Osmosis and diffusion
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
investigate the way in which materials can move into and out of cells, including but not limited to: • conducting a practical investigation modelling diffusion and osmosis (ACSBL046) • examining the roles of active transport, endocytosis and exocytosis (ACSBL046) • relating the exchange of materials across membranes to the surface-area-to-volume ratio, concentration gradients and characteristics of the materials being exchanged (ACSBL047)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
isotonic
Isotonic = the amount of water going into the cell is the same amount going out of the cell is at an equal rate
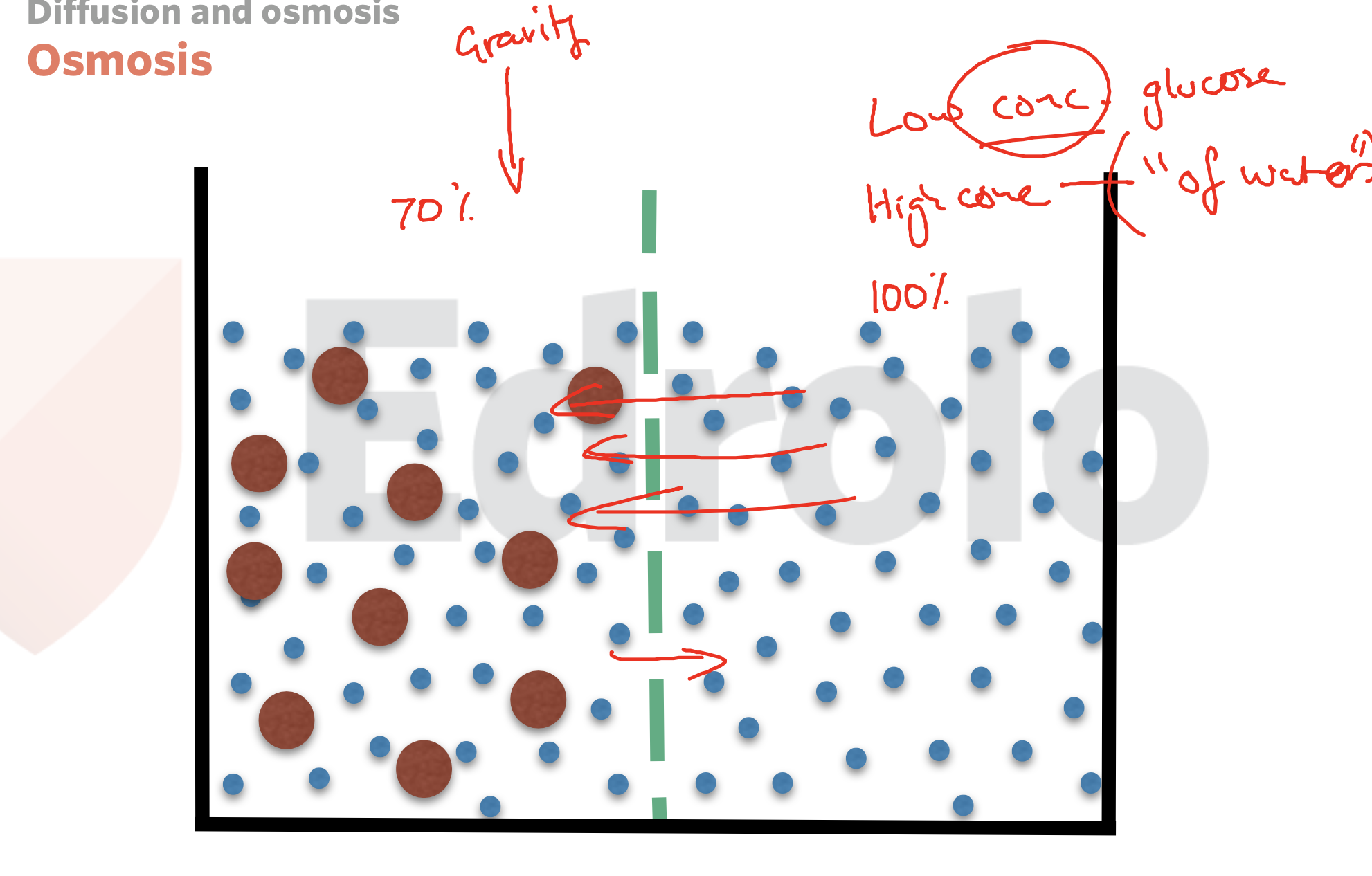
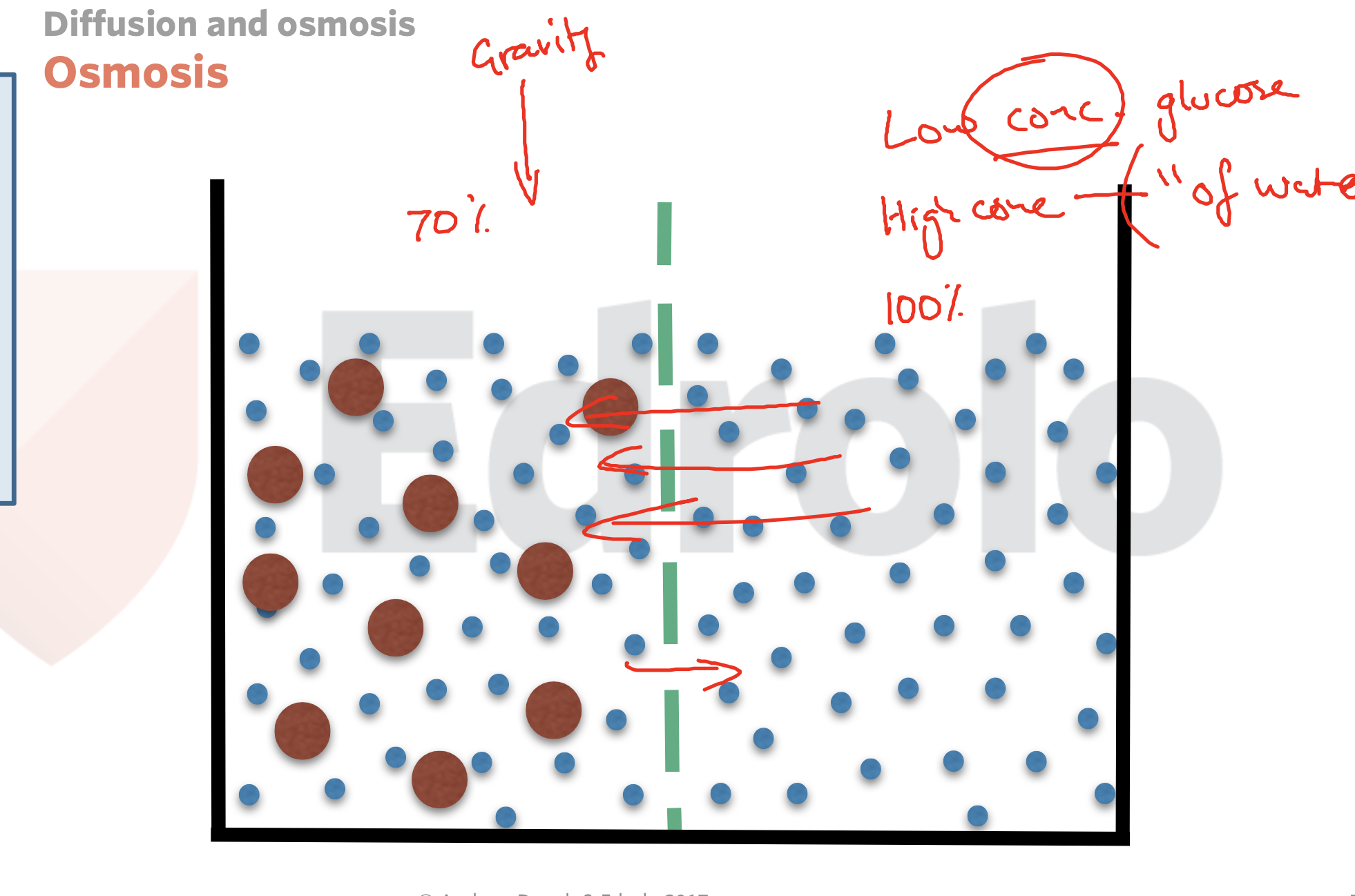
osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water from high to low concentration
It is passive doesn't need energy
Movement must travel across a semipermeable membrane
Water is the only thing that movies in osmosis
Semipermeable is selective
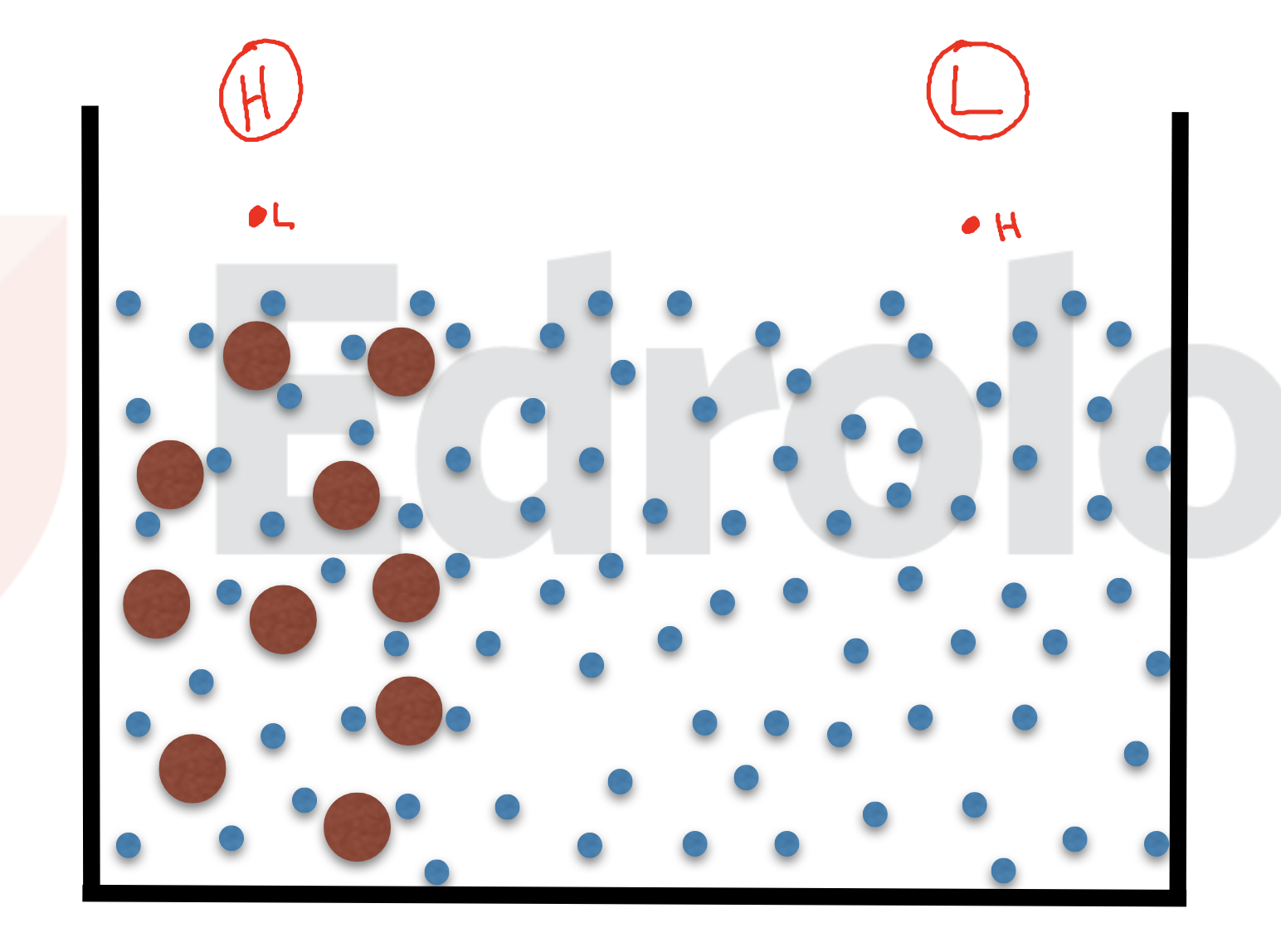
diffusion
Diffusion: Is the dispersion of molecules into an available space. High to low concentration
Passive diffusion= cell movement into other cells without energy
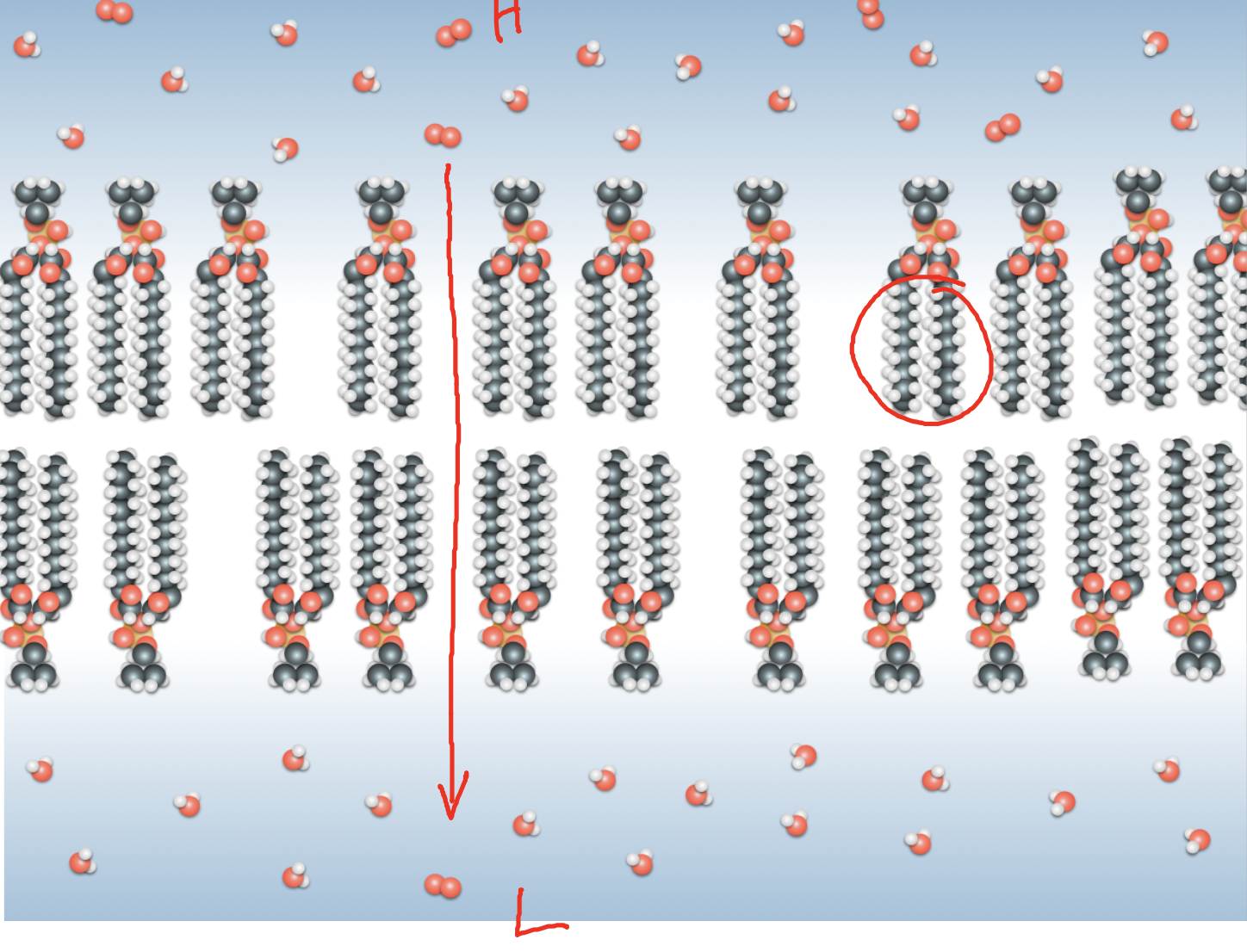
simple diffusion
The passive net
movement of a
substance from a
region with a high
concentration to a
region with a low
concentration.
facilitated diffusion
facilitated/active transport = cells changed shape in order to fit into the heads via channel or carrier proteins, channel means changing shape to pass through something.
carrier protien
Carrier protein hooks on to the cell and forces the cell to change shape and fit through the bilayer.
hypertonic
Hypertonic= water keeps moving out of the cell and shrinks or flaccid in plants
Hypotonic
Hypotonic = water keeps moving into the cell and cant allow water to get out keeps moving in.
passive diffusion
cell movement into other cells without energy
facilitated/active transport
Facilitated/active transport = cells changed shape in order to fit into the heads via channel or carrier proteins, channel means changing shape to pass through something.