Microscope
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
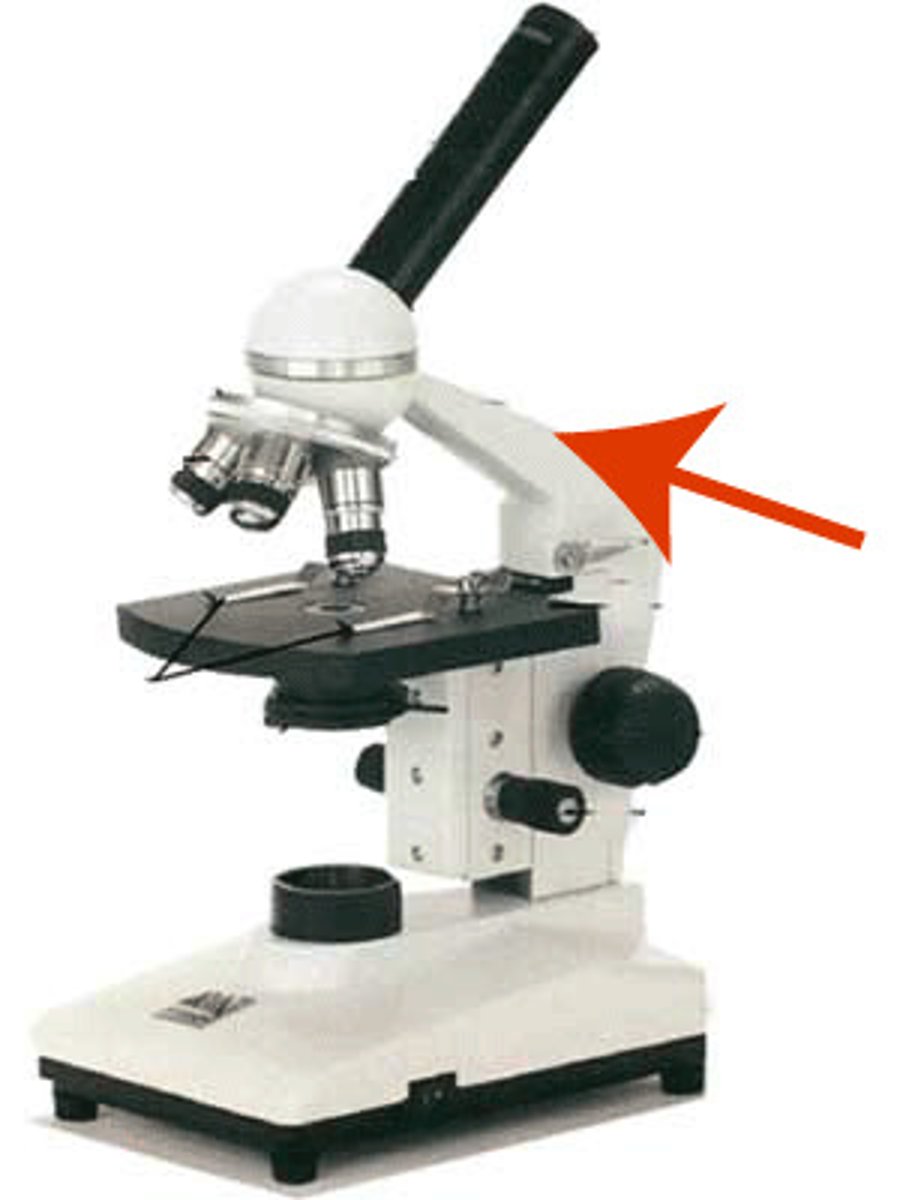
Arm
Supports the tube and connects it to the base
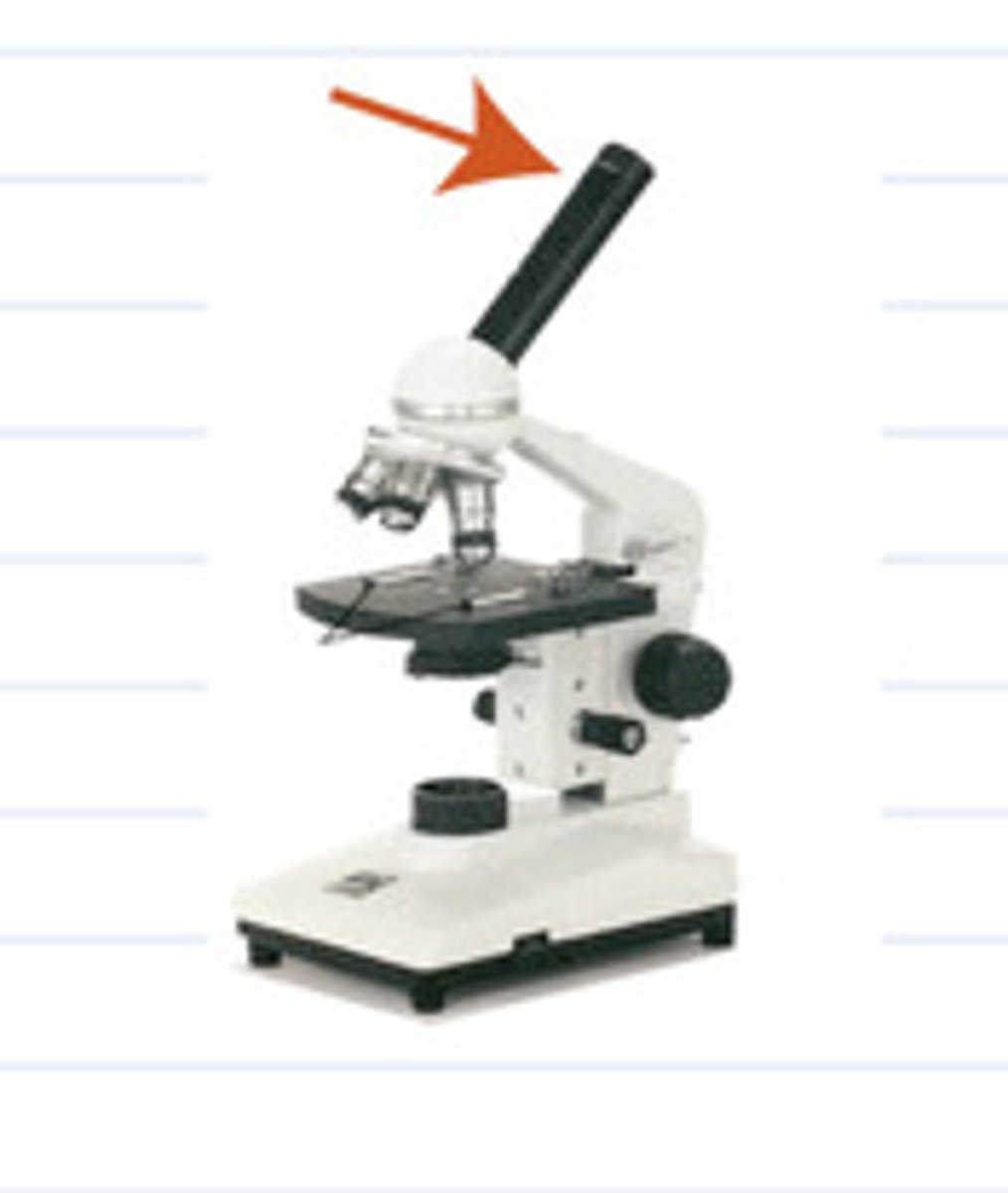
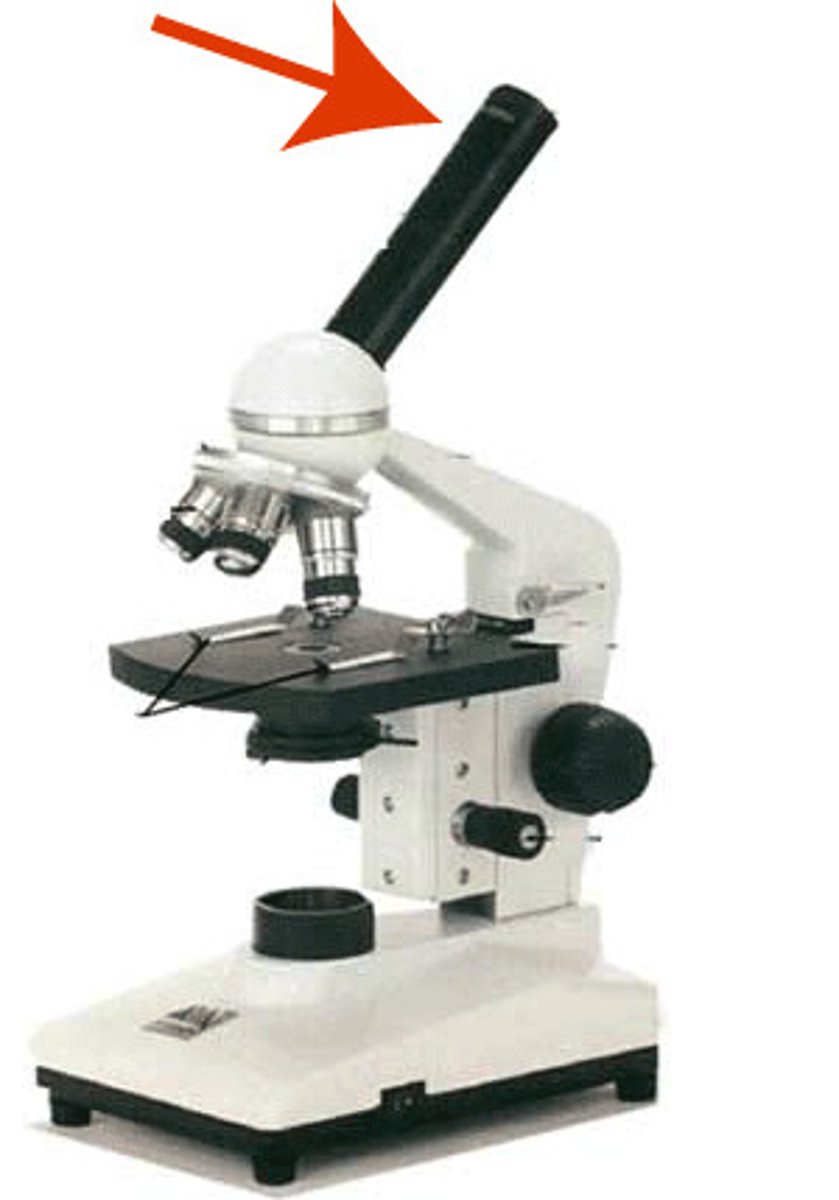
ocular lens
the lens at the top that you look through. They are 10X power.

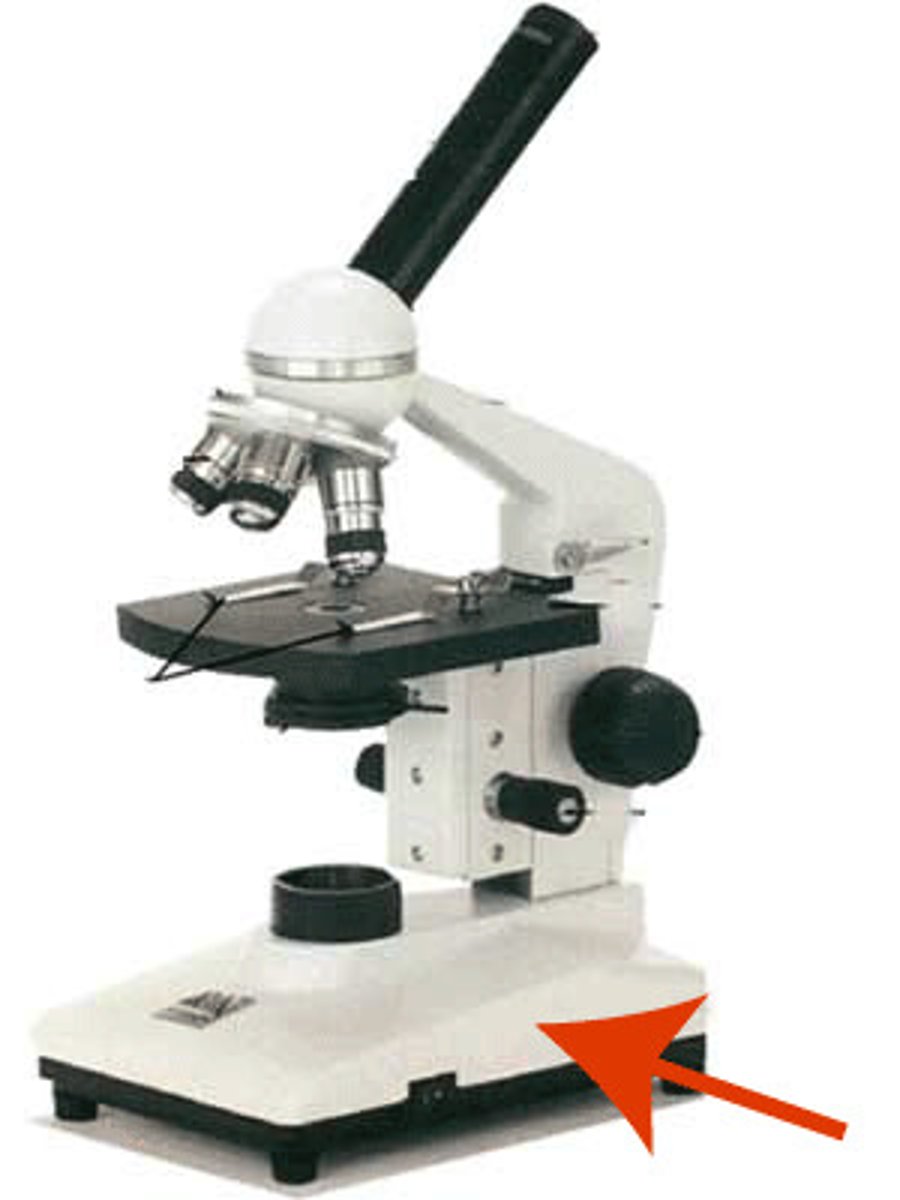
Base
The bottom of the microscope, used for support

Body tube/barrel
Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses
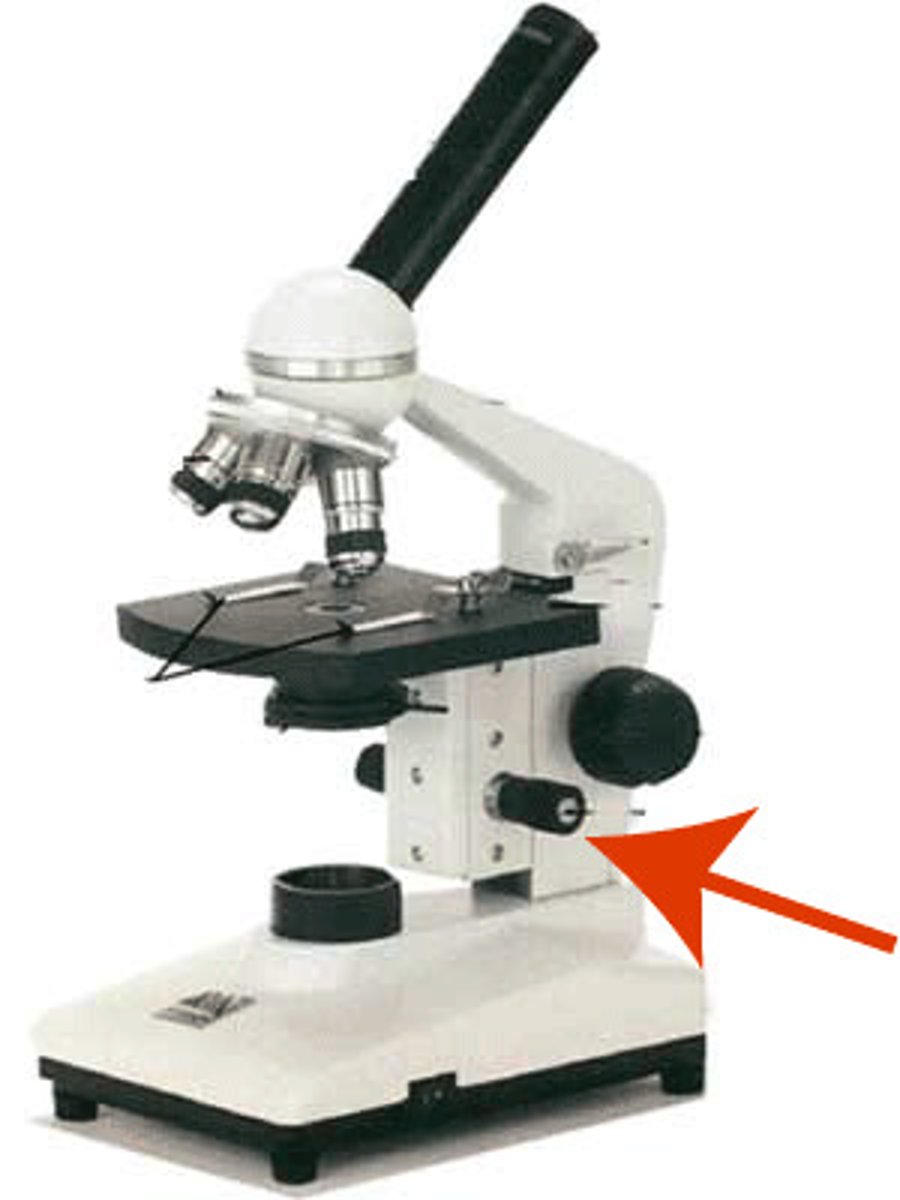
Coarse adjustment
Used for focus on scanning. Usually the low power lens is used enabling the movement of the tube.
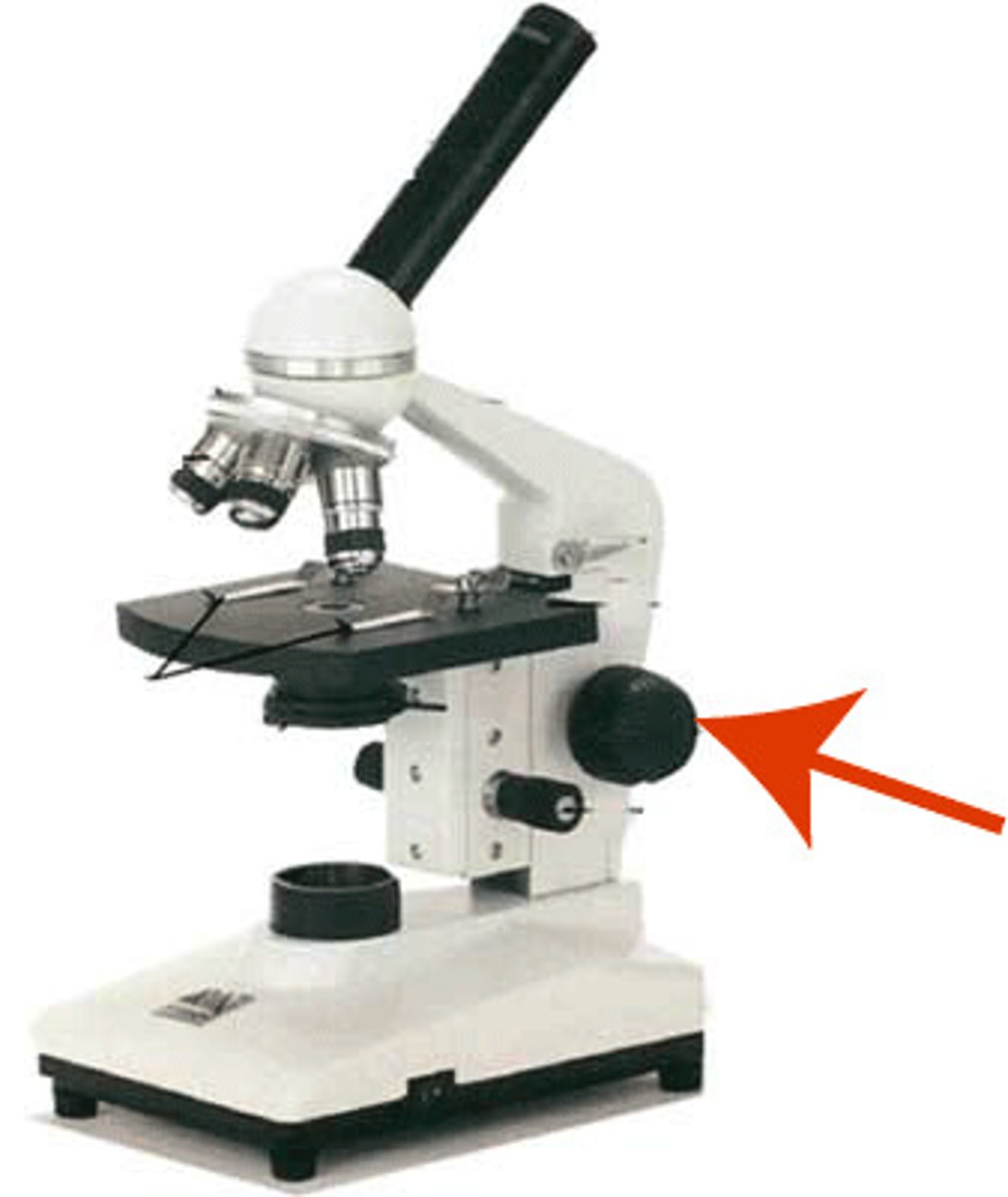

Fine adjustment
Used for focus on oil. Moves the body tube for focussing the high power lens.
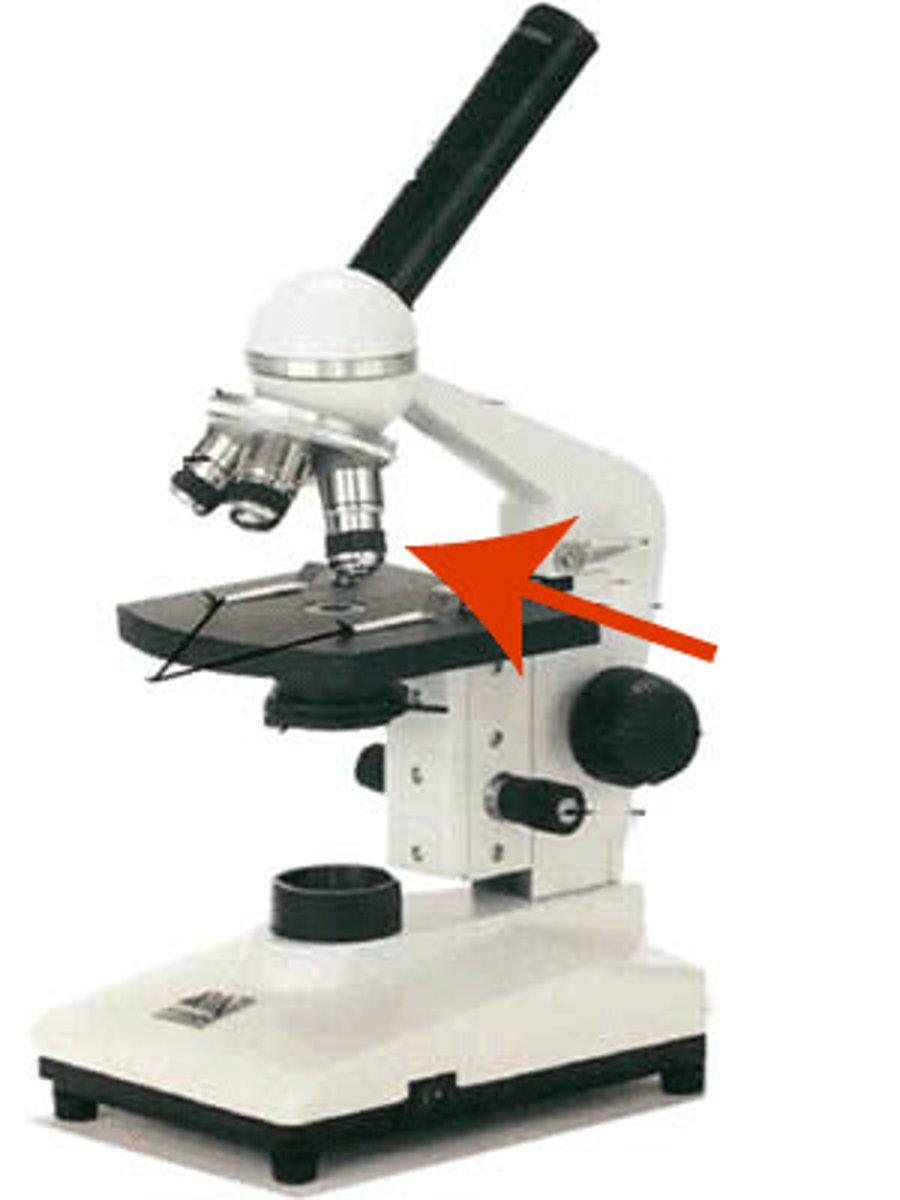
Objective lens
Generally, three or four objective lenses are found on a microscope, with ranges of 10X, 40X, 100X powers. Lenses are colour coded, the shortest lens is of the lowest power, and the longest lens is high power lenses.
illuminator
A steady light source (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If your microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom of the stage.
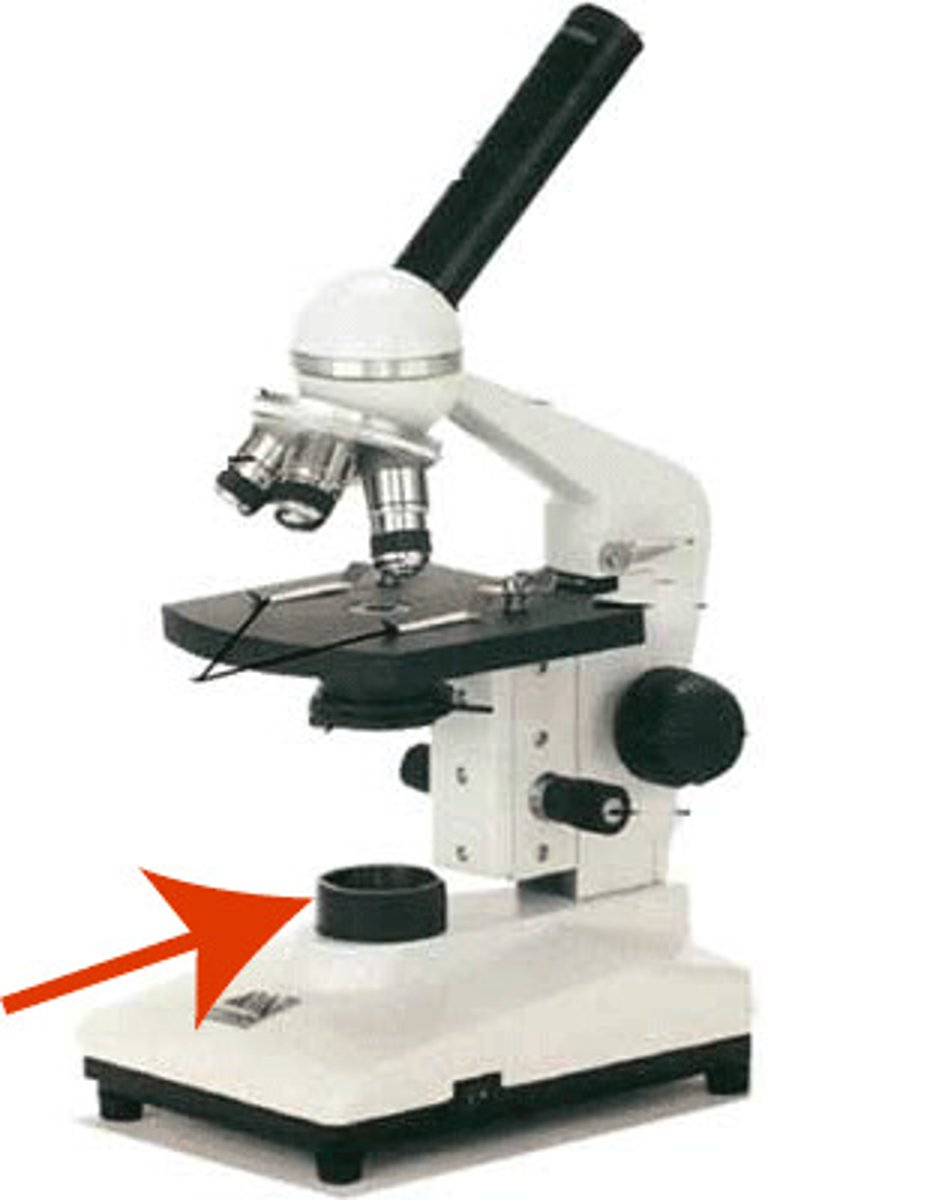

Stage
The flat platform where you place your slides. Stage clips hold the slides in place. If your microscope has a mechanical stage, you will be able to move the slide around by turning two knobs. One moves it left and right, the other moves it up and down.
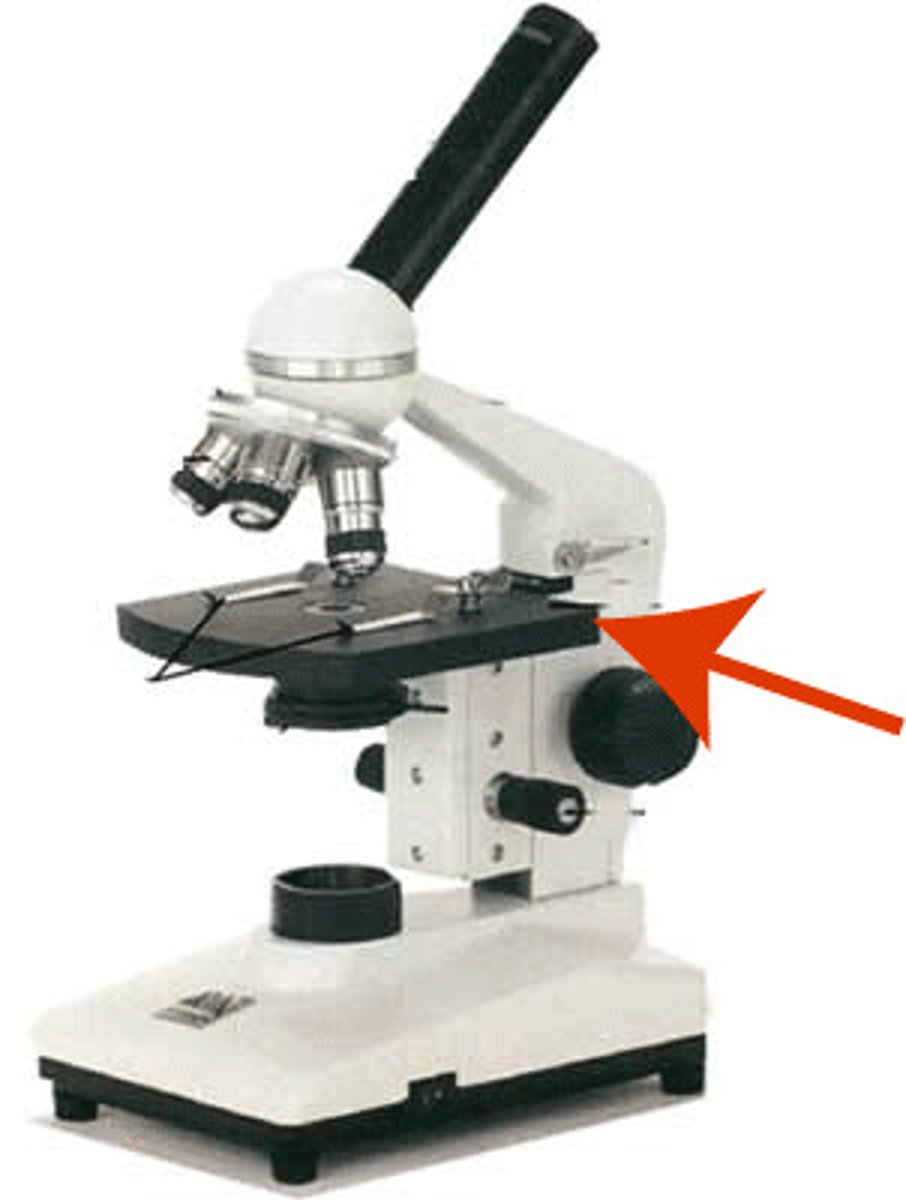
Stage clip
hold the slides in place.
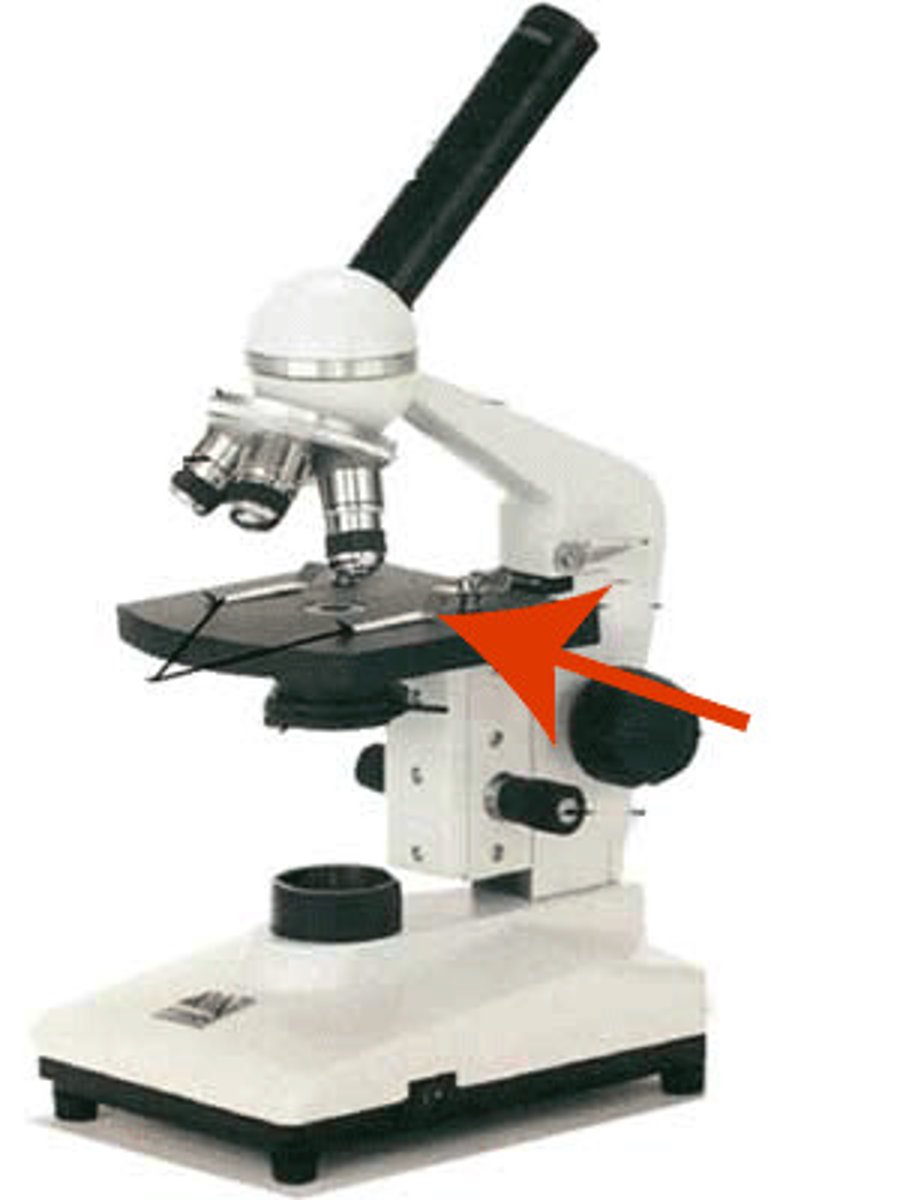
Revolving nosepiece
This is the part that holds two or more objective lenses and can be rotated to easily change
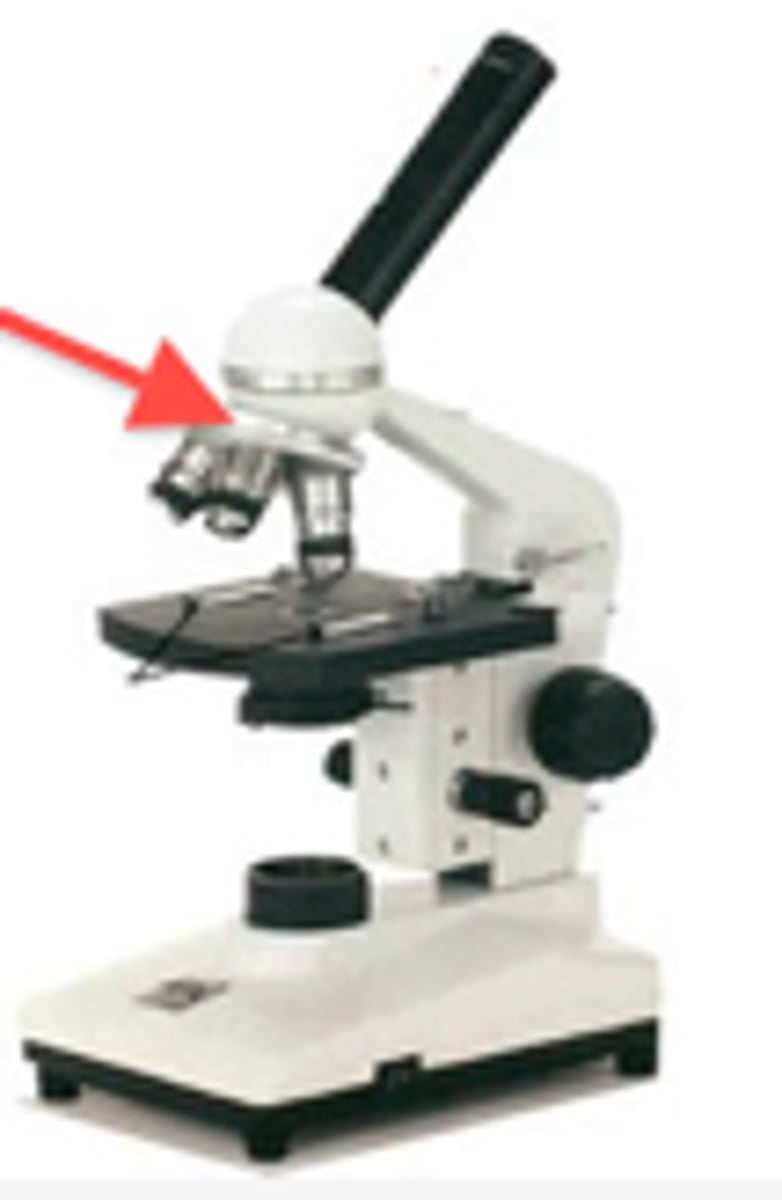
Diaphragm
Can adjust the amount of light.
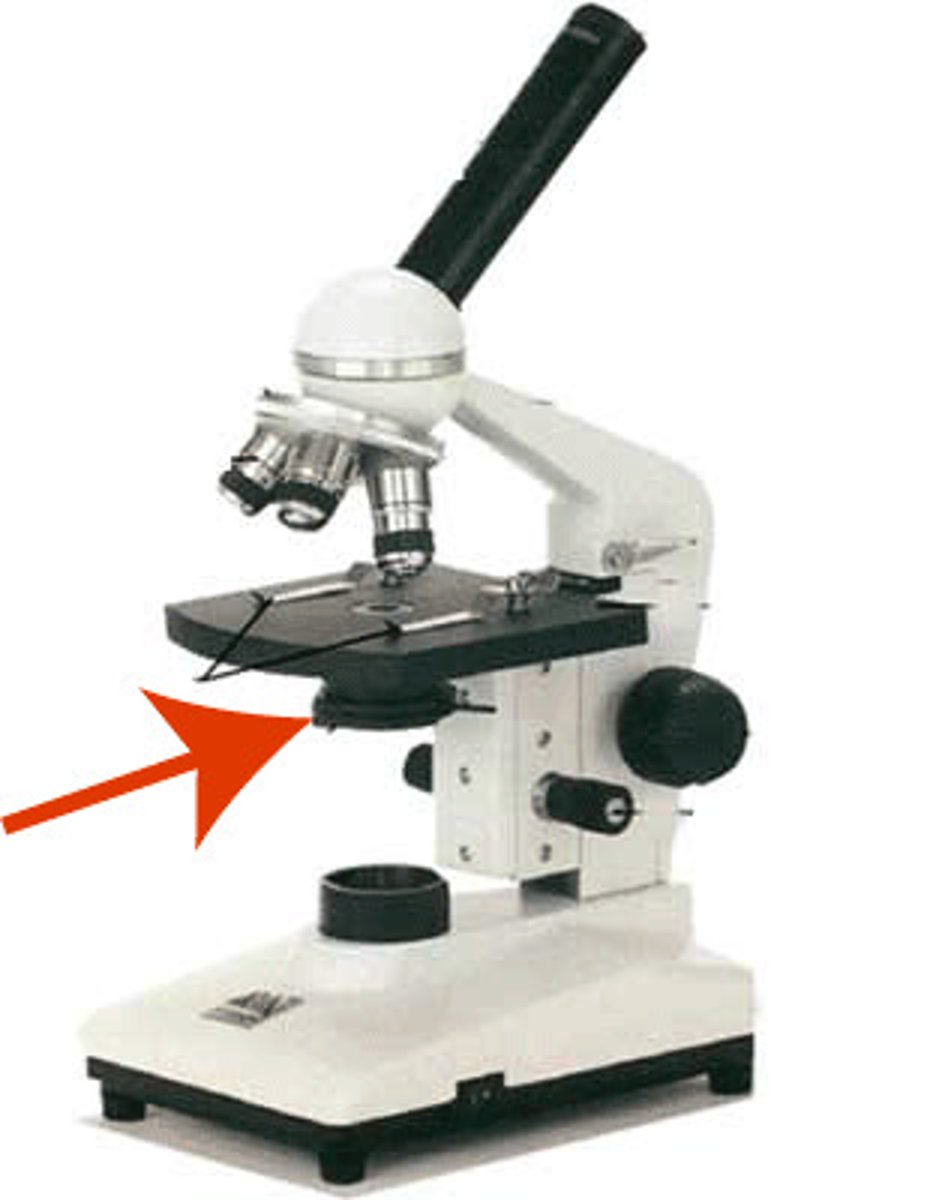
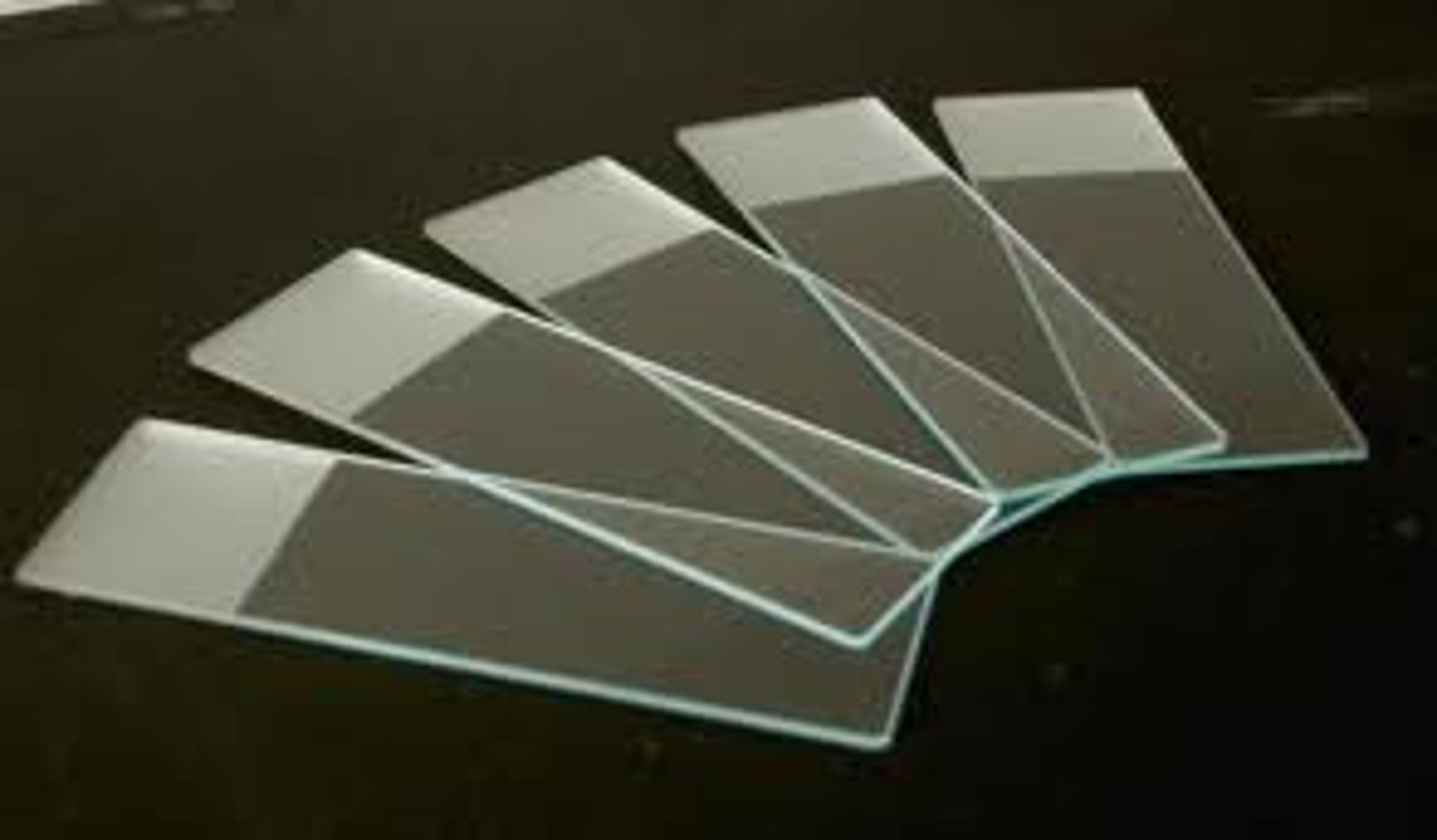
glass slide
used to hold specimen for viewing

cover slip
covers specimen on a slide
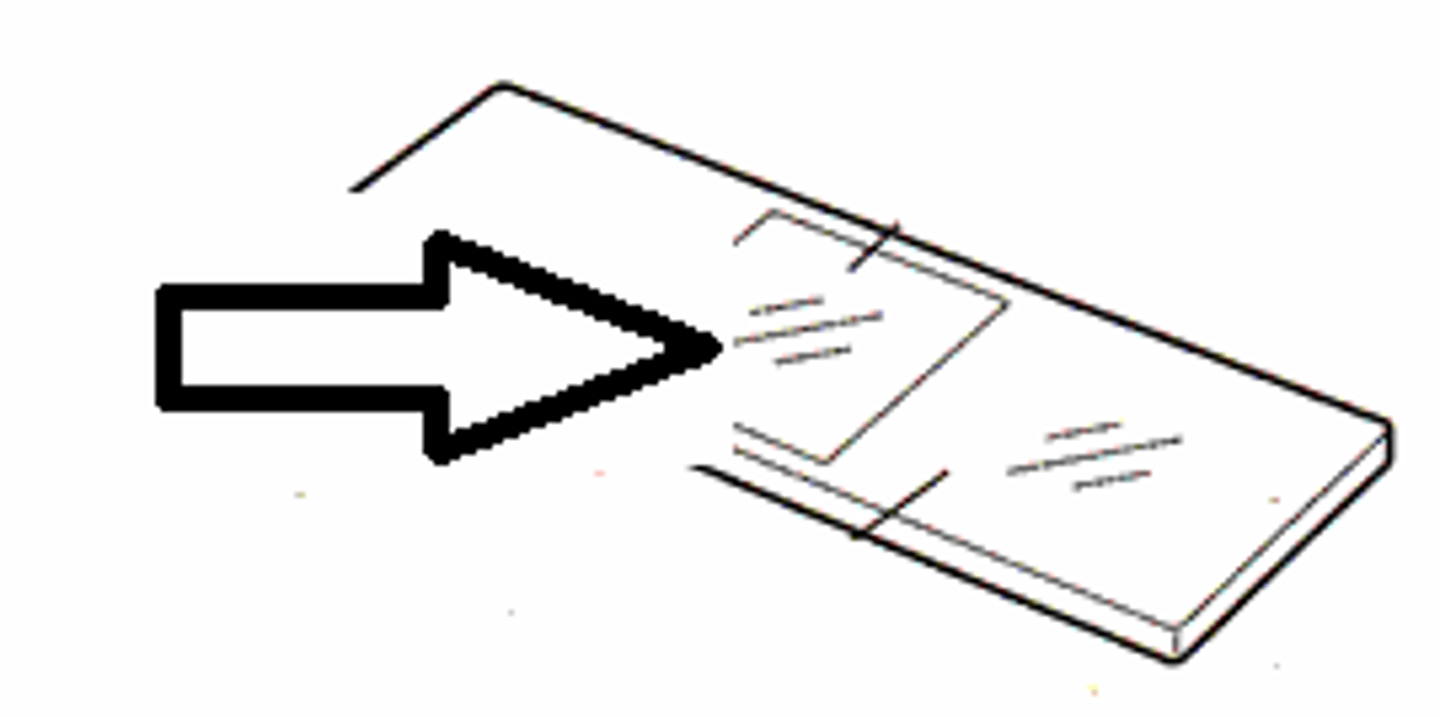
preparing a wet mount
Step 1: Slice thin sample and place on slide
Step 2: Add a drop of iodine solution to stain the cell
Step 3: Lower a coverslip gently on the slide
Step 4: Soak up any excess stain with paper towel
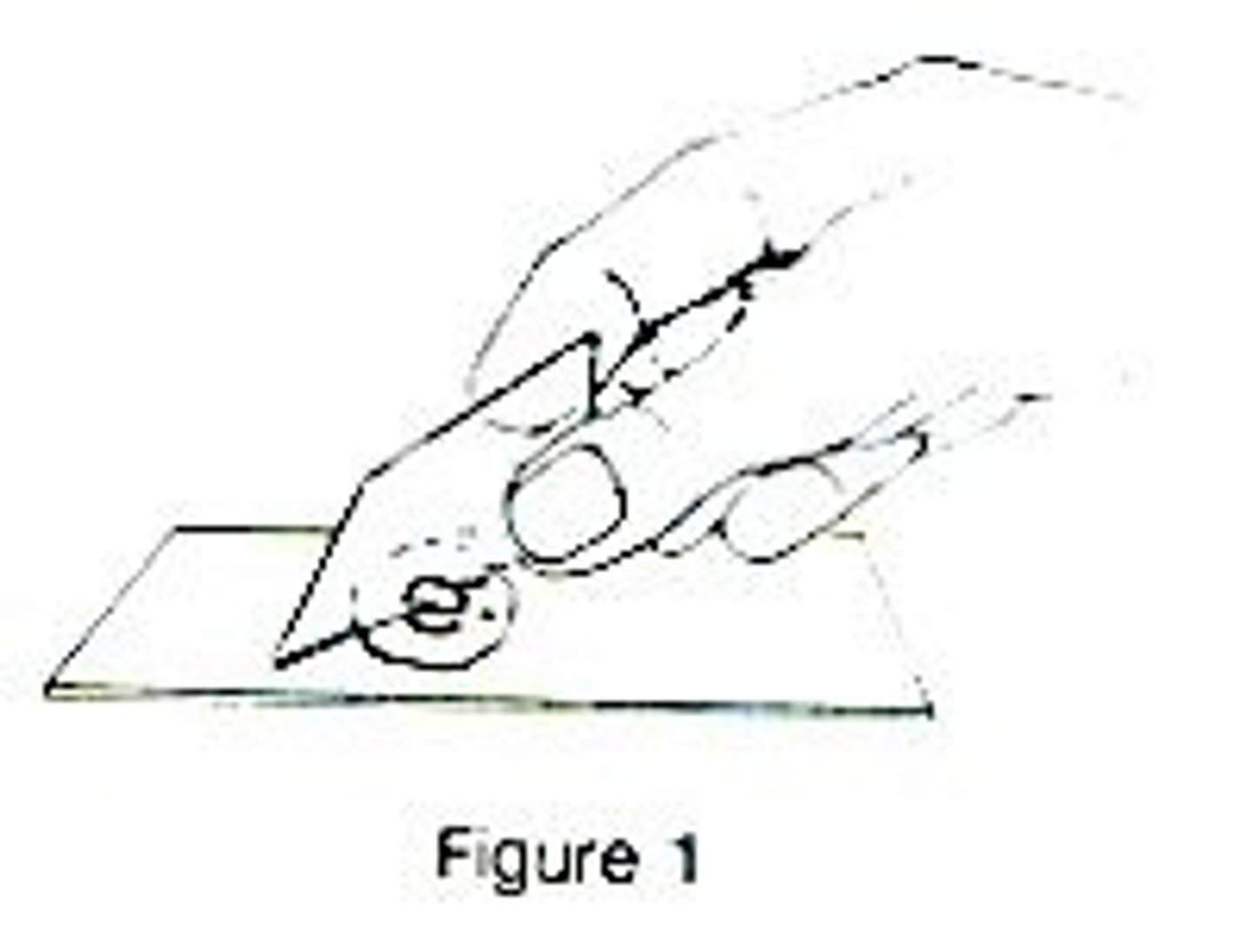
how to focus the micoscope
start with the stage at its lowest setting. Make sure the smallest objective lens is being used. Make sure its turned on and light is on. Using the course adjustment knob, slowing raise the slide until the picture is in view.
How to find total magnification
multiply the objective lens magnification by the eyepiece magnification
field of view
diameter of the circle of light when looking through a microscope
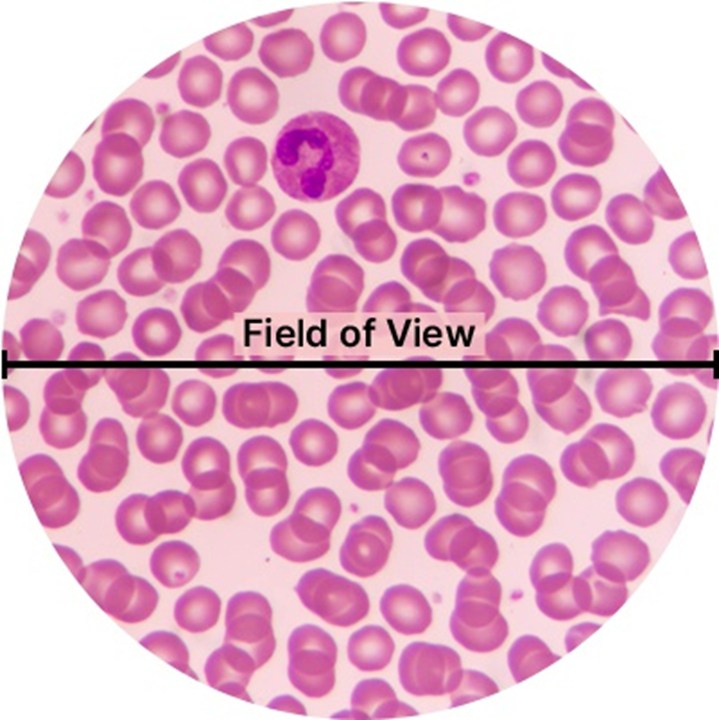
measuring specimens
measure FOV with a ruler and calculate how many of your specimen fit across FOV

what are the 4 lens magnification powers
4x, 10x, 40x, 100x
use pencil, draw fov, write total magnification, only draw the specimen not everything in the fov, label it with scientific names, write the title with the specimen name
dos for scientific diagrams
draw too big or small, make it sketchy, color or shade, draw how you think it should look like
donts for scientific diagrams