Hormones of the endocrine system.
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Estrogen
controls development of female secondary sexual characteristics; secreted from the ovaries
adrenaline (epinephrine)
released by adrenal medulla in response to critical stress; ;flight or fight; dialates pupils, increases blood pressure and oxygen levels.

insulin(BETA CELLS)
lowers blood glucose; instructs liver and muscle cells to absorb glucose and store it as glycogen.
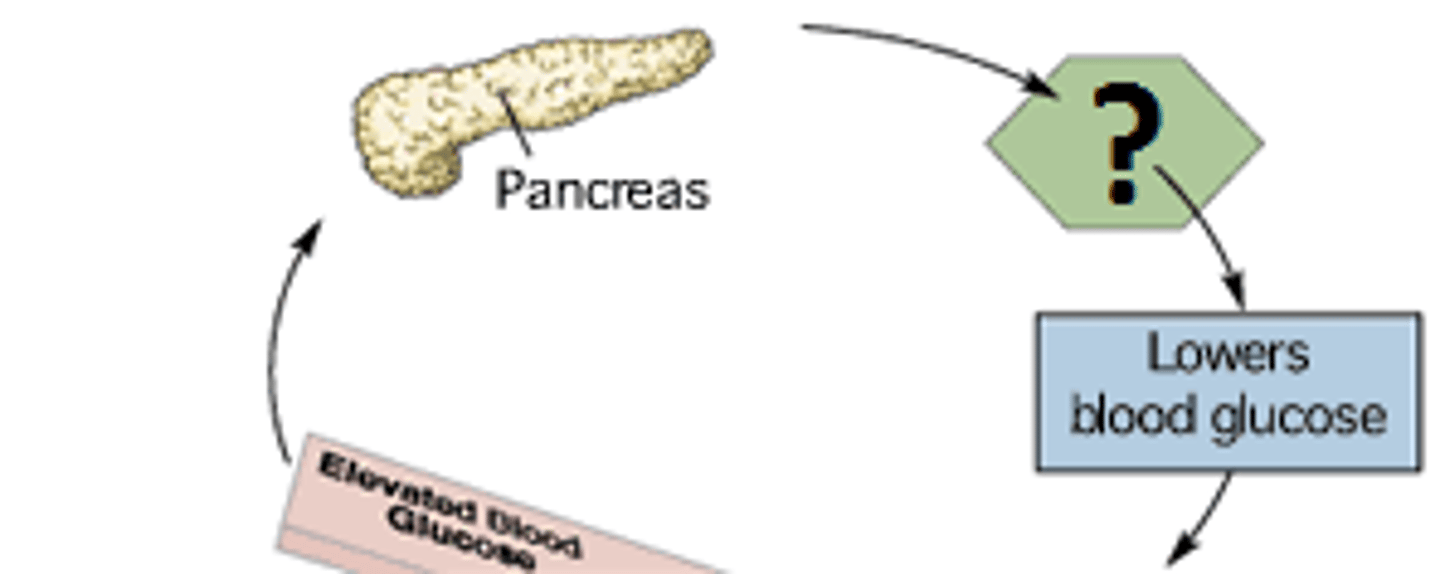
Glucagon (ALPHA CELL)
increases blood glucose levels; instructs liver and muscle cells to convert glycogen to glucose.
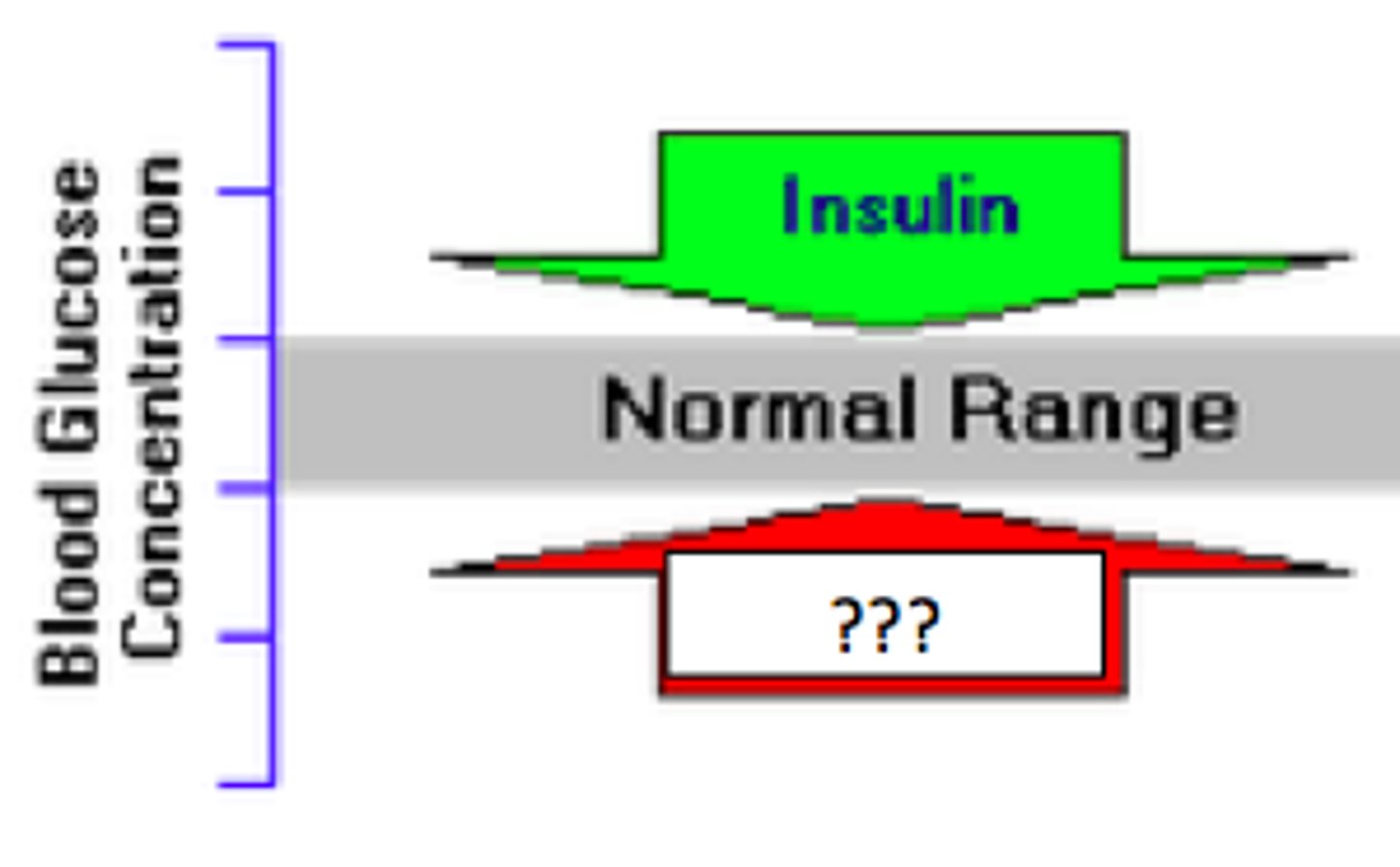
Testosterone
responsible for secondary sex characteristics; in men facial hair, deepened voice.
Hormone
a chemical messenger; secreted by glands directly into the bloodstream; travels round the body dissolved in blood plasma
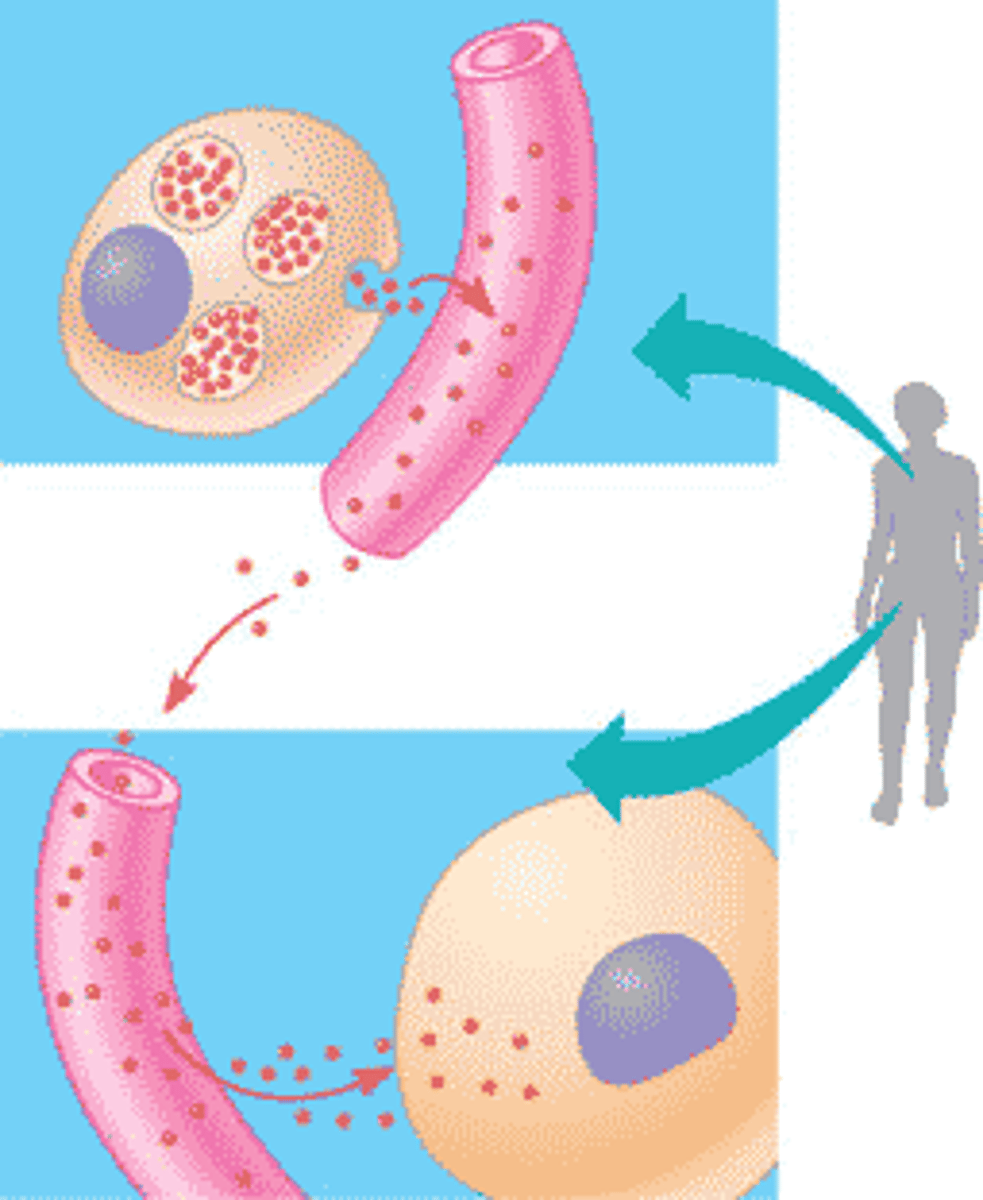
target organ/cells
contains receptors on its cells allowing the hormone to bind to the cell membrane and deliver its instructional message
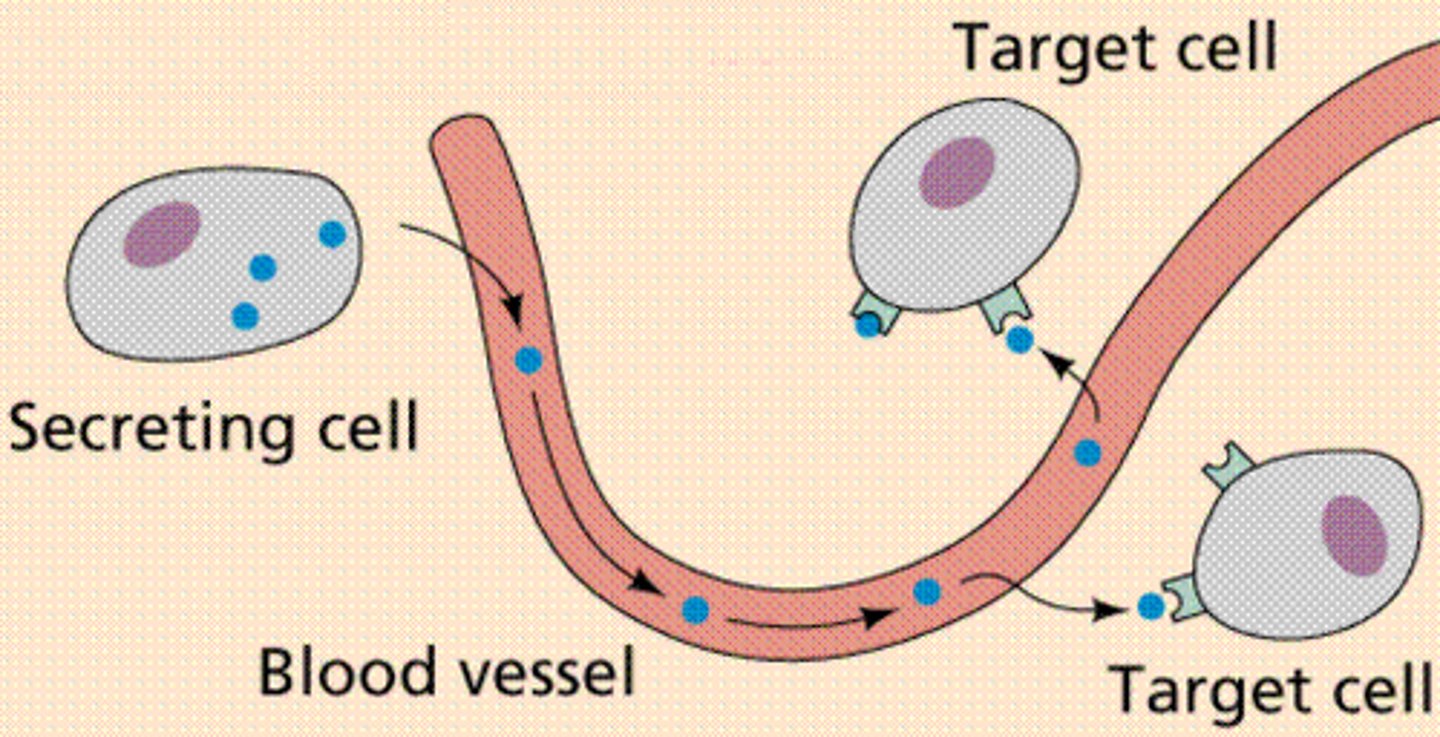
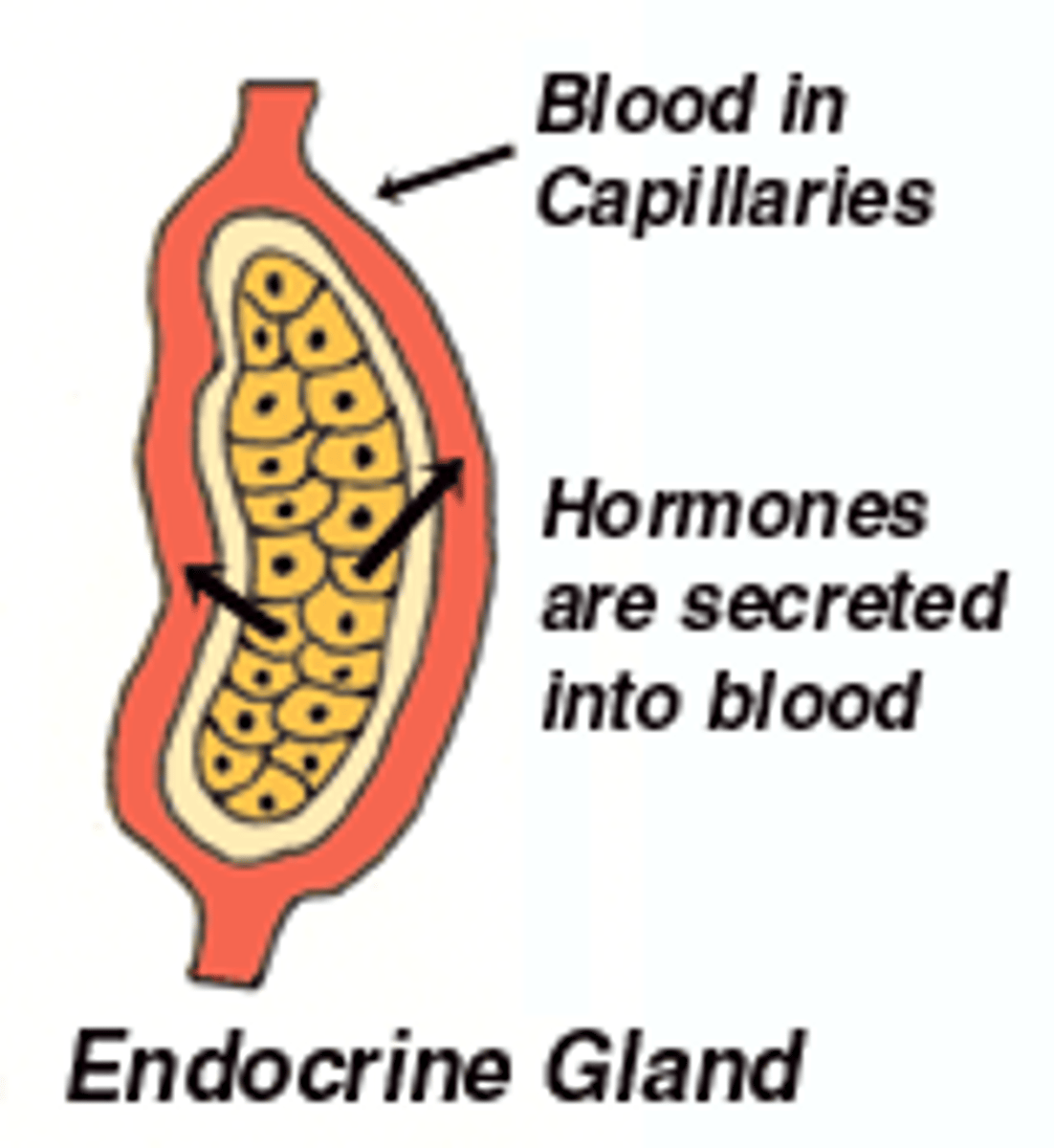
endocrine gland
ductless glands, secreting hormones directly into the blood vessels that pass through the gland
Steroid hormone
A lipid-soluble hormone which brings about a change by binding directly to receptors in the cytoplasm or on the nucleus, bringing about a transcriptional change

Non-steroid/Peptide hormone
A hydrophilic hormone which binds to a receptor on the cell surface membrane and brings about a transcriptional change via second messengers
Pancreas
Gland in the abdomen which produces insulin and glucagon
Pineal gland
Gland in the brain which produces melatonin
Pituitary gland
Gland in the brain responsible for regulating the endocrine system; releases ADH, growth hormone and gonadotrophins
Leptin
suppresses appetite; stimulates increased energy expenditure. secreted by adipocytes
Calcitonin
Decreases the amount of calcium in the blood;osteoblast
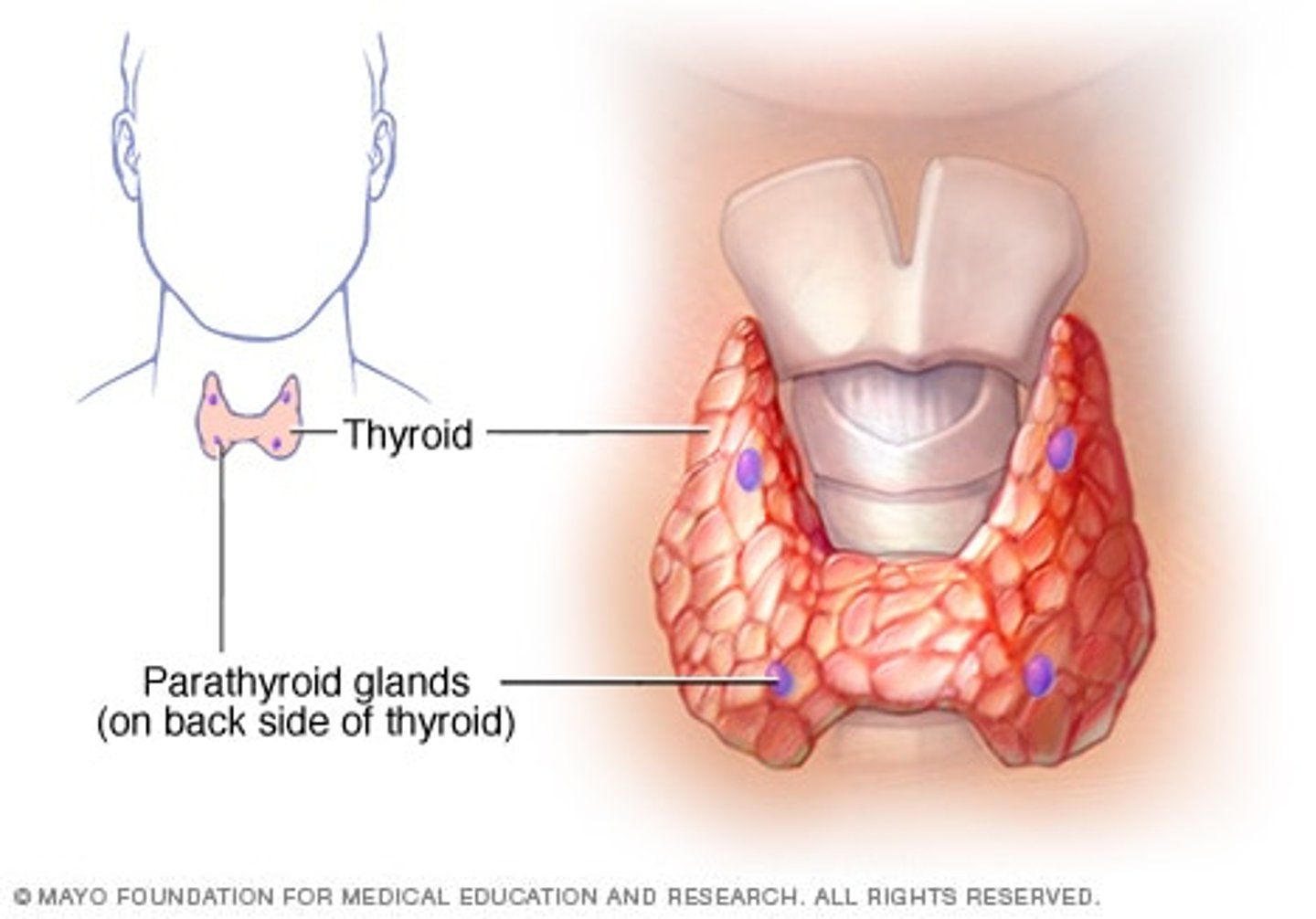
Parathyroid
Increases calcium levels in the blood.
ADH
Stops Urine production and reabsorbs water.
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone)
a hormone secreted by the hypothalamus that regulates the pituitary's secretion of gonad-stimulating hormones like FSH and LH
CTRH
Lutenizing (LH)
Stimulates ovulation; testosterone synthesis
CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone)
released by hypothalamus; stimulates release of ACTH
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
Promotes secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin (PRL)
GHRH (growth hormone releasing hormone)
stimulates release of growth hormone
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
a hormone that influences the maturing of eggs and production of sperm
LH (luteinizing hormone)
a hormone that causes the secretion of sex hormones by the testes and ovaries
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
stimulates secretion of hormones by adrenal cortex
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
Stimulates thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
Prolactin
stimulates milk production
Oxytocin
A hormone released by the posterior pituitary that stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and milk ejection during breastfeeding.
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH, vasopressin)
A hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that increases the permeability of cells membranes, so they absorb more water, especially from urine, stops urine production
Thymosin
stimulates the maturation of lymphocytes into T cells of the immune system
Hypothalamus
brain region controlling the pituitary gland
Thymus
thymosin
growth hormone
hormone secreted by anterior pituitary gland that stimulates growth of bones/muscles
Cortisol
stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex
parathyroid hormone
increases blood calcium levels by encouraging bone resorption by osteoclasts
Aldosterone
Hormone that stimulates the kidney to retain sodium ions and water; higher blood pressure.
Relaxin
a hormone secreted by the placenta that causes the cervix to dilate and prepares the uterus for the action of oxytocin during labor.
Inhibin
inhibits secretion of FSH
Melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that causes sleepiness.
melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
increases the production of melanin in melanocytes of the skin
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
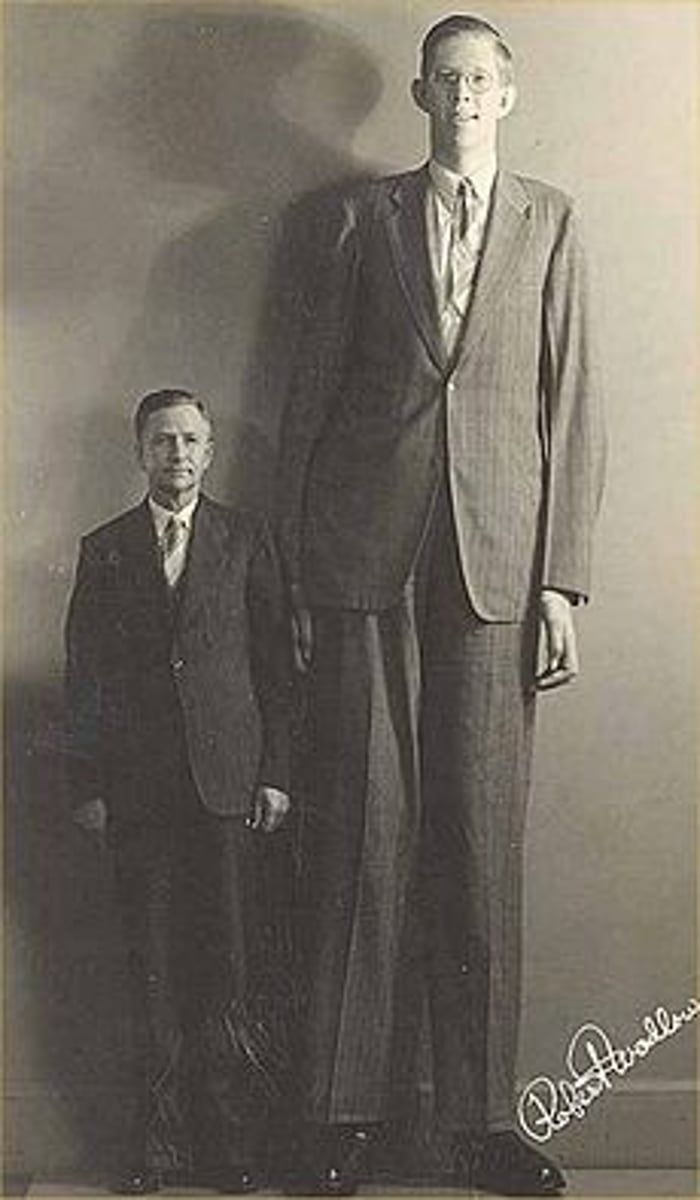
Gigantism
a condition produced by hypersecretion of growth hormone during the early years of life

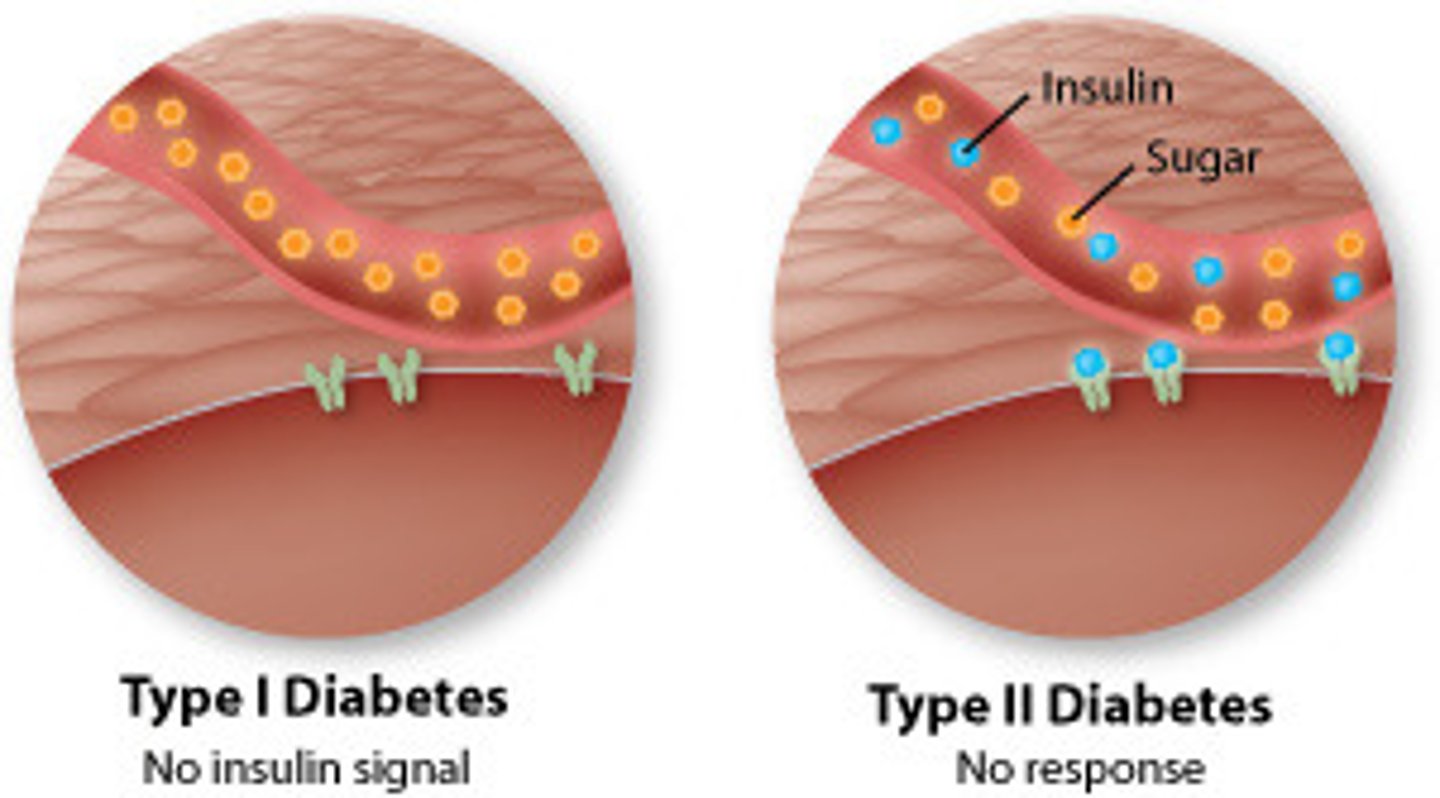
diabetes mellitus
hyposecretion of insulin or tissues are resistant to its effects.
Addison's disease
occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of the hormone's cortisol or aldosterone
Cushing's disease
Hypersecretion of cortisol; weight gain in belly and face.
Graves disease
an autoimmune disorder that is caused by hyperthyroidism and is characterized by bulging eyeballs, tremors, high heartrate, palpitations, and nervousness.
Drawfism
Short stature caused by deficient levels of growth hormones. Caused by hypopituitarism
