BIOL 2460 Chapter 13
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Main Goal
reduce microbial load and reduce infection of contamination
clean
it is all relevant
sterilization
removal/killing of ALL microbes
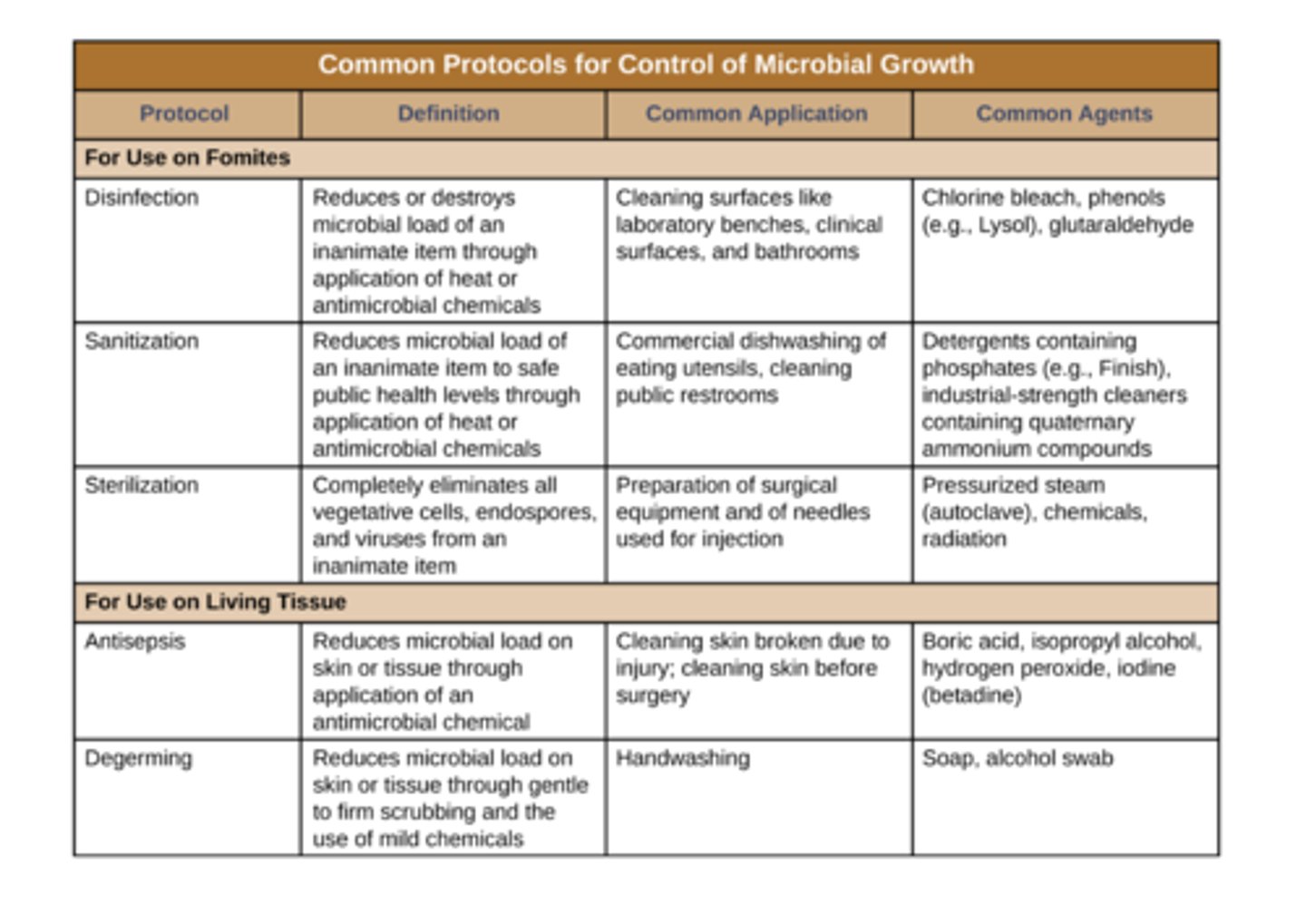
Disinfection/Antisepsis
inactivation of microbes
Sanitization/Degerming
decreasing microbial load
Who established the 4 levels of BSL
CDC, NIH, WHO
BSL 1
•Very little risk
•sink for handwashing & door to close off lab
•Agents that do not cause infection in healthy adults
•Nonpathogenic E. coli and B. subtilis
•(Ex. BIOL freshman labs)
BSL-2
•Pose moderate risk; restrictive access
•BSL-1 plus PPE, self closing doors, eyewash station, autoclave or sterilization method •S. aureus, Salmonella spp.
•Viruses like hepatitis, mumps, and measels
•(Ex. Micro labs)
BSL-3
•Potential to cause lethal infections by inhalation
•BSL-2 plus respirator, bio safety cabinets, hands-free wash sink, two sets of doors, directional air flow
•Indigenous or "exotic" pathogens
•M. tuberculosis, B. anthracis
•West Nile Virus, HIV
•(No example at UTA)
BSL-4
•Most dangerous; often fatal
• BSL-3 plus full biohazard suit, change clothing on entry, shower on exit, decontaminate all material on exit, lab must have own air supply
•"Exotic" pathogens; Ebola and Marburg viruses
•(only 13 in USA)
critical cleaning
must be sterile; items used inside the body (sterile tissue or bloodstream)
Ex: surgical instruments, catheters, IV fluids
semicritical cleaning
do not require high level sterilization; items might contact non-sterile tissue (gut) but not penetrate tissue
noncritical cleaning
do not require sterilization' items contact but do not penetrate intact skin (stethoscopes, bed lines, blood pressure cuffs)
Sterilization
Complete killing or removal of all microbes from fomite
Methods: Heat, pressure, filtration, chemical
aseptic technique
used to prevent sterile environment from becoming contaminated
disinfectant
inactivation/kill of microbes on fomites
(include vinegar and bleach)
some microbes may not be inactivated-- disinfection does not equal sterile
antiseptic
acts on microbes but not organism/tissue
(hydrogen peroxide, rubbing alcohol)
sanitization and degerming
Decrease of microbial load (amount of microbes)
sanitization
reduce microbial load on fomite (usually with heat or chemicals)
degerming
reduce microbial load on living tissue
(usually mechanical - washing hands, wiping with paper towels, etc)
may be used in combination with disinfectant to maximize microbial reduction
common protocols for control of microbial growth
measuring success of control
-methods can partial or full kill various microbes
- cides: kill
- static: stop growth
Ex:
Bactericidal vs Bacteriostatic
Viricidal; vs Viristatic
Fungicidal vs Fungistatic
-degree of control can be observed with microbial death curve
-many factors affect success of control
-length of exposure; concentration of agent; population level
microbial death curve
measure of percentage of kill
decimal reduction time DRT
how much time it takes to kill 90% (1 log reduction) of population
physical means of control
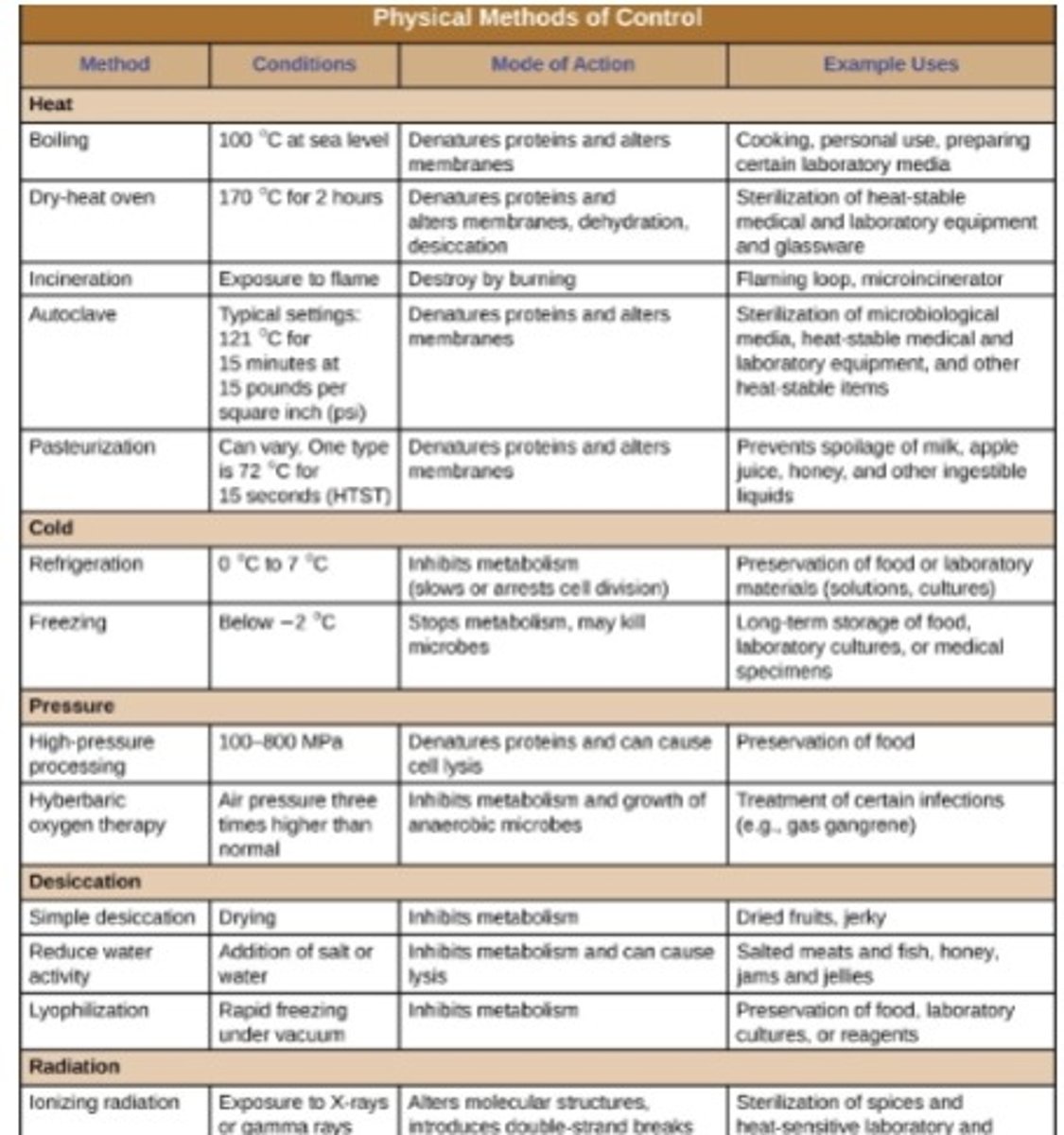
1. Temperature
2. Radiation
3. Filtration
4. Desiccation
5. Pressure
6. Sonication
Heat Sterilization
•Oldest and most common
•Alters membranes and/or denatures proteins
thermal death point
the lowest temperature required to kill all microbes in a sample in 10 minutes
thermal death time
the length of time required to kill all bacteria in a liquid culture at a given temperature
dry heat
•aka incineration; direct application of high heat (>250C)
• Bunsen burner
• Bacteria incinerator
moist heat
application of high temperature liquid/vapor
Beneficial b/c penetrates cells better than dry
Ex. autoclave
autocalve
raise temperature of water above boiling point 121C by raising pressure to 15 psi
kills viruses & endospores
Autoclave types
gravity: use steam to push out air
prevacuum: vacuums out air first
require periodic QC to check functionality: autoclave tape, spore tests, diack tubes, recorders
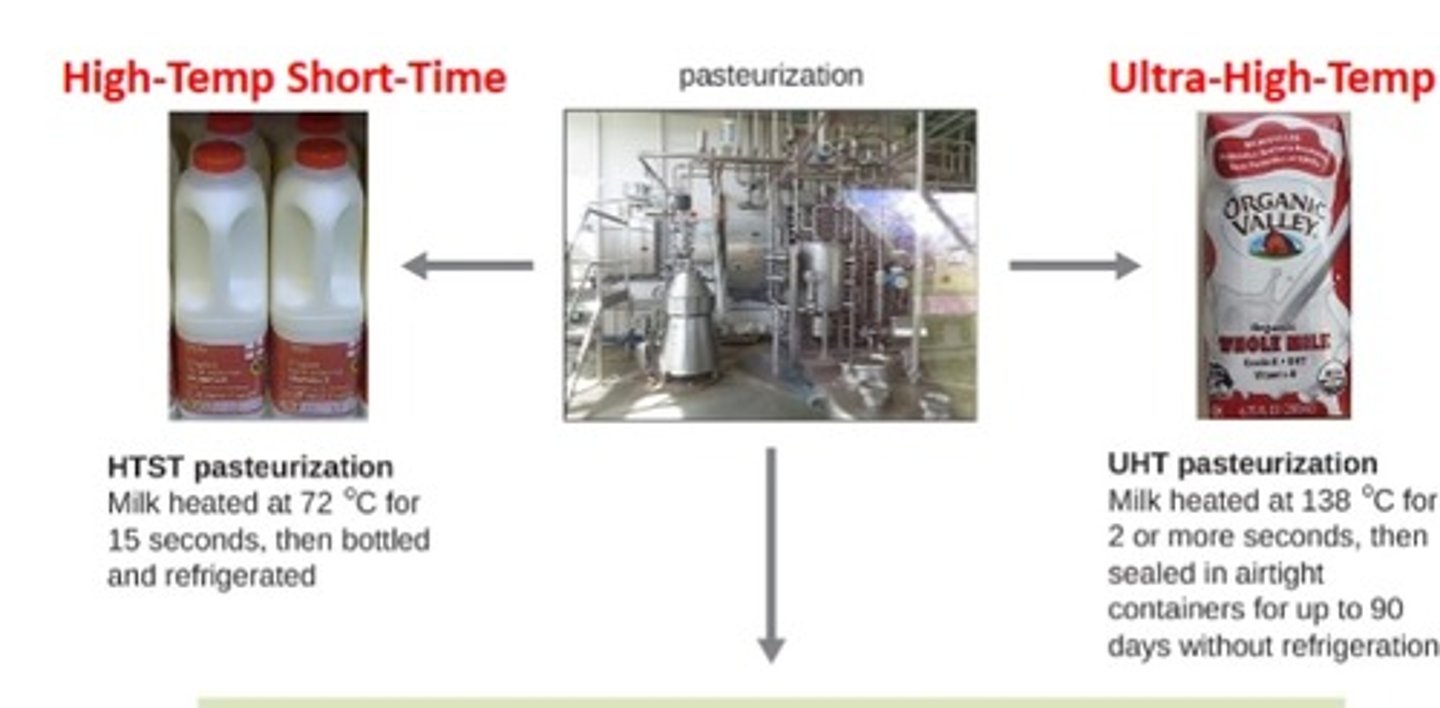
pasteurization
semi-sterilizes food but does not ruin food quality
many methods rely on "flash" heating foods to kill most mircobes
Refrigeration and Freezing
•Usually not sterilization method but static
•Slows metabolism but will grow when temps are raised
•(Reason why USDA recommends thawing at temps lower than optimal)
•Ultra low temps (-80C) can be used for preservation
pascalization
high pressure used in food industry to kill microbes
hyperbaric chambers can be used to treat infections - counters hypoxia by saturating infection site with oxygen
used in combination with temperature in autoclaves
desiccation
drying or dehydration
method used for millennia to preserve foods (raisins, prunes, jerky, etc)
all cells including microbes require water for metabolism and survival
doesn't kill all microbes, so they may regrow in favorable conditions
lyophilization
freeze-drying; rapid freezing then placed under vacuum
salts or sugars can used to lower water activity of foods/materials without physical drying (osmosis)
radiation
high energy radiation -used to kill or inhibit microbes
ionizing radiation
enters into cells and disrupts molecular structures such as DNA
X-rays & gamma rays
can be used to sterilize non-autoclavable items
can be alternative to pasteurization in canned foods
non-ionizing radiation
does not penetrate glass, plastics, etc. but can damage cells w/ direct exposure
UV irradiation
forms thymine dimers in DNA causing lethal mutations
sonication
high frequency sound waves to disrupt cell structure
causes bubbles to form inside cells and induce lysis
used in laboratory and clinical settings
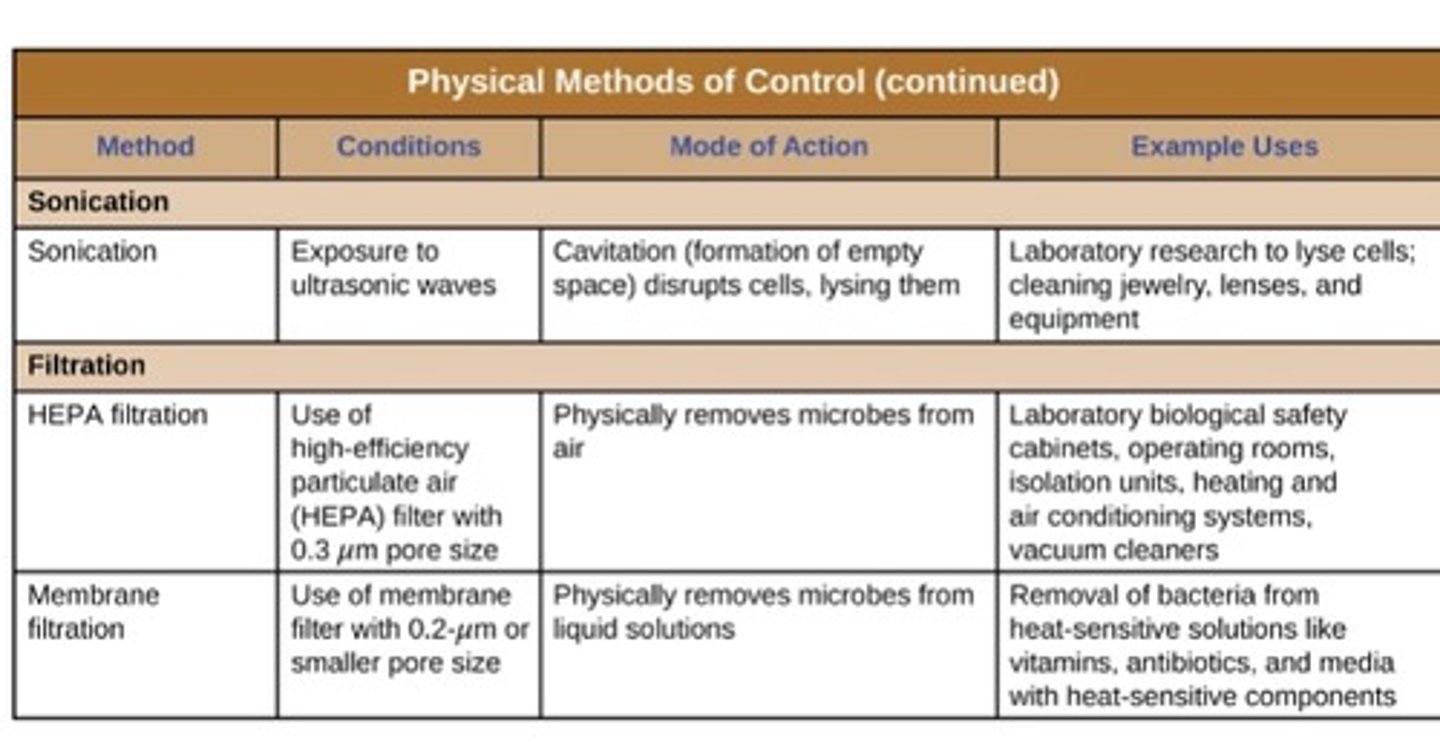
filtration
use of barrier to physically separate microbes
useful when media cannot be autocalved (urea broth, antibiotic and vitamin solutions)
filters usually have pore size of .2 um or smaller for viruses
membrane filtration
remove microbes from liquid samples
Air is commonly filtered through
High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters
used in households, biological safety cabinets, hospitals and surgical suites
physical methods of control
physical methods of control part 2
Chemical means of control
-Phenolics
-Heavy Metals
-Halogens
-Alcohols
-Surfactants
-Bisbiguanides
-alkylating agents
-peroxygens
-supercritical fluid
-food, cosmetic, and pharma preservatives
phenols
carbon molecule with benzene ring and -OH group
MOA: denature proteins and membranes
Ex: carbolic acid - first used by joseph lister for surgical wounds
lysol - original formulations (now is quaternary compound)
triclosan - commonly used in hand soaps, banned by FDA in 2017
heavy metals
MOA: binds to and inhibits proteins
not exclusive to mircobes
mercury
treated syphillis but banned b/c of neural toxicity effects
silver
used today to treat burn wounds, pediatric ophthalmia, neonatorum, and in antibiotics
sopper sulfate
used as algicide to treat pools
zinc
mouthwashes, calamine lotion, baby powder
iodine
oxidizes cellular components; commonly used as a iodophor (complex with organic molecule)
chlorine
hypochlorous acid - CL + H2O; used to treat water
sodium hypochlorite - bleach
chloramine - CL - NH3; very stable swimming pool smell
fluorine
most recongizable with dental products
deposits in tooth enamel and provides disruption in microbial fermentation and processes
alcohols
used as disinfectants and solvents.
- MOA: disrupts membranes and denatures cytoplasmic proteins - lysis
- used as 70% to allow better cell pernetration
- only viricidal for enveloped
- can be used in combo with iodine
surfactants
chemicals that lower surface tension of after
in most soaps and detergents; aid in gegerming
soaps
fatty acids salts
not -cidal or -static but means of mechanical removal
detergents
synthetic polar & non-polar molecules
Anionic - neg anion on chain
Cationic - pos anion on chain
quaternary ammonium salts
-Cationic detergents
-Similar to phospholipids & can insert into lipid bilayer
-Common day Lysol
bisbiguanides
•Cationic molecules that have antiseptic properties
•disrupt membrane & congeal cytoplasmic contents
•Not active against naked viruses, M. tuberculosis, and spores.
chlorhexidine
common surgical scrub and longer lasting than iodophors
alexidine
Faster acting surgical scrub "Up and coming" (Bisbiquanides)
alkylating agents
strong disinfecting agents
- replace hydrogen atom with alkyl group
M
OA: inactivates enzymes and nucleic acids
formaldehyde
fixes specimens by cross-linking proteinsw
glutaraldehyde
acts faster than formaldehyde; common disinfectant of surgical equipment
ethlyene oxide
gaseous sterilizer that has high penetrating ability
B-propionolactone
clear liquid or vapor with strong odor; wide variety of sterilization; medical, tissue, milk, etc.
peroxygens
Oxidizing agents used as disinfectants or antiseptics; produce radical oxygen to disrupt macromolecules
hydrogen peroixde
common and cheap disinfectant
peracetic acid
more effective than immune to activiation by and peroxidases
Benzoyl peroxide
present in acne meds; very effective against Propionibacterium acnes
Carbamide peroxide
agent in toothpaste that combats bioflims
ozone gas
used to clean air and water supply
supercritical fluids
•Pressure and temp are increased in molecules to have properties between liquid and gas
Ex. Supercritical CO2
•Allows for easier cell penetration and formation of carbonic acid and increase acidity
•Non-reactive, non-toxic, & non-flammable
•Good for many vulnerable materials such as foods and some tissues
preservatives
most inhibit microbial growth in food products
in foods, important to be non-toxic and flavorless
- sorbic acid
- benzoic acid
- propionic acid
- sulfur dioxide
- nitrites
- nisin
- natamycin
sorbic acid
•inhibits various cellular enzymes (e.g. in CAC, catalases, and oxidases)
•Increases efficacy as pH decreases
•Added into a variety of foods; dairy, bread, fruit & veg
benzoic acid
•decreases intracellular pH, interferes with oxidative phosphorylation and AA uptake
•Found naturally in fruits, berries, spices, and fermented foods
propionic acid
•inhibit enzymes and decrease intracellular pH
•More effective at higher pH than sorbic or benzoic
•Naturally produced by some cheeses
•Added to other cheeses, and baked goods
•Added to raw dough to prevent contamination by B. mesentericus
sulfur dioxide
MOA unclear (inhibit protein formation or reduce intracellular Ph)
- prevents browning of foods
- used in winemaking since ancient times
- dissolves in water readily (sulffites)
nitrites
•Nitric Oxide reacts with iron-sulfur groups (disrupts ETC)
•added to processed meats (maintains color; stops C. botulinum endospore germination)
•Nitrosamines (carcinogen) produced when nitrite-preserved meats are heated
nisin
•disrupts G+ cell wall production
•Produced by Lactococcus lactis
•Used to preserve cheeses, meats, and beverages
natamycin
•antifungal macrolide antibiotic
•Disrupts fungal cell membrane
•Prevents bacterial protein synthesis
•Used in cottage, sliced, and shredded cheese
Disinfectant/Preservative Effectiveness Testing
-Mandated by many agencies
-What level of kill can the agent have?
- how long does it last?
- what microbes does it work on?
3 levels of effectiveness
high - kill vegetative cells, fungi, viruses, and endospores
intermediate - less effective against endospores and viruses
low - kill only vegetative cells and enveloped viruses, not endospores
methods of effectiveness
-phenol coefficient
-disk diffusion
-use-dilution test
-in-use test
phenol coefficient
how strong is the agent relative to phenol
- staphyloccous aureus and salmonella enterica typhi used as test organisms
- exposed to agent diluted in water for 7.5 min
- phenol coefficent of:
1.0 = chemical has same effectiveness as phenol
<1.0 = chemical is less effective than phenol (formalin)
>1.0 = chemical is more effective than phenol (chloramine)
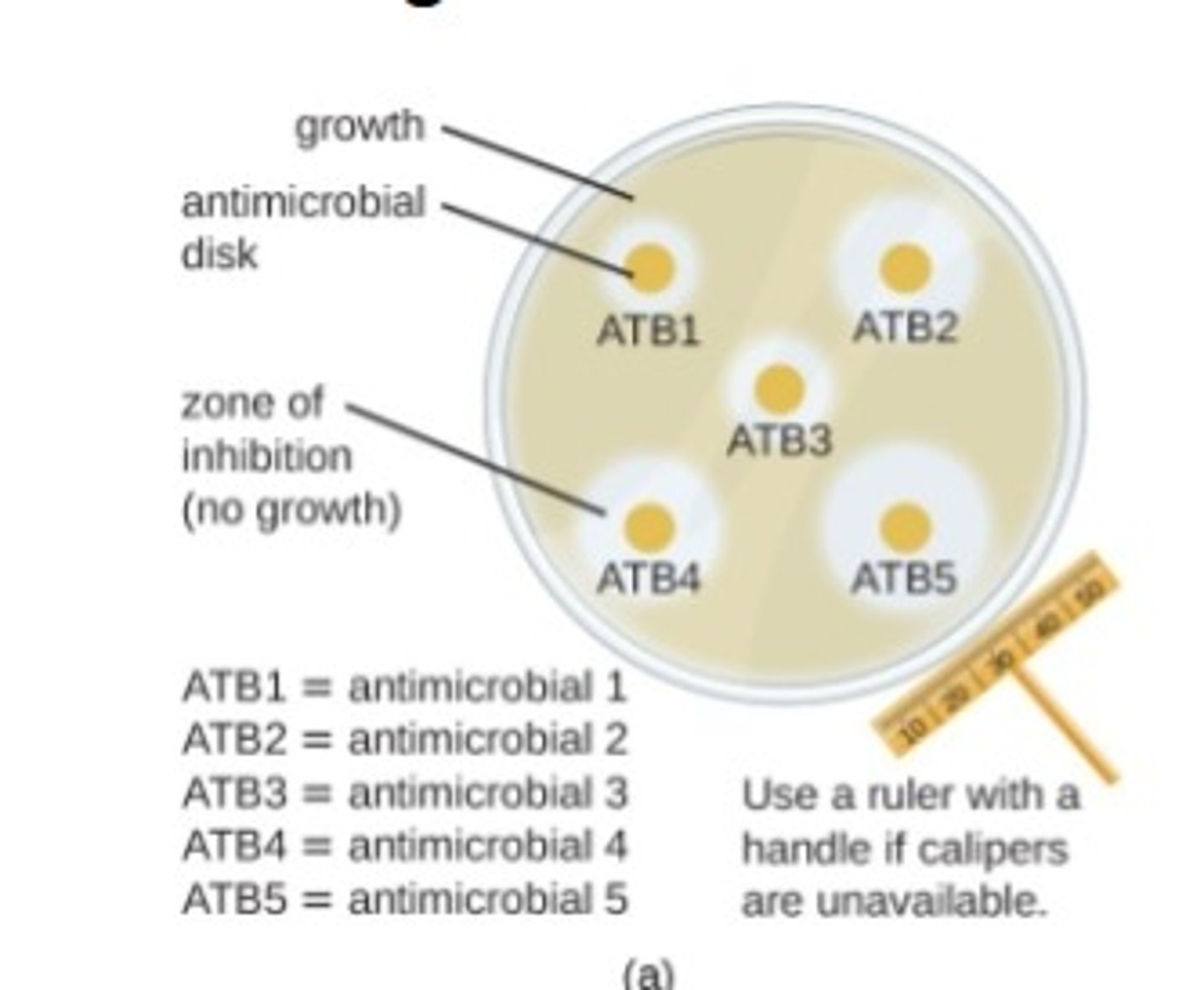
disk diffusion method
measures degree of inhibition using sterile filter paper disks with chemicals
- places on an inoculated agar plate
- lawn of bacteria exhibits zones of inhibition
- larger zone diameter correlates to increased inhibition
use-dilution test
•determines agent's effectiveness on an inanimate surface
•Stainless steel cylinder dipped in target culture then dried
•Cylinder then dipped into various concentrations of disinfectant
•Cylinder then transferred to fresh media
•Turbidity = bacterial survival
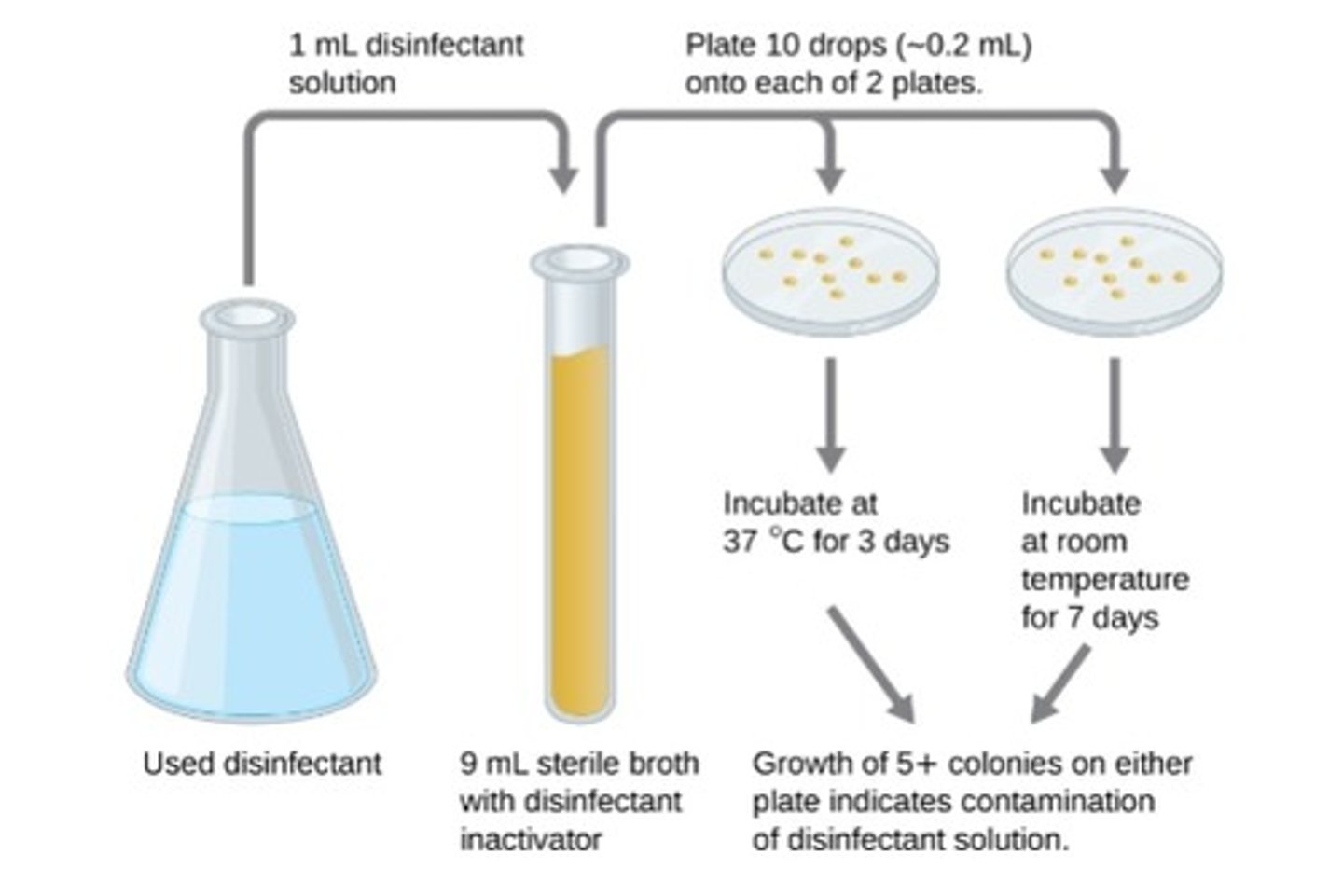
in-use test
•determine whether disinfectant is contaminated
•Usually used in clinical settings