Anatomy - Facial Bones, Girdles and Vertebral Column
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
The superior and middle nasal conchae are a part of what bone?
The ethmoid bone
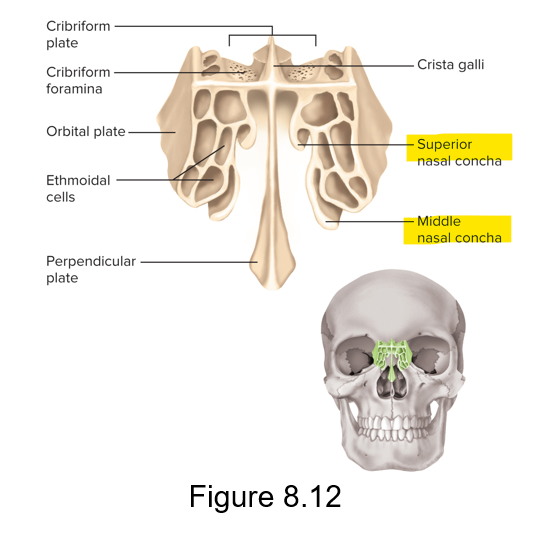
What other separate bone occupies most of the nasal cavity?
The inferior concha
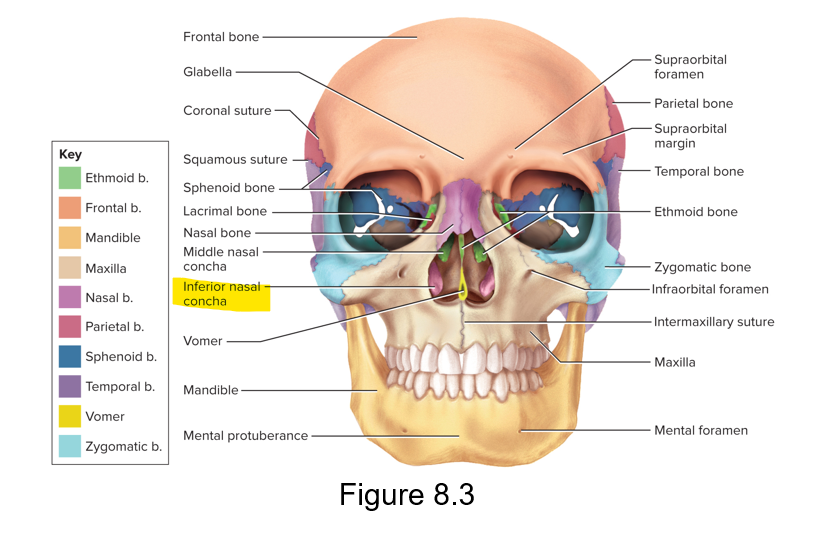
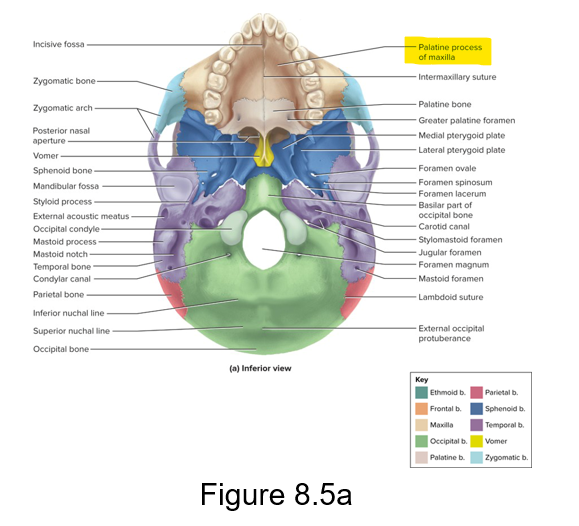
The maxillae forms the….
What is a part of the maxillae?
Upper jaw and most of the hard palate.
The palatine process if a part of the maxillae
What are the sockets that hold teeth?
Alveolus
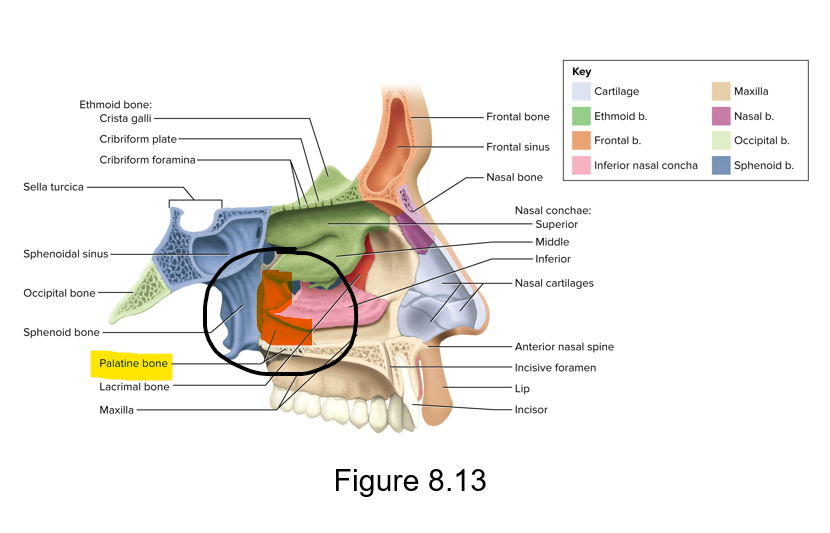
Palatine bones; Horizontal plates; Perpendicular plate
L-shaped bones that divide the oral and nasal cavities from each other posteriorly
Horizontal plates - Form posterior part of the hard palate
Perpendicular plate - Forms part of the lateral wall of the nasal orbit
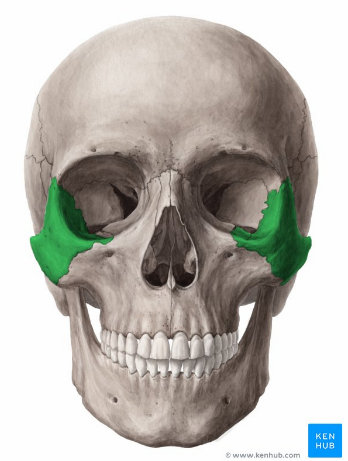
What do the zygomatic bones form?
Angles of cheekbones and part of each lateral orbital wall
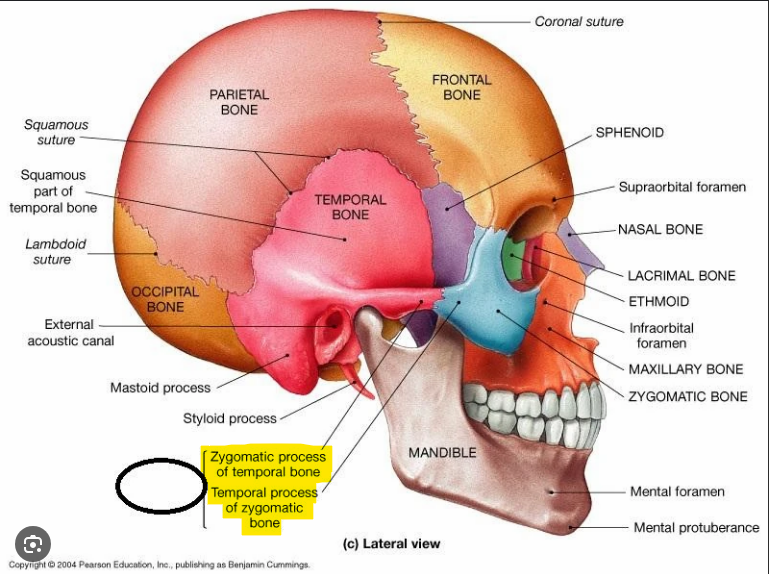
Zygomatic arch
Formed from the temporal process of the zygomatic bone and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone
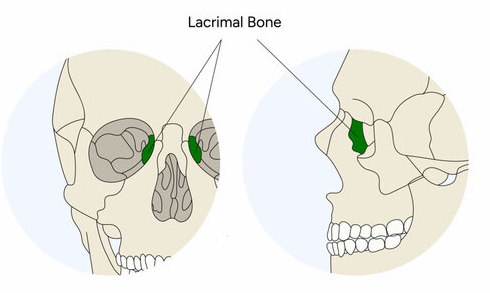
Lacrimal bones
Form part of the medial wall of each orbit
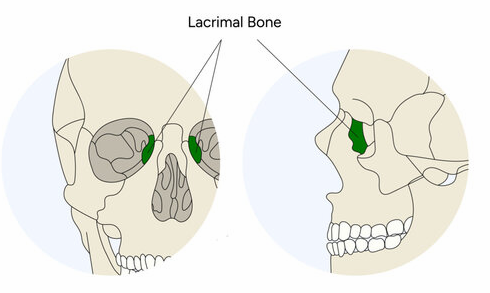
What houses the lacrimal sac and what is collected here?
Lacrimal fossa; tears collect in sac and drain into nasal cavity
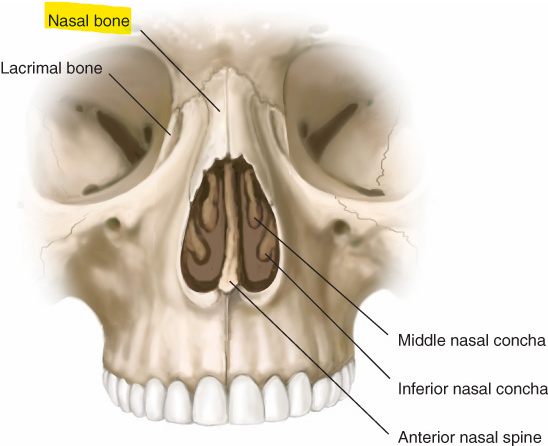
Nasal bones
Form the bridge of the nose
What is the vomer and what is it inferior to?
Inferior part of the nasal septum therefore, the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone is the superior part of the nasal septum
Inferior to the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid
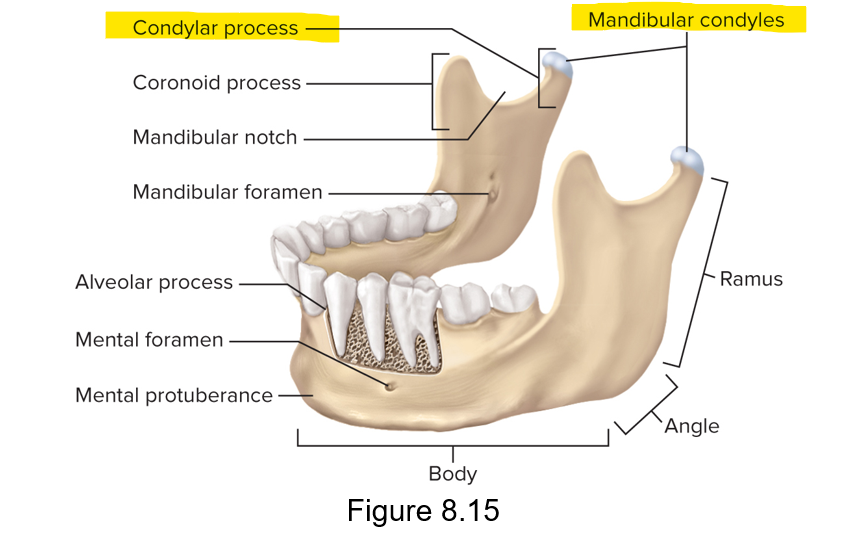
What does the mandible do?
Supports lower teeth and provides attachment for muscles of expression and chewing
What are the three parts of the mandible?
Body, ramus and angle
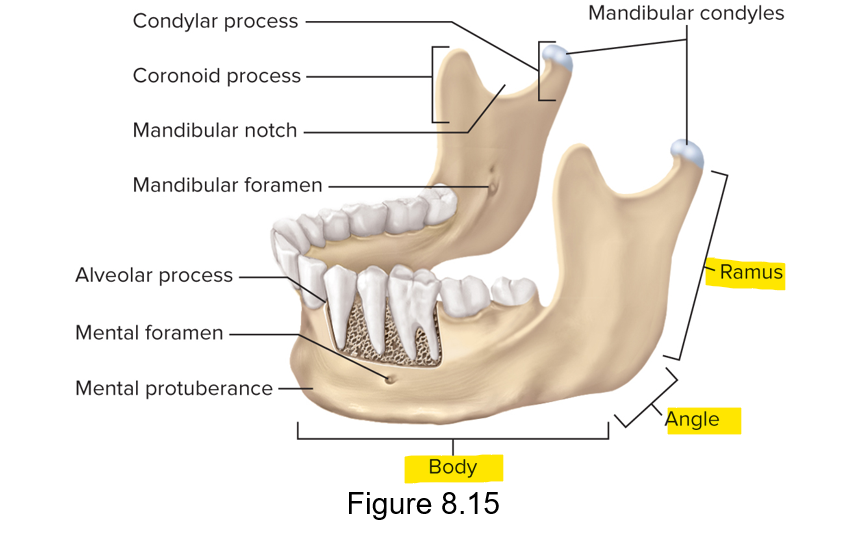
What does the ramus articulate with?
The temporal bone, condylar process and mandibular condyles
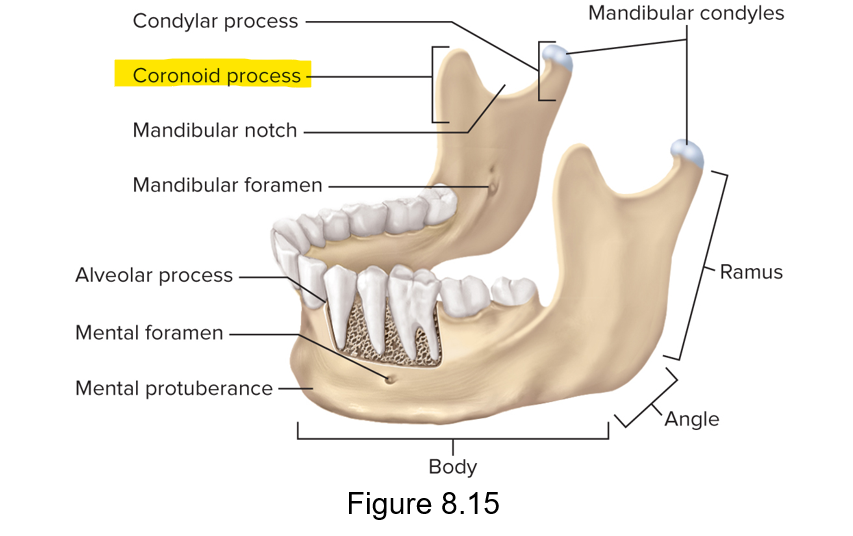
What elevates the mandible?
The coronoid process for the temporalis muscle
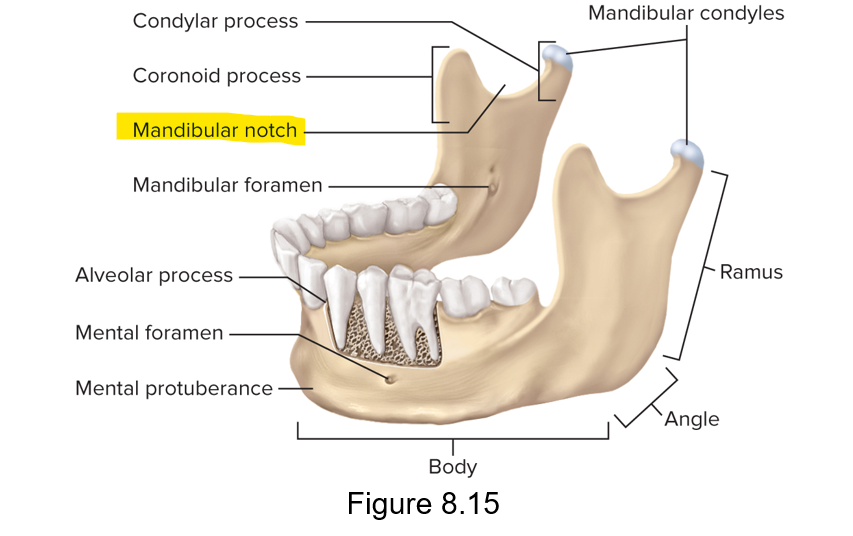
What is the notch between the coronoid process and condylar process?
Mandibular notch
Which process is posterior and which is anterior? Condylar process and coronoid process
Coronoid process is anterior; condylar process is posterior
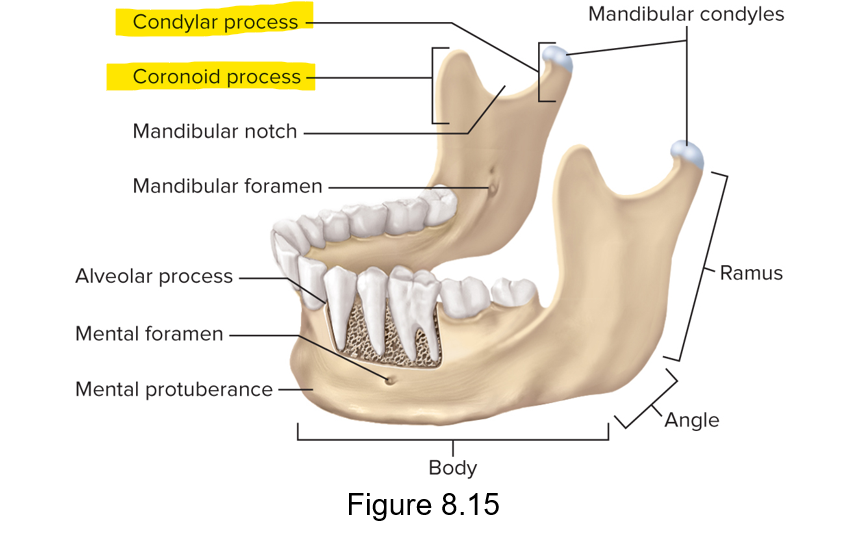
True or false; the condylar process articulates with the temporal bone
True; the condylar process has mandibular condyles
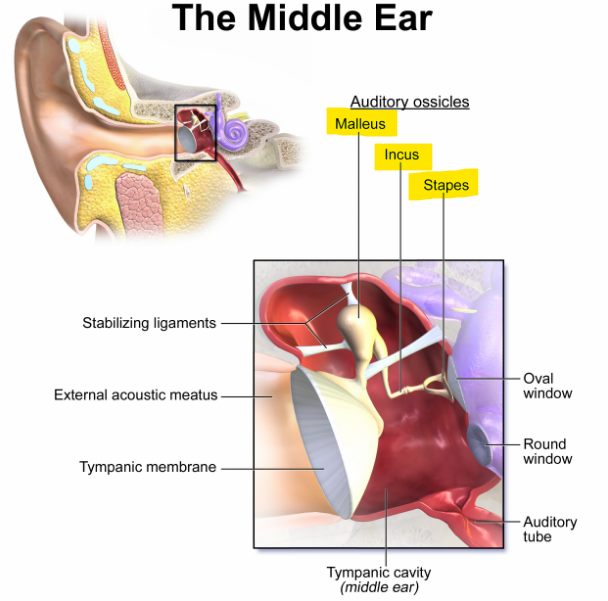
What are the three auditory ossicles in each middle-ear cavity?
Malleus, incus and stapes
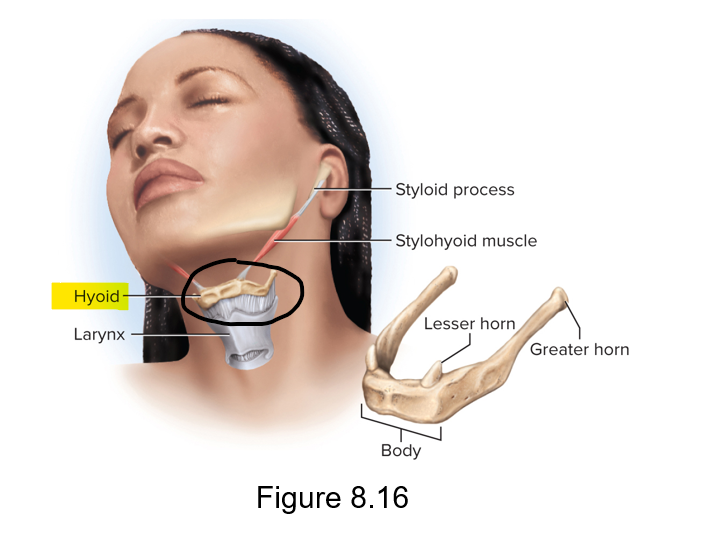
Hyoid bone
Slender u-shaped bone between chin and larynx.
Does not articulate with any other bone
For muscle attachment
What does the pectoral girdle consist of? What do these bones articulate with?
Clavicle and scapula
Clavicle articulates medially to the sternum and laterally to the scapula
Scapula articulates with the clavicle and humerus
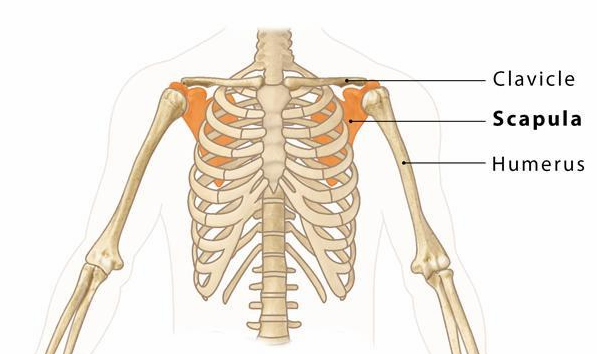
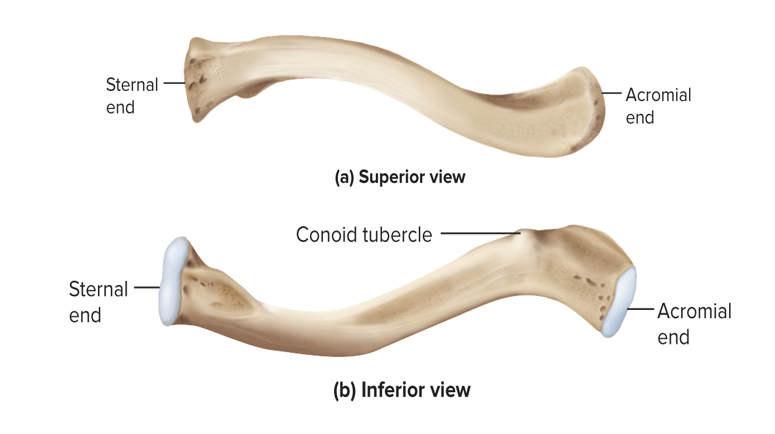
What does the clavicle do?
Braces shoulder and keeps arm away from the midline
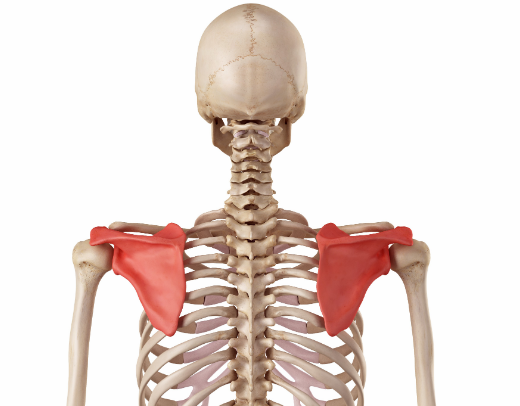
What is the scapula also known as?
The shoulder blade
Where is the spine of the scapula located?
On the posterior surface of the scapula
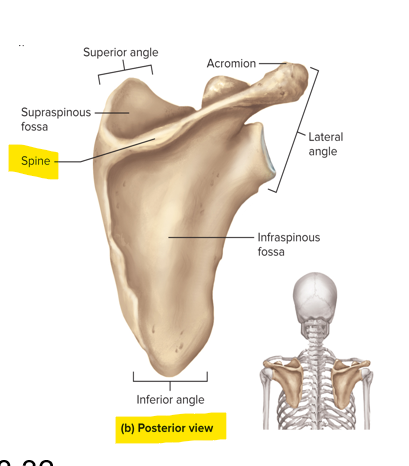
What is the supraspinous fossa and infraspinous fossa?
Supraspinous fossa - indentation superior to the spine of the scapula
Infraspinous fossa - surface inferior to the spine of the scapula
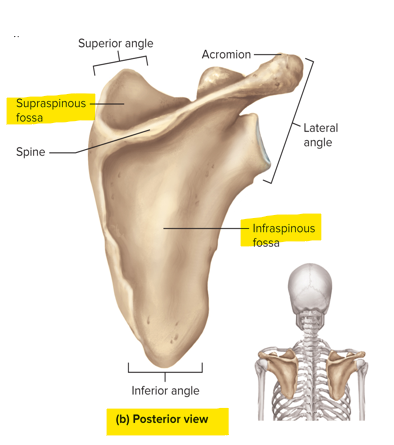
What is the subscapular fossa?
The anterior surface of the scapula
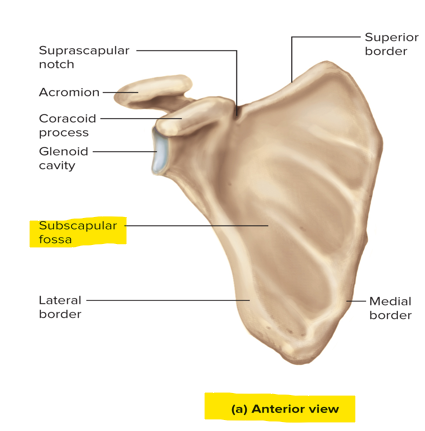
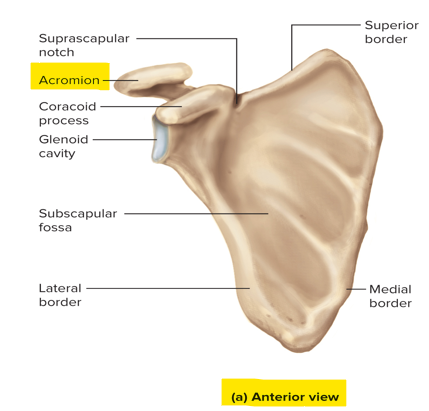
What is the acromion of the scapula and what does it articulate with?
A plate-like extension of the spine of the scapula; articulates with the clavicle
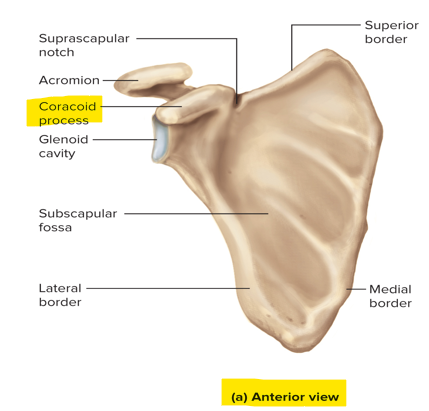
This process of the scapula provides attachment for tendons of biceps brachii and other arm muscles
Coracoid process
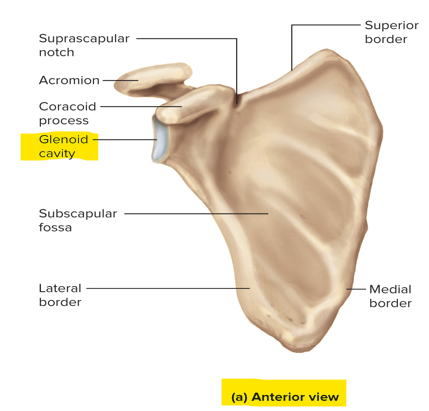
This shallow socket articulates with the head of the humerus
The glenoid cavity
What are the 3 regions of the upper limb?
Brachium (arm proper) - Humerus
Antebrachium (forearm) - Lateral radius and medial ulna
Hand - carpal region, metacarpals and phalanges in fingers
Features of the proximal end of the humerus
Head articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula
Greater and lesser tubercles
Deltoid tuberosity - an attachment to the deltoid muscle
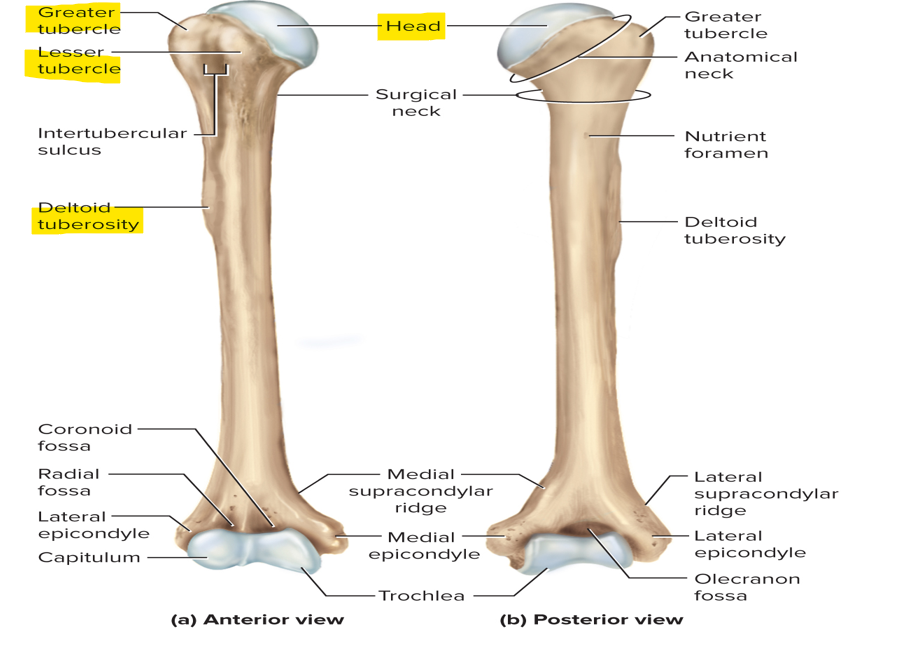
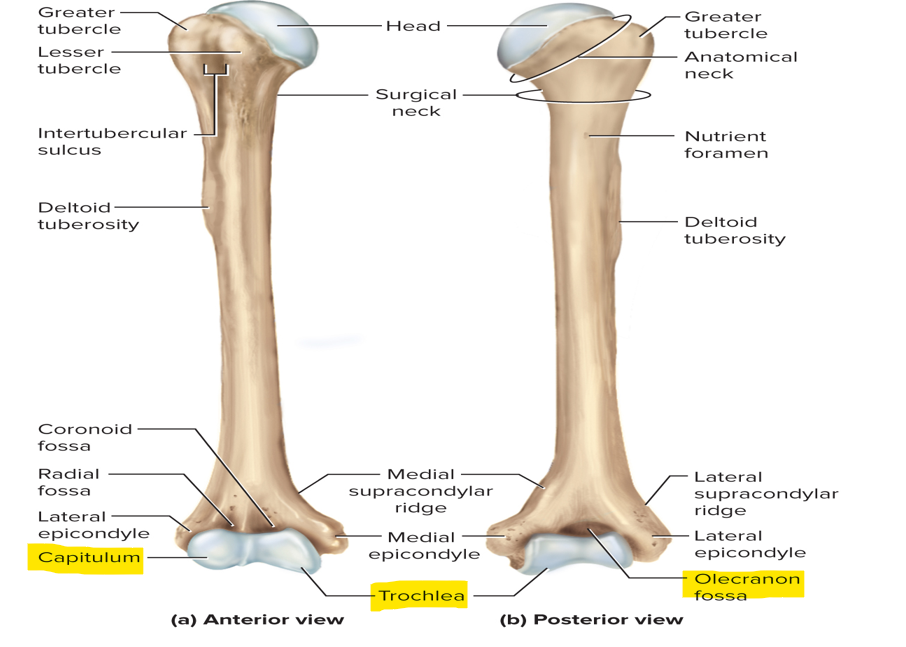
Features of the distal end of the humerus
Rounded capitulum - articulates with the head of the radius
Trochlea - articulates with the ulna
Olecranon fossa - holds olecranon process of ulna
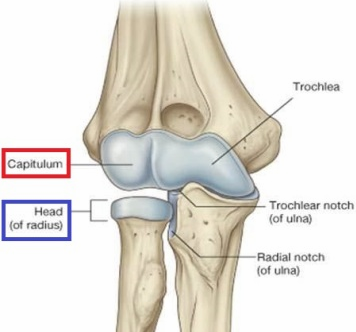
What does the disc-shaped head of the radius allow for? What does the superior surface of the radius articulate with?
Rotation during pronation (medial movement/rotation) and supination (lateral movement/rotation)
Superior surface of the radius articulates with capitulum on humerus
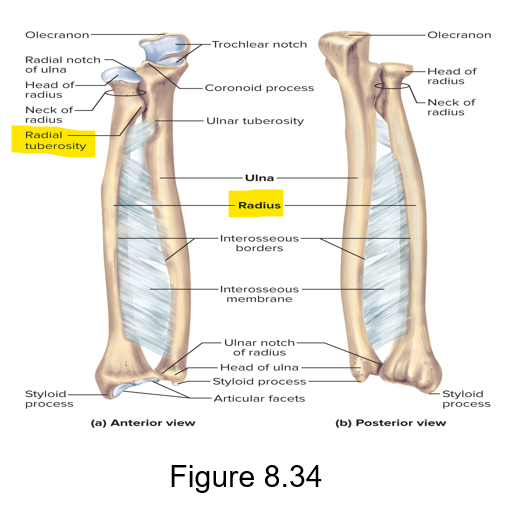
The radial tuberosity of the radius is for the ______ muscle
Biceps
The trochlear notch of the ulna articulates with the ______ of humerus
Trochlea
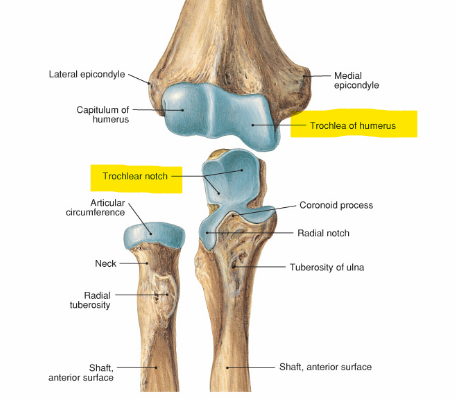
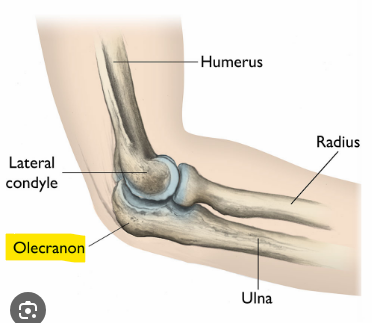
What is the bony point at the back of the elbow called?
Olecranon - this is a part of the ulna
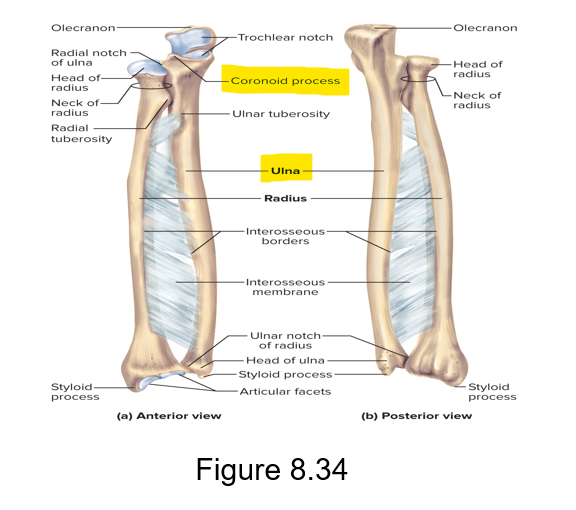
The coronoid process is a part of what bone?
The anterior of the ulna
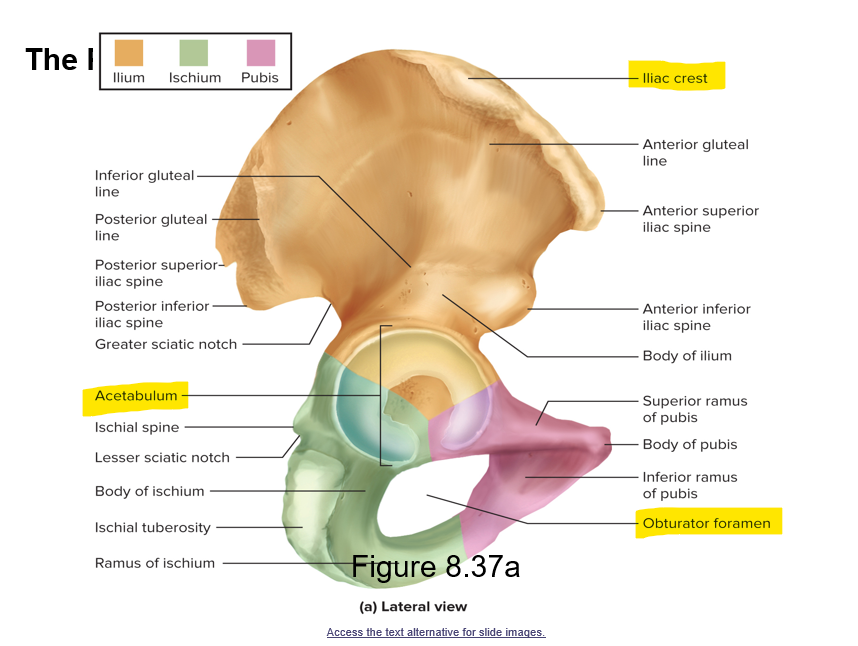
What 3 bones is the pelvic girdle composed of?
2 hip bones (coxal bones, also called ossa coxae)
1 sacrum
What 3 childhood bones fuse to form the hip bone?
Ilium, ischium and pubis
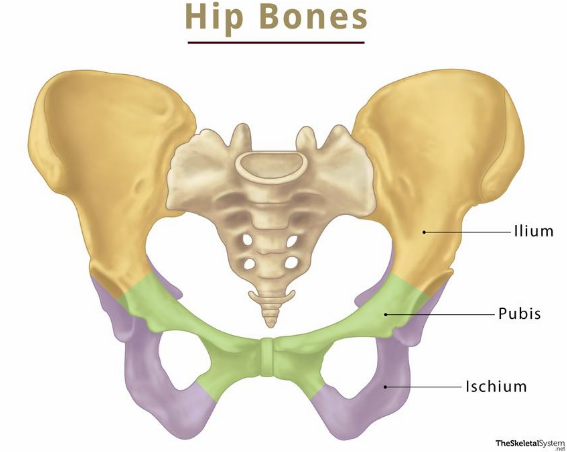
What are the 3 distinct features of the hip bone?
Iliac crest - superior crest of hip
Acetabulum - hip socket (articulates with the femur)
Obturator foramen - large hole below the acetabulum
What are the 3 regions of the lower limb?
Thigh (femoral region) - femur and patella
Leg proper (crural region) - medial tibia and lateral fibula
Foot - tarsal region, metatarsals and toes (digits)
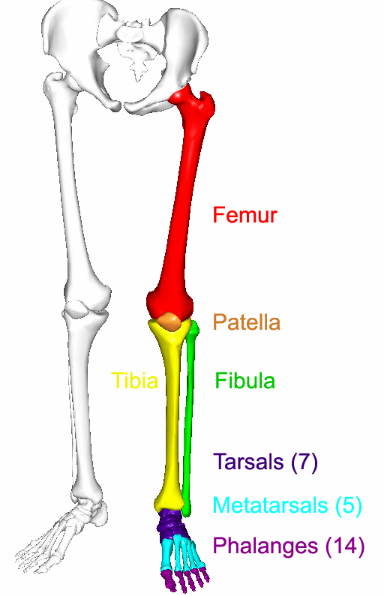
What is the thigh bone and what does this bone articulate with?
Femur; articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis
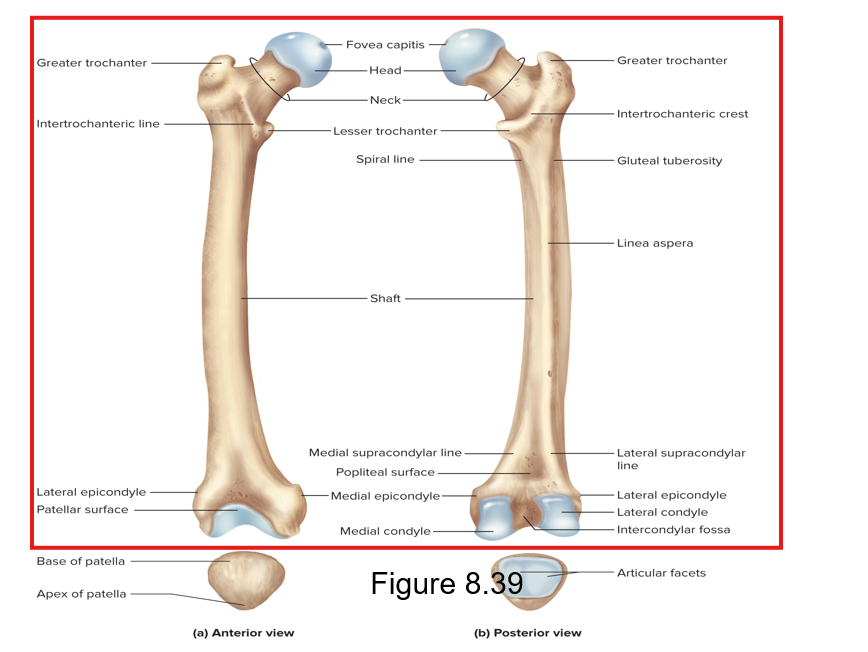
Patella
Triangular bone embedded in the tendon of the knee
This is the medial leg bone and the only weight bearing-bone in the leg proper area (crural region)
Tibia
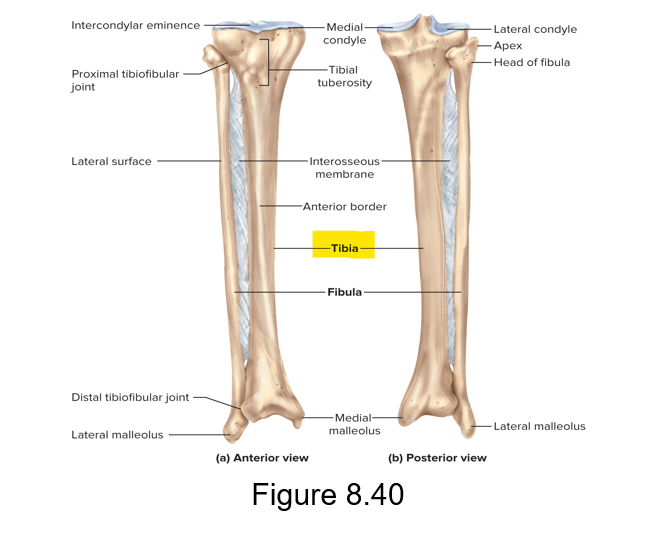
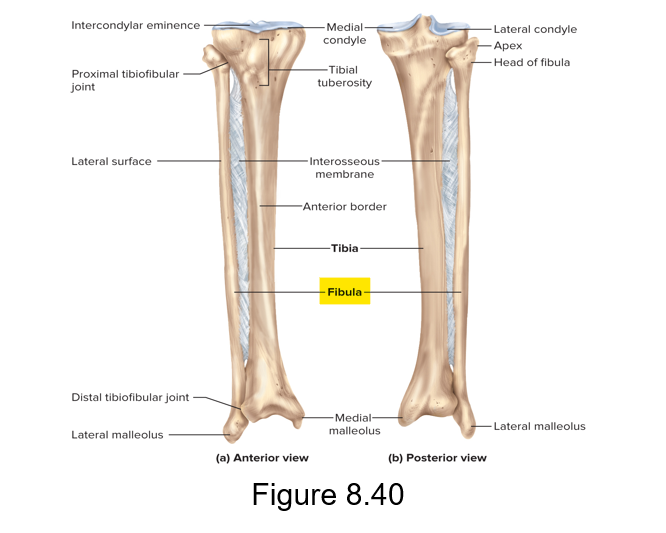
This is the lateral leg bone in the leg proper area (crural region)
Fibula
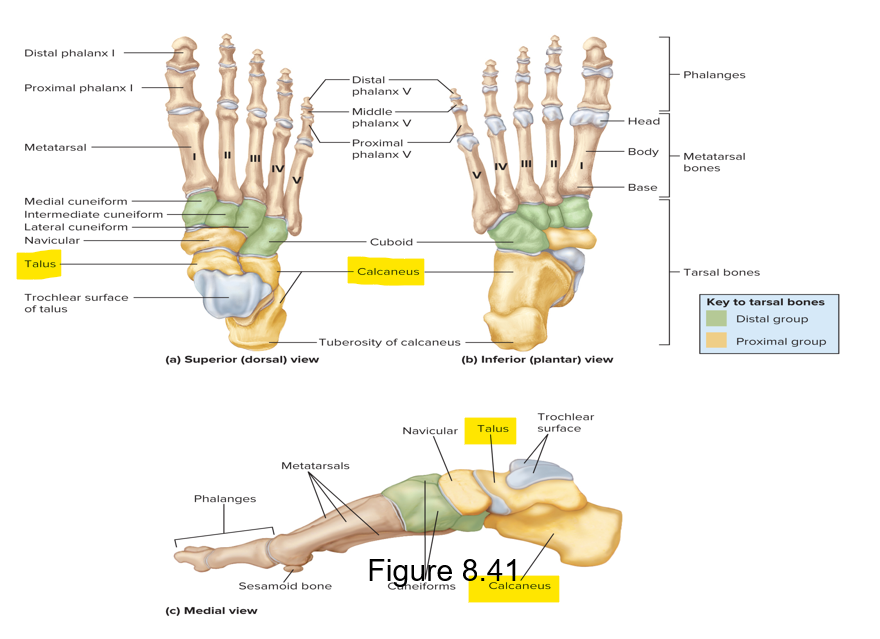
These tarsal bones in the ankle and foot differ from carpal bones due to their load-bearing role
Calcaneus - largest tarsal bone; the calcaneal (Achilles) tendon attaches to the distal portion
Talus - most super tarsal bone
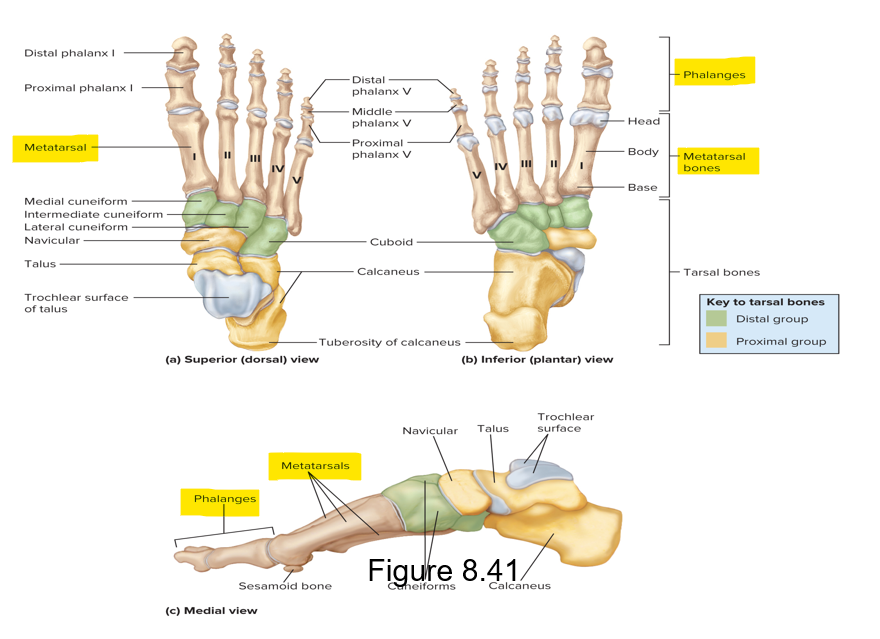
Other foot bones resemble the hand bones in name and positon
Metatarsals
Phalanges - digits/toes; 2 in great toes, 3 in all other toes
What is a function of the spine (vertebral column)?
Protect the spinal cord
What is the sequence of the vertebral regions?
7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
5 sacrum vertebrae
4 coccyx vertebrae
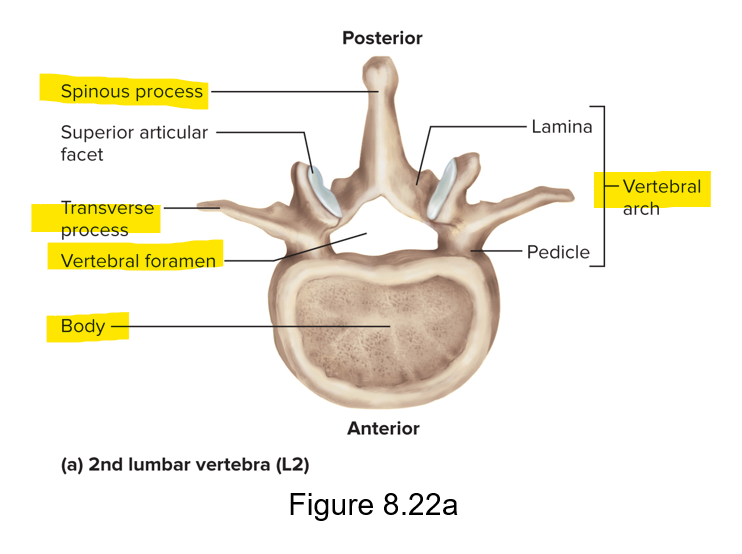
General structure of vertebra
Body - spongy bone with red marrow covered with compact bone; weight bearing portion
Vertebral foramina - collectively form the vertebral canal for the spinal cord; vertebral arch; spinous process
Transverse process
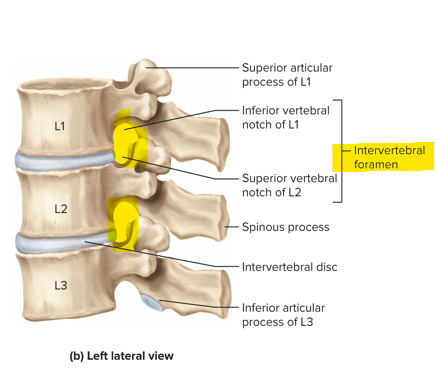
Intervertebral foramen
ONLY with 2 or more vertebrae; it’s an opening between 2 adjoining vertebrae and is a passageway for spinal nerves
What is a function of intervertebral discs?
Bind vertebrae together; support weight of the body; absorb shock
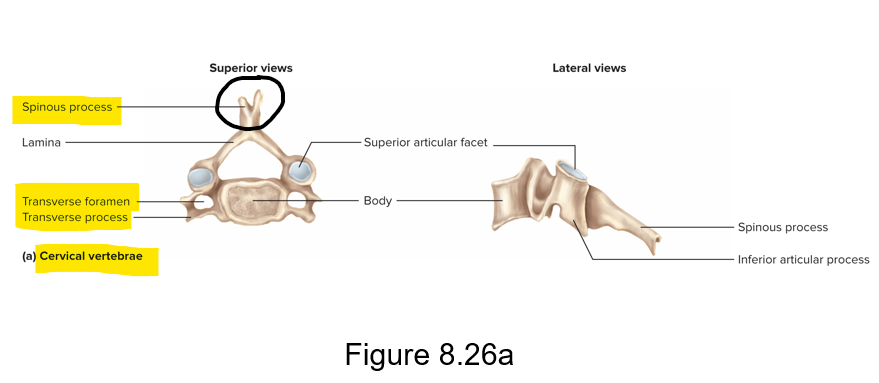
Characteristics of cervical vertebrae
C1-C7 - forked spinous process; transverse foramen in each transverse process that provides passage for vertebral artery and vertebral vein
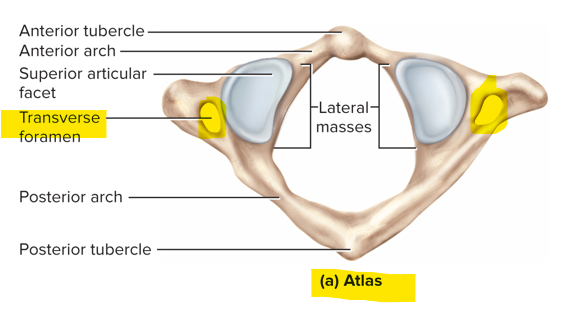
Atlas
C1 - supports the head; has no body; articulates with the occipital condyles; allows us to make the “yes” movement
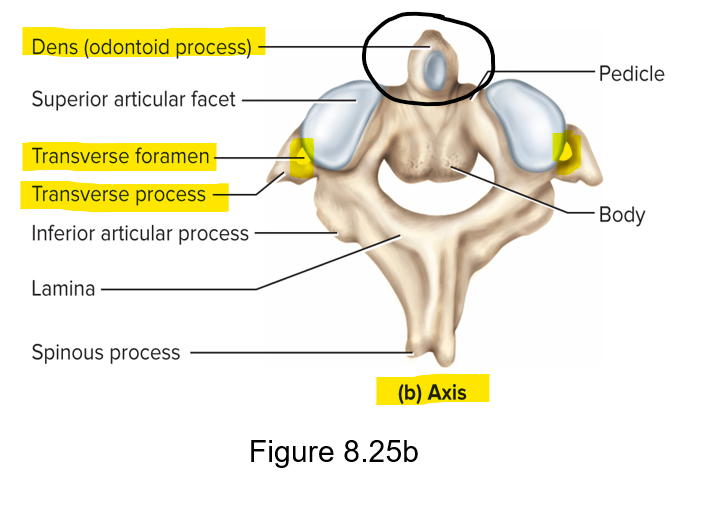
Axis
C2 - allows head rotation for saying “no”; dens/odontoid process
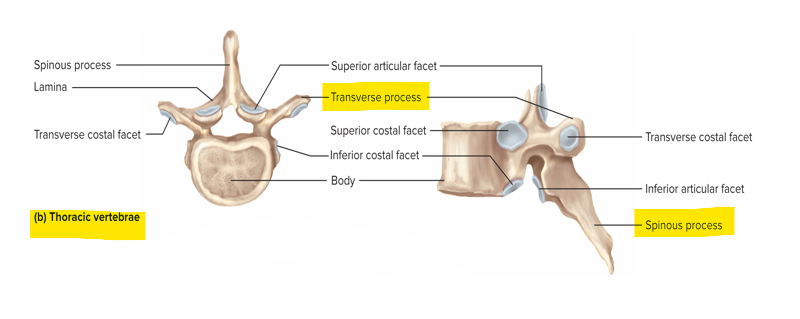
Characteristics of thoracic vertebrae
T1-T12 - spinous processes are angled sharply downward; no transverse foramina
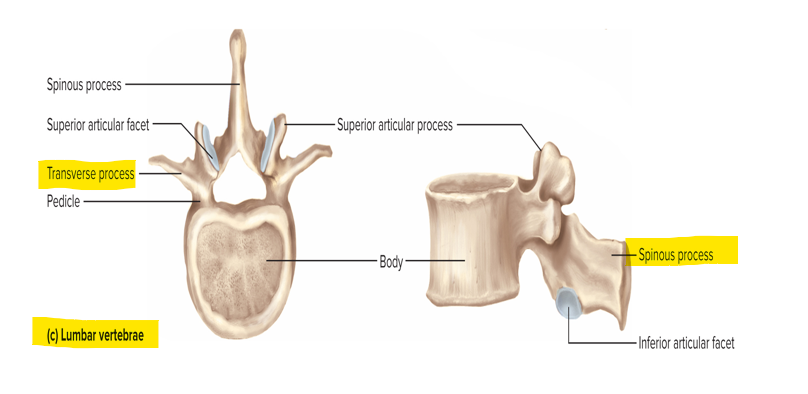
Characteristics of lumbar vertebrae
L1-L5 - thick, stout body; blunt, squarish spinous process
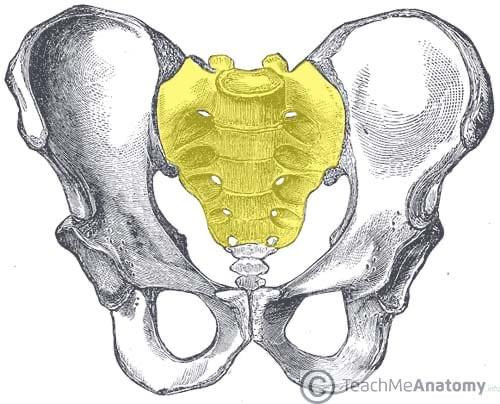
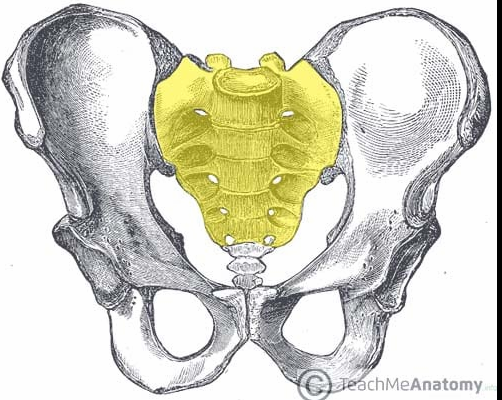
Identify this bone; what vertebrae are associated with this bone?
Sacrum; sacral vertebrae S1-S5
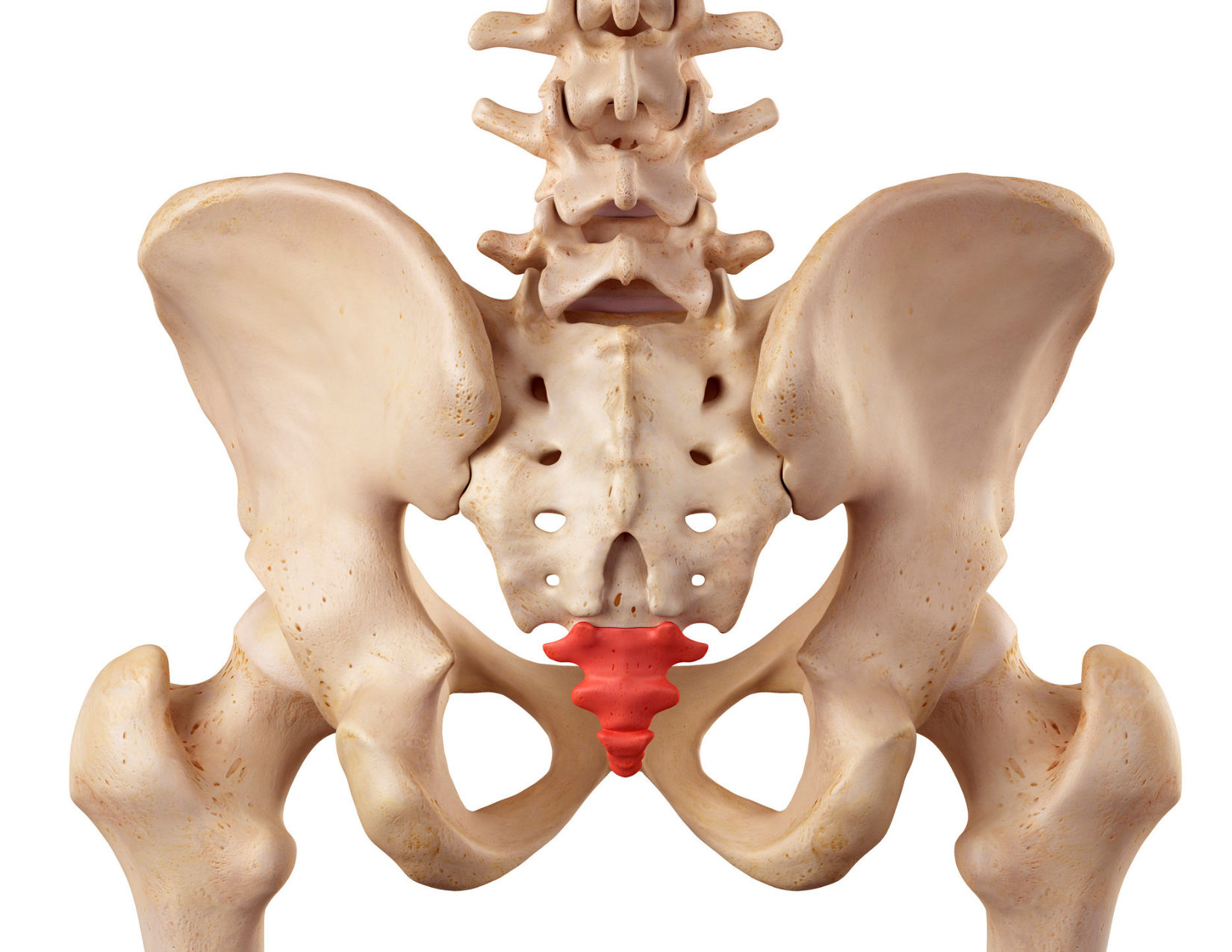
Identify this bone; what vertebrae are associated with this bone?
Coccyx; Co1-Co4
What does the thoracic cage consist of and what does it protect?
Consists of thoracic vertebrae, sternum and ribs; protects important organs
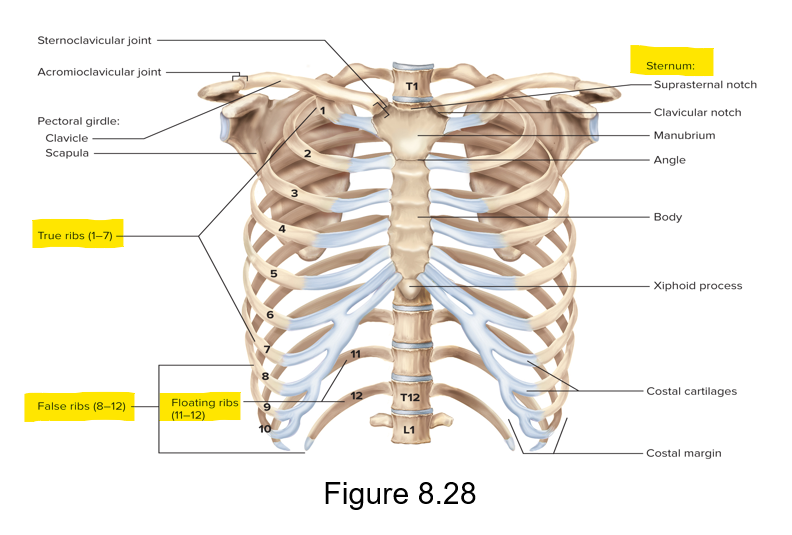
What is the sternum and what 3 regions does the sternum consist of?
Breastbone - bony plate anterior to the heart
Regions - manubrium (superior), body (middle) and xiphoid (inferior)
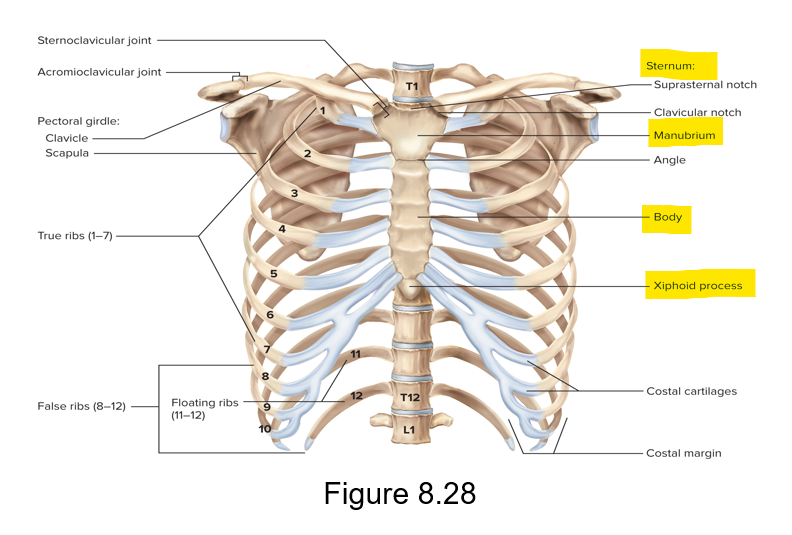
How many pairs of ribs are there and how do they attach to the body?
12 pairs of ribs; beginning of the ribs is posterior to the spinal column; the end of the ribs is anterior
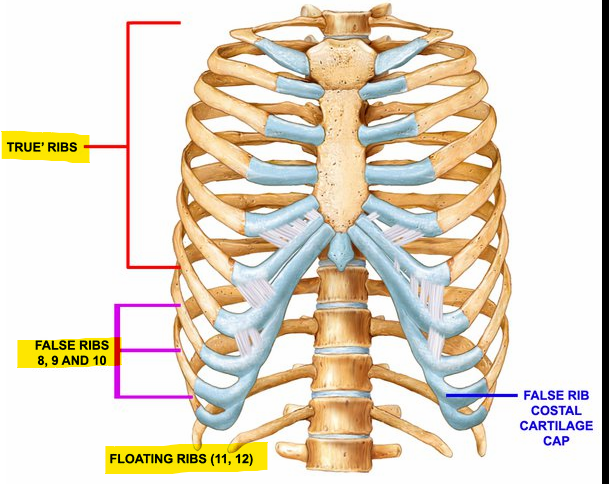
Define true ribs, false ribs and floating ribs
True ribs - 1-7, each is directly connected to the sternum
False ribs - 8-10, no direct connection to the sternum
Floating ribs - 11-12, no connection to sternum