Bio- Unit 6- Photosynthesis
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Which of the following statements concerning the role of redox reactions in photosynthesis and cellular respiration is true?
A. Photosynthesis involves both reduction and oxidation, while respiration involves only oxidation.
B.In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is reduced to form sugar, while in respiration sugar is oxidized to form carbon dioxide.
C. Photosynthesis involves only reductions, while respiration involves only oxidations.
D. In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is oxidized to form sugar, while in respiration sugar is reduced to form carbon dioxide
B
How many electrons get transferred during the redox reactions associated with cellular respiration and those associated with photosynthesis?
A. 24 electrons get transferred in cellular respiration and 12 in photosynthesis
B. 2 electrons get transferred in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis
C. 12 electrons get transferred in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis
D. 24 electrons get transferred in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis
D
Generation of proton gradients across membranes occurs during
A. photosynthesis.
B. cellular respiration.
C. both photosynthesis and respiration.
D. neither photosynthesis or respiration.
C
As energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ ions (protons) from the mitochondrial matrix in cellular respiration across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space. Something similar happens in photosynthesis as well. What is the end result of these processes?
A. The creation of a proton gradient.
B. The lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix and in the stroma.
C. The reduction of NAD+.
D. The formation of ADP
A
Photoautotrophs
A. use light energy to produce organic molecules from inorganic molecules.
B. include only the green plants.
C. are only found on land.
D. make sugar by using organic raw materials.
A
Chlorophyll A and B reflect primarily what color of light?
green
What is the purpose of pigments?
A. Chlorophylls A and B function to absorb heat energy, while carotenoids protect the plant from UV radiation
B. Turn the leaves of plants green making it harder for herbivores to see them
C. Absorb visible light energy from the sun
D. Reflect sunlight to keep plants from overheating
C
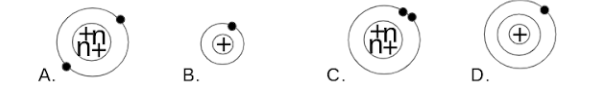
Which of the following pictures depicts a model of an atom with an electron in an excited state? (recall electron clouds can hold two electrons in the 1st energy level)
D
Plant cells
A. have mitochondria and chloroplasts.
B. lack mitochondria and chloroplasts.
C. have mitochondria but do not have chloroplasts.
D. lack mitochondria but have chloroplasts.
A
A packet of light energy is called a
photon
What purpose does light serve in the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis?
A. Light is not necessary in the light dependent reaction, the name is misleading
B. To split the water molecule at photosystem I
C. To warm the plant
D. To energize electrons
D
During the light dependent reaction, why is energy necessary to pump protons (H+ ion) from the stroma to the thylakoid space, and where does that energy come from?
A. Energy is necessary because the protons are going from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (passive transport). The energy comes from the flow of electrons through an electron transport chain.
B. Energy is necessary because the protons are going from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration (active transport). The energy comes from the flow of electrons through an electron transport chain.
C. Energy is necessary because the protons are going from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (passive transport). The energy comes from the hydrolysis of ATP.
D. Energy is necessary because the protons are going from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration (active transport). The energy comes from the hydrolysis ATP.
B
What molecule holds high-energy electrons and acts as an electron carrier in photosynthesis?
NADP+
During which step in photosynthesis does carbon fixation occur?
Calvin Cycle
How do plants replenish the carbon that is used to create glucose?
takes in carbon dioxide from atmosphere
What is the name of the enzyme that performs carbon fixation?
rubisco
Finish the sentence: ATP synthase makes ATP from
A. ADP + Pi and energy from the reflection of light
B. ADP + Pi and energy from the proton gradient
C. Directly from the splitting of H2O at the ATP synthase
D. From NADH going to NAD+
B
What happens to the parts of water when it is split during photosynthesis?
A. H+ is used to help create the proton gradient
B. Electrons replace those lost by photosystem II to the primary electron acceptor
C. Two oxygens combine to create oxygen gas
D. All of the above
D
How many CO2 are necessary to create one glucose molecule?
6
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration?
A. ATP molecules are produced in photosynthesis and used up in respiration.
B. Respiration is the exact reversal of the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis.
C. Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules, while respiration releases it.
D. Photosynthesis occurs only in plants and respiration occurs only in animals.
C
Write the overall equation for photosynthesis (words)
Energy + 6carbon dioxide + 6water —> glucose + 6oxygen
In the equation for photosynthesis, what parts are reduced?
carbon dioxide and glucose
In the equation for photosynthesis, what parts are oxidized?
water and oxygen
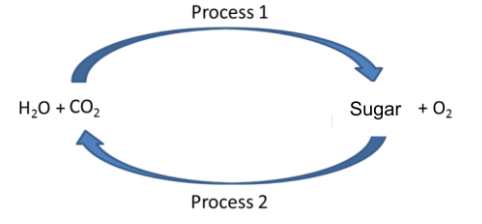
What is the name of process 1?
photosynthesis
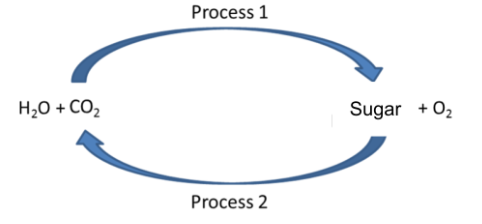
What electron carriers are involved in process 1?
NADP+
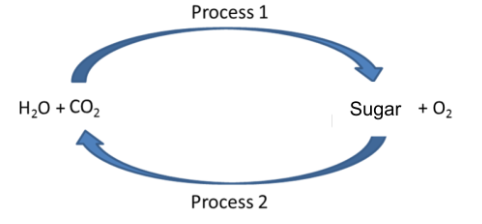
What is the name of the process 2?
cellular respiration
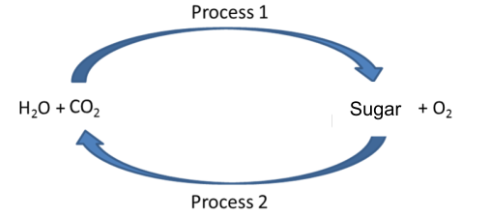
What electron carriers are involved in process 2?
FAD and NAD+
Is photosynthesis endergonic or exergonic?
endergonic
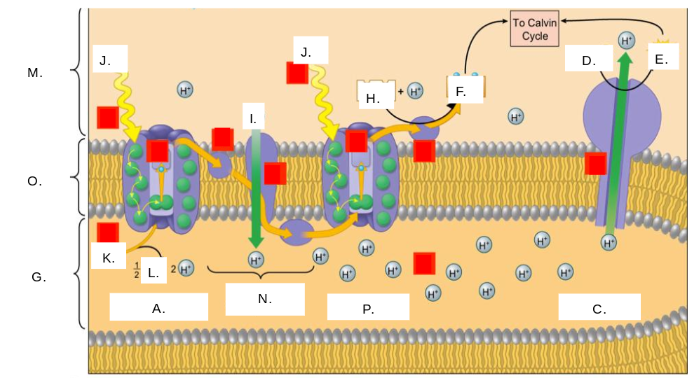
H2O
K
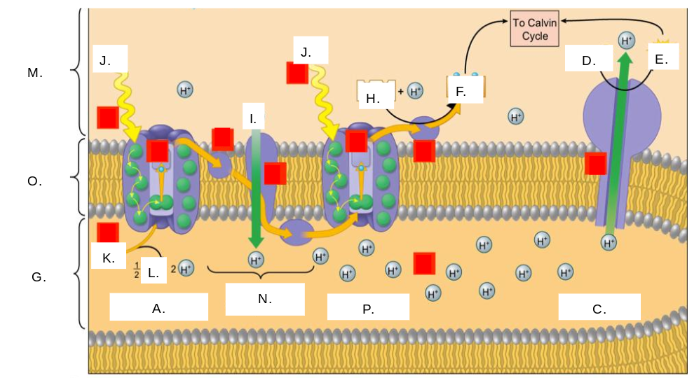
oxygen (O2)
L
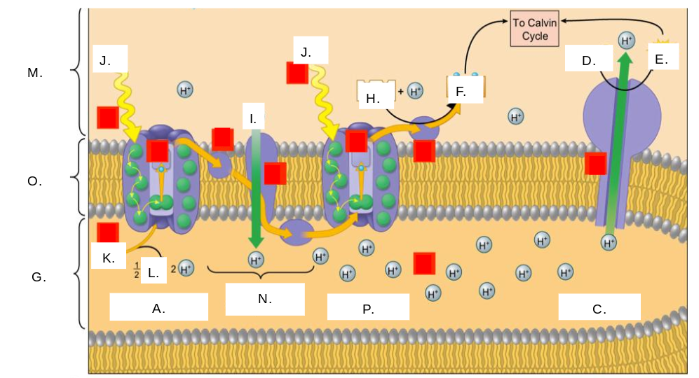
thylakoid space
G
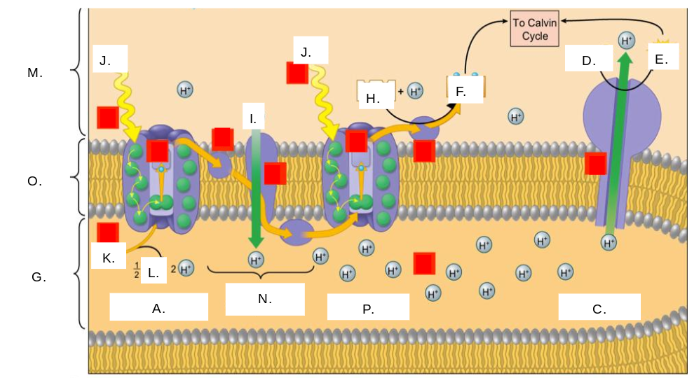
stroma
M
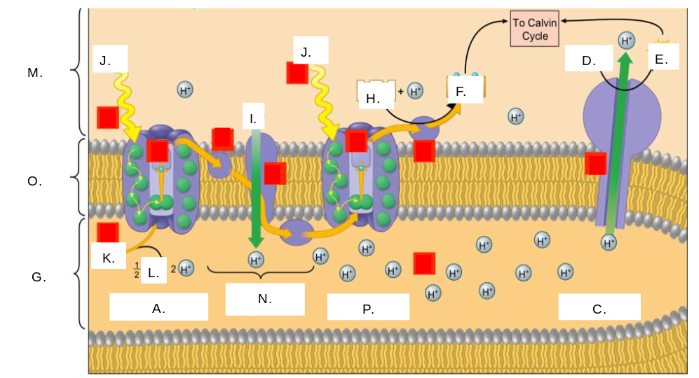
photosystem II
A
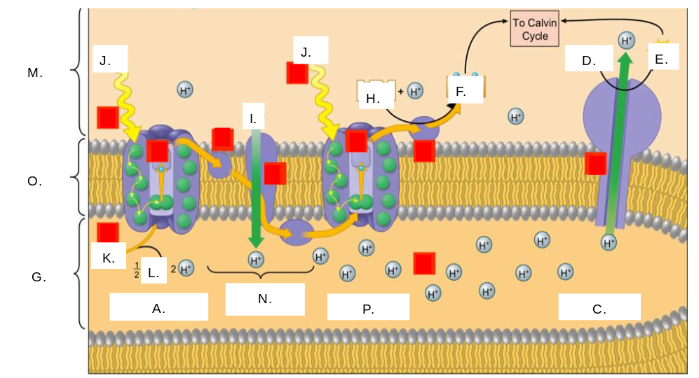
photons (light)
J
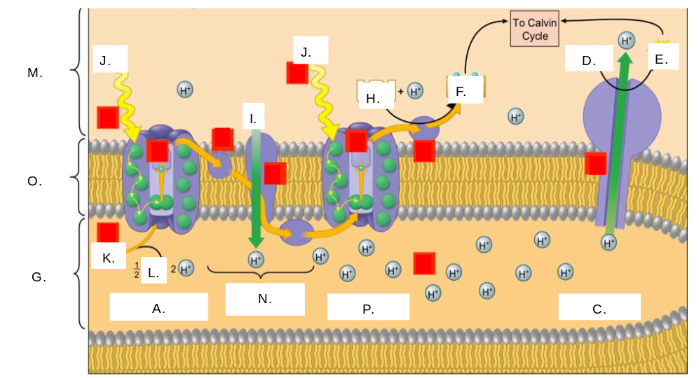
electron transport chain (ETC)
N
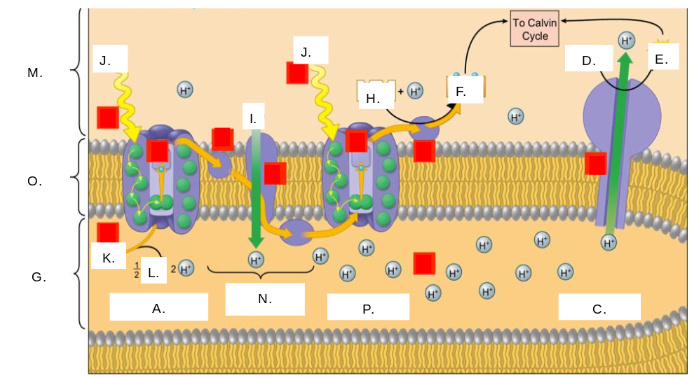
ATP synthase
C
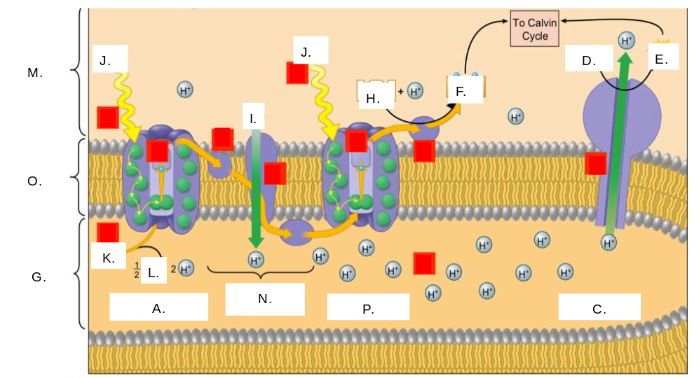
NADP+
H
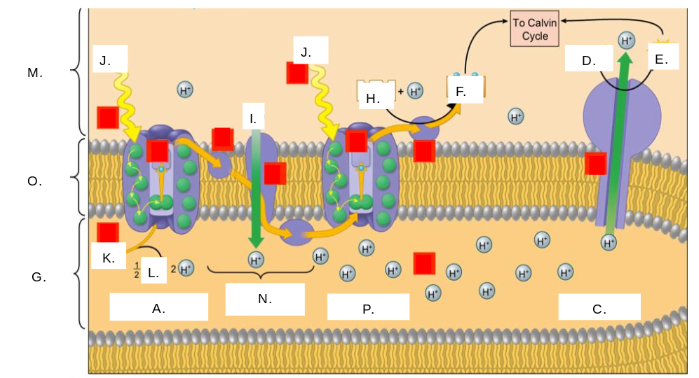
ATP
E
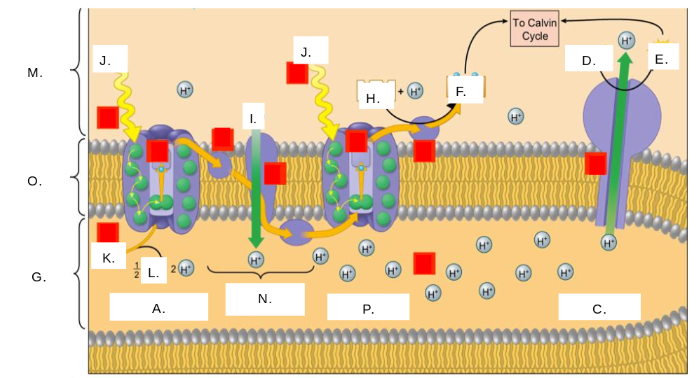
ADP + Pi
D
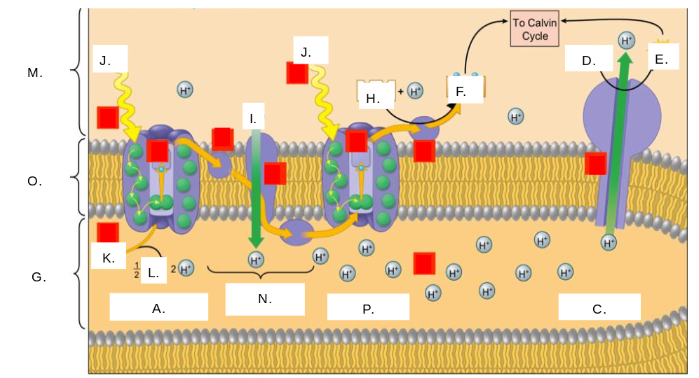
NADPH
F
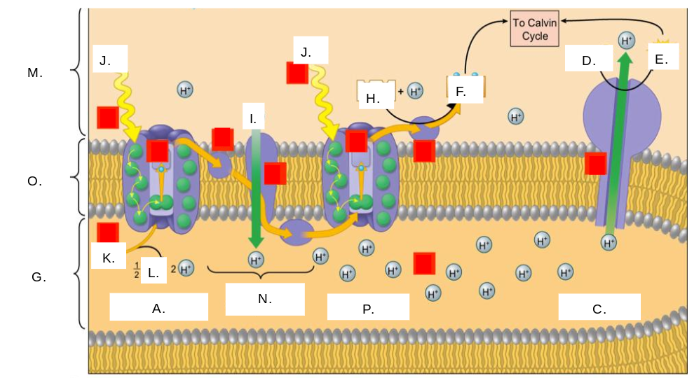
thylakoid membrane
O
HIGH OR LOW ENERGY:
While part of the water molecule
low
HIGH OR LOW ENERGY:
After going through photosystem II
high
HIGH OR LOW ENERGY:
After going through the electron transport chain
low
HIGH OR LOW ENERGY:
On NADPH as they are shuttled to the Calvin cycle
high
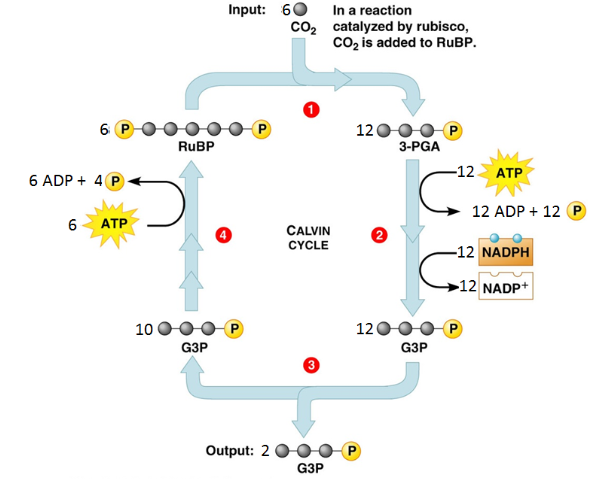
What step in photosynthesis is shown?
calvin cycle
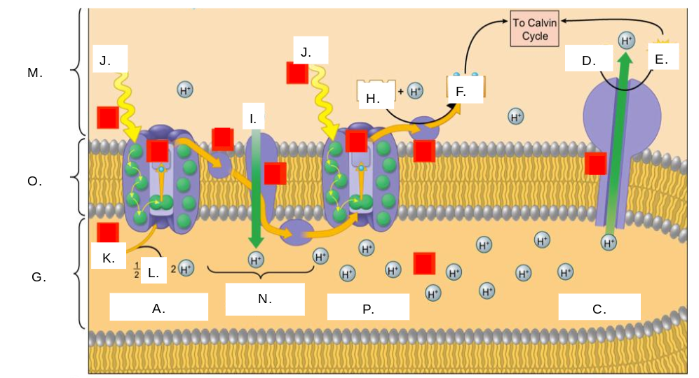
What step in photosynthesis is shown?
light reactions
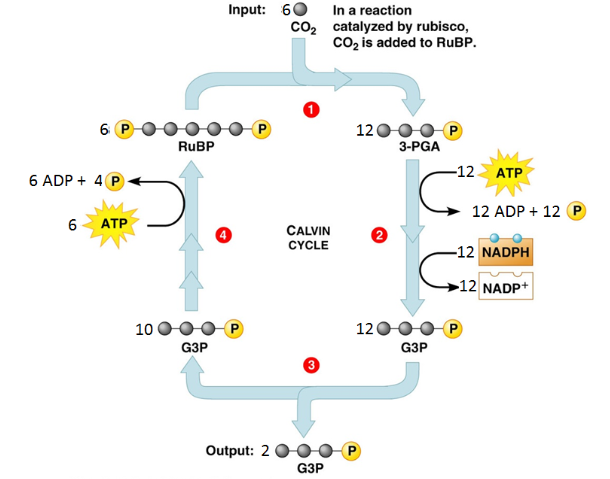
List all the reactants of the Calvin Cycle.
6 CO2, 18 ATP, 12 NADPH
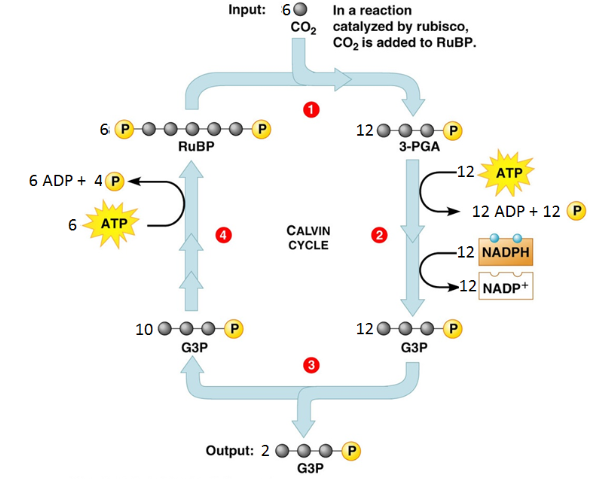
List all the products of the Calvin Cycle.
18 ADP + 16 Pi, 2 G3P, 12 NADP+
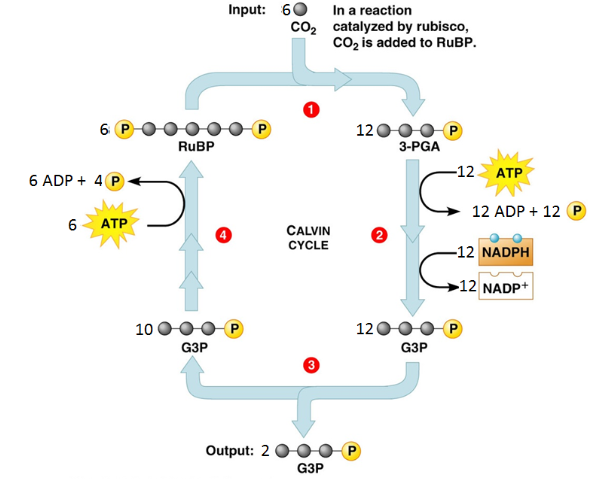
At the end of the Calvin cycle, the two G3P will combine to create what molecule?
glucose
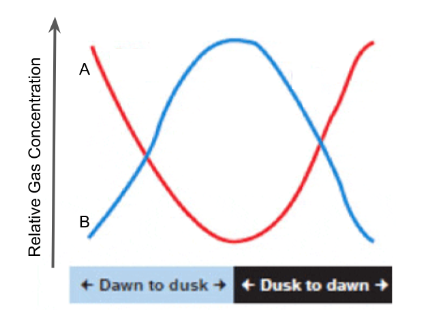
Which gas shown here represents carbon dioxide?
A (red)
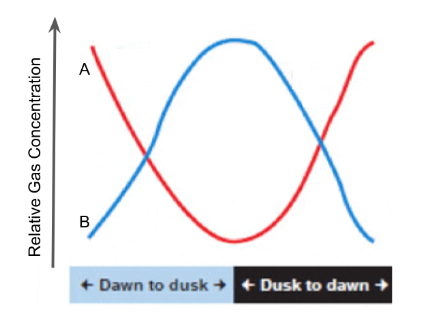
Which gas shown here represents oxygen?
B (blue)
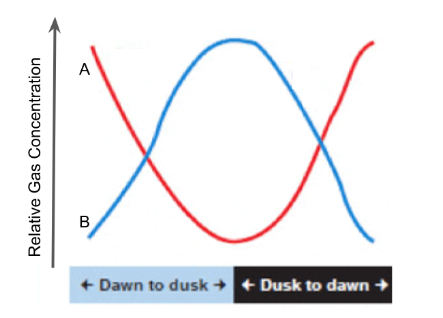
Name an organism that could be within this enclosed ecosystem that could contribute to the relative level change of gas B that would be consistent with its data for both day and night.
plant
Are the light reactions active or passive transport?
active
What are the three pigments of plants?
chlorophyll a and b, carotenoids
Where does the Calvin Cycle occur?
stroma
Where do the light reactions occur?
thylakoid membrane