Urinary gross and histopathic lesions
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What structures are normally present in the kidney?
glomeruli
tubules
collecting ducts
interstitial connective tissue
blood vessels
fibroblasts
What structures are normally present in the lower urinary tract?
transitional epithelium
smooth muscle
connective tissue
blood vessels
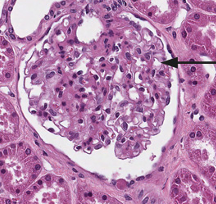
what is this structure?
glomerulus
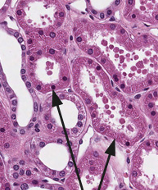
what is this structure?
proximal tubule
How can we tell if its PCT or DCT?
PCT
narrower lumen
thicker epithelial cells
DCT
wider lumen
thinner epithelial cells
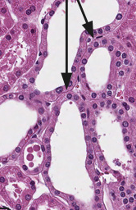
what are these structures?
Distal tubules
What features of glomeruli are important?
specialised structures
highly vulnerable to damage
unable to regenerate
What cell types can be found in the glomerulus?
podocyte cells - part of filtration barrier, contract to regulate filtration
mesangial cells - phagocytic to scavenge filtration entrapped debris
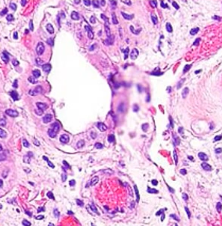
What is this structure?
collecting duct
largest and most robust
wide lumens
only found in medulla
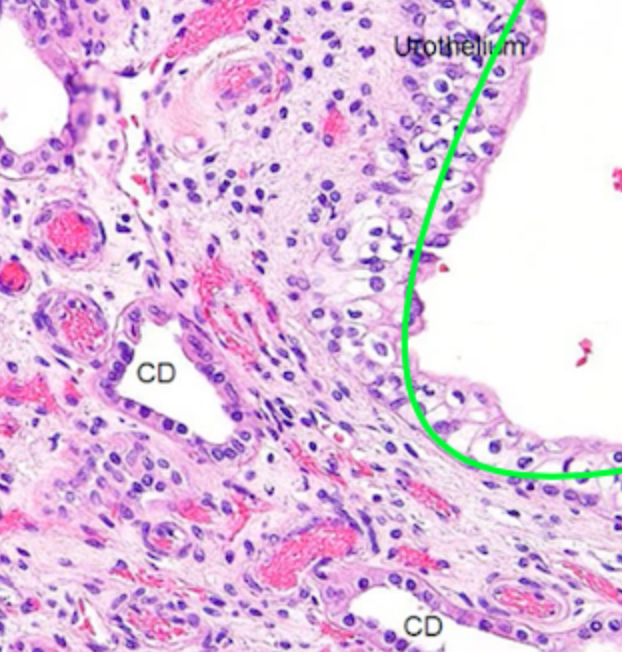
What is this structure?
renal pelvis
What is present in the interstitial tissue?
blood vessels
fibroblasts
lymphocytes (occasionally)
What type of cells line the bladder?
transitional epithelial cells
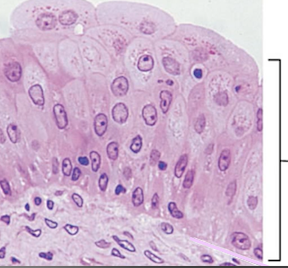
What are these cells?
transitional epithelial cells
what are 4 layers of the bladder wall?
(bladder lumen)
transitional epithelium
lamina propria
muscular layer (detrusor muscle)
adventitia (with fat cells)
What pathological additions may we see in the urinary tract grossly?
swelling
What pathological additions may we see in the urinary tract histologically?
inflammatory cells / leucocytes
exudate / oedema / cell debris
tumour cells
fibroblasts (for repair)
aetiological agents e.g. bacteria
What histopathological losses may we see to the urinary tract?
necrosis —> creates spaces
glomerular and tubular fibrosis —> collagen contracts so we see shrinkage
What would the effect be of glomerular fibrosis?
glomerulus and nephron non-functional
What if the effect of tubular necrosis?
if basement membrane intact
—> regeneration of epithelium
if basement membrane not intact
—> regeneration not possible (to 100%)
—> repair with fibrosis
—> collagen contracts so see shrinkage e.g. chronic infarct
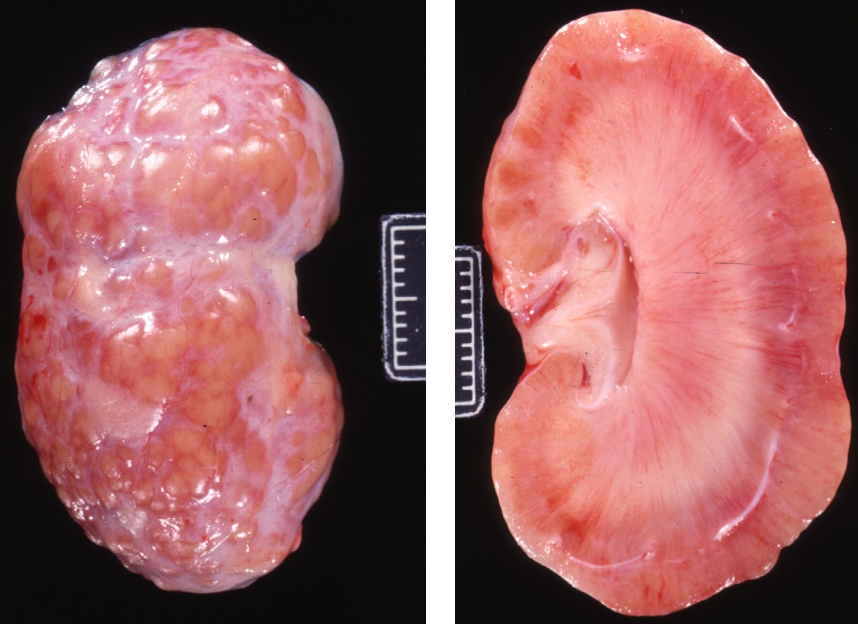
describe the gross lesion
organ is the kidney
pale pink/orange colour change
capsular surface is bumpy
raised multifocal to coalescing yellow/orange nodules on capsular surface - pus filled
medulla is pinky white (should be pale brown)
medulla is more firm than usual
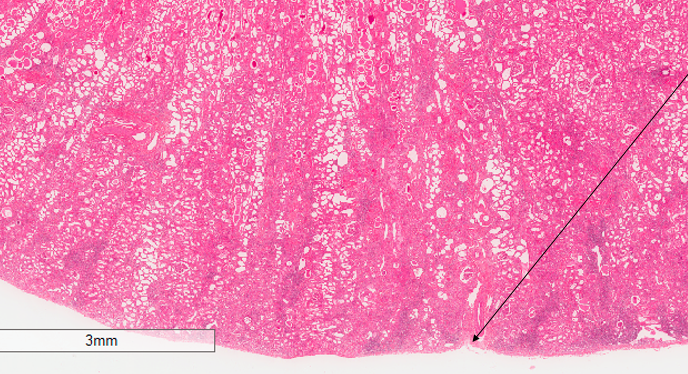
describe the capsular surface
capsular surface is not smooth
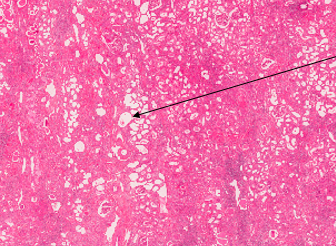
describe the tubular changes
dilated lumen of tubules in cortex and medulla
radially distributed (in lines)
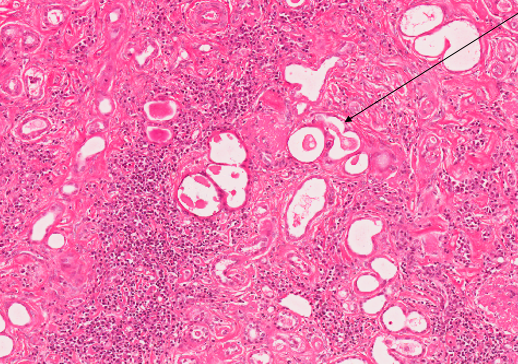
what can we see on this medium power histology view of kidney?
tubules with eosinophilic amorphous material in the lumen = protein in filtrate
arrow points to cell debris within lumen
lack of glomeruli
purple stippling in the interstitium - inflammatory cells
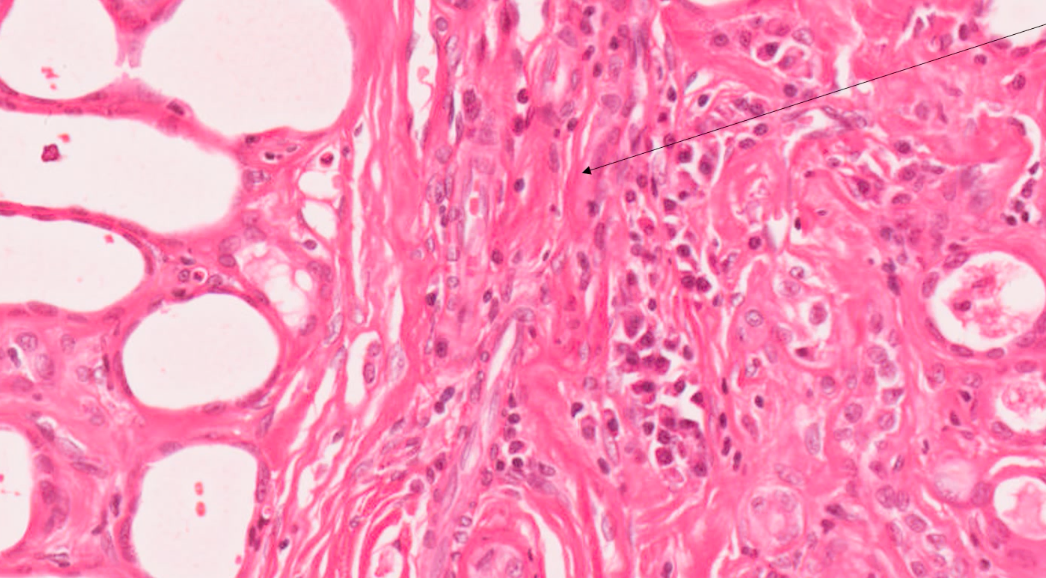
what can we see on this high power histology view of kidney?
red/pink strands within interstitium = collagen
tubules are being squashed / flattened
fibroblasts (elongated strand like cells) with the collagen
plasma cells and lymphocytes in the middle
macrophages present (larger potato shaped cells)
what would the disease and morphological diagnosis be, based off the following clinical signs and pathological features?
chronic PUPD
pale pink bumpy/nodular capsular surface of kidney
medulla pale pink and firm
collagen in interstitial tissue
inflammatory cells present in interstitium
debris and protein present in lumen of tubules
disease = chronic kidney disease
morphological diagnosis = fibrous interstitial nephritis with tubule dilation
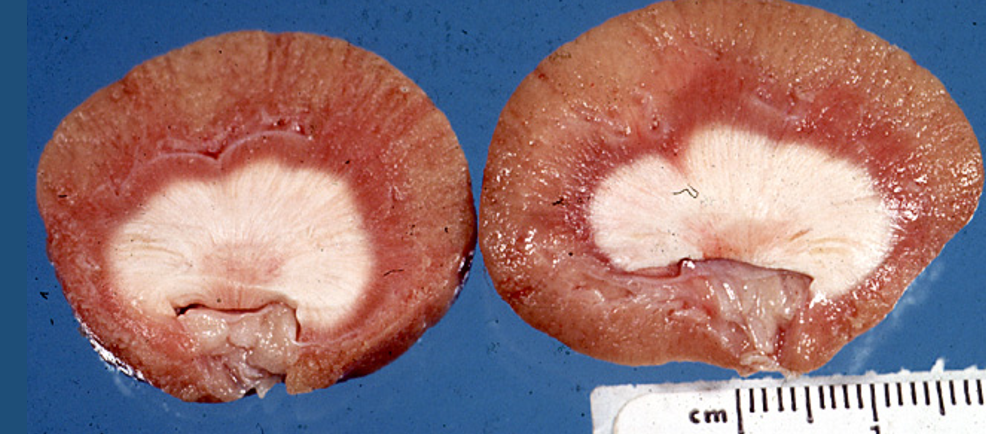
describe the gross changes to this kidney
organ is kidney
pale tan discolouration to cortex, and diffuse creamy white discolouration of medulla
consistency is firm
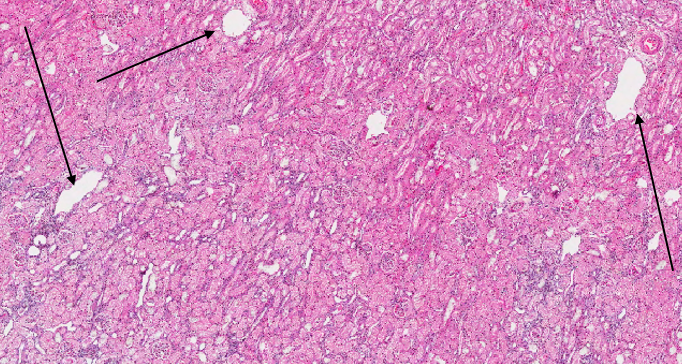
what can we see on this low power histology view of kidney?
dilated tubules / blood vessels
fine purple stippling = possibly inflammatory cells
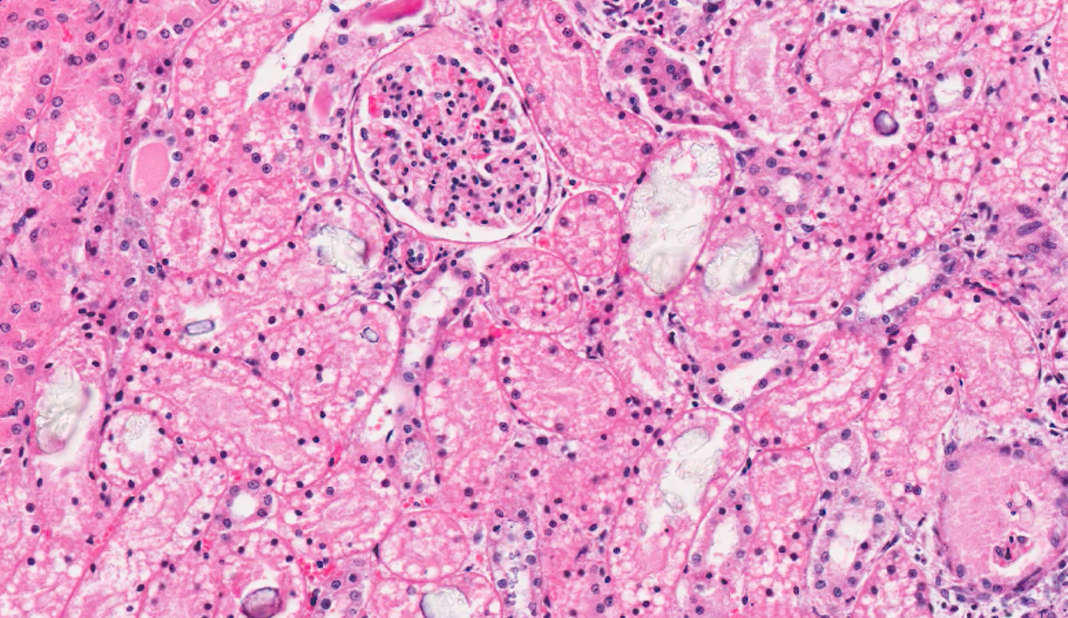
what can we see on this medium power histology view of kidney?
cell debris within lumen of tubules —> necrosis of epithelial cells
multifocal areas with crystalline structures within lumen of tubules
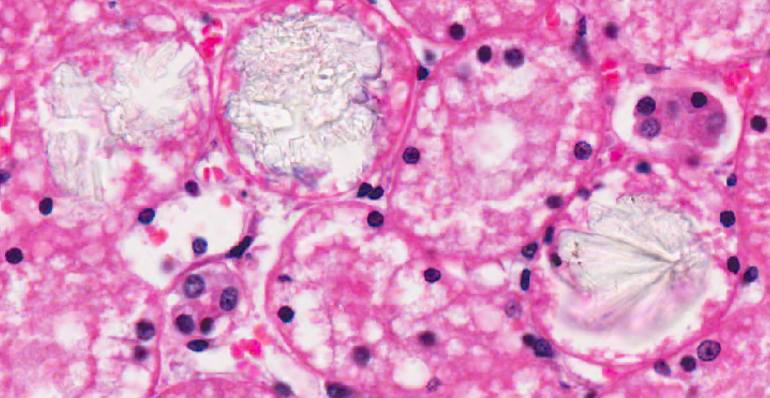
what can we see on this high power histology of kidney?
crystals within lumen of tubules - some granular and some stellate (star formation)
what would the disease and morphological diagnosis be based off the following clinical signs and pathological changes?
history = acute collapse and anuria
creamy white discolouration of medulla
blocking of tubule lumen with crystals
necrosis of epithelial lining of tubules
morphological diagnosis = acute diffuse severe mineralising nephropathy
disease = ethylene glycol toxicity
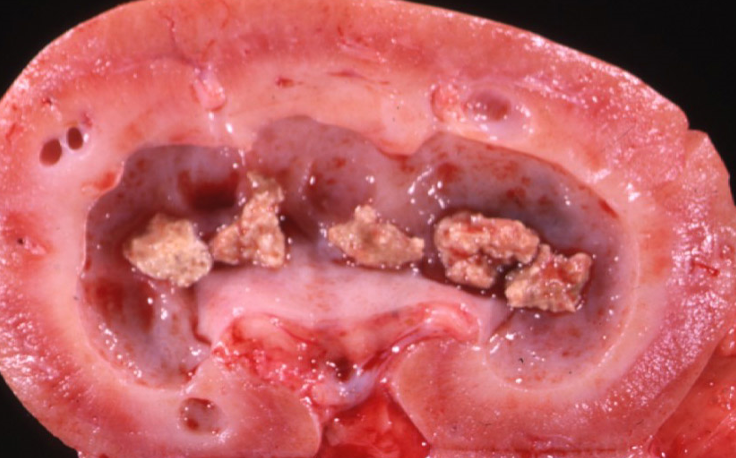
describe this gross lesion
mineralisation / masses (5mm x 5mm) in medulla of kidney —> calculi
calculi firm in consistency and pale tan colour
dilated tubules within medulla, extending slightly into cortex —> starting to become cystic
dilation of renal pelvis —> hydronephrosis
pressure atrophy of cortex and medulla
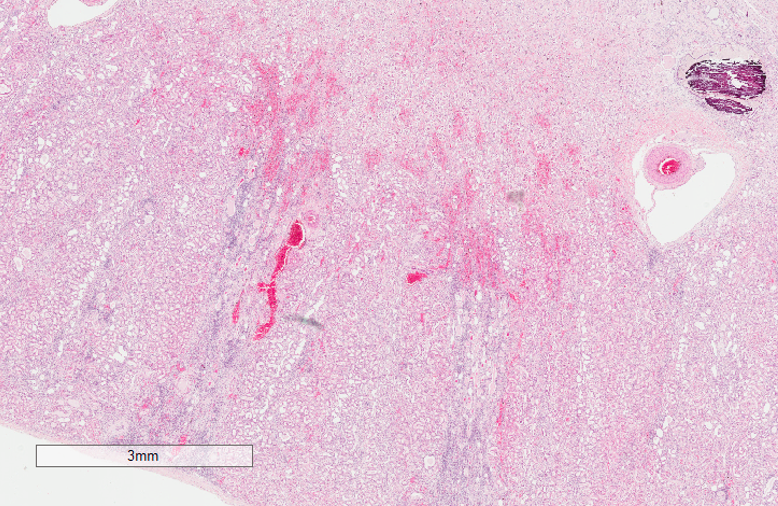
what can we see on this low power histology of kidney?
purple / black area in medulla - likely in tubule or collecting duct
red staining in cortex —> hyperaemia of blood vessels
purple stippling = inflammatory cells at the bottom of the image - radial pattern to purple stippling
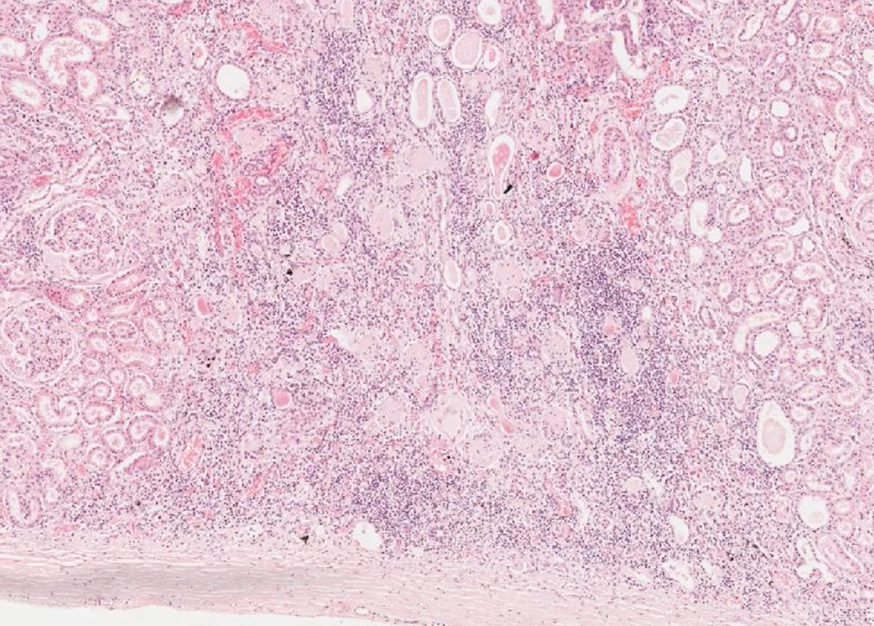
what can we see in this medium power histology of kidney?
purple stippling = inflammatory cells
tubules containing pink amorphous material = filtrate containing protein
dilation of tubules
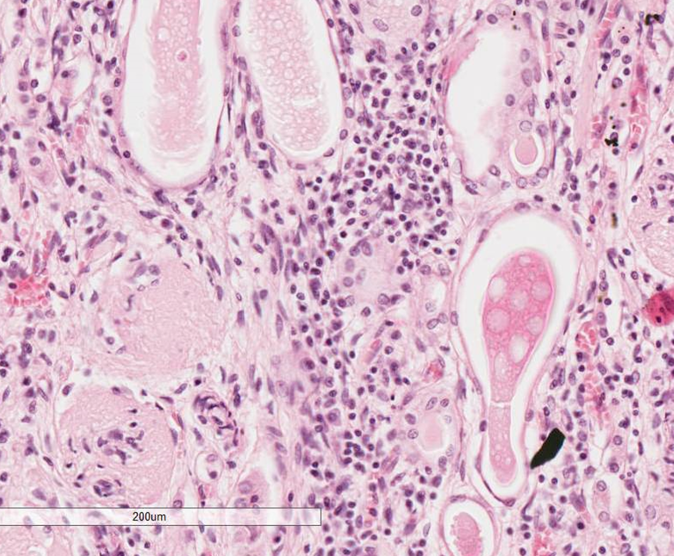
what can be seen on this high power histology of kidney?
dilation of tubules with eosinophilic material in lumen = protein within filtrate (but distribution of protein in the fluid is uneven)
pale pink strands and elongated nuclei = fibroblasts
glomeruli lacking nuclei on bottom left of image- being replaced by collagen —> glomerulus cirrhosis due to fibrous tissue
inflammatory cells - lymphocytes and plasma cells in middle of image
what would the disease and morphological diagnosis be based off the following clinical signs and pathological changes?
history = haematuria (blood in urine) and dysuria (difficulty urinating)
dilation of renal pelvis + calculi present
dilated tubules + tubule lumens with protein in filtrate
fibroblasts present in interstitium
glomeruli lacking nuclei with collagen forming
inflammatory cells = lymphocytes and plasma cells
morphological diagnosis = chronic fibronecrotising pyelonephritis with proteinuria
disease = pyelonephritis due to local trauma from calculi
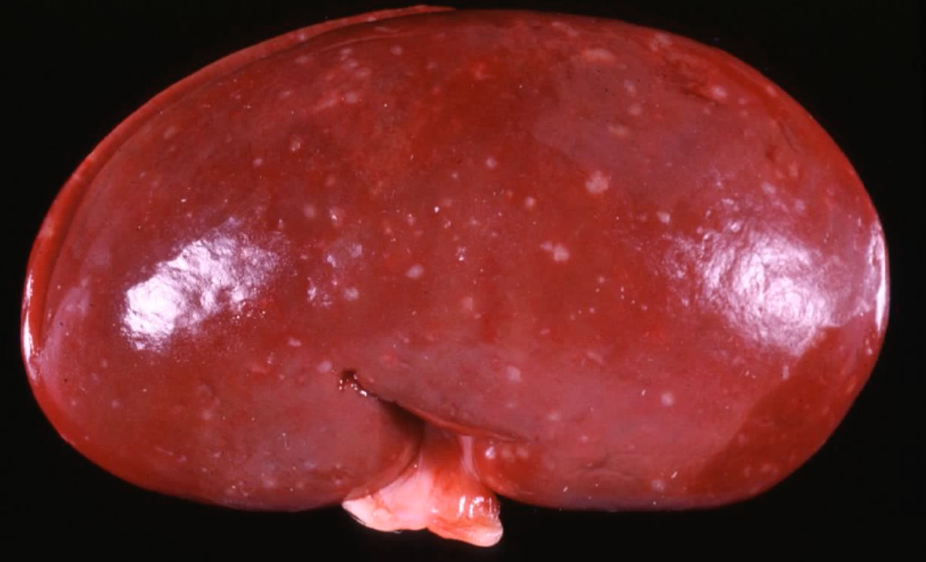
what can we see in this gross image of kidney?
multifocal 1mm pale tan lesions across the surface of kidney
kidney is diffusely red and swollen
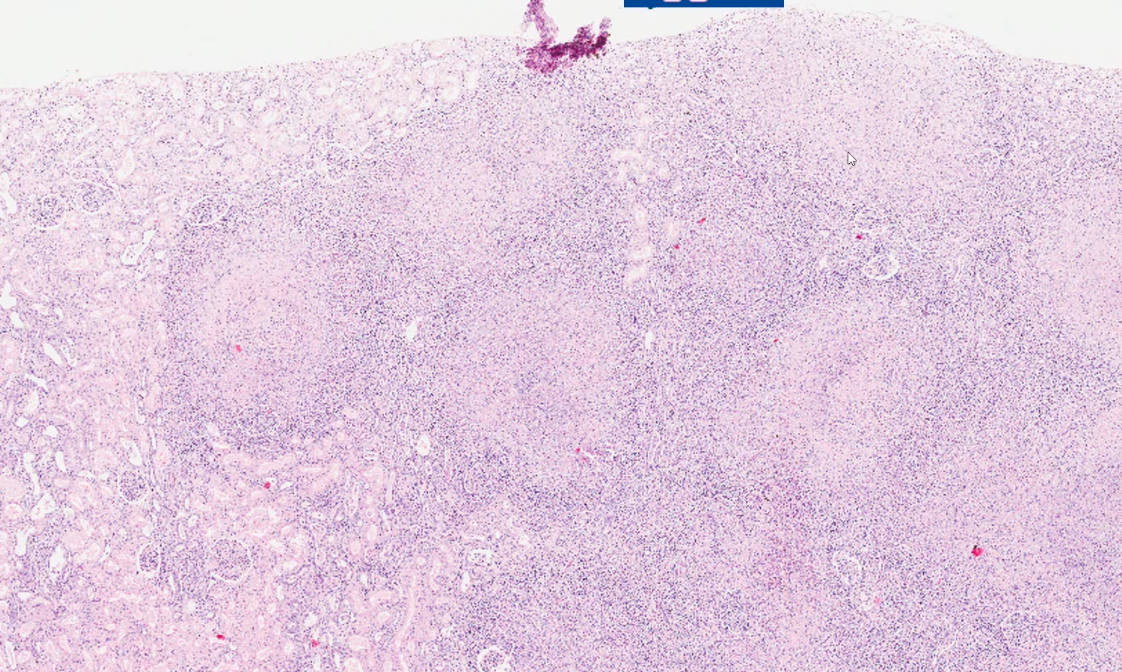
what can we see in this low power histology of kidney?
cortical surface is not smooth
structures with central eosinophilic staining with purple stippling around the border
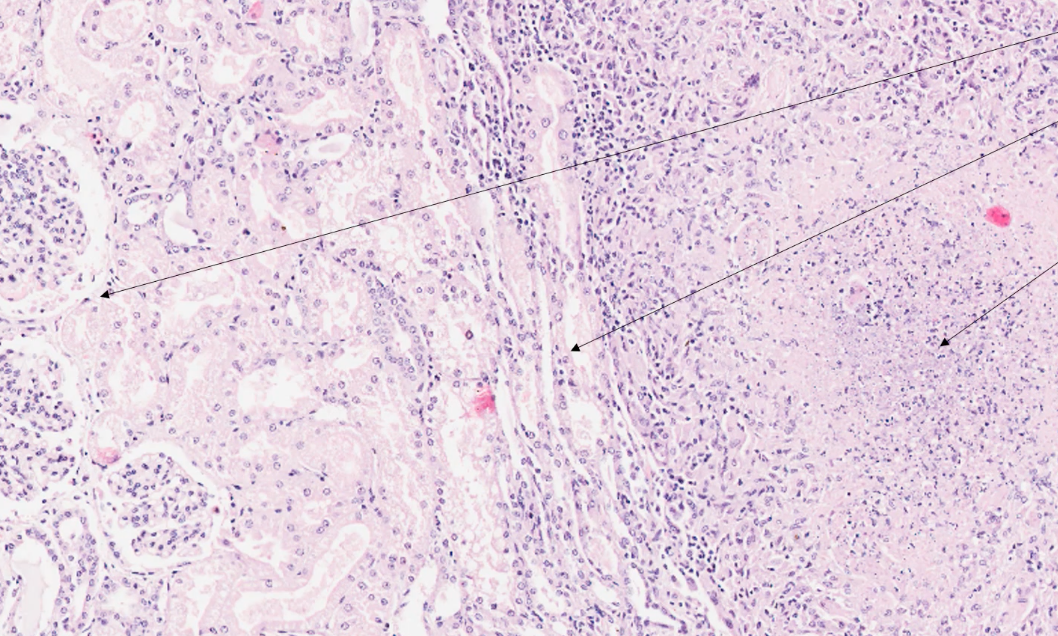
what can we see in this medium power histology of kidney?
on the left of the image there are tubules with pale eosinophilic amorphous material = protein in filtrate
in the middle of the image there are tubules with squashed / flattened lumen
right of the image shows nodule containing lots of fine purple stippling and eosinophilic material
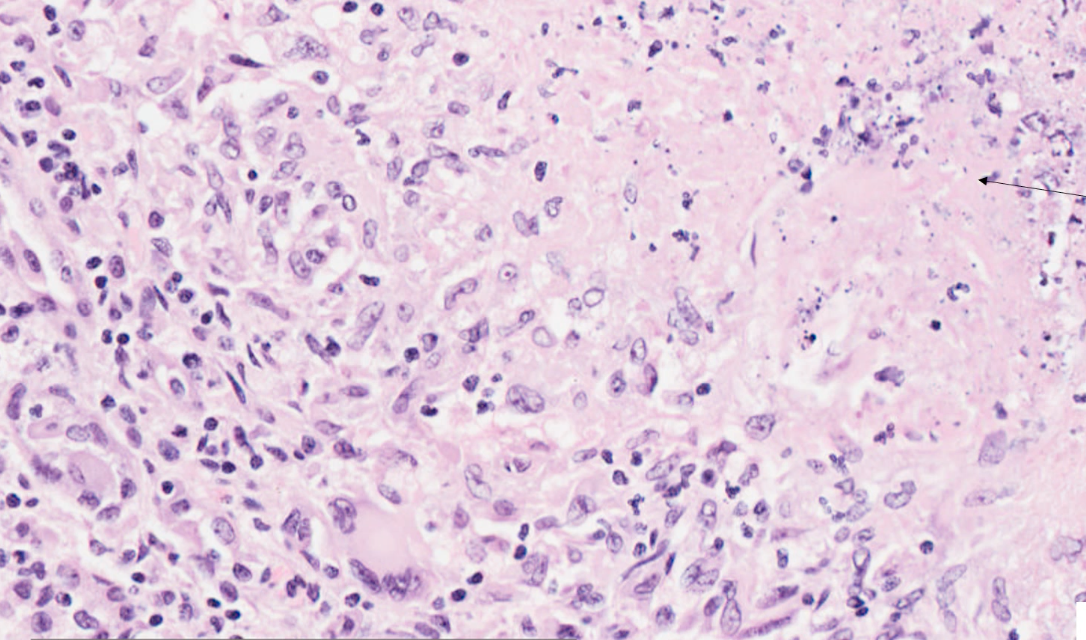
what can we see in this high power histology of kidney?
increased cellular density
bottom left - cells with large potato shaped nuclei = macrophages, multi-nucleated giant cells
top right - fragmented nuclei, eosinophilic material merging together = cell debris —> necrosis
what would the disease and morphological diagnosis be based off the following clinical signs and pathological changes?
history =
red swollen kidney with multifocal tan lesions
macrophages and multi-nucleated giant cells present
areas with concentrated cell debris and necrosis present
morphological diagnosis = chronic severe necrogranulomatous interstitial nephritis
disease = migrating parasite e.g. Toxocara canis