Primary Structure
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
The primary structure of a protein involves
peptide bonds
What atoms are connected by a peptide bond?
carboxyl group carbon with amino group nitrogen
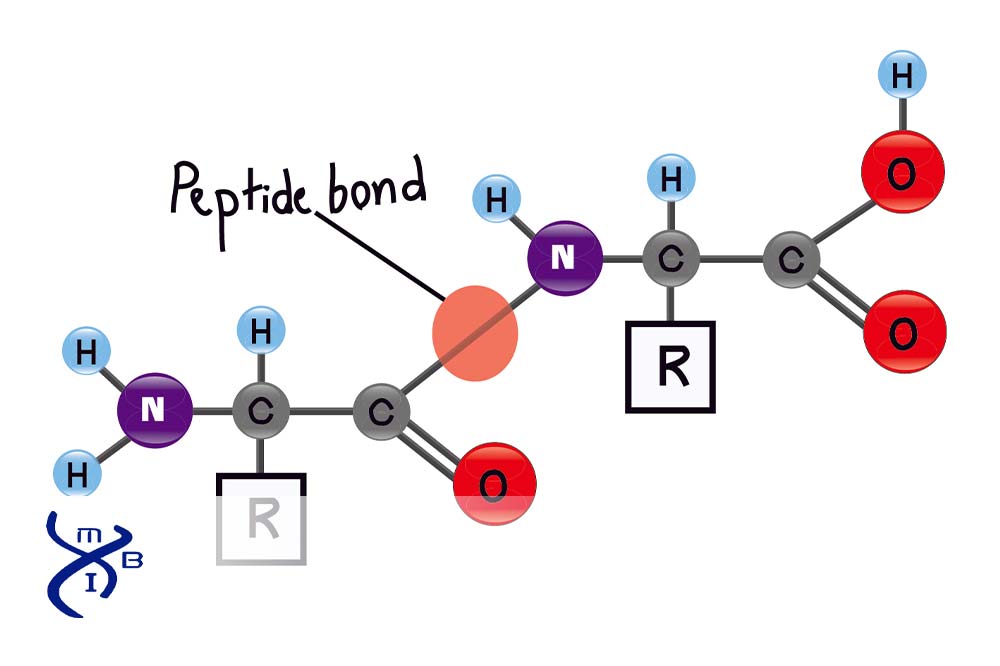
What is the name of the peptide bond formation reaction?
condensation
What represents the backbone arrangement of two peptide bonds?
N—Cα—C—N—Cα—C
What bonds within a peptide backbone show free rotation around both bonds?
Cα—C
N—Cα
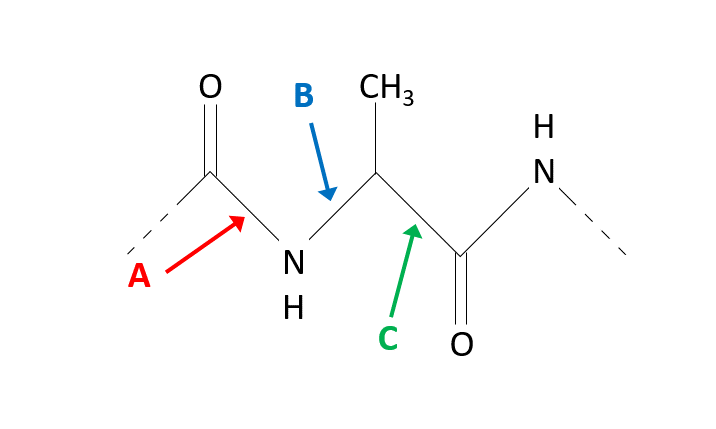
Arrow B is pointing to the φ angle around the N—Cα bond, C is pointing to the ψ angle around the Cα—C bond
The resonance structures that can be drawn for the peptide bond indicate that the peptide bond…
is stronger than an ordinary single bond
has partial double bond character
The peptide bond in proteins is…
usually trans unless proline is the next amino acid
In proteins, peptide bonds are typically in the trans configuration, where the alpha-carbons of adjacent amino acids are on opposite sides of the peptide bond. This minimizes steric clashes and is energetically more favorable.
What amino acids residue are shown in A and B?
Gly and Pro
A corresponds to Glycine (Gly) because of its flexibility.
B corresponds to Proline (Pro) because of its rigidity.
Ramachandran Plot A (Left):
This plot shows extensive allowable conformations, including regions that are usually disallowed for most amino acids.
Glycine is the only amino acid that lacks a side chain (its R-group is a hydrogen atom), making it highly flexible. This allows it to adopt many conformations, leading to an expanded Ramachandran plot.
Ramachandran Plot B (Right):
This plot shows restricted allowable conformations, with only a small area of the plot being favored.
Proline is unique because its side chain forms a ring with its backbone nitrogen, significantly restricting its φ (phi) and ψ (psi) angles. This leads to a highly constrained Ramachandran plot.
A tripeptide has
3 amino acids and 2 peptide bonds
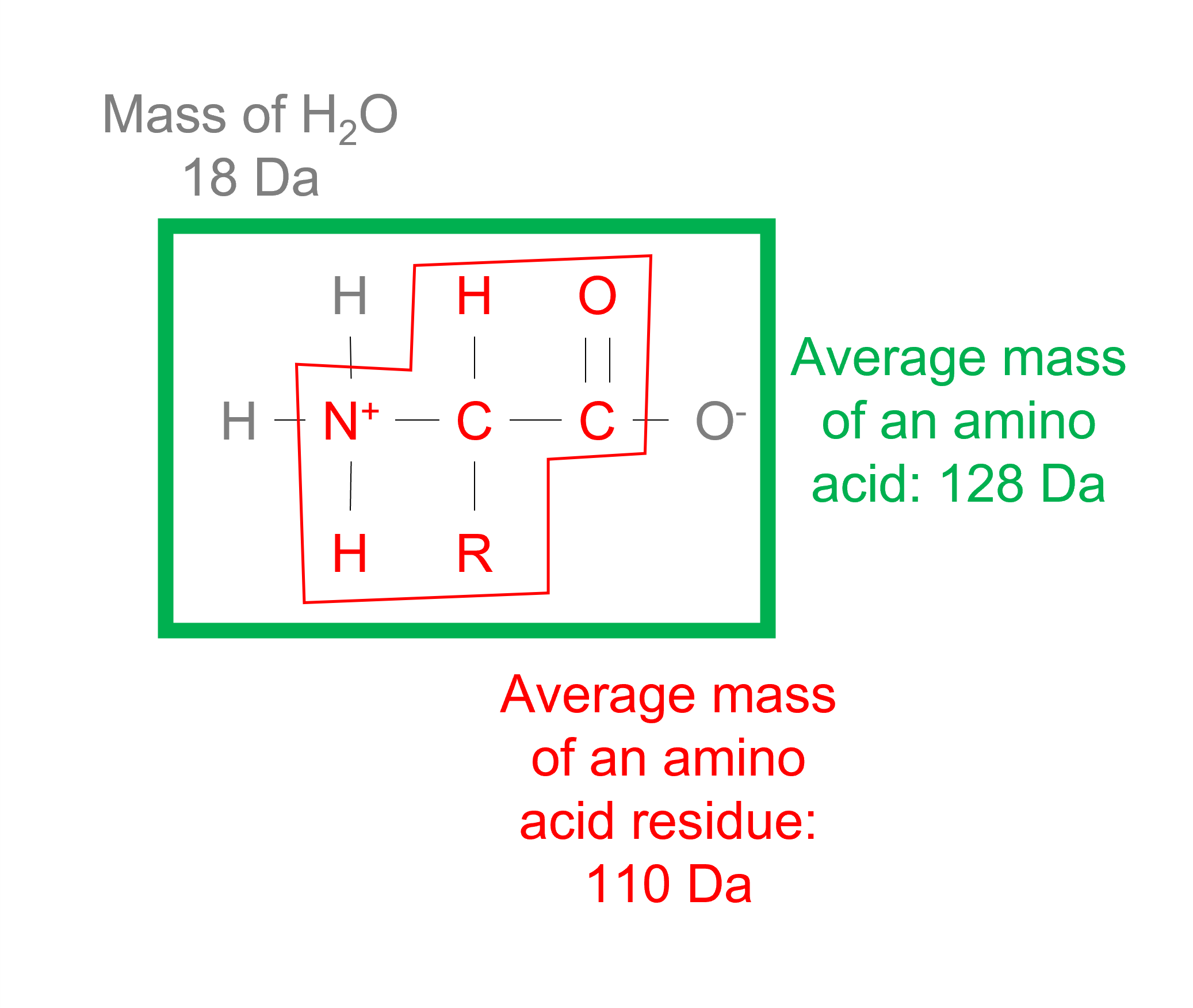
The average molecular weight of an amino acid residue is about [128] g/mol; the average molecular weight of an amino acid residue in a protein is about [110] g/mol.
The average molecular mass of an amino acid is approximately 128 Da, or 128 g/mol. However, a water (18 Da) is released when a peptide bond is formed. So, the average mass of an amino acid in a polypeptide is 110 Da.
The general rule of thumb that works for amino acids also works for peptides: Find the approximate pH where the net charge would be zero and average the closest pKa values on either side of this value.
If the side chains do not have ionizable groups, then the pI is simply the average of the -COOH pKa and the -NH3+ pKa values. For example, GAL has a pI of 5.56.
If the side chains have ionizable groups, then all pKa values need to be considered. How do I do this?
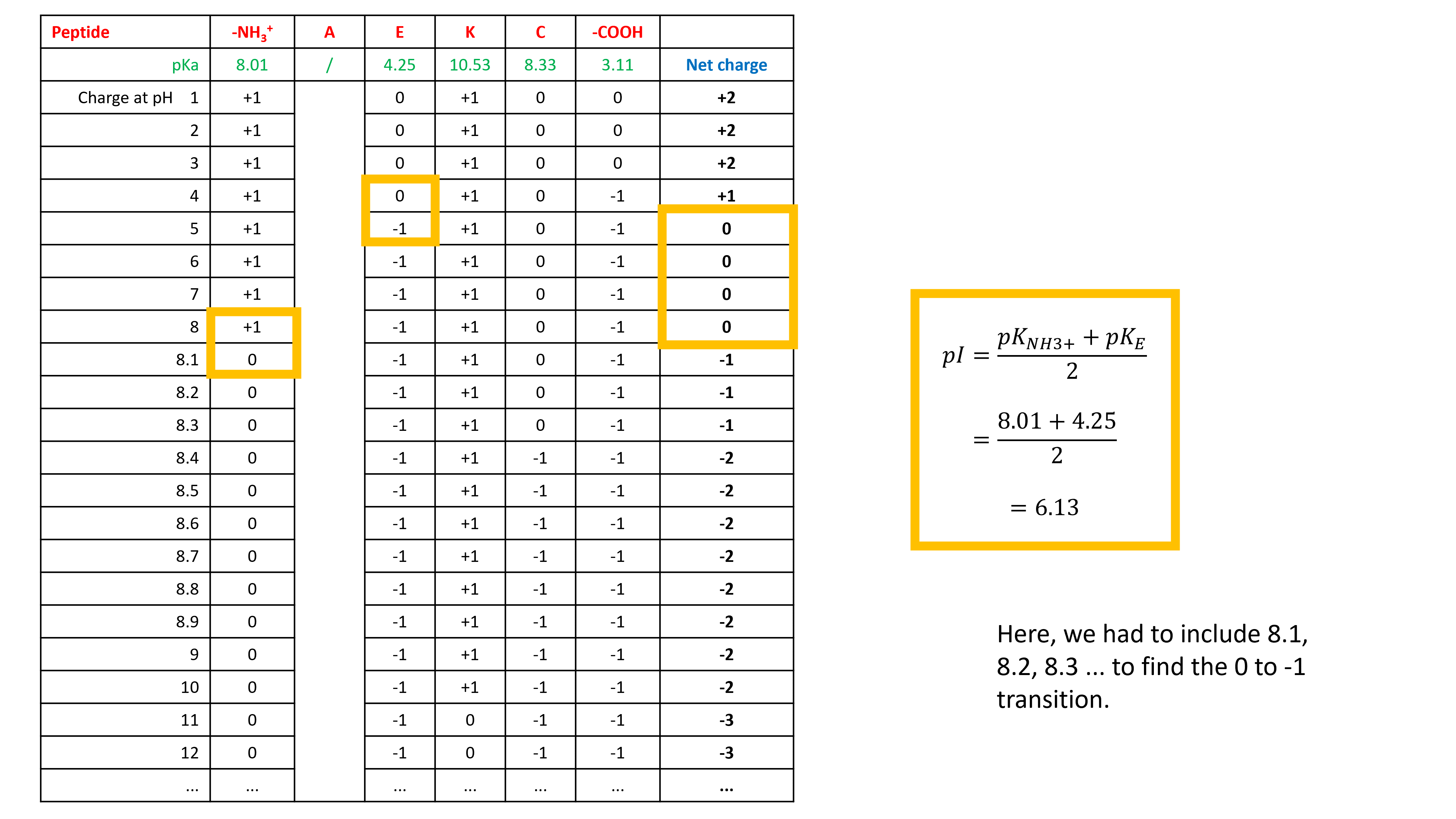
Let’s start with DGE. Write down the ionizable groups and their pKa values in a table.
For each pH, write down the charge of each ionizable group
Now calculate the net charge at each pH and identify the pH value(s) for which the net charge is 0
Sometimes writing down the net charge with only pH values 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, and 14 does not give us a net charge 0. We need to go into more detail where we expect net charge 0. In this case between pH 3 and pH 4.
Now we can identify the pH value(s) for which the net charge is 0. Average the closest pKa values on either side of this value to calculate the pI.
So, DGE has a pI of 3.49. I did the same for GRIEF. It has a pI of 6.13.
The procedure was repeated for AEKC, which has a pI of 6.13.
Sequence alignments help scientists…
to trace evolutionary relationships
to find the function of a newly discovered gene
to predict new members of protein families
Identify the most conservative amino acid substitution, assuming that these two residues occur at the same position in two homologous proteins.
Leu → Val
Both Leu and Val are hydrophobic amino acids. We assume this mutation to have the least effect on protein structure and function.
Pro is also hydrophobic, but the distinctive structure of proline gives it a conformational rigidity compared to Leu. Trp is also hydrophobic, but it is aromatic and much larger than Leu.
Asp and Lys are charged residues.
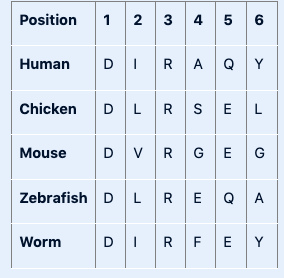
Shown below is a portion of a multiple sequence alignment.
Based on this information you can say:
positions 1 and 3 contain invariant residues
positions 2 and 5 contain conserved residues
positions 4 and 6 are the least conserved positions in this sequence