CSUF ART 201A Exam 1: Art History Terms & Definitions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
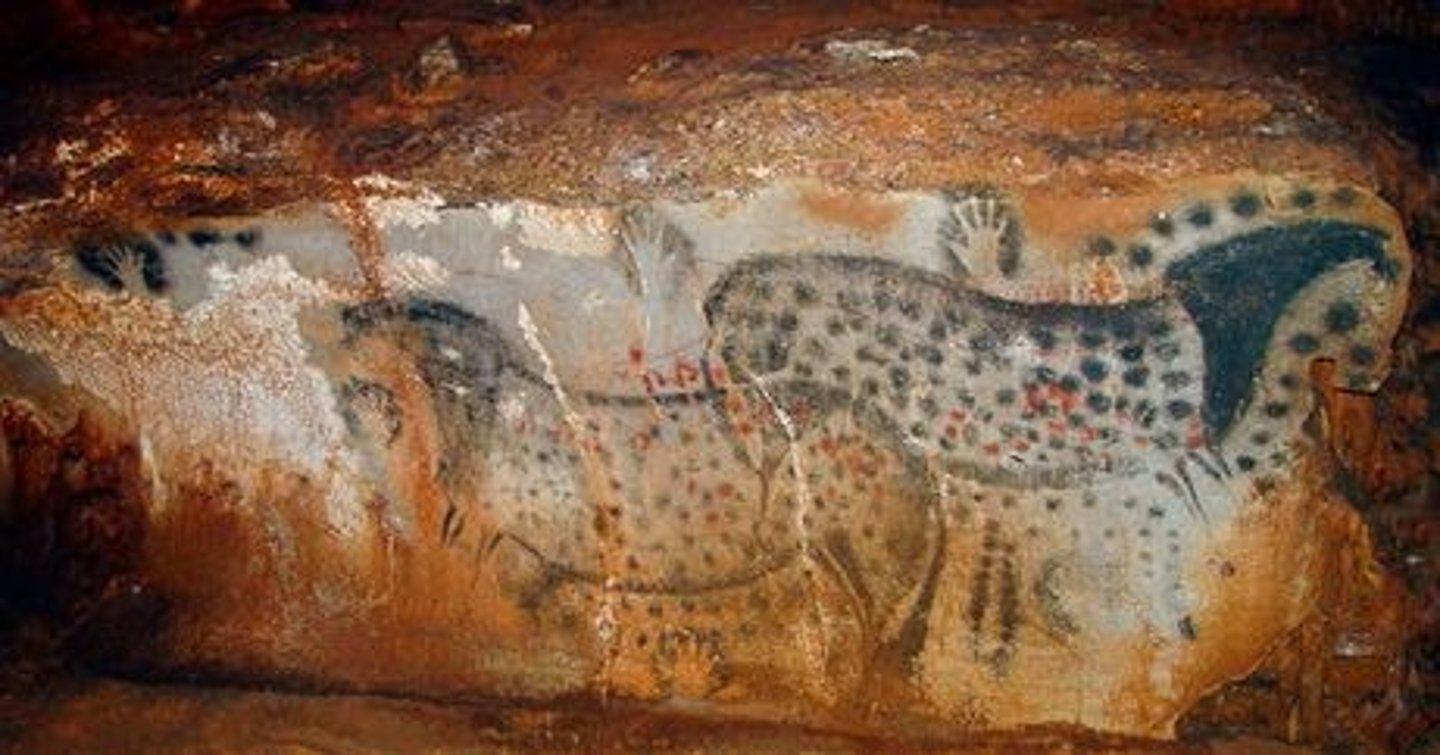
Spotted Horses and Human Hands, Paleolithic, Pech-Merle, France, opp. p. 1
FRANCE.
Paleolithic
- Prehistoric Cave Painting
- Pach-Mel, France
- Air brush technique with charcoal blown through a hollow bone.
- Used as teaching tools
- Evidence of children hand-marks and footprints
- Wanted to keep it private

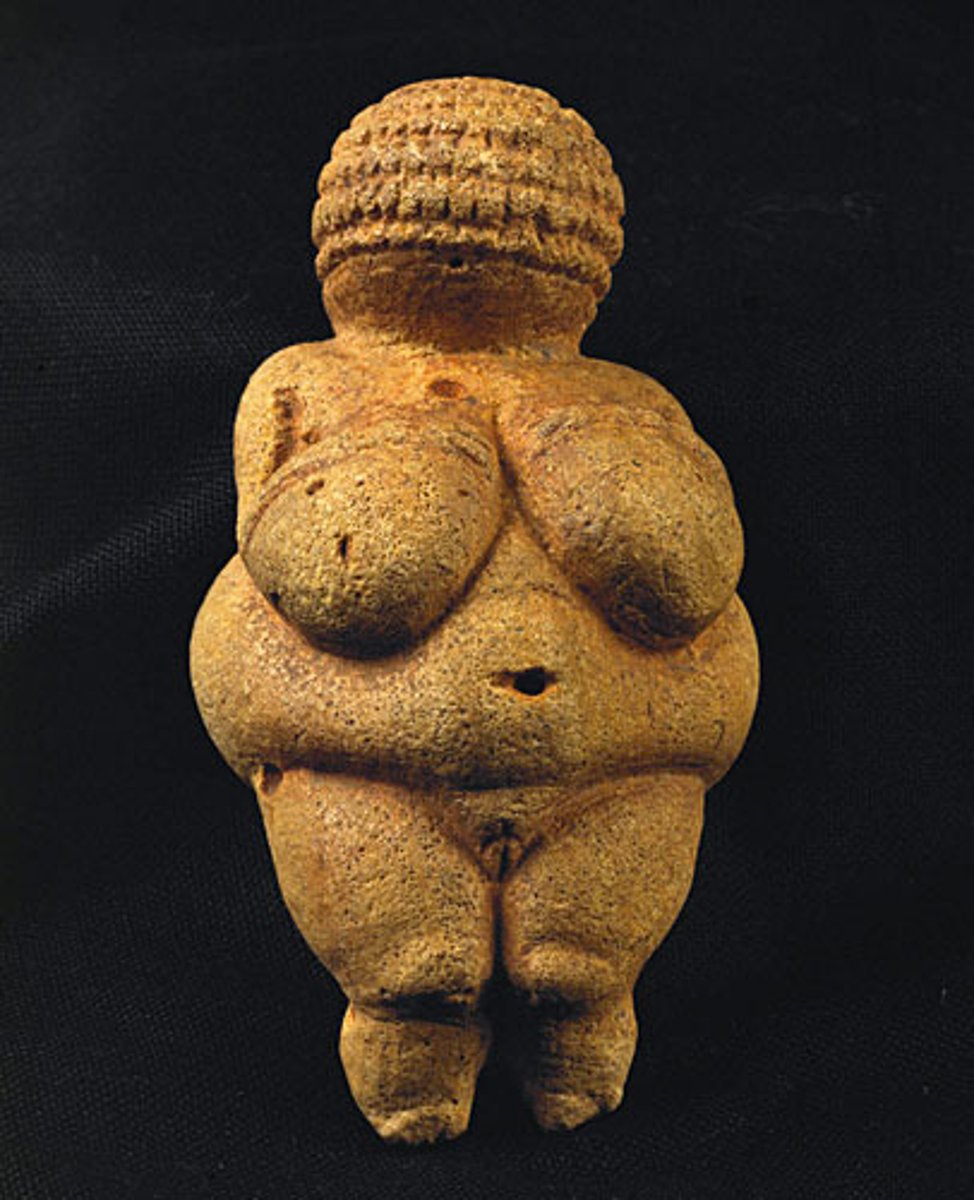
Woman from Willendorf, Austria, Paleolithic, p. 6
AUSTRIA.
Paleolithic
- Upper Paleolithic period
- Sculpture made from Limestone
- Austria
- Symbolic of health and fertility
- Believed to be the desired body type
- Motherhood/Fertility
from about 24,000 BCE (see "The Power of Naming" opposite).
-Carved from limestone and originally colored with red ocher
-The sculptor exaggerated the figure's female attributes by giving it pendulous breasts, a big belly with a deep navel (actually a natural indentation in
the stone), wide hips, and dimpled knees and buttocks.

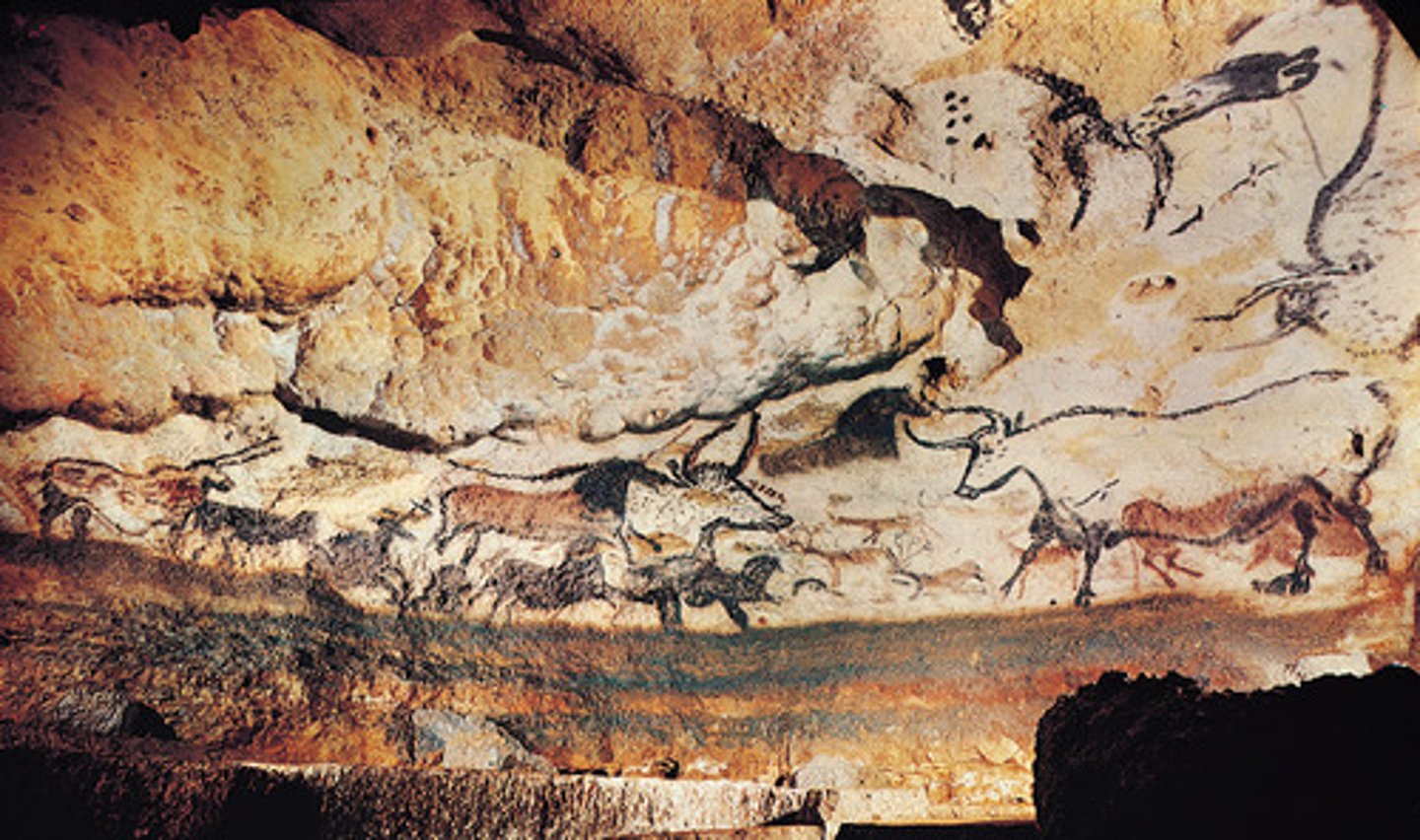
Hall of Bulls, Lascaux, France, Paleolithic, p. 10
FRANCE.
Paleolithic
- Prehistoric Cave Paintings on Limestone
- Lascaux Cave in Southern France
- Impressed Picaso
- Animals are full of life and are in composite pose
- Curving of wall suggest space
- Animals are overlapping and in rows
- High up on the ceilings
- Could have been used to teach children which animals to run away from
-the Lascaux painters depicted cows, bulls, horses, and deer along the natural ledges of the rock, where the smooth white limestone of the ceiling and upper wall meets a rougher surface below.
-They also used the curving wall to suggest space.
-animals full of life and energy

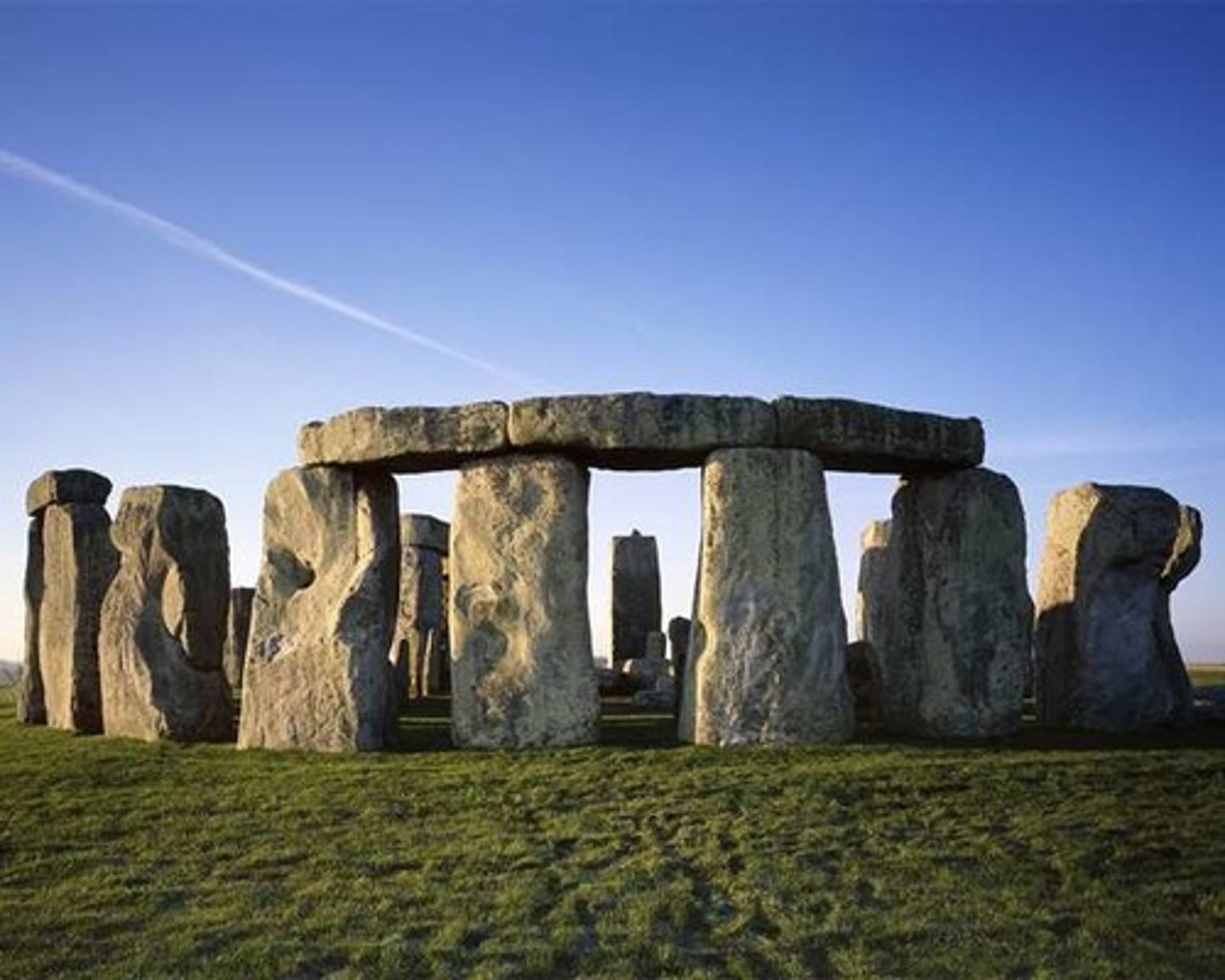
Stonehenge, England, Neolithic, p. 18
ENGLAND.
Neolithic
- Prehistoric
- Neolithic stretched to Bronze Age
- Megalithic Monument
- Bluestone and Gray Sandstone
- , England
- Started as cemetery of cremation burials
- Bluestone was transported (important)
- Ceremonial site
- Farmers used this to kept track of the time of the year (Calendar)
- Someone was able to direct all the labor. (Stones were heavy)
- Cemetery, Spiritual site, etc.
- A henge is a circle of stones or posts, often surrounded by a ditch with built- up embankments.
-The site started as a cemetery of cremation burials marked by a
circle of bluestones.
-function as a domain of
the dead.
-We now believethat Stonehenge was the site of cere- monies linked to death and burial.

Carved Vase, Sumerian, Iraq, p. 31
IRAQ.
Sumerian
- Narrative art
- Stories are related to the images
- Bottom = water & plants
- animals
- people
- Goddess of war and fertility
-shows how early Mesopotamian sculptors told stories in stone with great clarity and energy. They organized this visual narrative in three registers, or horizontal bands, and condensed the story to its essential elements.

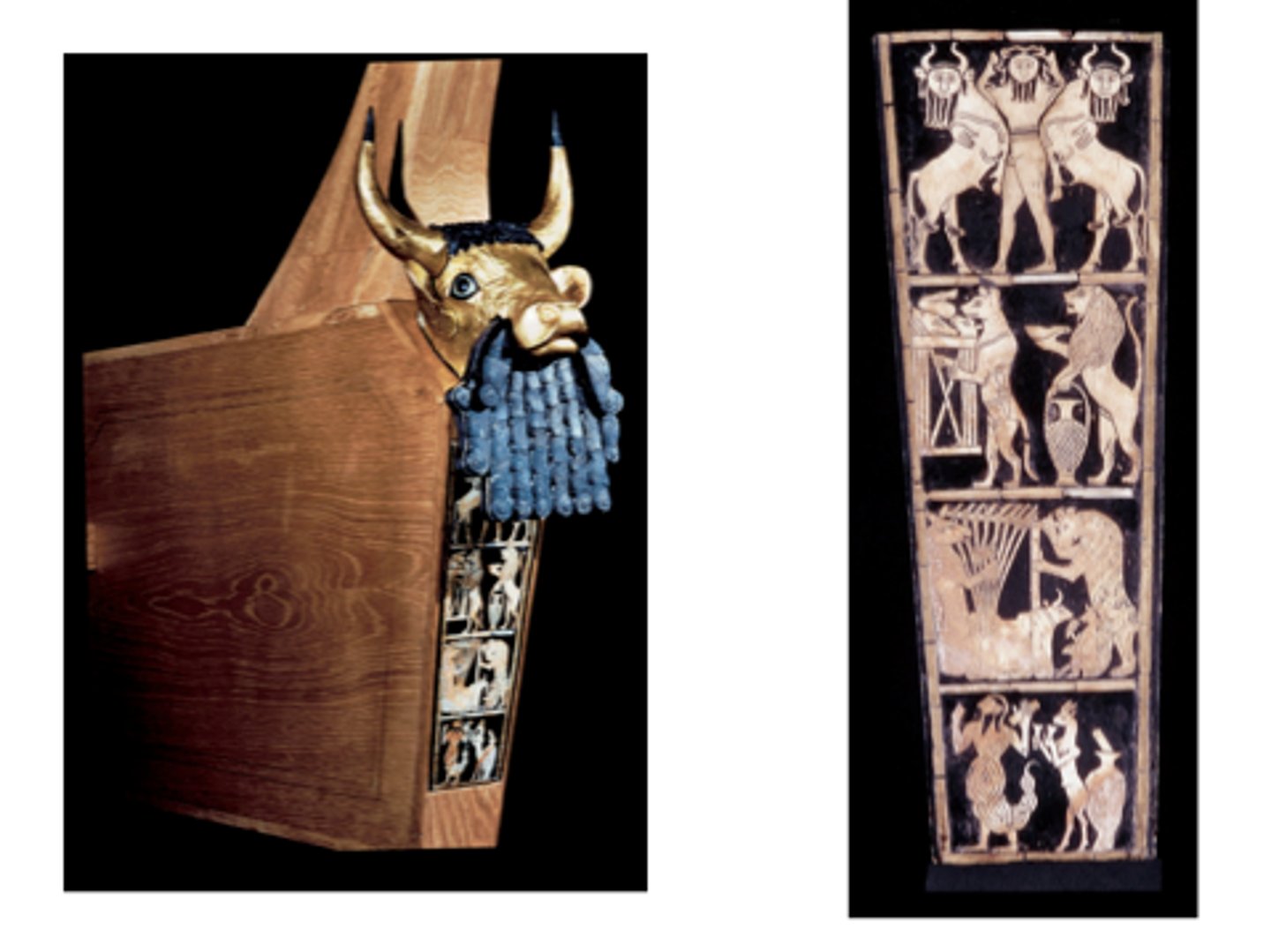
Great Lyre with Bull's Head and Front Panel, Sumerian, Iraq, p. 33
IRAQ.
Sumerian
- Sumerian Style
- From royal tomb in Ur
- Wood with gold, silver lapis lazuli, bitumen and shell
- Rested over body of woman who played lyre during funeral ceremonies
- On registers: donkey plucks strings of bull lyre and a fox is playing a rattle
- Next register: Animals bring food/drink for feast
- Hyena who is a butcher and lion with pouring vessel
- Bottom Register: From the "Epic of Gilgamesh"

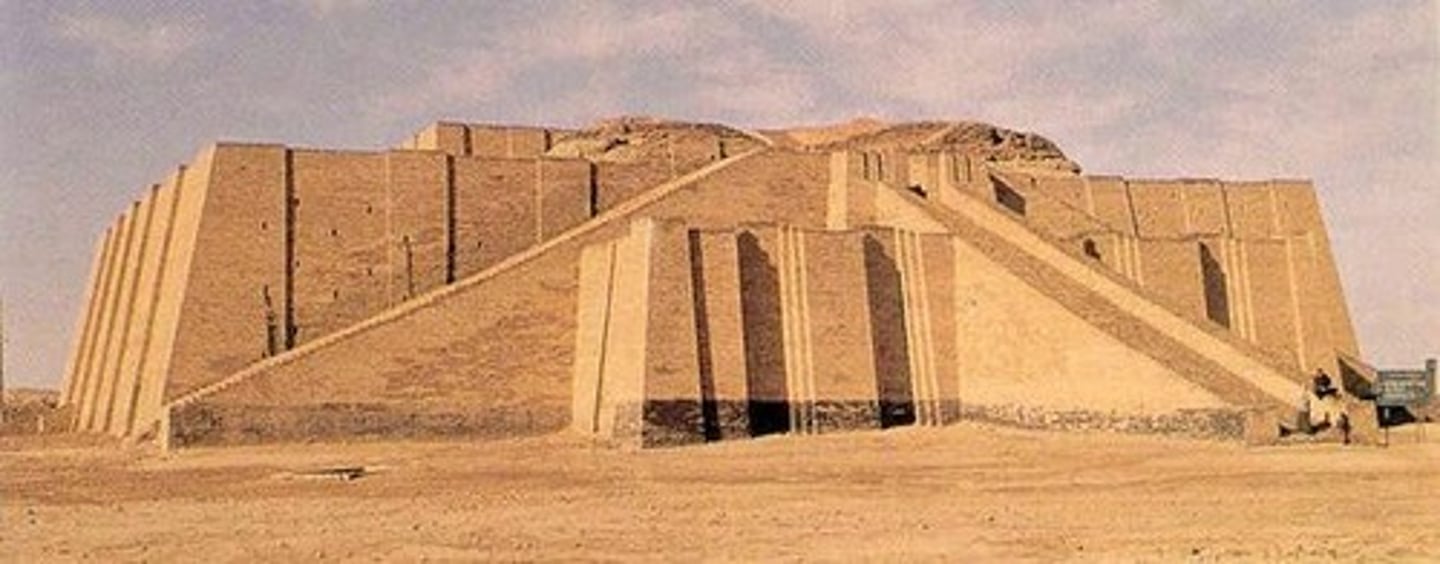
Ziggurat dedicated to Moon God Nanna, Sumerian, Iraq, p. 37
IRAQ.
Sumerian
-mud- brick faced with kiln-dried brick set with bitumen

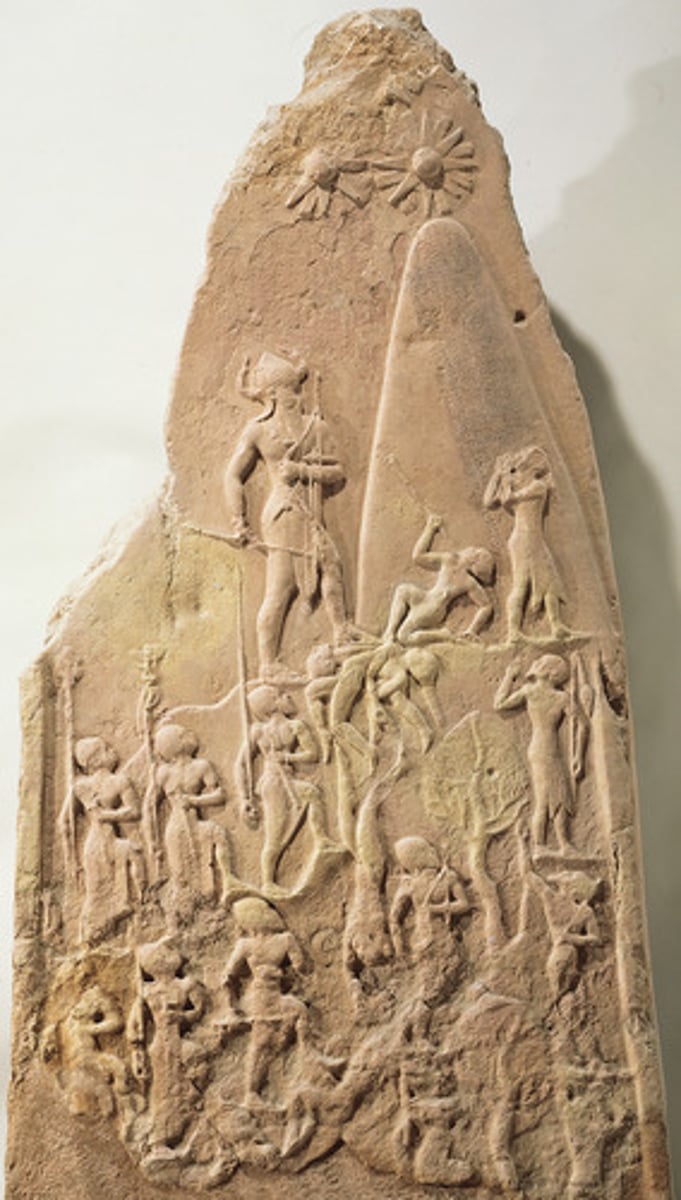
Stele of Naram-Sin, Akkadian, Iraq, p. 26
IRAQ.
Akkadian
- Showing us a "all powerful king"
- kicking and stepping on soldiers
- proclaiming himself a God on earth

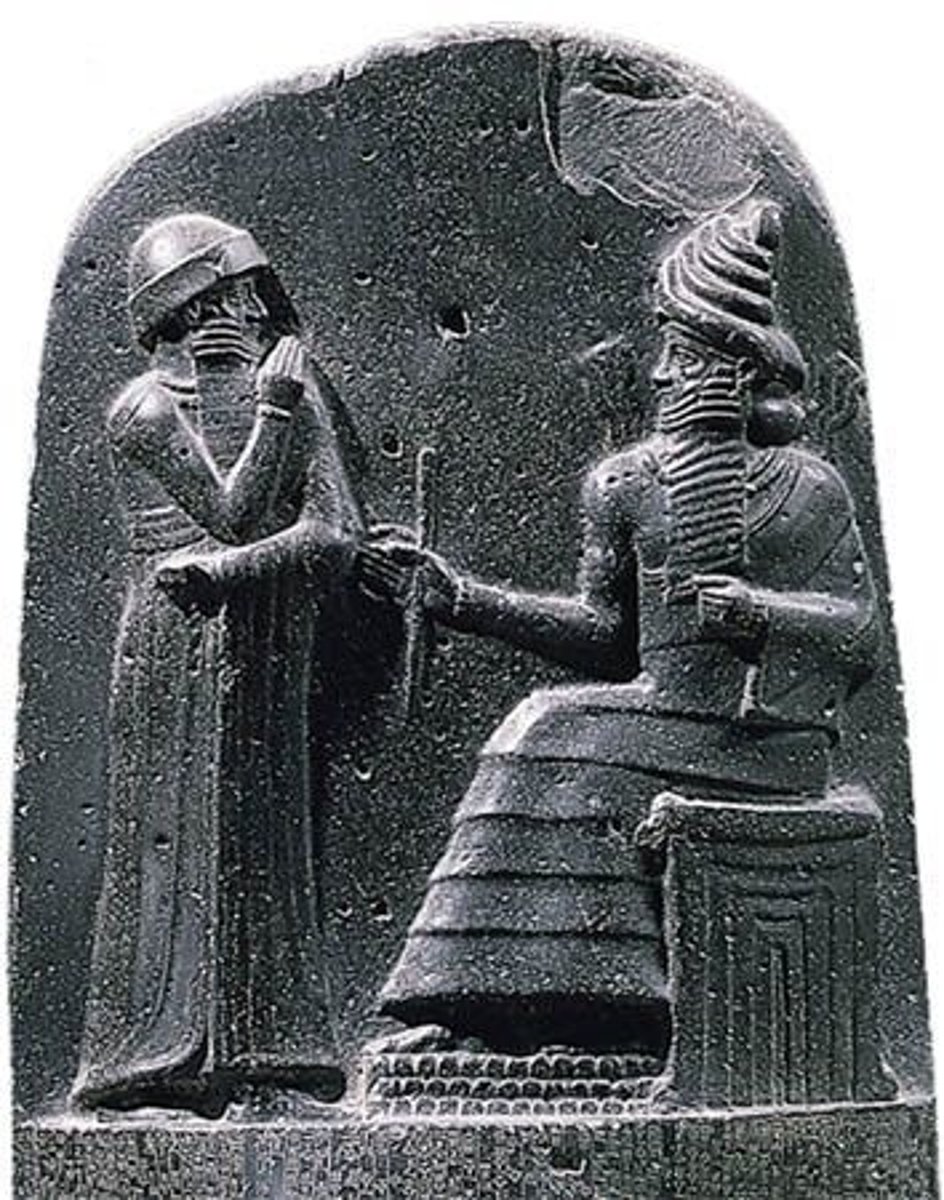
Stele of Hammurabi, Babylonian, Iraq, p. 39
IRAQ.
- Babylonian
- Everyone knew what the rules were, and consequences were
- If you're from the elite, punishment was less harsh
-Hammurabi standing in an attitude of prayer before Shamash, the sun god and god of justice.

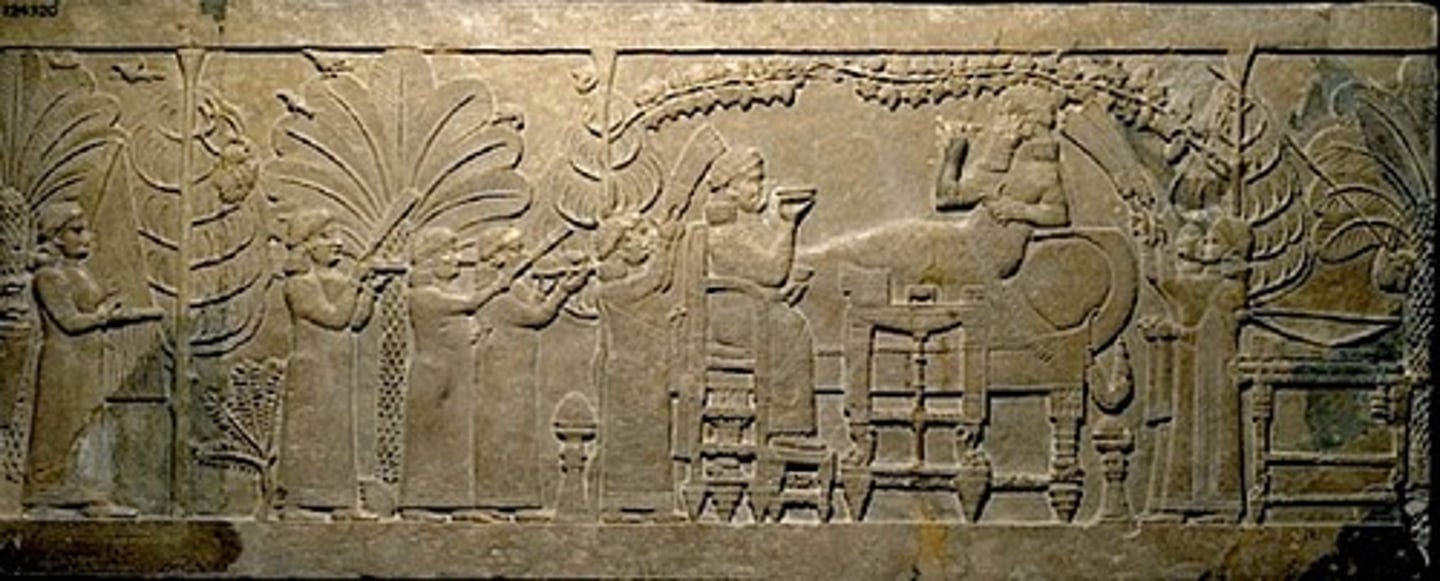
Assurbanipal and His Queen in the Garden, Assyrian, Iraq, p. 43
IRAQ.
- Assyrian
- Wife having a feast
- Fan holders
- Military victory
-victory celebration.

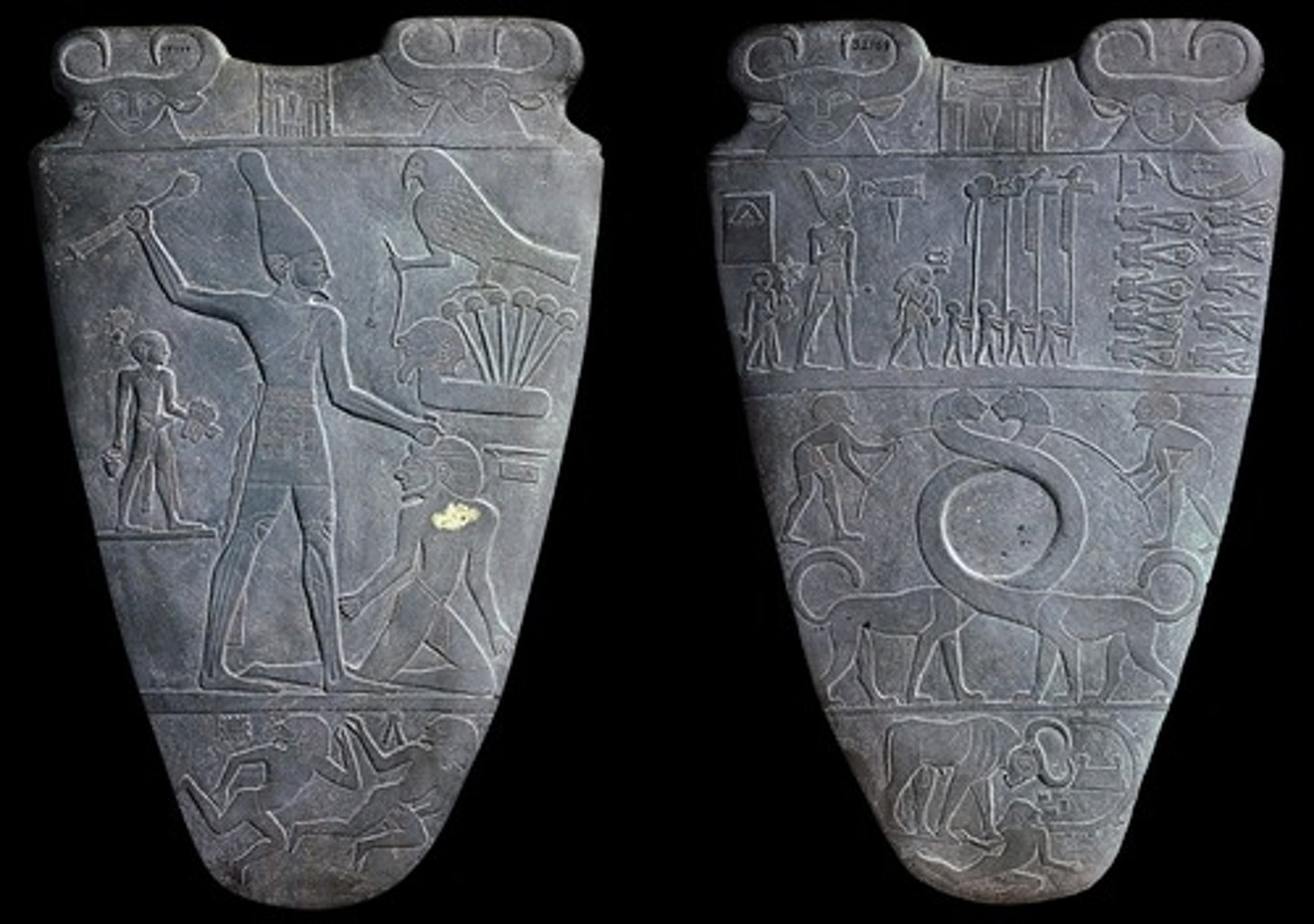
Palette of Narmer, Early Dynastic Egypt, p. 52
EGYPT.
Early Dynasty
- Horus
- Narmar is very powerful
- "Upper and Lower Egypt are equal"
- From Hierakonpolis. Early Dynastic Period
- Found in temple of Horus
- Made from Green schist
- Used to ground eye makeup & as a ceremonial piece
- Represents the unification of Egypt and the beginning of the country's growth as a powerful nation-state
"Narmer is beheading an enemy from lower Egypt
Above this is Horus (falcon) holds a rope tied around the neck of a head that has papyrus in it (Lower Egypt)
Cats curled and touching noses=peace between Upper and Lower Egypt"

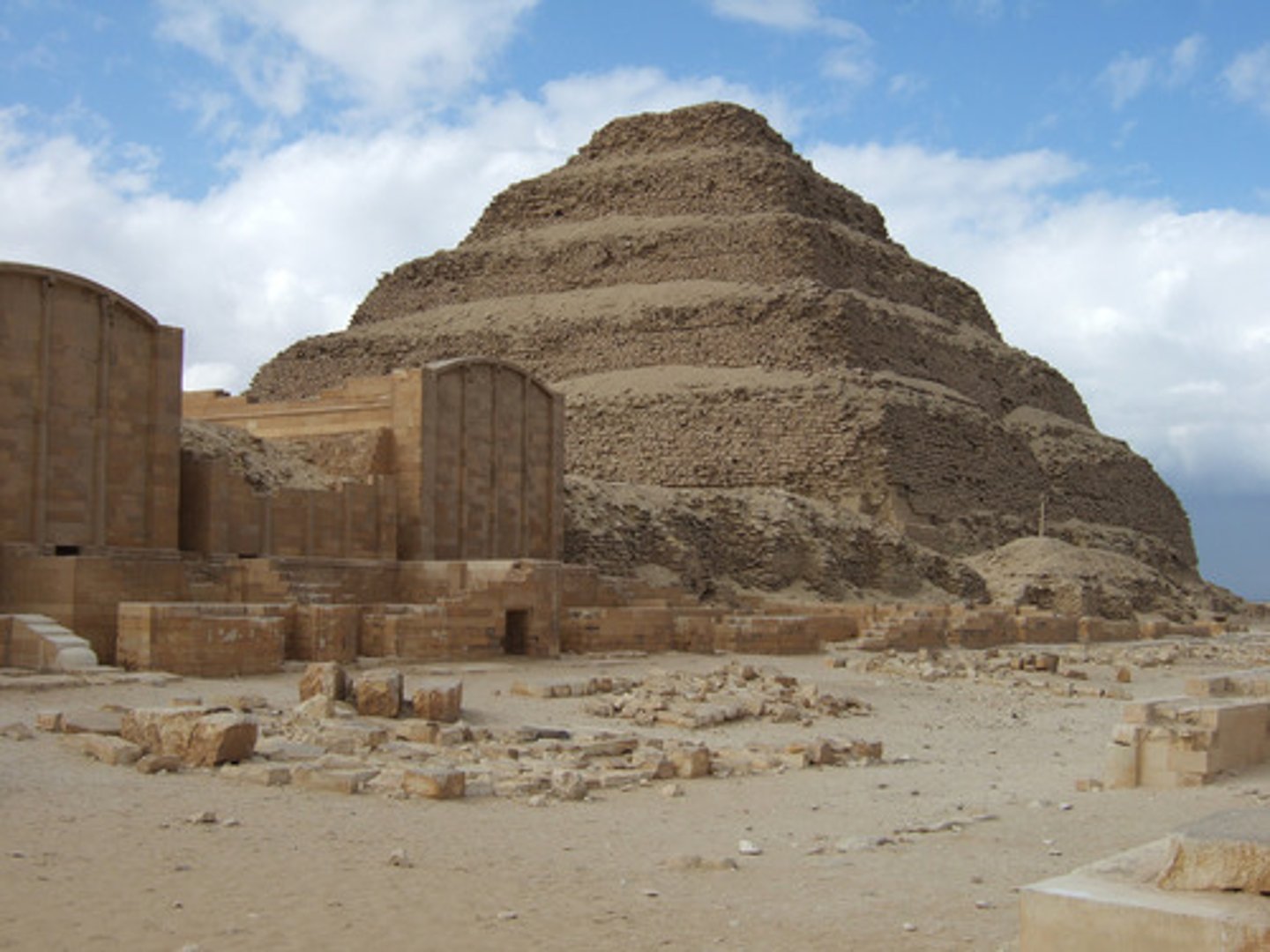
Step Pyramid and Funerary Complex of Djoser by Imhotep, Old Kingdom Egypt,
p. 54
EGYPT.
Old Kingdom
- First Egyptian pyramid
- Djoser's fake city
- Thought he would stay there after death

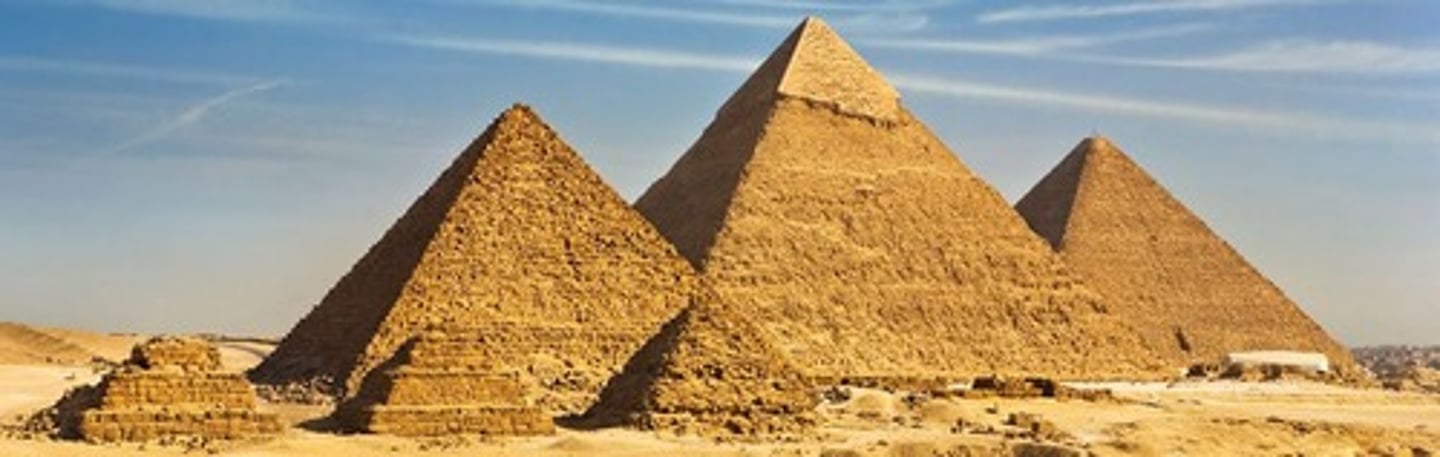
Pyramids of Giza, Old Kingdom Egypt, p. 56
EGYPT.
Old Kingdom (4th Dynasty)
- Limestone and granite
- Built by Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure
- Follow sun's east-west path
- Pathway from Nile to pyramid where king was carried into chamber

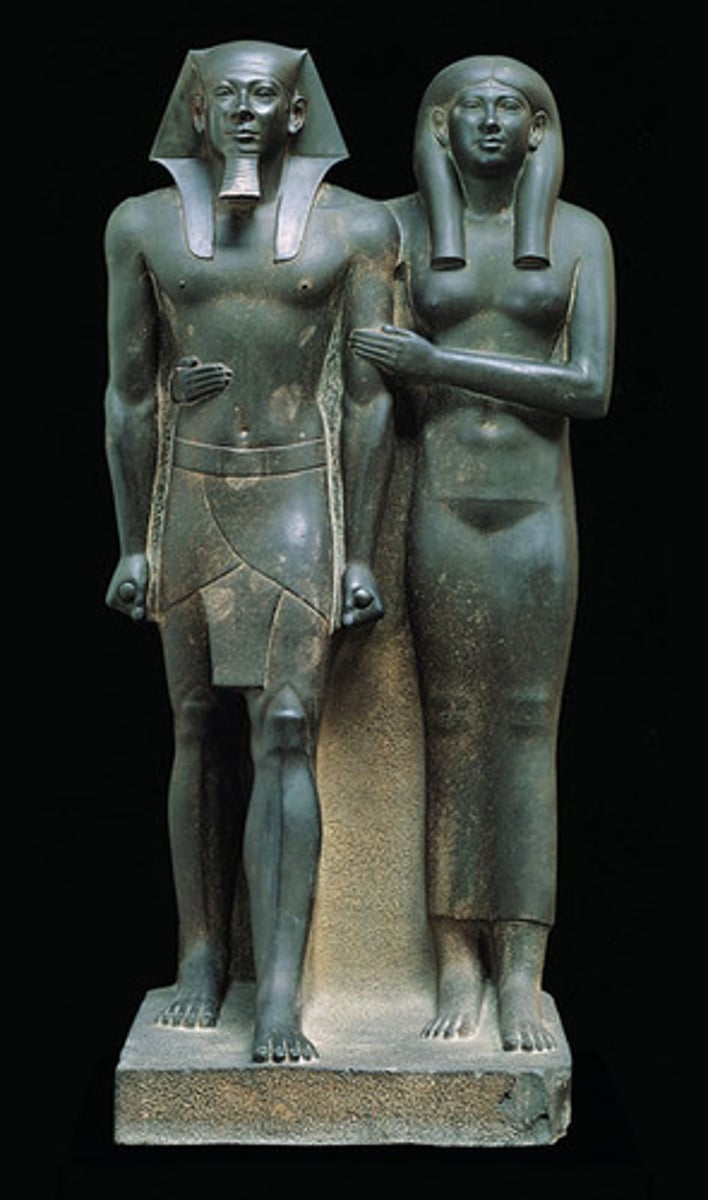
Menkaure and Queen, Old Kingdom Egypt, p. 59
EGYPT.
Old Kingdom
- Royal
- Stiff
- Wants to portray themselves and powerful

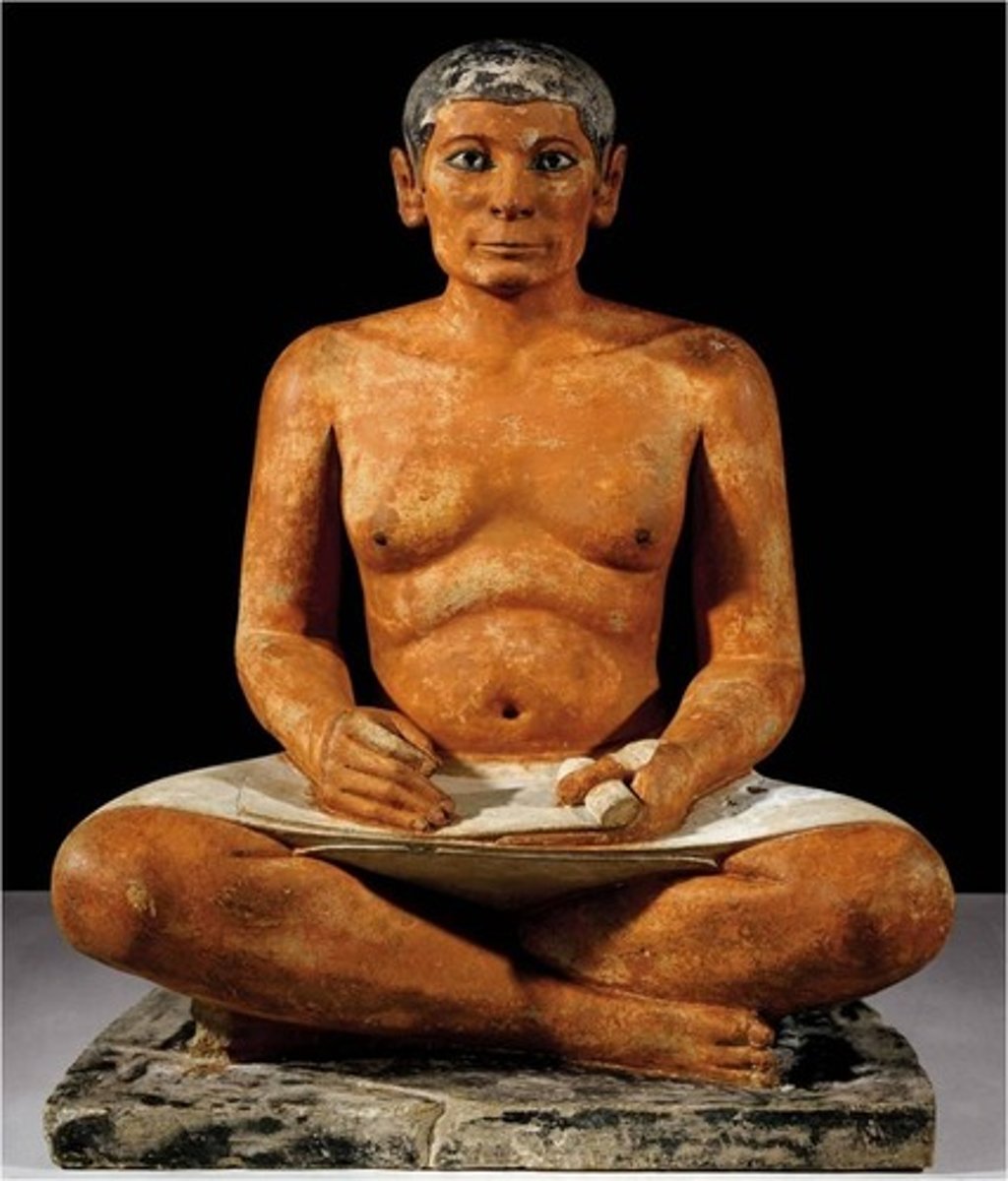
Seated Scribe, Old Kingdom Egypt, p. 60
EGYPT.
Old Kingdom
- Humble figure
- Someone educated and in elite class
- Body is soft unlike most of the people around the time who had to work hard, often ending up skinner and rougher
- Paid extra money for the sculpture (eyes are more life-like)
- Showed that Egyptians had the skill to carve realistically

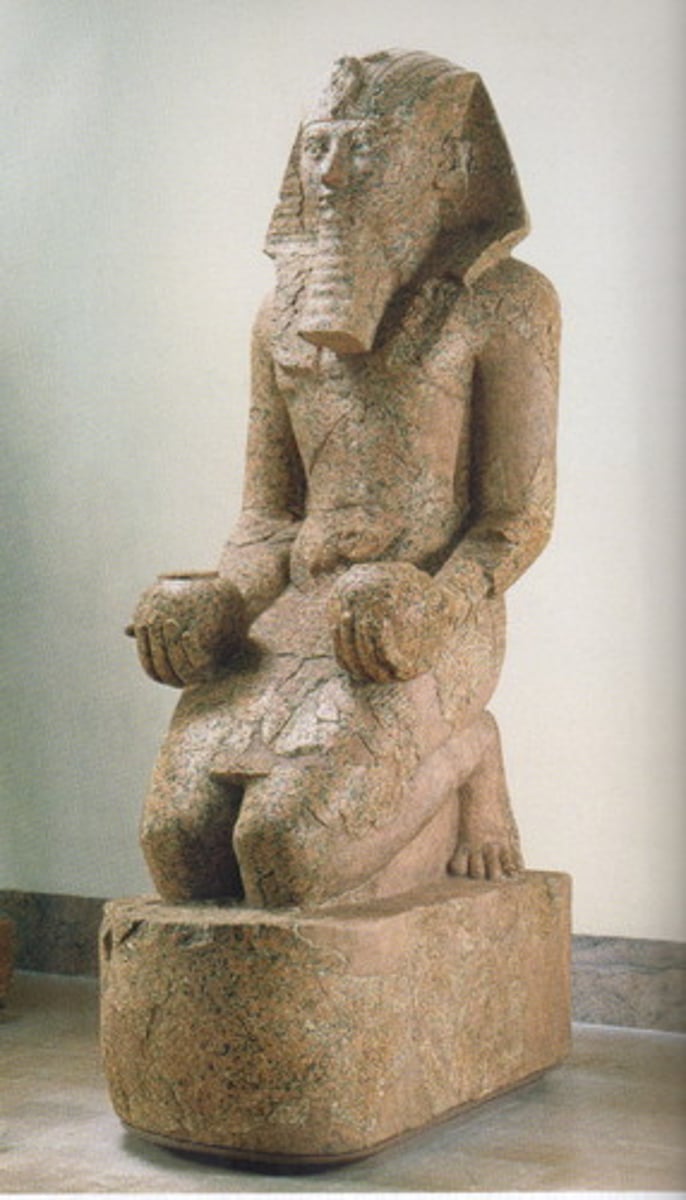
Hatshepsut Kneeling, New Kingdom Egypt, p. 68
EGYPT.
- New Kingdom
- Eighteenth Dynasty
- Red Granite
- Represented as a male king wearing a kilt & linen headdress, occasionally even a king's false beard
- She was adapted to conform to convention
- She adopted the male costume of a king

Akhenaten and His Family, New Kingdom Egypt, p. 71
EGYPT.
- New Kingdom
- Eighteenth Dynasty
- Painted limestone relief
- New Amarna Style
• Sun disc in the center is symbolic of Ahten (The Sun God)
Rays are giving them life
Sunken Relief: Figures are deeply incised
- For the first time the fidgety behavior of children is conveyed and the loving involvement of parents
- Atom was credited for giving life to people.

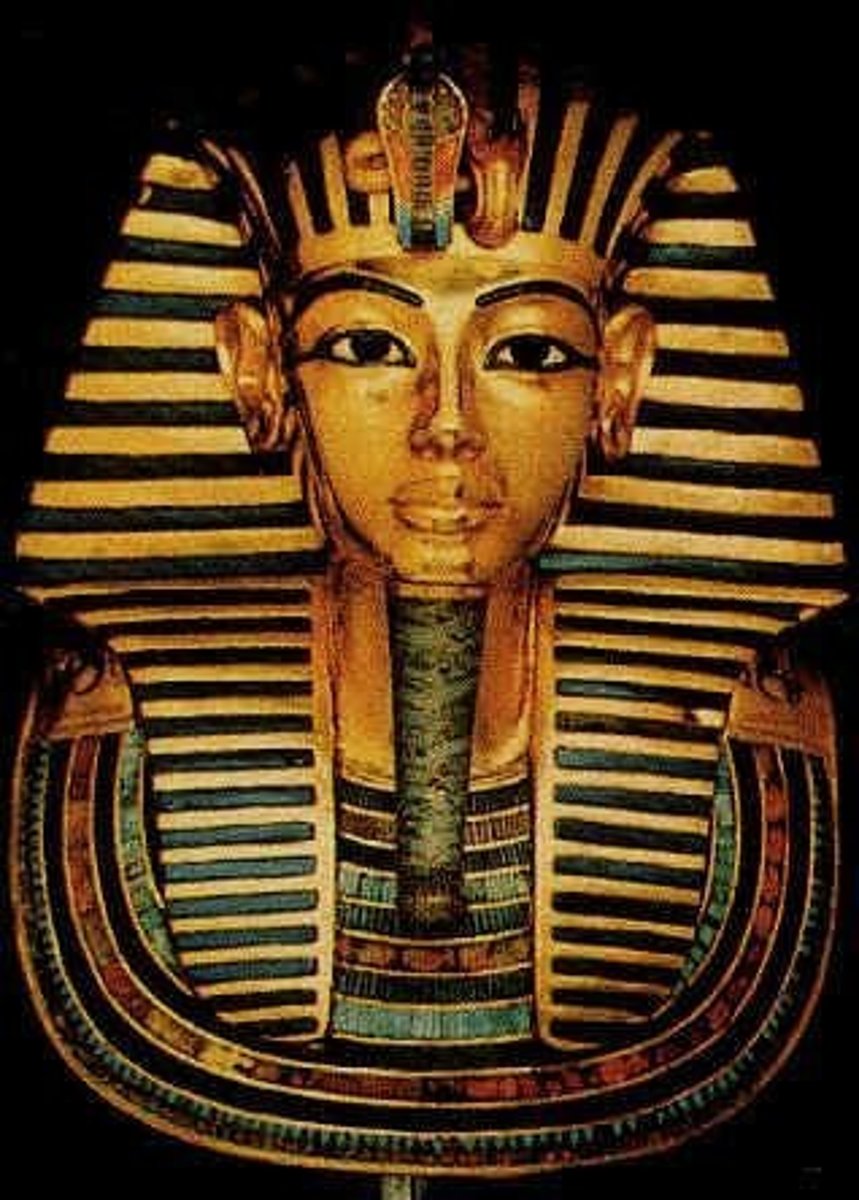
Funerary Mask of Tutankhamun, New Kingdom Egypt, p. 48
EGYPT.
- New Kingdom
- Eighteenth Dynasty
- New Kingdom
- Valley of the Kings
- Gold inlaid with glass & semiprecious stones
- Placed over head & shoulders of mummified body
• Solid gold
• Symbolic of being a military ruler
• Realism
"Believe that he was killed because he did not have any heirs & was young
Pulled major organs out and mummify them separately with salt to dry them
And wrap them in linen"

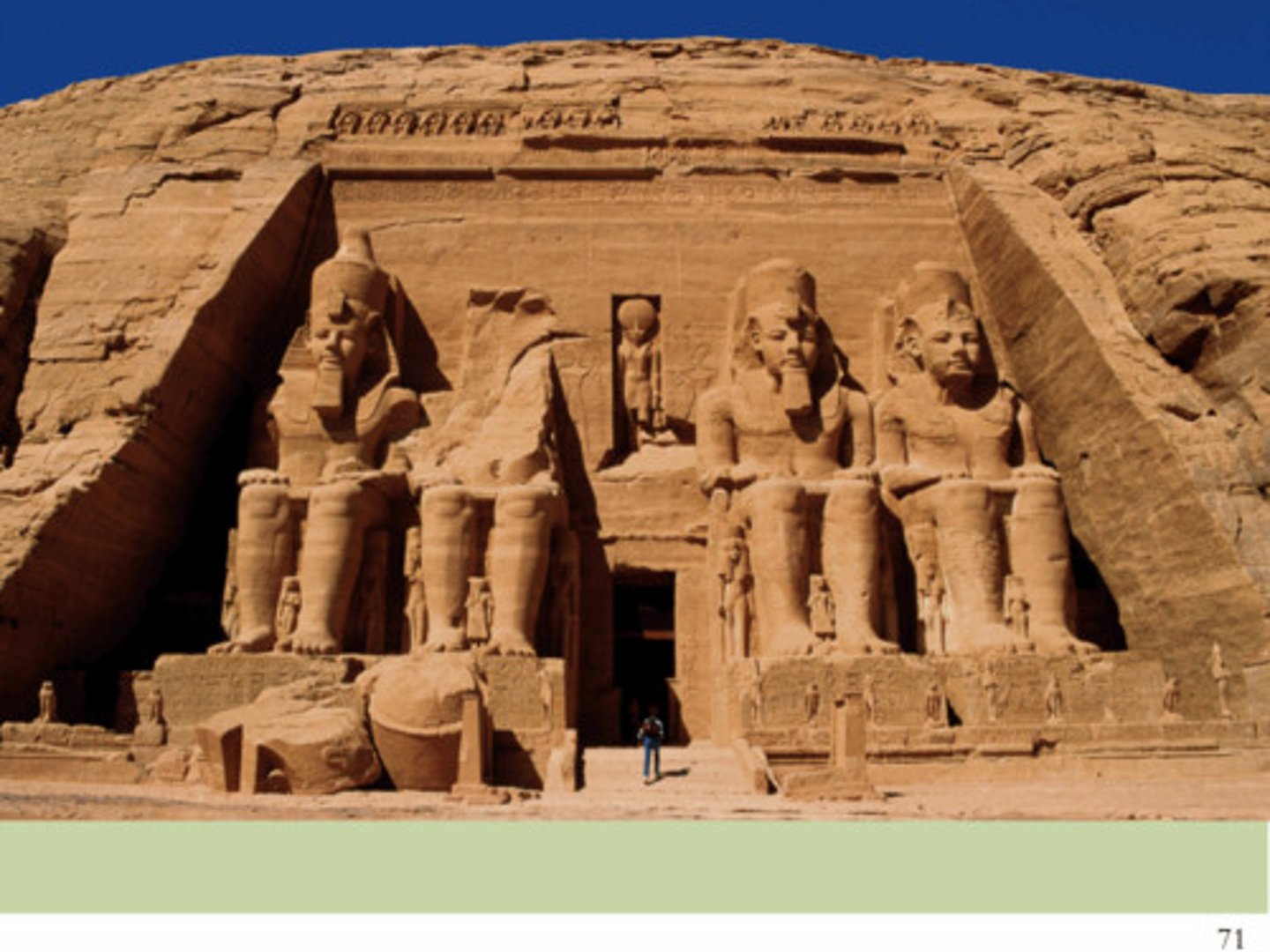
Temple of Ramses II, Abu Simbel, New Kingdom Egypt, p. 74
EGYPT.
- New Kingdom
- Monument
- Nineteenth Dynasty
- New kingdom
- Carved into the rock
- Four colossal statues of Ramses in a row and small statues of family members & Nefertari
- Honorary temple NOT funerary
• In the center is a dedication to Horus and Ra (disc on top of head)
• In between him are depictions of god
• Row of baboons are symbolic of dedication to Ra
They are greeting the rising sun
"Inside: 8 statues of Osiris with face of Ramses to proclaim his divinity
- The corridor they form leads to seated figures of Ptah, Amun, Ramses II, and Ra (twice a year the sun's rays illuminate the statues)"

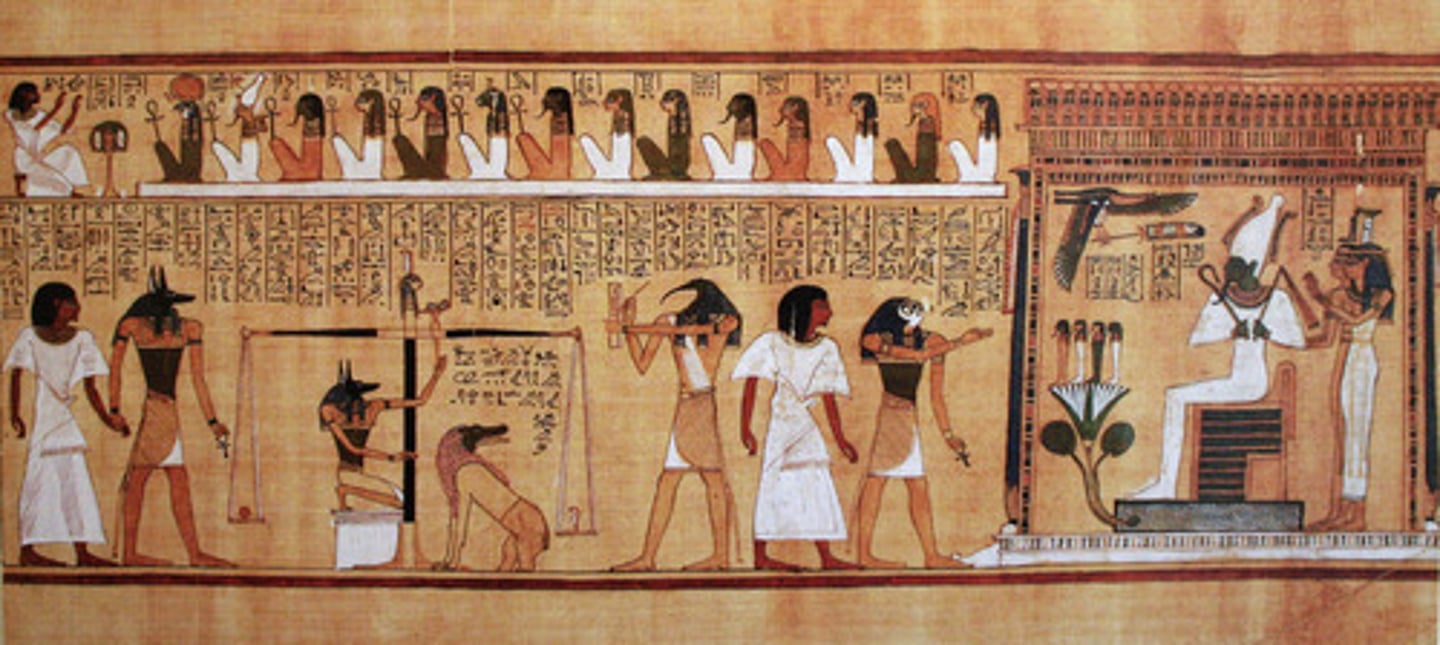
Last Judgement Before Osiris from a Book of the Dead, New Kingdom Egypt,
p. 77
EGYPT.
- New Kingdom
- Painted papyrus
- Nineteenth Dynasty
• Top: Hunefer is dedicating himself to all of the 14 gods of the afterlife
• Left: Hunefer led into scene by Anubis (god of embalming). He is holding an ankh.
• Maat is the Goddess of Justice
o Feather and heart are weighed against each other
• Light hearted=Pass
• Heavy hearted= Eaten by omit (hippo, lion, and crocodile)
• Thoth: Recorded everything going on
• Led over to Osiris by Horus holding an ankh
His throne sits on river symbolism made of natron, which was the salt that they embalmed with. Out of it sprouts a lotus flower, which is a symbol of Lower Egypt and everlasting life.
• On the lotus are Horus' four sons which stand for the major organs
Behind Horus are his two sisters
The eye of Horus: "the all-seeing eye". Links to the idea that he found his father, Seth's, body parts. Symbolic of him knowing everything that is happening

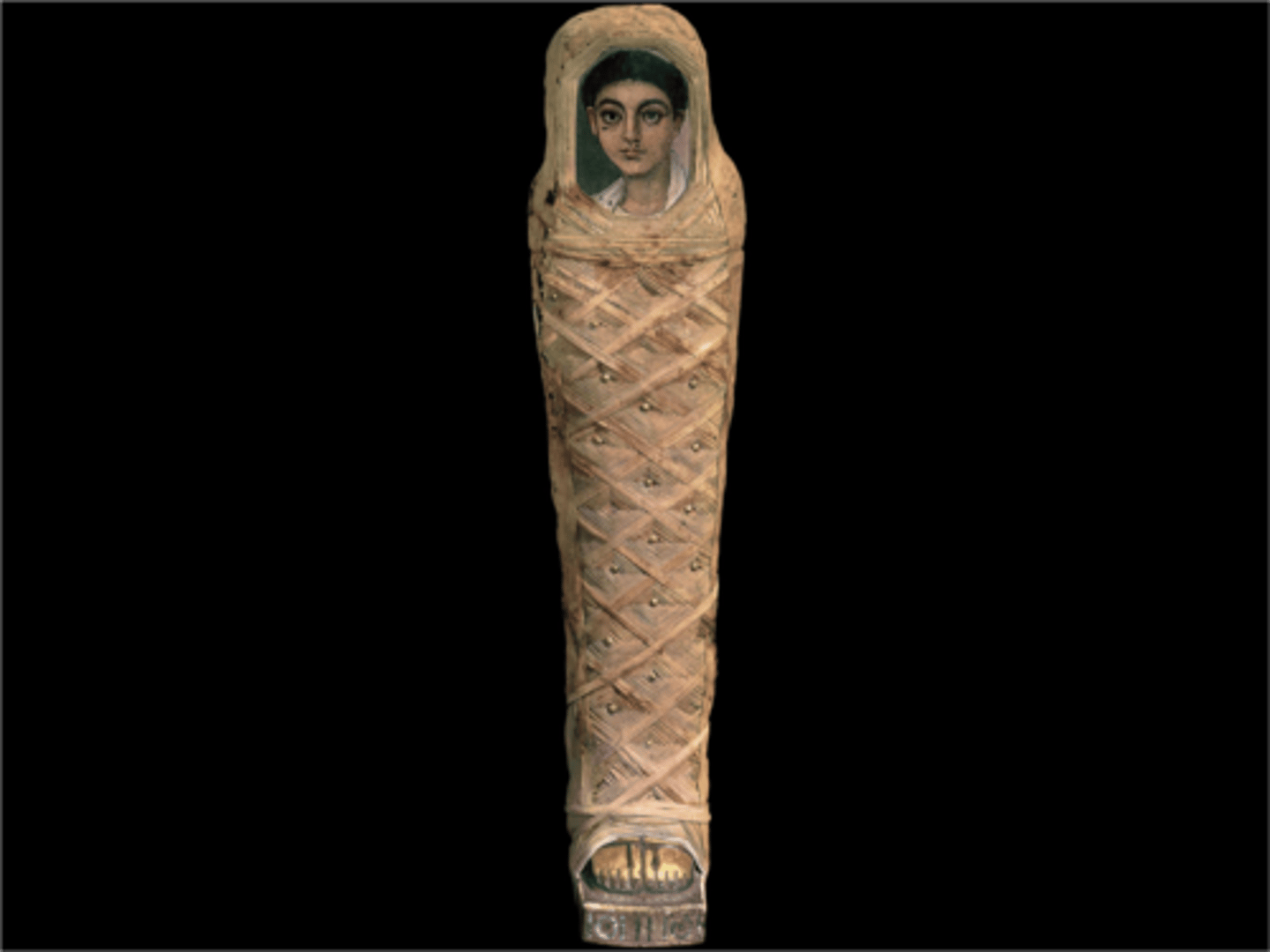
Mummy Wrapping of a Young Boy, Egypt, Roman period, Titanium
EGYPT.
- Roman Period
- First Century
- Ancient technique
- Roman and Egyptian style coming together

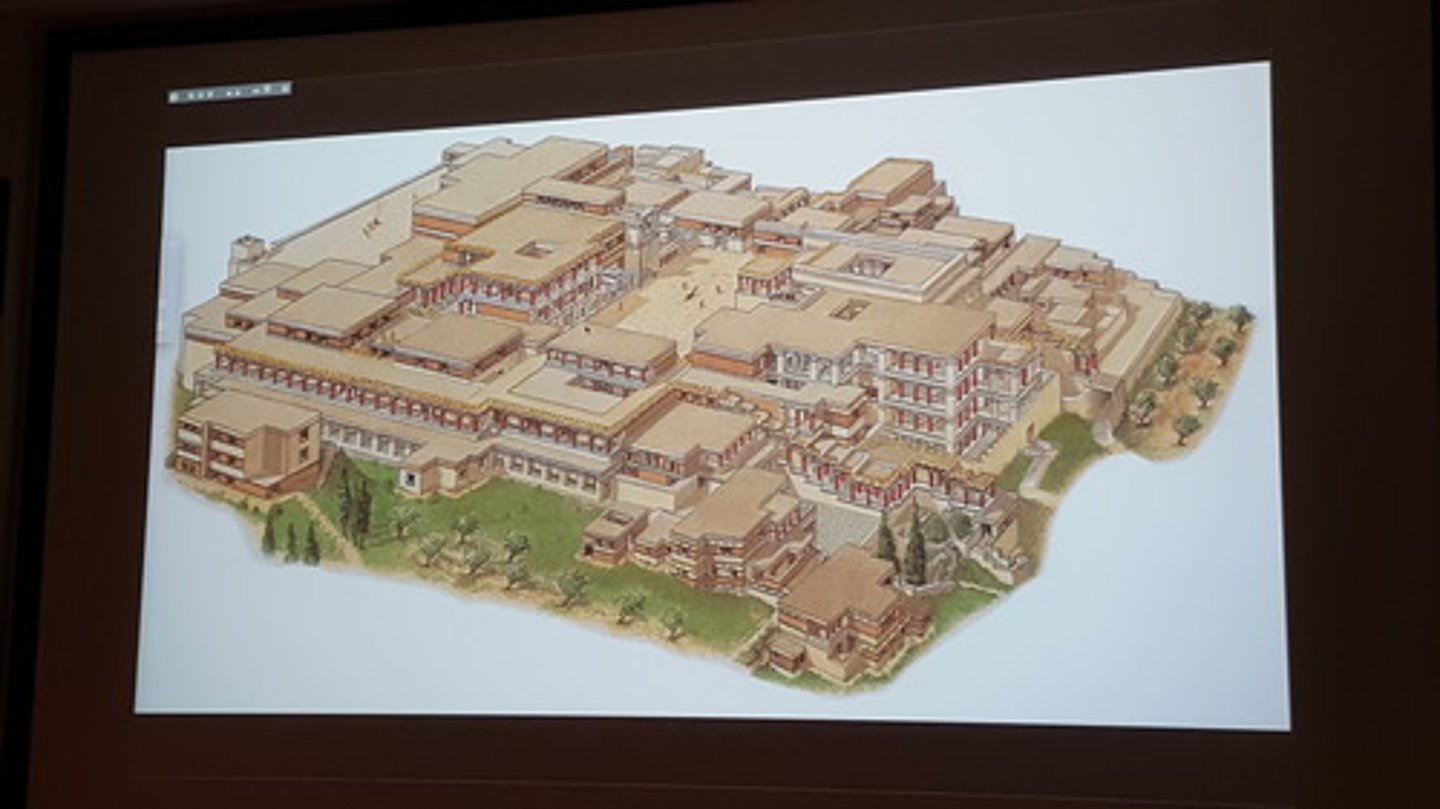
Reconstruction, "Palace" Complex, Knossos, Crete, Minoan, p. 86
MINOAN.
Knossos, Crete
-elaborate new one built after a terrible earthquake shook Crete in .c 1700 BE.
-New Palace period and is considered by many scholars to be the highest point of Minoan civilization. In its heyday, the Knossos complex covered six acres
Young Girl Gathering Saffron, wall painting (fresco), Minoan, p. 80
MINOAN.
Fresco (wall painting)
hair color indicates shes a young girl
- pluck the crocus flowers blooming on the hillside in front of her (FIG. 4-1), offers us a window into life in the ancient Aegean world. The image is from a fresco of .c 1650 BE found in a house in Akrotiri, a town on the
Aegean island of Thera that was said to be famous for the saffron harvested from its crocuses
-but the light blue color of her scalp indicates that her hair is beginning to grow out, suggesting that she is entering adolescence.
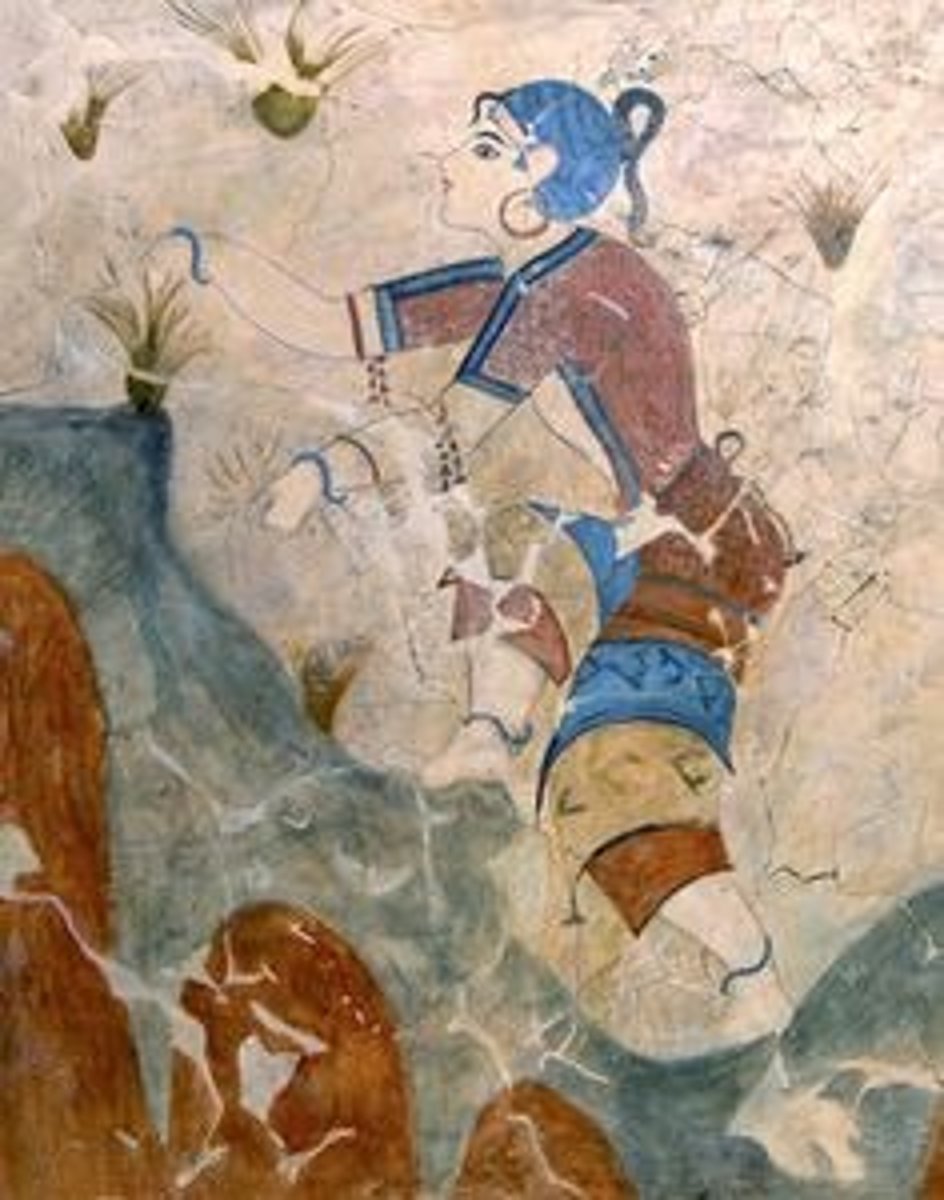

Bull Leaping (fresco), Palace of Knossos, Crete, Minoan, p. 87
MINOAN.
Palace of Knossos, Crete
Fresco
-The action-perhaps representing an ini- tiation or fertility ritual-shows three scantily clad youths around a gigantic, dappled bull, which is charging in the "flying-gallop" pose. The pale-skinned person at the right-her paleness probably identifying her as a woman is prepared to catch the dark-skinned man in the midst of his leap, and the pale-skinned woman at the left grasps the bull by its horns, perhaps to help steady it or to begin her own vault.

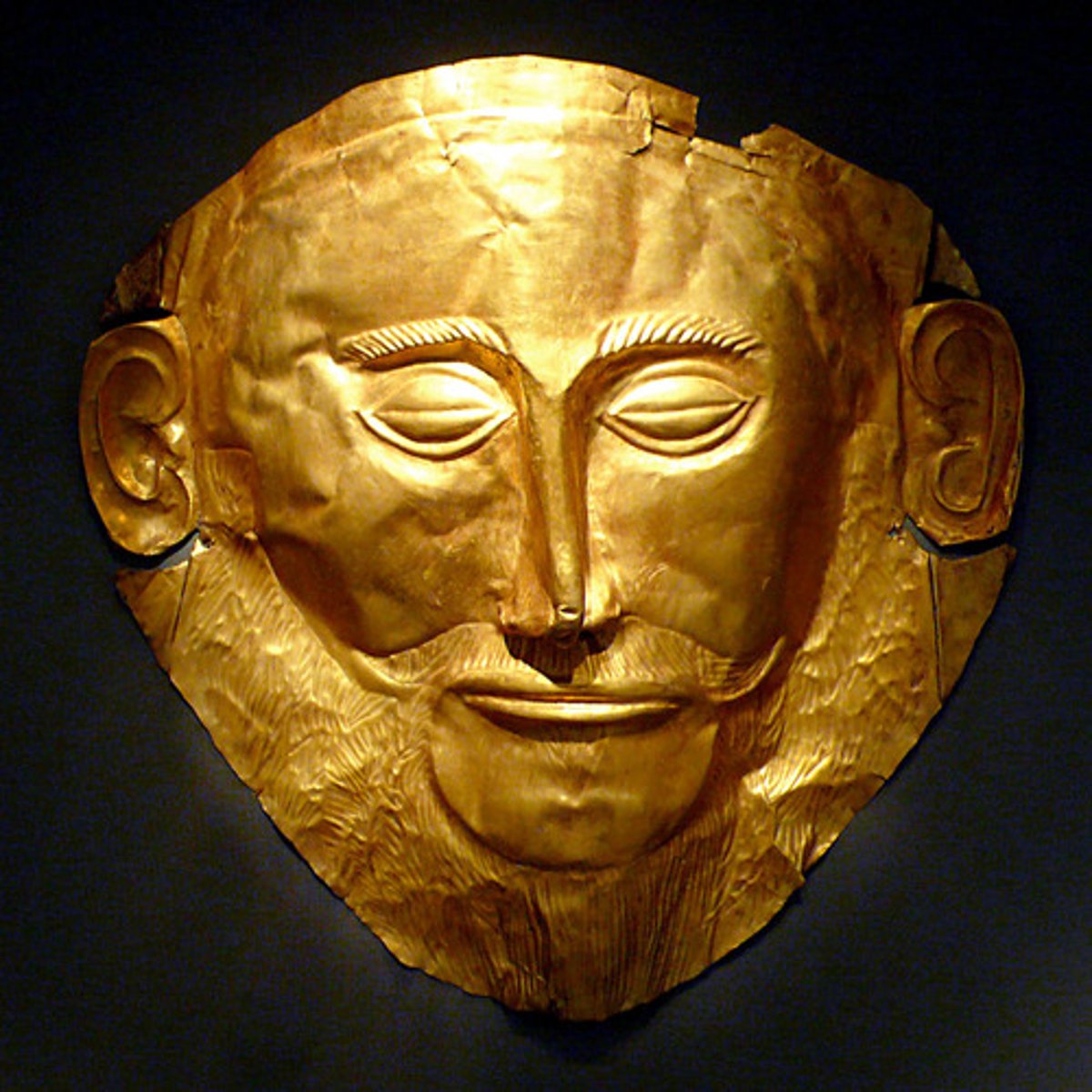
"Mask of Agamemnon," Funerary Mask from the Royal Tombs at Mycenae, p. 97
MYCENAE.
- Mycenian
- from Royal Tombs
- Funerary Mask
- First to ever depict mustache
-Most likely faked by Schliemann

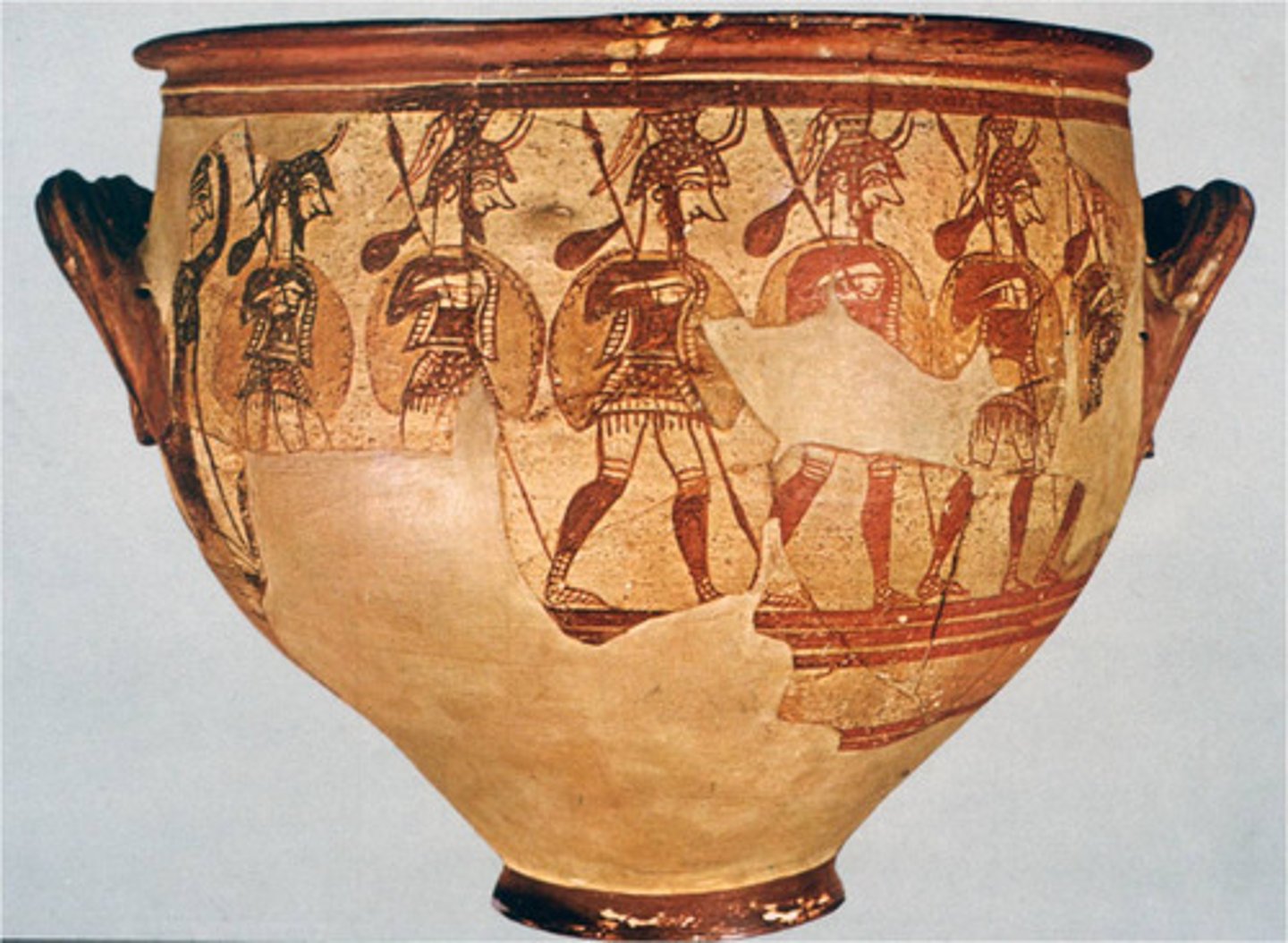
Warrior Vase (Krater), Mycenae, p. 99
MYCENAE.
- Mycenian
- Krater
- Girl grieving in the back
-On the side shown here, a woman at the far left bids farewell to a group of helmeted men with lances and large shields marching off to the right.
-The only indication of the woman's emotions is the gesture of an arm raised to her head, a symbol of mourning.

Woman with Snakes, "Palace" Complex, Crete, Minoan
Possibly depicting a goddess or a devotee of a Minoan religion.
