FNH 351 - Vitamins and Energy Metabolism #1
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Riboflavin
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Riboflavin is a precursor for what coenzymes?
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
These coenzymes are the metabolically active forms of riboflavin
They coenzyme over 100 reactions in the body
what is the UL for riboflavin?
no UL - only reported side effect of high intake lvls → bright yellow urine
what are some food sources containing riboflavin?
→ Mostly dairy
milk
cottage cheese
yogurt
→ Other
egg
meats
legumes
what foods are fortified with riboflavin in Canada?
Mandatory fortification
White flour
Simulated meat products
Meal replacements
Voluntary fortification
Breakfast Cereals
In what form do we find dietary riboflavin?
mainly as FAD, less as FMN and free riboflavin bound to proteins in food
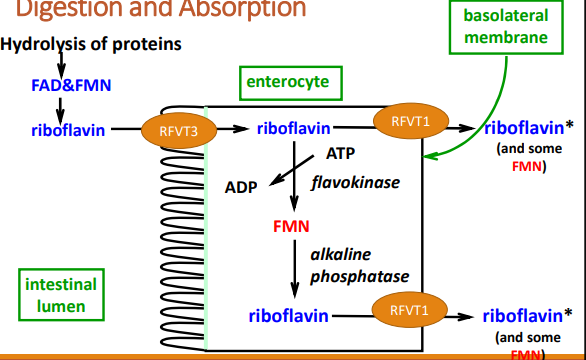
how is riboflavin digested?
riboflavin, FMN, and FAD are non-covalently bound to proteins (e.g., albumin) , thus HCl in the stomach and proteases from the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine separate the riboflavin from the protein. FMN and FAD are then hydrolyzed to free riboflavin.
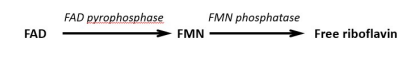
Where does the absorption of riboflavin occur? how does it occur?
in the upper small intestine
done so in the form of riboflavin. Active transport through riboflavin vitamin transporter 3 (RFVT 3) or through passive diffusion at high-dose intakes. Enters the portal circulation mainly as riboflavin
Riboflavin is transported in what form?
mainly as riboflavin (50%), FMN (10%), and FAD (40%), all bound to proteins (e.g., albumin)
what form of riboflavin enters the tissues?
riboflavin is the form that enters the tissues and is converted to coenzymes FAD and FMN in tissues
what percentage of riboflavin is converted into FMN and FAD in the tissues?
~60-95% converted to FMN and ~5-20% converted to FAD. So most is converted into FMN
where are larger amounts of riboflavin stored?
mainly in the liver, heart, and kidneys
body stores of riboflavin are estimated to last ___ weeks
2-6
how is riboflavin excreted?
excreted in the form of riboflavin, in the urine
what can chronic riboflavin deficiency cause?
Ariboflavinosis which may cause cheilosis and glossitis
what is cheilosis?
inflammation and cracking in the corner of the mouth
what is glossitis?
inflammation of the tongue
what are the risk factors and causes for riboflavin deficiency?
excessive alcohol consumption - impairs absorption
some medication
diabetics - due to increased urine output
phototherapeutic treatment of neonatal jaundice
light destruction of riboflavin
why do most counties have no nationwide data on riboflavin status?
bc of the lack of a convenient biomarker
implications of suboptimal riboflavin status are associated with what?
anemia
hypertension
pre-eclampsia in pregnancy
possibly increased risk of cardiovascular diseases and cancer
how is riboflavin status measured?
urinary excretion of riboflavin
plasma riboflavin/FAD/FMN
erythrocyte glutathione reductase activation coefficient (EGRAC)
how does urinary excretion of riboflavin measure riboflavin status?
reflects dietary intake when the tissues are saturated. usually requires 24hr urine collection
how does plasma riboflavin/FAD/FMN measure riboflavin status?
reflects recent dietary intake of riboflavin and it is easy to obtain the blood sample. There are no cutoffs established to date
what does erythrocyte glutathione reductase activation coefficient (EGRAC) reflect in terms of riboflavin status?
reflects long-term riboflavin intake. East to obtain blood sample/longer process. It is the gold standard for measuring riboflavin status.
how does erythrocyte glutathione reductase activation coefficient (EGRAC) measure riboflavin status? >___ is considered deficient
ratio of the enzyme acitivty measured with and without the addition of the cofactor FAD. An EGRAC of 1 indicates a complete saturation of EGR with intracellular FAD, while values higher than 1 indicate an incomplete saturation of the enzyme by intracellular FAD. >1.3 is considered deficient
what is the main limitation of erythrocyte glutathione reductase activation coefficient as a riboflavin indicator?
RBCs must be washed in saline 3 times as soon as they are collected. You need to design a study to measure EGRac from the beginning as washing RBCs is not commonly carried out

what are the metabolic functions of riboflavin (FMN & FAD)?
oxidation and reduction reactions
→ energy metabolism pathways:
TCA cycle (succinate dehydrogenase)
mitochondrial electron transport chain
beta oxidation: acyl CoA dehydrogenase
→ Antioxidant metabolism
→ vitamin B6 metabolism
→ FAD needed for synthesis of niacin (NAD)
how is riboflavin used in antioxidant metabolism?
reduction of oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG) to reduced form of glutathione (GSH)

how is riboflavin used in vitamin B6 metabolism?
riboflavin is required for the conversion of dietary vitamin B6 forms to pyridoxal 5’ phosphate (PLP), that is the coenzyme form (active form) of vitamin B6. Pyridoxine phosphate oxidase (PRO) required FMN as a coenzyme.
what are the nutrient-nutrient interactions of riboflavin?
Vitamin B6 requires FMN to convert dietary B6 into the B6 coenzyme form pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP) via the enzyme pyridoxine 5’ phosphate oxidase (PPO).
The co-enzyme forms of niacin, NAD and NADP, can be formed from tryptophan using FAD-dependent enzymes in the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway.
Riboflavin deficiency impairs internal iron utilization, e.g., release of iron from stores. It thereby impacts red blood cell formation.
Riboflavin deficiency may accelerate iron deficiency anemia.
Methyl nutrients: In one-carbon metabolism, the B-vitamins folate, B12, B6, and riboflavin have interdependent roles, for example, for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine.
describe the nutrient-gene interaction of riboflavin
MTHFR C677T is a common mutation in the MTHFR gene, in which ~10% of Canadians are homozygous for this genetic variant (both stands of DNA have the T base and not wild type C base): MTHFR 677TT genotype. MTHFR required FAD as a cofactor, but FAD falls off more readily in inds. w/ the MTHFR677TT genotype, compared to inds. w/ the MTHFR C677T wildtype (CC)
what do genetic studies report that the MTHFRC>T gene relates to? what may help to reduce this?
variability in blood pressure. Riboflavin supplementation may help to reduce high blood pressure in those with the MTHFRTT variant