Probability and Sampling Distributions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
frequentist probability
probability of any event A is the ratio of the number of times the event happens divided by the number of times any event happens
probability density functions
show more fine-grained probabilities than a histogram can show; curves -> theoretical distributions of statistics
normal (no skew)
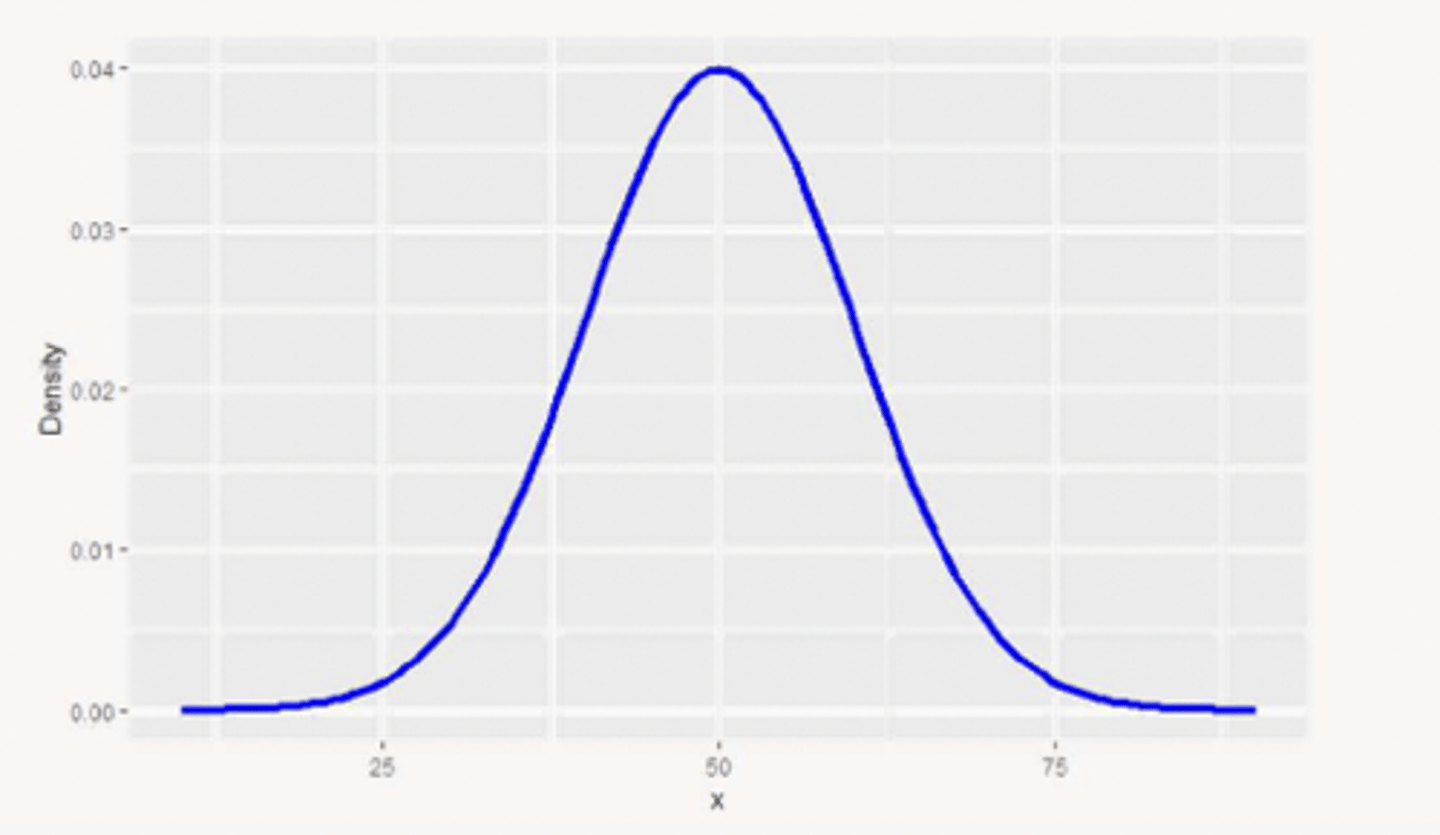
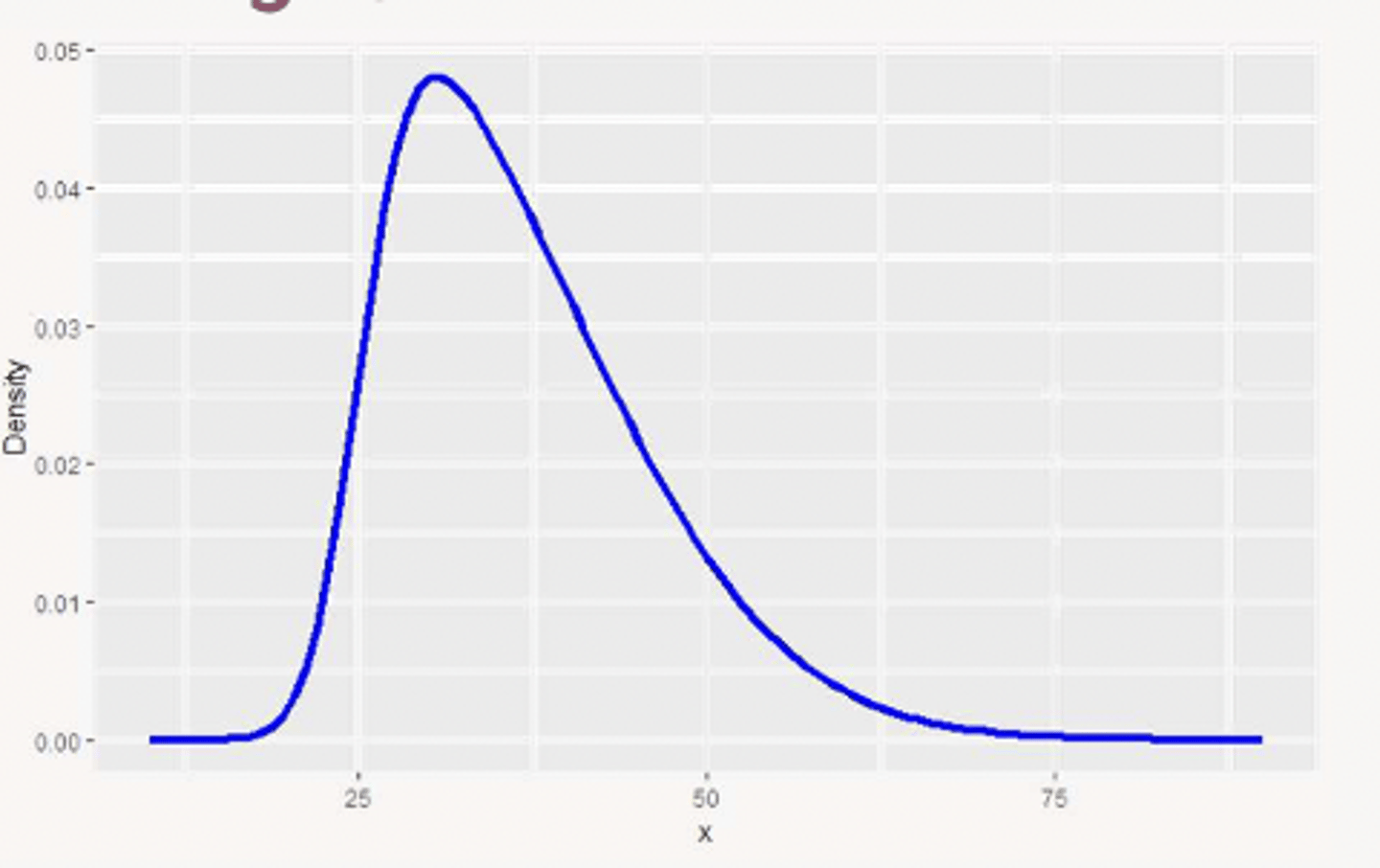
right/positive skewed
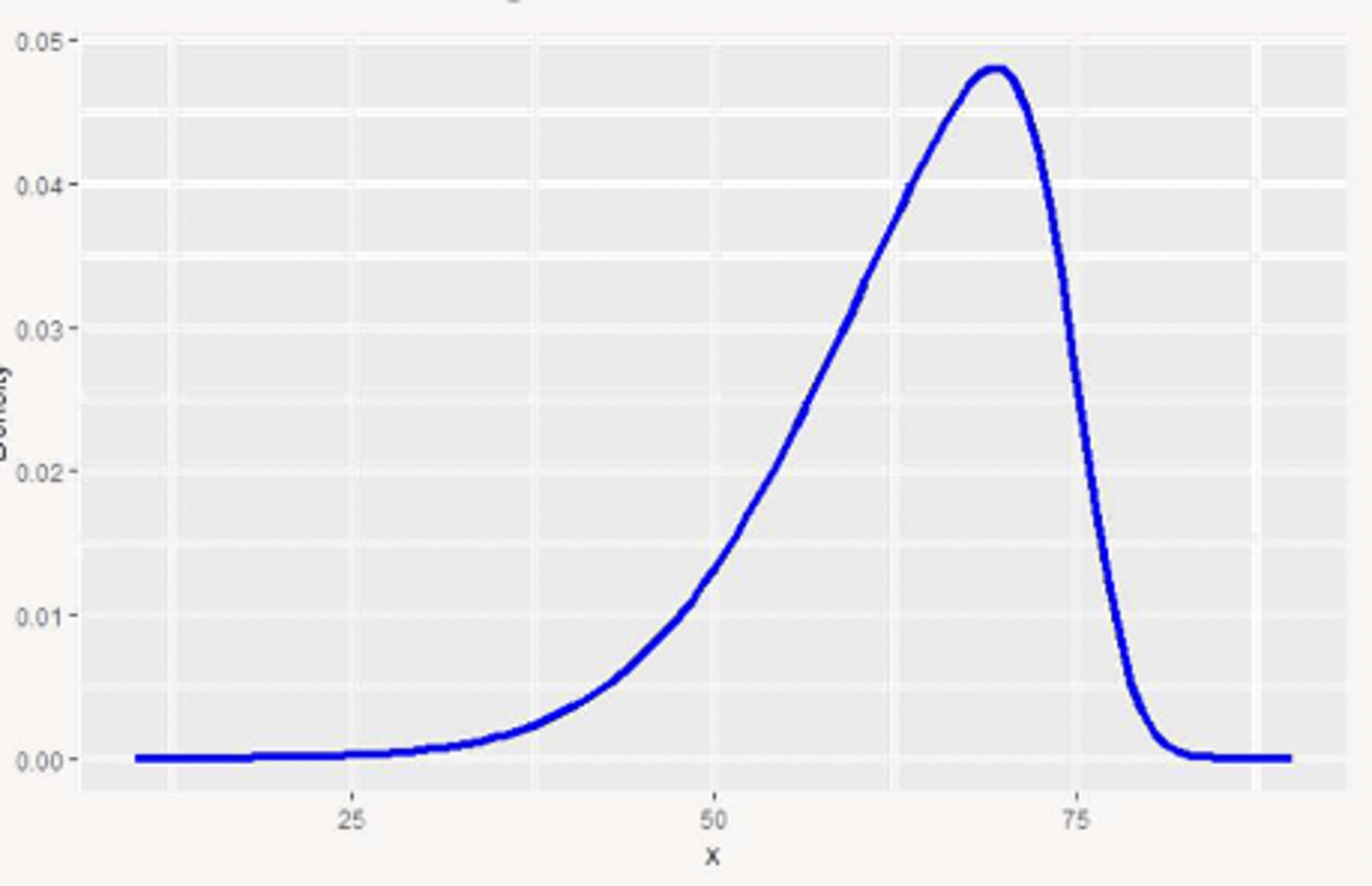
left/negative skewed
normal distributions of populations
N(µ, σ²)
standardizing a normal distribution
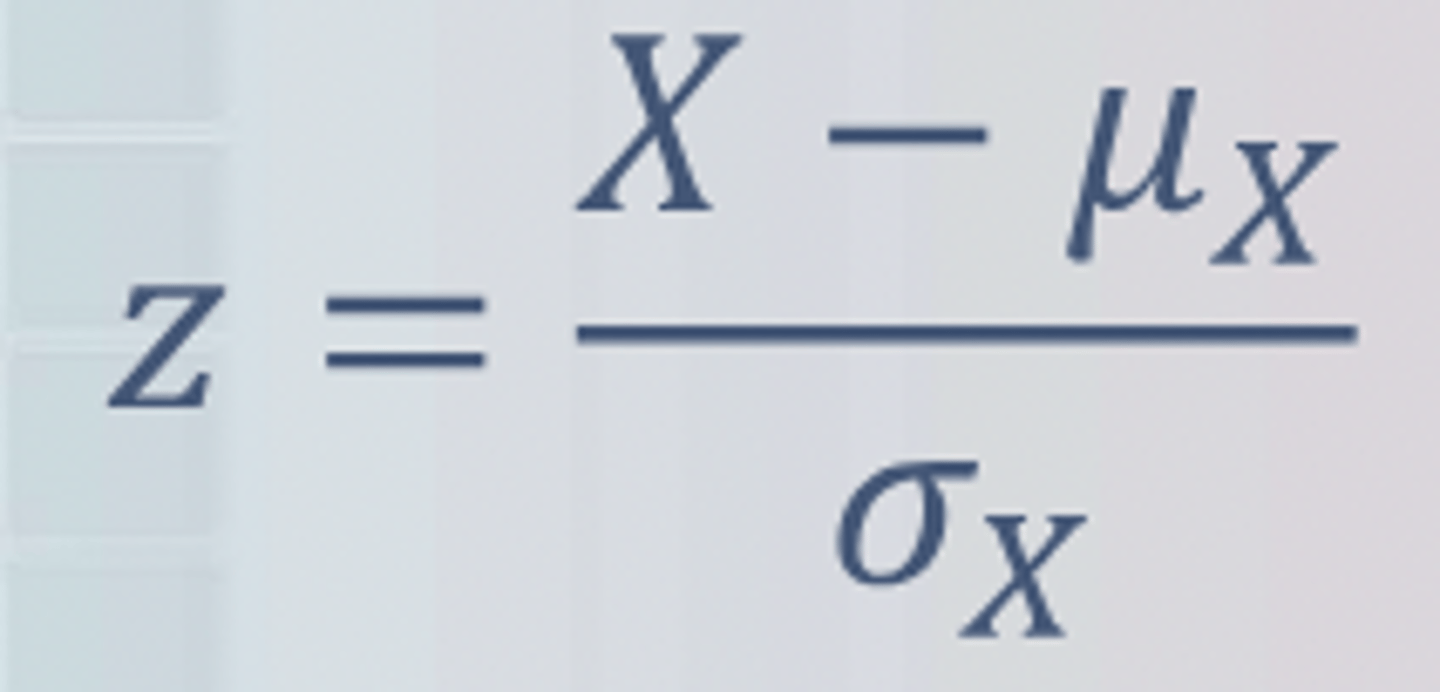
effect of larger samples on sampling distribution of means
less variable means
mean of sampling distribution of means
equal to the population mean
standard error of sampling distribution of means
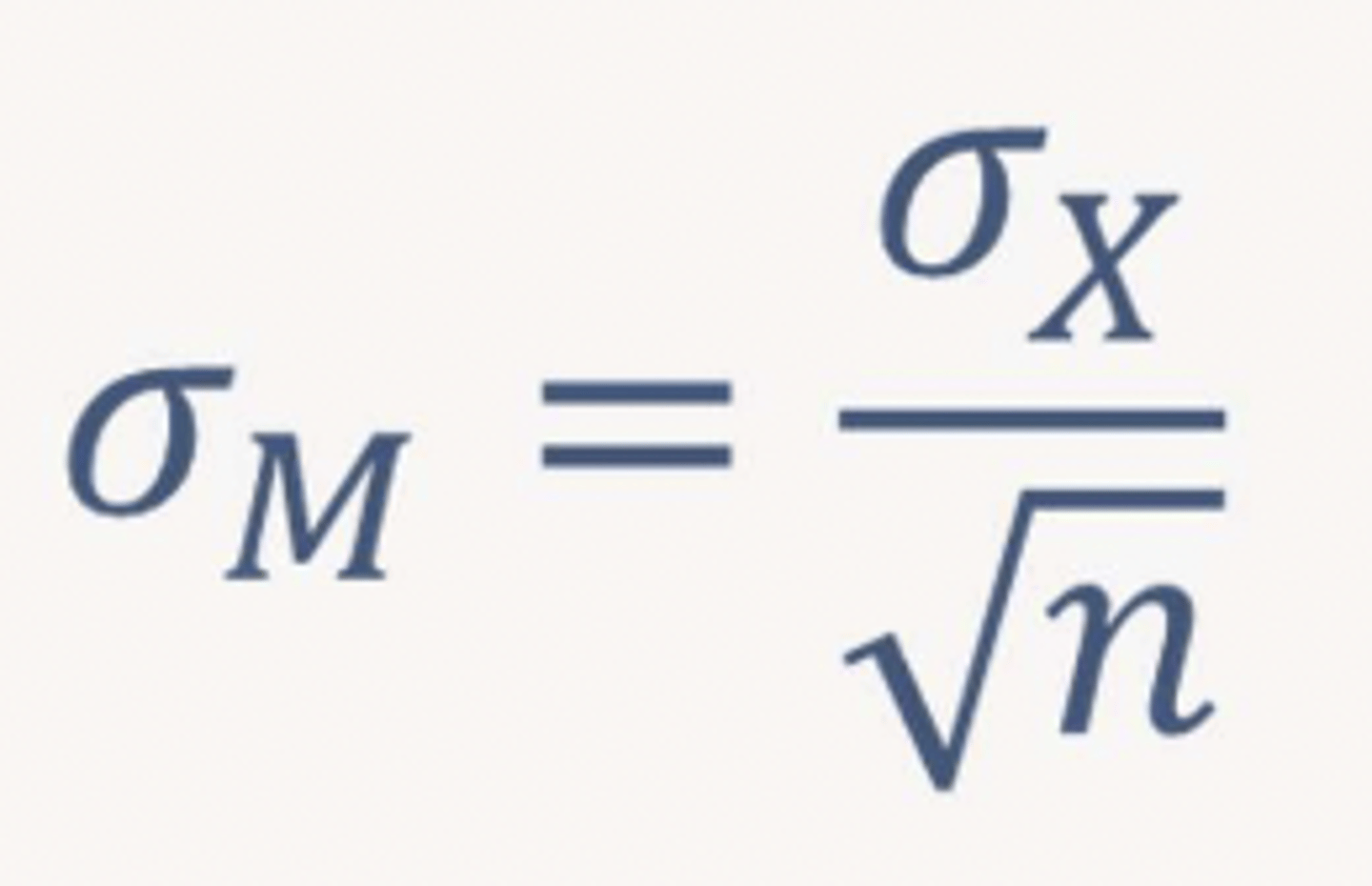
unbiased estimator
when the mean of a statistic across all samples of the same size equals the value of the parameter
central limit theorem
sampling distribution of sample means approaches normality even from non-normal populations, with large enough sample sizes
what does CLT allow us to do with statistical tests?
allows us to use a normal sampling distribution when calculating probabilities (to infer about population means)