OB First: Exam 1
1/279
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
280 Terms
Nursing
Nursing Shortage
Collaborative Practice
Standards of Nursing Care
Respected Profession
Changes in Maternal-Newborn Nursing
Family Centered Care:
Refers to the collaborative partnership among the individual, family, and caregivers to determine goals, share information, offer support, and formulate plans for healthcare.
Emphasis on Early Prenatal Care:
Early, adequate prenatal care has been long associated w/ improved pregnancy outcomes.
It is a comprehensive process in which problems associated w/ pregnancy are identified and treated.
40 reasons to go 40
Epidurals
Increase in C-Section Rates
Induction:
use of pitocin
Birth Plans
Newborns’ and Mother’s Health Portection Act of 1996
COVID-19 and Pregnancy & Birth

Maternal Mortality
Complications during pregnancy and childbirth are a leading cause of death and disability among women of reproductive age in developing countries.
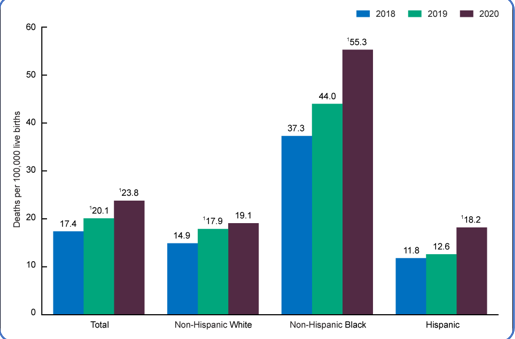
Maternal Death is…
the death of a woman while pregant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management, but not from accidental or incidental causes.
Types of Families
Nuclear
Dual-Career/Dual-Earner
Childless or Childfree
Extended
Single-Parent
Blended
Adopted
Foster
Binuclear
Cohabitating
Gay and Lesbian

Reproductive Assistance
Infertility: lack of conception despite unprotected intercourse for at least 12 months.
If 35 or older, lack of conception despite unprotected intercourse for at least 6 months.
_________________________________________________________
IVF
Fertility Clinic
Culture and Religion Influcences
Culture: the beliefs, values, attitudes, and practices that are accepted by a population, a community, or an individual.
Religion: institutionalized system that shares a common set of beliefs and practices.

Ethical Issues
Rights of Parents
Rights of Child
Court Decisions
Positive Drug Test
Impact on Families

What is gestation?
Period of time between conception & birth during which fertilized ovum matures & grows in the female's uterus.
AKA pregnancy

How long does gestation last?
40 weeks (280 days)
Female Reproductive Cycle
28 day cycle (typically)
Day 14 → ovulation (ovum released from ovary so can be fertilized)
Need to know cycle length to know when woman is ovulating so she can get pregnant.
Spermatogenesis is…
The production of sperm.
200-400 million sperm released during ejaculation, but only 200 make it to uterus.
Where does fertilization usually occur?
Outer third of Fallopian tube (ampulla)
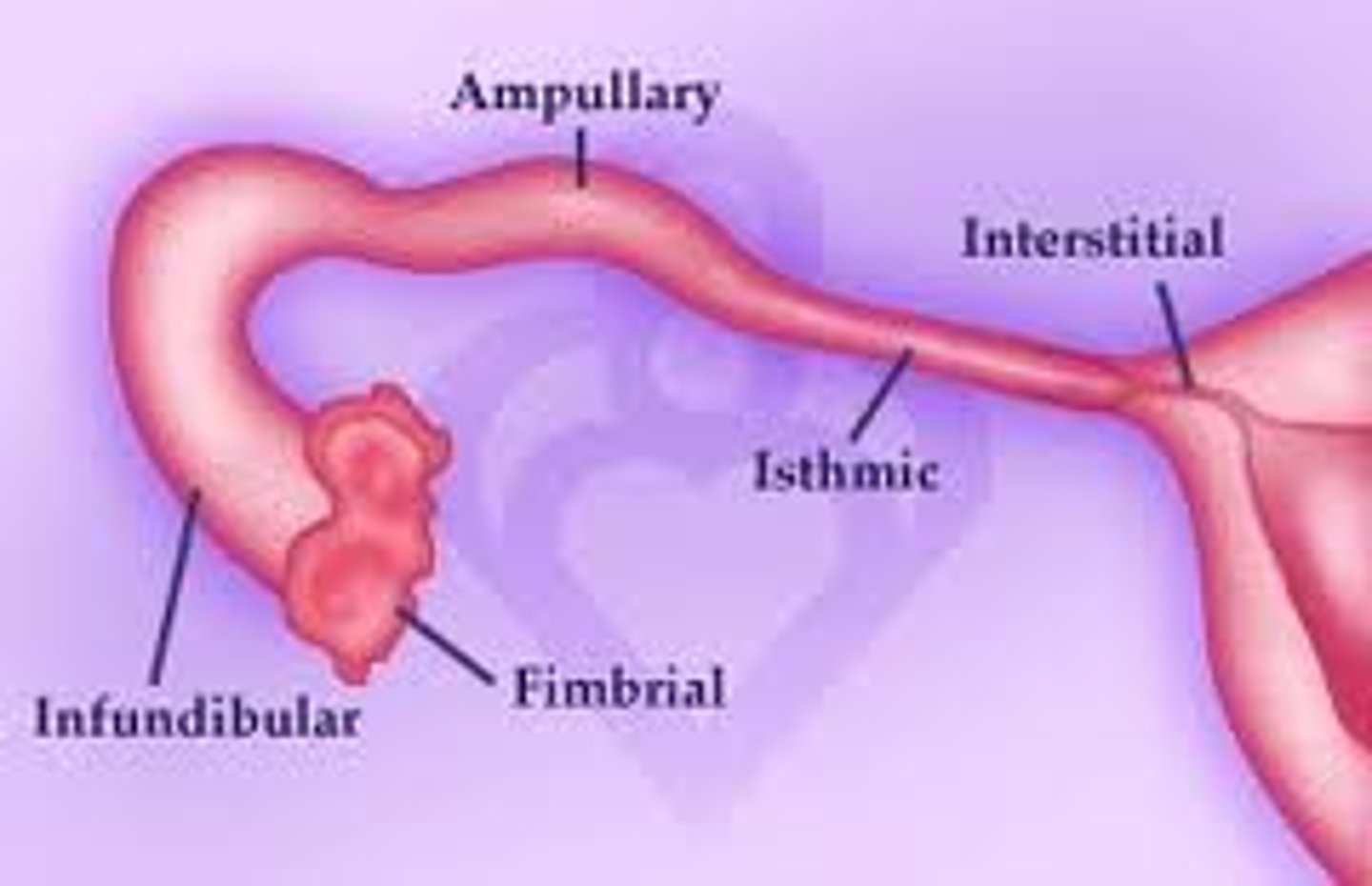
When is Ovum receptive to fertilization after release from Ovary?
24-48 hours
How long is sperm viable after ejaculation?
24-72 hours
What is a Zygote?
Fertilized Ovum will begin cell division
When does the Blastocyst implant to the endometrium & implant on top of Uterus?
6-10 days
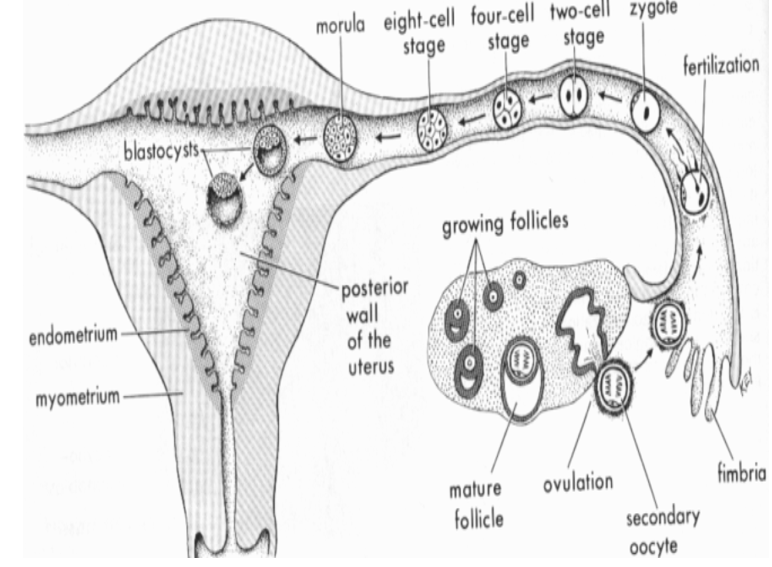
What is gestational age?
Age of pregnancy from last normal menstrual period (LMP); starts on 1st day of last period.
Most people reference this for their pregnancy.
What is fetal age?
The actual age of the growing baby from conception.
The pre-embryonic stage is the…
First 14 days
Embryonic Stage
15 days to 8 weeks
Most critical period b/c all main organ systems are being developed.
Most vulnerable to malformation by environmental teratogens.
The fetal stage lasts from __ weeks to __ weeks.
9 weeks to 40 weeks
When is the heart beating in an embryo?
4 weeks
When are the organs fully developed, but not fully functional?
8 weeks
Teratogens are…
Any agent or factor that induces or increase the incidence of abnormal prenatal development.
What are teratogenic agents?
Alcohol
Tobacco
Medications (Prescribed, OTC, illegal)
Infections
Herbs
What are other factors that affect development?
Quality of Sperm and Ovum:
older eggs possibly increase rx of down syndrome; older sperm quality diminishes and can cause some abnormal development.
Genetics
Maternal Nutrition
Maternal Hyperthermia:
extreme increases in body temperature (avoid hot tubs/saunas, etc. esp early on)
Trimesters
1st trimester: from conception to the end of 12th week
2nd trimester: from week 13 through 27
3rd trimester: from week 28 through 40
When are fetal heart tones heard by Doppler?
8-12 weeks
When can baby's gender be seen?
16 weeks
What occurs when baby is 20 weeks in uteuro?
Mom can feel movement called quickening—first movement of the baby.
Baby develops regular schedule of sleeping, sucking, & kicking.
Hands can grasp.
Head hair, eyebrows, & eyelashes present.
What happens when a baby is 24 weeks in uteuro?
Activity increases
Fetal respiratory movements begin (moves fluid in and out to practice for air)
What happens when a baby is 28 weeks in uteuro?
Eyes begin to open & close (fused before now)
2/3 baby's final size
What happens when a baby is 38+ weeks in uteuro?
Baby gets antibodies from mother (decreases risk for sickness)
Amniotic Fluid
Liquid surrounding the fetus in uterus.
Absorbs shocks, permits fetal movement, & prevents heat loss (absorbs & protects baby).
Volume of fluid changes constantly (increases w/ pregnancy) --- baby adds to fluid level b/c baby pees & kidneys start functioning.
Fetus swallow fluid for lung movement.
Fluid flows into & out of fetal lungs.
Fetus urinates
Oligohydramnios vs. Polyhydramnios
O: (too little fluid; cause: kidneys not functioning)
P: (too much fluid; cause: high BBG in mother—insulin resistant → mom is thirsty and pees a lot and then baby pees a lot → increased rx of rupturing)
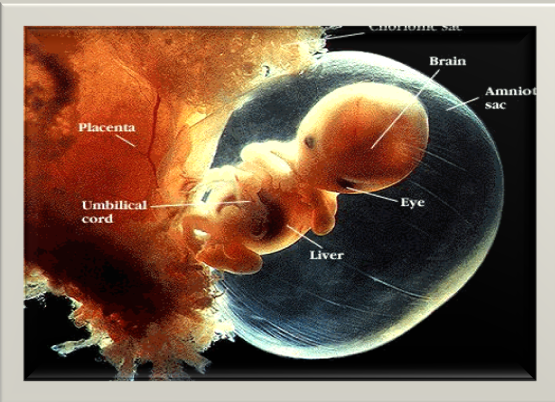
Amniotic Fluid Functions
Temperature Control
Protection
Growth & Development
allows room to grow—IUGR
Prevention
makes amnion not attach to baby, which can make something not grow like a hand, foot, fingers, toes, etc.
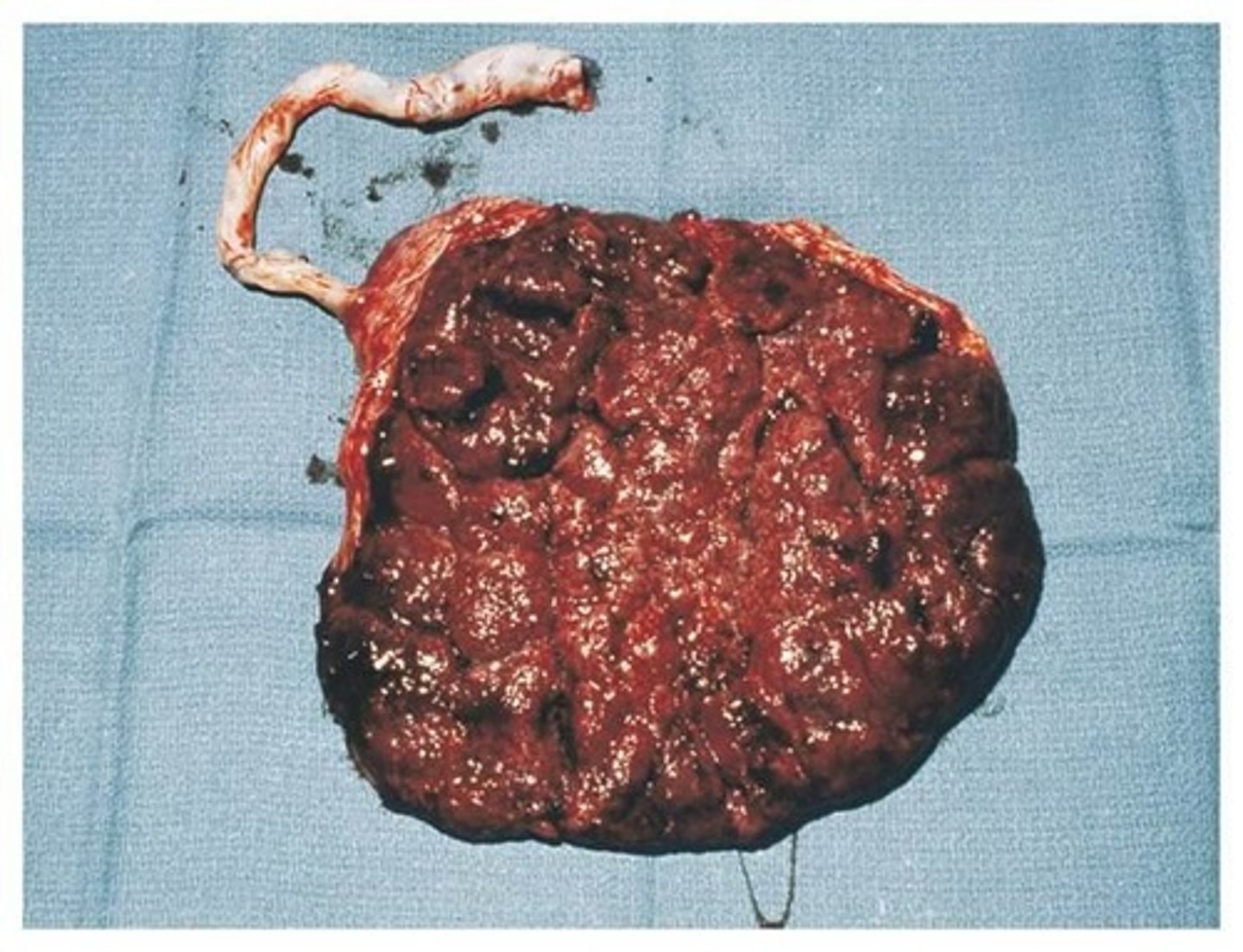
Dirty Duncan Side of Placenta is who's side?
Maternal blood supply & nutrients that are attached to mom.
Attached to uterine lining itself.
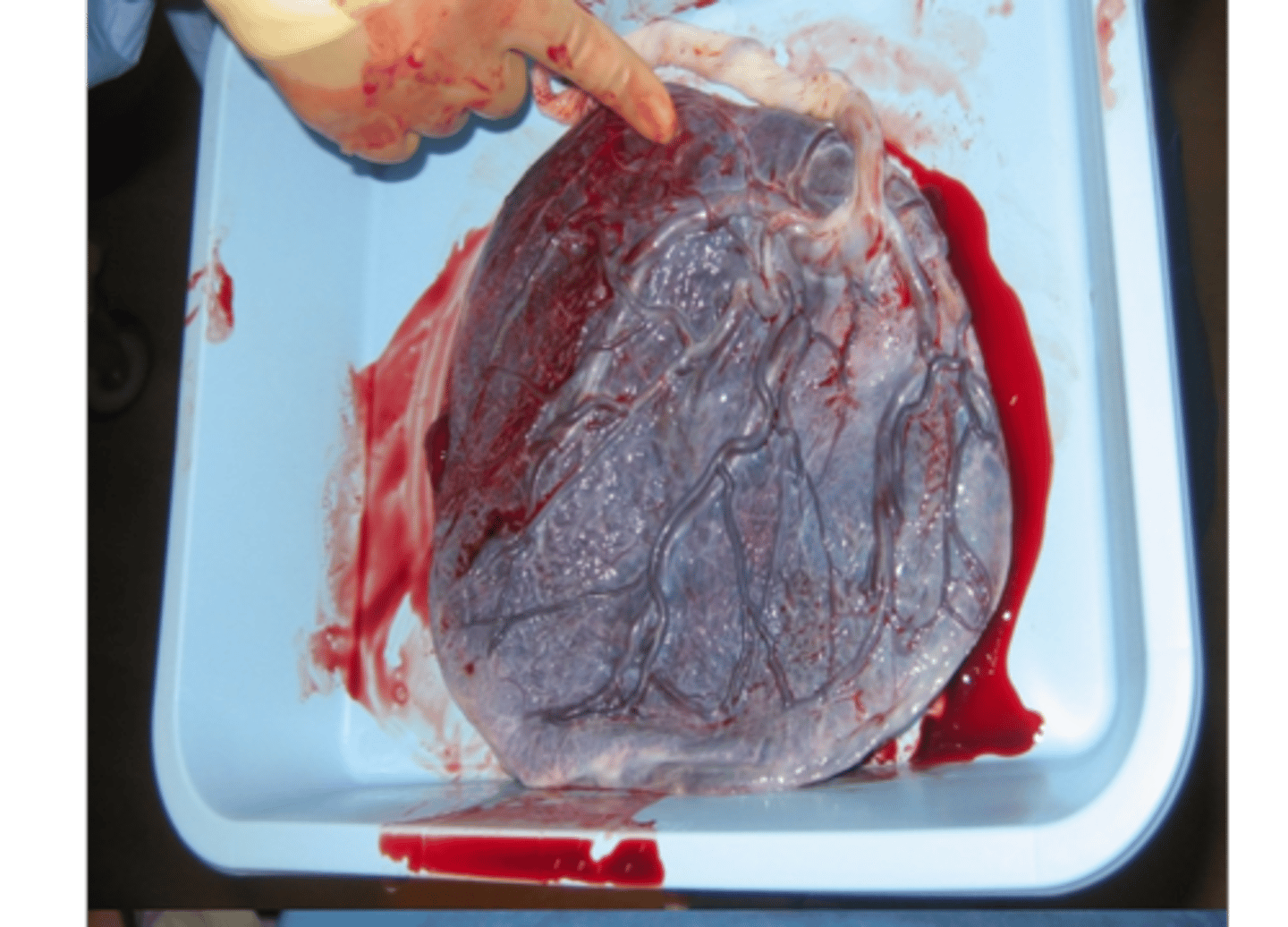
Shiny Schultz of Placenta is who's side?
The fetal side.
What does the Placenta provide?
Fetal Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide exchange
Essential nutrients
Excretion of metabolic waste products
Needed metabolic processes
Placenta Functions
Metabolism:
synthesizes glycogen in early pregnancy.
Organ of Transfer:
responsible for transfer of materials between maternal & fetal circulation.
Endocrine Synthesis:
hCG—human chorionic gonadotropin; picked up on prego tests & causes nausea in women; increases until 10 weeks.
hPL—human placental lactogen; insulin antagonist, allows glucose to be free to let baby grow; higher 24-28 weeks.
Estrogen & Progesterone—development & more.
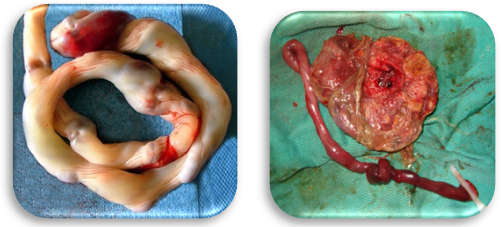
Umbilical Cord
Lifeline between baby & mom
AVA: 2 arteries & 1 vein
Wharton's Jelly: connective tissues keeps the cord open so no compression on the arteries or vein.
Usually around 22 inches long.
No nerve fibers in cord so won't hurt baby.
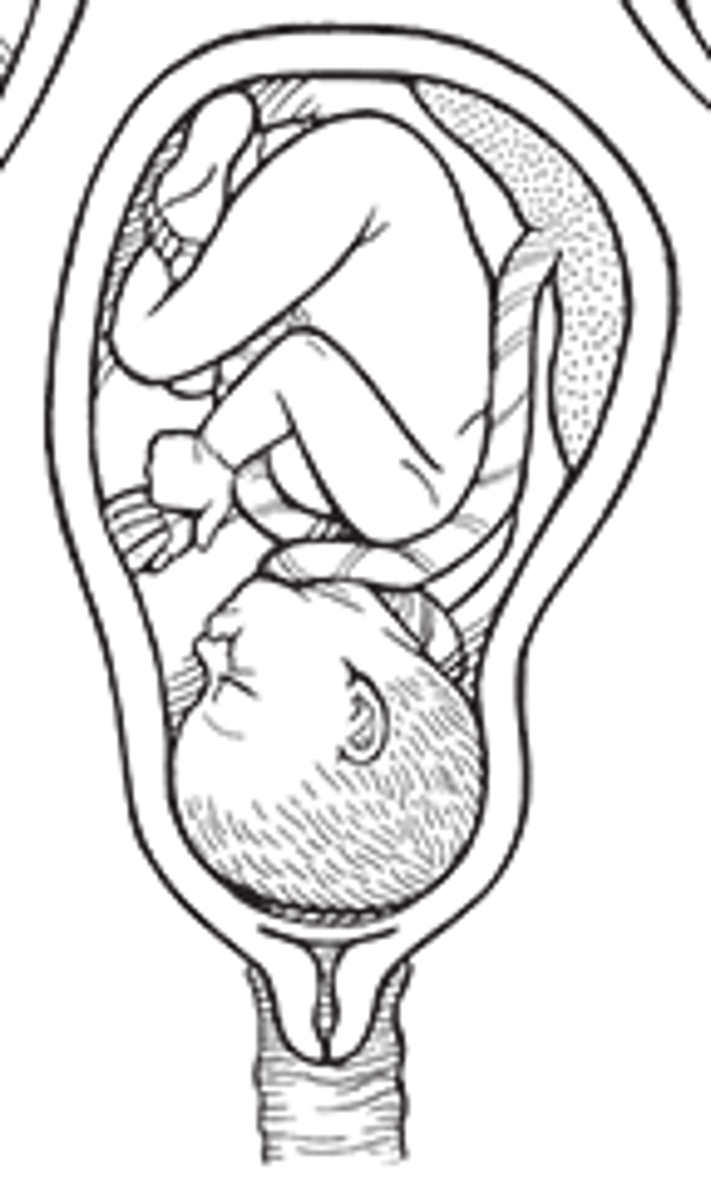
Nuchal Cord
It is a cord wrapped around baby (usually around neck).
Fetal Circulation
The cardiovascular system is the 1st organ system to function in developing human.
Most of blood supply bypass lungs (since no respiratory gas exchange).
Placenta assumes the function of the fetal lungs.
Path of Oxygenated blood from Placenta
1. Travel through umbilical vein
2. Ductus Venous (shunt @ liver)
3. Inferior Vena Cava
4. Right Atrium
5. Foramen Ovale (shunt to left atrium - bypasses lungs)
6. Left atrium
7. Left ventricle
8. Aorta
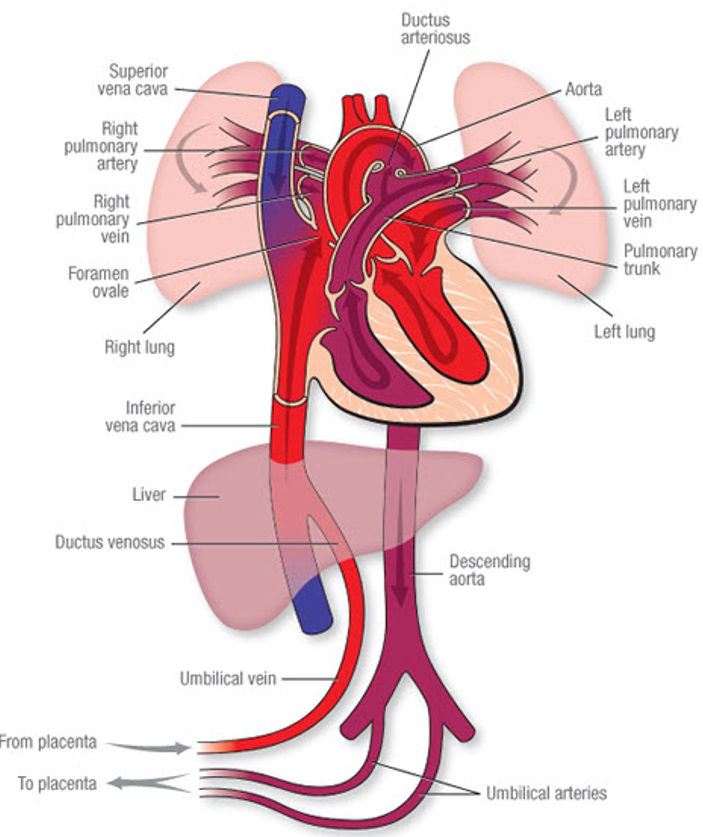
Path of Deoxygenated Blood Route to Placenta
1. Superior Vena Cava
2. Right atrium (through tricuspid valve)
3. Right ventricle
4. Ductus arteriosus (shunts from pulmonary artery from lungs since non-functioning)
5. Aorta
6. Descending Aorta
7. Umbilical arteries
8. Placenta
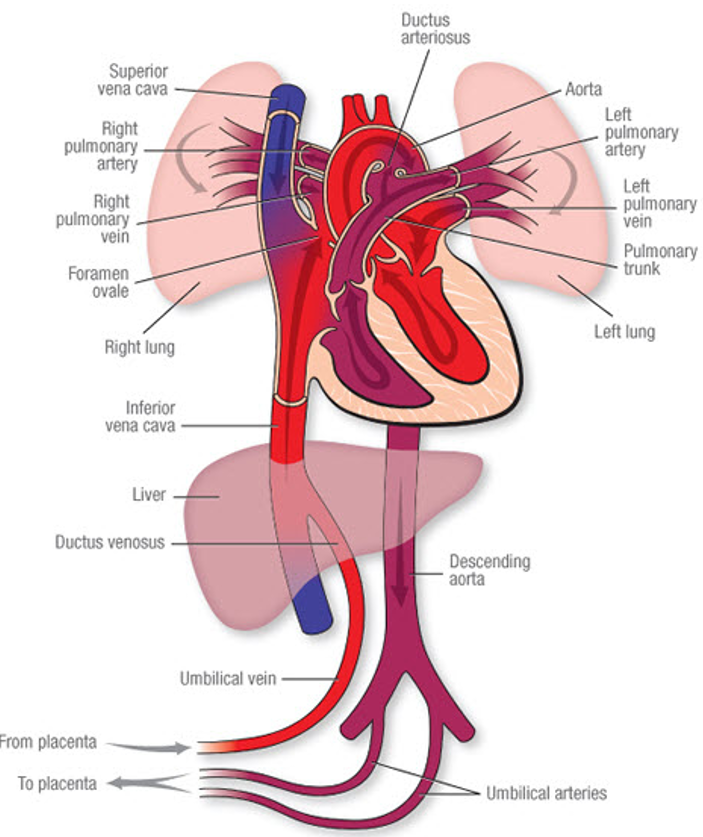
What are the shunts of Fetal Circulation?
Ductus Venosus: shunt @ liver
Foramen Ovale: shunts to the left atrium - bypasses lungs
Ductus Arteriosus: shunts from pulmonary artery from lungs since non-functioning
How long does the Foramen Ovale stay open?
24 hours after clamping; You can hear a murmur which is normal.
Presumptive Signs of Pregnancy
Amenorrhea (no menstrual period)
Nausea/vomiting (“morning sickness” but for some “all-day sickness”)
Urinary frequency
Breast changes
Fatigue
Probable Signs of Pregnancy
Enlargement of abdomen
Hegar's Sign: softening of uterus isthmus.
Goodell's Sign: softening of cervix.
Chadwick's Sign: blue discoloration of cervix b/c increased blood supply.
Positive pregnancy test:
false negatives can occur.
Pigmentation of skin:
chloasma—pigmentation of the face; butterfly effect.
linea nigra—dark line on abdomen.
Striae:
stretch marks.
Positive Signs of Pregnancy
Fetal heartbeat (using doppler)
Fetal movement on palpation
Ultrasound
Assessment Health History
Menstrual Cycles/Gynecological History
Obstetric:
prior pregnancies
Medical:
diabetes, HTN, mental health, meds, etc.
Health Care Activities:
exercise, jog, etc.
Nutrition:
Need Ca & Fe, limited folic acid
Exercise
Roles & Relationships:
support system for stress
Physiologic Changes During Pregnancy
Uterus: gets larger and pushes everything away as it's growing.
Cervix: softens & changes to have the baby; develops mucus plug to protect baby against infection.
Vagina: more muscular; vaginal secretions become more acidic for protection of baby, but increased rx for infection.
Breasts: enlarged for lactation, areola darken & leak colostrum (1st milk).
Thyroid Gland: release of T4 is increased so she stays warmer.
Respiratory: can't get good deep breaths b/c baby is pressing up on diaphragm and lungs.
Cardiovascular: produce 40% more blood volume, more hemoglobin; H&H decreased b/c diluted w/ blood volume.
Urinary: urgency & go a lot more.
Gastrointestinal: slowing of peristalsis b/c everything moved around; constipation which can lead to hemorrhoids.
Musculoskeletal: may waddle b/c things are relaxed in joints and lordosis.
Integumentary: darkening of areola, linea nigra, chloasma, acne, & patches of hair they didn't have before.
Neurological: baby may be pushing on certain nerves (sciatic).
Hormones for Pregnancy
Estrogen: helps prepare for lactation; will have lower level than progesterone during pregnancy b/c it will make uterus irritable, but after baby is delivered, estrogen levels will rise to allow uterus to contract.
Progesterone: level has to stay high to keep the uterine lining thick or else mom will lose the pregnancy; relaxes the uterus; prepares breast for lactation.
Relaxin: causes uterus not to contract; softens the cervix and relaxes joints in preperation for L&D.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG): hormone that is tested for in pregnancy tests; produced in the first several weeks; labwork to see if mom is losing the pregnancy)
Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Released from the placenta in increasing amounts.
Levels should double every 48 hours in a normally developing pregnancy.
Peaks at week 10 and then declines.
Almost undetectable at term.
Used for urine pregnancy test (positive 10 days after conception).
Nagele's Rule
Based on 28 day cycle.
1st day of last menstrual period (LMP) Subtract 3 months & add 7 days.
Ex: LMP - Aug 10, 2024 & EDD - May 17, 2025

Full term
Delivery is any birth 38+ weeks.
Pre term
Delivery is birth between 20-37 weeks.
Postdate
Delivery is any delivery after the completion of the 40th week.
Abortion
Delivery before the age of viability (before 20 weeks).
Gravida
Refers to the # of times that a woman has been pregnant.
nullgravida, primigravida, multigravida
Parity (Para-)
Refers to # of births
Gravida/Para Counting Systems: 5 Digit
G - # of pregnancies
T - # of term deliveries
P - # Preterm
A - # of abortions
L - # of living children
Gravida/Para Counting Systems: 2 Digit
Gravida (# of pregnancies)
Para (# of births 20 weeks +)
The quickie way used in the hospital setting.
Fundal Height
Is used to determine if baby is growing how it should.
The fundus measures the very top of the uterus.
Just a quick and easy tool; measured in cm.
Not as accurate towards the end of pregnancy as the baby drops.
(seen in second pic below)
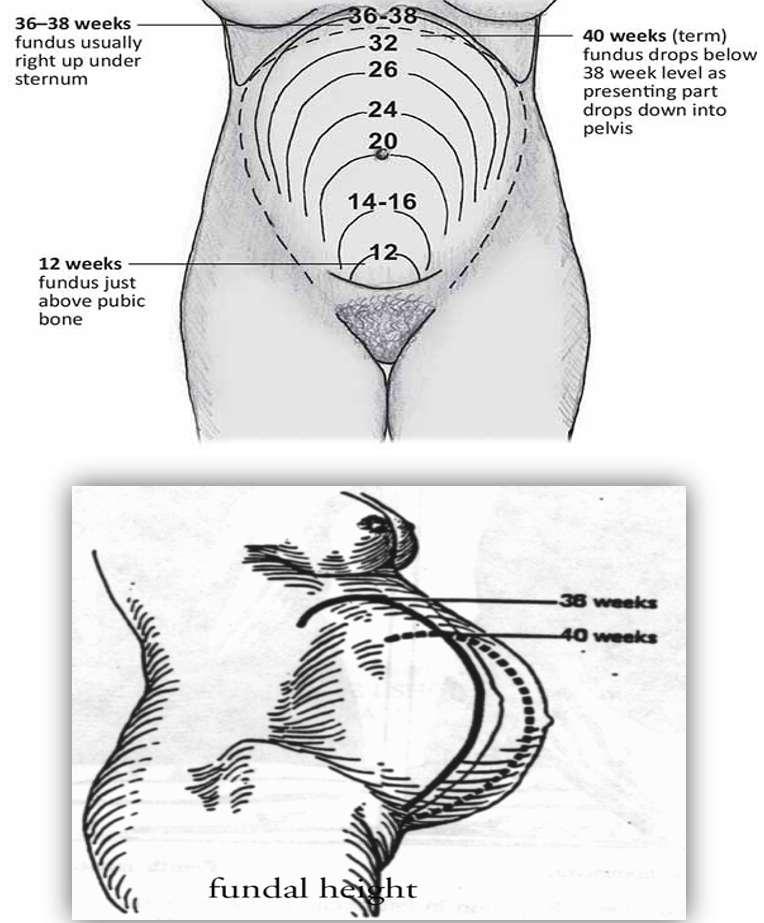
Prenatal Lab Tests
CBC
Blood Type & Rh factor:
+ or -; will have issues w/ future pregnancies.
Rubella titer:
If mom is not immune, we cannot give her the vaccine while she is pregnant b/c the vaccine is a live virus.
Urinalysis
STD's
Hepatitis B
HIV
Group B Strep:
inactive in the vaginal/rectal area and may become activated and make baby sick.
Quad Screen:
determines things like down syndrome - not 100%
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Fetal Heart Rate
Normal Range: 110-160
Doppler (easiest)
Fetal monitor
What is an ultrasound?
High-frequency sound waves that may be directed, through the use of a transducer, into the maternal abdomen.
The ultrasonic sound waves reflected by the underlying structures of varying densities allow identification of various maternal and fetal tissues, bones, and fluids.
Uses of Ultrasound
Location & presence of early pregnancy
Gestational age & maturity
Fetal weight
IUGUR (intra uterine growth restriction)
Polyhydramnios or Oligohydramnios
Fetal death
Placenta location:
should be in the upper part of the uterus; if low → placenta previa → c-section)
Biophysical profile:
anything below 8 then baby is compromised.
Fetal lie & presentation:
able to see if baby is in postion w/ head down ready for delivery.
Biophysical Profile
Fetal heart rate acceleration
Fetal breathing
Fetal movements
Fetal tone
Amniotic fluid volume
** Looking for fetal well-being when doing this.
** Monitor is placed to monitor fetal HR and the ultrasound is used to see other areas of the baby.
** Each category can get a score of a 2; there are 5 categories; a perfect score is a 10; a score below an 8 will make the provider think of negative outcomes.
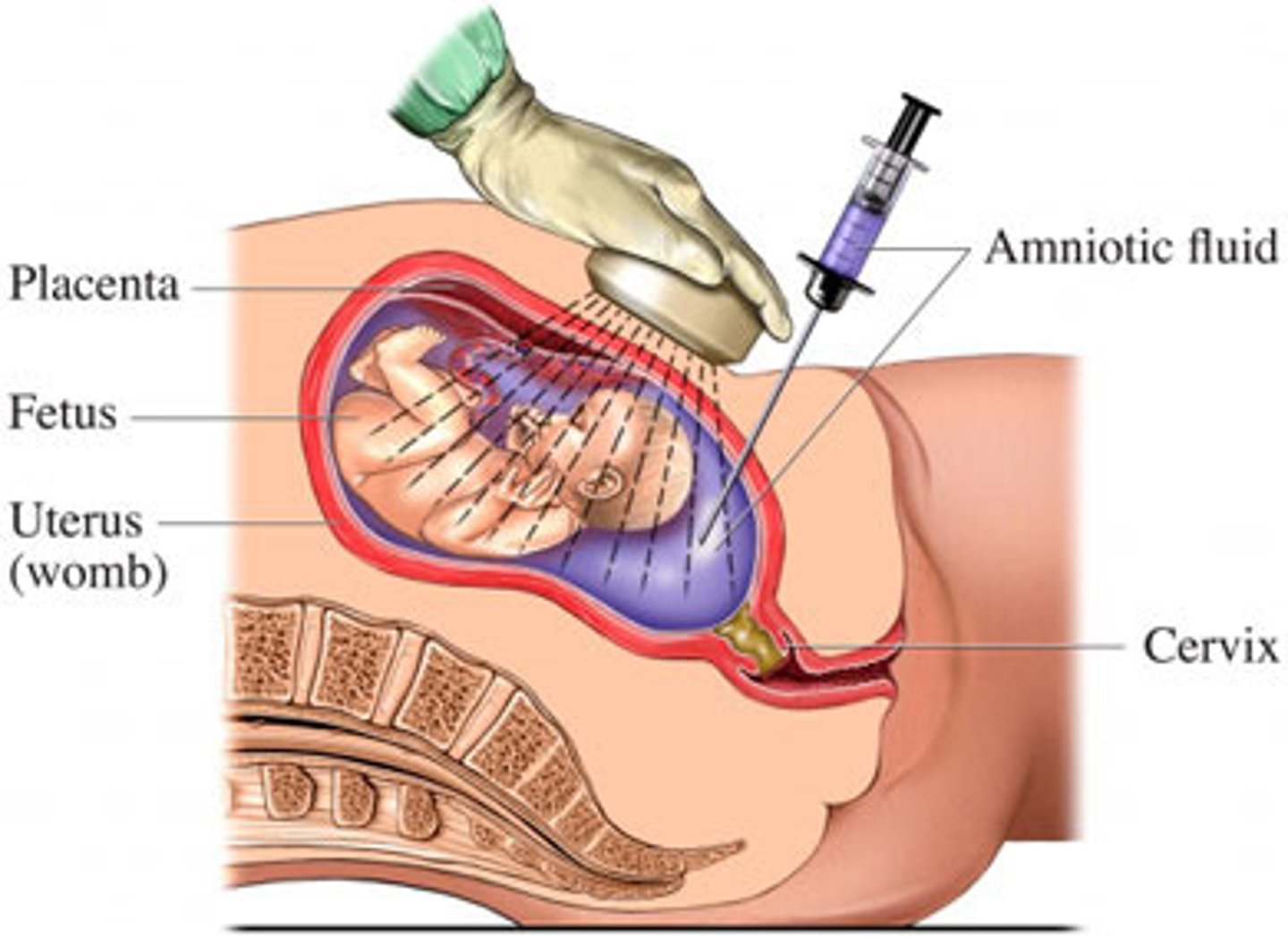
Amniocentesis
Procedure that is done to obtain amniotic fluid for testing.
Indications:
Diagnosis of genetic disorders or congenital anomalies
Assessment of pulmonary maturity
Diagnosis of hemolytic disease
Daily Fetal Movement Recording is a…
Maternal assessment of fetal activity; # of fetal movements within a specified time are counted.
AKA kick count
NonStress Test (NST)
Evaluation of fetal response (Fetal heart rate) to natural contractile uterine activity or to an increase in fetal activity.
Reactive:
at least 2 accelerations that occur w/ movement lasting 15 seconds with increase of 15 beats in 20 minutes.
Non-reactive:
above criteria not met.
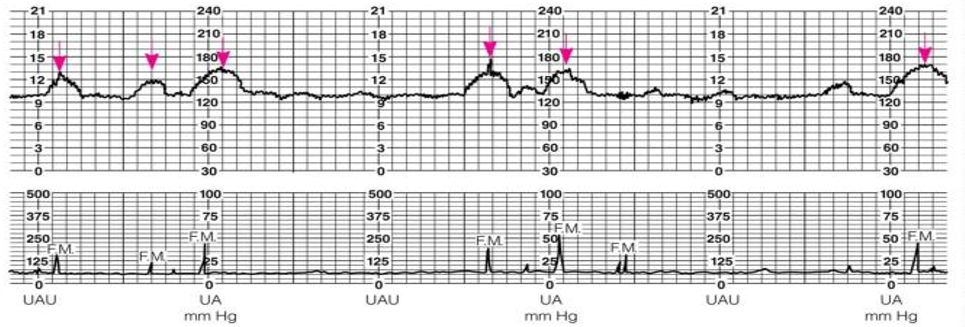
Reactive NST
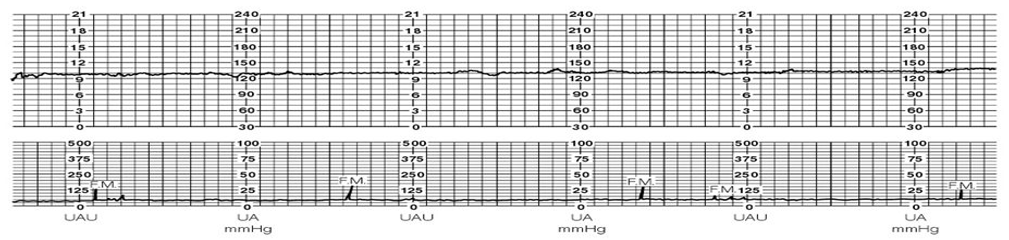
Nonreactive NST
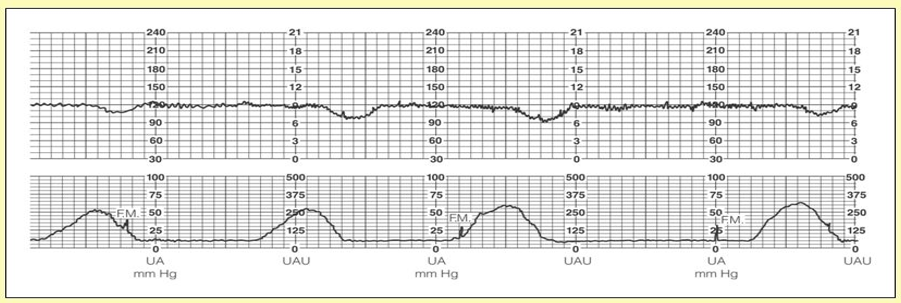
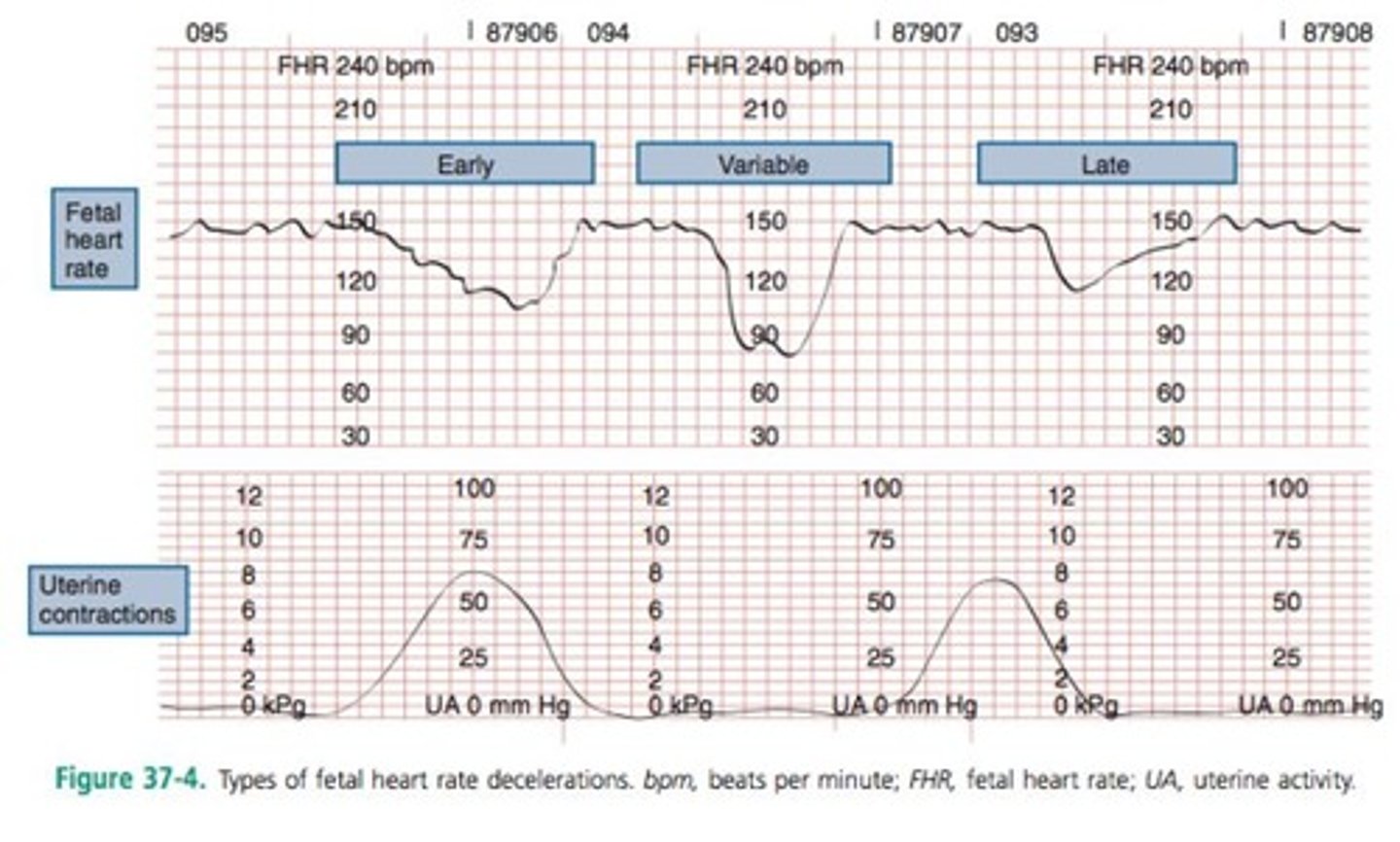
Contraction Stress Test
Test to stimulate uterine contractions for the purpose of assessing fetal response.
A healthy fetus doesn't react to contractions (a negative stress test).
The baby can handle the contractions so the baby HR increase.
A compromised fetus demonstrates late decelerations in fetal HR (a positive stess test; as shown in picture).
This means that the baby is not tolerating the contractions and they are not being well-oxygenated.
1st Trimester Discomforts
Nausea/Vomiting
Urinary Frequency/Urgency
Fatigue
Breast tenderness
Nasal stuffiness & epistaxis
2nd & 3rd Trimester Discomforts
Heartburn (pyrosis)
Hemorrhoids (no straining)
Ankle Edema
Varicosities
Leg cramps
Round Ligament Pain
Danger Signs of Pregnancy
Vaginal Bleeding
Edema face & fingers
Severe, continuous HA
Blurred vision, dizziness
Abdominal pain
Persistent vomiting
Fever & chills
Sudden or constant leakage of fluid from vagina
Scant amount of urine
Absence or decrease in fetal movement
Prenatal Visits
Every 4 weeks until 28 weeks.
Every 2 weeks until 36 weeks.
Every week until delivery after 36 weeks.
Weight Gain
Total weight gain: 25-35 lbs
1st trimester: 3-5 lbs
2nd & 3rd trimester: 1 lb/wk
_____________________________________
11 lbs - baby & amniotic fluid
2 lbs - uterus
4 lbs - increased blood volume
3 lbs - breast tissue
5-10 lbs - fat (maternal stores)
Antepartum: Keys to Nutrition
Calories
Folic Acid—leafy greens (spinach, asparagus), citrus friuits (oranges, grapefruits, lemons), fortified foods (cereals, bread, pasta), legumes (black beans, lentils, chickpeas)
Iron—red meat, poultry, fish, liver, spinach, tofu, etc.
Calcium—dairy products, kale, collard greens, orange juice, tofu, almonds.
Additional Care for Pregnant Women
Rest
Exercise
Sexual Activity (unless dr says no)
Travel (make sure you walk so no blood clots)
Preparation for Childbirth
Early pregnancy classes
Infant care classes
Breastfeeding classes
Sibling classes
Childbirth classes
Theories of Labor
Uterine distention, increasing uterine pressure
Aging of placenta
Increased sensitivity to Oxytocin (normal hormone that produces breast milk & induces labor)
Changes in barometric pressure --> more L&D's
Changes in hormonal concentration:
Estrogen increase
Progesterone decreases
What are early signs and symptoms of impending labor?
1. Lightening: (baby dropping) fetus descends into the pelvic inlet (engagement).
Pressure is then moved from the pressing up against the diaphragm to the lower abdominal area causing:
leg cramps, increased pelvic pressure, venous stasis, urinary frequency, increased vaginal secretions.
2. Braxton-Hicks Contractions: irregular intermittent contractions; may become uncomfortable ((False contractions/labor)).
3. Cervical changes: softening (ripening)
4. Bloody show: cervical secretions mixed with some blood from ruptured capillaries; mucus plug is expelled.
5. Ruptured Membranes: occurs in 8-10% of women prior to labor; 80% will go into labor within 24-48 hours.
6. Sudden burst of energy
7. Others: weight loss, back ache, indigestion, diarrhea.
What are the components of true labor?
Presence of Bloody Show:
pink mucus
Contractions:
regular pattern
interval shortens
intensity increases
duration increases
starts from back to front
intensified by walking
Cervix:
change in dilation and effacement
***WHAT DETERMINES TRUE LABOR IS DILATION OF THE CERVIX AND REGULAR CONTRACTIONS!!!
What are the components of false labor?
No Bloody Show:
brown mucus (old blood)
Contractions:
irregular pattern
no change in intervals
no change in intensity
stays in the front
not changed by walking
Cervix:
no change
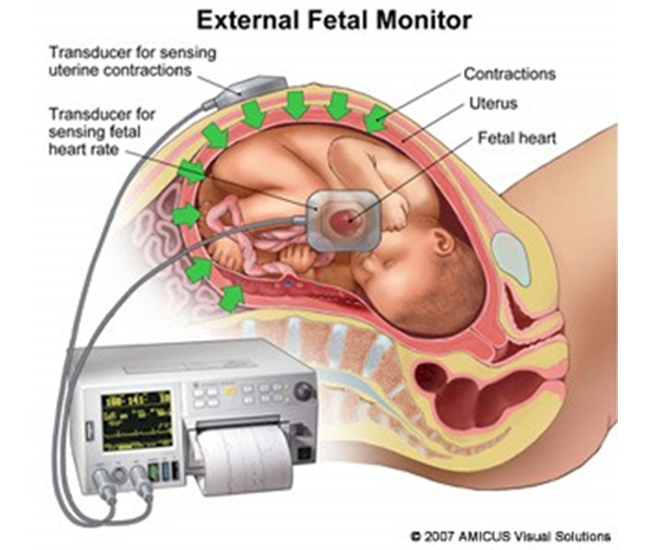
Electrical Fetal Heart Monitoring is…
Commonly used for tracking how well the baby is doing within the contracting uterus and for detecting signs of fetal distress.
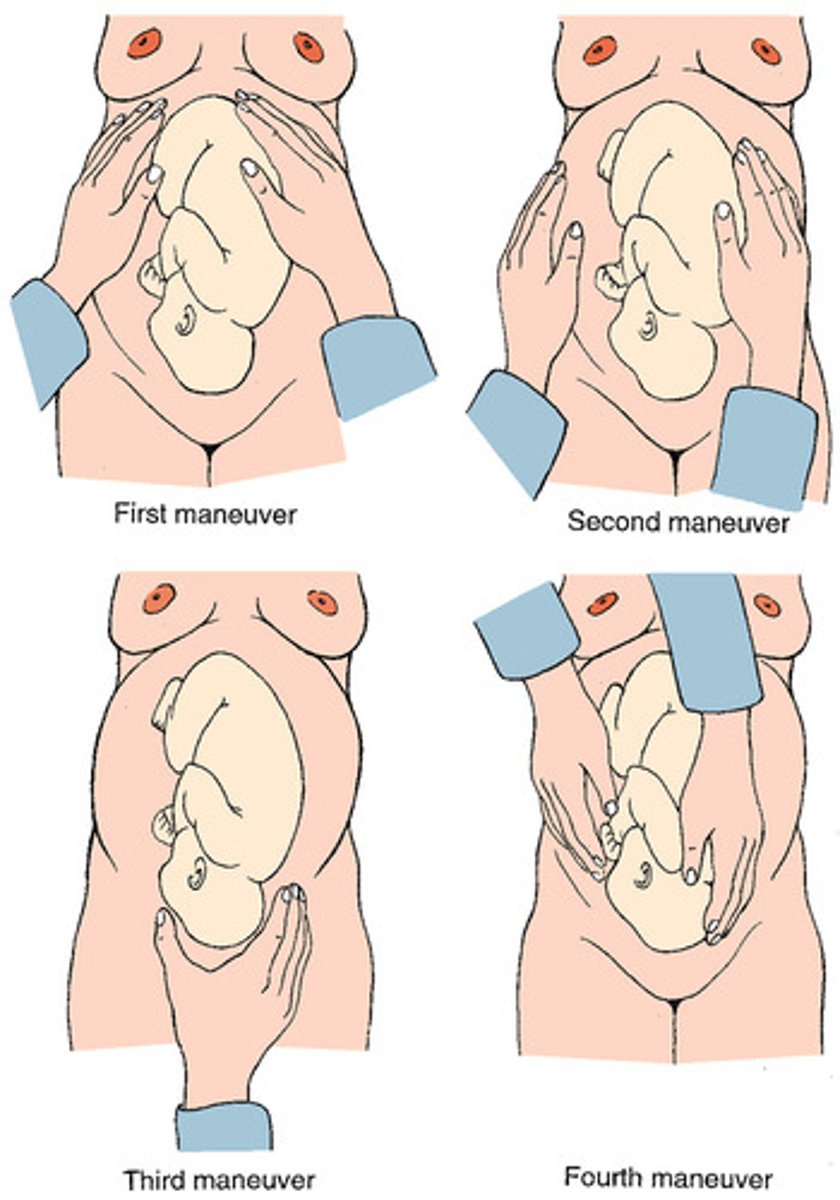
Leopold's Maneuver
What does the external fetal monitoring strip tell us?
Identifies baseline of fetal HR.
Determines whether there are accelerations or decelerations from the baseline.
Identifies patterns of uterine contractions.
Correlate accelerations & decelerations with uterine contractions.
With this, we can determine if the recording is reassuring/reactive, non reassuring/nonreactive, or ominous!
Segments of Contractions
Frequency: how often contractions come in minutes (from start of contraction to start of another); a range; increases if progressing.
Duration: length of contraction; a range (from the start of the contraction to the end of that contraction)
Intensity: how hard/strong contraction is (not accurate on external monitor--usually just ask momma—pain scale; feeling the fundus)
If there is minimal/absent variability on the strip, the baby could be sleeping, so you will give momma some…
SUGAR
Normal Fetal HR Range
110-160 bpm
Determine Baseline of Baby's HR
1. Average Fetal HR that occurs during a 10 min segment.
2. Excluding periodic rate changes.
3. Excluding time during a contraction.
What is variability?
Small up & down fluctuations.
Want in a healthy baby.
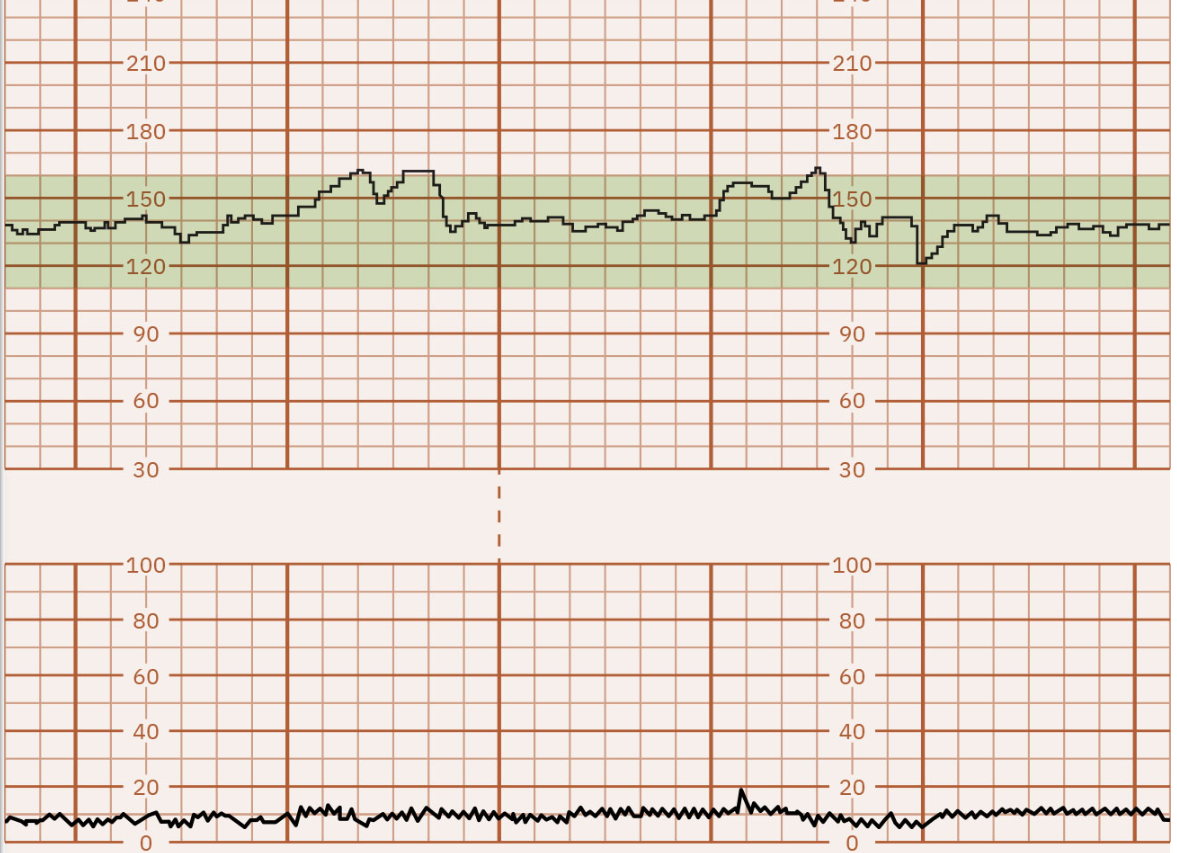
Moderate Variability means a…
Well developed, well oxygenated fetus, and a good sign for fetal well being.
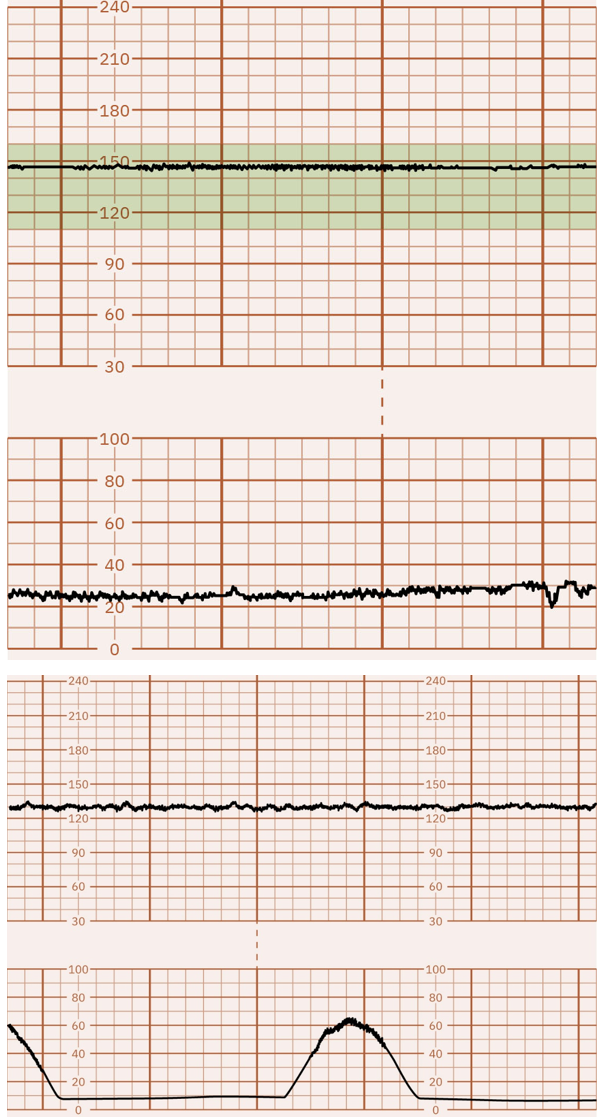
Absent or Minimal Variability is caused by…
Fetal Academia Secondary to Placental Insufficiency
Cord Compression
Preterm Fetus
Maternal Hypotension
mom is not well hydrated (Ex: bottoming out after an epidural)
Uterine Hyperstimulation
uterus is contracting too often → not enough oxygen going to baby.
Placental Abruption
placenta is pulling off the uterus.
Fetal Dysrhythmia
Marked Variability
More than 25 beats of fluctuation in the FHR baseline.
Usually caused by:
Cord Prolapse or Compression
Maternal Hypotension (mom is not well hydrated.)
Uterine Hyperstimulation/Tetonic—hard & stays hard (too many contractions, too close & uterus needs a break)
Placental Abruption—(placenta pulls away from uterus - no blood or O2)
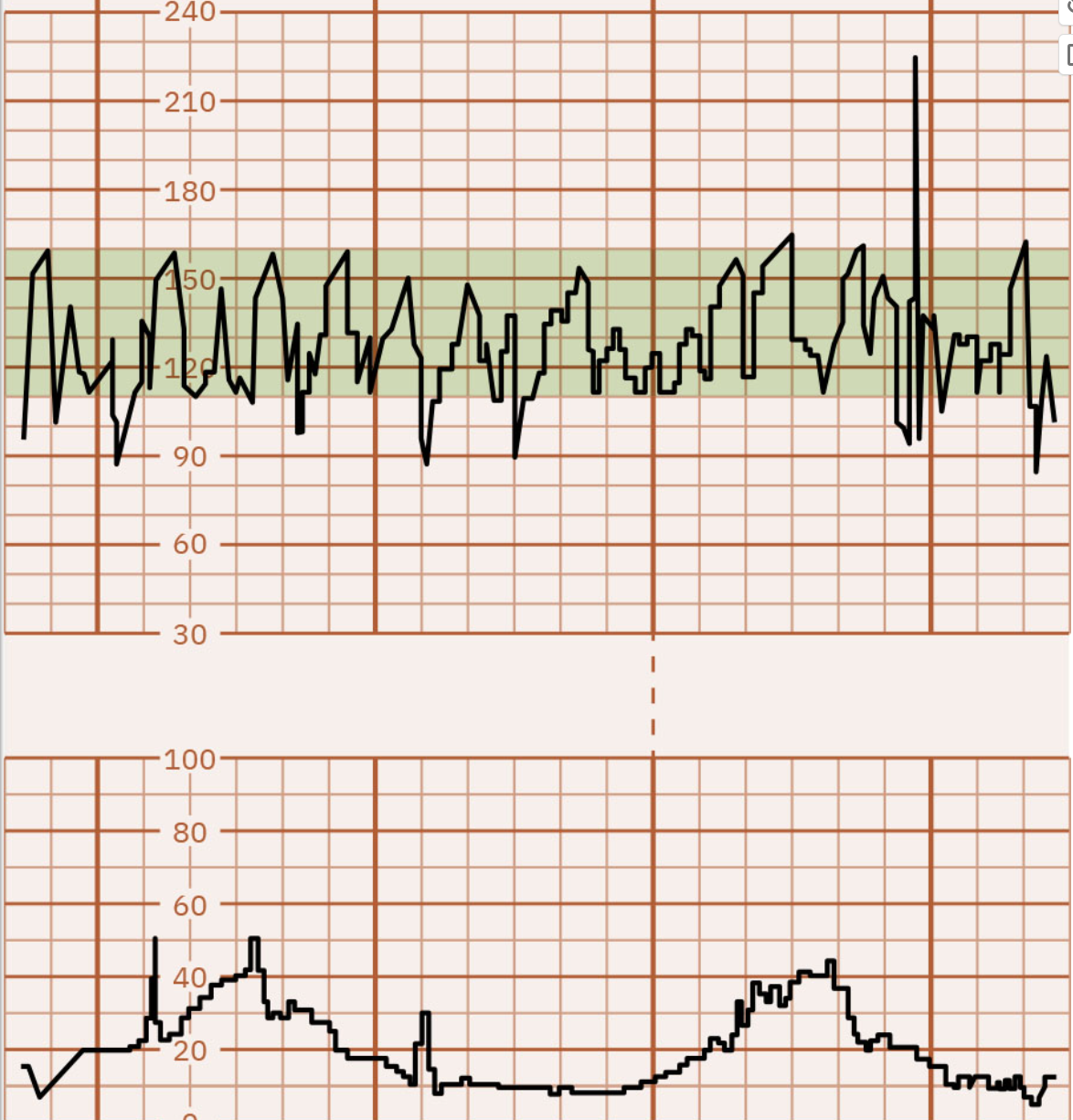
Interventions for Absent, Minimal, and Marked Variability
These are standing orders!
Lateral positioning of mother (left side is optimal; NO back)
Baby is laying on the cord!
Stop the Pitocin (oxcytocin) if infusion running
Increase IV fluid rate
decreased amniotic fluid, etc.
Administer Oxygen 8-10 mL/min by mask
mom needs oxygen
Consider internal fetal monitoring
Notify MD
One of the last things to do.
***If no change after these interventions, may need to prepare for C-section!***