AP World - Unit 4 Vocabulary Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Recommendation - Answer with TERM.
Last updated 5:41 PM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
Charters
Documents granting the right to organize settlements in an area
2
New cards
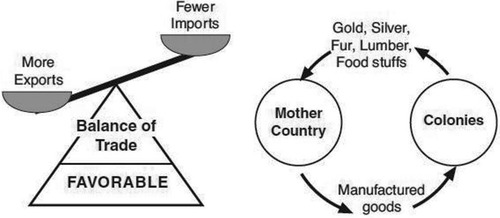
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase by selling more goods than they bought and utilizing colonies
3
New cards
Prince Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Prince of Portugal who established an observatory and school of navigation at Sagres and directed voyages that spurred the growth of Portugal's colonial empire.

4
New cards
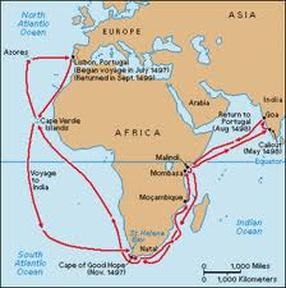
Portuguese Empire
took an early lead in European exploration (sponsored by Prince Henry); went East and established trading posts in West Africa, East Africa (Swahili City States) and India for spice trade
5
New cards
maritime
on or near the sea
6
New cards
Global Silver Trade
Trade between the Americas and Europe and onward to China from the 16th to 18th centuries. It had a profound effect on the world economy could also be considered the beginning of the global economy.
7
New cards
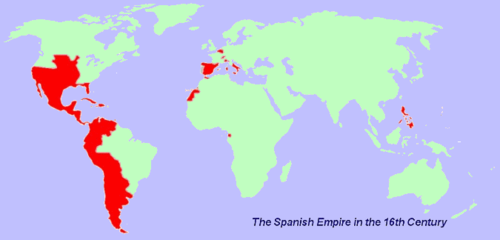
Spanish Empire
Made up of territories and colonies in Europe, Africa, and Asia controlled from Spain. At its strongest, it was one of the biggest empires in world history according to how much land they had, and one of the 1st global empires.
8
New cards
plantation agriculture
Production system based on a large estate owned by an individual, family, or corporation and organized to produce a cash crop.

9
New cards
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower.
10
New cards
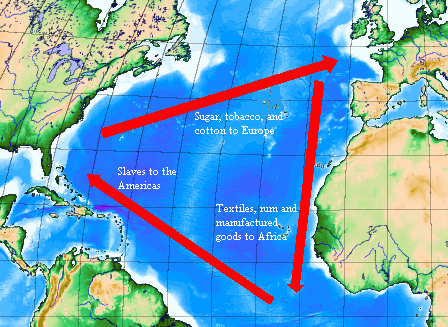
Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
The forced migration of between 12 - 15 million people from Africa to the Western Hemisphere from the middle of the 15th century to the end of the 19th century.

11
New cards
indigenous
native to a certain area
12
New cards
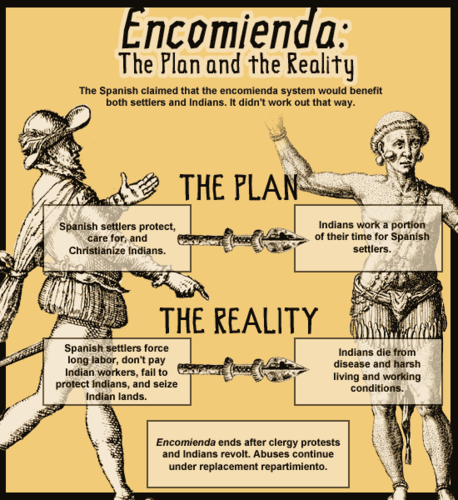
Encomienda System
It gave settlers the right to tax local Native Americans or to make them work and convert them to Christianity. It was a form of coercive labor.
13
New cards
syncretic religion
Combines two religious traditions into something distinctly new, while containing traits of both (ex: voodoo, santeria)

14
New cards
Dutch East India Company
Government-chartered joint-stock company that controlled the spice trade in the East Indies.

15
New cards
British East India Company
set up trading posts in India in the 1600s, beginning the British economic interest there

16
New cards
joint-stock company
A business, often backed by a government charter, that sold shares to individuals to raise money for its trading enterprises and to spread the risks (and profits) among many investors.
17
New cards
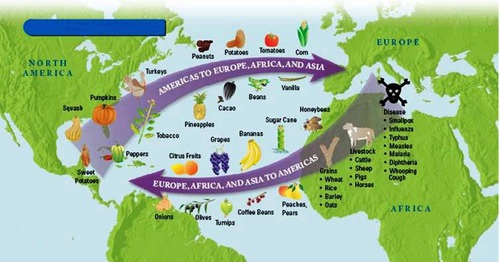
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
18
New cards
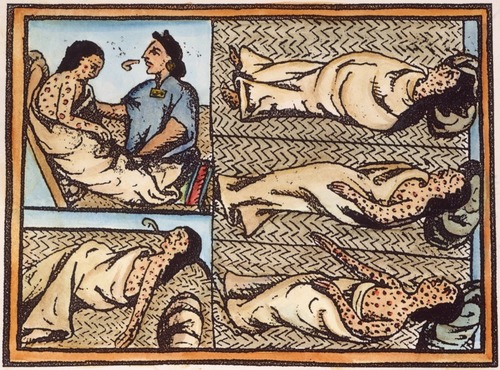
Smallpox
A highly contagious viral disease characterized by fever, weakness, and skin eruption with pustules that form scabs; responsible for killing Native Americans.
19
New cards
coercive labor
Any labor system that involves force (ex: slavery, serfdom, and encomienda)
20
New cards
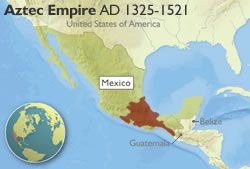
Aztec Empire
Central American empire constructed by the Mexica and expanded greatly during the fifteenth century during the reigns of Itzcoatl and Motecuzoma I.
21
New cards
Inca Empire
Empire in Peru. conquered by Pizarro, who began an empire for the Spanish in 1535
22
New cards
Voodoo
syncretic belief system that combines traditional African religious beliefs with elements of Christianity.

23
New cards
Santeria
Cuban religion that combines Catholic and West African beliefs

24
New cards
Candomble
African religious ideas and practices in Brazil, particularly among the Yoruba people.

25
New cards
Maroon Societies
Communities formed by escaped slaves in the Caribbean, Latin American. and the United States.
26
New cards
Slave Rebellions
Slaves resisted by working slowly, damaging goods, or running away; one of the largest uprisngs in the US was the German Coast Rebellion of 1811 in Louisiana; Nat Turner led a revolt in Virginia in 1831; Southern slaveowners enforced strict slave codes severe punishments and made it illegal to help run-away slaves;
27
New cards
Caravel
A small, highly maneuverable three-masted ship used by the Portuguese and Spanish in the exploration of the Atlantic.

28
New cards
Kongo
Central African state that began trading with the Portuguese around 1500; although their kings, such as King Affonso I (r. 1506-1543), converted to Christianity, they nevertheless suffered from the slave trade.
29
New cards
Asante Kingdom
kingdom that emerged in the 1700s in present-day Ghana and was active in the slave trade
30
New cards
compass
an instrument containing a magnetized pointer that shows the direction of magnetic north and bearings from it.
31
New cards
Creoles
In colonial Spanish America, term used to describe someone of European descent born in the New World.
32
New cards
Mestizos
People with mixed races between European and indigenous descent
33
New cards
Mulattoes
People with mixed races between European and African descent