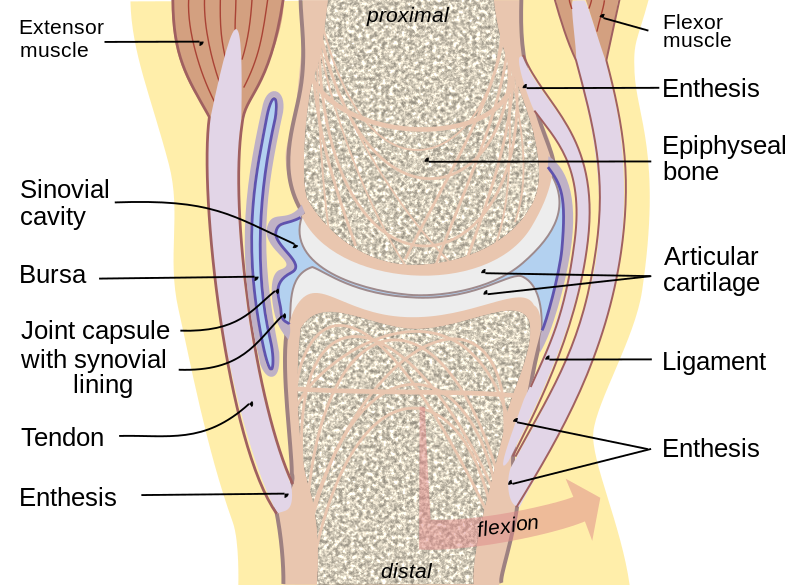
What is articular capsule?
2 structures
Outer: Fibrous capsule - help support and prevent joint separating
Inner: Synovial membrane - secrete synovial fluid to reduce friction
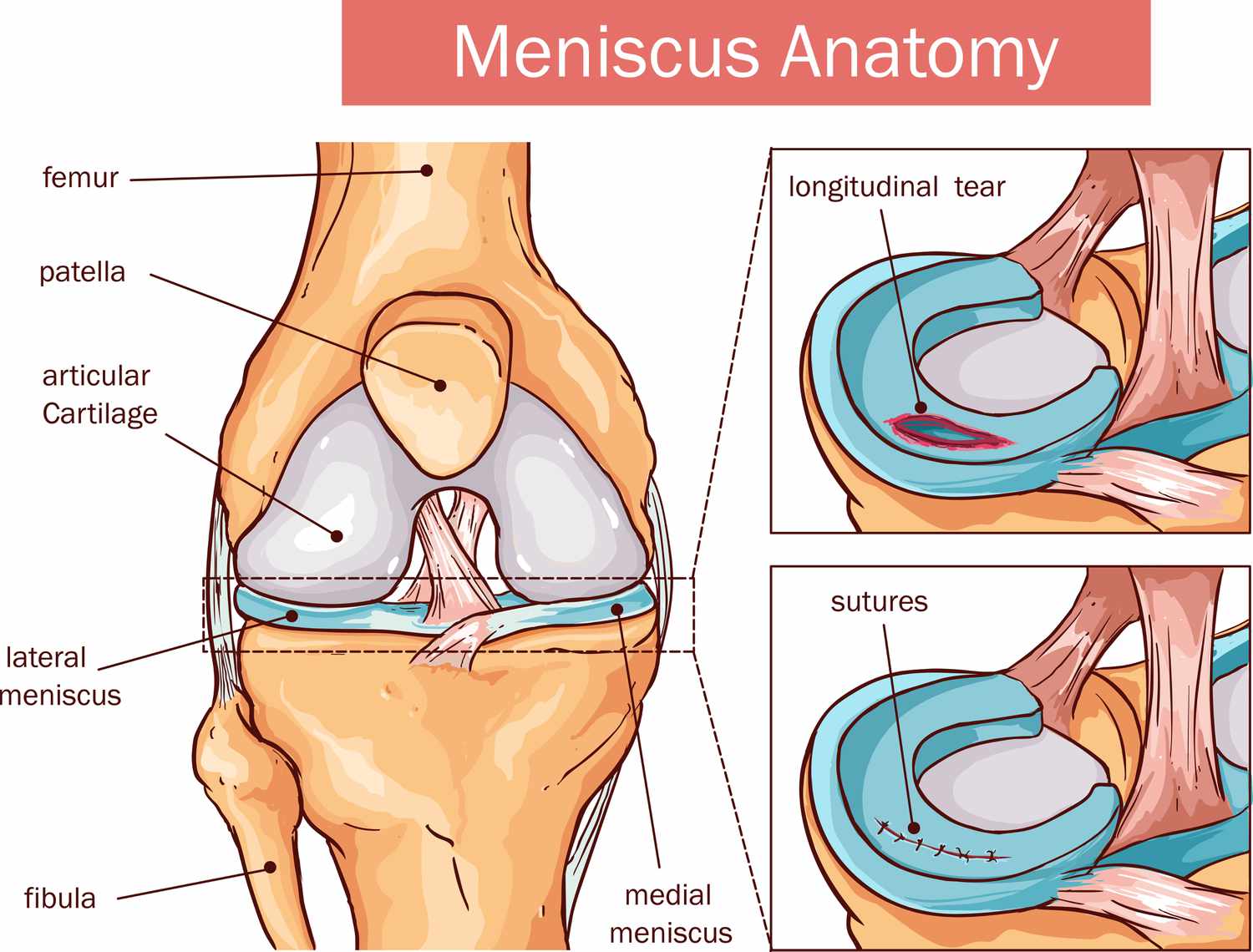
what is meniscus?
semilunar discs between some articulating bones
allow bones to fit together tightly
provide cushioning for joint
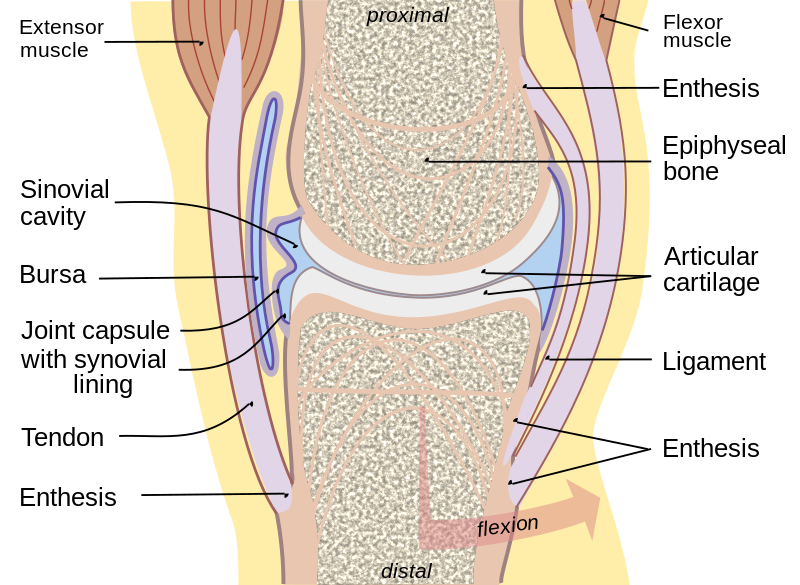
What is bursae?
small fluid-filled sac
prevents friction
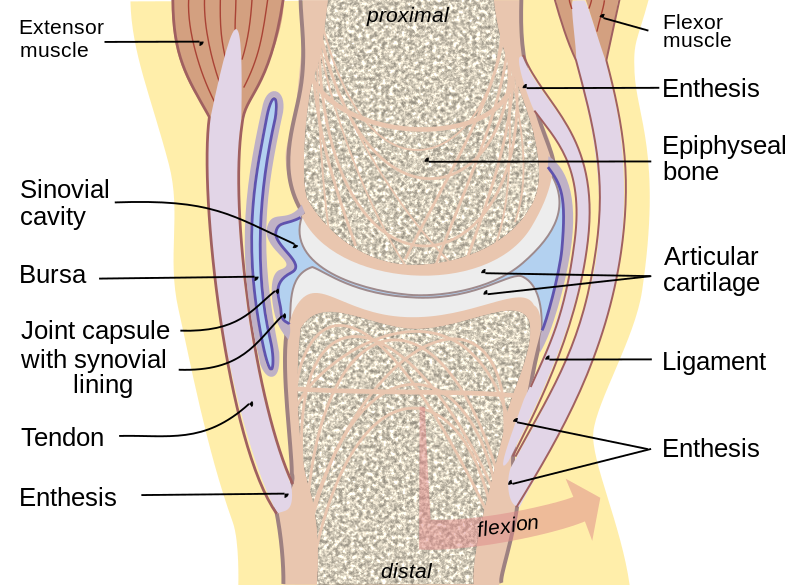
Origin of muscle
attachment of muscle tendon to a stationary bone
Insertion of muscle
attachment of muscle tendon to a moveable bone
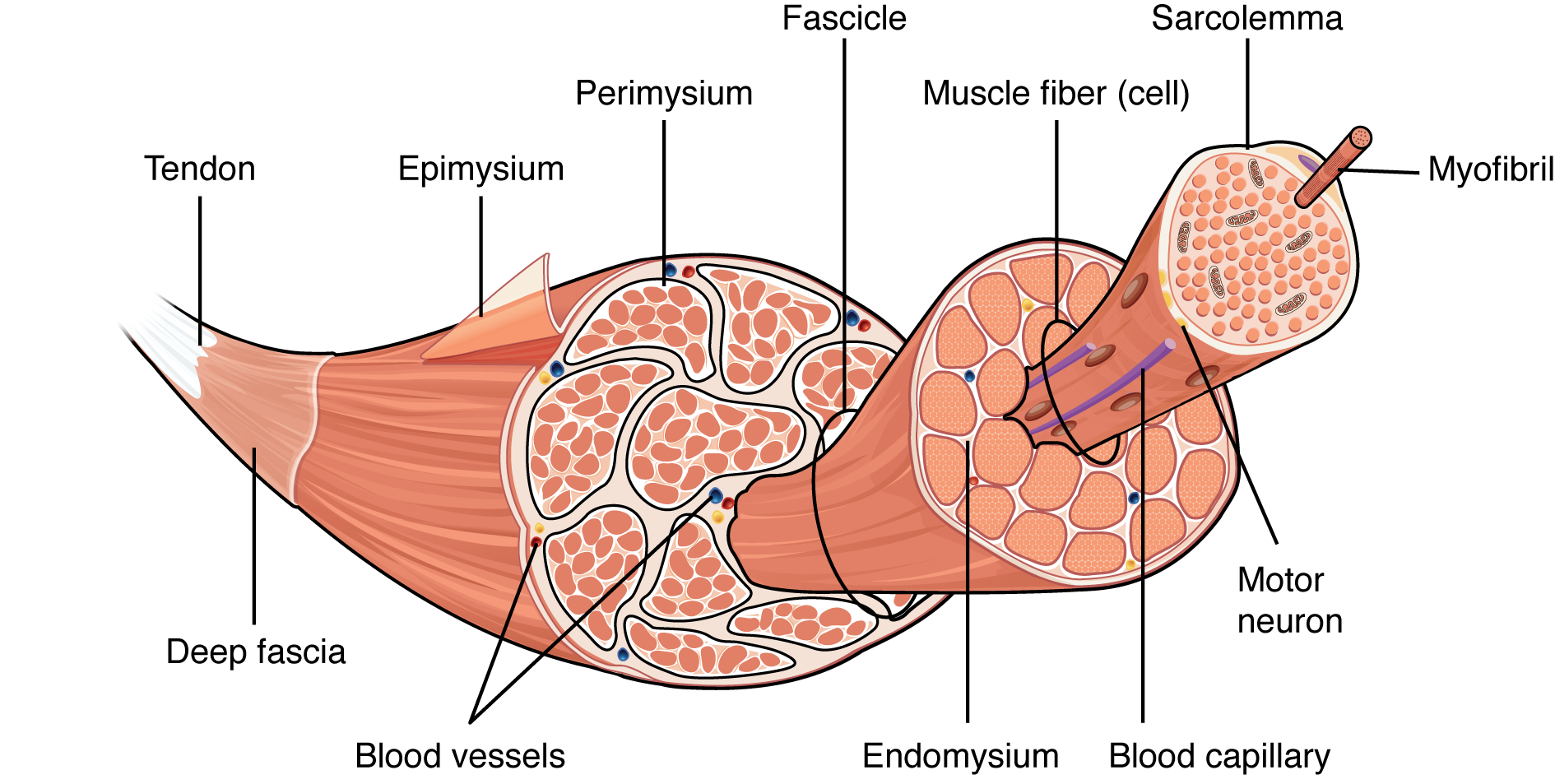
What is epimysium?
connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle (protects from friction against other muscles and bones)
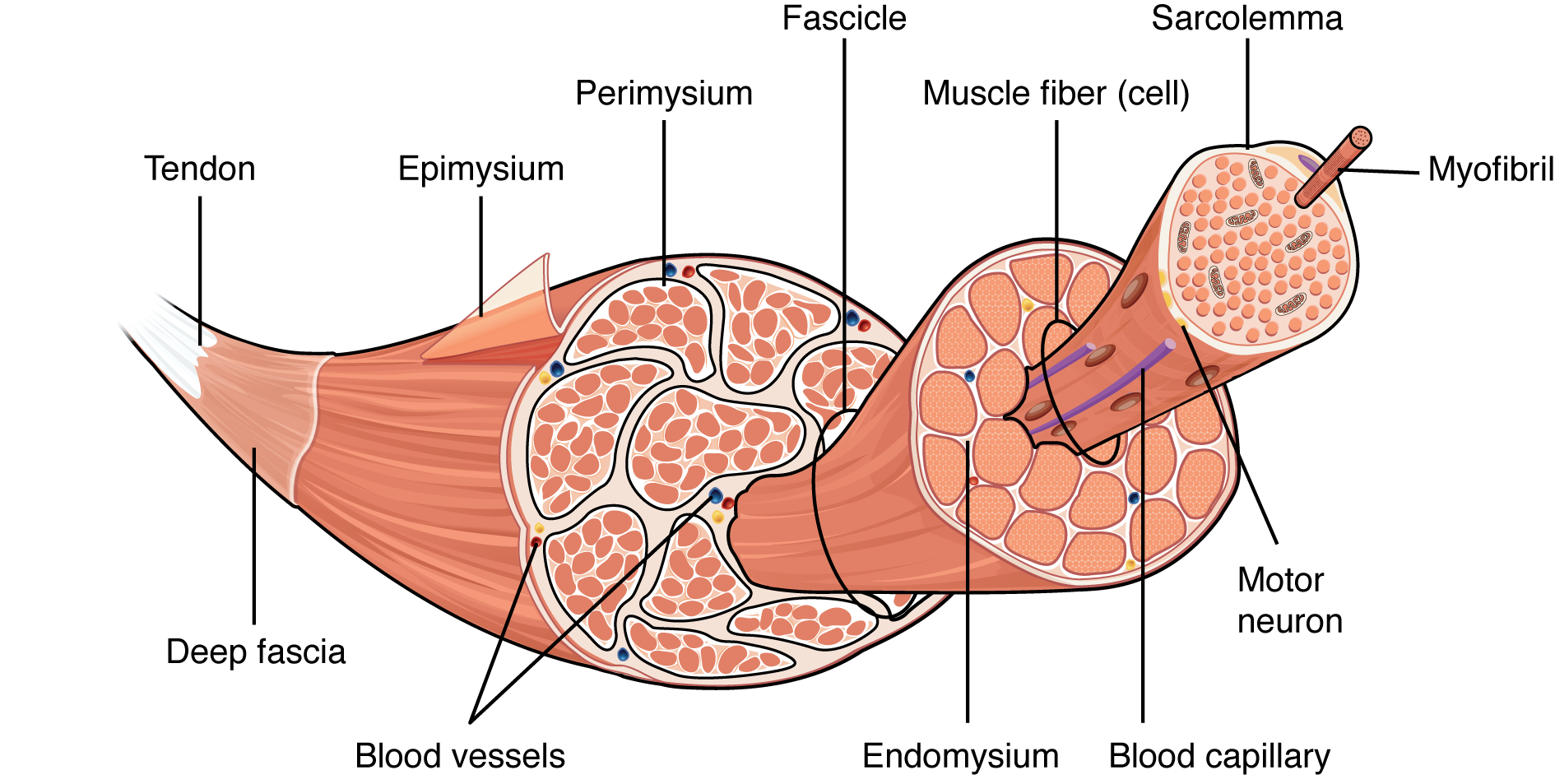
What is perimysium?
branching connective tissue within muscle tissue
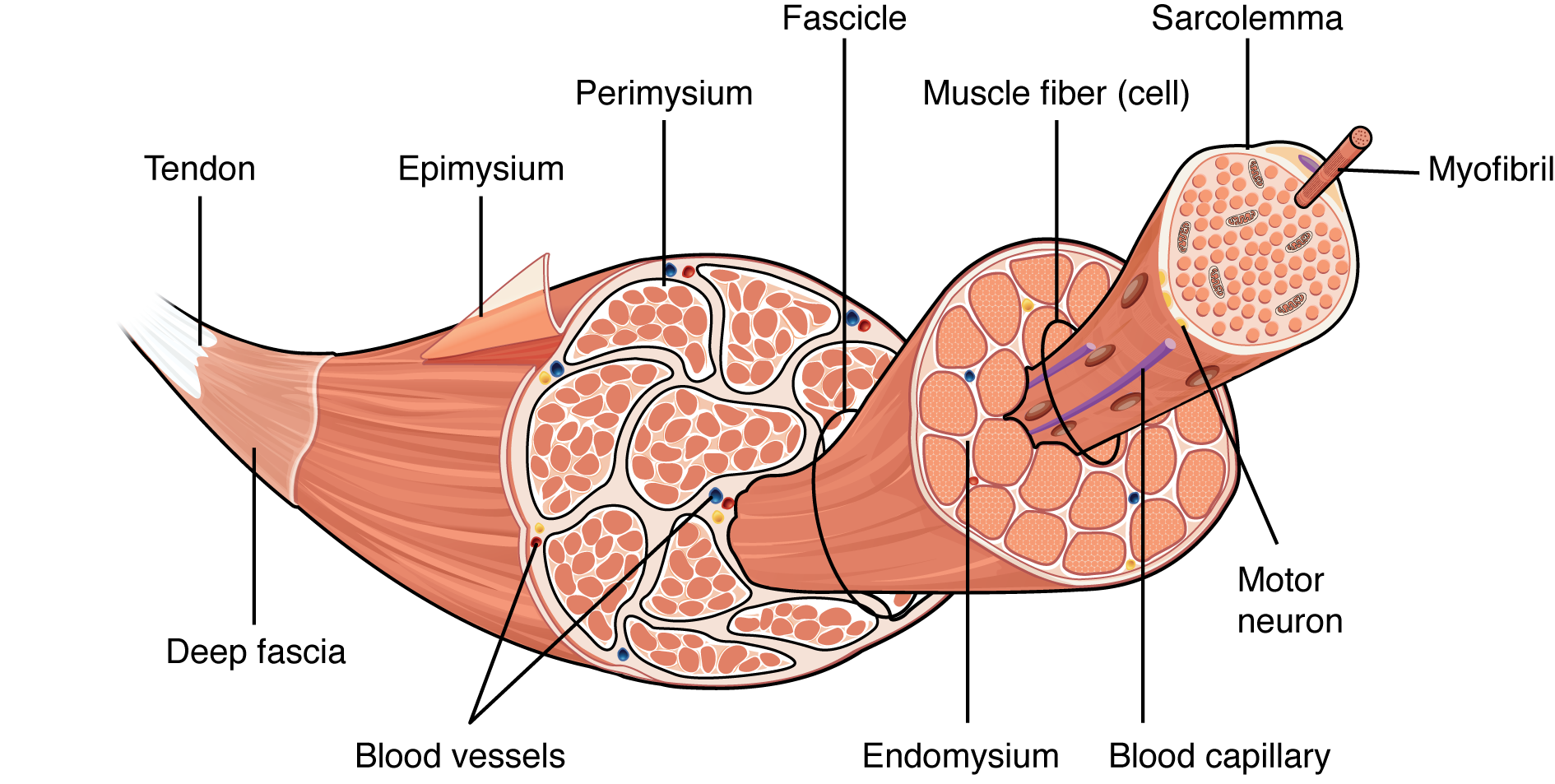
What is endomysium?
thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fibre
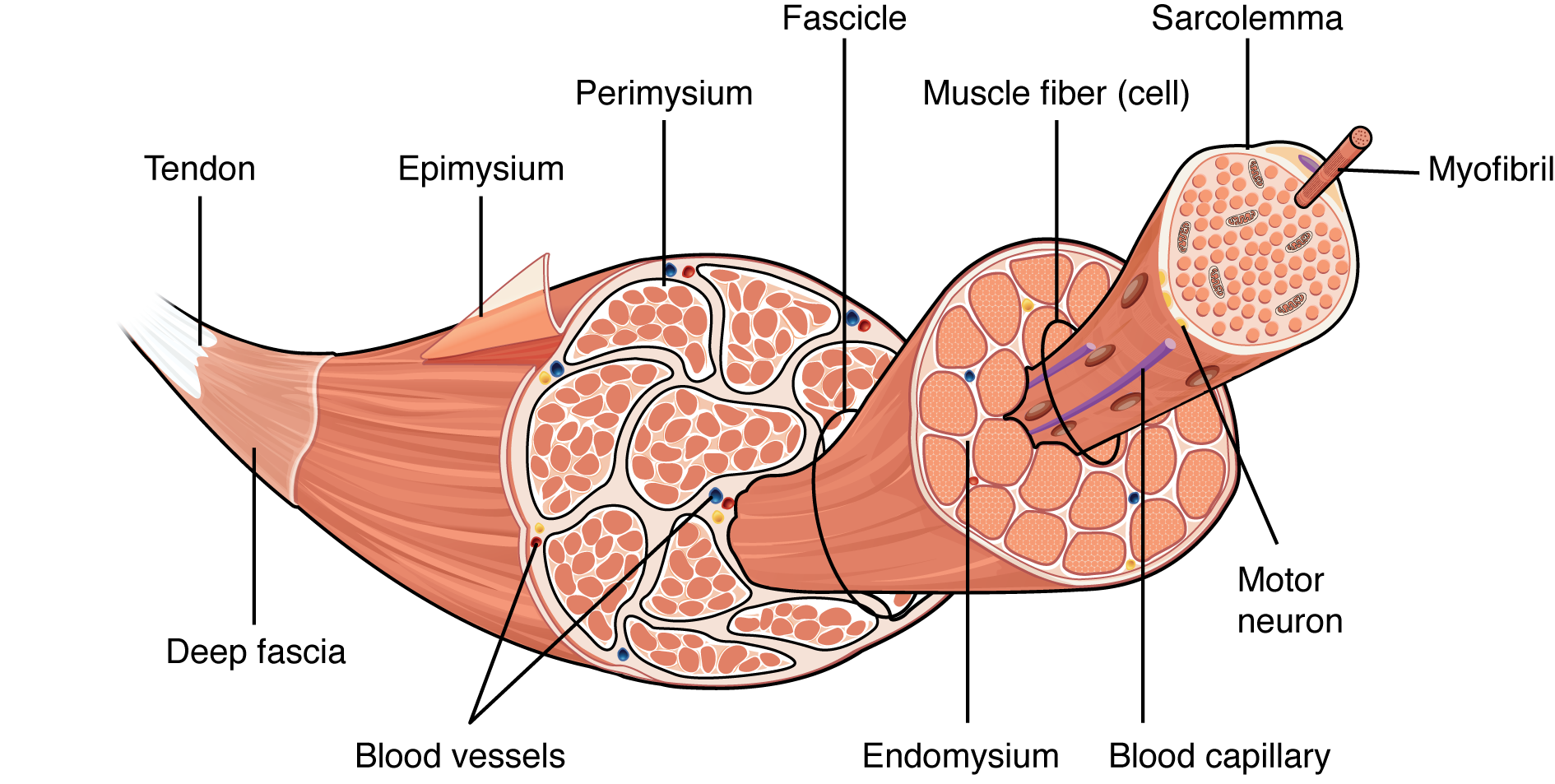
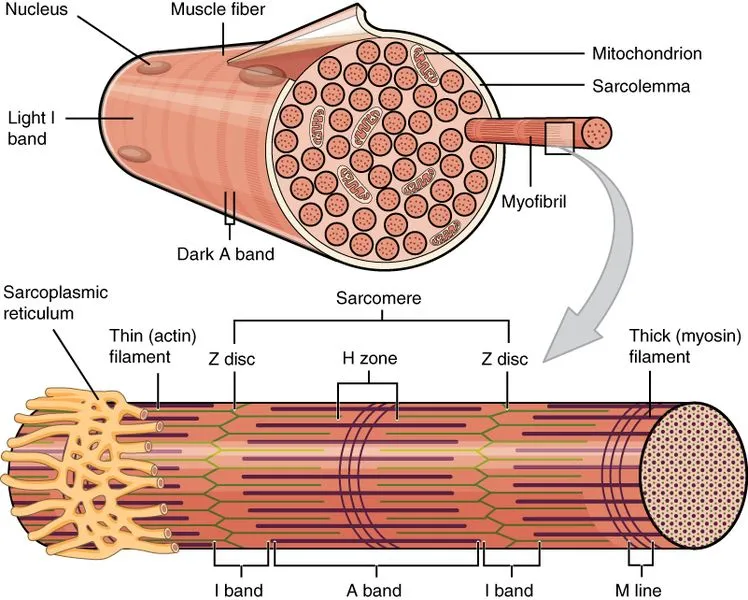
What is myofibril?
cylindrical structure within a muscle cell that has repeating segments of sarcomere
what is myofilaments?
inside the sarcomere → contract the muscle
thick = myosin
thin = actin
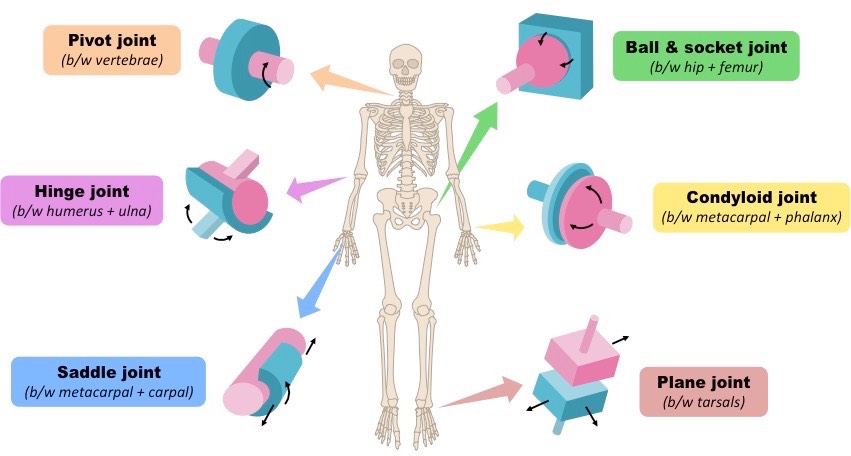
what are the types of synovial joints? (6)
gliding
pivot
hinge
condyloid
saddle
ball and socket
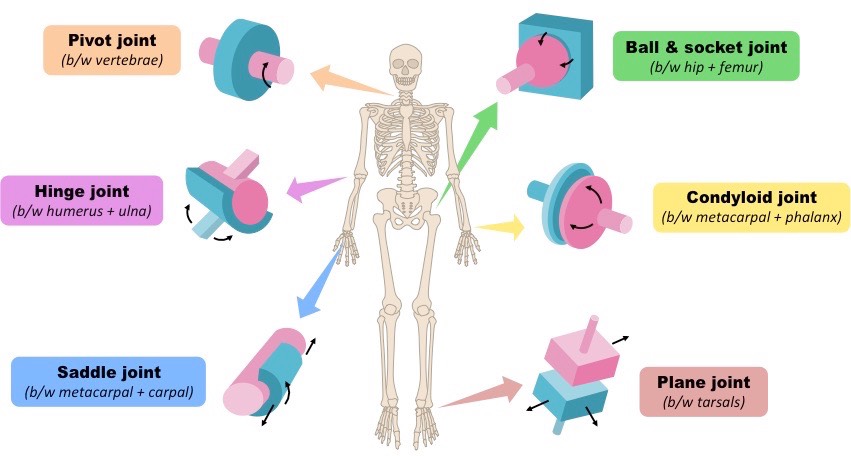
Gliding
Mono-axial
gliding movement
location: tarsals and carpals
Hinge
Mono-axial
extension & flexion
location: knee and elbow (ulna to humerus)
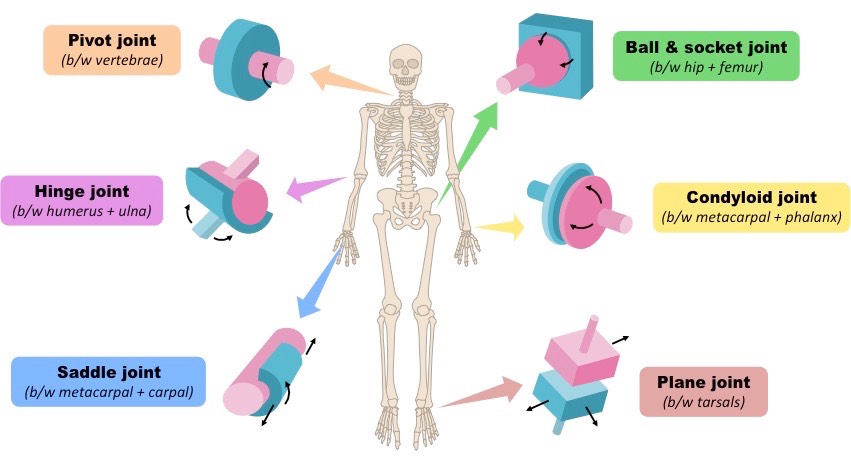
Pivot
mono-axial
rotation
location: neck - vertebrae (C1-2)
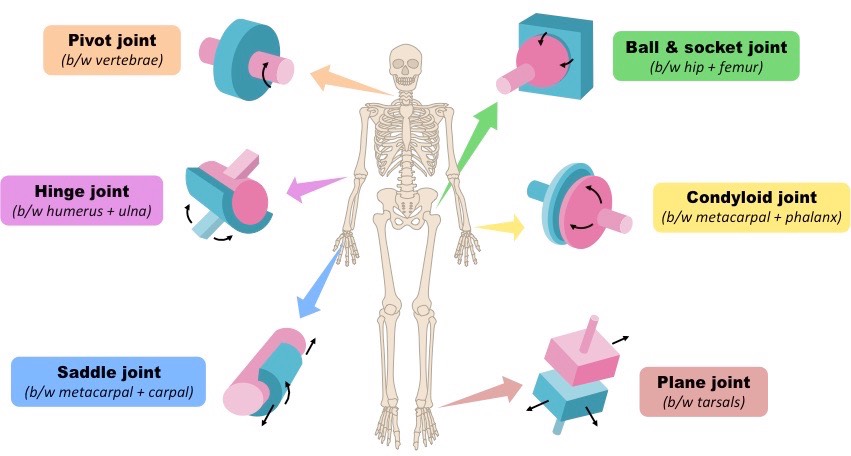
Saddle
bi-axial
extension/flexion, adduction/abduction, circumduction
location: thumb (metacarpals and carpals)
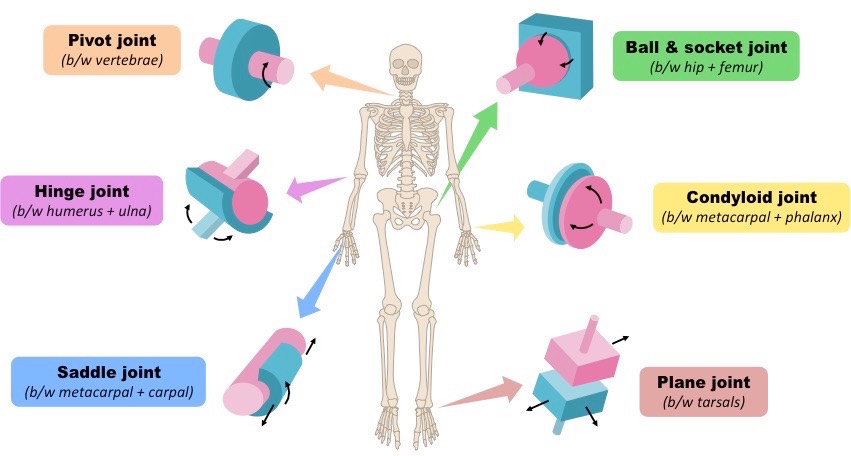
Condyloid
bi-axial
extension/flexion, adduction/abduction, circumduction
location: wrist (radius to carpals) and hand (metacarpals to phalanges)
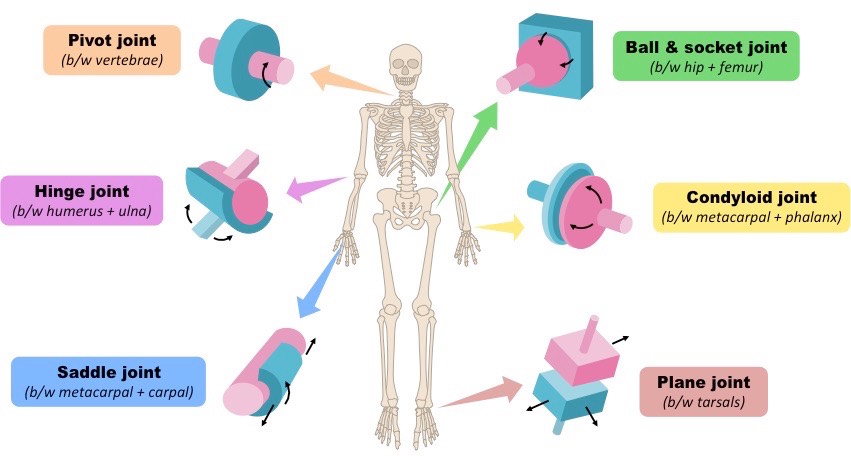
Ball and Socket
tri-axial (all movements)
extension/flexion, adduction/abduction, circumduction/rotation
Location: shoulder and hip
What is the appendicular and axial skeleton?
1) Axial - bones close to the midline
Cranium
Sternum
Vertebrae (include sacrum and coccyx)
Rib cage
2) Appendicular - bones that attach to the axial skeleton (more lateral)
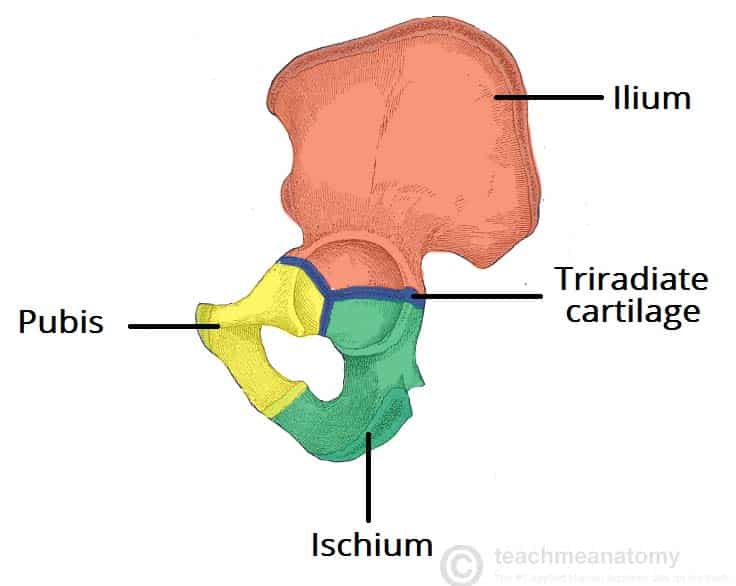
Pelvic girdle (illum and ischium)
Pectoral girdle (clavicle, scapula)
Humerus, ulna, radius
Femur, tibia, fibula
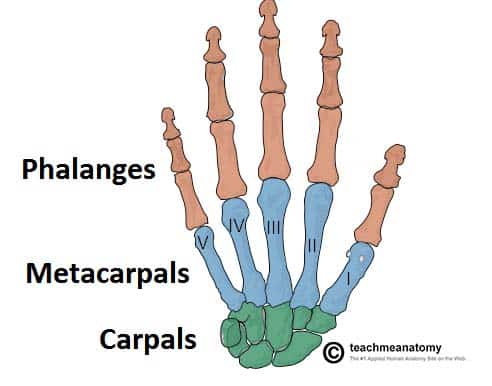
carpal + tarsal group
Draw the illum and ischium location
Hand structure (bone)
carpals → metacarpals → phalanges
tarsals → metatarsals → Phalanges
What are the 3 types of muscles?
Smooth (involuntary)
→ located in walls of hollow internal organs + intestines
Skeletal (voluntary)
→ attached to bones/other connective tissue
Cardiac (involuntary)
→ located in heart
Antagonistic pair of the knee/legs
Quadriceps (agonist when extending)
Hamstrings (agonist when flexing)
Antagonistic pair of the arm
Bicep brachii (agonist when flexing)
Tricep brachii (agonist when extending)
Antagonistic pair of the shoulder (adduction + abduction)
Deltoid (agonist when abduction)
pectoralis major (agonist when adduction)
Antagonistic pair of the shoulder (pulling shoulder blades back and forward)
trapezius and latissimus dorsi (shoulder posteriorly/behind)
pectoralis major (bringing it back)
Antagonistic pair of the chest
Shrugging (up)
Trapezius (agonist)
levator scapulae (antagonist)
what is linear and angular motion?
1) linear - movement straight line
2) angular - movement around a joint or axis of rotation
Define projectile motion
object that is thrown or projected into the air at an angle
define trajectory/flight path
a projectile’s path (curved)