Intro to Stars
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is a nebula?
Gigantic clouds of dust and gas, mainly hydrogen
What is a protostar?
A very hot, very dense sphere of condensing dust and gas that is on the way to becoming a star
How are protostars formed?
Gravitational attraction of dust and gas particles pull them towards each other, forming a dense cloud
Gravitational potential energy is transferred to thermal energy, causing this cloud to be very hot
This means we have a very hot and dense sphere of gas and dust - a protostar
How does a protostar become a star?
Nuclear fusion needs to start in the core
This only happens if the protostar gains enough mass that the kinetic energy of the hydrogen nuclei is large enough to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between them
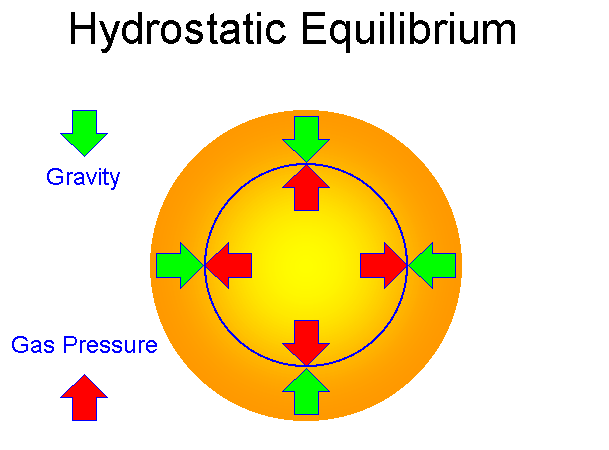
What is gas pressure (in the context of stars)?
the pressure of the nuclei in the star's core pushing outwards
What is radiation pressure (in the context of stars)?
pressure from the photons in the core of a star
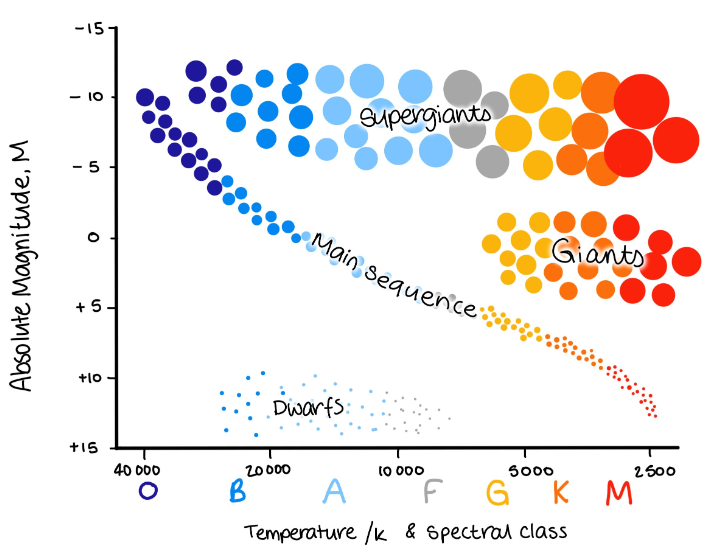
What is the main sequence on a HR diagram?
The main period on an H-R diagram in a star's life, during which it is stable
It goes from top left to bottom right of an HR diagram
What is a main sequence star?
stars in the stable phase of their lives
an object in orbit around a star which:
• has a large enough mass for its own gravity to give it a round shape
• has no fusion reactions
• has cleared its orbit of most other objects
Hertzsprung - Russell (HR) diagram
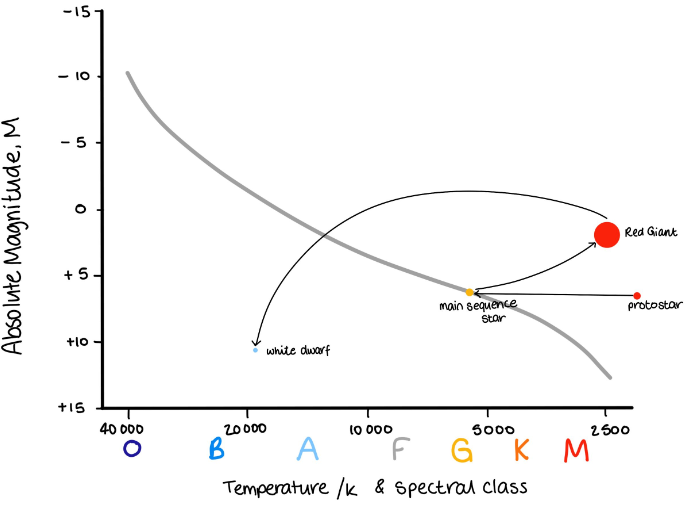
Annotate the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to show
the Sun’s evolution.
Slight curve upwards from red giant is important
the remnant core of a red supergiant after the it has gone supernova and the core (which has a mass greater than the Chandrasekhar limit) has collapsed under gravity to an extremely high density.
• the fusion process in the core slows down
• gravitational forces are greater than gas and radiation pressures
• the core begins to collapse
• as the core shrinks, the pressure increases enough to start fusion in a shell around the core
• no fusion takes place in the core since temperatures are not high enough
• fusion takes place in the shell around the core, causing the periphery of the star to expand
The layers around the core implode and bounce off the solid core, ejecting all the core material into space
their reactions need energy to be taken in, rather than releasing energy like the lighter elements.
Hydrostatic equilibium
The balance between inward and outward forces within a star; compressing force of gravity balanced by radiation and gas pressure which push outwards from the core