Mitosis
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Why do cells divide?
cells die & need to be replaced
allows organisms to increase in size
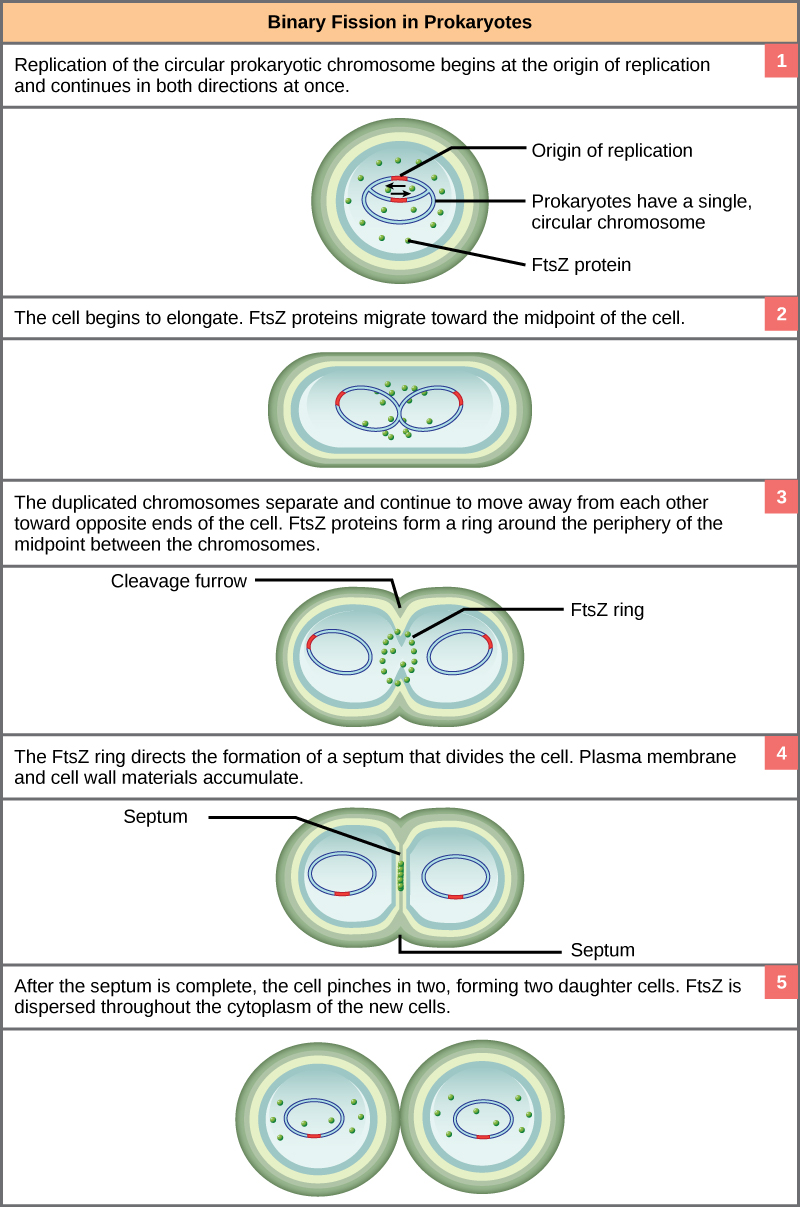
Prokaryotic Chromosomes
double stranded DNA
single round chromosome
replicate through binary fission
Matched pairs
chromosomes from each parent
Homologous
same in size & function
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46
How many match pairs of chromosomes?
22
Female
XX
Male
XY
Somatic cells
cells forming the body of the organism
Reproductive cells / Gametes
sex cells
Cell Cycle
Interphase G1
S phase
Interphase G2
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
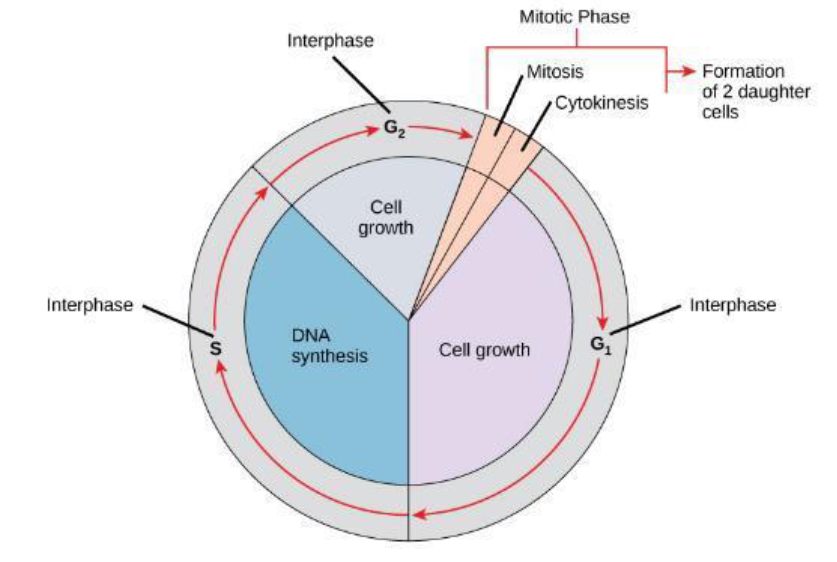
Interphase G1
cell growth & protein synthesis
S phase
DNA & centrosome replication
Interphase G2
further growth & protein synthesis
Mitosis
prophase
prometaphase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
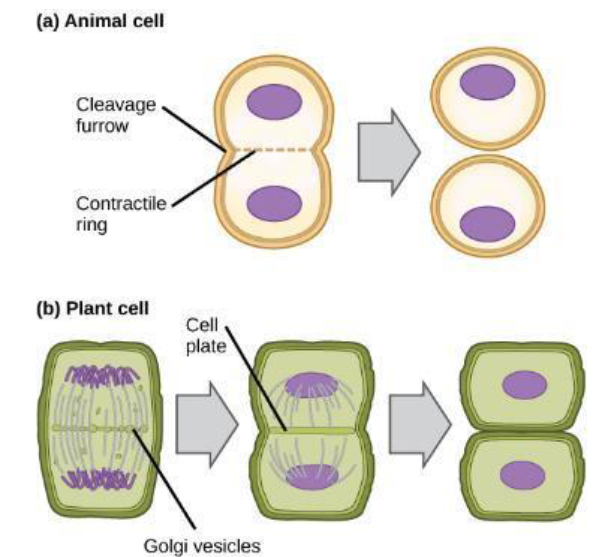
Cytokinesis
cytoplasm divided & forms two daughter cells
Red blood cell
replaced every 6 weeks
Intestinal lining cell
replaced every 3 weeks
Brain, heart, muscle cells
rarely divide
Checkpoints
points in cell cycle where progress is blocked
Strategic checkpoints
G1 checkpoint: DNA integrity
G2 checkpoint: chromosome duplication
M checkpoint: attachment kinetochore to spindle fiber
Oncogene-Tumor Suppressor Gene Theory
Oncogenes: accelerator
Tumor Suppressor genes: brakes
Benign
self-contained
can be removed
Malignant
cancerous cells
continuously replicate
Metastasis
spreading of cancer
Apoptosis / Programmed cell death
cell detects damaged DNA
cell is swallowed by a neighboring cell or a patrolling immune cell