Series and Parallel Circuits
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
In a series circuit how is current distributed across components?,
"The same current flows through all components in a series circuit. (I₁ = I₂ = ...)"
What formula links current voltage, and resistance in a circuit?,
"I = V ÷ R (Current = Potential Difference ÷ Total Resistance)"
In a series circuit how do you calculate total resistance?,
By adding the resistance of all components: (R_total = R1 + R2 + ...")
What happens to the total resistance when more resistors are added in series?
"The total resistance increases."
What happens to the total current in a series circuit if resistance increases?
"The total current decreases."
How is potential difference shared in a series circuit?
"The total potential difference is shared between components in proportion to their resistance."
What is the total resistance in a series circuit with a 6 Ω and 3 Ω resistor?
"9 Ω "
Calculate the current in a circuit with a 20 V battery and resistors of 2 Ω and 3 Ω in series.
4 A
What is a disadvantage of series circuits in real-world applications?
"If one component breaks, the whole circuit stops working."
A battery is connected in series with 4 Ω 5 Ω, and 6 Ω resistors. If 0.6 A flows through the circuit, what is the battery's potential difference?,"
9 V
How are components connected in a series circuit?
"In a line, end to end, between the +ve and -ve terminals of the power supply."
What happens if one component is removed or disconnected in a series circuit?
"The circuit is broken and all components stop working."
Why are series circuits not commonly used in real-world applications?
"If one component fails, the whole circuit stops working — not very practical."
How can series circuits be useful despite their limitations?
"They are used to measure quantities and test components in experiments."
What happens to the total potential difference when more cells are connected in series?
"The total potential difference increases, as the voltages of each cell add up."
What is the total voltage when two 1.5 V cells are connected in series the same way?
"3.0 V"
In a series circuit how is the total potential difference shared?
"It is shared between the components. The sum of the component voltages equals the supply voltage."
What formula is used to calculate the total potential difference in a series circuit?
"V_total = V₁ + V₂ + ..."
What is the role of an ammeter in a circuit?
"Ammeters measure current and must be connected in series."
What is the role of a voltmeter in a circuit?
"Voltmeters measure potential difference and must be connected in parallel."
Do voltmeters and ammeters count as part of the main circuit components?
"No, they are measurement tools and do not define circuit type."
How are components connected in a parallel circuit?
"Each component is connected separately to the +ve and -ve of the power supply."
What happens if one component is removed in a parallel circuit?
"The other components keep working — the circuit is not affected."
Why are parallel circuits commonly used in homes and cars?
"Because components can be controlled independently (e.g. switch off one without affecting the others)."
What types of circuits do most real-life circuits include?
"A mixture of series and parallel parts."
In parallel circuits how is the potential difference distributed?,
,"All components get the full source potential difference. V₁ = V₂ = V₃ = ..."
What does equal potential difference across components in parallel mean for bulbs?
"Identical bulbs will all have the same brightness."
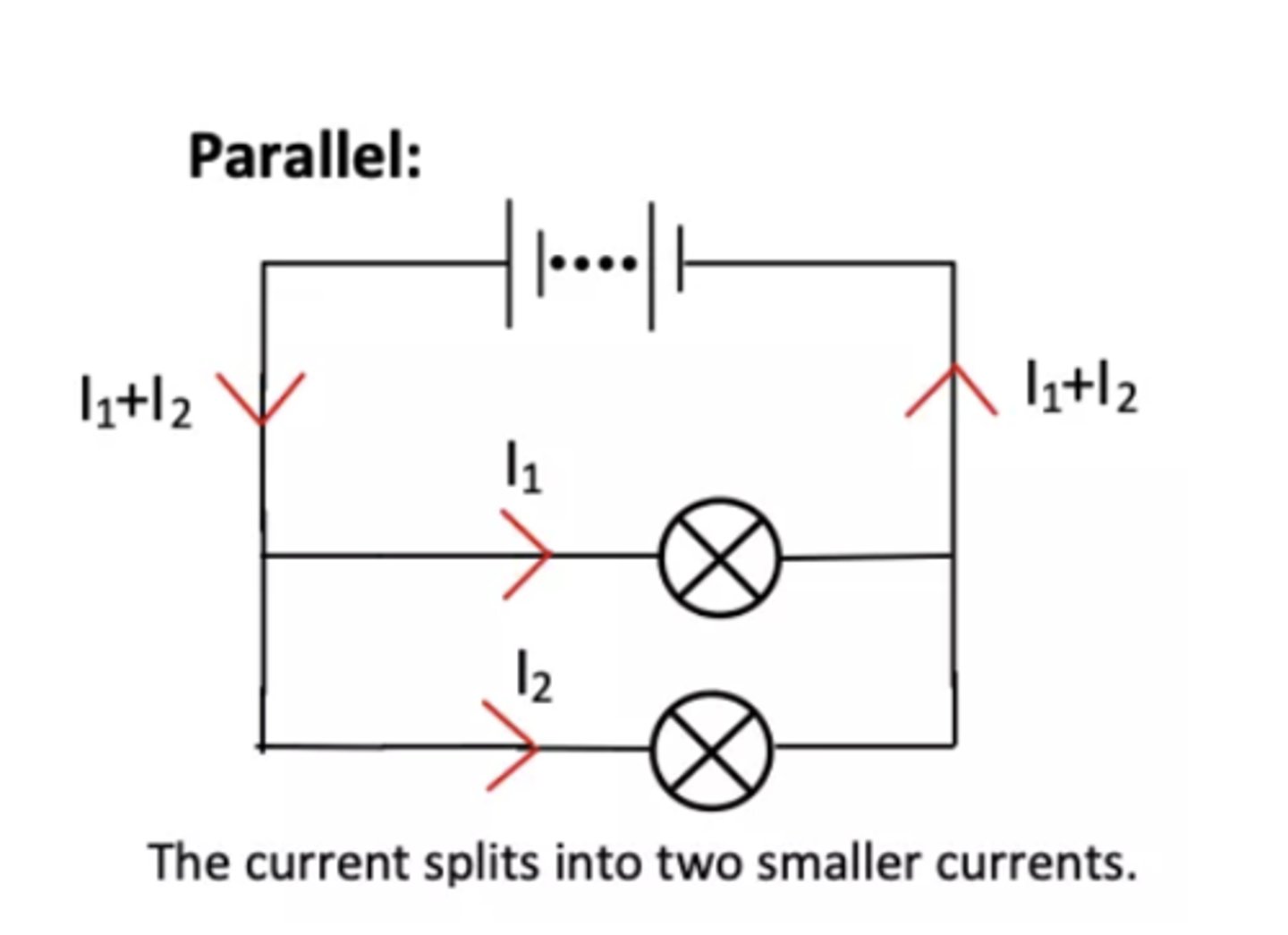
How is current shared in a parallel circuit?
"The total current is split between branches. I_total = I₁ + I₂ + ..."
What happens if two identical components are connected in parallel?
"The current splits equally — same current flows through each component."
What happens to current at a junction in a parallel circuit?
"The current splits or rejoins. The total current into a junction equals the total current out."
Why does adding a resistor in parallel reduce resistance?
"More branches mean more paths for current, increasing total current, which decreases total resistance (using V = IR)."
What is the effect of adding a resistor in parallel on total resistance?
"The total resistance decreases (it's less than the smallest individual resistance.")
What is the formula for calculating total resistance in a parallel circuit?
1/Rtotal=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3+...
Two resistors — 8 Ω and 4 Ω — are connected in parallel.What is the total resistance of the circuit?
Rtotal=8/3=2.67ohms
Three resistors — 6 Ω, 3 Ω, and 2 Ω — are connected in parallel. What is the total resistance?
1 ohms